Abstract
AIM
To explore the global trends and focus of glaucoma research from 2009 to 2018.
METHODS
Searching for glaucoma-related articles published in Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE) database during 2009-2018, and describing the distribution of the published year, countries, authors, institutions, funding agencies, journals, impact factor, citation and hot research topic of articles by using bibliometric methods. Meanwhile, we compared some of these indicators over two five-year periods, from 2009 to 2013 and from 2014 to 2018.
RESULTS
A total of 19 609 glaucoma-related articles were retrieved and the global SCIE articles have increased yearly from 2009 to 2018. The USA was the pioneer which has made great contributions. China kept the second place and the number of publications has increased rapidly between 2014 and 2018. The author with the highest number of publications was Weinreb, RN. Co-occurrence maps were built amongst the top 50 authors or the top 50 institutions with the most articles, which visualize the closer collaboration of international authors or institutions. The journal Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science has published the most papers. Glaucoma literature with an impact factor of 3-5 points accounted for the largest proportion (28.96%). The most frequently cited paper had 798 citations. The top three hot areas on glaucoma were intraocular pressure, optical coherence tomography (OCT) and retinal ganglion cells. And trabecular meshwork, primary angle-closure glaucoma and Spectral-domain OCT have become new hot research topics in recent five years during 2014-2018.
CONCLUSION
Bibliometric analysis is an effective method to describe the global literature on glaucoma. In a 10-year literature survey from 2009 to 2018, global glaucoma research has developed in a balanced manner, and the cooperation between various institutions and teams has become closer. Glaucoma-related pathogenesis research, imaging examinations of OCT and surgery therapy have attracted most attention.
Keywords: bibliometric analysis, Science Citation Index Expanded, glaucoma, ocular hypertension
INTRODUCTION
Glaucoma is the leading cause of irreversible blindness in the world[1]. Active research and innovations have been ongoing for decades in search of a better understanding as well as better treatments for glaucoma. Several noteworthy advances changed the landscape of the field of glaucoma within the past decade, including landmark randomized controlled trials investigating glaucoma medical[2], advanced diagnostic imaging modalities such as the optical coherence tomography (OCT)[3]–[4], new glaucoma treatments such as minimally invasive glaucoma surgery (MIGS) and many more[5]–[8]. Analysis of glaucoma-related papers, with systematic and comprehensive understanding of global research status and hotspots, plays an important role in the optimization of glaucoma research and clinical work.
Bibliometric analysis aim to understand the research trends and focus, and the contribution of any country, institution, funding agency, author or journal to scholarship[9]. Further, examining author keywords could reveal the current and future trends or hot research topic[10]–[11]. Meanwhile, text-based mining software Thomson Data Analyzer (TDA) was used to conduct a panoramic analysis of data mining and visualization analysis from multiple perspectives (author collaboration, institutional cooperation and keyword co-occurrence). Which will provide some valuable evidence for further understanding the development trend of glaucoma research, seeking for partners, determining research strategies and direction.
The purpose of this study was to provide a bibliographic perspective on glaucoma research in the past decade by analyzing glaucoma-related publications from 2009 to 2018 based on Science Citation Index Expanded Edition (SCIE) database, and to identify the global trends and themes in these publications.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
SCIE database established by Institute for Scientific Information (ISI) was used for the purpose of this study. This is a comprehensive multidisciplinary bibliographic database that covering over 9000 major journals across more than 178 scientific disciplines. It has become an important tool for many international scientific research review departments or related institutions to evaluate scientific research achievements. The search was performed with the aid of an expert medical librarian.
The search strategy was as follows: theme=(glaucoma OR ocular hypertension), and the “theme” field contains: title, abstract, author keywords, and keywords plus. Document type=(article), and other types of articles, such as case reports, reviews, letters to the editors, and so on, were excluded. The time period of publications was focused on the latest 10y from 2009 to 2018. And the search date was 2019-3-29.
Text-based mining software TDA was then used for the final bibliometric analysis of the search records. The following details were recorded for each article: year of publication, country of origin, authors, author institutions, funding agencies, journal name, impact factor, overall number of citations and keywords. Meanwhile, the visualized analysis was conducted for the author collaboration, institutional cooperation and keyword co-occurrence.
In addition, comparison of this period of publications were conducted with articles published five years before and after, i.e. 2009 to 2013 and 2014 to 2018, respectively.
