Abstract
Henry Miller stated that “to relieve a full bladder is one of the great human joys”.
Urination is critically important in health, and ailments of the lower urinary tract (LUT) cause extensive pathological burden. Nevertheless, we take urination for granted, and in-depth mechanistic insight is lacking. We have witnessed advances in understanding the central circuitry in the brain that facilitates urination1–3. Beyond central control, micturition reflexes that govern urination are all initiated by peripheral mechanical stimuli such as bladder stretch and urethral flow4. Surprisingly, the mechanotransduction molecules and the cell types that function as the primary stretch and pressure detectors in the urinary tract are mostly unknown. We find that the mechanosensitive ion channel PIEZO2 is expressed in lower urinary tract tissues, where it is required for low-threshold bladder stretch sensing and urethral micturition reflexes. We show that PIEZO2 acts as a sensor in both the bladder urothelium and innervating sensory neurons. Importantly, both humans and mice lacking functional PIEZO2 have impaired bladder control, and humans report deficient bladder-filling sensation. This study pinpoints PIEZO2 as a key mechanosensor in urinary function. These findings enable future work that will unlock how urothelial cells and sensory neurons interact to control urination.
The mechanotransduction channel necessary for urinary reflexes is unknown. Several ion channels are implicated in urinary tract function in vivo5–7, but none are shown to be required for micturition reflexes. Moreover, it is not clear which cells are the primary sensors: umbrella cells of the innermost layer in the urothelium have been proposed to be mechanosensory8,9, but the bladder is also innervated by mechanically sensitive afferents from dorsal root ganglia (DRG)1,10. PIEZO2 is the primary mechanosensor that mediates touch, proprioception, and mechanical allodynia in mice11–15. Remarkably, humans with loss-of-function mutations in PIEZO2 also showed complete deficits in these senses13,16. Furthermore, PIEZO2 mediates interoceptive processes like lung-stretch sensing and baroreception in the mouse17,18, but interoceptive deficits have not been studied in PIEZO2-deficient subjects. Given that urination is driven by mechanical interoceptive reflexes, we investigated whether PIEZO2 is important for urination.
To understand how PIEZO2 contributes to urination in humans, PIEZO2-deficient subjects (N=12; ages 5–43) answered questionnaires that are designed to capture pathology and have been validated against healthy controls to screen for voiding and elimination dysfunction19 (Fig. 1). We also assessed urologic history, previous medical evaluations and non-invasive bladder ultrasounds (Supplementary Table 1). All patients had decreased voiding frequency, reported as low as once or twice daily regardless of hydration status. Notably, the majority of subjects reported they could spend an entire day without feeling the need to void and therefore followed a voiding schedule. Healthy frequency is defined as 5–6 voids per day. Despite the lack of normal sensory feedback, all patients had achieved continence at the time of evaluation except for one 9-year-old. However, many subjects reported sudden urge incontinence where any delay in voiding resulted in urinary accidents. Two individuals reported occasional nocturnal enuresis, and four had stress incontinence caused by laughter, cough and/or postural changes, with one case being severe enough to require treatment. Several patients had a sensation of incomplete voiding and an irregular urinary stream. Three adults described a sensation of pelvic heaviness when their bladder was full, and all independently reported voiding by leaning over or using their hands to apply pressure to their lower abdomen. Overall, these data suggest that PIEZO2 plays an important functional role in human urination.
Figure 1. Human PIEZO2-deficient subjects have urinary dysfunction.
