This economic evaluation assesses the cost-effectiveness of screening for osteoporosis using dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry followed by osteoporosis treatment in a hypothetical sample of older men with a history of falls.
Key Points
Question
Is it cost-effective to screen for osteoporosis in older men with a history of falls?
Findings
In this model-based economic evaluation of a hypothetical cohort of men aged 65 years, screening with dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry followed by treatment for those diagnosed with osteoporosis had an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio of $33 169 per quality-adjusted life-year gained and was preferred over usual care at the willingness-to-pay threshold of $100 000 per quality-adjusted life-year gained.
Meaning
These findings suggest that, for older men who have fallen at least once in the past year, screening with dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry followed by treatment for those diagnosed with osteoporosis is a cost-effective use of resources.
Abstract
Importance
Falls and osteoporosis share the potential clinical end point of fractures among older patients. To date, few fall prevention guidelines incorporate screening for osteoporosis to reduce fall-related fractures.
Objective
To assess the cost-effectiveness of screening for osteoporosis using dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) followed by osteoporosis treatment in older men with a history of falls.
Design, Setting, and Participants
In this economic evaluation, a Markov model was developed to simulate the incidence of major osteoporotic fractures in a hypothetical cohort of community-dwelling men aged 65 years who had fallen at least once in the past year. Data sources included literature published from January 1, 1946, to July 31, 2020. The model adopted a societal perspective, a lifetime horizon, a 1-year cycle length, and a discount rate of 3% per year for both health benefits and costs. The analysis was designed and conducted from October 1, 2019, to September 30, 2020.
Interventions
Screening with DXA followed by treatment for men diagnosed with osteoporosis compared with usual care.
Main Outcomes and Measures
Incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER), measured by cost per quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) gained.
Results
Among the hypothetical cohort of men aged 65 years, the screening strategy had an ICER of $33 169/QALY gained and was preferred over usual care at the willingness-to-pay threshold of $100 000/QALY gained. The number needed to screen to prevent 1 hip fracture was 1876; to prevent 1 major osteoporotic fracture, 746. The screening strategy would become more effective and less costly than usual care for men 77 years and older. The ICER for the screening strategy did not substantially change across a wide range of assumptions tested in all other deterministic sensitivity analyses. At a willingness-to-pay threshold of $50 000/QALY gained, screening was cost-effective in 56.0% of simulations; at $100 000/QALY gained, 90.8% of simulations; and at $200 000/QALY gained, 99.6% of simulations.
Conclusions and Relevance
These findings suggest that for older men who have fallen at least once in the past year, screening with DXA followed by treatment for those diagnosed with osteoporosis is a cost-effective use of resources. Fall history could be a useful cue to trigger assessment for osteoporosis in men.
Introduction
Falls and osteoporosis are geriatric syndromes that share the potential clinical end point of fractures.1 Approximately 1 in 4 men 65 years or older fall each year in the United States, making falls a public health concern, particularly among older adults.2 Prevalence of osteoporosis also increases with age, affecting an estimated total of 2 million men.3 By 2030, the number of hip fractures in men is projected to increase to 109 000 each year.4 Hip fractures are overwhelmingly precipitated by falls.5 Many older men at risk for falls are predisposed to fractures by undetected osteoporosis.6,7,8,9 It therefore makes clinical sense to screen for osteoporosis as a part of routine fall prevention care. Performing dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) in those who have fallen could be crucial because a history of falls does not necessarily indicate osteoporosis and a need for osteoporosis treatment. To date, few fall prevention guidelines incorporate screening for osteoporosis to reduce fall-related fractures.10,11,12 Although several professional organizations have advocated routine screening for osteoporosis in older men, the US Preventive Services Task Force continues to conclude that evidence was insufficient to justify this practice.13,14,15,16 Medicare coverage for DXA is rather restrictive in men unless they have known skeletal abnormalities or secondary causes of osteoporosis.17 Despite a predicted rise in the number of hip fractures, osteoporosis remains underdiagnosed and undertreated in men.18 Recent clinical trials suggested that population-based screening for osteoporosis could reduce hip and osteoporotic fractures in older women.19,20,21,22 A similar clinical trial would be ideal to evaluate the efficacy of a screening practice in older men but unrealistic because of the need for a larger sample size. Accordingly, we developed a simulation model to evaluate the long-term health and economic effect of screening with DXA followed by treatment for those diagnosed with osteoporosis in older men with a history of falls.
Methods
Overview and Model Structure
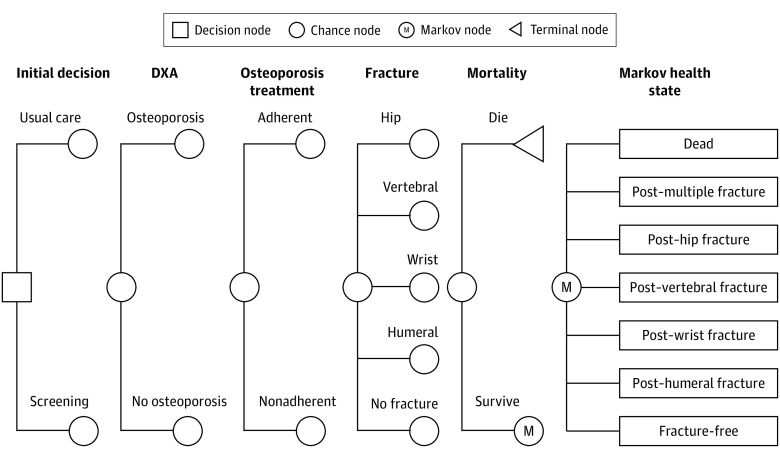
For this economic evaluation study, a Markov model was developed to simulate the prognosis of older men with a history of falls in the last year based on previously published models of screening for osteoporosis and the guideline by the European Society for Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis, Osteoarthritis, and Musculoskeletal Diseases and the US branch of the International Osteoporosis Foundation (Figure 1).23,24,25,26,27 Health states were determined by a history of major osteoporotic fractures to represent those who experienced any combination of different types of fractures. Data sources included literature published from January 1, 1946, to July 31, 2020. The model adopted a societal perspective, a lifetime horizon, a 1-year cycle length, and a discount rate of 3% per year for both health benefits and costs.28 The analysis was performed by using TreeAge Pro Suite 2018 software, version 18.2.1-v20180828 (TreeAge Software). This study follows the recommendations of the Consolidated Health Economic Evaluation Reporting Standards (CHEERS) reporting guideline.29
Figure 1. Markov Model Structure.