RESULTS
Number of Global Publications
A total of 19 609 glaucoma-related articles were found in the SCIE database that were published between the years of 2009 to 2018. The distribution of articles was analyzed by year of publication (Table 1). It shows that the number of publications increased overall from 1460 to 2297 from 2009 to 2018. In addition, most of the articles were published in 2017 (2383, 12.15%).
Table 1. Distribution of glaucoma-related articles during 2009-2018.
| Year | Numbers of articles | Percentage of 19609 articles |
| 2018 | 2297 | 11.71% |
| 2017 | 2383 | 12.15% |
| 2016 | 2306 | 11.76% |
| 2015 | 2081 | 10.61% |
| 2014 | 2053 | 10.47% |
| 2013 | 1933 | 9.86% |
| 2012 | 1791 | 9.13% |
| 2011 | 1774 | 9.05% |
| 2010 | 1531 | 7.81% |
| 2009 | 1460 | 7.45% |
Contributions of Countries (Top 10 Countries in the Number of Articles)
The distribution of articles was further analyzed by country of origin (Table 2). The top three countries were the USA, China, and Japan, which respectively accounted for 32.44%, 11.88% and 7.72% of the total number of articles from 2009 to 2018. The USA has made great contribution to this area. China kept the second place and the proportion of publications has increased rapidly in the past five years during 2014-2018. Germany and England produced the third and fourth highest number of manuscripts in the first half (2009-2013), while Japan produced the third highest publications in the second half of the decade (2014-2018). Many Asian countries (Japan, South Korea, and India) have risen in their ranking in terms of the proportion of articles in the latest five years.
Table 2. Top 10 countries in the number of articles during 2009-2018.
| Rank | 2009-2018 |
2009-2013 |
2014-2018 |
|||
| Country | Percentage of 19609 articles | Country | Percentage of 8489 articles | Country | Percentage of 11120 articles | |
| 1 | USA | 32.44% | USA | 34.07% | USA | 31.20% |
| 2 | China | 11.88% | China | 9.86% | China | 13.43% |
| 3 | Japan | 7.72% | Germany | 8.02% | Japan | 8.21% |
| 4 | Germany | 7.56% | England | 7.34% | Germany | 7.20% |
| 5 | England | 7.23% | Japan | 7.07% | England | 7.15% |
| 6 | South Korea | 5.54% | Australia | 4.90% | South Korea | 6.72% |
| 7 | India | 4.65% | South Korea | 3.99% | India | 5.23% |
| 8 | Australia | 4.63% | India | 3.90% | Turkey | 4.70% |
| 9 | Turkey | 4.09% | Canada | 3.77% | Australia | 4.42% |
| 10 | Italy | 3.66% | Italy | 3.77% | Italy | 3.57% |
Authors Published the Most Articles in the Top 10 Countries
We then examined the authors who published the greatest number of articles in the top 10 countries, and recorded their number of articles and their most cited articles (Table 3). The top three were Weinreb RN from the USA, Wang NL from China and Araie M from Japan.
Table 3. The authors who have published the most articles in the top ten countries, their number of articles and their most cited articles.
| Rank | Country | Author | Number of articles | Most cited articles | Cited times | Published time | Journal |
| 1 | USA | Weinreb RN | 325 | Retinal nerve fiber layer imaging with spectral-domain optical coherence tomography a variability and diagnostic performance study | 276 | Jul-2009 | Ophthalmology |
| 2 | China | Wang NL | 136 | Cerebrospinal fluid pressure in glaucoma: a prospective study | 232 | Feb-2010 | Ophthalmology |
| 3 | Japan | Araie M | 117 | Effects of age, sex, and axial length on the three-dimensional profile of normal macular layer structures | 107 | Nov-2011 | Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science |
| 4 | Germany | Jonas JB | 184 | Causes of vision loss worldwide, 1990-2010: a systematic analysis | 399 | Dec-2013 | Lancet Global Health |
