Figure 3. Neuromelanin forming SH-SY5Y cells are more susceptible to PhIP-mediated mitochondrial stress compare to cells without neuromelanin.
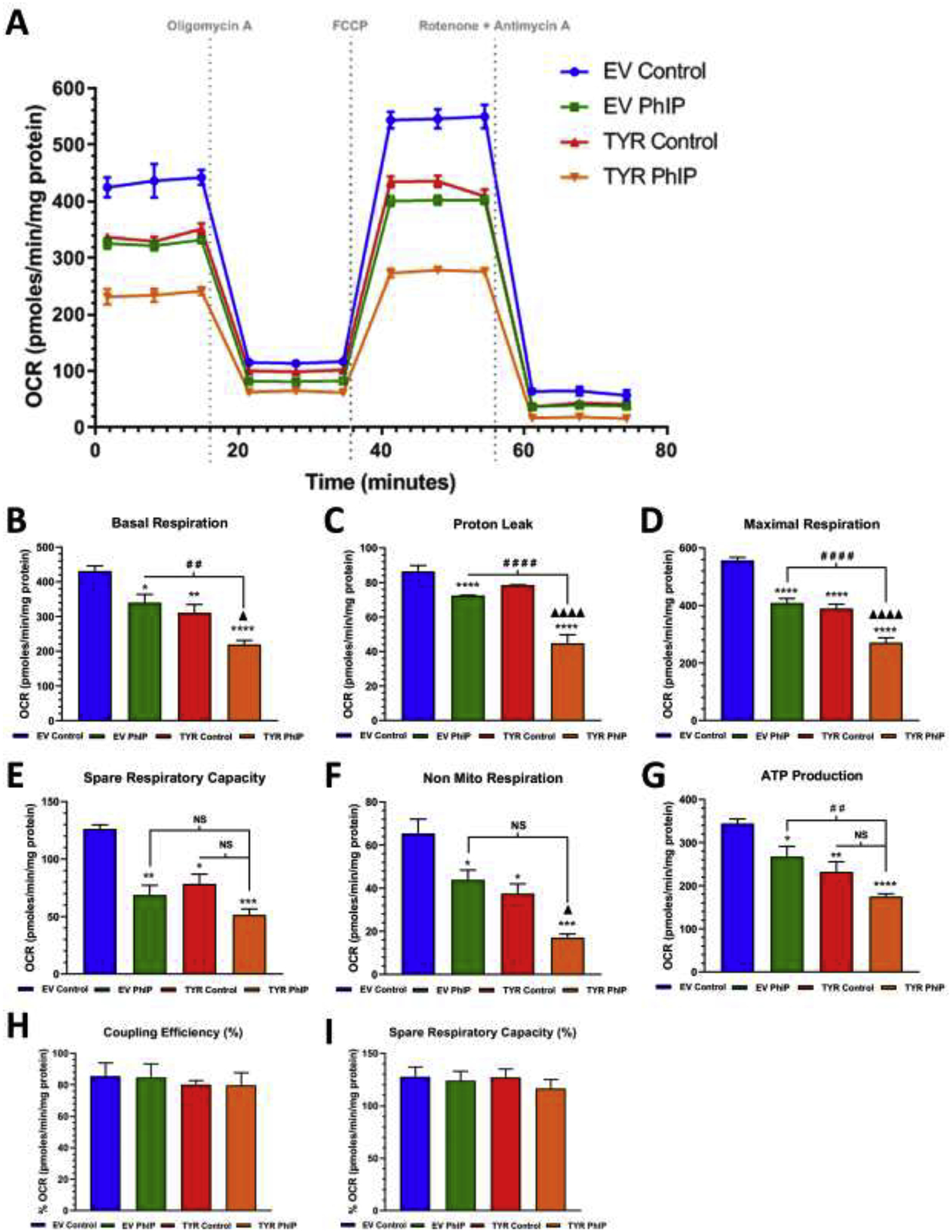
A. A schematic representation of the mitochondrial bioenergetics profile in relation to oxygen consumption rate levels, in both EV and TYR SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells treated with or without PhIP (10 μM) for 24 h. Post treatment, the change in the oxygen consumption rate (OCR) levels were determined using a Seahorse XFp analyzer. B Basal respiration, C proton leak, D maximum respiration, E spare respiratory capacity, F non-mitochondrial respiration, G ATP production, H coupling capacity (%) and I spare respiratory capacity (%) were calculated by measuring change in OCR levels post sequential addition of oligomycin (1 μM), FCCP (1 μM), and Rotenone (0.5 μM) +Antimycin A (0.5 μM), respectively, as indicated by arrows in the Figure 3A. Results are representative of at least 4 independent experiments performed in replicates of four. Data are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. *p<0.05, *p<0.01, ***p<0.001 and ****p<0.0001 vs EV Control group; # #p<0.01, # # #p<0.001 and # # # #p<0.0001 vs EV PhIP-treated cells; Δp<0.05 and Δ Δ Δ Δp<0.0001 vs TYR control cells.
