Abstract
Background
Patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) are important in clinical practice and research. The growth of electronic health technologies provides unprecedented opportunities to systematically collect information via PROMs.
Objective
The aim of this study was to provide an objective and comprehensive overview of the benefits, barriers, and disadvantages of the digital collection of qualitative electronic patient-reported outcome measures (ePROMs).
Methods
We performed a systematic review of articles retrieved from PubMED and Web of Science. The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines were followed during all stages. The search strategy yielded a total of 2333 records, from which 32 met the predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria. The relevant ePROM-related information was extracted from each study.
Results
Results were clustered as benefits and disadvantages. Reported benefits of ePROMs were greater patient preference and acceptability, lower costs, similar or faster completion time, higher data quality and response rates, and facilitated symptom management and patient-clinician communication. Tablets were the most used ePROM modality (14/32, 44%), and, as a platform, Web-based systems were used the most (26/32, 81%). Potential disadvantages of ePROMs include privacy protection, a possible large initial financial investment, and exclusion of certain populations or the “digital divide.”
Conclusions
In conclusion, ePROMs offer many advantages over paper-based collection of patient-reported outcomes. Overall, ePROMs are preferred over paper-based methods, improve data quality, result in similar or faster completion time, decrease costs, and facilitate clinical decision making and symptom management. Disadvantages regarding ePROMs have been outlined, and suggestions are provided to overcome the barriers. We provide a path forward for researchers and clinicians interested in implementing ePROMs.
Trial Registration
PROSPERO CRD42018094795; https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?RecordID=94795
Keywords: electronic patient-reported outcome measures, paper-based patient-reported outcome measures, systematic review, advantages, pitfalls
Introduction
In patient-centered care, patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) are the gold standard for efficiently evaluating patients’ feelings, thoughts, and complaints about a clinical intervention or disease [1].
Clinicians use PROMs to guide and audit routine care and support patient-centered care. Standard intake procedures already include many questionnaires such as generic quality of life questionnaires administered before arthroplastic surgeries [2]. At the patient level, the data can be used to monitor individual progress, investigate the effects of medical and surgical interventions [2], and improve communication between patients and caregivers [3]. On a larger scale, PROM data can be used to screen for health problems, compare outcomes between populations, and assess quality of care. They are widely implemented in clinical research [1,4], with positive effects on patient-clinician communication and mutual decision making. PROMs are traditionally measured using pen-and-paper questionnaires. We aimed to investigate whether pen-and-paper methods are the best option because unsupervised paper-based PROM data collection in clinical trials has resulted in unreadable, missing, or faulty data [5].
The growth of electronic health (eHealth) technologies provide unprecedented opportunities to systematically collect information via PROMs. Patients of all ages and sociodemographic backgrounds worldwide are comfortable using digital networks and services [6]. Furthermore, smartphones and lightweight computers or tablets with touchscreens are omnipresent. Supposed advantages of electronic PROMs (ePROMs) include more complete data capture and lower cost but it is unknown if the advantages of ePROM outweigh the disadvantages. Various research groups in different medical fields have investigated the use of electronic questionnaires in different patient groups; however, the benefits and disadvantages of ePROM collection have not yet been systematically explored. When transferring questionnaires from paper to electronic format, comparability is questioned. Many individual studies and several meta-analyses [7-10] have concluded that scores derived from ePROMs are equivalent to their original paper versions. In other words, scores derived from a computerized measure do not differ from scores derived from the pencil-and-paper version. The International Society for Pharmacoeconomics and Outcomes Research (ISPOR) reported 3 levels of modification (minor, moderate, and substantial) for the migration from original paper-based PROM to ePROM. The ISPOR also provides an effective strategy for testing measurement equivalence (reliability and validity). Minor modification means simply placing a paper-based scale form into a screen-based format without changing font size or altering items. Then, only a cognitive interview with 5-10 patients and a usability test is recommended. Moderate modifications are changes such as splitting single items into multiple screens, requiring the patient to use a scroll bar to see all the items or responses, or changing the order of items. With moderate modifications, equivalence testing with a randomized parallel group or randomized crossover design is advised in addition to usability testing. Major changes include removing items. With major modifications, full psychometric evaluation and large-scale usability testing in the target population are required [11]. However, recent evidence suggests that previous usability evidence in a representative group is sufficient to assume equivalence [12].
The ISPOR’s electronic patient-reported outcome (ePRO) System Validation Task Force also developed recommendations on the validation of electronic systems used to collect PRO data in clinical trials [13]. This report enhances the understanding of different steps needed to develop ePROM. Both reports, based on expert opinion, give important insights in the development of ePROM based on the paper-version counterpart.
Hence, there is growing emphasis on ePROMs with a clear shift towards electronic data capture driven by regulatory and practical considerations [14], and patients seem motivated to use these tools as long as they provide added value and quality of care [15]. While a number of reviews have summarized the equivalence of digital questionnaires, none of these reviews systematically assessed the benefits and disadvantages of ePROM. Since more people have gained access to the internet via many types of devices, many opportunities have arisen in the eHealth ecosystem. Weighing the advantages against the disadvantages is necessary and imperative for clinical practice and research purposes. This systematic review aimed to evaluate the scientific evidence for the use of digital questionnaires to assess PROMs and more particularly describe the benefits and disadvantages.
Methods
The protocol for this review was accepted in the PROSPERO systematic review database (ID: CRD42018094795) [16]. This systematic review was conducted and reported following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines [17].
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
The PICO model was used to define the criteria to assess study eligibility. To be included in this review, studies had to report about questionnaires that evaluated PROMs. These questionnaires had to be in digital format (ie, tablet, computer, or mobile app). The criteria did not include a comparison; both studies comparing digital against paper formats and studies solely reporting about a digital questionnaire were included. The outcome measures described either benefits or disadvantages of digital questionnaires. This systematic review focused on the use of digital questionnaires. The scope of digital questionnaires was broad, including any web-, tablet-, computer-, or mobile-based method to assess PROMs.
To be included, articles had to evaluate ePROMs, preferably those used by general practitioners, doctors, occupational therapists, physiotherapists, or other health care workers; assess questionnaires in a digital format; compare a digital questionnaire with a paper-based method; describe either benefits or disadvantages of a digital questionnaire; or describe a randomized controlled trial or cohort, case-control, longitudinal, descriptive, or qualitative research.
Articles were excluded when the questionnaire was not used in the health care setting, it did not describe one of the listed aspects or clinical parameters mentioned in the keywords, or it described a review, meta-analysis, case study, or case report.
Information Sources and Search Strategy
A systematic computerized search strategy was performed in PubMed and Web of Science in October 2017. Additionally, manual screening of reference lists of relevant published literature occurred in November 2017. Neither filters nor limitations on the query were used. We searched for articles using the keywords patient related outcomes, self-management, self-reported, self-administered, questionnaire, survey, PRO, ePRO, PROM, ePROM, electronic, web-based, tablet-based, and digital questionnaires in combination with the keywords advantages, disadvantages, benefits, efficacy, acceptability, feasibility, validity, reliability, reproducibility, and response rate.
Study Selection
Two reviewers (JM and NH) searched and screened the identified records based on the eligibility criteria. Screening and selection were performed first on the title and abstract and second on the full text. Only published full-text articles in English were included.
Data Collection
The following relevant information was extracted: study description, examined ePROMs, outcome measures, and main results.
Methodological Quality
Two researchers (NH and JM) independently assessed the methodological quality. Both researchers were not aware of the other’s evaluation before holding a consensus meeting. Methodological quality of the experimental studies was assessed with a 10-item checklist provided by the Dutch Cochrane Centre [18]. Observational studies were assessed with the 14-item Quality Assessment Tool for Observational Cohort and Cross-Sectional Studies [19]. Studies with high methodological quality were given more value when making final conclusions about the advantages and disadvantages of ePROMs.
Results
Study Selection
The results of the literature search and study selection are shown in Figure 1. In summary, 2333 records were identified after removing duplicates. After screening the titles and abstracts, 100 eligible studies remained, and the full-text versions were screened. After reading the full text, 32 articles that met the predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria were included in this systematic review. Two reviewers (NH and JM) screened the identified records using the eligibility criteria. Screening was first performed based on the titles and abstracts. Full-text articles were retrieved when a record was assessed as eligible. Each full-text article was once again assessed against the inclusion criteria. Disagreements were discussed between the researches, and consensus was always achieved. The intervention of a third reviewer (UVD) was not necessary.
Figure 1.

Flow diagram of the study selection process.
Study Characteristics
The results of this systematic review are based on 14 observational studies [20-33] and 18 experimental studies [34-51]. The retrieved experimental studies either compared an ePROM
versus a paper-based PROM in two separate groups [23,35,39,41,44,48,50] or compared the two modes of administration within the same groups, after randomizing in which order the modes of administration were completed [36-38,40,42,43,45-47,49,51].
The populations varied from healthy people [31,36,39,44,49] to patients with a certain condition or disease [20-22,24-30,32-35,38,40,41,43,45,51]. We did not differentiate the results by population since the goal was to systematically evaluate all possible advantages and disadvantages of ePROMs regardless of the population. Most articles were found in the field of cancer research (9/32) and musculoskeletal research (10/32).