| 5 | England | Foster PJ | 76 | Methodology of the Singapore Indian Chinese Cohort (SICC) Eye Study: quanttile ethnic variations in the epidemiology of eye diseases in Asians | 179 | Nov-Dec 2009 | Ophthalmic Epidemiology |
| 6 | South Korea | Park KH | 184 | Visualization of the lamina cribrosa using enhanced depth imaging spectral-domain optical coherence tomography | 119 | Jul-2011 | American Journal of Ophthalmology |
| 7 | India | Rao HL | 84 | Comparison of different spectral domain optical coherence tomography scanning areas for glaucoma diagnosis | 110 | Sep-2010 | Ophthalmology |
| 8 | Australia | Wong TY | 85 | Methodology of the Singapore Indian Chinese Cohort (SICC) Eye Study: quanttile ethnic variations in the epidemiology of eye diseases in Asians | 179 | Nov-Dec 2009 | Ophthalmic Epidemiology |
| 9 | Turkey | Irkec M | 19 | Twenty-four-hour intraocular pressure control with bimatoprost and the bimatoprost/timolol fixed combicountry administered in the morning, or evening in exfoliative glaucoma | 30 | Feb-2010 | British Journal ofOphthalmology |
| 10 | Italy | Supuran CT | 52 | Dithiocarbamates strongly inhibit carbonic anhydrases and show antiglaucoma action in vivo | 138 | Feb-2012 | Journal of Medicinal Chemistry |
Authors and Author's Co-occurrence Map
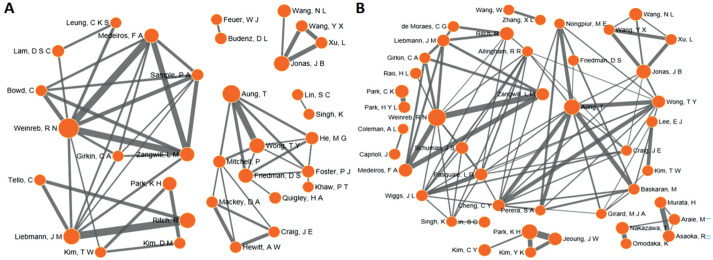
The top 20 authors with greatest number of related publications during 2009-2018 were listed in Table 4. First on the list was Weinreb RN from the USA, followed by Aung T from Singapore, Jonas JB from Germany and Park KH from South Korea were equally as the third rank. Co-occurrence maps were built to visualize the collaboration levels for the top 50 authors who published the most articles in the five years around 2009-2013 and 2014-2018 respectively (Figure 1). This visualizes the author's clustering results and reflects the cooperation between the authors to some extent.
Table 4. Top 20 authors with greatest number of related articles during 2009-2018.
| Rank | Author | Numbers |
| 1 | Weinreb RN | 325 |
| 2 | Aung T | 244 |
| 3 | Jonas JB | 184 |
| 4 | Park KH | 184 |
| 5 | Ritch R | 175 |
| 6 | Liebmann JM | 161 |
| 7 | Medeiros FA | 154 |
| 8 | Wong TY | 154 |
| 9 | Zangwill LM | 141 |
| 10 | Wang NL | 136 |
| 11 | Sun XH | 123 |
| 12 | Friedman DS | 120 |
| 13 | Park CK | 118 |
| 14 | Araie M | 117 |
| 15 | Pasquale LR | 108 |
| 16 | Kim CY | 105 |
| 17 | Pfeiffer N | 105 |
| 18 | Schuman JS | 100 |
| 19 | Jeoung JW | 96 |
| 20 | Nakazawa T | 95 |
Figure 1. The co-occurrence map of the top 50 authors with the greatest number of articles in the first (A, 2009-2013) and second (B, 2014-2018) halves of the decade from 2009 to 2018.
The larger the circle in the figure, the larger the number of articles published by the author. The thicker the lines, more cooperation among the authors. The connection will be displayed only when the number of the author's cooperative publication is no less than 12.
Author's Institutions and Author's Institutions Co-occurrence Map
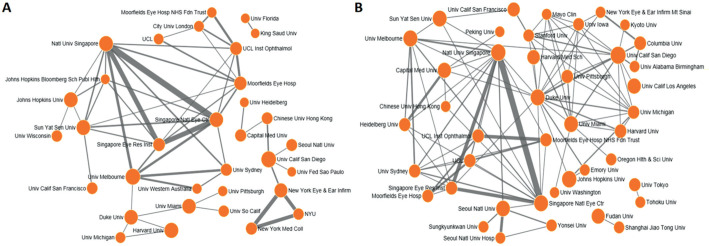
The top 3 institutions with the most publications were the University of California System, University of London and University College London (Table 5). Amongst the top 50 institutions with the largest number of publications in five years from 2009 to 2013 and 2014 to 2018, co-occurrence maps were respectively built to visualize the level of collaboration among institutions (Figure 2); which visualizes the results of the author's institutions clustering and reflects the trend of cooperation between institutions to some extent during this period of 10y.