All men entered the model in the fracture-free state. At the decision node, they were assigned to either usual care or screening. They had osteoporosis or no osteoporosis at baseline. Osteoporosis treatment was provided only if they were diagnosed with osteoporosis by screening and adherent to recommended therapy. Each year, they were at risk for sustaining a fracture or dying of other causes. If they sustained hip or clinical vertebral fractures, they were at risk of dying due to those fractures. Depending on an event experienced, they remained in the fracture-free state, proceeded to the postfracture states, or were absorbed into the dead state. In the actual model, the post–multiple fracture state was separated into 15 health states representing any combinations of different types of fractures. DXA indicates dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry.
Population
The model targeted a hypothetical cohort of US community-dwelling men aged 65 years who had fallen at least once in the past year. It was assumed that all men were fracture free at baseline.
Interventions
Men were assigned to either usual care or screening for osteoporosis. Those who were assigned to usual care underwent no screening for osteoporosis. Those who were assigned to screening for osteoporosis underwent DXA of the femoral neck and the lumbar spine and received treatment if they were diagnosed with osteoporosis. Osteoporosis was defined as a T score of bone mineral density (BMD) of less than −2.5 at either site using the reference for White women aged 20 to 29 years from the National Nutrition and Examination Survey (NHANES) III.30 An alternate scenario using the reference for White men aged 20 to 29 years was also tested in a scenario analysis. Alendronate sodium (70 mg orally once a week for 5 years) was selected as a drug of choice when osteoporosis treatment was indicated. An alternate scenario selecting zoledronic acid (5 mg intravenously once a year for 5 years) as a drug of choice was also tested in a scenario analysis. We assumed that a basic metabolic panel was ordered and comprehensive oral examination was performed before initiation of zoledronic acid therapy. Those receiving osteoporosis treatment were assumed to require an additional physician visit each year during a 5-year course of therapy and to incur the cost of DXA in the second and fourth year after treatment initiation.23,26,31 We also assumed that both groups were offered the same fall prevention measures and received a daily supplementation of calcium (1200 mg) and vitamin D (800 IU).
Input Parameters
Model parameters are summarized in Table 1 and eTable in the Supplement and described in detail below. Prevalence of osteoporosis, incidence of fractures, and utility for a fracture-free state were age dependent. Other parameters were considered as constant for each age group.
Table 1. Model Parameters.
| Parameter | Value (range) | Distribution | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Discount rate, % | 3 (0-6) | Not applied | Neumann et al28 (2016) |
| Prevalence of osteoporosis, %a | 3.3 (1.98-4.62) | Beta | Wright et al3 (2014) |
| Relative risk of hip fractures associated with a history of falls | |||
| Base case | 1.54 (1.21-1.95) | Log-normal | Leslie et al8 (2019) and Harvey et al9 (2018) |
| 1 Fallb | 1.51 (1.06-2.15) | ||
| 2 Fallsb | 1.88 (1.12-3.16) | ||
| ≥3 Fallsb | 3.41 (2.19-5.31) | ||
| Relative risk of nonhip fractures associated with history of falls | |||
| Base case | 1.51 (1.32-1.73) | Log-normal | Leslie et al8 (2019) and Harvey et al9 (2018) |
| 1 Fallb | 1.44 (1.23-1.67) | ||
| 2 Fallsb | 1.65 (1.31-2.08) | ||
| ≥3 Fallsb | 2.52 (2.05-3.11) | ||
| Relative risk of fractures associated with the presence of osteoporosis | |||
| Hip | 5.98 (3.50-9.06) | Log-normal | Looker et al32 (2012) and Johnell et al33 (2005) |
| Nonhip | 2.51 (2.01-3.12) | ||
| Relative risk of fractures associated with a history of prior fractures | |||
| Hip | 1.97 (1.12-3.48) | Log-normal | Kanis et al34 (2004) |
| Nonhip | 1.91 (1.50-2.43) | ||
| Relative risk of fractures during osteoporosis treatment | |||
| Clinical vertebral | 0.4 (0.11-1.51) | Log-normal | Nayak and Greenspan35 (2017) |
| Nonvertebral | 0.6 (0.40-0.90) | ||
| Treatment benefit offset, y | 5 (0-10) | Not applied | Hiligsmann et al27 (2019) |
| Adherence to osteoporosis treatment, % | |||
| Alendronate | 43 (32-54) | Beta | Kothawala et al36 (2007) and Koller et al37 (2020) |
| Zoledronic acidb | 36 (23-50) | ||
| Relative risk of death associated with a history of falls | 1.3 (0.90-1.80) | Log-normal | Dunn et al38 (1992) |
| Relative risk of death after hip fractures | |||
| First year | 3.7 (3.31-4.14) | Log-normal | Haentjens et al39 (2010) |
| Subsequent years | 2.53 (1.81-3.54) | ||
| Relative risk of death after clinical vertebral fractures | 1.83 (1.80-1.86) | Log-normal | Lau et al40 (2008) |
| Cost, $c | |||
| DXA | 39.99 | Gamma | American College of Rheumatology41 (2020) |
| Physician visit | 76.06 | American College of Rheumatology41 (2020) | |
| Osteoporosis treatment | |||
| Alendronate | 250 | Gamma | Drugs for postmenopausal osteoporosis42 (2020) |
| Zoledronic acidb | 515 | Gamma | Drugs for postmenopausal osteoporosis42 (2020), Insinga43 (2016), CMS44 (2020), California Department of Health Care Services45 (2015) |
| Fracture event | |||
| Hip | 31 713 | Gamma | Gabriel et al46 (2002) and Kilgore et al47 (2013) |
| Clinical vertebral | 9656 | ||
| Wrist | 8804 | ||
| Humeral | 5237 | ||
| Post–hip fracture state (per year) | 11 736 | Gamma | Schousboe et al23 (2007) |
| Utility multiplier | |||
| Fracture freea | 0.84 (0.80-0.85) | Log-normal | Hanmer et al48 (2006) and |
| History of falls | 0.97 (0.94-0.98) | Theim et al49 (2014) | |