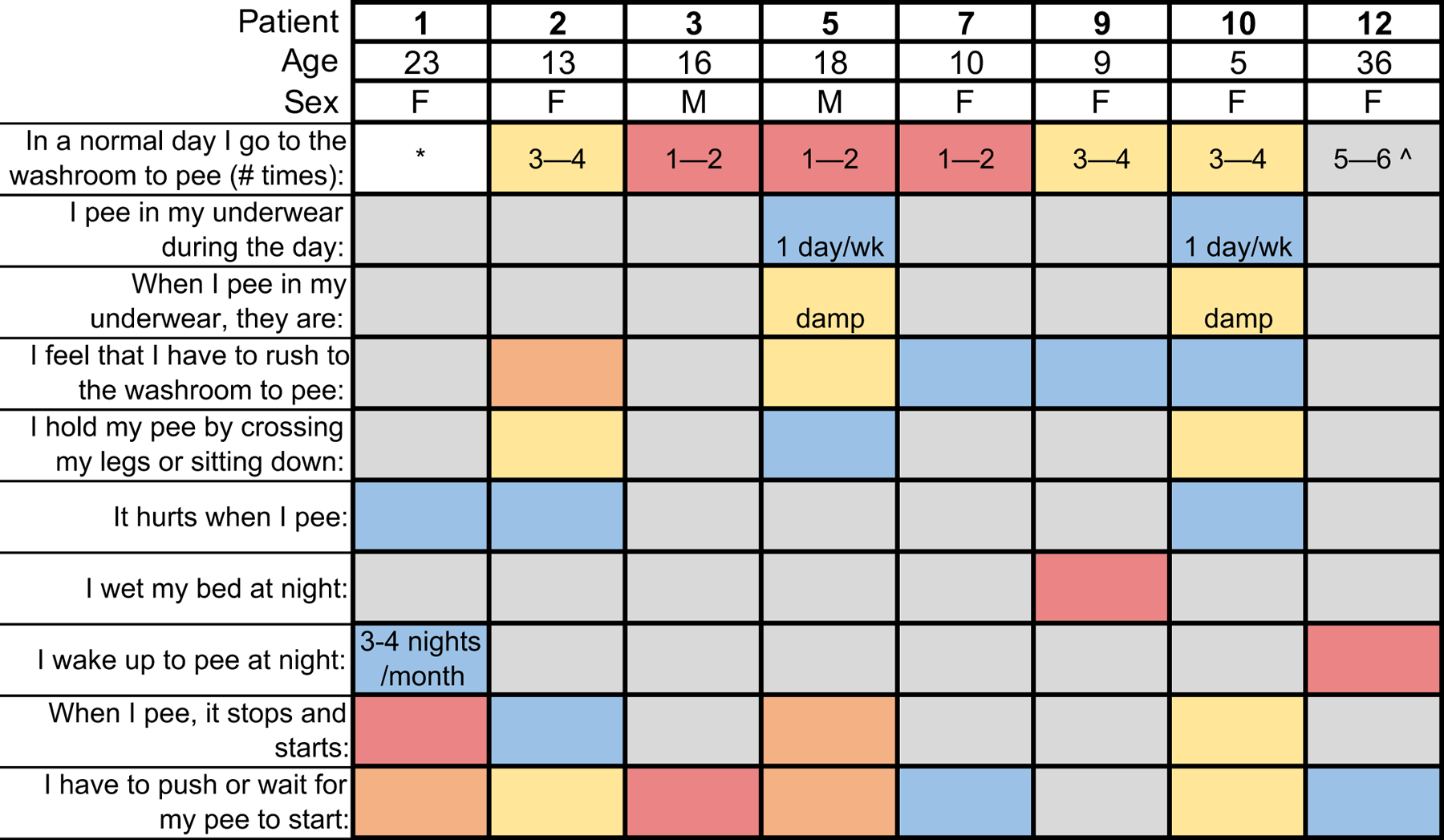
Patient numbers correspond to those in Supplementary Table 1. Grey indicates a neutral or non-pathological answer. Urinary frequency information is scored differently than other questions, and is color coded by the pathological score assigned to the answer in the questionnaire. Asterisk indicates an unanswered question. Unless otherwise noted, answers follow the scale: grey: never (no pathology), blue: less than half of the time (pathology score of 1), yellow: half of the time (pathology score of 2), orange: more than half of the time (pathology score of 3), red: every day or every night if nighttime is indicated in question (pathology score of 4). *Question not answered. Ŝubject answered 2X per day during clinical interview.