Table 5. Top 20 institutions with the most published articles during 2009-2018.
| Rank | Author's institution | Number of articles | Percentage of 19609 articles |
| 1 | University of California System | 1060 | 5.41% |
| 2 | University of London | 664 | 3.39% |
| 3 | University College London | 587 | 2.99% |
| 4 | Johns Hopkins University | 502 | 2.56% |
| 5 | Harvard University | 486 | 2.48% |
| 6 | National University of Singapore | 478 | 2.44% |
| 7 | Moorfields Eye Hospital NHS Foundation Trust | 462 | 2.36% |
| 8 | Singapore National Eye Center | 450 | 2.30% |
| 9 | University of California San Diego | 430 | 2.19% |
| 10 | Duke University | 393 | 2.00% |
| 11 | University of Melbourne | 387 | 1.97% |
| 12 | Sun Yat-sen University | 361 | 1.84% |
| 13 | VA Boston Healthcare System | 340 | 1.73% |
| 14 | Bascom Palmer Eye Institute | 330 | 1.68% |
| 15 | Wilmer Eye Institute | 312 | 1.59% |
| 16 | Capital Medical University | 309 | 1.58% |
| 17 | University of Miami | 306 | 1.56% |
| 18 | Seoul National University | 293 | 1.49% |
| 19 | Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary | 282 | 1.44% |
| 20 | New York Eye and Ear Infirmary of Mount Sinai | 278 | 1.42% |
Figure 2. The co-occurrence map of the top 50 authors' institutions with the greatest number of articles in the first (A, 2009-2013) and second (B, 2014-2018) halves of the decade from 2009 to 2018.
Organization only; the larger the circle in the figure, the larger the number of articles published by the organization. The thicker the lines, the higher the cooperation frequency between the organizations. The line will be only displayed when cooperation article numbers are no less than 20.
Distribution of Funding Agency (Top 10 Funding Agencies in the Number of Articles)
The top 10 funding agencies during 2009-2018 were listed in Table 6. The top three are Research to Prevent Blindness (1201, 6.12%), National Institutes of Health (1068, 5.45%), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (581, 2.96%).
Table 6. The top 10 funding agencies during 2009-2018.
| Rank | Field: funding agency | Number of articles | Percentage of 19609 articles |
| 1 | Research to Prevent Blindness | 1201 | 6.12% |
| 2 | National Institutes of Health | 1068 | 5.45% |
| 3 | National Natural Science Foundation of China | 581 | 2.96% |
| 4 | National Eye Institute | 443 | 2.26% |
| 5 | Pfizer | 266 | 1.36% |
| 6 | Allergan | 232 | 1.18% |
| 7 | Alcon | 181 | 0.92% |
| 8 | Medical Research Council | 155 | 0.79% |
| 9 | NEI NIH HHS | 153 | 0.78% |
| 10 | National Institute for Health Research | 132 | 0.67% |
Distribution of Journals (Top 20 Journals in the Number of Articles)
The top 20 journals with the greatest number of glaucoma articles in the SCIE during 2009-2018 were shown in Table 7. The first journal is Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science which published 1848 glaucoma-related articles, accounting for 9.42% of the total number of glaucoma articles. Followed by the Journal of Glaucoma, which published 1558 (7.94%), and PLoS One which published 773 (3.94%) glaucoma articles.
Table 7. Top 20 journals which most of the glaucoma articles were published in during 2009-2018.
| Rank | Journal | Number of articles | Percentage of 19609 articles |
| 1 | Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science | 1848 | 9.42% |
| 2 | Journal of Glaucoma | 1558 | 7.94% |
| 3 | PLoS One | 773 | 3.94% |
| 4 | Ophthalmology | 683 | 3.48% |
| 5 | American Journal of Ophthalmology | 537 | 2.74% |
| 6 | British Journal of Ophthalmology | 504 | 2.57% |
| 7 | Acta Ophthalmologica | 461 | 2.35% |
| 8 | Graefes Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology | 450 | 2.29% |
| 9 | Eye | 448 | 2.28% |
| 10 | Experimental Eye Research | 368 | 1.88% |
| 11 | Molecular Vision | 333 | 1.70% |
| 12 | Current Eye Research | 324 | 1.65% |
| 13 | International Journal of Ophthalmology | 318 | 1.62% |
| 14 | European Journal of Ophthalmology | 315 | 1.61% |
| 15 | BMC Ophthalmology | 291 | 1.48% |
| 16 | Journal of Ophthalmology | 280 | 1.43% |
| 17 | Indian Journal of Ophthalmology | 256 | 1.30% |
| 18 | Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology | 251 | 1.28% |
| 19 | Cornea | 245 | 1.25% |
| 20 | Ophthalmologe | 245 | 1.25% |
Distribution of Impact Factor and Citation
The impact factors (based on the impact factor in 2017) of the journals were listed in Table 8. Totally 19 031 of 19 609 articles had impact factors, while 578 did not have. Up to 5679 glaucoma articles had impact factors in the range of 3-5 points, accounting for 28.96% of the total number of articles published. As for the citation, 19 609 papers had been cited for 236 084 times until March 29, 2019. The top 10 cited papers were shown in the Table 9. The mean number of citations was 377±267, with a range of 233 to 798.
