Abstract
The Klebsiella pneumoniae complex comprises several closely related entities, which are ubiquitous in the natural environment, including in plants, animals, and humans. K. pneumoniae is the major species within this complex. K. pneumoniae strains are opportunistic pathogens and a common cause of healthcare-associated infections. K. pneumoniae can colonize the human gastrointestinal tract, which may become a reservoir for infection. The aim of this study was to investigate the fecal K. pneumoniae carriage in six healthy individuals during a 1 year period. Stool samples were obtained once a week. Using direct and pre-enriched cultures streaked on ampicillin-supplemented agar plates, up to eight individual colonies per positive sample were selected for further characterization. Whole genome sequencing (WGS) was performed for strain characterization. Sequence type (ST), core genome complex type (CT), K and O serotypes, virulence traits, antibiotic resistance profiles, and plasmids were extracted from WGS data. In total, 80 K. pneumoniae isolates were obtained from 48 positive cultures of 278 stool samples from five of the six test subjects. The samples of the five colonized volunteers yielded at most two, three, four (two persons), and five different strains, respectively. These 80 K. pneumoniae isolates belonged to 60 STs, including nine new STs; they were of 70 CTs, yielded 48 K serotypes, 11 O serotypes, and 39 wzc and 51 wzi alleles. Four of the five subjects harbored serotypes K20 and K47, as well as STs ST37, ST101, ST1265, and ST20, which had previously been linked to high-risk K. pneumoniae clones. In total, 25 genes conferring antibiotic resistance and 42 virulence genes were detected among all 80 isolates. Plasmids of 15 different types were found among 65 of the isolates. Fecal carriage of individual strains was of short duration: 70 strains were found on a single sampling day only, and 5 strains were isolated in samples collected over two consecutive weeks. Two of the five colonized individuals—working colleagues having meals together—shared identical K. pneumoniae types four times during the study period. Our findings point toward the potential role of food as a reservoir for K. pneumoniae in humans.
Keywords: Klebsiella pneumoniae, long-term study, colonization, whole genome sequencing, virulence, antimicrobial resistance
Introduction
Klebsiella pneumoniae was first described in 1882 as a bacterium isolated from the lungs of patients who had died from pneumonia (Friedlaender, 1882). The K. pneumoniae complex consists of closely related species designated as K. pneumoniae phylogroups Kp1-Kp7, comprising K. pneumoniae subsp. ozaenae, K. pneumoniae subsp. pneumoniae, K. pneumoniae subsp. rhinoscleromatis, K. quasipneumoniae subsp. quasipneumoniae, K. quasipneumoniae subsp. similipneumoniae, K. variicola subsp. variicola, K. variicola subsp. tropica, K. africana, and K. quasivariicola (Rodrigues et al., 2018, 2019). K. pneumoniae complex can be found ubiquitously in nature, including in plants, animals, and humans (Lai et al., 2019). Most K. pneumoniae infections in Europe and North America are healthcare-associated and caused by classical K. pneumoniae strains (cKp) (Russo et al., 2018). With the emergence of carbapenem-resistant strains, infections due to cKp have become a major public health threat (World Health Organization [WHO], 2017; Wyres and Holt, 2018) causing life-threatening nosocomial infections like urinary tract infections, bloodstream infections, and pneumonia in immunocompromised and critically ill patients (Podschun and Ullmann, 1998). K. pneumoniae is a listed ESKAPE pathogen, an acronym defined by the Infectious Diseases Society of America for antibiotic-resistant Enterococcus faecium, Staphylococcus aureus, K. pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Enterobacter spp. (Rice, 2008). In 1986, hypervirulent K. pneumonia (hvKp) strains emerged in Asian countries associated with community-acquired infections like pyogenic liver abscess, meningitis, endophthalmitis, soft tissue abscesses, urinary tract infections, and pneumonia (Martin and Bachman, 2018; Russo and Marr, 2019). In contrast to cKp strains, hvKp strains cause infections mainly in young and healthy individuals (Struve et al., 2015; Paczosa and Mecsas, 2016). In contrast to cKp, which is the dominating cause of infections in Western countries, hvKp are endemic mainly in countries of the Asia-Pacific region. A differentiation between cKp and hvKp is challenging due to overlapping characteristics in both pathotypes (Russo and Marr, 2019). Several virulence factors present on large virulence plasmids (pK2044 and pLVPK) have been identified, allowing the most accurate discrimination of cKp to hvKp (Lee et al., 2017; Russo et al., 2018; Russo and Marr, 2019). Key virulence factors necessary for infection are the polysaccharide capsule (K antigen) and lipopolysaccharide (O antigen), which contribute to serum resistance and resistance to phagocytosis (Cortés et al., 2002). HvKp clones circulating in the community are associated with particular capsule types, mainly K1, K2, K20, and K57 (Lee et al., 2016) and certain sequence types (STs) like ST23, ST65, ST86, ST375, and ST380 (Bialek-Davenet et al., 2014; Lin et al., 2014; Lee et al., 2017). The convergence of carbapenem-resistance and virulence resulted in the emergence of carbapenem-resistant hvKP strains in China, which is expected to become a serious future public health issue (Zhao et al., 2020).
K. pneumoniae can colonize the nasopharynx and the gastrointestinal tract. The gastrointestinal colonization of healthy individuals with undefined pathotypes ranged from 5 to 35% in Western countries (Martin et al., 2016; Gorrie et al., 2017) and from 19 to 88% in Asian countries (Chung et al., 2012). Nasopharyngeal colonization of healthy humans ranged from 1 to 5% in Western countries and from 1.4 to >20% in Asian countries and Brazil (Lima et al., 2010; Farida et al., 2013; Dao et al., 2014). Contamination of food with K. pneumoniae and a general poor sanitation status have been associated with increased colonization of healthy humans (Farida et al., 2013; Huynh et al., 2020). In a study from Malaysia, 32% of street food samples tested positive for K. pneumoniae (Haryani et al., 2007). Colonization has been identified as a potential reservoir for infection with Kp strains (Gorrie et al., 2017) and the infection risk with K. pneumoniae is considered to be four times higher for colonized patients compared to non-carriers (Selden et al., 1971; Martin et al., 2016). During warm months, K. pneumoniae bloodstream infection rates are 1.5 times higher, reflecting an increased fecal carriage rate in humans in summer (Anderson et al., 2008). Therefore, screening of healthy individuals is a recommended action to obtain an overview on strain diversity and to detect emerging resistant and virulent strains (Russo and Marr, 2019).
To our best knowledge, there is no longitudinal Kp colonization study of healthy individuals. Most studies are focused on short/long-term colonization of hospitalized patients. Therefore, the aim of this study was to investigate the colonization pattern of K. pneumoniae in healthy humans during a 1 year period.
Materials and Methods
Sample Collection and Microbiological Culturing of K. pneumoniae
From calendar week (CW) 15/2018 to CW14/2019, fecal samples from six healthy individuals were screened for the presence of K. pneumoniae. Fecal samples of about 2 g were collected in sterile plastic containers once a week and processed in the laboratory within 24 h. Volunteers lived in six different households in Vienna (subject 1) and Graz (subjects 2–6). Subjects 2 and 4 often spent lunch breaks together, having their meals in various restaurants. Subject 1 was 60–65 years old, subjects 2 and 4 were aged 25–30, subject 3 was aged 40–45, and subjects 5 and 6 were aged 50–55 years. Subject 4 followed a gluten-free diet. Subject 6 was vegetarian but ate fish.
To detect K. pneumoniae, all feces samples were plated on Simmons Citrate Agar with 1% Innositol (SCAI) (BIO-RAD, Hercules, United States) and incubated for 48 h at 44°C. In addition, broth enrichment was performed (1 g feces in 9 ml LB medium with 10 μg/l ampicillin overnight at 37°C), followed by cultivation on an SCAI medium for 48 h at 44°C. Up to eight single colonies resembling K. pneumoniae morphologically were selected from each agar plate and subcultured for further processing. Species confirmation was carried out using matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF-MS) Biotyper (Bruker, Billerica, MA, United States) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Antimicrobial Resistance Testing
A selection of K. pneumoniae strains were forwarded to ESBL confirmatory testing using cefotaxime 30 μg (CTX) and cefotaxime 30 μg with clavulanic acid 10 μg (CTX-CV) disks as well as ceftazidime 30 μg (CAZ) and ceftazidime 30 μg with clavulanic acid 10 μg (CAZ-CV) disks (Mast Group, Bootle Merseyside, United Kingdom). The inhibition zone diameters were measured and assessed according to EUCAST guidelines (EUCAST, 2017).
A second plate was used for agar diffusion test with ceftazidime 10 μg (CAZ), cefotaxime 5 μg (CTX), ceftriaxone 30 μg (CRO), and amoxicilline-clavulanic acid 20/10 μg (AMC), and the inhibition zone diameters were assessed according to EUCAST criteria (EUCAST, 2020).
DNA Extraction and Whole Genome Sequencing
DNA was isolated from bacterial cultures using the MagAttract HMW DNA Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s protocol for gram-negative bacteria. The amount of input DNA was quantified on a Lunatic instrument (Unchained Labs, Pleasanton, CA, United States). Ready to sequence libraries were prepared using Nextera XT DNA library preparation kit (Illumina, San Diego, CA, United States); paired-end sequencing with a read length of 2 × 300 bp using Reagent Kit v3 chemistry (Illumina) was performed on a Miseq instrument (Illumina).
