Abstract
Paracoccidioides is a genus of thermodimorphic fungi that causes paracoccidioidomycosis. When in the host, the fungus undergoes several challenges, including iron deprivation imposed by nutritional immunity. In response to the iron deprivation triggered by the host, the fungus responds in a ternary manner using mechanisms of high affinity and specificity for the uptake of Fe, namely non-classical reductive iron uptake pathway, uptake of host iron proteins, and biosynthesis and uptake of siderophores. This triple response resembles the rhythmic structure of a waltz, which features three beats per compass. Using this connotation, we have constructed this review summarizing relevant findings in this area of study and pointing out new discoveries and perspectives that may contribute to the expansion of this “little iron waltz”.
Keywords: siderophores, CFEM proteins, reductive iron uptake pathway
1. Introduction
One of the greatest things about studying the host–pathogen interaction is to gradually understand that despite the storm of molecular events that support the adaptation process, there is organization! This organization is often referred to as “orchestration” or an “orchestrated response” [1,2,3]. It truly makes sense to trace an association between molecular events and the performance of music in an orchestrated way; in both cases, there is a myriad of individuals acting, albeit in an organized manner, which provides a final result of completeness. The host, through its immunity, employs several strategies that generate stress to pathogens, which in most cases makes it impossible for microorganisms to persist in it [4,5]. One of these strategies is nutritional immunity, a network of processes that culminate in limiting the bioavailability of nutrients and micronutrients for pathogens [6,7,8]. Without nutrients, there are two alternatives for microorganisms: succumbing to death or adapting to an environment of scarcity [9].
Iron is one of the micronutrients that is deprived through nutritional immunity. This transition metal is widely employed as a cofactor of several enzymes involved in crucial cellular processes, such as DNA synthesis and repair, energy metabolism, antioxidant systems, and biopolymer synthesis, among many others [10]. Obviously, iron is important for both the host and the pathogen, given its participation in elementary processes for life. This massive recruitment of iron is due to its flexibility of oxidation states, switching from ferric ion (Fe3+) to ferrous ion (Fe2+) with remarked facility [11]. Like a double-edged sword, this transition metal characteristic also makes it harmful if free in the intracellular environment, as this electron movement can damage biomolecules, which require that both host and pathogens employ mechanisms for the strict control of metal’s bioavailability [12,13].
In the context of the host–pathogen interface, it is advantageous for the host, through nutritional immunity, to limit the bioavailability of iron to pathogens, given the metal’s importance for the maintenance of vital cellular processes; if pathogens do not have access to the metal, the inevitable path is their death [14]. However, pathogens that have infectious success, like pathogenic bacteria and protozoa, are able to supplant nutritional immunity through highly sensitive and specific mechanisms for iron uptake [9,15]. Regarding pathogenic fungi, this is also a reality. In a generalist way, these microorganisms respond to iron deprivation by three main events: (1) the reductive iron assimilation pathway (as described for Cryptococcus neoformans); (2) exploration of iron-containing host proteins, such as hemoglobin (as described for Candida albicans) and; (3) biosynthesis and uptake of siderophores (as described for Aspergillus fumigatus) [16,17].
Latin America is the endemic region of a genus of pathogenic fungi named Paracoccidioides, which causes paracoccidioidomycosis (PCM), a systemic mycosis that affects both immunocompetent and immunocompromised individuals and can cause severe sequelae and even death, if proper treatment is not employed [18,19]. Despite the extensive work found in the scientific literature relative to the pathogen’s biology and disease’s pathobiology, more effective treatments, regarding the duration, are still current challenges [20]. Recent work has shown that the Paracoccidioides genus is composed of five species: Paracoccidioides lutzii, Paracoccidioides restrepiensis, Paracoccidioides venezuelensis, Paracoccidioides americana, and the cosmopolitan species Paracoccidioides brasiliensis, certainly the most investigated among the five species [21].
Paracoccidioides spp., like most living creatures, also need iron for the maintenance of cellular activity and consequently to obtain infectious success. This is evidenced in several ways. For example, the well-known MMcM (McVeigh and Morton) modified medium for growth of Paracoccidioides spp. contains in its composition a solution of trace elements, of which iron is the metal that appears in the highest molarity (approximately 3.6 µM; the next most abundant metal is zinc, with approximately 2.8 µM) [22]. Additionally, it has been shown that in the interaction with macrophages, the addition of iron chelators promotes a decrease in the pathogen’s survival, which points to the interdependence of the metal’s presence and successful parasitism [23,24].
In response to the iron deprivation imposed by the host, Paracoccidioides spp. modulate their metabolism prioritizing the use of glycolysis and negatively regulating iron-dependent pathways, such as the tricarboxylic acid cycle [25]. Additionally, the pathogen employs three high affinity and specific pathways for the uptake of iron, which allows the fungus to survive and persist, forming a ternary response [26,27,28]. Below we discuss these mechanisms and list new findings in this field of knowledge, ones that suggest this “little iron waltz” may mean improving therapeutic approaches to PCM.
2. “Time Signature”: The Transcriptional Reprogramming of Paracoccidioides spp. Facing Iron Deprivation
The ternary response of Paracoccidioides spp., when deprived of iron, resembles the rhythmic structure of a waltz, which features three beats per compass (ternary compass). Following this connotation, in this review we call a “beat” each of the three events that compose Paracoccidioides spp. response to iron deprivation. These events are orchestrated from a transcriptional reprogramming that occurs in the face of metal deprivation. Thus, still following the connotation of the performance of orchestrated music, the transcriptional reprogramming works just like the time signature at the beginning of a music sheet, which contains the global information for playing a song.