We next turned to studies in mice to understand where and how PIEZO2 functions in the urinary tract. To test whether Piezo2 is present in bladder sensory neurons, we used fluorescent in situ hybridization (RNAscope) in bladder and dorsal root ganglion (DRG) tissue taken from three animals after injection of a neuronal tracer into the bladder wall (Fig. 2a, Cholera Toxin B-Alexa 488 (CTB)). Out of 92 bladder-innervating neurons labeled with CTB, 75 expressed Piezo2 transcript (81.5%). Piezo2 transcript was also detected in a subset of Krt20-positive urothelial cells (Fig. 2b), a marker of umbrella cells that line the bladder lumen and are proposed to contribute to bladder filling detection8. Quantification revealed that 74% of umbrella cell nuclei were associated with Piezo2 transcript, and 12.6% of cells had high expression (1 SD above mean). Piezo2-positive cell density varied across the bladder. These results show that Piezo2 is expressed in two distinct cell types within the lower urinary tract and could function in detecting relevant mechanical stimuli. We confirmed that urothelial cells express other mechanosensory proteins (Extended Data Fig. 1), but the functional deficits in PIEZO2-deficient humans focused our work on this protein.
Figure 2. The lower urinary tract expresses Piezo2, and sensory neurons require PIEZO2 for detecting low-pressure bladder filling.
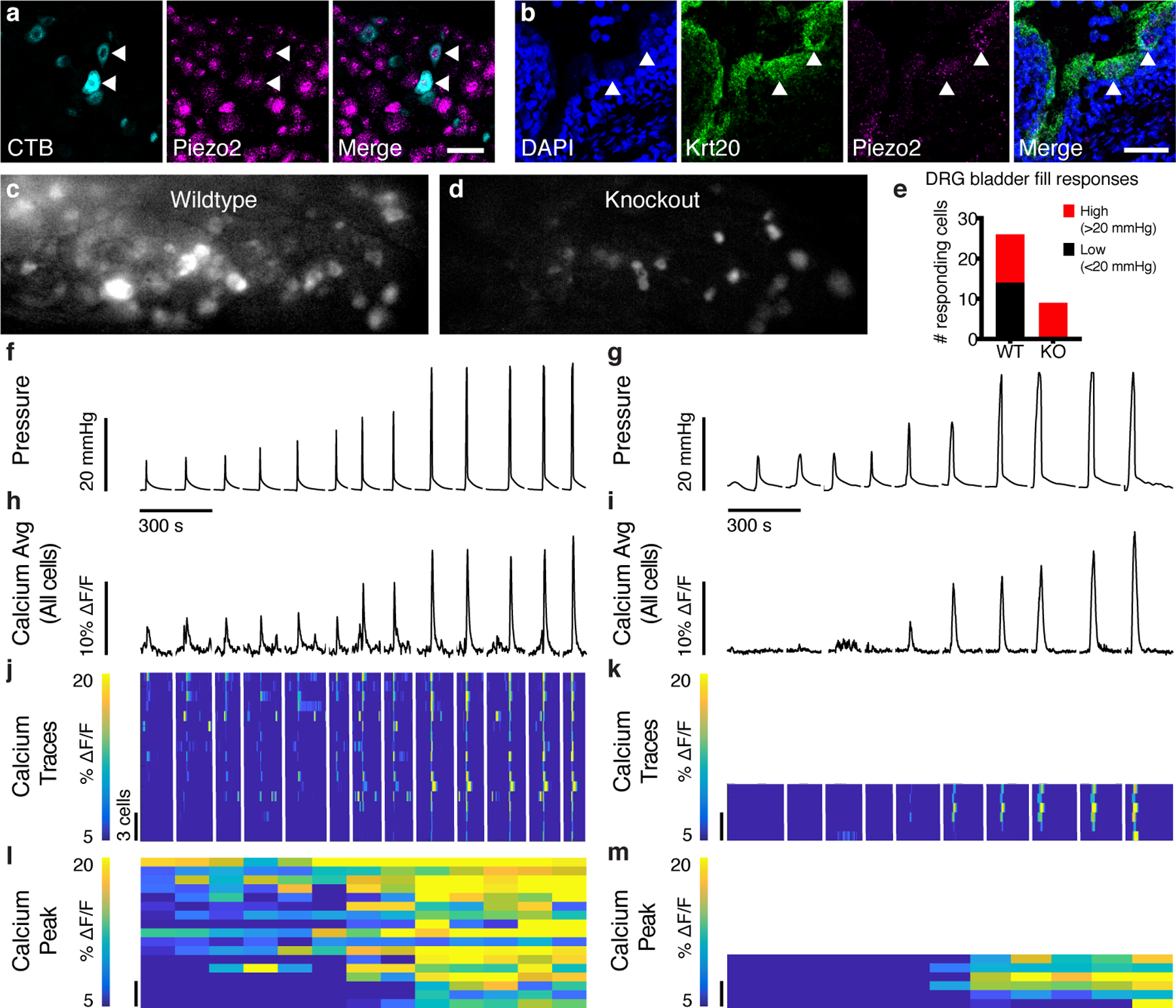
a, DRG neurons were retrogradely labeled using CTB-488. (cyan, left) fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) of DRGs with probes targeting Piezo2 (magenta, middle). Arrowheads point to Piezo2+ bladder neurons. Scale: 50 μm. Tracing experiment was repeated using three mice, N=22–36 cells analyzed per animal. b, FISH of bladder, probes against Krt20 (green) and Piezo2 (magenta). DAPI in blue. Arrowheads point to Piezo2+ umbrella cell examples. Scale: 50 μm. RNAscope was performed on three bladders, with two technical replications. Analysis was performed on 80–117 nuclei per bladder. c, Image z-stack from GCaMP6f+/+ control mouse S1 DRG during bladder fill. d, Example image from Piezo2cKO mouse S1 DRG during bladder fill. e, Count of cells responding to low- (black) and high-pressure (red) stimuli in WT (N=3 animals) and KO (N=4 animals) DRG. f, Example pressure trace from a wildtype DRG and g, knockout DRG. Stimuli were interleaved during recording, but are shown sorted low to high, hence the discontinuous line. Data below these graphs is sorted together with the respective pressure peaks. h, i, Average percent change in calcium fluorescence for all responding cells during the pressure peaks shown above in f and g, respectively. j, Calcium traces for individual wildtype cells that responded to pressure stimuli in f (N=17). Scale for cell number applies to j-m. k, Calcium traces from all knockout cells responding to pressure stimuli shown in g (N=6). Each cell’s responses are shown on the same horizontal line. Cells are sorted by cumulative response to the four lowest-pressure stimuli. l, m, Maximum calcium response for the cells shown above, 1 s after pressure peak.