Table 8. Distribution of journals' impact factor.
| Influence factor distribution interval | Number of articles | Percentage of 19609 articles |
| ≥50 | 5 | 0.03% |
| ≥40<50 | 9 | 0.05% |
| ≥30<40 | 3 | 0.02% |
| ≥20<30 | 20 | 0.10% |
| ≥10<20 | 135 | 0.69% |
| ≥5<10 | 1425 | 7.27% |
| ≥3<5 | 5679 | 28.96% |
| ≥2<3 | 4414 | 22.51% |
| ≥1<2 | 5629 | 28.71% |
| ≥0<1 | 1712 | 8.73% |
| No impact factor | 578 | 2.95% |
Table 9. Top 10 glaucoma-related articles with highest citation frequency during 2009-2018.
| Rank | Title | Corresponding author | Journal | Impact factor (2017) | Citations |
| 1 | Global prevalence of glaucoma and projections of glaucoma burden through 2040: a systematic review and Meta-Analysis | Ching-Yu Cheng | Ophthalmology | 7.479 | 798 |
| 2 | Glaucoma | Harry A Quigley | Lancet | 53.254 | 507 |
| 3 | Causes of vision loss worldwide, 1990-2010: a systematic analysis | Rupert R A Bourne | Lancet Global Health | 18.705 | 399 |
| 4 | Detection of macular ganglion cell loss in glaucoma by fourier-domain optical coherence tomography | Ou Tan | Ophthalmology | 7.479 | 374 |
| 5 | Treatment outcomes in the tube versus trabeculectomy (TVT) study after five years of follow-up | Steven J. Gedde | American Journal of Ophthalmology | 4.795 | 312 |
| 6 | The molecular basis of retinal ganglion cell death in glaucoma | AdrianaDi Polo | Progress In Retinal and Eye Research | 11.653 | 303 |
| 7 | Retinal nerve fiber layer imaging with spectral-domain optical coherence tomography: a variability and diagnostic performance study | Christopher Kai-shun Leung | Ophthalmology | 7.479 | 276 |
| 8 | Glaucomatous damage of the macula | Donald C. Hood | Progress In Retinal and Eye Research | 11.653 | 270 |
| 9 | Optical coherence tomography angiography of optic disc perfusion in glaucoma | David Huang | Ophthalmology | 7.479 | 263 |
| 10 | Genome-wide association study identifies susceptibility loci for open angle glaucoma at TMCO1 and CDKN2B-AS1 | Jamie E Craig | Nature Genetics | 27.125 | 233 |
Distribution of Keywords and Keywords Co-occurrence Map
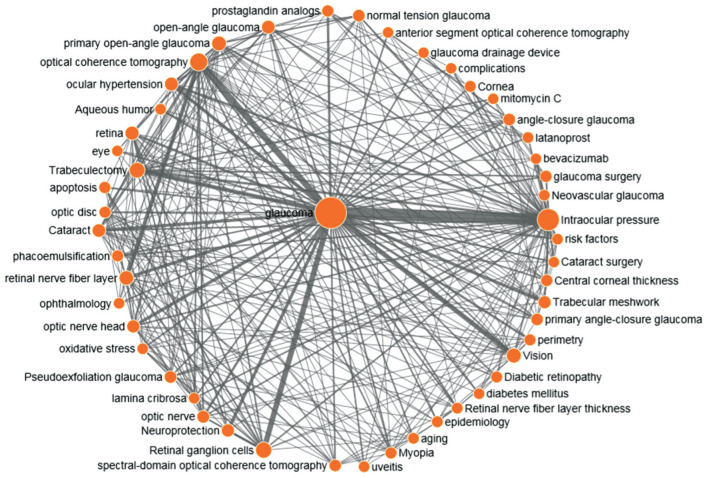
Given the large number of studies included in the database during a 10-year period, keywords were analyzed as a surrogate for major topics and themes for the published glaucoma articles. The top 3 keywords amongst all published glaucoma articles were intraocular pressure (IOP), OCT and retinal ganglion cells (Table 10). A co-occurrence map was built to visualize the top 50 keywords and their clustering pattern (Figure 3). The hotspots of glaucoma research based on the co-occurrence map in the past decade were mainly on: 1) glaucoma and IOP; 2) glaucoma and OCT; 3) glaucoma and retinal ganglion cells; 4) glaucoma and vision; 5) glaucoma and trabeculectomy and so on. It can be seen that glaucoma-related pathogenesis research, OCT and other imaging examinations in the diagnosis and treatment, glaucoma surgery has attracted much attention. And trabecular meshwork, primary angle-closure glaucoma and spectral-domain OCT have become new hot research topics in recent five years during 2014-2018.