Sequence Data Analysis
All study isolates were sequenced to obtain a coverage of at least 80-fold. Obtained raw reads were quality controlled using FastQC v0.11.9 and de novo assembled using SPAdes (version 3.9.0) (Bankevich et al., 2012) to produce draft genomes. Contigs were filtered for a minimum coverage of 5 × and a minimum length of 200 bp using SeqSphere + software v6.0.0) (Ridom, Münster, Germany). The classical multilocus sequence type (MLST) (Diancourt et al., 2005) and the public K. pneumoniae sensu lato core genome MLST (cgMLST1) were determined using SeqSphere+. For MLST, new combinations of alleles or new allele types composing new sequence types (STs) were submitted to the curators of the MLST database2. For phylogenetic analysis, minimum spanning trees (MSTs) were calculated based on the sensu lato cgMLST scheme; related isolates were identified with a complex type (CT) distance of 15 alleles (see footnote 1).
The diversity of capsule synthesis loci (K loci), lipopolysaccharide O antigen (O loci), and allele diversity of K locus genes wzc and wzi were determined using Kaptive Web3 (Wick et al., 2018).
Plasmids and genes conferring antibiotic resistance were detected using PlasmidFinder 1.3 (Carattoli et al., 2014) available from the Center for Genomic Epidemiology4 and the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database (CARD) (Jia et al., 2017). Virulence genes were detected using the virulence allele library from the Institut Pasteur BIGSdb database for K. pneumoniae5 (Bialek-Davenet et al., 2014).
Nucleotide Sequence Accession Numbers
This Whole Genome Shotgun project has been deposited at the DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank under the accession PRJNA663884. The version described in this paper is the first version. The raw sequence reads have been deposited in the Sequence Read Archive (SRA) under accession no. SRR12653693–SRR12653772.
Results
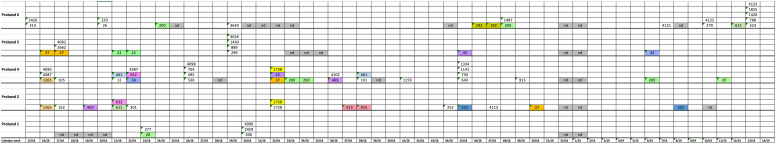
During the study period from CW15 in 2018 to CW14 in 2019, a total of 278 stool samples (43–49 samples/patient) were analyzed from the six study participants (Figure 1). Forty-eight of these 278 stool samples yielded K. pneumoniae: subject 1 in two of 46 weekly samples (in total: 5 clones); subject 2 in 13 of 49 samples (in total: 13 clones); subject 3 in 0 of 45 samples (in total: 0 clones); subject 4 in 15 of 48 samples (in total: 26 clones); subject 5 in 7 of 47 samples (in total: 10 clones); and subject 6 in 11 of 43 stool samples (in total: 17 clones) (Figure 1 and Table 1). Altogether, 80 K. pneumoniae isolates were retrieved from the 278 stool samples. Subject 3 was negative for K. pneumoniae colonization during the whole study period. The remaining five test persons were colonized with K. pneumoniae strains in samples accounting for a total of 2–15 weeks periods [mean: 8; median: 9] during the 1 year study period. No correlation between the number of K. pneumoniae positive stool samples and seasons could be observed (Figure 1).
FIGURE 1.
Schematic representation of K. pneumoniae isolation from stool samples of five test persons during the 1 year study period. Numbers show a successful isolation and represent the sequence type. Colors show isolates with the same sequence types. nd, no samples analyzed.
TABLE 1.
Typing results for isolates obtained from subjects 1–6 (no isolates were obtained from subject 3).
| Proband | Sample ID | CW | ST | CT | wzc | wzi | K Serotype | O Serotype |
| 1 | 510056-18 | 23/18 | 20 | 2,732 | 939 | 173 | KL102 | O2v2 |
| 510059-18 | 277 | 2,733 | 914 | 97 | KL46 | O3b | ||
| 510076-18 | 30/18 | 4,099 | 2,743 | 940 | 114 | KL111 | O3b | |
| 510077-18 | 306 | 2,744 | 12 | 11 | KL11 | O3/O3a | ||
| 510078-18 | 2,459 | 2,747 | 930 | 193 | KL125 | O3b | ||
| 2 | 510005-18 | 16/18 | 1,265 | 2,688 | nd | nd | KL33 | O3b |
| 510017-18 | 17/18 | 152 | 2,695 | 22 | 87 | KL163 | O1v1 | |
| 510029-18 | 19/18 | 469 | 2,721 | nd | 75 | KL105 | O3b | |
| 510034-18 | 21/18 | 632 | 2,724 | nd | 202 | KL141 | O4 | |
| 510035-18 | 611 | 2,725 | 930 | 193 | KL125 | O3b | ||
| 510046-18 | 22/18 | 301 | 2,729 | 42 | 42 | KL42 | O4 | |
| 510084-18 | 32/18 | 1,728 | 2,749 | 941 | 180 | KL116 | O2v1 | |
| 510087-18 | 1,758 | 2,750 | 28 | 187 | KL27 | O4 | ||
| 510119-18 | 37/18 | 915 | 2,759 | nd | 150 | KL107 | OL101 | |
| 510126-18 | 38/18 | 915 | 2,759 | nd | 150 | KL107 | OL101 | |
| 510320-18 | 44/18 | 252 | 2,874 | 76 | 81 | KL81 | O1v2 | |
| 510340-18 | 45/18 | 322 | 2,876 | 18 | 50 | KL17 | O4 | |
| 510370-18 | 47/18 | 4,113 | 2,879 | 903 | 2 | KL30 | O3b | |
| 510871-19 | 50/18 | 37 | 3,275 | 24 | 83 | KL23 | O2v2 | |
| 510902-19 | 8/19 | 322 | 2,876 | 18 | 50 | KL17 | O4 | |
| 4 | 510929-19 | 11/18 | 20 | 3,312 | 29 | 84 | KL28 | O1v2 |
| 510009-18 | 16/18 | 4,087 | 2,690 | 58 | 130 | KL58 | O3b | |
| 510010-18 | 1,265 | 2,688 | nd | nd | KL33 | O3b | ||
| 510011-18 | 4,090 | 2,691 | 923 | 173 | KL112 | O2v2 | ||
| 510021-18 | 17/18 | 105 | 2,696 | 939 | 383 | KL102 | O2v2 | |
| 510038-18 | 21/18 | 12 | 2,726 | 923 | 173 | KL112 | O2v2 | |
| 510041-18 | 461 | 2,727 | nd | 123 | KL136 | O2v1 | ||
| 510049-18 | 22/18 | 632 | 2,724 | nd | 202 | KL141 | O4 | |
| 510050-18 | 34 | 2,731 | 23 | 27 | KL37 | O1v1 | ||
| 510064-18 | 26/18 | 4,098 | 2,735 | 47 | 47 | KL47 | O1v1 | |
| 510065-18 | 704 | 2,739 | 32 | 31 | Kl31 | O1v1 | ||
| 510066-18 | 492 | 2,737 | 15 | 23 | KL14 | O3b | ||
| 510067-18 | 530 | 2,736 | 54 | 115 | KL54 | O1v2 | ||
| 510088-18 | 32/18 | 1,758 | 2,750 | 28 | 187 | KL27 | O4 | |
| 510089-18 | 37 | 2,751 | 930 | 85 | KL125 | O3/O3a | ||
| 510090-18 | 45 | 2,753 | 62 | 149 | KL62 | O2v1 | ||
| 510092-18 | 33/18 | 200 | 2,754 | 28 | 150 | KL27 | O3b | |
| 510096-18 | 34/18 | 200 | 2,754 | 28 | 150 | KL27 | O3b | |
| 510112-18 | 36/18 | 469 | 2,721 | nd | 75 | KL105 | O3b | |
| 510113-18 | 4,102 | 2,758 | 29 | 84 | KL28 | O1v2 | ||
| 510127-18 | 38/18 | 461 | 4,860 | 26 | 133 | KL25 | O1v1 | |
| 510128-18 | 101 | 2,765 | 921 | 29 | KL106 | O1v2 | ||
| 510306-18 | 41/18 | 1,159 | 2,870 | 29 | 84 | KL28 | O2v1 | |
| 510324-18 | 45/18 | 643 | 2,891 | 39 | 160 | KL39 | O1v1 | |
| 510325-18 | 1,141 | 2,893 | 940 | 114 | KL111 | O3b | ||
| 510326-18 | 1,334 | 2,892 | nd | nd | OCL6 | O3/O3a | ||
| 510334-18 | 730 | 2,895 | nd | 356 | KL117 | O1/O2v2 | ||
| 510851-19 | 49/18 | 913 | 3,060 | 940 | 16 | KL111 | O3b | |
| 510880-19 | 6/19 | 200 | 3,277 | 23 | 385 | KL22 | O3b | |
| 5 | 510013-18 | 16/18 | 37 | 2,692 | nd | 123 | KL136 | O2v2 |
| 510025-18 | 17/18 | 2,662 | 2,720 | nd | 163 | KL161 | O4 | |
| 510026-18 | 4,092 | 2,809 | nd | 356 | KL117 | O2v2 | ||
| 510027-18 | 37 | 2,692 | nd | 123 | KL136 | O2v2 | ||
| 510042-18 | 21/18 | 22 | 2,728 | 9 | 9 | KL9 | O2v2 | |
| 510052-18 | 22/18 | 22 | 2,728 | 9 | 9 | KL9 | O2v2 | |
| 510068-18 | 29/18 | 889 | 2,738 | 903 | 73 | KL104 | O1v1 | |
| 510069-18 | 299 | 2,740 | 7 | 7 | KL7 | O2v1 | ||
| 510070-18 | 1,430 | 2,741 | 41 | 39 | KL107 | OL102 | ||
| 510071-18 | 3,626 | 2,768 | 8 | 114 | KL8 | O3b | ||
| 510336-18 | 45/18 | 45 | 2,894 | 25 | 101 | KL24 | O2v1 | |
| 510884-19 | 6/18 | 34 | 3,278 | 940 | 114 | KL111 | O3b | |
| 6 | 510001-18 | 15/18 | 314 | 2,687 | 24 | 82 | KL23 | O2v2 |
| 510003-18 | 2,426 | 2,686 | nd | 356 | KL117 | O2v2 | ||
| 510030-18 | 20/18 | 253 | 2,722 | 919 | 50 | KL15 | O4 | |
| 510031-18 | 26 | 2723 | 44 | 267 | KL142 | O1v1 | ||
| 510060-18 | 24/18 | 200 | 2,734 | 14 | 39 | KL13 | O3b | |
| 510072-18 | 29/18 | 3,640 | 2,742 | 64 | 333 | KL64 | O1v1 | |
| 510366-18 | 46/18 | 192 | 2,877 | 940 | 113 | KL111 | O3b | |
| 510378-18 | 47/18 | 192 | 2,877 | 940 | 113 | KL111 | O3b | |
| 510386-18 | 48/18 | 1,487 | 2,883 | nd | 197 | KL141 | O4 | |
| 510836-18 | 200 | 3,239 | 932 | 354 | KL114 | O3b | ||
| 510894-19 | 7/19 | 4121 | 3450 | 921 | 29 | KL106 | O2v2 | |
| 510919-19 | 10/19 | 279 | 3280 | 937 | 415 | KL151 | O5 | |
| 510920-19 | 4,122 | 3,281 | 32 | 31 | KL31 | O1v1 | ||
| 510931-19 | 12/19 | 611 | 3,313 | 45 | 9 | KL45 | O2v2 | |
| 510939-19 | 13/19 | 1,426 | 3,315 | 21 | 177 | KL20 | O3/O3a | |
| 510940-19 | 788 | 3,316 | 914 | 26 | KL46 | O3b | ||
| 510941-19 | 1,825 | 3,314 | nd | 361 | KL126 | OL101 | ||
| 510945-19 | 4,123 | 3,318 | 58 | 22 | KL58 | O3b | ||
| 510946-19 | 323 | 3,319 | 61 | 155 | KL62 | O5 |
CW, calendar week of isolation; ST, sequence type; CT, complex type.