We next used calcium imaging to determine whether bladder stretch responses in sensory neurons were Piezo2-dependent. Whether neurons detect bladder stretch directly or downstream of urothelial cell activation, we expect this stimulus to cause calcium influx. A viral vector carrying Cre recombinase was injected into P0-P3 pups carrying the Cre-dependent calcium indicator GCaMP6f and a conditional Piezo2 knockout allele, Piezo2cKO (Piezo2f/f /GCaMP6f+/+, controls were only GCaMP6f+/+)13. Thus, Piezo2 was deleted anywhere GCaMP6f was expressed. We observed rapid, robust responses in control S1 DRG neurons in response to manual, high-pressure bladder filling with saline (Fig. 2c), but these responses were dramatically attenuated in Piezo2cKO DRG cells (Fig. 2d). Interestingly, cells responding to low-pressure stimuli were completely absent in Piezo2 knockout DRG (Fig. 2e). Calcium traces for cells in wildtype DRG reveal graded responses to pressure stimuli, with many cells responding to low and high pressures, but Piezo2cKO cells were silent at low pressures. Piezo2cKO DRG also had fewer bladder-stretch responding cells (Fig. 2f–m) but normal responses to painful pinch (Extended Data Fig. 1). This suggests that PIEZO2 is a key sensor of bladder stretch.
Mechanically-evoked micturition reflexes coordinate the bladder detrusor muscle and the urethral sphincter muscles to mediate efficient urinary control, and are critical for efficient voiding4. We hypothesized that reflex responses rely on PIEZO2 function to provide feedback control over bladder pressure and urethra activity. We therefore investigated micturition reflexes in mice lacking PIEZO2 in all caudal tissues. In these Hoxb8Cre;Piezo2f/f animals, Cre recombinase is expressed in bladder-innervating DRG neurons14 and bladder urothelium (Extended Data Fig. 2a). We used cystometry with urethral EMG to simultaneously monitor bladder pressure and sphincter activity. With continual filling at 30 μl/min, control animals initiated bladder contractions at regular intervals, which are observed as pressure peaks that correspond to micturition events (Fig. 3a, Extended Data Fig. 2b). Piezo2 knockout animals displayed irregular micturition timing (Fig. 3b, Extended Data Fig. 2c) and on average, longer intervals between bladder contractions that resulted in urination (Fig. 3c, Extended Data Fig. 2h). Therefore, PIEZO2-deficient animals are less sensitive to bladder filling, as it takes more volume to initiate bladder contractions. Knockout animals also displayed higher bladder pressures five seconds before contraction peaks (Fig. 3d, Extended Data Fig. 2i). In healthy animals, low pressures are maintained during bladder filling because the detrusor muscle relaxes. The higher pressures that were observed before contractions suggest that this relaxation process or bladder compliance is impaired in knockout animals.