Table 10. Distribution of related keywords in the articles during 2009-2018.
| Ranking | 2009-2018 | 2009-2013 | 2014-2018 |
| 1 | Glaucoma | Glaucoma | Glaucoma |
| 2 | Intraocular pressure | Intraocular pressure | Intraocular pressure |
| 3 | Optical coherence tomography | Optical coherence tomography | Optical coherence tomography |
| 4 | Retinal ganglion cells | Trabeculectomy | Retinal ganglion cells |
| 5 | Trabeculectomy | Retinal ganglion cells | Trabeculectomy |
| 6 | Vision | Vision | Primary open-angle glaucoma |
| 7 | Primary open-angle glaucoma | Primary open-angle glaucoma | Vision |
| 8 | Retinal nerve fiber layer | Ocular hypertension | Retinal nerve fiber layer |
| 9 | Retina | Cataract | Retina |
| 10 | Ocular hypertension | Retina | Open-angle glaucoma |
| 11 | Open-angle glaucoma | Retinal nerve fiber layer | Optic nerve head |
| 12 | Cataract | Open-angle glaucoma | Trabecular meshwork |
| 13 | Neuroprotection | Angle-closure glaucoma | Ocular hypertension |
| 14 | Optic nerve head | Neuroprotection | Cataract |
| 15 | Trabecular meshwork | Central corneal thickness | Neuroprotection |
| 16 | Optic nerve | Prostaglandin analogs | Optic nerve |
| 17 | Angle-closure glaucoma | Optic nerve | Primary angle-closure glaucoma |
| 18 | Pseudoexfoliation glaucoma | Pseudoexfoliation glaucoma | Normal tension glaucoma |
| 19 | Normal tension glaucoma | Normal tension glaucoma | Spectral-domain optical coherence tomography |
| 20 | Primary angle-closure glaucoma | Optic nerve head | Pseudoexfoliation glaucoma |
Figure 3. The co-occurrence map of the top 50 keywords appeared most in the articles.
The larger the circle in the figure, the larger the number of the article. The thicker the lines, and the stronger the correlation between keywords. The inter-keyword connection will be displayed only when they appeared simultaneously in no less than 5 articles.
DISCUSSION
In the current investigation, there were over 19 000 glaucoma-related publications searchable on SCIE published from 2009 to 2018. We observed a trend of gradual increase in the number of publications in glaucoma annually from 2009 to 2017. This gradual increase was followed by a slight decline in 2018. This may be related to a lag in time between publication and availability on SCIE: the search time for our investigation was March 2019, so some articles of 2018 may not have been included on SCIE.
The USA, China, and Japan have become the top three countries with the greatest number of glaucoma-related publications during this period of 10y. This is consistent with the distribution of reported funding agencies. Research to Prevent Blindness (RPB) and National Institutes of Health (NIH) were the most reported funding agencies, followed by National Natural Science Foundation of China.
