Abstract
The treatment of severe trauma, especially multiple injuries, requires multidisciplinary collaboration. The current study aims to highlight the challenges of consultation mode for severe trauma in general hospitals and emphasizes the need to create a new temporary-sustainable team. It suggests developing an information consultation mode and enforcing the fine management to improve the quality and safety of the medical treatment. The management mode of a temporary-sustainable team will reduce the cost and improve the treatment efficiency. Overall, a temporary-sustainable team has significant advantages over a traditional multidisciplinary team for severe trauma treatment.
Keywords: Trauma, Temporary-sustainable team, Multidisciplinary team
Introduction
The diagnosis and treatment of trauma, especially multiple injuries, require the comprehensive ability of a medical team. The treatment of severe trauma often involves the cooperation of multidisciplinary medical teams, including neurosurgeons, thoracic surgeons, abdominal surgeons, orthopedic surgeons, and maxillofacial surgeons. Due to the complexity of this disease, the refinement of diagnosis and treatment, the diversification of medical methods, the diagnosis and treatment of severe trauma are facing great challenges.1 The multidisciplinary team (MDT) model has attracted extensive attention because of its advantages of multidisciplinary collaboration and personalized treatment.2
The MDT model refers to developing a standardized, individualized, continuous and the most reasonable treatment plan for a particular disease, which is through the regular, timely, and address meetings and relying on a multidisciplinary expert team and multidisciplinary collaborative discussions.3 The United States first proposed the concept of MDT, and subsequently the United Kingdom, Australia, Japan, and other countries also realized its importance, which was promoted, and adopted as a standard medical treatment plan in medical institutions.4 In China, multidisciplinary diagnosis and treatment began in 1990, and many high-level general hospitals successively explored the MDT model for multiple clinical diseases, and established a team of multidisciplinary experts.5 Implementation of the MDT model in the clinic has proved that it can promote the rational allocation of medical resources, improve the accuracy and rationality of disease diagnosis and treatment, and effectively solve the social problems of complex medical treatment.6
The new model: a temporary-sustainable team
A temporary-sustainable team
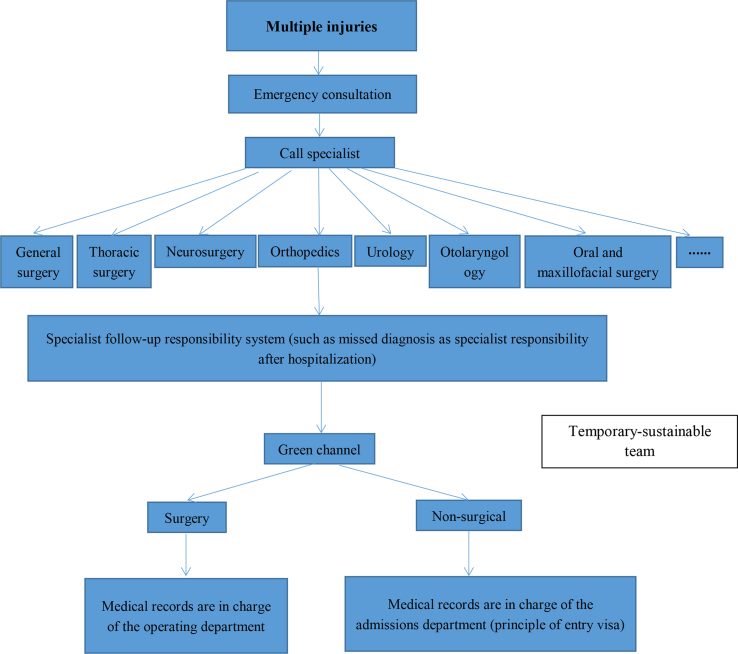
We propose a new model: a temporary-sustainable team. Compared with the traditional MDT, which only focuses on the emergency treatment and lacks of follow-up of inpatient treatment, the temporary-sustainable team significantly pays attention to the continuity of treatment. Once a temporary-sustainable team is formed, the therapeutic process will be implemented and monitored until the treatment is completed. The diagnosis and treatment process of severe trauma is shown in Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.