| Fracture event | |||
| Hip | 0.55 (0.53-0.57) | Log-normal | Svedbom et al50 (2018) and Lesnyak et al51 (2020) |
| Clinical vertebral | 0.68 (0.65-0.70) | ||
| Wrist | 0.83 (0.82-0.84) | ||
| Humeral | 0.76 (0.72-0.79) | ||
| Postfracture state | |||
| Hip | 0.86 (0.84-0.90) | Log-normal | Svedbom et al50 (2018) and Lesnyak et al51 (2020) |
| Clinical vertebral | 0.85 (0.82-0.87) | ||
| Wrist | 0.99 (0.97-1.00) | ||
| Humeral | 0.89 (0.85-0.92) |
Abbreviations: CMS, Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services; DXA, dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry.
Age-specific variable. See the eTable in the Supplement.
Tested in a scenario analysis.
Range is 50% to 200% of the base-case costs.
Prevalence of Osteoporosis
The age-dependent prevalence of osteoporosis was based on a cross-sectional study from the 2005-2010 NHANES.3 The cohort studies from 3 countries6,7,8 did not observe a significant difference in BMD among men with and without a history of falls. Therefore, we assumed that the prevalence of osteoporosis was not affected by a history of falls or the number of falls in the previous year. The base-case estimate of the prevalence of osteoporosis was altered widely in sensitivity analyses.
Incidence of Fractures
The age-dependent fracture rates were obtained from hospital discharge data from the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project Nationwide Inpatient Sample.52,53 The model modified the fracture rates based on a history of falls, the presence of osteoporosis, and a history of fractures. The relative risks of fractures associated with a history of falls were taken from a meta-analysis of cohort studies from 3 countries.9 Pooled data from men with a history of a single fall and multiple falls were obtained and were assumed to last as long as 10 years. An alternate scenario considering the number of falls was also tested in a scenario analysis. The relative risks of fractures stratified by the number of falls (ie, 1, 2, or ≥3) in the past year were based on the combined data for men and women from a cohort study in Canada.8 The relative risks of fractures associated with the presence of osteoporosis were calculated using BMD data from the 2005-2008 NHANES and a meta-analysis of cohort studies from 12 countries.32,33 The excess risks of fractures associated with a history of fractures were taken from a meta-analysis of cohort studies from 11 countries.34
Treatment Effect
Relative risk reductions of fractures by osteoporosis treatment were taken from a meta-analysis of clinical trials of bisphosphonates in men.35 We assumed that a history of falls did not alter the fracture reduction benefit by osteoporosis treatment. The model used the reduction in nonvertebral fracture rates as a surrogate for the reduction in hip, wrist, and humeral fracture rates.27 The fracture reduction benefit was assumed to appear in the second year of therapy.54 The model incorporated a linear decrease in the fracture reduction benefit during 5 years after its termination.27 Adherence to alendronate and zoledronic acid treatment was based on meta-analyses of multiple observational studies.36,37 The model adopted a conservative assumption that only those who completed a 5-year course of osteoporosis treatment gained the fracture reduction benefit. Adverse effects of treatment were not modeled based on a systematic review.16
Mortality
The background mortality rates were based on 2017 US life tables published by the National Center for Health and Statistics.55 Excess mortality attributable to a history of falls was taken from the Longitudinal Study on Aging.38 Excess mortality after hip fractures was taken from a meta-analysis of cohort studies from 7 countries.39 Excess mortality after clinical vertebral fractures was taken from a retrospective data analysis of Medicare claims.40 An alternate scenario excluding excess mortality after clinical vertebral fractures was also tested in a scenario analysis.27
Costs
The costs of DXA and a physician visit were obtained from the 2020 Medicare National Average Rates (Current Procedural Terminology [CPT] codes 77080 and 99213, respectively).41 The wholesale acquisition costs of alendronate and zoledronic acid were used as the medication costs.42 Those who did not adhere to alendronate therapy accrued the medication cost for only 6 months. Those who did not adhere to zoledronic acid therapy accrued the medication cost for only the first year. Infusion and related supply costs of zoledronic acid were taken from a US claim-based cost analysis.43 Costs of the basic metabolic panel (CPT code 80048) and comprehensive dental examination (CPT code D 0150) were based on the national mean commercial rates.44,45 Acute costs of managing each type of fracture were taken from a US claim-based cost analyses.46,47 The long-term cost of hip fractures (eg, increased admission to long-term care facilities) was incorporated.23 All costs were inflated to 2019 US dollars using the Consumer Price Index for Medical Care for All Urban Consumers.56
Quality of Life
The age-dependent, fracture-free utility values were based on EuroQol-5 Dimension (EQ-5D) scores collected from nationally representative US community-dwelling samples.48 The utility multiplier for a history of falls was calculated using a EQ-5D survey in Germany.49 The utility multiplier for each type of fracture was taken from the International Costs and Utilities Related to Osteoporotic Fractures Study.50,51 If individuals sustained a fracture, for example, their baseline utilities were multiplied by the utility of that fracture event in the first year and by the utility of that postfracture health state in subsequent years.
