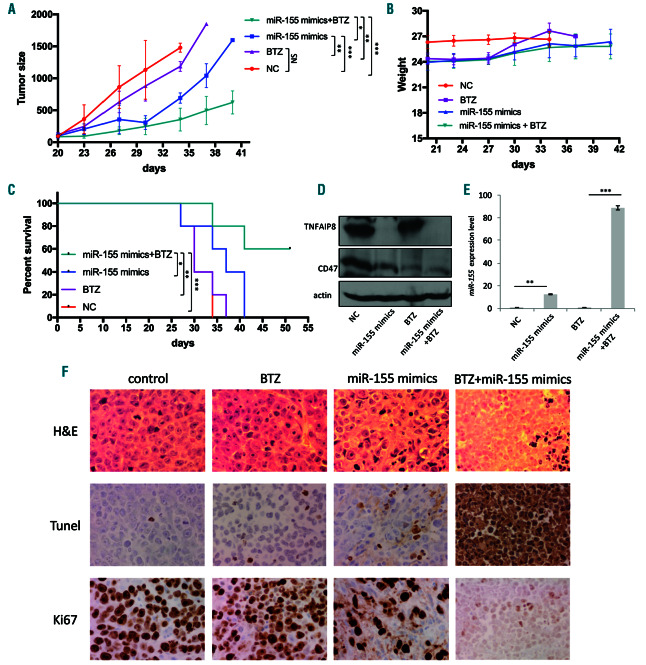
Figure 5.
Synthetic miR-155 retards tumor growth and prolongs survival in human multiple myeloma (MM) mouse xenograft model. Intratumoral injection with either miR-155 mimics or control miRNA (1 mg/kg), with or without intraperitoneal injection of 0.5 mg/kg BTZ (n=5 mice per group) was carried out at an interval of 3 days for 15 days. (A) Overexpression of miR-155 enhanced BTZ-induced retardation of tumor growth in vivo. (B) Body weight was measured from first day of drug injection (day 20) every 3 days till day 42 and presented as mean ± standard error mean (SEM). (C) Survival was evaluated using Kaplan-Meier curves and log-rank analysis from the first day of tumor cells injection until death or occurrence of an event. (D) Mice tumors from in vivo experiment were analyzed by immunoblotting for CD47 and TNFAIP8 protein expression. (E) The total RNA including miRNA was isolated from the mice of four groups and the level of miR-155 was measured by qualitative-polymerase chain reaction (q-PCR) to evaluate the delivery efficiency of miRNA mimics into tumor cells after intratumoral injection of miR-155 mimics using the novel formulation of neutral lipid emulsion (NLE; MaxSuppressor in vivo RNA Lancer II, BIOO Scientific). Fold change was expressed as log2-fold induction over control group (mean ±SEM). (F) Representative microscopic images of immunohistochemical analysis of tumor sections from four treated groups with hematoxylin & eosin, the proliferation index (Ki-67) and the apoptotic index, TUNEL staining. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, and significant difference based on the 95% of confidence intervals.