Some of the most prolific authors in the field focused their research efforts on glaucoma imaging, particularly OCT. Dr. Weinreb from the USA published a total of 325 articles in 10y from 2009 to 2018, making him the most prolific author in this period. His most cited article was Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Imaging with Spectral-domain Optical Coherence Tomography A Variability and Diagnostic Performance Study[12], which was cited as high as 276 times. This was the article that showed that spectral-domain OCT had less variability than time-domain OCT in the measurement of the retinal nerve fiber layer, guiding the application of OCT in assessment of glaucoma progression. Japanese professor Dr. Araie published 117 articles in this period of 10y, among which the most cited article was Effects of Age, Sex, and Axial Length on the Three-Dimensional Profile of Normal Macular Layer Structures[13]. This article further provides information regarding the clinical application of OCT and accurate structural measurement. Other examples included Korean professor Lee's research on enhanced-depth imaging technique and lamina cribrosa, Indian professor Rao's investigation of RTVueOCT for retinal nerve fiber layer and retinal macular thickness measurements. These four authors and their research focus were congruent with the trend of increased application of OCT in the diagnosis and treatment of glaucoma. This trend was also confirmed in the co-occurrence of keywords, as glaucoma and OCT were one of the top co-occurring keywords in the glaucoma literature in the past 10y.
The pathogenesis of glaucoma has been better understood in 10y from 2009 to 2018. For example, the most frequently cited article by Dr. Wang was Cerebrospinal Fluid Pressure in Glaucoma: A Prospective Study[14], which had 232 citations. Dr. Wang firstly discovered that nearly 70% normal-tension glaucoma (NTG) patients had lower intracranial pressure (ICP). The pressure gradient across the lamina cribrosa increased with higher IOP or lower ICP. In addition to reducing IOP, NTG might also be treated by regulating the ICP through systemic therapy, for the reason to rebalance the trans-lamina cribrosa pressure gradient. Moreover, the trend towards focusing on the pathogenesis was also reflected in the journal of Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, which published the greatest number of glaucoma-related articles focusing more on laboratory and translational research in ophthalmology.
Comparing the first and second halves of the decade from 2009 to 2018, the proportion of articles from the USA declined in the last five years, while the proportion of published papers in several Asian countries increased significantly, such as China, South Korea, Japan, and India. This was an encouraging trend given that Asian patients were at higher risk of developing primary angle-closure glaucoma which could be prevented or treated with better public health access. This was certainly reflected in an increased effort in epidemiological studies related to glaucoma. For example, the most prolific German author Dr. Jonas published an important study that showed that in 2010, the world had 65% of blind patients, and 76% of moderate to severe visual impairment patients were due to a cause that could be prevented or treated[15]. In addition, although not in the top ten countries, an article originated from Singapore Institute of Ophthalmology conducted a Meta-analysis of global prevalence of glaucoma and projections of glaucoma burden through 2040[16]. The article was cited for 798 times and became the most cited articles in this period. This may reflect an encouraging trend on the increasing awareness and efforts to guide better public health education and campaigns to prevent glaucoma-related blindness in Asian countries and the rest of the world.
For the top 10 most cited articles on glaucoma during 2009-2018. As expected, all of these articles were published in top quartile journals by impact factor with a range of 4.80 to 53.25. In addition to the epidemiology, diagnosis and treatment of glaucoma, molecular mechanism and genetic study of glaucoma were widely cited.
Co-occurrence maps were built to visualize the collaboration levels for the top 50 authors or the top 50 institutions with the largest number of articles in the five years during 2009-2013 and 2014-2018 respectively. The frequency of cooperation among authors and among global institutions have become closer in the second halves of the decade. This again reflects an increasing trend of international and global collaboration in the field of glaucoma.
This research was an exploratory research based on the published literature, and might have some limitations. First, we only retrieved the data from SCIE database, some relevant articles might be omitted because of the database bias. Second, papers in different publication year were compared according to citations numbers, some relatively new and high-quality publications might not receive enough attention due to their lower citation frequency. Third, an inherent limitation of bibliographic databases might still exist when the bibliometric indicators proposed in this study were imported directly from the SCIE database, the names of authors and institutions might be inaccurate. Finally, based on the frequency of keyword occurrence, the research hotspots may miss the latest hotspots. However, it basically conforms to the development law of the international glaucoma field in the past ten years.
In conclusion, the global trends and focus of glaucoma research were delineated through bibliometric analysis. In a 10-year literature survey from 2009 to 2018, global glaucoma research has developed in a balanced manner, and the cooperation between various institutions and teams has become closer. The research hotspots were concentrated in the pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment of glaucoma. This study is based on the analysis of large samples and has important reference value for glaucoma research. We believe that strengthening international exchanges and cooperation will be important to promote scientific research in the field of glaucoma.
Acknowledgments
Authors' contributions: Conception and design: Sun YX, Cao K; Data analysis: Sun YX, Cao K; Writing: Sun YX, Liu YN, Han Y; Data collection: Zhang Y, Kong FQ, Labisi SA.