Model Validation
To assess its external validity, the model simulated the prognosis of men aged 50 years without a history of falls receiving usual care. The predicted lifetime risk of hip fracture was 11%; clinical vertebral fracture, 9%; wrist fracture, 3%; and humeral fracture, 3%. These predicted risks approximated well with published estimates.57
Statistical Analysis
The analysis was designed and conducted from October 1, 2019, to September 30, 2020. We measured health outcomes in quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs). The incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) of a strategy was calculated as the additional cost of that strategy divided by its additional health benefit compared with the competing strategy. Deterministic sensitivity analyses were conducted on discount rates, age at screening, treatment characteristics (ie, treatment effect during treatment and after discontinuation), medication treatment adherence, excess mortality after fractures, treatment costs, fracture costs, and effect of fractures on utility. The 95% CI of each parameter was obtained, when available; otherwise, 50% to 200% of the base-case estimates were used. Because the reduction in nonvertebral fractures with treatment was used as a surrogate for reduction in hip fracture rates, this assumption was tested rigorously in sensitivity analyses. A probabilistic sensitivity analysis was also conducted in which the model was run using a value for each parameter down randomly from the distribution assigned to that parameter. The model ran 100 000 iterations to generate a cost-effectiveness acceptability curve showing the probability that either strategy was cost-effective using varying willingness-to-pay (WTP) thresholds.
Results
Base-Case Analysis
For the base-case population, 1876 men needed to undergo screening to prevent 1 hip fracture, and 746 men needed to undergo screening to prevent 1 major osteoporotic fracture (Table 2). The screening strategy improved quality-adjusted survival by 0.0026 QALYs, increased costs by $87, and had an ICER of $33 169/QALY gained. Therefore, the screening strategy would be preferred over usual care at the conventional WTP threshold of $100 000/QALY gained.
Table 2. Cost-effectiveness According to Age at Screening.
| Strategy | Number needed to screen | Cost, $ | QALYs | ICER, $/QALY | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hip fracture | MOF | ||||
| Aged 65 y (base case) | |||||
| Usual care | NA | NA | 6447 | 9.6146 | Reference |
| Screening | 1876 | 746 | 6534 | 9.6173 | 33 169 |
| Aged 70 y | |||||
| Usual care | NA | NA | 7396 | 7.8295 | Reference |
| Screening | 739 | 393 | 7451 | 7.8339 | 12 631 |
| Aged 75 y | |||||
| Screening | NA | NA | 8061 | 6.1953 | Reference |
| Usual care | 482 | 309 | 8094 | 6.2002 | 6670 |
| Aged 80 y | |||||
| Usual care | NA | NA | 9017 | 4.6041 | Dominated |
| Screening | 183 | 104 | 8932 | 4.6152 | Reference |
Abbreviations: ICER, incremental cost-effectiveness ratio; MOF, major osteoporotic fracture; NA, not applicable; QALY, quality-adjusted life-year.
Sensitivity Analyses
These results were sensitive to assumptions about the age at screening (Table 2). As the target population became older, numbers needed to screen to prevent 1 hip fracture and 1 major osteoporotic fracture would become smaller and the screening strategy would become increasingly cost-effective. The screening strategy would become dominant (ie, more effective and less costly than usual care) for men 77 years or older. These results were also sensitive to the assumption about the treatment effect during osteoporosis treatment. Under the most conservative assumption about the relative risk of nonvertebral fractures during osteoporosis treatment (ie, 0.90), the ICER for the screening strategy would slightly exceed the conventional WTP threshold of $100 000/QALY gained. The screening strategy would be preferred over usual care for men 66 years or older. The ICER for the screening strategy did not substantially change across a reasonable range of assumptions tested in all other deterministic sensitivity analyses (Table 3).
Table 3. One-Way Deterministic Sensitivity Analyses.
| Parameter | ICER, $/QALY | Range |
|---|---|---|
| Discount rate, % | 19 477-51 655 | 0-6 |
| Prevalence of osteoporosis, % | 21 461-64 966 | 1.98-4.62 |
| Relative risk of fracture on osteoporosis treatment | ||
| Clinical vertebral | 28 034-80 949 | 0.11-1.51 |
| Nonvertebral | 16 765-104 340 | 0.40-0.90 |
| Treatment benefit offset, y | 22 013-67 222 | 0-10 |
| Adherence to osteoporosis treatment, % | 23 806-48 967 | 32-54 |
| Relative risk of death after hip fracture | ||
| First year | 33 053-33 277 | 3.31-4.14 |
| Subsequent years | 32 184-34 421 | 1.81-3.54 |
| Relative risk of death after vertebral fracture | 33 085-33 253 | 1.80-1.86 |
| Cost, $ | ||
| Osteoporosis treatment | 29 557-40 392 | 50%-200% of the base-case costs |
| Fracture event | ||
| Hip | 25 986-36 760 | |
| Clinical vertebral | 31 791-33 857 | |
| Wrist | 32 911-33 298 | |
| Humeral | 32 768-33 369 | |
| Post–hip fracture health state (per year) | 20 208-39 649 | |
| Utility multiplier | ||
| Fracture event | ||
| Hip | 33 019-33 320 | 0.53-0.57 |
| Clinical vertebral | 33 027-33 263 | 0.65-0.70 |
| Wrist | 33 157-33 181 | 0.82-0.84 |
| Humeral | 33 067-33 245 | 0.72-0.79 |
| Postfracture health state | ||
| Hip | 32 686-34 178 | 0.84-0.90 |
| Clinical vertebral | 32 369-33 581 | 0.82-0.87 |
| Wrist | 33 066-33 220 | 0.97-1.00 |
| Humeral | 32 756-33 485 | 0.85-0.92 |
Abbreviations: ICER, incremental cost-effectiveness ratio; QALY, quality-adjusted life year.