Iron deprivation suffered by pathogens when in the host leads to a transcriptional response that induces the expression of several proteins involved in obtaining metals from the host during infection. The expression of iron uptake pathways is part of a mechanism finely regulated by fungi, in which several transcriptional factors are activated to produce a rapid response to metal deprivation imposed by the host. As previously mentioned, the acquisition of iron from host by fungi is mediated by three uptake systems, of which one, the reductive iron assimilation pathway, is formed by ferric reductases [26]. The expression of these proteins is regulated by conditions such as metal deprivation and pH variation. In this way, the pathogenic fungus C. albicans has 15 putative ferric reductases, and the expression of some of those genes is under control of transcriptional factors; for example, ferric reductases FRE2p and FRP1p are regulated positively by the transcriptional factor Rim 101, in response to an alkaline environment [29]. In addition to the variation in response to pH, the expression of the ferric reductase FRP1p is increased during iron deprivation and the transcriptional factor Rim 101 also regulates the expression of this protein in C. albicans under this condition [30]. In C. neoformans, Rim 101 is involved in the use of heme from the host [31]. Additionally, the homeostasis of iron in C. neoformans is regulated by several other mechanisms. For example, the global repressor Tup1 is involved in the production of melanin; formation of capsules; and positive regulation of copper uptake transporter (CTR4p), ferric reductase transmembrane component (FRTp1), and siderophore–iron transporter (SIT2p) [32]. In C. albicans, Tup1 is also involved in the repression of genes such as rbt5 for the capture of host heme [33,34]. In fungi of the Paracoccidioides complex, the expression of these transcriptional factors is still being elucidated. The expression of Rim 101 and Tup1 are induced during iron deprivation, and their expression seems to undergo a regulation mediated by miRNAs, differentially expressed during the deprivation of this metal (de Curcio, personal communication), indicating that these two genes are involved with the fine transcriptional response to iron deprivation, contributing to the control of iron homeostasis in fungi of this complex.
In A. fumigatus, the response to iron deprivation is regulated by transcription factors encoded by genes sreA and hapX [35,36]. The transcription factor SreA is reduced in iron deprivation, promoting the depression of HapX, an essential event for induction of the siderophore biosynthesis pathway [37]. In addition, the influence of SreA on genes involved in iron capture systems was observed [35]. Another gene that plays a role in the adaptation of A. fumigatus in low iron is tptA, which is homologous to the Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene tpc1. The study carried out by Huang and collaborators [38] showed that tptA loss reduces the expression of hapX and that the overexpression of hapX in the tptA mutant strain restored the growth defect and the production of siderophores.
During iron deprivation, an increase in the expression of the transcriptional regulator hapX and in siderophores biosynthesis and uptake genes sidA and sit1, respectively, was observed in P. brasiliensis [25]. After 10 min of iron deprivation, the transcriptional regulator hapX level increased 2.3 times and remained increased up to 1 h. The sidA expression increased nine fold after 30 min of incubation and remained elevated for 24 h [25]. SrbA of P. brasiliensis restored the mutant’s defective growth phenotype of a null mutant strain of A. nidulans, demonstrating the functionality of this gene during iron deprivation [39]. As mentioned, mobilization of transcription factors orchestrates the response of fungi to Fe deprivation.
3. “The First Beat”: The Non-Classical Reductive Pathway of Iron Assimilation in Paracoccidioides spp.
The “first beat” of this “little iron waltz”, as mentioned above, is a strategy that some fungi use to circumvent iron deprivation, which is conventionally called the reductive pathway for iron assimilation and consists of multi-enzyme complexes that promote oxidation and reduction of the metal and internalize it [9]. Fungi such as C. albicans and C. neoformans have this ability, which is subsidized by iron reductases, copper-dependent ferroxidases and iron permeases that act together in the process [40,41]. This iron assimilation pathway allows the capture of free Fe3+, which is insoluble and therefore not bioavailable. However, since the amount of free metal in the host is minimal, this pathway is used mainly to sequester iron from host metalloproteins [40]. In Histoplasma capsulatum, a extracellular glutathione-dependent ferric reductase activity has been reported, in a process where glutathione is cleaved by a gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (Ggt1) and a dipeptide with high reductive power is generated, acting on the reduction of Fe3+ that feeds the metal’s internalization system [42,43].
The investigation of the ability of Paracoccidioides spp. to use this reductive pathway began with in silico analyses that pointed to the presence in the fungus genome of ferric reductases (like fre1, fre3, fre5, fre7, and frp1), Ggt1, and copper-dependent ferroxidase orthologues (like fetp). However, it was surprising to find that Paracoccidioides spp. do not show ferric permeases [44]. As a way of investigating this path in more detail, a specific methodology was employed to accompany the steps of reduction, oxidation, and internalization of the metal in members of the genus Paracoccidioides [45]. This methodology, employing 59Fe uptake assays, suggested that the Fe uptake process occurs differently between P. brasiliensis and P. lutzii, so that P. lutzii has an inefficient reductive iron assimilation (RIA) pathway [26]. The absence of orthologs for ferric permeases also suggests that in the Paracoccidioides genus a non-classical reductive iron assimilation pathway (non-classical RIA) occurs [26]. The non-classical term refers to the fact that under iron deprivation, the transcripts of zinc permeases (Zrts) have positive regulation, suggesting that Zrts act in a promiscuous way, transporting both Zn2+ and Fe2+ during deprivation. In other words, Zrts would not be specific for zinc but a generalist divalent metal carrier [26]. In agreement with the in silico analyses that pointed to the presence of a Ggt1 orthologue in the genomes of Paracoccidioides spp., transcriptional data showed that Ggt1 undergoes positive regulation when the fungus is grown in iron deprivation [46]. However, the extent to which Ggt1 acts in conjunction with the non-classical RIA is still unknown. Once this question is resolved, new perspectives will certainly be outlined. This question has been the subject of studies by our group.
4. “The Second Beat”: Exploring the Host’s Iron-Containing Proteins
The “second beat” of this “waltz” is the ability of Paracoccidioides spp. to explore a host’s iron-containing proteins directly. In order to limit the toxicity of iron and the bioavailability of the metal for pathogens, the host associates the metal with various proteins, such as hemoglobin and myoglobin (in the form of a heme group), albumin, transferrin, ferritin, and lactoferrin, among others [47]. This variety of iron alternative sources caused pathogens to develop specific mechanisms for metal capture from those sources [9,40].
C. albicans, for example, uses a protein called Als3 to allow iron uptake from ferritin [40,48]. C. albicans is also able to use a host’s heme-containing proteins, especially hemoglobin and serum albumin, through a network of hemophores (Csa2, Rbt5, Pga7) located on the cell surface that allow the sequestration and internalization of these iron sources [28,33,49,50]. The performance of hemophores is based on the presence of the CFEM (common in several fungal extracellular membrane proteins) domain, which has been reported in other fungal species, such as Candida glabrata and Candida parapsilosis [51,52,53]. The internalization of the heme group by C. albicans is dependent on the ESCRT (endosomal sorting complex required for transport) endocytosis system [54]. Like C. albicans, C. neoformans also uses heme through the Cig1 hemophore, which differs from Candida spp. hemophores by not presenting the CFEM domain [55]. The internalization of heme by C. neoformans is also dependent on the ESCRT system [56,57].
