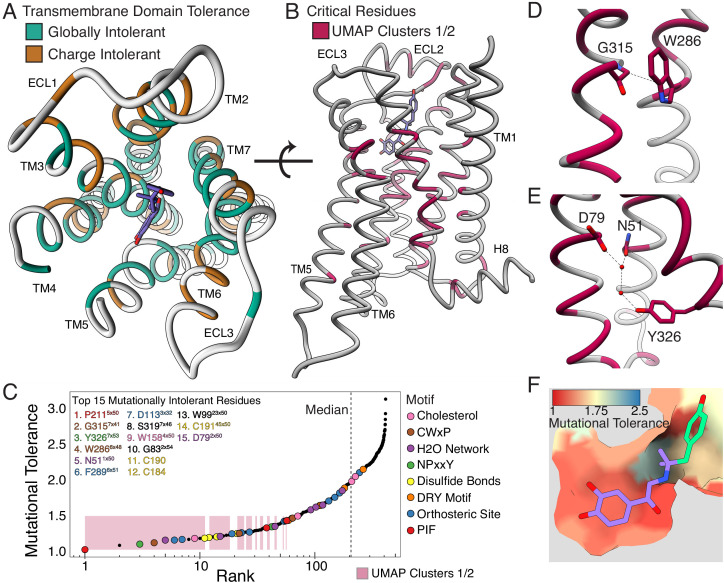
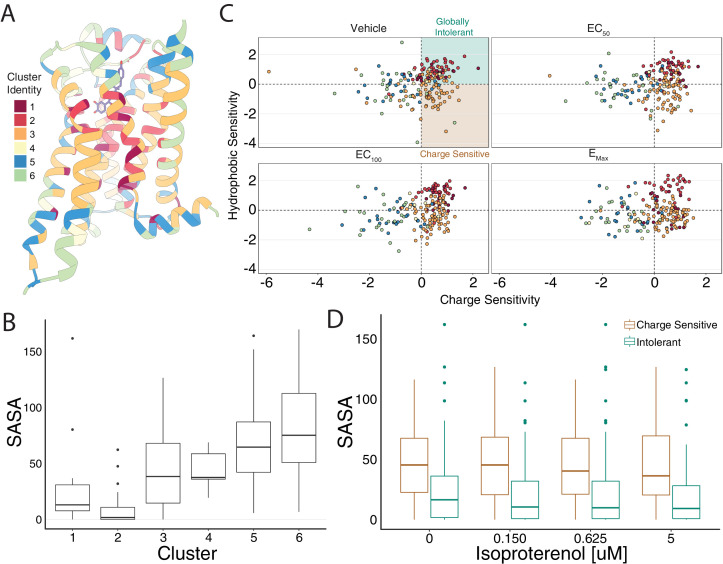
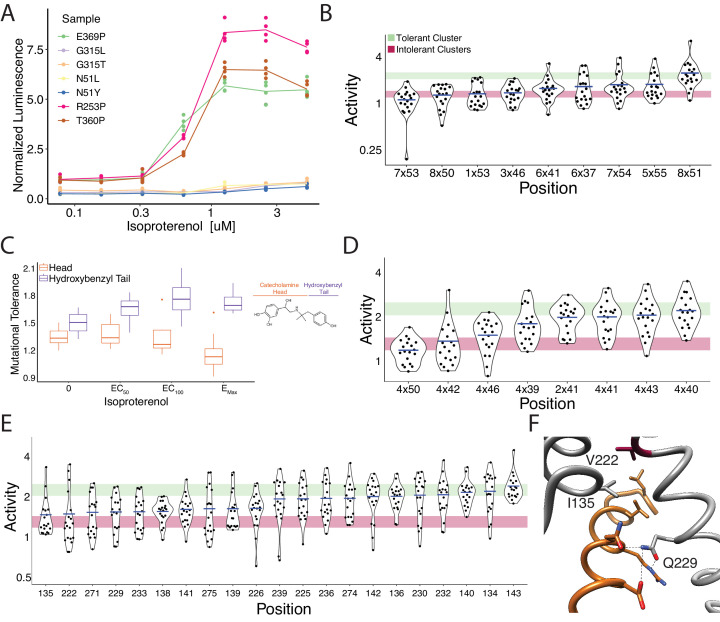
Figure 5. Mutational tolerance elucidates broad structural features and critical residues of the β2AR.
(A) Residues within the transmembrane domain colored by their tolerance to particular classes of amino acid substitution. Teal residues are intolerant to both hydrophobic and charged amino acids (globally intolerant), and brown residues are tolerant to hydrophobic amino acids but intolerant to charged amino acids (charge intolerant). The charge-sensitive positions’ side chains are enriched pointing into the membrane, while the globally intolerant positions’ side chains face into the core of the protein (see Figure 5—figure supplement 1). (B) The crystal structure of the hydroxybenzyl isoproterenol-activated state of the β2AR (PDB: 4LDL) with residues from the mutationally intolerant Clusters 1 and 2 highlighted in maroon. (C) 412 β2AR residues rank ordered by mutational tolerance at the EC100 isoproterenol condition. Residues in known structural motifs (colored points) are significantly more sensitive to mutation than other positions on the protein (p<<0.001). Dashed line demarcates the median of the ranking. The top 15 mutationally intolerant residues are listed and colored by motif association. (D-F) Selected vignettes of residues from the mutationally intolerant UMAP clusters and ranking. (D) W2866x48 of the CWxP motif and the neighboring G3157x41 are positioned in close proximity. Substitutions at G3157x41 are likely to cause a steric clash with W2866x48 (PDB: 4LDL). (E) An inactive-state water-mediated hydrogen bond network (red) associates N511x50 and Y3267x53 (PDB: 2RH1). Disruption of this network may destabilize the receptor. (F) The ligand-bound orthosteric site surface colored by mutational tolerance. Receptor-ligand contacts with the catecholamine head (present in agonist used in assay) are more intolerant to mutation than those in the hydroxybenzyl tail (not present in agonist used in assay) of the isoproterenol analog depicted in this crystal structure (PDB: 4LDL).