Probabilistic Sensitivity Analysis
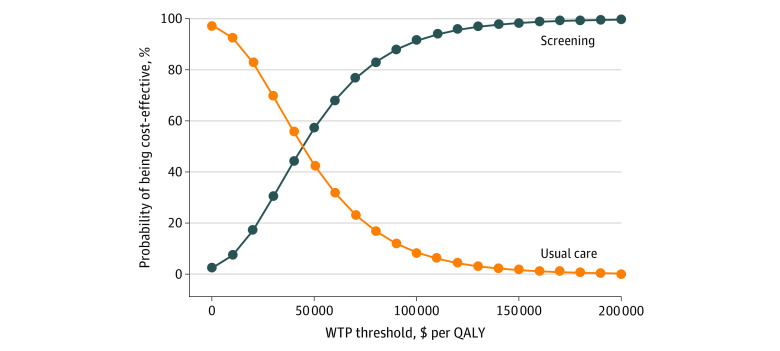
The result of the probability sensitivity analysis in the base-case population is displayed in the cost-effectiveness acceptability curve (Figure 2). At the WTP threshold of $50 000/QALY gained, the screening strategy would be cost-effective in 56.0% of stimulations; at $100 000/QALY gained, 90.8% of simulations; and at $200 000/QALY gained, 99.6% of simulations.
Figure 2. Cost-effectiveness Acceptability Curve.
A range of willingness-to-pay (WTP) thresholds were plotted on the horizontal axis against the probability that either usual care or the screening strategy would be cost-effective at that WTP threshold on the vertical axis. QALY indicates quality-adjusted life-year.
Scenario Analyses
If the reference for White men aged 20 to 29 years was applied for the diagnosis of osteoporosis, an ICER for the screening strategy would decrease to $31 039/QALY gained. If zoledronic acid was selected as a drug of choice when osteoporosis treatment was indicated, an ICER for the screening strategy would increase to $52 653/QALY gained. If men with a history of a single fall in the past year were targeted, an ICER for the screening strategy would increase to $34 705/QALY gained. If men with a history of multiple falls in the past year were targeted, an ICER for the screening strategy would decrease to $25 159/QALY gained for men with a history of 2 falls and $5478/QALY gained for men with a history of at least 3 falls. If excess mortality after clinical vertebral fractures was excluded from the model, an ICER for the screening strategy would increase to $36 360/QALY gained. Therefore, across various scenarios tested, the screening strategy would remain preferred over usual care at the conventional WTP threshold of $100 000/QALY gained.
Discussion
This study found that screening with DXA followed by treatment for those diagnosed with osteoporosis would be reasonably cost-effective for men aged 65 years who have fallen at least once in the past year. If the target population was older than 77 years, it would simultaneously improve health outcomes and save money from the societal perspective. These findings were robust to wide variations of the model assumptions and concur with previous cost-effectiveness analyses indicating that screening could be justified when targeted to men at higher risk for osteoporotic fractures.23,24,25,26 These findings are also promising given the emerging evidence that population-based screening using fracture risk assessment and DXA is effective to reduce hip and osteoporotic fractures in postmenopausal women.19,20,21,22 The observed numbers needed to screen to prevent a hip and an osteoporotic fracture (ie, 272 and 247, respectively) from these clinical trials are comparable with our model estimates for men aged 75 to 80 years.22
Determining whether the patient has fallen in the past year is the first step in preventing future falls and the major injuries that can result from falling.58 Fall risk assessment is integrated into the Welcome to Medicare examination and the Medicare Annual Wellness Visit.59 In a recent review undertaken by the US Preventive Services Task Force, multifactorial interventions or single exercise-based interventions were found to reduce fall risk, but their effect on fracture risk was not significant.10 Fracture prevention could be achieved by screening and treatment for osteoporosis without reducing the number of falls.60 These findings do not suggest that fall prevention measures should not be included in patient management but do raise a concern that, for individuals with significant skeletal risk factors, fall prevention measures alone might not be sufficient to reduce fall-related fractures. On the other hand, combined with older age, the presence of osteoporosis accounts for only one-third of all fracture cases in men.61 The BMD-based approach is likely to miss a large number of individuals who do not have osteoporosis and have nonskeletal risk factors (eg, falls) and is unlikely to reduce a large number of fractures. A combined approach to address both falls and osteoporosis is not a new concept.62 Because fracture prevention is the ultimate goal, inclusion of screening for osteoporosis into the fall prevention algorithm could potentially lead to a further reduction of fractures in individuals who have fallen.63
Limitations
The study should be interpreted in light of several cautions. First, we assumed that the fracture reduction efficacy by osteoporosis treatment was not altered by a history of falls. In a clinical trial of clodronate in postmenopausal women,64 fall risk did not significantly affect its fracture reduction efficacy. In a clinical trial of zoledronic acid in institutionalized, functionally impaired women with osteoporosis,65,66 improvements in BMD were comparable to those observed in community-dwelling, functionally unimpaired women. None of the clinical trials of bisphosphonates in men were adjusted for their underlying fall risk.35 Therefore, we varied the assumption about treatment effectiveness widely in sensitivity analyses. Second, the characterization of risk factors for fracture that contribute significantly to fracture risk, beyond that provided by BMD, has stimulated the development of risk assessment tools to determine a treatment threshold. The more adequately evaluated tools include the Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX) tool (University of Sheffield),67 Garvan bone fracture risk calculator (Garvan Institute of Medical Research),68 and the QFracture risk calculator (ClinRisk Ltd).69 Both the Garvan and QFracture tools include a history of falls, whereas the FRAX tool does not. Recognizing the limitations of falls data in the current FRAX cohorts, an expert panel recommended that FRAX probability might be modified to account for a history of falls, with the output inflated by 30% for each past fall (for ≤5 falls).70 In this study, the model did not consider these risk assessment tools to determine a treatment threshold because drug efficacy in preventing fractures has been proven only in individuals with osteoporosis defined based on BMD or fracture history.