Overall, the included studies represented 11,006 individuals (mean age 49 years, range 13-93 years) exposed to an ePROM or asked their opinion about it. Not all studies [30,31,38,51] reported the ratio between male and female participants, meaning the sex of 3038 of the 11,006 participants was unknown. Based on the available data, 61% (4827/7968) of the subjects were female, and 39% (3141/7968) were male.
The different ePROM modalities were personal digital assistants (2/32, 6%), smartphones (2/32, 6%), tablets (14/32, 44%), computers (9/32, 28%), or not specified (5/32, 16%). Web-based systems were used the most (26/32, 81%).
The characteristics of the studies are presented in Table 1, and the results are presented in Table 2.
Table 1.
Characteristics of the studies included in the systematic review.
| Study | Risk of bias scorea | Level of evidencea | Population | Sample size, n (male/female) | Age (years), mean (range) | Setting |
| [46]b | 6/10 | A2 | Patients with a skin condition | 104 (45/59) 57 (29/28; group 1) 47 (16/13; group 2) |
51.5 (20-89) 51.5 (19.3c; group 1) 51.4 (18.2c; group 2) |
Outpatient clinic |
| [20]d | 9/14 | C | Patients post-major gynecologic cancer surgery | 49 (0/49) | 56 (23-74) | –h |
| [45]b | 6/10 | B | Cardiology patients | – | – | Outpatient clinic |
| [31]d | 6/14 | C | People from Andalucia | 2493 | – | At home |
| [41]b | 3/10 B |
B | Patients who had undergone hand surgery | 468 (216/270) | 48.3 (18-91) | Private practice |
| [23]b | 4/10 | B | Patients in a cardiac, pulmonary, occupational, or cancer rehabilitation program | 126 (56/70) | 56.3 | Prior to rehabilitation at home |
| [49]b | 7/10 | B | Healthy aging adults | 49 (13/36) | 64 (57-71) | Research center |
| [28]d | 10/14 | B | Patients with a cancer diagnosis | 1484 (607/877) | 56.3 | Inpatient reference center |
| [47]b | 6/10 | B | Patients with rheumatoid arthritis | 40 (17/23) | 65 (44-83) | In the clinic |
| [26]d | 9/14 | B | Patients with adjuvant and metastatic breast cancer | 202 (0, 202) | 54 (20-85) | Outpatient visit |
| [34]d | 7/14 | C | Patients with cancer pain | – | – | Outpatient oncology clinic |
| [43]b | 4/10 | B | Patients with lung cancer | 148 (84/64) | 67 (35-81) | Community centers |
| [29]d | 9/14 | B | Patients with sickle cell disease | 15 (9/6) | 26 (16-54) | At home |
| [25]d | 8/14 | C | Patients with multiple sclerosis | 55 | 46.3 | At home |
| [51]b | 6/10 | B | Patients with asthma or rhinitis | 116 | 17-65e | Clinic visit |
| [48]b | 5/10 | B | Patients with THRf or TKPg | 100 (41/59) | 67 (36.7-88) | Outpatient clinic |
| [32]d | 7/14 | A2 | Patients with THR or TKP | 565 (198/367; THR) 387 (126/261; TKR) |
65.9 (10.6c; THR) 68.9 (9.7c; TKR) |
At home |
| [50]b | 8/10 | A2 | Healthy women referred for mammography | 533 (0/533) | 20-67e | At home |
| [21]d | 7/14 | C | Patients with epilepsy | 502 (272/230) | 27.98 (15-73) | At home |
| [44]b | 7/10 | A2 | Healthy adolescents | 591 (272/319) | 14 (13-17) | At school |
| [27]d | 9/14 | C | Geriatric patients (>70 years) with gastrointestinal cancer | 37 (17/20) | 77 (70-89) | Outpatient institute |
| [39]b | 7/10 | A2 | Adolescents | 933 (432/501) | 14.7 (13-17) | At school |
| [33]d | 9/14 | C | Ambulatory neurological patients | 323 (134/190) | 32.2 | Ambulatory clinic |
| [42]b | 6/10 | A2 | Patients with rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, or spondyloarthritis | 153 (47/106) | 45.7 | Outpatient care center |
| [40]b | 6/10 | A2 | Patients with rheumatoid arthritis | 87 (29/58) | 14.7 (34-83) | Outpatient clinic |
| [37]b | 6/10 | B | Patients with axial spondyloarthritis | 55 (45/10) | 51 (34-63) | Outpatient clinic |
| [30]d | 6/14 | C | Dialysis patients | 66 | 66 (36-91) | Home dialysis units |
| [22]d | 10/14 | C | Patients with HIV | 42 (28/14) | 50 (26-66) | Outpatient clinic and at home |
| [35]b | 7/10 | A2 | Orthopedic patients (upper extremity, spine, or arthroplasty) | 483 (235/248) | 55.7 (14-93) | Three subspecialty services during outpatient visits |
| [38]b | 6/10 | A2 | Patients from an orthopedic clinic (spine, upper extremity, and trauma) | 308 | – | Outpatient clinic |
| [36]b | 7/10 | A2 | Healthy volunteers | 147 (68, 79) | 62.7 (49-75) | At home |
| [24]d | 8/14 | C | Cancer patients | 158 (116/42) | 51.9 (22-81) | clinic and home |
aBased on the Dutch Centraal BegeleidingsOrgaan-classificatiesysteem (CBO) [52].
bExperimental study.
cMean (SD).
dObservational study.
eRange.
fTHR: total hip replacement.
gTKR: total knee replacement.
hNot applicable.
Table 2.
Results of the studies included in the systematic review.
| Study | Electronic delivery method | ePROMa, outcome, and results | |||
|
|
Web/PCb | Device |
|
|
|
| [46] | Web | Tablet | DLQIc | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Preference | 76% prefer electronic |
|
|
|
|
|
Completion time | Electronic took 9 s longer than pencil and paper (P=.008), older participants took longer (r2=.257, P=.012) |
|
|
|
|
|
Agreement | ICCd=.98, CI 0.97-0.99 |
| [20] | Web | – | EORTCe, QLQ-C30f | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Completion rate | 92% completed the first measurement, 74% completed the 6-month measurement, 82% completed ≥4 of 7 sessions |
|
|
|
|
|
Satisfaction and other outcomes | 92% found it easy to use, 85% continued using it, 85% recommended it |
| [45] | Web | PC | SAQg, SF-36h | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Preference | 82% preferred electronic, there was no effect on preference with age, sex, race, computer use, education, visual impairment, or reading level |
|
|
|
|
|
Completion rate | No differences in the completion rate |
|
|
|
|
|
Completion time | SAQ completion time: 5.53 min electronic, 4.78 min paper (P<.05); SF-36 completion time: 6.76 min electronic, 5.44 min paper (P<.05); the log-on procedure was not significantly different |
|
|
|
|
|
Agreement between electronic and paper | For the 5 SAQ domains r=0.84-0.93; for the 8 SF-36 subscales: r=0.54-0.75 |
| [31] | Web | PC | – | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Preference | 83.6% preferred pencil and paper, 14.4% preferred internet |
|
|
|
|
|
Data completion | Unanswered questions: 9.3% pencil and paper, 4.9% internet (==t =14.85, P=.01) |
|
|
|
|
|
Data missing | Internet answers were more detailed than pencil and paper answers in 4 of 5 questions (P<.05) |
| [41] | Web | Tablet | DASHi | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Data completion | 24% of questions were unscorable with pencil and paper, compared with 2% for electronic (P<.001); electronic was more likely to be scorable (ORj=13.5, P<.001) |
|
|
|
|
|
Data missing | Mean (SD) of 2.6 (4.4) with pencil and paper vs 0.1 (0.8) with electronic (P<.001), electronic format had an inverse relationship with omitted questions (beta=–0.358, P<.001) |
| [23] | Web | – | PAM-13k, MacNewl, FQm, EORTC, QLQ-C30, HADSn | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Demographic factors | Preferred electronic over paper: younger age (P=.008), married/cohabitating (P=.004), internet available (P<.001), educated (P=.092) |
|
|
|
|
|
Preference | 77.8% prefer web-based forms |
|
|
|
|
|
Completion time | Web-based, ~9.5 min; paper-based, ~24 min |
|
|
|
|
|
Data completion | Inadequate responses did not exist for the web version due to the system design |
|
|
|
|
|
Data missing | Fewer total data points missing on paper-based forms than on web-based forms (P<.001) |
| [49] | Web | Tablet | PASEo, BARSEp, PSQIq | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Demographic factors | Factors affecting preference of electronic vs paper: daily computer use, perceived ease of use, reported anxiety while completing the digital questionnaire (all P<.05) |
|
|
|
|
|
Preference | Electronic preferred over pencil and paper (z=4.96, SE 3.428, P<.001) |
| [28] | PC | Tablet | EORTC, QLQ-30 | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Completion rate | Completion rate 43%-58% from 2005-2010, <20% since 2011 (ePROr) |
|
|
|
|
|
Adherence and compliance | Pencil and paper associated with non-completion (OR=2.72, P<.001) and poor adherence (OR=2.23, P<.001), male sex associated with poor adherence (OR=1.69, P=.010) |
| [47] | PC | PC | RAQoLs | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Satisfaction | Electronic > P-P (P=.003) |
|
|
|
|
|
Preference | 64% prefer electronic |
|
|
|
|
|
Completion time | Pencil and paper, 6 min; electronic, 5 min P=.194 |
|
|
|
|
|
Agreement between electronic and paper | ICC=.982 |
| [26] | Web | Tablet | EORTC, QLQ-C30 | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Attitude/ willingness |
92.3% of those exposed to both electronic and paper vs 59% of those exposed only to paper (P=.001) were willing; patients exposed only to paper more likely to report barriers: data privacy (P=.003), technical knowledge (P=.02), discomfort using technology (P=.02), no internet (P=.05) |
| [34] | Web | Tablet | – | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Adherence | Patient adherence: 76.8% for pain monitoring, 50.4% for medication monitoring, and 100% for education |