Paracoccidioides spp. are capable of using various iron-containing proteins such as lactoferrin, ferritin, transferrin, and hemoglobin [27]. Regarding hemoglobin uptake, the event occurs through a receptor that also has the CFEM domain, homologous to C. albicans Rbt5. The knock-down of rbt5 compromises the capacity of Paracoccidioides spp. survive on macrophages and colonize murine’s spleen [27]. Despite these data, it remains to be clarified whether Paracoccidioides spp. use only Rbt5 for using heme/hemoglobin or if other hemophores and ancillary proteins may be involved. It is important to highlight that in different Paracoccidioides genomes there are at least four sequences that code for proteins that contain the CFEM domain (Table 1). There is still a need for elucidating whether those proteins are involved in the capture of iron-containing proteins from the host. Additionally, it is not clear yet which endocytic system the fungus uses to internalize the molecule. It is also necessary to investigate whether Paracoccidioides spp. have other proteins dedicated to the use of specific iron sources in the host.
Table 1.
The putative CFEM proteins in Paracoccidioides spp. Genomes *.
| Species a | Gene ID b | Product Description c | CFEM (E-Value) d |
GPI Modification Site Prediction? e |
SignalP f | SecretomeP g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P. lutzii | PAAG_04763 | Hypothetical protein | 2.0 × 10−8 | None | Yes | - |
| PAAG_11627 | Hypothetical protein | 2.8 × 10−13 | None | Yes | - | |
| PAAG_05158 | Rbt5 # | 3.3 × 10−15 | Yes | Yes | - | |
| PAAG_02225 | Csa1 # | 5.2 × 10−12 | None | Yes | - | |
| PAAG_00918 | Hypothetical protein | 5.5 × 10−11 | None | Yes | - | |
| P. brasiliensis | PADG_11659 | Hypothetical protein | 1.5 × 10−11 | None | - | - |
| PADG_05363 | Csa1 # | 1.5 × 10−11 | None | Yes | - | |
| PADG_02506 | Hypothetical protein | 1.7 × 10−8 | None | Yes | - | |
| PADG_03909 | Hypothetical protein | 2.1 × 10−8 | Yes | Yes | - | |
| PADG_06374 | Hypothetical protein | 3.6 × 10−13 | None | - | Yes | |
| PADG_05000 | Rbt5 # | 4.5 × 10−15 | Yes | Yes | - | |
| P. americana | PABG_12009 | Hypothetical protein | 1.6 × 10−11 | None | Yes | - |
| PABG_00115 | Hypothetical protein | 1.7 × 10−8 | None | Yes | - | |
| PABG_01323 | Hypothetical protein | 2.4 × 10−8 | Yes | Yes | - | |
| PABG_04599 | Rbt51 # | 4.5 × 10−15 | Yes | Yes | - |
* The search for probable CFEM proteins in the genomes of Paracoccidioides was carried out using the online tool available at https://fungidb.org/fungidb/ (genes; sequence analysis; protein motif pattern). The term used in the search was CFEM. a Paracoccidioides species with genomes available in the FungiDB database. b Access code of the predicted CFEM-containing sequences. c Annotation available on FungiDB. d Confidence score of the prediction for CFEM domain presence. e Site prediction for GPI anchor modification. The prediction was performed by the online tool big-PI Predictor available at http://mendel.imp.ac.at/gpi/gpi_server.html. f Classical secretion prediction performed by the online tool SignalP 4.0 available at http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/SignalP-4.0/. g Non-classical secretion prediction performed by the online tool SecretomeP 2.0 available at http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/SecretomeP/. # Names assigned to the sequences as suggested by Bailão et al. (2014) [27].
5. “The Third Beat”: Biosynthesis and Uptake of Siderophores by Paracoccidioides spp.
Finally, but just as important as the other events described so far, there is the “waltz’ third beat”: the non-reducing mechanism of iron uptake mediated by siderophores [58]. From the Greek “iron carriers”, siderophores are low-molecular-weight (usually 1 KDa) molecules that solubilize ferric iron (Fe3+). Siderophores can also act in the storage of iron [59]. The iron uptake process by this mechanism occurs by excretion of siderophores and binding to the free iron ions, forming the iron–siderophore complex. After uptake, this complex is linked to specific receptor proteins, like Sit1 of C. albicans and C. neoformans and, MirB and MirC of Aspergillus nidulans, present in the cell membrane and through active transport are internalized [60,61,62]. There are different types of siderophores. Carboxylate siderophores are produced mainly by bacteria such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which synthesizes carboxymicobactin [63]. Catecholate siderophores are produced mainly by bacteria, like enterobactin (or enterochelin) produced by Escherichia coli and other Enterobacteriaceae [64]. However, most of the siderophores produced by fungi belong to the hydroxamate group, with the exception of the rizzoferrin, siderophores of the carboxylate type, which are produced by several Mucorales sp., as well as the catecholate-type pistilarin, produced by Penicillium bilaii [17].
Hydroxamate siderophores are the most commonly found in nature and are grouped into four structural families: rhodotoluric acid, fusarinines, coprogens, and ferricromes [17]. In bacteria, hydroxamates are composed of acylated and hydroxylated alkylamines, while in fungi they are derived from ornithine, a non-proteinogenic amino acid, which is hydroxylated and alkylated [65]. The importance of siderophores in fungal virulence is well characterized by detailed studies with the pathogen A. fumigatus, which produces siderophores belonging to the ferricrome family (ferricrocin), which are intracellular, and fusarinins (fusarinin C, triacetylfusarinica (TAFC)), which are extracellular. The production of intracellular ferricrocin siderophores is coordinated according to the morphology of the fungus; that is, ferricrocin is produced during filamentous growth, while hydroxyferricrocin is produced in spores of conidia, which are the infectious particles [9]. The iron–siderophore complex is transported back to cells via membrane proteins called siderophore transporters. In A. nidulans, MirA, MirB, and MirC were characterized as transporters of siderophores, with MirA and MirB being carriers of enterobactin and TAFC, respectively. Although MirC shows a high degree of conservation with other siderophore transporters, its exact role in capturing siderophores has not yet been found [66].