Figure 3. PIEZO2 is required for efficient micturition reflexes.
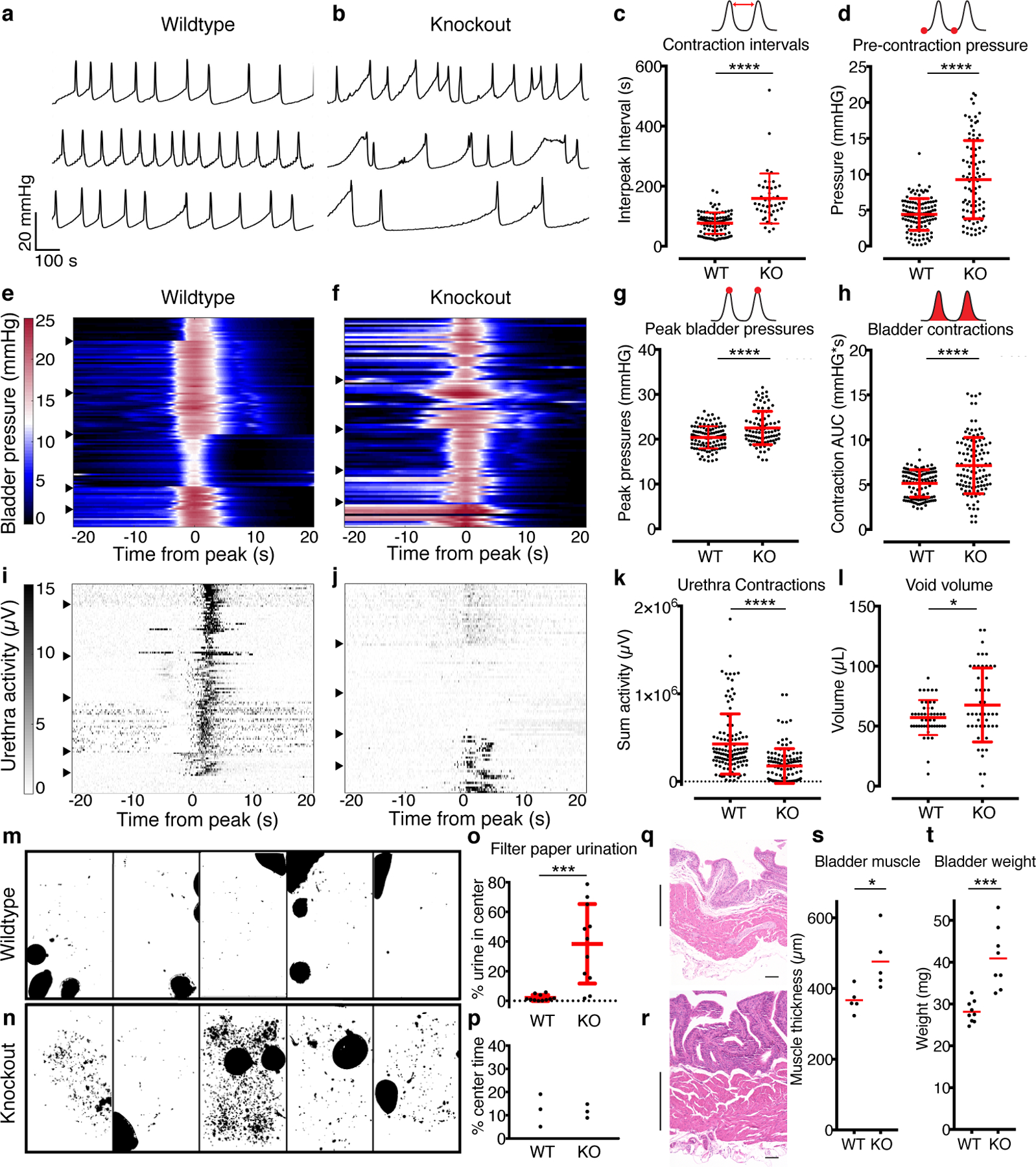
a, Example pressure traces from three female WT mice and b, three female HoxB8Cre;Piezo2f/f KO mice during continuous bladder filling. Scale in a also applies to b. c, Bladder contraction intervals (P<0.0001). d, bladder pressure five seconds before contraction peaks (P<0.0001). e, Heatmaps showing bladder contractions for six WT female mice and f, five HoxB8Cre;Piezo2f/f female KO mice. Color scale in e also applies to f. Each row represents bladder pressure during a single micturition event, with peaks aligned at 0. Arrows mark where data from one animal ends and another begins. g, Peak bladder pressures (P<0.0001) and h, area under the curve for bladder contractions (P<0.0001). i, Heatmap showing urethra activity, with each row from corresponding to bladder contraction events in e. j, Urethra activity from the HoxB8Cre;Piezo2f/f KO bladder contraction events shown in f. Scale in i also applies to j. k, Urethra activity during micturition (P<0.0001). l, Void volume measurements (P=0.03). P values from Student’s t-tests with Welch’s correction. N=6 WT and N=5 KO female mice for c through l. N=10–29 bladder contractions analyzed per mouse. m, Urination patterns of five WT mice and n, five HoxB8Cre;Piezo2f/f KO mice. o, Quantification of urine in the middle 50% of the cage (P=0.0001). N=11 female mice per group. p, Mice spend the same amount of time in cage center. q, H&E staining from WT and r, KO bladder sections, from littermates, 6–7 months, scale 100 μm. Muscle layer is marked by vertical lines. Scale for q and r is 200 μm. s, Bladder muscle wall thickness (N=5, P=0.016) and t, total bladder weights (N=9 and 8, P=0.0002). For o, s and t, Mann-Whitney test, all others are two-sided Student’s t-tests with Welch’s correction. Red lines indicate mean +/− standard deviation.