Conclusions
The results of this economic evaluation suggest that for older men who have fallen at least once in the past year, screening with DXA followed by treatment for those diagnosed with osteoporosis may be a cost-effective use of resources. In clinical practice, fall history could be a useful cue to trigger assessment for osteoporosis in men. The study also suggests that Medicare coverage of screening with DXA could be expanded to older men with a history of falls.
eTable. Age-Dependent Model Parameters
References
- 1.Colón-Emeric C, Whitson HE, Berry SD, et al. AGS and NIA bench-to bedside conference summary: osteoporosis and soft tissue (muscle and fat) disorders. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2020;68(1):31-38. doi: 10.1111/jgs.16248 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bergen G, Stevens MR, Burns ER. Falls and fall injuries among adults aged ≥65 years—United States, 2014. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2016;65(37):993-998. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6537a2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wright NC, Looker AC, Saag KG, et al. The recent prevalence of osteoporosis and low bone mass in the United States based on bone mineral density at the femoral neck or lumbar spine. J Bone Miner Res. 2014;29(11):2520-2526. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.2269 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Stevens JA, Rudd RA. The impact of decreasing US hip fracture rates on future hip fracture estimates. Osteoporos Int. 2013;24(10):2725-2728. doi: 10.1007/s00198-013-2375-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Parkkari J, Kannus P, Palvanen M, et al. Majority of hip fractures occur as a result of a fall and impact on the greater trochanter of the femur: a prospective controlled hip fracture study with 206 consecutive patients. Calcif Tissue Int. 1999;65(3):183-187. doi: 10.1007/s002239900679 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Harvey NC, Johansson H, Odén A, et al. FRAX predicts incident falls in elderly men: findings from MrOs Sweden. Osteoporos Int. 2016;27(1):267-274. doi: 10.1007/s00198-015-3295-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Su Y, Leung J, Kwok T. The role of previous falls in major osteoporotic fracture prediction in conjunction with FRAX in older Chinese men and women: the Mr OS and Ms OS cohort study in Hong Kong. Osteoporos Int. 2018;29(2):355-363. doi: 10.1007/s00198-017-4277-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Leslie WD, Morin SN, Lix LM, et al. Fracture prediction from self-reported falls in routine clinical practice: a registry-based cohort study. Osteoporos Int. 2019;30(11):2195-2203. doi: 10.1007/s00198-019-05106-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Harvey NC, Odén A, Orwoll E, et al. Falls predict fractures independently of FRAX probability: a meta-analysis of the Osteoporotic Fractures in Men (MrOS) study. J Bone Miner Res. 2018;33(3):510-516. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.3331 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Guirguis-Blake JM, Michael YL, Perdue LA, Coppola EL, Beil TL, Thompson JH Interventions to prevent falls in community-dwelling older adults: a systematic review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. Published April 2018. Accessed June 17, 2020. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK525700/pdf/Bookshelf_NBK525700.pdf [PubMed]
- 11.Panel on Prevention of Falls in Older Persons, American Geriatrics Society and British Geriatrics Society Summary of the Updated American Geriatrics Society/British Geriatrics Society clinical practice guideline for prevention of falls in older persons. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2011;59(1):148-157. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2010.03234.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention STEADI initiative for health care providers: materials for health care providers. Updated August 12, 2020. Accessed June 17, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/steadi/materials.html
- 13.Watts NB, Adler RA, Bilezikian JP, et al. ; Endocrine Society . Osteoporosis in men: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97(6):1802-1822. doi: 10.1210/jc.2011-3045 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Cosman F, de Beur SJ, LeBoff MS, et al. ; National Osteoporosis Foundation . Clinician’s guide to prevention and treatment for osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. 2014;25(10):2359-2381. doi: 10.1007/s00198-014-2794-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.International Society for Clinical Densitometry 2019. ISCD official positions—adults. Updated January 9, 2020. Accessed June 17, 2020. https://www.iscd.org/official-positions/2019-iscd-official-positions-adult/
- 16.US Preventive Services Task Force Final recommendation statement: osteoporosis to prevent fractures: screening. Published June 26, 2018. Accessed June 17, 2020. https://uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/osteoporosis-screening
- 17.Medicare.gov Bone mass measurements. Accessed June 17, 2020. https://www.medicare.gov/coverage/bone-mass-measurements
- 18.Colón-Emeric CS, Pieper CF, Van Houtven CH, et al. Limited osteoporosis screening effectiveness due to low treatment rates in national sample of older men. Mayo Clin Proc. 2018;93(12):1749-1759. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2018.06.024 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Shepstone L, Lenaghan E, Cooper C, et al. ; SCOOP Study Team . Screening in the community to reduce fractures in older women (SCOOP): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2018;391(10122):741-747. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32640-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Rubin KH, Rothmann MJ, Holmberg T, et al. Effectiveness of a two-step population-based osteoporosis screening program using FRAX: the randomized Risk-Stratified Osteoporosis Strategy Evaluation (ROSE) study. Osteoporos Int. 2018;29(3):567-578. doi: 10.1007/s00198-017-4326-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Merlijn T, Swart KM, van Schoor NM, et al. The effect of a screening and treatment program for the prevention of fractures in older women: a randomized pragmatic trial. J Bone Miner Res. 2019;34(11):1993-2000. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.3815 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Merlijn T, Swart KMA, van der Horst HE, Netelenbos JC, Elders PJM. Fracture prevention by screening for high fracture risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int. 2020;31(2):251-257. doi: 10.1007/s00198-019-05226-w [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Schousboe JT, Taylor BC, Fink HA, et al. Cost-effectiveness of bone densitometry followed by treatment of osteoporosis in older men. JAMA. 2007;298(6):629-637. doi: 10.1001/jama.298.6.629 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ito K, Hollenberg JP, Charlson ME. Using the osteoporosis self-assessment tool for referring older men for bone densitometry: a decision analysis. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2009;57(2):218-224. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2008.02110.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ito K, Elkin EB, Girotra M, Morris MJ. Cost-effectiveness of fracture prevention in men who receive androgen deprivation therapy for localized prostate cancer. Ann Intern Med. 2010;152(10):621-629. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-152-10-201005180-00002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Nayak S, Greenspan SL. Cost-effectiveness of osteoporosis screening strategies for men. J Bone Miner Res. 2016;31(6):1189-1199. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.2784 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hiligsmann M, Reginster JY, Tosteson ANA, et al. Recommendations for the conduct of economic evaluations in osteoporosis: outcomes of an experts’ consensus meeting organized by the European Society for Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis, Osteoarthritis and Musculoskeletal Diseases (ESCEO) and the US branch of the International Osteoporosis Foundation. Osteoporos Int. 2019;30(1):45-57. doi: 10.1007/s00198-018-4744-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Neumann PJ, Sanders GD, Russel LB, Siegel JE, Ganiats TG, eds. Cost-Effectiveness in Health and Medicine. 2nd ed Oxford University Press, 2016. doi: 10.1093/acprof:oso/9780190492939.001.0001 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Husereau D, Drummond M, Petrou S, et al. ; CHEERS Task Force . Consolidated Health Economic Evaluation Reporting Standards (CHEERS) statement. Value Health. 2013;16(2):e1-e5. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2013.02.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kanis JA, McCloskey EV, Johansson H, Oden A, Melton LJ III, Khaltaev N. A reference standard for the description of osteoporosis. Bone. 2008;42(3):467-475. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2007.11.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Tosteson AN, Melton LJ III, Dawson-Hughes B, et al. ; National Osteoporosis Foundation Guide Committee . Cost-effective osteoporosis treatment thresholds: the United States perspective. Osteoporos Int. 2008;19(4):437-447. doi: 10.1007/s00198-007-0550-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Looker AC, Borrud LG, Hughes JP, Fan B, Shepherd JA, Melton LJ III. Lumbar spine and proximal femur bone mineral density, bone mineral content, and bone area: United States, 2005-2008. Vital Health Stat 11. 2012;251(251):1-132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Johnell O, Kanis JA, Odén A, et al. Predictive value of BMD for hip and other fractures. J Bone Miner Res. 2005;20(7):1185-1194. doi: 10.1359/JBMR.050304 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kanis JA, Johnell O, De Laet C, et al. A meta-analysis of previous fracture and subsequent fracture risk. Bone. 2004;35(2):375-382. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2004.03.024 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Nayak S, Greenspan SL. Osteoporosis treatment efficacy for men: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2017;65(3):490-495. doi: 10.1111/jgs.14668 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Kothawala P, Badamgarav E, Ryu S, Miller RM, Halbert RJ. Systematic review and meta-analysis of real-world adherence to drug therapy for osteoporosis. Mayo Clin Proc. 2007;82(12):1493-1501. doi: 10.1016/S0025-6196(11)61093-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Koller G, Goetz V, Vandermeer B, et al. Persistence and adherence to parenteral osteoporosis therapies: a systematic review. Osteoporosis Int. 2020;31(11):2093-2102. doi: 10.1007/s00198-020-05507-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Dunn JE, Rudberg MA, Furner SE, Cassel CK. Mortality, disability, and falls in older persons: the role of underlying disease and disability. Am J Public Health. 1992;82(3):395-400. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.82.3.395 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Haentjens P, Magaziner J, Colón-Emeric CS, et al. Meta-analysis: excess mortality after hip fracture among older women and men. Ann Intern Med. 2010;152(6):380-390. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-152-6-201003160-00008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lau E, Ong K, Kurtz S, Schmier J, Edidin A. Mortality following the diagnosis of a vertebral compression fracture in the Medicare population. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(7):1479-1486. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.G.00675 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.American College of Rheumatology 2018 Medicare national fee schedule. Accessed June 17, 2020. https://www.rheumatology.org/Portals/0/Files/Medicare-National-Fee-Schedule-Table1-2018.pdf
- 42.Drugs for postmenopausal osteoporosis. Med Lett Drugs Ther. 2020;62(1602):105-112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Insinga RP. Administration costs of denosumab and zoledronic acid for postmenopausal osteoporosis. Am J Pharm Benefits. 2016;8(3):e42-e47. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services Clinical laboratory fee schedule. Updated September 23, 2020. Accessed June 17, 2020. https://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Medicare-Fee-for-Service-Payment/ClinicalLabFeeSched/index.html
- 45.California Department of Health Care Services Medi-Cal dental services rate review. Published July 1, 2015. Accessed June 17, 2020. https://www.dhcs.ca.gov/services/Documents/2015_Dental-Services-Rate-Review.pdf