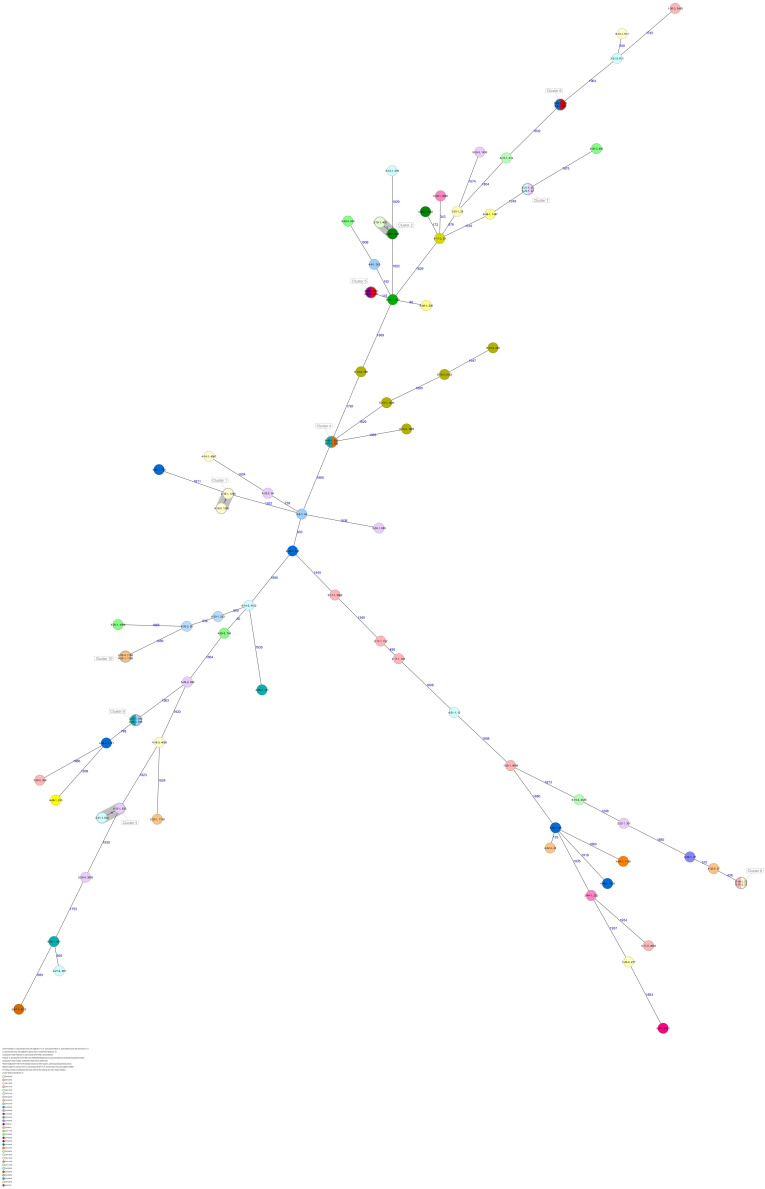
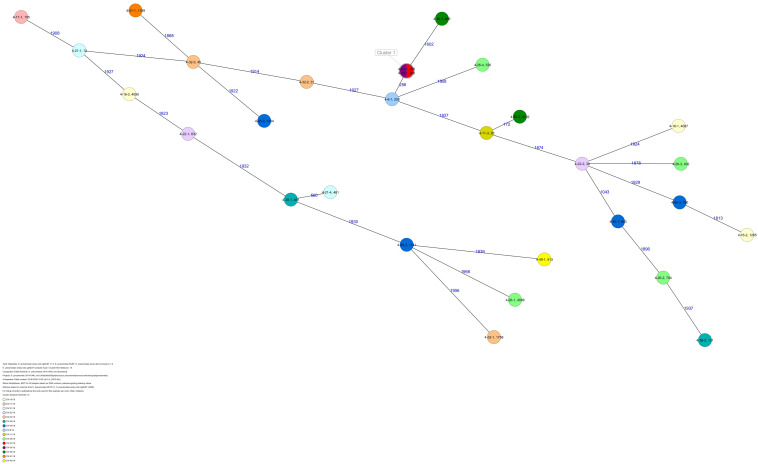
The 80 K. pneumoniae isolates were assigned to 60 different classical STs and 70 cgMLST complex types (CTs) (Table 1 and Figure 2). On average, all study isolates had 99.7% (98.6–100%) good core genome targets of the defined cgMLST scheme6. For nine isolates, which were obtained from the five colonized volunteers, new STs were determined and submitted to the K. pneumoniae MLST database7 : volunteer 1 (ST4099), volunteer 2 (ST4133), volunteer 4 (ST4090, ST4098, ST4102), volunteer 5 (ST4092), and volunteer 6 (ST4121, ST4122, and ST4123) (Table 1 and Figure 1). Serotype analysis from WGS data identified 39 wzc and 51 wzi alleles, 48 K serotypes, and 11 O serotypes (Table 1 and Supplementary Table 1). Eighteen isolates had no wzc, and in addition, three of these had no wzi either. Among the 48 K serotypes 22 had low or non-match confidence as defined by Kaptive-web (Supplementary Table 1). As shown above, inter- and intra-proband strain diversity was high with 60 different STs and 70 different CTs among 80 isolates. The volunteers were colonized with strains belonging to the same STs (ST20, ST34, ST37, ST45, and ST200) several times during the study period (Figures 1, 2 and Table 1). CgMLST analysis revealed an inter-patient core genome diversity of strains with the same ST from 88 to 679 allelic differences. Subjects 2 and 4 shared four strains with identical STs, CTs, and K serotypes: ST1265/CT2688/K33 isolates (Figure 2, cluster 1) were collected in CW16/18 and differed by one allele in their cgMLST (both volunteers had the same meal in the same restaurant the day before sampling); ST632/CT2724/K141 strains (Figure 2, cluster 3) were collected in CW21/18 and CW22/18 and differed by four alleles (both volunteers had the same meal at a birthday party in CW21); ST1758/CT2750/K27 strains (Figure 2, cluster 10) were collected in CW32/18 and shared the identical set of cgMLST alleles (both volunteers had the same meal at a birthday party in CW31); and ST469/CT2721/K105 strains (Figure 2, cluster 2) were collected in an interval of 17 CWs (CW19/18 and CW36/18) showing one allelic difference (no correlation detectable).
FIGURE 2.
Minimum spanning tree (MST) based on cgMLST analysis of 80 K. pneumoniae isolates derived from subjects 1, 2, 4, 5, and 6. Numbers on connection lines represent allelic differences between isolates. Isolates are colored by sequence type (ST).