The flowchart of a temporary-sustainable team. It is divided into four stages: diagnosis and treatment process, preparation of consultation, consultation, and follow-up of consultation.
To ensure the smooth implementation of a temporary-sustainable team model, the institute established a temporary team with the dean in charge as the team leader and the relevant section directors as team members. Their responsibilities were to comprehensively guide, coordinate and promote the construction work of a temporary-sustainable team. Meanwhile, based on the complexity of injuries and the needs of patients, the hospital gradually established a multidisciplinary team of professionals. According to the configuration of an emergency department, the team combined neurosurgery with other related departments to optimize the allocation of resources, integrate their specialties, and establish standardized diagnostic procedures. Each professional team was constituted by several members in the expert database. The members in the expert database are clinicians with qualifications of chief physician and deputy chief physician, who have rich clinical diagnosis and treatment experiences, and are fully trusted by patients. There are one or two chief experts in each professional team to lead and conduct consultations, and one secretary to collect the data of multidisciplinary diagnosis and treatment, and assist the consultations. After completed the prerequisites, a temporary-sustainable team is formed, and the team members will be in charge of a patient during the in-hospital until he/she is cured and discharged. The above measures referred to as the “specialist physician tracking system”, effectively prevents many temporary adverse changes to patients caused by doctors, which affects the condition, diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnosis and treatment process of a temporary-sustainable team
Proposal for consultation
To ensure the quality of treatment of MDT, an application for the consultation of emergency patient was implemented by the hospital. According to the multidisciplinary consultation indication, the emergency physician submits an application to the multidisciplinary team of professionals and the medical office records it. The consultation application includes: the brief introduction of the condition, history of previous treatment, diagnosis and treatment, proposed emergency consultation subject, time and place of the consultation, etc. The goal of the consultation is to provide an optimum diagnosis and treatment of the patient by an expert in a designated place and indicated time.
Preparation of consultation
The result of multidisciplinary consultation will be informed to the patients and their family members. The attending physician will be responsible for signing the informed consent. The patient needs to accept related auxiliary examinations according to the consultation and his/her health condition. After various diagnosis and treatment information were recorded, the doctor in charge will organize and analyze the examination results.
Consultation
The consultation is supervised by the leader of the first consultation expert team. The doctor in charge reports the patient's information of medical history, diagnosis, test results and treatment. Next, the director of the treatment team or department makes supplements and raises various problems which need to be solved. The experts in the consultation stated their opinions for discussion with other members. The leader in consultation expert team summarizes the opinions, and the secretary makes a record of the meeting and the opinions.
Follow-up of consultation
The doctor in charge (main consultation) will record the detailed consultation opinions in the medical record, which will be reviewed and signed by the team leader of the consultation expert. The doctor in charge, the head of the treatment team, or the head of the department is responsible for informing the patient or his/her family for a conclusion of the consultation. The inpatient treatment team performed consultations or changed treatment plans. Patients should have a priority right to transferring to other departments if needed.
Management of a temporary-sustainable team
To ensure the precise work flow, the staff of multidisciplinary diagnosis and treatment team must cooperate and supervise each other. The information of patient's diagnosis and treatment are tracked and summarized each month by the multidisciplinary team of professionals to inspect the implementation of treatment, which are regularly confirmed by the chief expert in the team every quarter. The medical service department will supervise the whole process of consultation, actively promote the cooperation of multidisciplinary team and solve problems in the work.