- 46.Gabriel SE, Tosteson AN, Leibson CL, et al. Direct medical costs attributable to osteoporotic fractures. Osteoporos Int. 2002;13(4):323-330. doi: 10.1007/s001980200033 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kilgore ML, Curtis JR, Delzell E, et al. A close examination of healthcare expenditures related to fractures. J Bone Miner Res. 2013;28(4):816-820. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.1789 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Hanmer J, Lawrence WF, Anderson JP, Kaplan RM, Fryback DG. Report of nationally representative values for the noninstitutionalized US adult population for 7 health-related quality-of-life scores. Med Decis Making. 2006;26(4):391-400. doi: 10.1177/0272989X06290497 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Thiem U, Klaaßen-Mielke R, Trampisch U, Moschny A, Pientka L, Hinrichs T. Falls and EQ-5D rated quality of life in community-dwelling seniors with concurrent chronic diseases: a cross-sectional study. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2014;12:2. doi: 10.1186/1477-7525-12-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Svedbom A, Borgstöm F, Hernlund E, et al. Quality of life for up to 18 months after low-energy hip, vertebral, and distal forearm fractures—results from the ICUROS. Osteoporos Int. 2018;29(3):557-566. doi: 10.1007/s00198-017-4317-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Lesnyak O, Svedbom A, Belova K, et al. Quality of life after fragility fracture in the Russian Federation: results from the Russian arm of the International Cost and Utility Related to Osteoporotic Fractures Study (ICUROS). Arch Osteoporos. 2020;15(1):37. doi: 10.1007/s11657-020-0699-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Burge R, Dawson-Hughes B, Solomon DH, Wong JB, King A, Tosteson A. Incidence and economic burden of osteoporosis-related fractures in the United States, 2005-2025. J Bone Miner Res. 2007;22(3):465-475. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.061113 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Ettinger B, Black DM, Dawson-Hughes B, Pressman AR, Melton LJ III. Updated fracture incidence rates for the US version of FRAX. Osteoporos Int. 2010;21(1):25-33. doi: 10.1007/s00198-009-1032-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Black DM, Thompson DE, Bauer DC, et al. ; Fracture Intervention Trial; FIT Research Group . Fracture risk reduction with alendronate in women with osteoporosis: the Fracture Intervention Trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000;85(11):4118-4124. doi: 10.1210/jcem.85.11.6953 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Arias E, Xu J. United States life tables, 2017. Natl Vital Stat Rep 2019;68(7). Published June 24, 2019. Accessed June 17, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nvsr/nvsr68/nvsr68_07-508.pdf [PubMed]
- 56.US Bureau of Labor Statistics Consumer Price Index (CPI) databases. Accessed June 17, 2020. https://www.bls.gov/cpi/data.htm
- 57.Borgström F, Karlsson L, Ortsäter G, et al. ; International Osteoporosis Foundation . Fragility fractures in Europe: burden, management and opportunities. Arch Osteoporos. 2020;15(1):59. doi: 10.1007/s11657-020-0706-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Ganz DA, Bao Y, Shekelle PG, Rubenstein LZ. Will my patient fall? JAMA. 2007;297(1):77-86. doi: 10.1001/jama.297.1.77 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Center for Medicare & Medicaid Services Annual wellness visit. Published August 2018. Accessed June 17, 2020. https://www.cms.gov/Outreach-and-Education/Medicare-Learning-Network-MLN/MLNProducts/Downloads/AWV_Chart_ICN905706.pdf
- 60.Condurache CI, Chiu S, Chotiyarnwong P, et al. ; SCOOP Study Team . Screening for high hip fracture risk does not impact on falls risk: a post hoc analysis from the SCOOP study. Osteoporos Int. 2020;31(3):457-464. doi: 10.1007/s00198-019-05270-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Mai HT, Tran TS, Ho-Le TP, Center JR, Eisman JA, Nguyen TV. Two-thirds of all fractures are not attributable to osteoporosis and advancing age: implications for fracture prevention. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019;104(8):3514-3520. doi: 10.1210/jc.2018-02614 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Close JC, McMurdo ME; British Geriatrics Society Falls and Bone Health Section . Falls and bone health services for older people. Age Ageing. 2003;32(5):494-496. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afg079 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Department of Health National service framework for older people. Published March 2001. Accessed June 17, 2020. https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/198033/National_Service_Framework_for_Older_People.pdf
- 64.Kayan K, Johansson H, Odén A, et al. Can fall risk be incorporated into fracture risk assessment algorithms: a pilot study of responsiveness to clodronate. Osteoporos Int. 2009;20(12):2055-2061. doi: 10.1007/s00198-009-0942-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Greenspan SL, Schneider DL, McClung MR, et al. Alendronate improves bone mineral density in elderly women with osteoporosis residing in long-term care facilities: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 2002;136(10):742-746. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-136-10-200205210-00009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Greenspan SL, Perera S, Ferchak MA, Nace DA, Resnick NM. Efficacy and safety of single-dose zoledronic acid for osteoporosis in frail elderly women: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2015;175(6):913-921. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2015.0747 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.University of Sheffield FRAX® Fracture Risk Assessment Tool. Accessed June 17, 2020. https://www.sheffield.ac.uk/FRAX/
- 68.Garvan Institute of Medical Research Bone fracture risk calculator. Accessed June 17, 2020. https://www.garvan.org.au/bone-fracture-risk
- 69.ClinRisk. Welcome to the QFracture®-2016 risk calculator. Accessed June 17, 2020. https://qfracture.org/
- 70.Masud T, Binkley N, Boonen S, Hannan MT; FRAX(®) Position Development Conference Members . Official positions for FRAX® clinical regarding falls and frailty: can falls and frailty be used in FRAX®? from Joint Official Positions Development Conference of the International Society for Clinical Densitometry and International Osteoporosis Foundation on FRAX®. J Clin Densitom. 2011;14(3):194-204. doi: 10.1016/j.jocd.2011.05.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
eTable. Age-Dependent Model Parameters