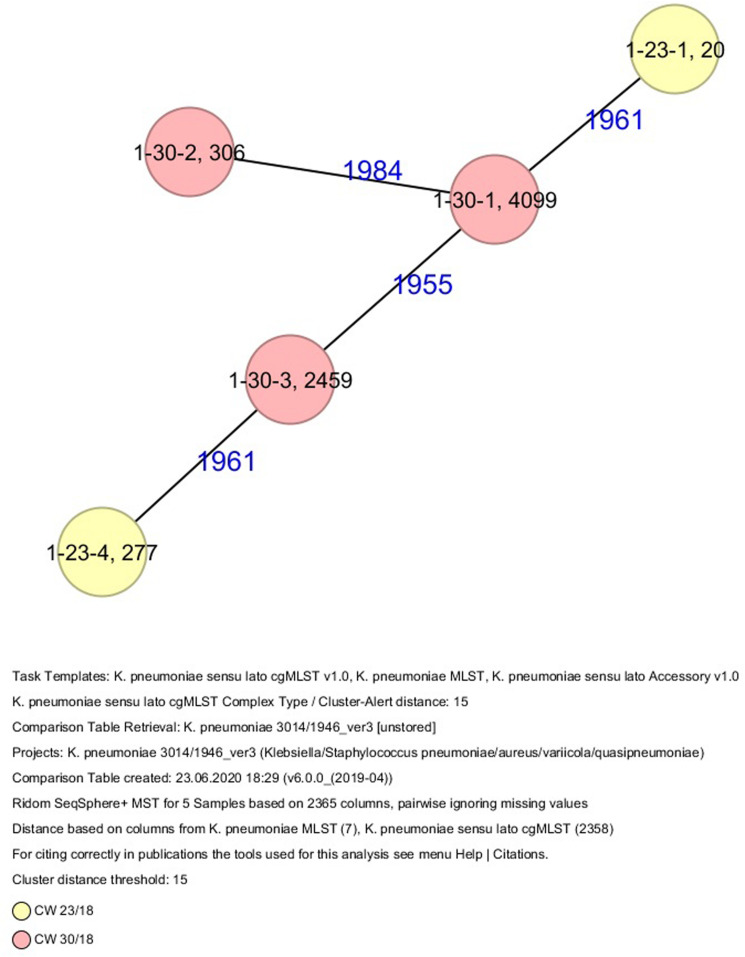
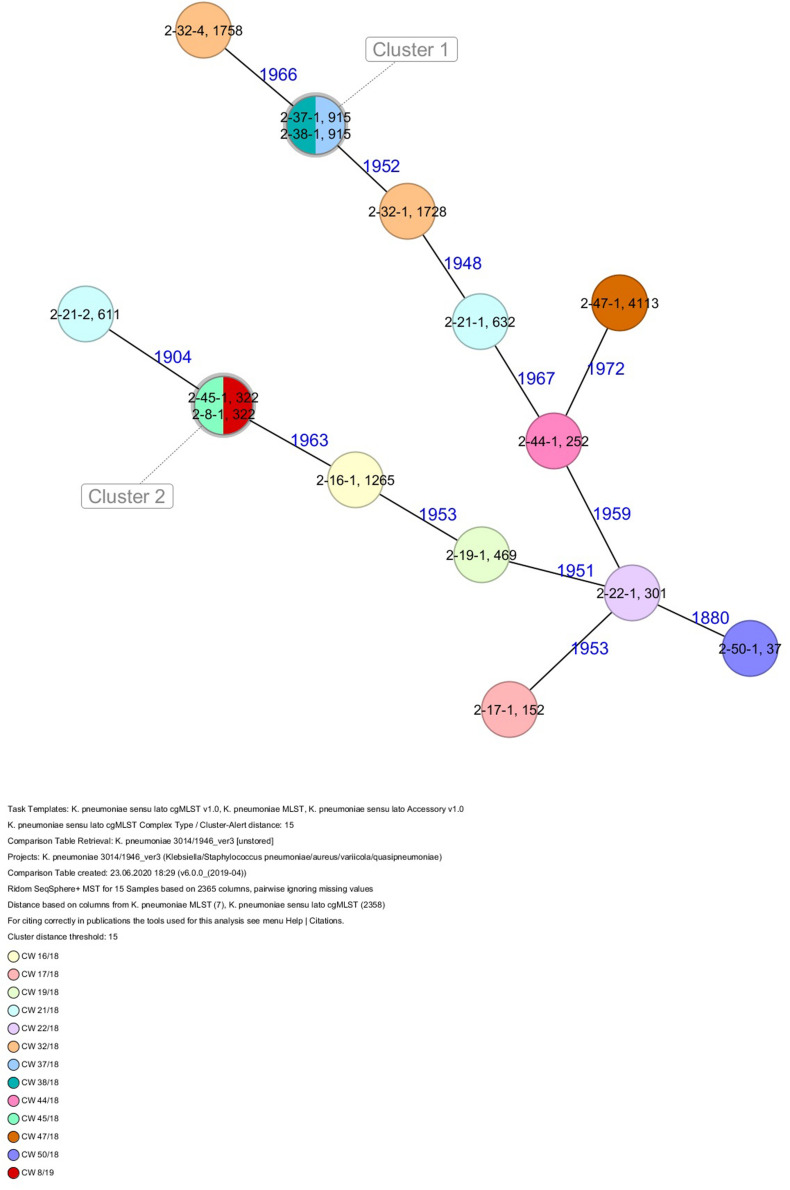
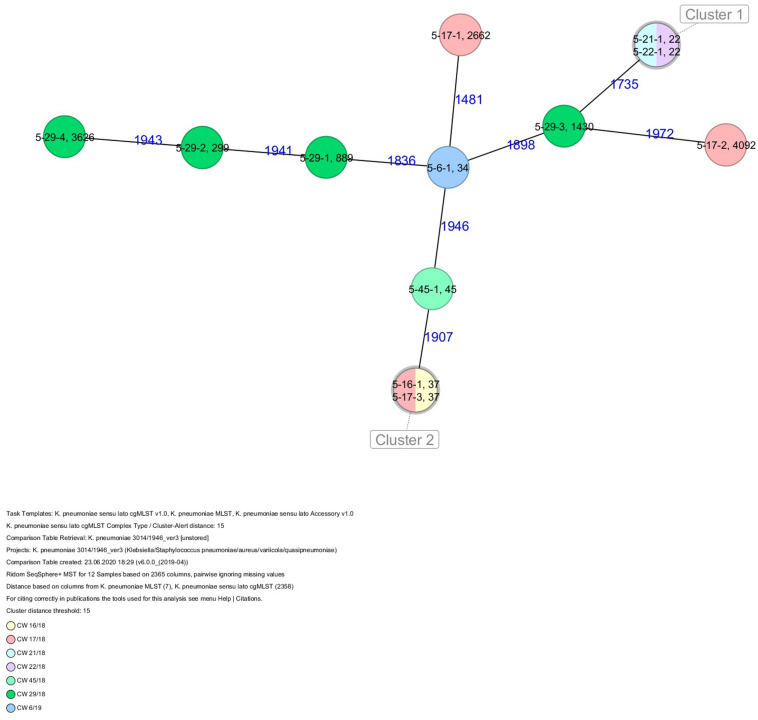
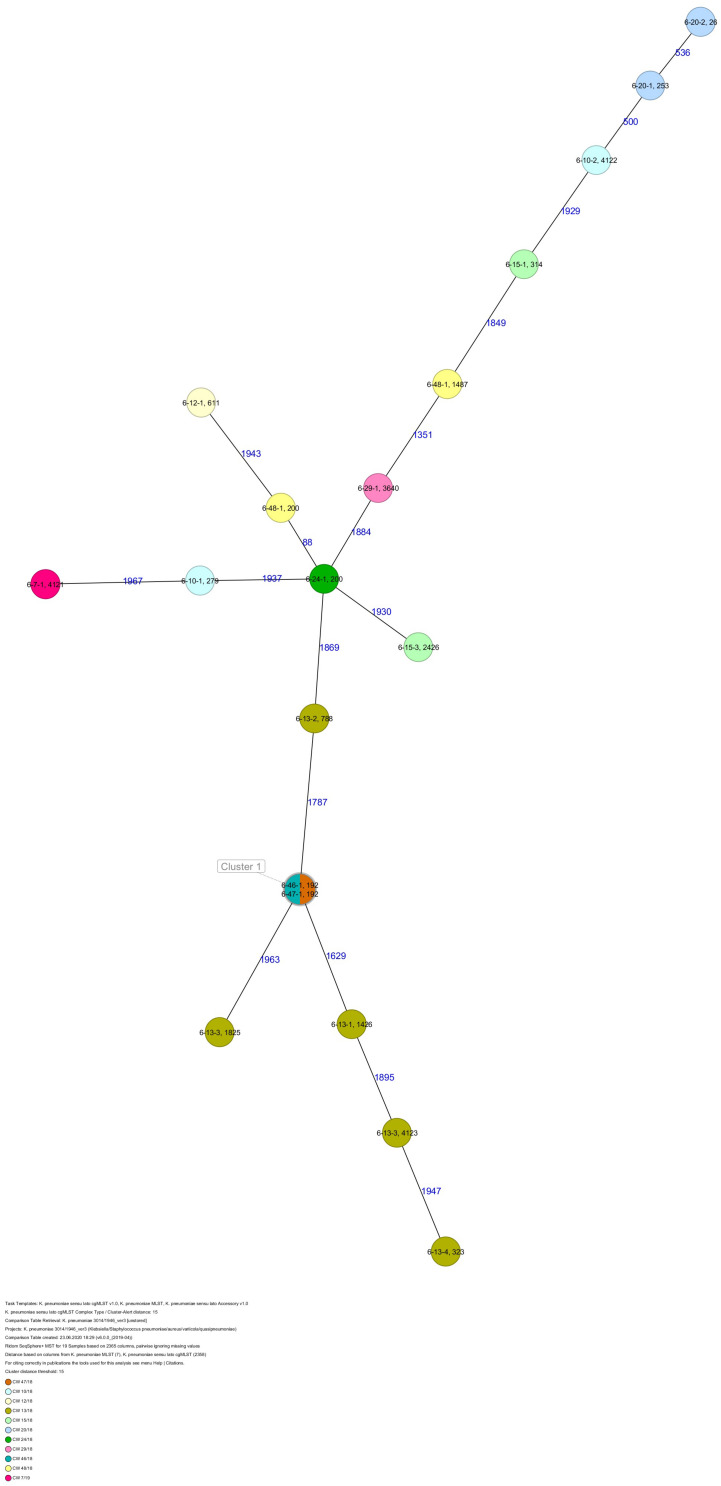
All five isolates of proband 1, which were derived from two stool samples, were unrelated as determined by ST, wzc and wzi allele typing, serotyping, and cgMLST analysis (Figures 2, 3 and Table 1). From proband 2, 15 isolates were cultured and assigned to 13 different STs and 13 different K serotypes. The volunteer was colonized with an ST915/CT2759/K107 isolate for two consecutive CWs (CW37/18-38/18) and with an ST322/CT2876/K17 isolate in CW45/18 and again 15 weeks later in CW8/19 (Figures 1, 4). Volunteer 2 was colonized with two different clones in CW21/18 and CW32/18 (Figures 1, 2, 4). From volunteer 4, 21 isolates were obtained and assigned to 26 different STs, 28 different CTs, and 23 K serotypes (Table 1 and Figure 5). Subject 4 was colonized for two consecutive CWs (CW33/18-34/18) with the same isolate (ST200/CT3277/K27) and was again colonized in CW 6/19 with an ST200/K27 isolate with CT2754 differing by 256 core genome alleles from isolate ST200/CT3277/K27. Later on, in CW 6/19, volunteer 4 was colonized with two different K. pneumoniae types in CW21/18, CW36/18, and CW38/18; with three different clones in CW16/18, CW22/18, and CW32/18. In CW26/18 and CW45/18, volunteer 4 was colonized with four different K. pneumoniae types (Figure 1 and Table 1). Subject 5 was colonized with 12 isolates that could be assigned to 10 different STs and 10 different K serotypes. Volunteer 5 was colonized with two identical isolates (ST22 and ST37) for two consecutive CWs (Figure 1 and Table 1). In CW17/18 and CW29/18, subject 5 was concurrently colonized with three and four respective different K. pneumoniae strains (Figure 1 and Table 1). Volunteer 6 was colonized by a total of 19 isolates, which were assigned to 17 different STs and 19 different K serotypes (Table 1). Volunteer 6 was colonized with an ST192 isolate for two consecutive CWs (CW46/18–47/18) (Figure 1 and Table 1). The other isolates differed by a maximum of 2012 alleles in their cgMLST (Figure 6). The volunteer was colonized with two different K. pneumoniae strains in CW15/18, CW20/18, CW48/18, and CW10/19 (Figure 1 and Table 1). In CW13/19, the volunteer was simultaneously colonized with five different K. pneumoniae strains (Figure 1 and Table 1).
FIGURE 3.
Minimum spanning tree (MST) based on cgMLST analysis of five K. pneumoniae isolates derived from subject 1. Numbers on connection lines represent allelic differences between isolates. Isolates are colored by date of isolation.
FIGURE 4.
Minimum spanning tree (MST) based on cgMLST analysis of 15 K. pneumoniae isolates derived from subject 2. Numbers on connection lines represent allelic differences between isolates. Isolates are colored by date of isolation.
FIGURE 5.
Minimum spanning tree (MST) based on cgMLST analysis of 29 K. pneumoniae isolates derived from subject 4. Numbers on connection lines represent allelic differences between isolates. Isolates are colored by date of isolation.
FIGURE 6.
Minimum spanning tree (MST) based on cgMLST analysis of 12 K. pneumoniae isolates derived from subject 5. Numbers on connection lines represent allelic differences between isolates. Isolates are colored by date of isolation.
FIGURE 7.
Minimum spanning tree (MST) based on cgMLST analysis of 19 K. pneumoniae isolates derived from subject 6. Numbers on connection lines represent allelic differences between isolates. Isolates are colored by date of isolation.
Strains with capsule types K20, K47, and STs ST20, ST37, ST45, ST101, ST152, ST323, and ST1265 (a single locus variant of hvKp ST23), which have been linked to high-risk clones (Huynh et al., 2020), were obtained several times (Table 1). Isolates with these capsule types or STs carried neither the characteristic hvKp virulence gene repertoire (Table 2 and Supplementary Table 1) nor the typical virulence plasmids (Supplementary Table 1).
TABLE 2.
Virulence genes detected in K. pneumonia isolates of Probands 1–2 and 4–6.
| Proband | Sample ID | ST | kfu | kvgA | fyuA | irp | mrk | ybt | Other genes |
| 1 | 510056-18 | 20 | A,B,D,F,H,I,J | ||||||
| 510059-18 | 277 | A,B,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510076-18 | 4,099 | A,B,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510077-18 | 306 | A,B,D,F,H,I,J | allD, allS, arcC, glxR | ||||||
| 510078-18 | 2,459 | A,B,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 2 | 510005-18 | 1,265 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | ||||||
| 510017-18 | 152 | A,F,H,I | |||||||
| 510029-18 | 469 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510034-18 | 632 | A,C | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | ||||||
| 510035-18 | 611 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510046-18 | 301 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | A,Q,S,T,X | ||||||
| 510084-18 | 1,728 | A,C | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | ||||||
| 510087-18 | 1,758 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510119-18 | 915 | A,C | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | ||||||
| 510126-18 | 915 | A,C | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | ||||||