|
|
|
|
|
Satisfaction | Limited effort, comfortable, education session appreciated, added value with self-management, medication overview with reminders was supportive |
|
|
|
|
|
Experience | Measured using a Likert scale, mean (SD): learnability, 4.8 (0.4); usability, 4.8 (0.5); desirability, 4.6 (0.4); and would recommend app, 4.8 (0.4) |
| [43] | PC | PDAt | LCSSu | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Satisfaction | 98% of patients reported it acceptable and easy to use, 80% learned it in <3 minutes, 100% of nurses and 86% of physicians said it’s easy to use |
|
|
|
|
|
Completion time | Electronic, 2.2 min; pencil and paper, 3-5 min |
|
|
|
|
|
Agreement between electronic and paper | Pearson r=0.92, ICC=.92, Lin's CCCv=.92 |
| [29] | Web | iPhone, iPad, or iPod | Pain VASw | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Completion rate, adherence, compliance | Compliance decreases over time, >35 years old had increased compliance (P<.05), compliance greater with iPad than iPhone (P<.0025), technical difficulties decreased compliance (P<.0025), |
|
|
|
|
|
Demographic factors | Information technology comfort level had no impact on adherence |
|
|
|
|
|
Agreement | iPhone, ICC=.99 (95% CI 0.92-1.00); iPad, ICC=.97 (95% CI 0.88-0.99) |
| [25] | Web | – | MSIPx, MSQoL-54y, MFIS-5z, LMSQoLaa | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Other symptom insights | 46% have greater insights into symptoms; 18% feel better able to handle symptoms; 65.4% feel it’s important for other health care professionals to have access; advantages include availability, overview of symptoms, gain insights, forced to reflect, look back on history; disadvantages include it’s tiring, lot of work, complicated, repeated questions, grammatical errors, no space for free text, monthly completion, login problems, not used friendly, data aren't used by physician |
| [51] | Web | PDA | AQLQbb, ACQcc, RQLQdd | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Agreement between electronic and paper | AQLQ (P=.009), ACQ (P=.12), RQLQ (P=.05) |
| [48] | Web | Tablet | WOMACee, FJS-12ff | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Completion time | WOMAC: pencil and paper 170 s, electronic 117 s (P<.001); FJS-23: pencil and paper 22 s, electronic 37 s (P<.001) |
| [32] | Web | – | SF-36 | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Preference | THRgg 81.8% preferred pencil and paper (CI 78.8-84.7), TKRhh 86.8% preferred pencil and paper (CI 83.1-89.8) |
|
|
|
|
|
Demographic factors | Preferred electronic over paper: younger age (P<.001), male sex (P<.001), higher education level (P<.001), higher BMI (P=.004) |
| [50] | Web | PC | SF-36, MFI-20ii, HADS | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Completion rate | 73.2% with pencil and paper vs 17.9% with internet: difference of 55.3 (48.3-62.3); after a reminder: 76.5% with pencil and paper vs 64.2% with internet: difference 12.2 (4.5-20) |
|
|
|
|
|
Preference | 55.4% prefer pencil and paper |
|
|
|
|
|
Data completion, missing data | 63.4% data completion with pencil and paper vs 97.8% with internet (P<.001): difference 34.5 (26.6-42.3) |
| [21] | Web | Smartphone | MMAS-8jj | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Demographic factors | Preferred electronic over paper: younger age (P=.002), live in the city (P<.001), higher education level/stable employment (P<.001), more seizures (P=.01), lower medication adherence and own a smartphone (P=.001) |
|
|
|
|
|
Attitude/willingness | 65.5% would use it if it was free, 72.3% if it was easy to operate, 59% think it decreases medical visits and related costs, 71.7% say privacy must be protected |
| [44] | Web | PC | KIVPAkk | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Preference | Mean (SD) pleasantness: 2.7 (0.9) for pencil and paper vs 3.0 (0.8) for internet (P<.01); mean (SD) difficulty: 3.6 (0.7) for pencil and paper vs 3.9 (0.7) for internet (P<.01) |
| [27] | PC | Tablet | CSGAll | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Feasibility in older patients | ≥50% unable complete without assistance (reason: computer illiteracy) |
| [39] | Web | PC | CHQ-CFmm | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Data completion, missing data | 0.54% with paper vs 0.04% with internet (P<.01) |
| [33] | Web | PC and tablet | EQ-5Dnn, PHQ-9oo | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Satisfaction | 92.3% found it easy to use, 87.6% thought it time appropriate, 77.3% saw a perceived benefit |
|
|
|
|
|
Other factors affecting perception of benefit | Provider review (OR 6.56, P<.001) |
| [42] | Web | Tablet | FFbHp, BASDAIqq, SF-36 | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Experience | Older age requires more support |
|
|
|
|
|
Preference | 62.1% prefer electronic, especially those of younger age and with increased computer knowledge (P<.01) |
|
|
|
|
|
Data completion | Significantly greater with electronic |
|
|
|
|
|
Agreement between electronic and paper | r=0.87-0.98; P>.05 |
| [40] | PC | PC | VAS GH, VAS Pain, VAS PGArr, ROADss, TJCtt | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Preference | 86% prefer electronic |
|
|
|
|
|
Completion time | Electronic 7.3 min, pencil and paper 7.9 min (P=.006); older age requires greater time for both (electronic: P=.02, pencil and paper: P=.005) |
|
|
|
|
|
Agreement between electronic and paper | No difference between methods and high correlation (all P>.05, CCC>.849) |
| [37] | PC | Tablet | BASDAI, BASFIuu, NRSvv | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Preference | 83.4% prefer the tablet |
|
|
|
|
|
Completion time | Tablet 5.1 min, paper 7.9 min (P=.04) |
|
|
|
|
|
Agreement | ICC>0.9 (P<.0001) |
| [30] | Web | Tablet | KDQOL-36ww, ESASxx | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Logistics | Internet/cellular access, link to electronic health records |
|
|
|
|
|
Infection control | Hand sanitizer, stylus |
|
|
|
|
|
Financials | Financial support necessary? |
|
|
|
|
|
Design | Minimalistic, large font, black writing on white background, no distracting graphics, adapted to population |
| [22] | Web | – | Symptom self-management tool for PLWHyy | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Symptoms diminish with targeted strategies | Decreased frequency (effect size=.37) and intensity (effect size=–8.41) over time for all symptoms except diarrhea |
| [35] | Web | Tablet | EQ-5D, ODIzz, NDI1, HOOS2, KOOS3, QuickDASH4 | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Completion rate | No differences in unanswered questions (P>.05) |
|
|
|
|
|
Preference | Satisfaction similar; however, 41.4% prefer the tablet (P<.001); total 60.38% |
|
|
|
|
|
Data completion | No difference in completion rate (P=.208) |
|
|
|
|
|
Completion time | No difference in the completion time (P>.05) |
| [38] | Web | Tablet | PSS5, FFI6, ODI | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Preference | 68% prefer electronic |
|
|
|
|
|
Data completion | Pencil and paper 14 times greater completion (PSS, P=.008), 260 times greater completion (FFI, P<.001), 11 times greater completion (ODI, P<.001) |
|
|
|
|
|
Agreement between electronic and paper | Differences in patient-reported outcomes scores not significant (P>.05) |
| [36] | Web | PC | Nutrinet Sante | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Preference | 92.2% prefer web; web considered more acceptable (P=.002) and with fewer barriers (P=.03) |
|
|
|
|
|
Data completion | No data missing in web |
|
|
|
|
|
Completion time | No significant differences in completion time |
|
|
|
|
|
Cost | For a cohort of 500,000 subjects: paper €4,965,833 (€9.94/subject); web-based tool €150,000 (€0.3/subject) |
|
|
|
|
|
Agreement between electronic and paper | Agreement ICC=.86-1.00 qualitative variables; ICC=.69-1.00 for 18 qualitative variables (height, weight, hip circumference, waist circumference were all different) |
| [24] | Web | Tablet | EORTC | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Preference | 65.98% prefer electronic |
|
|
|
|
|
Habits and attitudes | 64.4% of the clinic ePROM group and 91.1% of the home ePROM group found it useful and adequate for QOL; 82.2% would appreciate discussing results with a physician |
|
|
|
|
|
Feasibility and suggestions | Perceived benefits included that it was always available, feeling well cared at home, and low cost; the disadvantages included that it was too impersonal and technical issues; suggestions included adjustable font size |
aePROM: electronic patient-reported outcome measure.
bPC: personal computer.
cDermatology Life Quality Index.
dICC: interclass correlation coefficient.
eEORTC: EORTC: European Organization for the Research and Treatment of Cancer.
fQLQ-C30: Quality of Life Questionnaire Core 30.
gSAQ: Seattle Angina Questionnaire.
hSF-36: Short Form-36.
iDASH: Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand.
jOR: odds ratio.
kPAM-13: Patient Activation Measure short form.
lMacNew: MacNew Heart Disease Health-related Quality of Life questionnaire.