The mechanisms of iron uptake mediated by siderophores in fungi of the Paracoccidioides genus were investigated. These fungi conserve homologues genes related to the biosynthesis and uptake of siderophores, and transcripts of such genes are positively regulated during iron deprivation [44,46]. The genomes of members of the Paracoccidioides genus encode the orthologue genes for siderophore biosynthesis, namely sidA, sidF, sidC, sidD, sidI, and sidH, as well as the orthologues for the capture of siderophores, namely sit1, mirB, and mirC. During iron deprivation in Paracoccidioides spp., the synthesis and secretion of siderophores of the hydroxamate type coprogen B and dimerumic acid occurs, which are extracellular siderophores, and ferricrocin and ferricromes C, which are intracellular siderophores. The capacity for synthesis and secretion of siderophores by Paracoccidioides spp. was attested by a crossfeeding experiment, whereby a strain of A. nidulans unable to produce siderophores had its growth restored when grown in MMcM without iron, in co-cultivation with Paracoccidioides spp., which pointed out that A. nidulans can use siderophores produced and secreted by P. brasiliensis [28].
Members of the Paracoccidioides genus can use xenosiderophores as a source of iron, such as ferrioxamine B (FOB) [67,68]. In the presence of FOB, the suppression on synthesis of endogenous siderophores occurs, indicating the use of ferric ions linked to FOB as an iron source. Additionally, proteomic and enzymatic analyzes demonstrated that SidA, the enzyme that promotes ornithine hydroxylation during siderophore biosynthesis, was negatively regulated, suggesting the blockade of the pathway due to the alternative source of iron. To investigate the role of siderophore production in fungus virulence, P. brasiliensis knockdown strains for sidA were obtained, depicting a reduction in the production of siderophores as well as a reduction in the pathogenicity in the Tenebrio molitor model of infection, when compared to wild type strains [68].
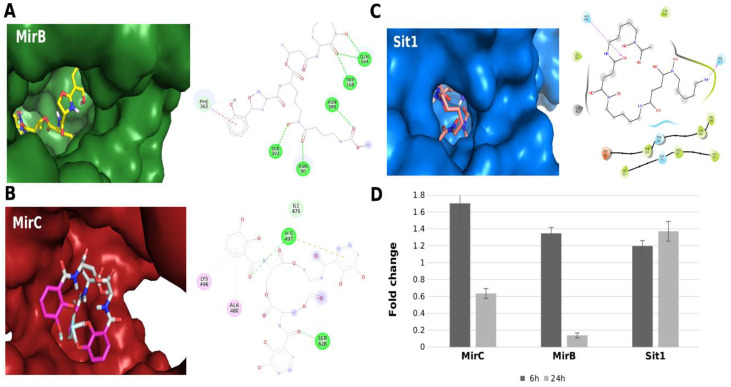
As mentioned above, members of the Paracoccicioides genus can use xenosiderophores [67,68]. Since FOB is a hydroxamate siderophore, a class produced by the genus, it seems interesting to question whether Paracoccidioides spp., such as A. nidulans, would have the ability to transport siderophores from groups other than hydroxamates, produced by bacteria for example. In this sense, with the intention of pointing out aspects of the response of Paracoccidioides spp. to iron deprivation that need to be clarified, we performed molecular dynamics simulation. The three-dimensional structures of the MirB, MirC, and Sit1 proteins of Paracoccidioides spp. were subjected to molecular modeling using the I-TASSER server [69]. The structures of the siderophores enterobactin, ferrioxamine B, and carboxymicobactin were obtained in the literature [70,71,72], and molecular docking was performed between siderophores and proteins using AutoDock Vina [73]. Based on the quality of obtained data (Supplementary Table S1), we present here preliminary results based on molecular dynamics of the P. brasiliensis siderophore receptors suggesting capture of hydroxamates, catecholates, or carboxylates, as shown in Figure 1. The energy interaction data are presented in Supplementary Table S2 and suggest that although all P. brasiliensis siderophores receptors have the apparent ability to interact with any type of siderophore (for additional information on molecular dynamics experiments, see Supplementary Material), MirB would have a higher affinity for carboxymycobactin (a carboxylate, Figure 1A), and MirC would have a higher affinity for enterobactin (a catecholate, Figure 1B), while Sit1 may have a higher affinity for FOB (a hydroxamate, Figure 1C). In accordance with the molecular dynamics data, we carried out analyzes of the transcripts of the siderophore transporters sit1, mirB, and mirC. For this, P. brasilienses yeast cells were incubated in MMcM supplemented with BPS or FOB, and after 6 and 24 h, the cells were collected and extraction of total RNA was performed. Transcriptional analyzes were performed using the standard curve method for relative quantification [74] for calculating the relative expression levels of transcripts of interest. Surprisingly, the transcripts of sit1, mirB, and mirC increased in the first 6 h in the presence of FOB. However after 24 h, it was noticed that the transcript of sit1 remained elevated, corroborating the possible preferential interaction of Sit1 with FOB (Figure 1D). Obviously, these data are preliminary and require further investigation, but have information that points to the capacity of Paracoccidioides spp. of using any type of siderophore, which is exciting because it could yield discoveries about the biology of the pathogen not explored to date.
Figure 1.
Interactions between three-dimensional models and siderophores. (A) Interaction between MirB and carboxymycobactin. The left panel shows the coupling of siderophore in the MirB pocket (green). In the right panel, it is observed that the interaction is maintained by conventional hydrogen bonds (green), carbon–hydrogen bonds (light blue), and pi–pi stacked interaction (pink) between the aromatic rings of carboxymycobactin and PHE362. (B) Interaction between MirC and enterobactin. The left panel shows the coupling of the siderophore in the MirC pocket (red). In the right panel, the interaction is maintained by conventional hydrogen (green) and carbon–hydrogen (light blue) bonds, in addition to the pi–alkyl (pink) interaction between the aromatic enterobactin ring and the amino acids LYS496 and ALA480 and the pi–cation interaction (yellow) between the aromatic ring and the HIS497. (C) Interaction between Sit1 and ferrioxamine B. The left panel shows the coupling of the siderophore in the Sit1 pocket (blue). In the right panel, it is observed that the ligand ferrioxamine B is maintained mainly by hydrophobic affinity (green) to the pocket of Sit1. (D) Levels of transcripts from siderophore transporter genes accessed by RT-qPCR after cultivation of P. brasiliensis in Fe deprivation or in the presence of FOB for 6 h and 24 h. For a list of the primers used in the experiments, see Supplementary Table S3. Additional information on this transcriptional analysis is available in the Supplementary Materials.