The efficacy of a temporary-sustainable team
Standardize the diagnosis and treatment and maximize the use of resources
Based on the evidence-based medicine theory and the actual situation of each department, the consultation team develops a set of diagnosis and treatment procedures and measures for complex diseases, which are more standardized, professional, and accurate. The improvements in bed utilization and turnover rate played a positive role. The temporary-sustainable team model effectively integrates the medical resources of the entire hospital, eliminates the differences in diagnosis and treatment between departments and teams, and avoids under-treatment or over-diagnosis caused by isolated treatment.6,7
Enhance the strength of subject with interaction and collaboration
In a temporary-sustainable team model, all subjects of the hospital jointly discuss difficult cases and overcome academic difficulties. They find and solve the unreasonable problems in time, and thus to form a good interaction platform of hospital. After multidisciplinary discussions, the relevant departments cooperate with each other. Patients who need to be hospitalized or transferred to other departments will have a priority for an arrangement. Outpatients will also complete the auxiliary examination through the green channel. The implementation of the new model has improved the professional techniques and diagnostic capabilities of medical staff, and broadened the thinking of scientific diagnosis and treatment. Furthermore, it facilitated the integration of various disciplines, and promoted the improvement of the medical care of hospitals.6,8
Thoughts on a temporary-sustainable team model
Create a continuous learning temporary-sustainable team and promote the improvement of diagnosis and treatment
The complete macro medical management model is useful, which runs through the entire process of the diagnosis and treatment in a temporary-sustainable team. By optimizing the process of diagnosis and treatment, rationally integrating medical resources, and promoting disciplinary cooperation and communication, we can achieve a well-balanced situation for patients, doctors and hospitals.9 To effectively promote the development of the temporary-sustainable team model, it is necessary to pay more attention to the development of various subjects, grasp the latest development in related fields, and create a temporary-sustainable learning team. Academic activities, such as lectures and seminars, and some trainings on the key point should be organized regularly, which include standardized processes, specialized basic knowledge, academic achievements, surgical procedures, nutrition support, guidance of medication, management of follow-up, health education, and so on. It will promote interdisciplinary cooperation and penetration, and improve the professional knowledge and skills of medical staff.9
Improve the follow-up work and manage the full process
To ensure the orderly progress of the work, after implementing the decision of a temporary-sustainable team, patients need to be managed and followed up for a long time to evaluate the implementation of the plan and the outcome. However, in practice, the related feedback needs to be further improved.8 Taking neurotrauma as an example, besides paying attention to the complications, recurrence rate, survival rate, complications, and providing treatment in the early stage of relapse in the follow-up, the psychological tolerance of patients should be improved. It should establish an effective consultation system of follow-up, and arrange a full-time staff to monitor the efficacy of treatment in hospital. This will help to achieve the goals of the management for patients, and promote the standardized and precise medical treatment, which ensure the safety and develop the quality of medical management.6,9
In conclusion, a temporary-sustainable team can provide a higher-quality medical assistance and improve the efficiency and effectiveness of treatment for patients with multiple injuries.
Funding
Nil.
Ethical Statement
Not applicable.
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Footnotes
Peer review under responsibility of Chinese Medical Association.
References
- 1.Powell H.A., Baldwin D.R. Multidisciplinary team management in thoracic oncology: more than just a concept? Eur Respir J. 2014;43:1776–1786. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00150813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Saghir N.S.E., Nancy L.K., Carlson R.W. Tumor boards: optimizing the structure and improving efficiency of multidisciplinary management of patients with cancer worldwide. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2014:461–466. doi: 10.14694/EdBook_AM.2014.34.e461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Yang B., Tan J.J., Wang P. Application and practice of project management mode in multi-disciplinary collaborative diagnosis and treatment of hospitals. J Milit Surg Southwest Chin. 2017;19(6):588–589. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7193.2017.06.032. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ryan J., Faragher I. Not all patients need to be discussed in a colorectal cancer MDT meeting. Colorectal Dis. 2014;16:520–526. doi: 10.1111/codi.12581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zhang H.H., Han L., Liu Q. Discussion on the multidisciplinary collaborative diagnosis and treatment model in deepening hospital discipline construction. Chin Hosp Manage. 2018;38:29–30. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ji J., Chen H., Gao B.L. Implementation and management of multidisciplinary collaborative diagnosis and treatment in tuberculosis department. Mod Hosp. 2017;17:1729–1731. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Xu Y., Fang Q., Li Y.F. The practice and efficacy of tumor multidisciplinary treatment modalities in general hospital. Chin Hosp. 2014;18:58–59. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chu D.Q., Zhao J.F., Wang H. Discussion on the multidisciplinary diagnosis and treatment model of oncology hospitals and general hospitals. Shanxi Med J. 2016;45:2564–2565. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9926.2016.21.041. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Xu H.L., Wei S.Z. Practice of multidisciplinary treatment in Hubei cancer hospital. Cancer Res Prev Treat. 2018;45:437–440. [Google Scholar]