mFQ: Fatigue Questionnaire.
nHADS: Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale.
oPASE: Physical Activity Scale for the Elderly.
pBARSE: Barriers Self-Efficacy Scale.
qPSQI: Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index.
rePRO: electronic patient-reported outcome.
sRAQol: Rheumatoid Arthritis Quality of Life Questionnaire.
tPDA: personal digital assistant.
uLCSS: Lung Cancer Symptom Scale.
vCCC: concordance correlation coefficient.
wVAS: visual analogue scale.
xMSIP: Multiple Sclerosis Impact Profile.
yMSQoL-54: Multiple Sclerosis Quality of Life-54.
zMFIS-5: Modified Fatigue Impact Scale-5.
aaLMSQoL: Leeds Multiple Sclerosis Quality of Life.
bbAQLQ: Asthma Quality of Life Questionnaire.
ccACQ: Asthma Control Questionnaire.
ddRQLQ: Rhinoconjunctivitis Quality of Life Questionnaire.
eeWOMAC: Western Ontario and McMaster Universities.
ffFJS: Forgotten Joint Score.
ggTHR: total hip replacement.
hhTKR: total knee replacement.
iiMFI-20: Multidimensional Fatigue Inventory.
jjMMAS-8: Morisky Medication Adherence Scale.
kkKIVPA: Korte Indicatieve Vragenlijst voor Psychosociale Problematiek bij Adolescenten.
llCSGA: Cancer-Specific Geriatric Assessment.
mmCHQ-CF: Child Health Questionnaire-Child Form.
nnEQ-5D: European Quality of Life-5 Dimensions (General Health).
ooPHQ-9: Patient Health Questionnaire-9.
ppFFbH: Hannover Functional Ability Questionnaire.
qqBASDAI: Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index.
rrPGA: Patient Global Disease Activity.
ssROAD: Recent-Onset Arthritis Disability Index.
ttTJC: tender joint count.
uuBASFI: Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index.
vvNRS: numeric rating scale.
wwKDQOL-36: Kidney Disease Quality of Life Instrument.
xxESAS: Edmonton Symptom Assessment System.
yyPLWH: people living with HIV/AIDS.
zzODI: Oswestry Disability Index.
1NDI: Neck Disability Index.
2HOOS: Hip Disability and Osteoarthritis Outcomes Score.
3KOOS: Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcomes Score.
4QuickDASH: abbreviated version of Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand.
5PSS: Perceived Stress Scale.
6FFI: Foot Function Index.
7None mentioned in particular.
Methodological Quality
The risk of bias scores and the level of evidence, based on the classification of the Dutch Centraal BegeleidingsOrgaan-classificatiesysteem [52], are reported in Table 1. Scores ranged from 3/10 to 8/10 for the experimental studies and from 6/14 to 10/14 for the observational studies. Level A2 evidence was determined for 10 studies [32,35,36,38-40,42,44,46,50], level B for 12 studies [23,26,28,29,37,41,43,45,47,51], and level C for 10 studies [20-22,24,25,27,30,31,33,34].
Benefits for Patients
Preference and Satisfaction
The preferred modality (electronic vs paper) was reported in 14 studies [23,25,31,32,35-38,40,42,45,50], and electronic administration was preferred in 11 studies [23,25,35-38,40,42,45-47]. One study reported a significantly greater preference for the tablet-delivered questionnaires (z=4.96, SE 3.428, P<.001) [49]. Another study asked patients to rate which mode of administration was the most pleasant and least difficult to use with a Likert scale [44]. Overall, of the 16 studies that reported user preference [23,24,31,32,35-38,40,42,44-47,49,50], a preference for ePROM was reported in 13 studies [23,24,35-38,40,42,44,49]. An overview of the reported percentages can be found in Figure 2.
Figure 2.
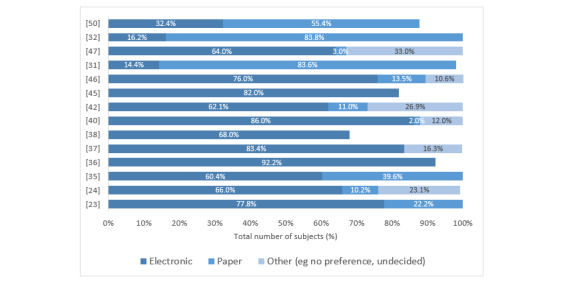
Preferred mode of form administration.
Additionally, 4 [23,32,42,49] of the 16 studies reported sociodemographic variables that significantly influenced the preference for electronic administration (Table 3).
Table 3.
Sociodemographic variables influencing the preference for electronic patient-reported outcome measures.
| Study | Population | Significantly preferred electronic patient-reported outcome measures |
| Engan et al 2016 [23] | Patients in cardiac, lung, occupational, and cancer rehabilitation programs | Younger age (P=.008), married/cohabitating (P=.004), internet availability (P<.001) |
| Richter et al 2008 [42] | Patients with rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, or spondyloarthritis | Younger age, better computer knowledge (P<.01) |
| Keurentjes et al 2013 [32] | Patients post-THRa or TKRb | Younger age (P<.001), men (P<.001), higher education level (P<.001), higher BMI (P=.004) |
| Fanning et al 2014 [49] | Healthy aging adults (n=47) | Daily computer use (rs=.42, P<.05), perceived ease of use (rs=.665, P<.001), reported anxiety while completing digital questionnaires (rs=.552, P<.001) |
aTHR: total hip replacement.
bTKR: total knee replacement.
The satisfaction with and attitude towards ePROMs were reported in 7 studies. Most patients who were exposed to an ePROM found it easy to learn, easy to use, would recommend it to other patients, and would like to continue using it [20,21,33,34,43,47]. In a feasibility and acceptability study of a smartphone app for seizure self-management, patients with epilepsy thought ePROMs would reduce medical visits and health-related costs. Positive satisfaction levels with ePROMs were found for people who were younger (P=.002), lived in a city (P<.001), had higher education levels (P=.001), had stable employment (P<.001), had more frequent seizures (P=.01), had poor medication adherence, and owned a smartphone (P=.001) [21]. In breast cancer patients, willingness to use ePROM was higher in the group with previous experience with ePROM than in the group with previous experience with only paper PROM (92.3% and 59%, respectively, P=.001) [26]. Finally, reviewing the results with a health care professional was associated with 6.6-fold increased odds (P<.001) of perceiving systematic ePROMs as a benefit [33].
Completion Time
Time to complete electronic and paper-based questionnaires was reported in 9 studies [35-37,40,43,45-48], and 3 of these studies reported no significant differences in completion time [35,47]. In one study, however, subjects reported that the completion time for the electronic variant was more acceptable (P=.02) and was perceived as less of a barrier (P=.003) compared to the paper version [36]. Significantly lower times for the electronic variant were reported in 3 other studies [37,40,43]. Only 2 of the 9 studies reported significantly lower completion times for the paper version [45,46], owing to the longer log-on procedure required for the ePROM [45]. One study was indecisive. A detailed overview of the completion times can be found in Table 4. Overall, the completion times for ePROMs were at least equal to or faster than those for paper forms.
Table 4.
Completion times for electronic questionnaires, compared with the paper-based counterpart.
| Study and instrument | Time for electronic completion, mean | Time for paper completion, mean | P value | Remarks | |
| Shah et al 2016 [35] | N/A | ||||
|
|
EQ-5Da | 88 s | 81 s | .105 |
|
|
|
ODIb | 145 s | 143 s | .869 |
|
|
|
NDIc | 124 s | 117 s | .716 |
|
|
|
HOOSd | 247 s | 238 s | .829 |
|
|
|
KOOSe | 255 s | 259 s | .916 |
|
|
|
QuickDASHf | 111 s | 117 s | .723 |
|
| Touvier et al 2010 [36] | |||||
|
|
NutriNet-Sante anthropometric questionnaire | —v | — | .07 | Time for electronic considered more acceptable (P=.02) and less a barrier (P=.003) |
| Salaffi et al 2013 [37] | |||||
|
|
BASDAIg, BASFIh, NRSi | 5.1 min | 7.9 min | .04 | Computer skills, age, and education had no impact (P>.05) |
| Salaffi et al 2009 [40] | |||||
|
|
VASj GHk, VAS Pain, VAS PGAl, ROADm, TJCn | 7.3 min | 7.9 min | .006 | Older age was associated with slower times for both electronic (P=.02) and paper (P=.005) |
| Hollen et al 2013 [43] | |||||
|
|
LCSSo | 2.2 min | 3-5 min | N/A | N/A |
| Bliven et al 2001[45] | Not significant without the time for the log-on procedure | ||||
|
|
SAQp | 5.53 min | 4.78 min | <.05 |
|
|
|
SF-36q | 6.76 min | 5.44 min | <.05 |
|
| Ali et al 2017 [46] | |||||
|
|
DLQIr | 78 s | 73 s | .008 | Older age was associated with longer time (r2=.257, P=.012) |
| Greenwood et al 2006 [47] | |||||
|
|
RAQols | 5 min | 6 min | .194 | N/A |
| Kesterke et al 2015 [48] | When data entry is added, WOMAC electronic signature was faster (P<.001) and no difference for FJS (P=.169) | ||||
|
|
WOMACt | 117 s | 170 s | <.001 |
|
|
|
FJSu | 37 s | 22 s | <.001 |
|
aEQ-5D: EQ-5D: European Quality of Life-5 Dimensions (General Health).
bODI: Oswestry Disability Index.
cNDI: Neck Disability Index.
dHOOS: Hip Disability and Osteoarthritis Outcomes Score.
eKOOS: Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcomes Score.
fQuickDASH: abbreviated version of Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand.
gBASDAI: Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index.
hBASFI: Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index.
iNRS: numeric rating scale.
jVAS: visual analogue scale.
kGH: global health.
lPGA: Patient Global Disease Activity.
mROAD: Recent-Onset Arthritis Disability Index.
nTJC: tender joint count.
oLCSS: Lung Cancer Symptom Scale.
pSAQ: Seattle Angina Questionnaire.
qSF-36: Short Form-36.
rDLQI: Dermatology Life Quality Index.
sRAQol: Rheumatoid Arthritis Quality of Life Questionnaire.
tWOMAC: Western Ontario and McMaster Universities.
uFJS: Forgotten Joint Score.
vNo statistically significant difference between ePROMs and paper PROMs in unanswered questions or complete questionnaires.