| 510320-18 | 252 | A,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510340-18 | 322 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510370-18 | 4,113 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | mceA–E, mceG–J | ||||||
| 510871-19 | 37 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510902-19 | 322 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 4 | 510929-19 | 20 | 1,2 | H,I,J | A,E,P,Q,S,T,U,X | ||||
| 510009-18 | 4,087 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510010-18 | 1,265 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510011-18 | 4,090 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510021-18 | 105 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | A,E,P,Q,S,T,U,X | mceA–E, mceG–J | |||||
| 510038-18 | 12 | A,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510041-18 | 461 | A,B,C | C,D,F,H,I,J | ||||||
| 510049-18 | 632 | A,B,C | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | ||||||
| 510050-18 | 34 | A,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510064-18 | 4,098 | A,B,C | C,D,F,H,I,J | ||||||
| 510065-18 | 704 | 1,2 | B,C,H,I | A,E,P,Q,S,T,U,X | |||||
| 510066-18 | 492 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510067-18 | 530 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510088-18 | 1,758 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510089-18 | 37 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510090-18 | 45 | 1,2 | A,B,C,D,H,I,J | A,E,P,Q,S,T,U,X | |||||
| 510092-18 | 200 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510096-18 | 200 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510112-18 | 469 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510113-18 | 4,102 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510127-18 | 461 | A,B,C | A,H,I,J | ||||||
| 510128-18 | 101 | A,B,C | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | ||||||
| 510306-18 | 1,159 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510324-18 | 643 | A,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510325-18 | 1,141 | A,B,C | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | ||||||
| 510326-18 | 1,334 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510334-18 | 730 | A,D,H,I | |||||||
| 510851-19 | 913 | A,B,C | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | mceA–E, mceG–J | |||||
| 510880-19 | 200 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 5 | 510013-18 | 37 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | ||||||
| 510025-18 | 2,662 | H,I | |||||||
| 510026-18 | 4,092 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510027-18 | 37 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510042-18 | 22 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510052-18 | 22 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510068-18 | 889 | A,B,C | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | allD, KP1_1371 | |||||
| 510069-18 | 299 | B,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510070-18 | 1,430 | A,B,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510071-18 | 3,626 | A,B,C | C,D,H,I | ||||||
| 510336-18 | 45 | 1,2 | A,B,C,D,H,I,J | A,E,P,Q,S,T,U,X | |||||
| 510884-19 | 34 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 6 | 510919-19 | 279 | 1,2 | A,B,C,D,H,I,J | A,E,P,Q,S,T,U,X | ||||
| 510920-19 | 4,122 | 1,2 | A,B,D,H,I,J | A,E,P,Q,S,T,U,X | |||||
| 510931-19 | 611 | 1,2 | A,B,C,D,H,I,J | A,E,P,Q,S,T,U,X | |||||
| 510939-19 | 1,426 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510940-19 | 788 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510941-19 | 1,825 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510945-19 | 4,123 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510946-19 | 323 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510001-18 | 314 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510003-18 | 2,426 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510030-18 | 253 | H,I | |||||||
| 510031-18 | 26 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510060-18 | 200 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510072-18 | 3,640 | A,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510366-18 | 192 | 1,2 | A,B,C,D,H,I,J | A,E,P,Q,S,T,U,X | |||||
| 510378-18 | 192 | 1,2 | A,B,C,D,H,I,J | A,E,P,Q,S,T,U,X | |||||
| 510386-18 | 1,487 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J | |||||||
| 510836-19 | 200 | A,C,D,H,I | allB, allD, allS, KP1-1371, hyi, ybbW | ||||||
| 510894-19 | 4,121 | A,B,C,D,F,H,I,J |
The analysis for the presence of virulence genes identified a total of 42 different virulence genes among all 80 isolates (Table 2). Genes belonging to the type 3 fimbrial gene cluster (mrk) were present in all isolates. Three isolates [3.75%, ST306 (volunteer 1), ST889 (volunteer 5), and ST200 (volunteer 6)] harbored additional genes associated with the allantoin metabolism (all, glx, hyi), 14 isolates (17.5%, volunteers 2, 4, and 5) harbored genes encoding an intestinal colonization factor (kfu), 10 isolates (12.5%, volunteers 2 and 5) carried genes that contribute to capsule formation (kvg), 3 isolates (3.75%, volunteers 2 and 4) harbored genes belonging to the mammalian cell entry (mce) gene cluster, and 10 isolates (12.5%, volunteers 2, 4, 5, and 6) had genes encoding yersiniabactin (ybt) (Table 2 and Supplementary Table 1).