Conflicts of Interest: Sun YX, None; Liu YN, None; Han Y, None; Kong FQ, None; Zhang Y, None; Labisi SA, None; Cao K, None.
REFERENCES
- 1.Resnikoff S, Pascolini D, Etya'ale D, Kocur I, Pararajasegaram R, Pokharel GP, Mariotti SP. Global data on visual impairment in the year 2002. Bull World Health Organ. 2004;82(11):844–851. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ahmed IIK, Fea A, Au L, Ang RE, Harasymowycz P, Jampel HD, Samuelson TW, Chang DF, Rhee DJ, COMPARE Investigators A prospective randomized trial comparing hydrus and iStent microinvasive glaucoma surgery implants for standalone treatment of open-angle glaucoma: the COMPARE study. Ophthalmology. 2020;127(1):52–61. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2019.04.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Werner AC, Shen LQ. A review of OCT angiography in glaucoma. Semin Ophthalmol. 2019;34(4):279–286. doi: 10.1080/08820538.2019.1620807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Pellegrini M, Vagge A, Ferro Desideri LF, Bernabei F, Triolo G, Mastropasqua R, Del Noce CD, Borrelli E, Sacconi R, Iovino C, Di Zazzo AD, Forlini M, Giannaccare G. Optical coherence tomography angiography in neurodegenerative disorders. J Clin Med. 2020;9(6):E1706. doi: 10.3390/jcm9061706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Rosdahl JA, Gupta D. Prospective studies of minimally invasive glaucoma surgeries: systematic review and quality assessment. Clin Ophthalmol. 2020;14:231–243. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S239772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Shah M. Micro-invasive glaucoma surgery - an interventional glaucoma revolution. Eye Vis (Lond) 2019;6:29. doi: 10.1186/s40662-019-0154-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bua S, Supuran CT. Diagnostic markers for glaucoma: a patent and literature review (2013-2019) Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2019;29(10):829–839. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2019.1667336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Juliana FR, Kesse S, Boakye-Yiadom KO, Veroniaina H, Wang HH, Sun MH. Promising approach in the treatment of glaucoma using nanotechnology and nanomedicine-based systems. Molecules. 2019;24(20):E3805. doi: 10.3390/molecules24203805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Wallin JA. Bibliometric methods: pitfalls and possibilities. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2005;97(5):261–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-7843.2005.pto_139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ellegaard O, Wallin JA. The bibliometric analysis of scholarly production: How great is the impact? Scientometrics. 2015;105(3):1809–1831. doi: 10.1007/s11192-015-1645-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.González LM, García-Massó X, Pardo-Ibañez A, Peset F, Devís-Devís J. An author keyword analysis for mapping Sport Sciences. PLoS One. 2018;13(8):e0201435. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0201435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Leung CK, Cheung CY, Weinreb RN, Qiu QL, Liu S, Li HT, Xu GH, Fan N, Huang LN, Pang CP, Lam DS. Retinal nerve fiber layer imaging with spectral-domain optical coherence tomography: a variability and diagnostic performance study. Ophthalmology. 2009;116(7):1257–1263. 1263.e1–2. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2009.04.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ooto S, Hangai M, Tomidokoro A, Saito H, Araie M, Otani T, Kishi S, Matsushita K, Maeda N, Shirakashi M, Abe H, Ohkubo S, Sugiyama K, Iwase A, Yoshimura N. Effects of age, sex, and axial length on the three-dimensional profile of normal macular layer structures. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52(12):8769–8779. doi: 10.1167/iovs.11-8388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ren RJ, Jonas JB, Tian G, Zhen Y, Ma K, Li SN, Wang HT, Li B, Zhang XJ, Wang NL. Cerebrospinal fluid pressure in glaucoma: a prospective study. Ophthalmology. 2010;117(2):259–266. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2009.06.058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bourne RR, Stevens GA, White RA, Smith JL, Flaxman SR, Price H, Jonas JB, Keeffe J, Leasher J, Naidoo K, Pesudovs K, Resnikoff S, Taylor HR, Vision Loss Expert Group Causes of vision loss worldwide, 1990-2010: a systematic analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2013;1(6):e339–e349. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(13)70113-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Tham YC, Li X, Wong TY, Quigley HA, Aung T, Cheng CY. Global prevalence of glaucoma and projections of glaucoma burden through 2040: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology. 2014;121(11):2081–2090. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2014.05.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]