Benefits for Health Care Workers or Centers
Cost
Engan et al [23] calculated and compared the human resource (HR) costs, specifically the time spent by an employee preparing, receiving, and handling data, of web-based and paper-based questionnaires. The mean HR cost for the web version was 9.5 minutes, whereas the mean HR cost for the paper version was 24 minutes.
Based on a cohort of 500,000 subjects [36], the financial costs of a paper-based questionnaire were calculated, including printing, mailing, returns, and double data entry. In total, it cost €4,965,833 (€9.94/subject) to use a paper-based version. In comparison, the development of a web-based tool by professionals was estimated to cost only €150,000 (€0.3/subject) or just 3% of the amount of the paper version.
Overall, these results indicate that digital data collection is less expensive, especially with large sample sizes, and it reduces HR-related costs.
Data Quality and Completion
Of the 10 studies [23,31,35,36,38,39,41,42,45,50] that reported on missing and incomplete data, 7 studies [23,31,36,38,39,41,50] indicated that electronic methods are associated with less missing data and more complete data. Integrated controls embedded in their ePROM administration was reported by 3 articles [23,35,36]. When a question wasn’t answered, an alert message provided the option to revise the answer prior to submission. As such, data entry mistakes in the form of missing, inconsistent, or abnormal values could theoretically be reduced to zero [23,36]. Regarding unanswered questions or incomplete questionnaires, 2 studies reported no statistically significant differences between ePROMs and paper PROMs [35,45]. One study [42] found significantly more missing items in the electronic version. And, one study reported that the answers were more detailed in 4 of 5 open questions on their electronic questionnaire (P<.05) [31]. Details of these results can be found in Table 5. Based on these results, we conclude that data quality is higher with ePROMs.
Table 5.
Data quality of electronic questionnaires compared to their pencil-and-paper counterpart.
| Study and missing data, unanswered questions, or incomplete forms | ||||||||
| Instrument and outcome unit | Electronic | Paper | P value | Remarks | ||||
| Engan et al 2016 [23] | ||||||||
|
|
PAM-13a, MacNewb, FQc, EORTCd, QLQ-C30e, HADSf |
|
|
|||||
|
|
Mean number of missing answers per patient | 0.55 | 2.15 | <.001 | No inadequate responses in the web version due to integrated controls | |||
| Shah et al 2016 [35] | No difference in unanswered questions | |||||||
|
|
EQ-5Dg |
|
|
|||||
|
|
Mean number of unanswered questions | 1.08 | 1.30 | .083 |
|
|||
|
|
ODIh |
|
|
|||||
|
|
Mean number of unanswered questions | 1.14 | 1.23 | .619 |
|
|||
|
|
NDIi |
|
|
|||||
|
|
Mean number of unanswered questions | 1 | 1.75 | .541 |
|
|||
|
|
HOOSj |
|
|
|||||
|
|
Mean number of unanswered questions | 6.7 | 5.5 | .788 |
|
|||
|
|
KOOSk |
|
|
|||||
|
|
Mean number of unanswered questions | 1.5 | 3.8 | .220 |
|
|||
|
|
QuickDASHl |
|
|
|||||
|
|
Mean number of unanswered questions | 1 | 1 | 1 |
|
|||
| Touvier et al 2010 [36] | N/Am | Non-existent in web-based version due to integrated controls | ||||||
|
|
NutriNet Sante questionnaire |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
Data entry mistakes | 0 | 82 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
Missing values | 0 | 60 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
Inconsistent values | 0 | 57 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
Abnormal values | 0 | 3 |
|
|
||
| Smith et al 2016 [38] | ||||||||
|
|
PSSn |
|
|
|||||
|
|
Incomplete forms | 3 | 29 | <.001 | 14 times more likely to be incomplete | |||
|
|
FFIo |
|
|
|||||
|
|
Incomplete forms | 0 | 20 | <.001 | 260 times more likely to be incomplete | |||
|
|
ODI |
|
|
|||||
|
|
Incomplete forms | 1 | 10 | <.001 | 11 times more likely to be incomplete | |||
| Raat et al 2007 [39] | ||||||||
|
|
CHQ-CFp |
|
|
|||||
|
|
Mean % missing answers per item | 0.04% | 0.54% | <.01 | N/A | |||
| Dy et al 2012 [41] | ||||||||
|
|
DASHq |
|
|
|||||
|
|
Mean number of missing questions | 0.1 | 2.6 | <.001 | N/A | |||
| Richter et al 2008 [42] | ||||||||
|
|
FFbHr, BASDAIs, SF-36t |
|
|
|||||
|
|
Number of missing items | NRu | NR | <.05 | N/A | |||
|
Bliven et al 2001 [45]
| ||||||||
|
|
SAQv |
|
|
|||||
|
|
Incomplete forms | 5 | 5 | N/A | N/A | |||
|
|
SF-36 |
|
|
|||||
|
|
Incomplete forms | 4 | 4 | N/A | N/A | |||
| De Rada et al 2014 [31] | ||||||||
|
|
SAQ |
|
|
|||||
|
|
% unanswered questions | 4.9% | 9.3% | <.01 | N/A | |||
| Kongsved et al 2007 [50] | ||||||||
|
|
SF-36, MFI-20w, HADS |
|
|
|||||
|
|
% complete forms | 97.8% | 63.4% |
<.001 | N/A | |||
aPAM-13: Patient Activation Measure short form.
bMacNew: MacNew Heart Disease Health-related Quality of Life questionnaire.
cFQ: Fatigue Questionnaire.
dEORTC: European Organization for the Research and Treatment of Cancer.
eQLQ-C30: Quality of Life Questionnaire Core 30.
fHADS: Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale.
gEQ-5D: European Quality of Life-5 Dimensions (General Health).
hODI: Oswestry Disability Index.
iHOOS: Hip Disability and Osteoarthritis Outcomes Score.
jKOOS: Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcomes Score.
kQuickDASH: abbreviated version of Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand.
lBASDAI: Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index.
mN/A: not applicable.
nPSS: Perceived Stress Scale.
oFFI: Foot Function Index.
pCHQ-CF: Child Health Questionnaire-Child Form.
qDASH: Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand.
rFFbH: Hannover Functional Ability Questionnaire.
sBASDAI: Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index.
tSF-36: Short Form-36.
uNR: not reported.
vSAQ: Seattle Angina Questionnaire.
wMFI-20: Multidimensional Fatigue Inventory.
Response Rate, Adherence, and Compliance
A retrospective cohort analyzed the annual data from PROM non-completers. PROM monitoring was completed via paper until 2010, and in 2011, ePROMs were implemented. The initial rate of PROM non-completers was 43%-58%. This decreased to less than 20% since the implementation of ePROMs in 2011 [28]. One randomized controlled trial reported response rates of 17.9% in the internet group and 73.2% in the paper group. After sending a reminder, response rates were 64.2% and 76.5%, respectively (risk difference 12.2%, P=.002) [50]. Another study found no differences in completion rates between ePROMs and paper PROMs (P=.208) [35].
There is conflicting evidence on the effect of electronic data collection on response rates and adherence. Adherence to ePROM declines over time [20,29]. The opportunity to send automated reminders (eg, email or notification) to subjects can improve response rates and compliance [20,50].
Other Benefits
The role of ePROMs in symptom management and decision making was acknowledged in multiple studies. Andikyan et al [20] and Schnall et al [22] reported that electronic symptom self-reporting was important in clinical decision making. Automated data collection and processing via ePROM can generate automated alerts to health care professionals when a patient reports disturbing or severe symptoms [20]. It allows early detection of complications, immediate action, and potentially reduction in symptom burden, complications, and readmissions to the hospital. Furthermore, it empowers patients and improves patient-clinician communication [22,24,42]. This is facilitated by the opportunity to plot results visually with a graph or visual aids and gives both the patient and clinicians better insight in the evolution of the patient’s health status [25,34,43].
ePROMs have the advantage of always being available [24,25]. There is no paper waste [34,41], and ePROMs are portable and can be used to measure across multiple devices [42,46,49]. These reported ‘other benefits’ originate from studies with the lowest methodological quality.