Phenotypic testing of isolates for their ESBL producing capacity revealed that all isolates were ESBL negative. The analysis for antibiotic resistance genes revealed 25 genes among all 80 isolates in total (Table 3 and Supplementary Table 1). Out of these 25 resistance genes, 13 were present in all investigated isolates: baeR (antibiotic efflux), CRP (antibiotic efflux), emrB (antibiotic efflux), emrR (antibiotic efflux), fosA (antibiotic efflux), marA (antibiotic efflux), marR (antibiotic efflux), msbA (antibiotic efflux), H-NS (antibiotic efflux), oqxA/B (antibiotic efflux), EF-Tu (R234F, antibiotic target alteration), uhpT (E350Q, antibiotic target alteration), and blaSHV (antibiotic inactivation). The isolates carried 18 different SHV variants (Table 3 and Supplementary Table 1).
TABLE 3.
Resistance genes/mechanisms, SHV variants and ESBL phenotypes detected in K. pneumoniae isolates of this study.
| Proband | Sample ID | ST | emr | FosA | Kp-acrA | vgaC | SHV | Other genes | ESBL phenotypic testing |
| 1 | 510056-18 | 20 | B,R | 6 | 1 | S | |||
| 510059-18 | 277 | B,R | 6 | 27 | S | ||||
| 510076-18 | 4,099 | B,R | 6 | 1 | nd | ||||
| 510077-18 | 306 | B,R | 6 | 1 | nd | ||||
| 510078-18 | 2,459 | B,R | 6 | 1 | nd | ||||
| 2 | 510005-18 | 1,265 | B,R | 5 | 36 | nd | |||
| 510017-18 | 152 | B,R | 6 | 1 | nd | ||||
| 510029-18 | 469 | B,R | 5 | 11 | nd | ||||
| 510034-18 | 632 | B,R | 6 | 108 | S | ||||
| 510035-18 | 611 | B,R | 6 | 27 | S | ||||
| 510046-18 | 301 | B,R | 6 | 27 | S | ||||
| 510084-18 | 1,728 | B,R | 6 | 11 | nd | ||||
| 510087-18 | 1,758 | B,R | 6 | 1 | nd | ||||
| 510119-18 | 915 | B,R | 6 | 11 | nd | ||||
| 510126-18 | 915 | B,R | 6 | 11 | nd | ||||
| 510320-18 | 252 | B,R | 6 | 1 | nd | ||||
| 510340-18 | 322 | B,R | 6 | 11 | nd | ||||
| 510370-18 | 4,113 | B,R | 5 | 142 | nd | ||||
| 510871-19 | 37 | B,R | 5 | 11 | S | ||||
| 510902-19 | 322 | B,R | 6 | 11 | nd | ||||
| 4 | 510929-19 | 20 | B,R | 5 | 187 | nd | |||
| 510009-18 | 4,087 | B,R | 6 | 11 | nd | ||||
| 510010-18 | 1,265 | B,R | 5 | 36 | nd | ||||
| 510011-18 | 4,090 | B,R | 6 | 1 | nd | ||||
| 510021-18 | 105 | B,R | 6 | 1 | nd | ||||
| 510038-18 | 12 | B,R | 6 | 11 | nd | ||||
| 510041-18 | 461 | B,R | 5 | 1 | nd | ||||
| 510049-18 | 632 | B,R | 6 | 108 | nd | ||||
| 510050-18 | 34 | B,R | 5 | 71 | nd | ||||
| 510064-18 | 4,098 | B,R | 5 | 75 | nd | ||||
| 510065-18 | 704 | B,R | 5 | 36 | nd | ||||
| 510066-18 | 492 | B,R | 5 | 11 | nd | ||||
| 510067-18 | 530 | B,R | 5 | 1 | nd | ||||
| 510088-18 | 1,758 | B,R | 6 | 1 | nd | ||||
| 510089-18 | 37 | B,R | 6 | 51 | nd | ||||
| 510090-18 | 45 | B,R | 6 | 1 | nd | ||||
| 510092-18 | 200 | B,R | 5 | 1 | nd | ||||
| 510096-18 | 200 | B,R | 5 | 1 | nd | ||||
| 510112-18 | 469 | B,R | 5 | 11 | nd | ||||
| 510113-18 | 4,102 | B,R | 5 | 187 | nd | ||||
| 510127-18 | 461 | B,R | 5 | 1 | nd | ||||
| 510128-18 | 101 | B,R | 6 | 1 | nd | ||||
| 510306-18 | 1,159 | B,R | 6 | 11 | nd | ||||
| 510324-18 | 643 | B,R | 5 | 26 | nd | ||||
| 510325-18 | 1,141 | B,R | 6,7 | 11 | nd | ||||
| 510326-18 | 1,334 | B,R | 6 | 164 | nd | ||||
| 510334-18 | 730 | B,R | 5 | 1 | nd | ||||
| 510851-19 | 913 | B,R | 6,7 | 28 | oprN, mexF | nd | |||
| 510880-19 | 200 | B,R | 5 | 1 | nd | ||||
| 5 | 510013-18 | 37 | B,R | 5 | 11 | nd | |||
| 510025-18 | 2,662 | B,R | 6 | 26 | nd | ||||
| 510026-18 | 4,092 | B,R | 6 | 1 | APH(3?)-lb, APH(6)-ld | S | |||
| 510027-18 | 37 | B,R | 6 | 11 | nd | ||||
| 510042-18 | 22 | B,R | 6 | 1 | nd | ||||
| 510052-18 | 22 | B,R | 6 | 1 | nd | ||||
| 510068-18 | 889 | B,R | 6 | 108 | qnrS | S | |||
| 510069-18 | 299 | B,R | 6 | 1 | nd | ||||
| 510070-18 | 1,430 | B,R | 6 | 26 | tetD | nd | |||
| 510071-18 | 3,626 | B,R | 6 | 37 | rpoB2 | S | |||
| 510336-18 | 45 | B,R | 6 | 1 | nd | ||||
| 510884-19 | 34 | B,R | 6 | 50 | nd | ||||
| 6 | 510919-19 | 279 | B,R | 6 | 11 | nd | |||
| 510920-19 | 4,122 | B,R | 5 | 36 | nd | ||||
| 510931-19 | 611 | B,R | 6 | 27 | S | ||||
| 510939-19 | 1,426 | B,R | 6 | 11 | nd | ||||
| 510940-19 | 788 | B,R | 5 | 52 | tetC | S | |||
| 510941-19 | 1,825 | B,R | 6 | 11 | nd | ||||
| 510945-19 | 4,123 | B,R | 5 | 11 | nd | ||||
| 510946-19 | 323 | B,R | 5 | 52 | tetC | nd | |||
| 510001-18 | 314 | B,R | 6 | 1 | nd | ||||
| 510003-18 | 2,426 | B,R | 6 | 27 | S | ||||
| 510030-18 | 253 | B,R | 5 | 36 | nd | ||||
| 510031-18 | 26 | B,R | 5 | 36 | acrA-MDR, APH(3”)-lb, acrD | S | |||
| 510060-18 | 200 | B,R | 5 | 1 | nd | ||||
| 510072-18 | 3,640 | B,R | 5 | 40 | S | ||||
| 510366-18 | 192 | B,R | 5 | 60 | nd | ||||
| 510378-18 | 192 | B,R | 5 | 60 | nd | ||||
| 510386-18 | 1,487 | B,R | 5 | 11 | nd | ||||
| 510836-19 | 200 | B,R | 5 | 1 | nd | ||||
| 510894-19 | 4,121 | B,R | 6 | 168 | mfbA, SAT-2,tetA, tetR, aadA | S |
S, sensitive; nd, not done.
The resistance genes ompK37 (bacterial porin), acrA (antibiotic efflux), and vgaC (antibiotic target protection) were present in 97.5% (n = 78), 91.3% (n = 73), and 48.8% (n = 39) of all isolates.
Variants of the tet resistance gene [tet(A), tet(C), and tet(D)], which encode antibiotic efflux and confer tetracycline resistance, were present in isolates from subjects 5 (n = 1) and 6 (n = 4).
Resistance genes APH(3″)-Ib and APH(6)-Id, both conferring resistance to aminoglycoside antibiotics by antibiotic inactivation, were detected in two isolates (ST4092 and ST26) from subjects 5 and 6 in different CWs. Three resistance genes were detected exclusively in isolates from subject 6: aadA (antibiotic inactivation), mfpA (antibiotic target protection), and sat-2 (antibiotic inactivation) (Table 3). Two determinants conferring resistance were present in two isolates only from subject 5: qnrS2 (antibiotic target protection) and rpoB2 (antibiotic target alteration). Two genes (mexF, oprN), encoding antibiotic efflux, were only present in two isolates from subject 4 (Table 3).
