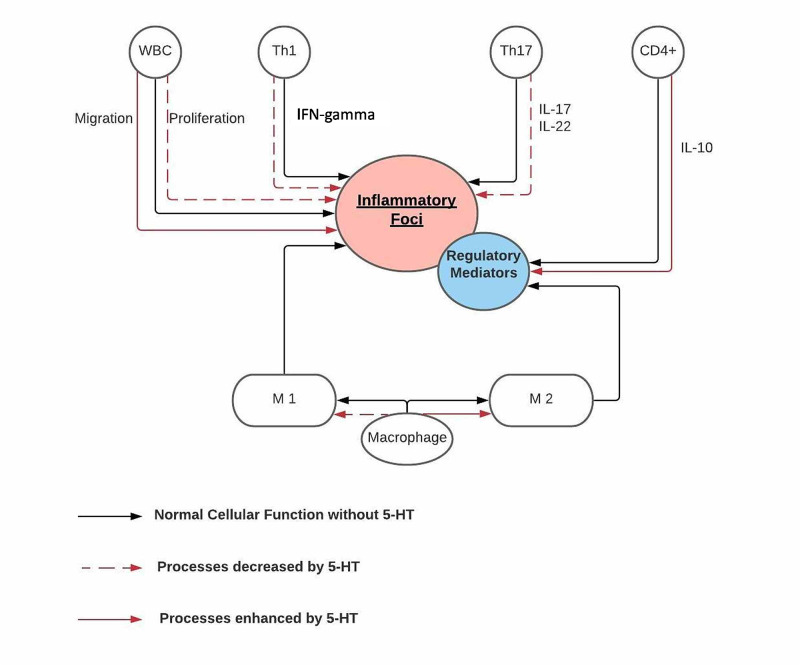
Figure 2. Serotonin's effects on the immune system.
The figure summarizes the findings of previous studies about the effects of serotonin on the immune system. Overall, 5-HT decreases the proliferation of WBC, suppresses the synthesis of inflammatory cytokines like IFN-γ, IL-17, and IL-22 by TH1 and Th2 cells, respectively. The NT also enhances the synthesis of IL-10, a regulatory cytokine, from CD4+ cells and acts on macrophages, enhancing its polarization into the M2 subset, a population that secretes regulatory mediators to control inflammation. Finally, the addition of 5-HT to WBCs increases their migration through the BBB into the inflammatory foci
5-HT: serotonin; IFN-γ: interferon gamma; IL: interleukin; WBC: white blood cells; NT: neurotransmitter