Disadvantages
As of May 25, 2018, all European organizations are expected to be compliant with the General Data Protection Regulations. This is reassurance for patients that the law is on their side when it comes to the use of their personal health data. All included articles and studies were performed before the implementation of the General Data Protection Regulations. However, privacy concerns were reported in 2 studies [21,26]. Liu et al [21] reported that the majority of patients (71.7%) thought their privacy should be adequately protected. In another study, patients were asked whether there were any barriers related to privacy and technology that would negatively influence their willingness to use ePROMs, and 30% were concerned about privacy issues. The study showed that barriers can be overcome by exposing the patients to an ePROM, which significantly influenced the willingness to participate in electronic assessments [26].
Disadvantages due to technical issues were addressed in 5 articles. The difficulty of or problems with login procedures were addressed in 3 studies [24,45]. Furthermore, technical difficulties adversely impacted compliance; patients who experienced technical difficulties completed fewer daily symptom entries (41.0%) than those who did not (76.0%) [29]. In another study, the needs and possible technological support structures were investigated. The importance of different possible support services to help complete a web-based questionnaire was assessed. Onsite support services were rated as being moderately or highly important by 38%. Technical telephone support was rated as moderately important or very important by 52%. At least 61% would appreciate receiving direct feedback after using the ePROM app [26].
Electronic data collection may require a large initial financial investment (eg, to purchase tablets or computer infrastructure and software, equipment costs, hiring computer programmers, or accessing cellular internet) [30,36,45].
A major disadvantage of ePROM is the potential of a ‘digital divide’. People who are computer illiterate, are older, or have no access to infrastructure could be disadvantaged. One study reported that more than 50% of >70 year olds were not able to complete the electronic version without assistance due to computer illiteracy; less assistance was required for patients completing the paper version [27]. In a second study, patients who needed support were significantly older [42]. The digital divide was also illustrated in another study with cancer patients. Patients who refused ePROM or chose phone calls over (home-based) ePROMs were approximately 10 years older. Patients may differ in terms of available internet, user experience, and affinity for new media. Older or computer-illiterate patients need opportunities to familiarize themselves with the devices [24]. Older patients with poorer health-related quality of life and fewer pre-existing technical skills reported barriers for ePROMs more frequently [26]. Wintner et al [24] reported that patients found ePROMs too impersonal.
Suggestions
Suggestions and tips for ePROM apps were extracted from 12 studies [20,21,24,27,29,30,32-35,38,42]. ePROMs should be free, simple, and minimalistic. They should have a good design, good user experience, adjustable font size, and adaptable user interface. When you start implementing ePROMs, provide educational sessions or support, think of the link with electronic health records, and review the results of the ePROMs with the patients because of the increased perception of benefit. ePROMs should provide positive reinforcement for the patients. Based on our results and discussion, we created a comprehensive overview of the benefits, disadvantages, and suggestions for ePROMs (see Figure 3).
Figure 3.

Comprehensive overview of the benefits of, disadvantages of, and suggestions for electronic patient-reported outcome measures (ePROMs).
Discussion
Principal Findings
The goal of this systematic review was to systematically and critically summarize the evidence on the use of ePROMs and find the potential benefits and disadvantages. We conclude that ePROM collection is feasible and accepted in healthy people and a wide range of patients with different conditions. Taking into account the results from the strongest methodological studies and the items that were reported in multiple studies, electronic data collection is preferred over paper-based collection, costs less, improves data quality, results in similar or faster completion times, and requires less administration time. Clinical decision making in combination with adequate symptom management can be facilitated. Expressed opinions reflected positive thoughts and attitudes towards ePROMs. Overall, participants found it easy to use, found it easy to learn, and would recommend it to others.
Strengths and Limitations
Although our findings are generally favorable towards ePROMs, we cannot ignore the potential disadvantages. Aspects to consider are privacy protection, the one-time large financial investment, and exclusion of certain populations. Patients may be unwilling or unable to complete ePROMs due to higher age or computer illiteracy. Some patients have no internet access, do not have technological devices, or are not acquainted with technological devices. These reported disadvantages and barriers need to be considered when implementing a digital data collection tool in any population. Potential solutions may include an educational session on the use of the digital app and providing sufficient support [24,27,42]. It is also useful to at least provide back-up pen-and-paper data collection to avoid excluding segments of the population from receiving the best possible health care [20,32]. Several suggestions to keep in mind when creating an ePROM are also mentioned in this literature review, which could increase patient experience, usability, and acceptability.
Considering the influence of age, 2 studies suggest that it is an important factor that could potentially increase completion time [40,46]. In contrast, one study found no relationships between completion time and computer skills, age, or education [37]. Older people in particular have reservations concerning modern computer technology and need to be properly approached, especially since we found that younger people had a significantly greater preference for ePROMs [23,32,42]. In our systematic review, we found that various groups of patients with a chronic disease preferred ePROMs over paper versions. On the aspect of completion time, only the time for the patient to complete the questionnaire was measured in the included articles. However, one of the greatest reported advantages of electronic data collection is automated data processing [36,38,41-43,45,49], which subsequently reduces HR time [23], and data are less prone to administration errors. Clinical-based decision-making models using daily registration of PROMs can thus be created.
The strengths of this literature review are that 32 studies concerning the research question were retrieved. Not all studies were comparative trials but assessed patient satisfaction or attitude towards a single ePROM [21,24,25,32,33]. These studies, although not methodologically the strongest, provided capital insights for the research question.
In this systematic literature search, we only searched two databases. It is, therefore, possible that we missed some clinical studies. Moreover, the limited methodological quality of some of the included studies diminished the power of the recommendations.
The overall methodological quality of the included articles was moderate. Disadvantages were a lack of blinding of participants, heterogeneity of outcome measures, heterogeneity of patient populations, different ePROM questionnaires, and different ePROM modalities/formats. Generalizing or comparing results is therefore more difficult, and the results should be interpreted with caution.
The most frequently used screen-based device was tablets. This may be because tablet screens are larger than traditional handheld devices, are easy to use, and can be used for device-based systems. They can provide access to web-based portals or can be used with downloadable apps, which makes them the primary platform for site-based (ie, hospital, care centers) ePROM collection. On the contrary, desktops usually lack touch screen functionality and require the use of a keyboard and/or mouse to respond to questions [14]. Different electronic modes were used in the different articles. The advantages and disadvantages of the different electronic modes are difficult to conclude from this study. Contrasting evidence was found in previously published literature. Two reviews reported their concerns of equivalence between different electronic modes [8,10]; however, White et al [10] found small differences in the correlations, which were not significant regardless of the electronic mode used. In clinical trials, multiple modes of administration may be used, and new findings may be compared to findings that used a different electronic mode of data collection. Further research is warranted regarding the influence of the electronic mode on measurement equivalence. Our findings predominantly complement those from other published literature. Belisario et al [53] conducted a review to assess the impact of apps on the quality of survey questionnaire responses and reported contradictory results regarding completion times but acknowledged that apps might improve data completeness with more complete records than paper administration. Similar to our findings, they reported that there is not enough evidence that apps impact adherence to sampling protocols. Muehlhausen et al [9] conducted a meta-analysis on the equivalence of electronic and paper administration of PROMs and showed that ePROMs yielded comparable results to those of the paper-based variant. Their findings also confirmed the ISPOR taskforce’s conclusion that full psychometric testing of new ePROMs is not necessary for migrations with minor changes only [12]. For researchers and sponsors, this is a clinically and financially reassuring aspect that might facilitate the decision-making process to migrate from paper to digital data collection. The bring-your-own-device (BYOD) approach for ePROM data collection shows potential. BYOD allows participants to use their own computer device (eg, smartphone, tablet, laptop) to access and complete ePROMs [14]. However, there are still a number of issues (eg, software, security, ownership) that need to be resolved before BYOD becomes widely used.
Future Work
The importance of PROMs is widely accepted. Collecting PROMs with paper-based questionnaires requires many subsequent time-consuming steps [45] that hamper wide implementation in daily care. Electronic collection of PROMs overcomes many of these steps. The potential to collect, score, analyze, visualize, and almost instantly review the results may facilitate workflow. Clinically, we believe ePROMs will improve the interchangeability of information between health care workers, patient-clinician communication, and patient care due to its always available nature. In addition, automated data processing in combination with targeted strategies (eg, automated alerts when patients report disturbing symptoms) has major clinical implications. Clinicians and researchers will also benefit from digital data collection since it reduces administration time. Furthermore, integration of ePROMs into electronic health records may be fundamental to advancing clinical care to improve patient engagement and health outcomes.
Conclusion
Based on this study, we found multiple advantages for the use of ePROMS in several fields of care. ePROMs are preferred over paper-based forms, cost less, improve data quality, result in similar or faster completion times, reduce administration times, and facilitate clinical decision making in combination with adequate symptom management. Subjects expressed positive thoughts and attitudes towards electronic data collection. Potential disadvantages have been mapped but they are not of the magnitude to disregard ePROMs. Furthermore, suggestions have been provided to counteract the disadvantages. This review allows researchers and clinicians to consider both the advantages and disadvantages of selecting one mode over the other. While electronic modes offer advantages for all involved parties (eg, patients, hospitals, government), implementing (new) ePROMs requires careful considerations of the implications on the study population and may require additional steps (eg, provision of internet access, acquiring electronic devices) to include participants who would be excluded otherwise.