The detection of plasmids via the PlasmidFinder tool revealed that 65 (81.3%) isolates carried plasmids. Among these 65 isolates, 16 different plasmid types: [Col(IMGS31) (n = 1); Col440I (21); Col440II (10); FII(pBK30683) (1); IncFIA(HI1) (6); IncFIB(K) (41); IncFIB(Mar) (3); IncFIB(pKPHS1) (5); IncFIB(pQil) (1); IncFII (7); IncFII(K) (28); IncFII(Yp) (2); IncHI1B (7); IncN3 (1); IncR (23); IncX3 (1)] were detected and the number of plasmids per isolate varied from 1 to 5 plasmids (Supplementary Table 1). No plasmids described as hvKp specific, i.e., pK2044 and pLVPK, were detected (Supplementary Table 1).
Discussion
Recent studies have shown that gastrointestinal colonization with K. pneumoniae is a common and significant reservoir for the transmission and subsequent infection of patients (Martin et al., 2016; Dorman and Short, 2017; Gorrie et al., 2017).
In our study, K. pneumoniae was found in 0.0–31.3% (mean 17.2%) of stool samples tested. This is lower than in previous studies with a colonization rate of 37.5% (Marques et al., 2019) and 55.9% (Huynh et al., 2020) but is in concordance with other studies reporting 4–10% colonization rates for test subjects (Choby et al., 2020). In contrast to other studies, where an increased fecal carriage rate during the summer was reported (Anderson et al., 2008), no such seasonal correlation could be observed in our study. It is of interest that one individual remained K. pneumoniae free during the entire 1 year study period. An explanation for this colonization failure might be a specific composition of the test persons’ microbiota that prevented K. pneumoniae from persisting in the gut, as has previously been shown in ICU patients (Collingwood et al., 2020). All other five participants in our study were colonized with K. pneumoniae strains in at least one of the weekly obtained samples, with individual stool samples yielding up to five different strains.
Colonization with multiple strains has already been reported in other studies (Marques et al., 2019). K. pneumoniae high-risk clonal lineages are either multidrug-resistant strains mainly causing severe infections in hospitals (Navon-Venezia et al., 2017) or are drug-susceptible hypervirulent strains (hvKp) causing infections in the community mainly in younger and healthy individuals (Paczosa and Mecsas, 2016). High-risk clonal lineages of the multidrug-resistant type exist worldwide and can be assigned to certain K. pneumoniae STs (Roe et al., 2019; Huynh et al., 2020). Although mainly found in hospitals, these clones can also colonize individuals outside hospitals (Holt et al., 2015). Since colonization is a potential reservoir for infection with K. pneumoniae strains (Gorrie et al., 2017), investigation of the rates and duration of carriage is of importance to assess the potential risk for that community. In our study, the diversity of isolates colonizing the test persons was high and colonization with specific strains occurred for a maximum of two consecutive weeks. Also based on the finding that two individuals who regularly ate meals together were colonized several times with identical strains, we hypothesize that the high diversity of isolates in our study is due to the consumption of contaminated food; food as a source of K. pneumoniae carriage has been previously described (Huynh et al., 2020; Koliada et al., 2020). The observed colonization of healthy individuals with diverse strains but for short time periods is in contrast to the situation in hospitals where patients are colonized over long periods of time with specific resistant clones due to treatment with antibiotics (Martin et al., 2016). In our study, no multidrug-resistant K. pneumoniae isolates were found, which is concordant to recent studies on healthy individuals without reported use of antibiotics (Marques et al., 2019; Huynh et al., 2020). In total, 25 resistance genes—mainly genes encoding for efflux pumps—were found among all 80 K. pneumoniae isolates. All isolates carried SHV beta-lacatamases.
In contrast to Asian countries, where the prevalence of hvKp is high (Chung et al., 2012), no hvKp isolates were detected in our study. None of the isolates carried the unique hvKp virulence gene repertoire or virulence plasmids in combination with hvKp-specific K serotypes or STs (Struve et al., 2015; Gu et al., 2018; Choby et al., 2020; Yang et al., 2020). However, some isolates carried single hvKp-specific virulence genes. Two isolates, ST306/K11/O3/O3a and ST1487/K141 (non-match confidence)/O4, carried the allantoinase gene cluster, reported to be exclusively present in hvKp CC23 and ST25 clonal lineages (Struve et al., 2015). Virulence factors kfu or the yersiniabactin gene cluster ybt were found in 10 isolates with diverse STs and K serotypes. Two patients were colonized with ST20 isolates, which have been described as an international outbreak clone (Mavroidi et al., 2014; Yu et al., 2016; Patil et al., 2019). The isolates had different K serotypes and carried SHV-1 and SHV-187 in contrast to the outbreak strains described, which were SHV-5, NDM-1, OXA-48, and KPC-2 producers (Mavroidi et al., 2014; Yu et al., 2016; Patil et al., 2019).
In conclusion, our study revealed that fecal K. pneumoniae carriage is intermittent and of high clonal diversity. Colonization with specific strains could be observed for a maximum of only two consecutive calendar weeks. Two of the five colonized individuals—working colleagues having the same meals together several times—shared identical K. pneumoniae types four times during the study period pointing toward the potential role of food as a reservoir of K. pneumoniae for humans as also described recently (Huynh et al., 2020). In contrast to E. coli, which is a lifelong colonizer of the human gut (Palmer et al., 2007), K. pneumoniae seems unable to colonize a healthy human permanently.
Data Availability Statement
The whole genome sequencing datasets generated for this study can be found in the DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank; accession PRJNA663884.
Ethics Statement
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by Dr. Michael Tamchina, Co-chair of the Ethics committee of the city of Vienna, Thomas Klestil Platz 8, 1030 Vienna, michael.tamchina@wien.gv.at. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author Contributions
SL, KH, CS, BS, FA, and WR: conceptualization. SL, KH, ASc, CS, ASt, CV, and SP-A: methodology. SL and WR: software analysis. KH, ASc, CS, CV, and FA: resources. SL, KH, ASc, and WR: data curation. SL, KH, BS, FA and WR: writing–original draft preparation. SL, KH, ASc, BS, FA, and WR: writing–review and editing. CS, BS, and FA: project administration. BS and FA: funding acquisition. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Funding. Part of the sequencing-work was supported financially by the MedVetKlebs project, a component of the One Health European Joint Programme, which has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Programme under Grant Agreement No 773830.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2020.581081/full#supplementary-material
References
- Anderson D. J., Richet H., Chen L. F., Spelman D. W., Hung Y.-J., Juang A. T., et al. (2008). Seasonal variation in Klebsiella pneumoniae bloodstream infection on 4 continents. J. Infect. Dis. 197 752–756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bankevich A., Nurk S., Antipov D., Gurevich A. A., Dvorkin M., Kulikov A. S., et al. (2012). SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 19 455–477. 10.1089/cmb.2012.0021 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bialek-Davenet S., Criscuolo A., Ailloud F., Passet V., Jones L., Delannoy-Vieillard A. S., et al. (2014). Genomic definition of hypervirulent and multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae clonal groups. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 20:1812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carattoli A., Zankari E., García-Fernández A., Larsen M. V., Lund O., Villa L., et al. (2014). In silico detection and typing of plasmids using PlasmidFinder and plasmid multilocus sequence typing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 58 3895–3903. 10.1128/aac.02412-14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choby J. E., Howard-Anderson J., Weiss D. S. (2020). Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae - clinical and molecular perspectives. J. Intern. Med. 287 283–300. 10.1111/joim.13007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung D. R., Lee H., Park M. H., Jung S. I., Chang H. H., Kim Y. S., et al. (2012). Fecal carriage of serotype K1 Klebsiella pneumoniae ST23 strains closely related to liver abscess isolates in Koreans living in Korea. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 31 481–486. 10.1007/s10096-011-1334-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collingwood A., Blostein F., Seekatz A. M., Wobus C. E., Woods R. J., Foxman B., et al. (2020). Epidemiological and microbiome associations between Klebsiella pneumoniae and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus colonization in intensive care unit patients. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 7:ofaa012. 10.1093/ofid/ofaa012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortés G., Borrell N., Astorza D., Gómez C., Sauleda J., Albertí S. (2002). Molecular analysis of the contribution of the capsular polysaccharide and the lipopolysaccharide O side chain to the virulence of Klebsiella pneumoniae in a murine model of pneumonia. Infect. Immun. 70 2583–2590. 10.1128/iai.70.5.2583-2590.2002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dao T. T., Liebenthal D., Tran T. K., Ngoc Thi Vu B., Ngoc Thi Nguyen D., Thi Tran H. K., et al. (2014). Klebsiella pneumoniae oropharyngeal carriage in rural and urban Vietnam and the effect of alcohol consumption. PLoS One 9:e91999. 10.1371/journal.pone.0091999 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diancourt L., Passet V., Verhoef J., Grimont P. A., Brisse S. (2005). Multilocus sequence typing of Klebsiella pneumoniae nosocomial isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 43 4178–4182. 10.1128/JCM.43.8.4178-4182.2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorman M. J., Short F. L. (2017). Klebsiella pneumoniae: when a colonizer turns bad. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 15:384. 10.1038/nrmicro.2017.64 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EUCAST (2017). Available online at: https://www.eucast.org/resistance_mechanisms (accessed October 14, 2020). [Google Scholar]
- EUCAST (2020). Available online at: https://www.eucast.org/clinical_breakpoints (accessed October 14, 2020). [Google Scholar]