6. “The Addition of Chialteras”: Recent Findings and Future Perspectives on the Response of Paracoccidioides spp. to Fe Deprivation
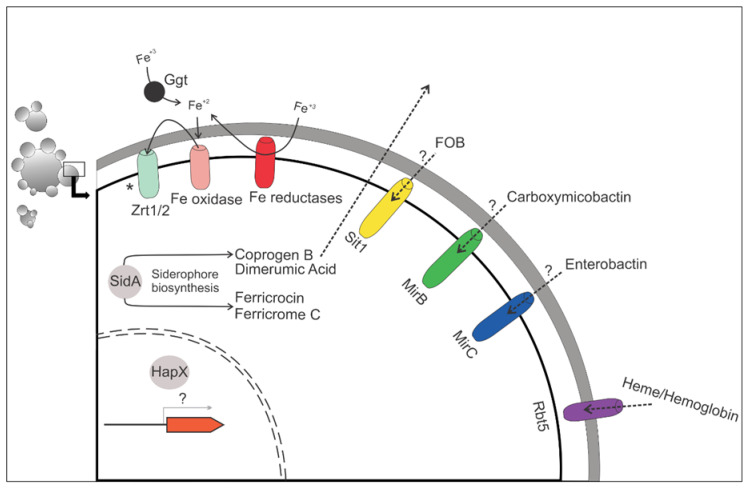
In this review, we compare the response of Paracoccidioides spp. to iron deprivation and the execution of a waltz. In music, notes (like chialteras) can suddenly appear and surprise those who hear. Similarly, in science, new discoveries can bring new concepts and break paradigms. It is justified to continue studying the mechanisms that Paracoccidioides spp. employ when challenged by iron deprivation, as shown in Figure 2. We also cite some events that occur in other fungal species when subjected to iron deprivation, as summarized in Table 2.
Figure 2.
Overview of the mechanisms of iron uptake used in species of the Paracoccidioides complex. During iron deprivation Paracoccidioides spp. employ several mechanisms of iron uptake, such as siderophore transporters (Sit1, MirB, and MirC); binding to the heme group, mediated by Rbt5; or by iron and zinc transporters and iron-reductases. Rbt5 and SidA are described as virulence factors in Paracoccidiodes spp. “*” In P. lutzii, RIA is apparently ineffective, because after the metal reduction step, there is no uptake of this. “?” points to aspects that still require elucidation.
Table 2.
Mechanisms of fungi response to iron deprivation.
| Species | Described Mechanism | Proteins Involved |
|---|---|---|
| Paracoccidioides spp. | Non-classical RIA a,b | Ferric reductases, ferroxidase, GGT, Zrt1/2 |
| Use of host Fe-proteins | Rbt5 (heme/hemoglobin uptake) | |
| Biosynthesis and uptake of siderophores | SidA, Sit1, MirB, MirC | |
| Candida albicans | RIA | Ferric reductases, ferroxidases, ferric permeases |
| Use of host Fe-proteins | Rbt5, Pga7, Csa2 (heme/hemoglobin uptake); Als3 (iron uptake from ferritin) | |
| Uptake of siderophores | Sit1 | |
| Cryptococcus neoformans | RIA | Ferric reductases, ferroxidases, ferric permeases |
| Use of host Fe-proteins | Cig1 (heme/hemoglobin uptake) | |
| Uptake of siderophores | Sit1 | |
| Aspergillus spp. | Biosynthesis and uptake of siderophores | SidA, MirA, MirB, MirC |
a RIA: reductive iron assimilation. b Non-classical RIA: in Paracoccidioides spp. RIA is referred to as non-classical because the internalization of iron is not performed by a ferric permease but by a zinc/iron permeases called Zrt1/2.
Our group has been working on this challenge, and soon new information about proteins of the pathogen involved in the capture of iron from the host and even the participation of miRNAs in this process will be published. In this review, we also present preliminary data that point out that Paracoccidioides spp. is capable of using siderophores of all classes, including carboxymycobactin, a siderophore produced by M. tuberculosis, which is a bacterium that has already been described as causing coinfection with Paracoccidioides spp. [75,76]. This is a very relevant fact to be studied, considering that in a recent work by our group, it was seen that offering the FOB xenosiderophore to P. brasiliensis causes downregulation of SidA, the initial enzyme in the siderophore biosynthesis pathway, which raises questions about how pathogens respond to the presence of xenosiderophores in vivo [68]. In this sense, characterizing the potential xenosiderophores used by the Paracoccidioides complex aggregates information about the mechanisms used by these fungi for the development in conditions of iron deprivation, such as that found during the colonization of the host. In addition, all this data point to the challenge of understanding not only how Paracoccidioides spp. interact with the host but also with other pathogenic microorganisms and even the commensal microbiota. Certainly, all these findings will add more and more compasses to this “waltz” and, from a “little iron waltz”, soon we will be able to appreciate a “complete symphony”.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2309-608X/6/4/221/s1, Figure S1: RMSD in molecular dynamics simulations of the models, Figure S2: 3D and 2D interactions between siderophores receptors models and carboxymycobactin, Figure S3: 3D and 2D interactions between siderophores receptors models and enterobactin, Figure S4: 3D and 2D interactions between siderophores receptors models and ferrioxamine B, Table S1: Quality of three-dimensional models after molecular dynamics simulation, Table S2: Scores of binding energies between proteins and siderophores, Table S3: Sequences of forward and reverse oligonucleotides.
