Abstract
Quercus variabilis (Chinese cork oak) is an economically valuable oak as the source of industrial cork, which was widely distributed in eastern Asia. In this study, the complete mitochondrial genome of Q. variabilis was sequenced using the Illumina Hiseq and PacBio Sequel technique. The mitogenome is 412,886 bp in length and the GC content is 45.76%. The genome consists of 36 protein-coding genes, 3 ribosomal-RNA genes, and 21 transfer-RNA genes. Phylogenetic analysis based on protein-coding genes showed that Q. variabilis was close to the species in the Cucurbitaceae family.
Keywords: Quercus variabilis, mitochondrial genome, phylogenetic analysis
Quercus variabilis (Chinese cork oak), the oak species, which is an economically valuable oak and one of the most important afforestation tree species in China is used as the source of industrial cork (Wang et al. 2016; Liu et al. 2018). In this study, we reported the complete mitogenome of Q. variabilis using high-throughput sequencing and PacBio sequencing technique. The annotated mitogenome of Q. variabilis has been deposited in GenBank under the accession number MN199236.
The sample of Q. variabilis adopted in this study was collected from Jiaozuo boai county of Henan Province, China (35°20′38.29″N, 113°09′42.98″E). The fresh leaves were collected and then frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80 °C. The voucher specimens were deposited in the State Key Laboratory of Tree Genetics and Breeding, Research Institute of Forestry, Chinese Academy of Forestry, Beijing, China (voucher number: QV201905003). The mtDNA were isolated with an improved extraction method (Chen et al. 2011), and the mitochondrial genome were sequenced by Pacbio Sequel system and Illumina Hiseq system. Then, the genome were assembled by both the Pacbio Sequel data and the Illumina Hiseq data using SPAdes v3.10.1 (Antipov et al. 2016). The mitochondrial genes were annotated by homology alignments and de novo prediction.
The complete mitogenome of Q. variabilis is 412,886 bp in length, with the overall GC contents approximate to 45.76%. The mitogenome of Q. variabilis comprises of 36 protein-coding genes, 3 ribosomal-RNA genes, and 21 transfer-RNA genes. The total sequence length of protein-coding gene was 33,270 bp and the average length of genes was 924 bp.
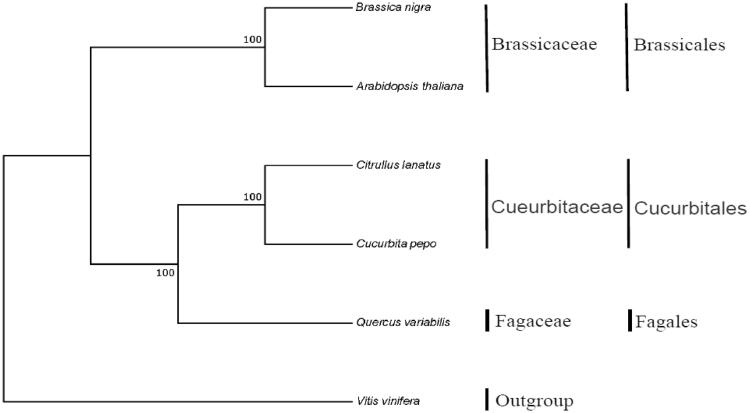
The phylogenetic relationships of Q. variabilis and five other plant mitogenome were reconstructed using Bayesian analysis based on protein-coding genes (Figure 1). Sequences were aligned using MEGA X software (Kumar et al. 2018). Phylogenetic analysis confirmed that Q. variabilis was close to the species in the Cueurbitaceae family. All members in the phylogenetic tree provided the relationships among the Brassicales, Cucurbitales, Fagales, and Vitales.
Figure 1.
The phylogenetic tree based on six complete mitochondrial genomes. Accession number: Arabidopsis thaliana (Y08501), Brassica nigra (NC_029182), Citrullus lanatus (GQ856147), Cucurbita pepo (GQ856148), Vitis vinifera (NC012119.1), and Quercus variabilis (MN199236).
Disclosure statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
References
- Antipov D, Korobeynikov A, Mclean JS, Pevzner PA. 2016. HYBRIDSPADES: an algorithm for hybrid assembly of short and long reads. Bioinformatics. 32(7):1009–1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J, Guan R, Chang S, Du T, Zhang H, Xing H. 2011. Substoichiometrically different mitotypes coexist in mitochondrial genomes of Brassica napus L. PLoS One. 6(3):e17662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K. 2018. MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol. 35(6):1547–1549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu JF, Deng YP, Wang XF, Ni YY, Wang Q, Xiao WF, Lei JP, Jiang ZP, Li MH. 2018. The Concentration of non-structural carbohydrates, N, and P in Quercus variabilis does not decline toward its northernmost distribution range along a 1500 km transect in China. Front Plant Sci. 9:1444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J, Yu H, Li G, Zhang F. 2016. Growth and nutrient dynamics of transplanted Quercus variabilis seedlings as influenced by pre-hardening and fall fertilization. Silva Fenn. 50(2):1–18. [Google Scholar]