Abbreviations
- ACQ
Asthma Control Questionnaire
- AQLQ
Asthma Quality of Life Questionnaire
- BARSE
Barriers Self-Efficacy Scale
- BASDAI
Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index
- BASFI
Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index
- CBO
Centraal BegeleidingsOrgaan-classificatiesysteem
- CCC
concordance correlation coefficient
- CHQ-CF
Child Health Questionnaire-Child Form
- CSGA
Cancer-Specific Geriatric Assessment
- DASH
Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand
- DLQI
Dermatology Life Quality Index
- eHealth
electronic health
- EORTC
European Organization for the Research and Treatment of Cancer
- ePRO
electronic patient-reported outcome
- ePROM
electronic patient-reported outcome measure
- EQ-5D
European Quality of Life-5 Dimensions (General Health)
- ESAS
Edmonton Symptom Assessment System
- FFbH
Hannover Functional Ability Questionnaire
- FFI
Foot Function Index
- FJS
Forgotten Joint Score
- FQ
Fatigue Questionnaire
- GH
global health
- HADS
Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale
- HOOS
Hip Disability and Osteoarthritis Outcomes Score
- HR
human resource
- ICC
intraclass correlation coefficient
- ISPOR
International Society for Pharmacoeconomics and Outcomes Research
- KDQOL-36
Kidney Disease Quality of Life Instrument
- KIVPA
Korte Indicatieve Vragenlijst voor Psychosociale Problematiek bij Adolescenten
- KOOS
Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcomes Score
- LCSS
Lung Cancer Symptom Scale
- LMSQoL
Leeds Multiple Sclerosis Quality of Life
- MacNew
MacNew Heart Disease Health-related Quality of Life questionnaire
- MFI-20
Multidimensional Fatigue Inventory
- MFIS-5
Modified Fatigue Impact Scale-5
- MMAS-8
Morisky Medication Adherence Scale
- MSIP
Multiple Sclerosis Impact Profile
- MSQoL-54
Multiple Sclerosis Quality of Life-54
- NDI
Neck Disability Index
- NRS
numeric rating scale
- ODI
Oswestry Disability Index
- OR
odds ratio
- PAM-13
Patient Activation Measure short form
- PASE
Physical Activity Scale for the Elderly
- PDA
personal digital assistant
- PGA
Patient Global Disease Activity
- PHQ-9
Patient Health Questionnaire-9
- PLWH
people living with HIV/AIDS
- PRISMA
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
- PRO
patient-reported outcome
- PROM
patient-reported outcome measure
- PSQI
Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index
- PSS
Perceived Stress Scale
- QLQ-C30
Quality of Life Questionnaire Core 30
- QuickDASH
abbreviated version of Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand
- RAQol
Rheumatoid Arthritis Quality of Life Questionnaire
- ROAD
Recent-Onset Arthritis Disability Index
- RQLQ
Rhinoconjunctivitis Quality of Life Questionnaire
- SAQ
Seattle Angina Questionnaire
- SF-36
Short Form-36
- THR
total hip replacement
- TJC
tender joint count
- TKR
total knee replacement
- VAS
visual analogue scale
- WOMAC
Western Ontario and McMaster Universities
Footnotes
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
References
- 1.CDRH Strategic Priorities 2016-2017. [2018-09-12]. Value and Use of Patient Reported Outcomes (PROs) in Assessing Effects of Medical Devices https://www.fda.gov/media/109626/download.
- 2.Rolfson O, Bohm E, Franklin P, Lyman S, Denissen G, Dawson J, Dunn J, Eresian Chenok K, Dunbar M, Overgaard S, Garellick G, Lübbeke Anne, Patient-Reported Outcome Measures Working Group of the International Society of Arthroplasty Registries Patient-reported outcome measures in arthroplasty registries Report of the Patient-Reported Outcome Measures Working Group of the International Society of Arthroplasty Registries Part II. Recommendations for selection, administration, and analysis. Acta Orthop. 2016 Jul 26;87 Suppl 1(sup1):9–23. doi: 10.1080/17453674.2016.1181816. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/27228230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kyte DG, Calvert M, van der Wees PJ, ten Hove R, Tolan S, Hill JC. An introduction to patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) in physiotherapy. Physiotherapy. 2015 Jun;101(2):119–25. doi: 10.1016/j.physio.2014.11.003. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0031-9406(14)00113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration. 2009. [2018-09-12]. Guidance for Industry Patient-Reported Outcome Measures: Use in Medical Product Development to Support Labeling Claims https://www.fda.gov/media/77832/download.
- 5.Allen L. Ganser, Stephen A. Raymond, Jay D. Pearson . ePro Electronic Solutions for Patient-Reported Data. London: Gower; 2010. Data Quality and Power in Clinical Trials: A Comparison of ePRO and Paper in a Randomized Trial. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Stefan Biesdorf. Florian Biedermann Healthcares digital future. 2014. Jul, [2018-09-12]. Healthcare's digital future https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/healthcare-systems-and-services/our-insights/healthcares-digital-future.
- 7.Gwaltney CJ, Shields AL, Shiffman S. Equivalence of electronic and paper-and-pencil administration of patient-reported outcome measures: a meta-analytic review. Value Health. 2008 Mar;11(2):322–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4733.2007.00231.x. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1098-3015(10)60526-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Campbell N, Ali F, Finlay AY, Salek SS. Equivalence of electronic and paper-based patient-reported outcome measures. Qual Life Res. 2015 Aug;24(8):1949–61. doi: 10.1007/s11136-015-0937-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Muehlhausen W, Doll H, Quadri N, Fordham B, O'Donohoe P, Dogar N, Wild DJ. Equivalence of electronic and paper administration of patient-reported outcome measures: a systematic review and meta-analysis of studies conducted between 2007 and 2013. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2015 Oct 07;13:167. doi: 10.1186/s12955-015-0362-x. https://hqlo.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12955-015-0362-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.White MK, Maher SM, Rizio AA, Bjorner JB. A meta-analytic review of measurement equivalence study findings of the SF-36® and SF-12® Health Surveys across electronic modes compared to paper administration. Qual Life Res. 2018 Jul;27(7):1757–1767. doi: 10.1007/s11136-018-1851-2. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/29663258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Coons SJ, Gwaltney CJ, Hays RD, Lundy JJ, Sloan JA, Revicki DA, Lenderking WR, Cella D, Basch E, ISPOR ePRO Task Force Recommendations on evidence needed to support measurement equivalence between electronic and paper-based patient-reported outcome (PRO) measures: ISPOR ePRO Good Research Practices Task Force report. Value Health. 2009 Jun;12(4):419–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4733.2008.00470.x. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/VHE470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Byrom B, Gwaltney C, Slagle A, Gnanasakthy A, Muehlhausen W. Measurement Equivalence of Patient-Reported Outcome Measures Migrated to Electronic Formats: A Review of Evidence and Recommendations for Clinical Trials and Bring Your Own Device. Ther Innov Regul Sci. 2019 Jul 29;53(4):426–430. doi: 10.1177/2168479018793369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zbrozek A, Hebert J, Gogates G, Thorell R, Dell C, Molsen E, Craig G, Grice K, Kern S, Hines S. Validation of electronic systems to collect patient-reported outcome (PRO) data-recommendations for clinical trial teams: report of the ISPOR ePRO systems validation good research practices task force. Value Health. 2013 Jun;16(4):480–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2013.04.002. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1098-3015(13)01797-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Coons SJ, Eremenco S, Lundy JJ, O'Donohoe Paul, O'Gorman Hannah, Malizia W. Capturing Patient-Reported Outcome (PRO) Data Electronically: The Past, Present, and Promise of ePRO Measurement in Clinical Trials. Patient. 2015 Aug 10;8(4):301–9. doi: 10.1007/s40271-014-0090-z. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/25300613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Brian Dolan Mobihealth News. 2014. Jul 14, [2018-09-12]. Surveypercent of patients want digital health services https://www.mobihealthnews.com/34804/survey-75-percent-of-patients-want-digital-health-services.
- 16.PROSPERO. [2018-09-12]. https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?RecordID=94795.
- 17.Moher D, Schulz KF, Altman DG. The CONSORT statement: revised recommendations for improving the quality of reports of parallel-group randomised trials. The Lancet. 2001 Apr;357(9263):1191–1194. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)04337-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Cochrane Netherlands. [2018-09-12]. http://netherlands.cochrane.org/beoordelingsformulieren-en-andere-downloads.
- 19.NIH National Heart Lung and Blood Institute. [2019-09-12]. Quality assessment Tool for Observational Cohort and Cross-Sectional Studies https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/study-quality-assessment-tools.