Author Contributions
C.M.d.A.S. provided the reagents. A.F.d.S., M.S.d.P., R.M.L., M.G.S., J.S.d.C., M.P., and C.M.d.A.S. contributed to the literature review and writing and to the manuscript formatting. R.M.L. and M.P. performed the analysis of molecular dynamics and generated the figures. A.F.d.S., J.S.d.C. and M.G.S. performed RT-qPCR analyzes. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
We thank the CAPES and CNPq for providing fellowships to A.F.S., M.S.P., R.M.L., M.G.S., and J.S.C. CMAS and MP are fellows from Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq). This work was supported by grants from Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) and Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Goiás (FAPEG), Instituto Nacional de Ciência e Tecnologia (INCT) de Estratégias de Interação Patógeno-Hospedeiro (grant number 201810267000022/INCT-FAPEG).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design or writing of this manuscript.
References
- 1.Abraham S.N., St. John A.L. Mast cell-orchestrated immunity to pathogens. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010;10:440–452. doi: 10.1038/nri2782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Audia J.P., Webb C.C., Foster J.W. Breaking through the acid barrier: An orchestrated response to proton stress by enteric bacteria. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2001;291:97–106. doi: 10.1078/1438-4221-00106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lemon B., Tjian R. Orchestrated response: A symphony of transcription factors for gene control. Genes Dev. 2000;14:2551–2569. doi: 10.1101/gad.831000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Asehnoune K., Villadangos J., Hotchkiss R.S. Understanding host–pathogen interaction. Intensive Care Med. 2016;42:2084–2086. doi: 10.1007/s00134-016-4544-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Casadevall A., Pirofski L.A. Host-pathogen interactions: Basic concepts of microbial commensalism, colonization, infection, and disease. Infect. Immun. 2000;68:6511–6518. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.12.6511-6518.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Weinberg E.D. Nutritional Immunity. J. Am. Mecical Assoc. 1975;231:39–41. doi: 10.1001/jama.1975.03240130021018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ganz T. Iron and infection. Int. J. Hematol. 2018;107:7–15. doi: 10.1007/s12185-017-2366-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Cassat J.E., Skaar E.P. Iron in Infection and Immunity. Cell Host Microbe. 2013;13:509–519. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2013.04.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Caza M., Kronstad J.W. Shared and distinct mechanisms of iron acquisition by bacterial and fungal pathogens of humans. Front. Celullar Infect. Microbiol. 2013;3:1–23. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2013.00080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Dlouhy A.C., Outten C.E. The Iron Methallome in Eukaryotic Organisms. Met. Ions Life Sci. 2013;12:241–278. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-5561-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Aisen P., Enns C., Wessling-Resnick M. Chemistry and biology of eukaryotic iron metabolism. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2001;33:940–959. doi: 10.1016/S1357-2725(01)00063-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Papanikolaou G., Pantopoulos K. Iron metabolism and toxicity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005;202:199–211. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2004.06.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Tandara L., Salamunic I. Iron metabolism: Current facts and future directions. Biochem. Medica. 2012;22:311–328. doi: 10.11613/BM.2012.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Malavia D., Crawford A., Wilson D. Nutritional Immunity and Fungal Pathogenesis: The Struggle for Micronutrients at the Host–Pathogen Interface. 1st ed. Volume 70. Elsevier Ltd.; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Huynh C., Yuan X., Miguel D.C., Renberg R.L., Protchenko O., Philpott C.C., Hamza I., Andrews N.W. Heme uptake by Leishmania amazonensis is mediated by the transmembrane protein LHR1. PLoS Pathog. 2012;8:36. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Bairwa G., Hee Jung W., Kronstad J.W. Iron acquisition in fungal pathogens of humans. Metallomics. 2017;9:215–227. doi: 10.1039/C6MT00301J. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Haas H. Fungal siderophore metabolism with a focus on Aspergillus fumigatus. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014;31:1266–1276. doi: 10.1039/C4NP00071D. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Shikanai-Yasuda M.A., Telles Filho F.D.Q., Mendes R.P., Colombo A.L., Moretti M.L., Kono A., Tresoldi A.T., Wanke B., Carvalho C.R., Benard G., et al. Consenso em paracoccidioidomicose. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2006;39:297–310. doi: 10.1590/S0037-86822006000300017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Brummer E., Castaneda E., Restrepo A. Paracoccidioidomycosis: An update. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1993;6:89–117. doi: 10.1128/CMR.6.2.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Shikanai-Yasuda M.A., Mendes R.P., Colombo A.L., Queiroz-telles F.D., Satie A., Kono G., Paniago A.M.M., Nathan A., Carlos A., Bagagli E. Brazilian guidelines for the clinical management of paracoccidioidomycosis. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2017 doi: 10.1590/0037-8682-0230-2017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Turissini D.A., Gomez O.M., Teixeira M.M., Mcewen J.G., Matute D.R. Species boundaries in the human pathogen Paracoccidioides. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2017;106:9–25. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2017.05.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Restrepo A., Jiménez B.E. Growth of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis yeast phase in a chemically defined culture medium. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1980;12:279–281. doi: 10.1128/JCM.12.2.279-281.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Cano L.E., Gomez B., Brummer E., Restrepo A., Stevens D.A. Inhibitory effect of deferoxamine or macrophage activation on transformation of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis conidia ingested by macrophages: Reversal by holotransferrin. Infect. Immun. 1994;62:1494–1496. doi: 10.1128/IAI.62.4.1494-1496.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Dias-Melicio L.A., Calvi S.A., Peraçoli M.T.S., Soares Â.M.V.D.C. Inhibitory effect of deferoxamine on Paracoccidioides brasiliensis survival in human monocytes: Reversal by holotransferrin not by apotransferrin. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo. 2005;47:263–266. doi: 10.1590/S0036-46652005000500005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Parente A.F.A., Bailão A.M., Borges C.L., Parente J.A., Magalhães A.D., Ricart C.A.O., Soares C.M.A. Proteomic analysis reveals that iron availability alters the metabolic status of the pathogenic fungus Paracoccidioides brasiliensis. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e22810. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bailão E.F.L.C., Lima P.d.S., Silva-Bailão M.G., Bailão A.M., Fernandes G.d.R., Kosman D.J., Soares C.M.d.A. Paracoccidioides spp. ferrous and ferric iron assimilation pathways. Front. Microbiol. 2015;6:1–12. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bailão E.F.L.C., Parente J.A., Pigosso L.L., de Castro K.P., Fonseca F.L., Silva-Bailão M.G., Báo S.N., Bailão A.M., Rodrigues M.L., Hernandez O., et al. Hemoglobin Uptake by Paracoccidioides spp. Is Receptor-Mediated. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014;8:e2856. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kuznets G., Vigonsky E., Weissman Z., Lalli D., Gildor T., Kauffman S.J., Turano P., Becker J., Lewinson O., Kornitzer D. A Relay Network of Extracellular Heme-Binding Proteins Drives C. albicans Iron Acquisition from Hemoglobin. PLoS Pathog. 2014;10:e1004407. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Baek Y.U., Li M., Davis D.A. Candida albicans ferric reductases are differentially regulated in response to distinct forms of iron limitation by the Rim101 and CBF transcription factors. Eukaryot. Cell. 2008;7:1168–1179. doi: 10.1128/EC.00108-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Liang Y., Gui L., Wei D.S., Zheng W., Xing L.J., Li M.C. Candida albicans ferric reductase FRP1 is regulated by direct interaction with Rim101p transcription factor. FEMS Yeast Res. 2009;9:270–277. doi: 10.1111/j.1567-1364.2008.00468.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kronstad J.W., Hu G., Jung W.H. An encapsulation of iron homeostasis and virulence in Cryptococcus neoformans. Trends Microbiol. 2013;21:457–465. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2013.05.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Lee H., Chang Y.C., Varma A., Kwon-Chung K.J. Regulatory diversity of TUP1 in Cryptococcus neoformans. Eukaryot. Cell. 2009;8:1901–1908. doi: 10.1128/EC.00256-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Weissman Z., Kornitzer D. A family of Candida cell surface haem-binding proteins involved in haemin and haemoglobin-iron utilization. Mol. Microbiol. 2004;53:1209–1220. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04199.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Braun B.R., Head W.S., Wang M.X., Johnson A.D. Identification and characterization of TUP1-regulated genes in Candida albicans. Genetics. 2000;156:31–44. doi: 10.1093/genetics/156.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Schrettl M., Kim H.S., Eisendle M., Kragl C., Nierman W.C., Heinekamp T., Werner E.R., Jacobsen I., Illmer P., Yi H., et al. SreA-mediated iron regulation in Aspergillus fumigatus. Mol. Microbiol. 2008;70:27–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06376.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Hortschansky P., Eisendle M., Al-Abdallah Q., Schmidt A.D., Bergmann S., Thön M., Kniemeyer O., Abt B., Seeber B., Werner E.R., et al. Interaction of HapX with the CCAAT-binding complex—A novel mechanism of gene regulation by iron. EMBO J. 2007;26:3157–3168. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Schrettl M., Beckmann N., Varga J., Heinekamp T., Jacobsen I.D., Jöchl C., Moussa T.A., Wang S., Gsaller F., Blatzer M., et al. HapX-Mediated adaption to iron starvation is crucial for virulence of Aspergillus fumigatus. PLoS Pathog. 2010;6:e1001124. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Huang J., Ma Z., Zhong G., Sheppard D.C., Lu L., Zhang S. The mitochondrial thiamine pyrophosphate transporter TptA promotes adaptation to low iron conditions and virulence in fungal pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus. Virulence. 2019;10:234–247. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2019.1596505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lima P.d.S., Chung D., Bailão A.M., Cramer R.A., Soares C.M.d.A. Characterization of the Paracoccidioides Hypoxia Response Reveals New Insights into Pathogenesis Mechanisms of This Important Human Pathogenic Fungus. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015;9:e0004282. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Almeida R.S., Wilson D., Hube B. Candida albicans iron acquisition within the host. FEMS Yeast Res. 2009;9:1000–1012. doi: 10.1111/j.1567-1364.2009.00570.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Han K., Do E., Jung W.H. A human fungal pathogen Cryptococcus neoformans expresses three distinct iron permease homologs. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012;22:1644–1652. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1209.09019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Zarnowski R., Woods J.P. Glutathione-dependent extracellular ferric reductase activities in dimorphic zoopathogenic fungi. Microbiology. 2005;151:2233–2240. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.27918-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Zarnowski R., Cooper K.G., Brunold L.S., Calaycay J., Woods J.P. Histoplasma capsulatum secreted γ-glutamyltransferase reduces iron by generating an efficient ferric reductant. Mol. Microbiol. 2008;70:352–368. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06410.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Silva M.G., Schrank A., Bailão E.F.L.C., Bailão A.M., Borges C.L., Staats C.C., Parente J.A., Pereira M., Salem-Izacc S.M., Mendes-Giannini M.J.S., et al. The homeostasis of iron, copper, and zinc in Paracoccidioides brasiliensis, Cryptococcus neoformans var. Grubii, and Cryptococcus gattii: A comparative analysis. Front. Microbiol. 2011;2:1–19. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2011.00049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Kosman D.J., Bailão E.F.L.C., Silva-Bailão M.G., Soares C.M.d.A. 59Fe Uptake Assays in Paracoccidioides Species. Bio-Protocol. 2016;6:e1930. doi: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1930. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Bailão E.F.L.C., Parente A.F.A., Parente J.A., Silva-Bailão M.G., de Castro K.P., Kmetzsch L., Staats C.C., Schrank A., Vainstein M.H., Borges C.L., et al. Metal Acquisition and Homeostasis in Fungi. Curr. Fungal Infect. Rep. 2012;6:257–266. doi: 10.1007/s12281-012-0108-8. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Núñez G., Sakamoto K., Soares M.P. Innate Nutritional Immunity. J. Immunol. 2018;201:11–18. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1800325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Almeida R.S., Brunke S., Albrecht A., Thewes S., Laue M., Edwards J.E., Filler S.G., Hube B. The hyphal-associated adhesin and invasin Als3 of Candida albicans mediates iron acquisition from host ferritin. PLoS Pathog. 2008;4:e1000217. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Okamoto-Shibayama K., Kikuchi Y., Kokubu E., Sato Y., Ishihara K. Csa2, a member of the Rbt5 protein family, is involved in the utilization of iron from human hemoglobin during Candida albicans hyphal growth. FEMS Yeast Res. 2014;14:674–677. doi: 10.1111/1567-1364.12160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Pinsky M., Roy U., Moshe S., Weissman Z., Kornitzer D. Human Serum Albumin Facilitates Heme-Iron Utilization by Fungi. MBio. 2020;11:1–14. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00607-20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Nasser L., Weissman Z., Pinsky M., Amartely H., Dvir H., Kornitzer D. Structural basis of haem-iron acquisition by fungal pathogens. Nat. Microbiol. 2016;1:16156. doi: 10.1038/nmicrobiol.2016.156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Ding C., Vidanes G.M., Maguire S.L., Guida A., Synnott J.M., Andes D.R., Butler G. Conserved and divergent roles of Bcr1 and CFEM proteins in Candida parapsilosis and Candida albicans. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e28151. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Srivastava V.K., Suneetha K.J., Kaur R. A systematic analysis reveals an essential role for high-affinity iron uptake system, haemolysin and CFEM domain-containing protein in iron homoeostasis and virulence in Candida glabrata. Biochem. J. 2014;463:103–114. doi: 10.1042/BJ20140598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Weissman Z., Shemer R., Conibear E., Kornitzer D. An endocytic mechanism for haemoglobin-iron acquisition in Candida albicans. Mol. Microbiol. 2008;69:201–217. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06277.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Cadieux B., Lian T., Hu G., Wang J., Biondo C., Teti G., Liu V., Murphy M.E.P., Creagh A.L., Kronstad J.W. The mannoprotein cig1 supports iron acquisition from heme and virulence in the pathogenic fungus Cryptococcus neoformans. J. Infect. Dis. 2013;207:1339–1347. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jit029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Hu G., Caza M., Cadieux B., Chan V., Liu V., Kronstad J. Cryptococcus neoformans requires the ESCRT protein Vps23 for iron acquisition from heme, for capsule formation, and for virulence. Infect. Immun. 2013;81:292–302. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01037-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Guanggan H., Caza M., Cadieux B., Bakkeren E., Do E., Jung W.H., Kronstad J.W. The ESCRT machinery influences haem uptake and capsule elaboration in Cryptococcus neoformans. Mol. Microbiol. 2015;96:973–992. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12985.The. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Saha M., Sarkar S., Sarkar B., Sharma B.K., Bhattacharjee S., Tribedi P. Microbial siderophores and their potential applications: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016;23:3984–3999. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-4294-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Neilands J.B. Siderophores. Arq. Biochem. Biophys. 1993;302:1–3. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1993.1172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Nevitt T. War-Fe-re: Iron at the core of fungal virulence and host immunity. Biometals. 2011;24:547–558. doi: 10.1007/s10534-011-9431-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Miethke M., Marahiel M.A. Siderophore-Based Iron Acquisition and Pathogen Control. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2007;71:413–451. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00012-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Sah S., Singh R. Siderophore: Structural And Functional Characterisation—A Comprehensive Review. Agriculture. 2015;61:97–114. doi: 10.1515/agri-2015-0015. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Wells R.M., Jones C.M., Xi Z., Speer A., Danilchanka O., Doornbos K.S., Sun P., Wu F., Tian C., Niederweis M. Discovery of a Siderophore Export System Essential for Virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. PLoS Pathog. 2013;9:e1003120. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Raymond K.N., Dertz E.A., Kim S.S. Enterobactin: An archetype for microbial iron transport. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2003;100:3584–3588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0630018100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Khan A., Singh P., Srivastava A. Synthesis, nature and utility of universal iron chelator—Siderophore: A review. Microbiol. Res. 2018;212–213:103–111. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2017.10.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Raymond-Bouchard I., Carroll C.S., Nesbitt J.R., Henry K.A., Pinto L.J., Moinzadeh M., Scott J.K., Moore M.M. Structural requirements for the activity of the MirB ferrisiderophore transporter of Aspergillus fumigatus. Eukaryot. Cell. 2012;11:1333–1344. doi: 10.1128/EC.00159-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Silva-Bailão M.G., Bailão E.F.L.C., Lechner B.E., Gauthier G.M., Lindner H., Bailão A.M., Haas H., Soares C.M.d.A. Hydroxamate production as a high affinity iron acquisition mechanism in Paracoccidioides Spp. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e105805. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Silva M.G., de Curcio J.S., Silva-Bailão M.G., Lima R.M., Tomazett M.V., de Souza A.F., Cruz-Leite V.R.M., Sbaraini N., Bailão A.M., Rodrigues F., et al. Molecular characterization of siderophore biosynthesis in Paracoccidioides brasiliensis. IMA Fungus. 2020;11:11. doi: 10.1186/s43008-020-00035-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Yang J., Zhang Y. I-TASSER server: New development for protein structure and function predictions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43:W174–W181. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Moynié L., Milenkovic S., Mislin G.L.A., Gasser V., Malloci G., Baco E., McCaughan R.P., Page M.G.P., Schalk I.J., Ceccarelli M., et al. The complex of ferric-enterobactin with its transporter from Pseudomonas aeruginosa suggests a two-site model. Nat. Commun. 2019;10:3673. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11508-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Podkowa K.J., Briere L.A.K., Heinrichs D.E., Shilton B.H. Crystal and solution structure analysis of FhuD2 from Staphylococcus aureus in multiple Unliganded conformations and bound to ferrioxamine-B. Biochemistry. 2014;53:2017–2031. doi: 10.1021/bi401349d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Agoro R., Mura C. Iron supplementation therapy, a friend and foe of mycobacterial infections? Pharmaceuticals. 2019;12:75. doi: 10.3390/ph12020075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Trott O., Olson A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010;31:455–461. doi: 10.1002/jcc.21334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Bookout A.L., Cummins C.L., Kramer M.F., Pesola J.M., Mangelsdorf D.J. High-Throughput Real-Time Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2006;73:15.8.1–15.8.28. doi: 10.1002/0471142727.mb1508s73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Juan N.R., Daniela S.M., Tania V.L., Sergio E.G., Alejandrina R.F., Rito Z.L. Paracoccidioidomicosis y TBC-MR en portador de VIH/VHC. Rev. Chil. Infectol. 2010;27:551–555. doi: 10.4067/s0716-10182010000700011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Torres-Pereira C., Giovanini A.F., Stramandinoli R.T., Amenabar J.M., Piazzetta C.M. Oral paracoccidioidomycosis and pulmonary tuberculosis co-infection: Relevance of oral biopsy in establishing the diagnosis and therapeutic approach. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2007;13:112–114. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2008.04.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.