- Farida H., Severin J. A., Gasem M. H., Keuter M., van den Broek P., Hermans P. W., et al. (2013). Nasopharyngeal carriage of Klebsiella pneumoniae and other Gram-negative bacilli in pneumonia-prone age groups in Semarang, Indonesia. J. Clin. Microbiol. 51 1614–1616. 10.1128/JCM.00589-13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedlaender C. (1882). Über die schizomyceten bei der acuten fibrösen pneumonie. Archiv. Patholog. Anat. Physiol. Klinische Med. 87 319–324. 10.1007/bf01880516 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Gorrie C. L., Mirceta M., Wick R. R., Edwards D. J., Thomson N. R., Strugnell R. A., et al. (2017). Gastrointestinal carriage is a major reservoir of Klebsiella pneumoniae infection in intensive care patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 65 208–215. 10.1093/cid/cix270 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu D., Dong N., Zheng Z., Lin D., Huang M., Wang L., et al. (2018). A fatal outbreak of ST11 carbapenem-resistant hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae in a Chinese hospital: a molecular epidemiological study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 18 37–46. 10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30489-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haryani Y., Noorzaleha A. S., Fatimah A. B., Noorjahan B. A., Patrick G. B., Shamsinar A. T., et al. (2007). Incidence of Klebsiella pneumoniae in street foods sold in Malaysia and their characterization by antibiotic resistance, plasmid profiling, and RAPD-PCR analysis. Food Control 18 847–853. 10.1016/j.foodcont.2006.04.009 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Holt K. E., Wertheim H., Zadoks R. N., Baker S., Whitehouse C. A., Dance D., et al. (2015). Genomic analysis of diversity, population structure, virulence, and antimicrobial resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae, an urgent threat to public health. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 112 E3574–E3581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huynh B.-T., Passet V., Rakotondrasoa A., Diallo T., Kerleguer A., Hennart M., et al. (2020). Klebsiella pneumoniae carriage in low-income countries: antimicrobial resistance, genomic diversity and risk factors. Gut Microb. 11 1287–1299. 10.1080/19490976.2020.1748257 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jia B., Raphenya A. R., Alcock B., Waglechner N., Guo P., Tsang K. K., et al. (2017). CARD 2017: expansion and model-centric curation of the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Nucleic Acids Res. 45 D566–D573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koliada A., Moseiko V., Romanenko M., Piven L., Lushchak O., Kryzhanovska N., et al. (2020). Seasonal variation in gut microbiota composition: cross-sectional evidence from Ukrainian population. BMC Microbiol. 20:100. 10.1186/s12866-020-01786-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai Y. C., Lu M. C., Hsueh P. R. (2019). Hypervirulence and carbapenem resistance: two distinct evolutionary directions that led high-risk Klebsiella pneumoniae clones to epidemic success. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 19 825–837. 10.1080/14737159.2019.1649145 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. R., Lee J. H., Park K. S., Jeon J. H., Kim Y. B., Cha C. J., et al. (2017). Antimicrobial resistance of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: epidemiology, hypervirulence-associated determinants, and resistance mechanisms. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 7:483. 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00483 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee I. R., Molton J. S., Wyres K. L., Gorrie C., Wong J., Hoh C. H., et al. (2016). Differential host susceptibility and bacterial virulence factors driving Klebsiella liver abscess in an ethnically diverse population. Sci. Rep. 6:29316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lima A. B., de Oliveira Leão L. S., Oliveira L. S., Pimenta F. C. (2010). Nasopharyngeal Gram-Negative bacilli colonization in brazilian children attending day-care centers. Braz. J. Microbiol. 41 24–27. 10.1590/S1517-83822010000100005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. C., Koh T. H., Lee N., Fung C. P., Chang F. Y., Tsai Y. K., et al. (2014). Genotypes and virulence in serotype K2 Klebsiella pneumoniae from liver abscess and non-infectious carriers in Hong Kong, Singapore and Taiwan. Gut Pathog. 6:21. 10.1186/1757-4749-6-21 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marques C., Belas A., Aboim C., Cavaco-Silva P., Trigueiro G., Gama L. T., et al. (2019). Evidence of sharing of Klebsiella pneumoniae strains between healthy companion animals and cohabiting humans. J. Clin. Microbiol. 57:e01537-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. M., Bachman M. A. (2018). Colonization, infection, and the accessory genome of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 8:4 10.3389/fcimb.2018.0004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. M., Cao J., Brisse S., Passet V., Wu W., Zhao L., et al. (2016). Molecular epidemiology of colonizing and infecting isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae. mSphere 1:e0261-16. 10.1128/mSphere.00261-16 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavroidi A., Liakopoulos A., Gounaris A., Goudesidou M., Gaitana K., Miriagou V., et al. (2014). Successful control of a neonatal outbreak caused mainly by ST20 multidrug-resistant SHV-5-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae, Greece. BMC Pediatr. 14:105. 10.1186/1471-2431-14-105 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navon-Venezia S., Kondratyeva K., Carattoli A. (2017). Klebsiella pneumoniae: a major worldwide source and shuttle for antibiotic resistance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 41 252–275. 10.1093/femsre/fux013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paczosa M. K., Mecsas J. (2016). Klebsiella pneumoniae: going on the offense with a strong defense. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 80 629–661. 10.1128/MMBR.00078-15 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer C., Bik E. M., DiGiulio D. B., Relman D. A., Brown P. O. (2007). Development of the human infant intestinal microbiota. PLoS Biol. 5:e50177. 10.1371/journal.pbio.0050177 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patil S., Chen X., Wen F. (2019). Exploring the phenotype and genotype of multi-drug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae harbouring blaCTX-M group extended-spectrum β-lactamases recovered from paediatric clinical cases in Shenzhen, China. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 18:32. 10.1186/s12941-019-0331-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podschun R., Ullmann U. (1998). Klebsiella spp. as nosocomial pathogens: epidemiology, taxonomy, typing methods, and pathogenicity factors. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 11 589–603. 10.1128/cmr.11.4.589 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice L. B. (2008). Federal funding for the study of antimicrobial resistance in nosocomial pathogens: no ESKAPE. J. Infect. Dis. 197 1079–1081. 10.1086/533452 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues C., Passet V., Rakotondrasoa A., Brisse S. (2018). Identification of Klebsiella pneumoniae, Klebsiella quasipneumoniae, Klebsiella variicola and Related Phylogroups by MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry. Front. Microbiol. 9:3000. 10.3389/fmicb.2018.03000 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues C., Passet V., Rakotondrasoa A., Diallo T. A., Criscuolo A., Brisse S. (2019). Description of Klebsiella africanensis sp. nov., Klebsiella variicola subsp. tropicalensis subsp. nov. and Klebsiella variicola subsp. variicola subsp. nov. Res. Microbiol. 170 165–170. 10.1016/j.resmic.2019.02.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roe C. C., Vazquez A. J., Esposito E. P., Zarrilli R., Sahl J. W. (2019). Diversity, virulence, and antimicrobial resistance in isolates from the newly emerging Klebsiella pneumoniae ST101 lineage. Front. Microbiol. 10:542. 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00542 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo T. A., Marr C. M. (2019). Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Clin. Microbiol, Rev. 32:e00001-19. 10.1128/CMR.00001-19 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo T. A., Olson R., Fang C. T., Stoesser N., Miller M., MacDonald U., et al. (2018). Identification of biomarkers for differentiation of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae from classical K. pneumoniae. J. Clin. Microbiol. 56:e0776-18. 10.1128/JCM.00776-18 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selden R., Lee S., Wang W. L., Bennett J. V., Eickhoff T. C. (1971). Nosocomial Klebsiella infections: intestinal colonization as a reservoir. Ann. Intern. Med. 74 657–664. 10.7326/0003-4819-74-5-657 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struve C., Roe C. C., Stegger M., Stahlhut S. G., Hansen D. S., Engelthaler D. M., et al. (2015). Mapping the evolution of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. mBio 6:e00630 10.1128/mBio.00630-615 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wick R. R., Heinz E., Holt K. E., Wyres K. L. (2018). Kaptive web: user-friendly capsule and Lipopolysaccharide serotype prediction for Klebsiella genomes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 56:e0197-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization [WHO] (2017). Global Priority List of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria to Guide Research, Discovery, and Development of New Antibiotics. Geneva: WHO. [Google Scholar]
- Wyres K. L., Holt K. E. (2018). Klebsiella pneumoniae as a key trafficker of drug resistance genes from environmental to clinically important bacteria. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 45 131–139. 10.1016/j.mib.2018.04.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Q., Jia X., Zhou M., Zhang H., Yang W., Kudinha T., et al. (2020). Emergence of ST11-K47 and ST11-K64 hypervirulent carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in bacterial liver abscesses from China: a molecular, biological, and epidemiological study. Emerg. Microb. Infect. 9 320–331. 10.1080/22221751.2020.1721334 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu J., Tan K., Rong Z., Wang Y., Chen Z., Zhu X., et al. (2016). Nosocomial outbreak of KPC-2- and NDM-1-producing Klebsiella pneumoniaes in a neonatal ward: a retrospective study. BMC Infect. Dis. 16:563. 10.1186/s12879-016-1870-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao Y., Zhang S., Fang R., Wu Q., Li J., Zhang Y., et al. (2020). Dynamic epidemiology and virulence characteristics of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in Wenzhou, China from 2003 to 2016. Infect. Drug Resist. 13 931–940. 10.2147/IDR.S243032 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The whole genome sequencing datasets generated for this study can be found in the DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank; accession PRJNA663884.