- 20.Andikyan V, Rezk Y, Einstein MH, Gualtiere G, Leitao MM, Sonoda Y, Abu-Rustum NR, Barakat RR, Basch EM, Chi DS. A prospective study of the feasibility and acceptability of a Web-based, electronic patient-reported outcome system in assessing patient recovery after major gynecologic cancer surgery. Gynecologic Oncology. 2012 Nov;127(2):273–277. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2012.07.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Liu X, Wang R, Zhou D, Hong Z. Feasibility and acceptability of smartphone applications for seizure self-management in China: Questionnaire study among people with epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2016 Feb;55:57–61. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2015.11.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Schnall R, Wantland D, Velez O, Cato K, Jia H. Feasibility testing of a web-based symptom self-management system for persons living with HIV. J Assoc Nurses AIDS Care. 2014 Jul;25(4):364–71. doi: 10.1016/j.jana.2013.09.002. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/24434198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Engan HK, Hilmarsen C, Sittlinger S, Sandmæl Jon Arne, Skanke F, Oldervoll LM. Are web-based questionnaires accepted in patients attending rehabilitation? Disabil Rehabil. 2016 Dec;38(24):2406–12. doi: 10.3109/09638288.2015.1129449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wintner LM, Giesinger JM, Zabernigg A, Rumpold G, Sztankay M, Oberguggenberger AS, Gamper EM, Holzner B. Evaluation of electronic patient-reported outcome assessment with cancer patients in the hospital and at home. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2015 Dec 23;15(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s12911-015-0230-y. https://bmcmedinformdecismak.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12911-015-0230-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Jongen PJ, Sinnige LG, van Geel BM, Verheul F, Verhagen WI, van der Kruijk RA, Haverkamp R, Schrijver HM, Baart JC, Visser LH, Arnoldus EP, Gilhuis HJ, Pop P, Booy M, Heerings M, Kool A, van Noort E. The interactive web-based program MSmonitor for self-management and multidisciplinary care in multiple sclerosis: utilization and valuation by patients. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2016 Mar;10:243–50. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S93786. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S93786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hartkopf AD, Graf J, Simoes E, Keilmann L, Sickenberger N, Gass P, Wallwiener D, Matthies L, Taran F, Lux MP, Wallwiener S, Belleville E, Sohn C, Fasching PA, Schneeweiss A, Brucker SY, Wallwiener M. Electronic-Based Patient-Reported Outcomes: Willingness, Needs, and Barriers in Adjuvant and Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients. JMIR Cancer. 2017 Aug 07;3(2):e11. doi: 10.2196/cancer.6996. https://cancer.jmir.org/2017/2/e11/ [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.McCleary NJ, Wigler D, Berry D, Sato K, Abrams T, Chan J, Enzinger P, Ng K, Wolpin B, Schrag D, Fuchs CS, Hurria A, Meyerhardt JA. Feasibility of computer-based self-administered cancer-specific geriatric assessment in older patients with gastrointestinal malignancy. Oncologist. 2013 Jan;18(1):64–72. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2012-0241. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2012-0241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Gamper EM, Nerich V, Sztankay M, Martini C, Giesinger JM, Scarpa L, Buxbaum S, Jeller M, Holzner B, Virgolini I. Evaluation of Noncompletion Bias and Long-Term Adherence in a 10-Year Patient-Reported Outcome Monitoring Program in Clinical Routine. Value Health. 2017 Apr;20(4):610–617. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2017.01.009. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1098-3015(16)30072-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Jonassaint CR, Shah N, Jonassaint J, De Castro Laura. Usability and Feasibility of an mHealth Intervention for Monitoring and Managing Pain Symptoms in Sickle Cell Disease: The Sickle Cell Disease Mobile Application to Record Symptoms via Technology (SMART) Hemoglobin. 2015;39(3):162–8. doi: 10.3109/03630269.2015.1025141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Schick-Makaroff K, Molzahn A. Strategies to use tablet computers for collection of electronic patient-reported outcomes. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2015 Jan 22;13:2. doi: 10.1186/s12955-014-0205-1. https://hqlo.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12955-014-0205-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Rada VDD, Domínguez-Álvarez JA. Response Quality of Self-Administered Questionnaires. Social Science Computer Review. 2013 Oct 31;32(2):256–269. doi: 10.1177/0894439313508516. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Keurentjes JC, Fiocco M, So-Osman C, Ostenk R, Koopman-Van Gemert AWMM, Pöll R G, Nelissen RGHH. Hip and knee replacement patients prefer pen-and-paper questionnaires: Implications for future patient-reported outcome measure studies. Bone Joint Res. 2013 Nov;2(11):238–44. doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.211.2000219. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/24203164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Recinos PF, Dunphy CJ, Thompson N, Schuschu J, Urchek JL, Katzan IL. Patient Satisfaction with Collection of Patient-Reported Outcome Measures in Routine Care. Adv Ther. 2017 Feb;34(2):452–465. doi: 10.1007/s12325-016-0463-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Hochstenbach LMJ, Zwakhalen SMG, Courtens AM, van Kleef M, de Witte LP. Feasibility of a mobile and web-based intervention to support self-management in outpatients with cancer pain. Eur J Oncol Nurs. 2016 Aug;23:97–105. doi: 10.1016/j.ejon.2016.03.009. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1462-3889(16)30027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Shah Kalpit N, Hofmann M, Schwarzkopf R, Pourmand D, Bhatia N, Rafijah G, Bederman S. Patient-Reported Outcome Measures: How Do Digital Tablets Stack Up to Paper Forms? A Randomized, Controlled Study. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ) 2016;45(7):E451–E457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Touvier M, Méjean Caroline, Kesse-Guyot E, Pollet C, Malon A, Castetbon K, Hercberg S. Comparison between web-based and paper versions of a self-administered anthropometric questionnaire. Eur J Epidemiol. 2010 May;25(5):287–96. doi: 10.1007/s10654-010-9433-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Salaffi F, Gasparini S, Ciapetti A, Gutierrez M, Grassi W. Usability of an innovative and interactive electronic system for collection of patient-reported data in axial spondyloarthritis: comparison with the traditional paper-administered format. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2013 Nov;52(11):2062–70. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ket276. http://rheumatology.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=23955646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Smith MJ, Reiter MJ, Crist BD, Schultz LG, Choma TJ. Improving Patient Satisfaction Through Computer-Based Questionnaires. Orthopedics. 2016 Dec 23;39(1):e31–5. doi: 10.3928/01477447-20151218-07. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Raat H, Mangunkusumo RT, Landgraf JM, Kloek G, Brug J. Feasibility, reliability, and validity of adolescent health status measurement by the Child Health Questionnaire Child Form (CHQ-CF): internet administration compared with the standard paper version. Qual Life Res. 2007 May;16(4):675–85. doi: 10.1007/s11136-006-9157-1. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/17286197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Salaffi F, Gasparini S, Grassi W. The use of computer touch-screen technology for the collection of patient-reported outcome data in rheumatoid arthritis: comparison with standardized paper questionnaires. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2009;27(3):459–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Dy CJ, Schmicker T, Tran Q, Chadwick B, Daluiski A. The Use of a Tablet Computer to Complete the DASH Questionnaire. The Journal of Hand Surgery. 2012 Dec;37(12):2589–2594. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2012.09.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Richter JG, Becker A, Koch T, Nixdorf M, Willers R, Monser R, Schacher B, Alten R, Specker C, Schneider M. Self-assessments of patients via Tablet PC in routine patient care: comparison with standardised paper questionnaires. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008 Dec;67(12):1739–41. doi: 10.1136/ard.2008.090209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Hollen PJ, Gralla RJ, Stewart JA, Meharchand JM, Wierzbicki R, Leighl N. Can a computerized format replace a paper form in PRO and HRQL evaluation? Psychometric testing of the computer-assisted LCSS instrument (eLCSS-QL) Support Care Cancer. 2013 Jan 10;21(1):165–72. doi: 10.1007/s00520-012-1507-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Mangunkusumo RT, Moorman PW, Van Den Berg-de Ruiter AE, Van Der Lei J, De Koning HJ, Raat H. Internet-administered adolescent health questionnaires compared with a paper version in a randomized study. J Adolesc Health. 2005 Jan;36(1):70.e1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2004.02.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Bliven B D, Kaufman S, Spertus J. Electronic collection of health-related quality of life data: validity, time benefits, and patient preference. Qual Life Res. 2001;10(1):15–22. doi: 10.1023/a:1016740312904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Ali F, Johns N, Finlay A, Salek M, Piguet V. Comparison of the paper-based and electronic versions of the Dermatology Life Quality Index: evidence of equivalence. Br J Dermatol. 2017 Nov 12;177(5):1306–1315. doi: 10.1111/bjd.15314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Greenwood M C, Hakim A, Carson E, Doyle DV. Touch-screen computer systems in the rheumatology clinic offer a reliable and user-friendly means of collecting quality-of-life and outcome data from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2006 Jan;45(1):66–71. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kei100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Kesterke N, Egeter J, Erhardt JB, Jost B, Giesinger K. Patient-reported outcome assessment after total joint replacement: comparison of questionnaire completion times on paper and tablet computer. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2015 May 10;135(7):935–941. doi: 10.1007/s00402-015-2222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Fanning J, McAuley E. A comparison of tablet computer and paper-based questionnaires in healthy aging research. JMIR Res Protoc. 2014 Jul 16;3(3):e38. doi: 10.2196/resprot.3291. https://www.researchprotocols.org/2014/3/e38/ [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kongsved SM, Basnov M, Holm-Christensen K, Hjollund NH. Response rate and completeness of questionnaires: a randomized study of Internet versus paper-and-pencil versions. J Med Internet Res. 2007 Sep 30;9(3):e25. doi: 10.2196/jmir.9.3.e25. https://www.jmir.org/2007/3/e25/ [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Juniper EF, Langlands JM, Juniper BA. Patients may respond differently to paper and electronic versions of the same questionnaires. Respir Med. 2009 Jun;103(6):932–4. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2008.10.019. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0954-6111(08)00385-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Harbour R, Miller J. A new system for grading recommendations in evidence based guidelines. BMJ. 2001 Aug 11;323(7308):334–336. doi: 10.1136/bmj.323.7308.334. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/11498496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Marcano Belisario JS, Jamsek J, Huckvale K, O'Donoghue J, Morrison CP, Car J. Comparison of self-administered survey questionnaire responses collected using mobile apps versus other methods. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jul 27;(7):MR000042. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000042.pub2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