We next investigated individual micturition events to determine whether the bladder pressure required for sustaining micturition was abnormal. We observed consistent pressure increases within and between wildtype animals (Fig. 3e, Extended Data Fig 2d), but bladder pressure traces in knockouts were highly variable (Fig. 3f, Extended Data Fig 2e). Knockouts had higher peak pressures (Fig. 3g), and importantly, required significantly more pressure during contractions, suggesting that the detrusor muscle must work harder to accomplish micturition (Fig. 3h, Extended Data Fig 2j). We also assessed whether sensory input via PIEZO2 is important for urethral reflexes, which sustain efficient urination. During bladder contractions in wildtype animals, there was coordinated engagement of the urethra muscle (Fig. 3i). This reliable urethral activity was greatly attenuated in knockouts (Fig. 3j, k, Extended Data Fig 2k). Knockout urethra responses varied from silent or weak coordination to inappropriately timed hyperactivity (Extended Data Fig. 2c). Hyperactivity is a sign of detrusor-sphincter dyssynergia, a condition involving uncoordinated communication between the muscle groups responsible for urination. This indicates that the urethra was not receiving the appropriate sensory input to govern its activity during micturition. Animals lacking PIEZO2 also had more variable, larger void volumes, as longer periods between contractions allows for more bladder filling (Fig. 3l). Together, these data indicate that PIEZO2 sets stretch sensitivity in the lower urinary tract and initiates appropriately timed reflexes that contribute to efficient urination.
Next, we tested if urination behavior is altered in Piezo2 knockout animals. We placed animals on filter paper for four hours and imaged the resulting urination patterns with UV illumination. We used only female mice to preclude territorial scent-marking behavior. Wildtype mice typically urinated in the corners and edges of the cage in large spots (Fig 3m). Knockout mice had a variety of urination patterns, and some displayed urine leaking (small spots) or large voids towards the cage center (Fig. 3n,o). This phenotype was not attributed to knockouts spending more time in the middle of the cage (Fig. 3p). Thus, knockout mice have abnormal urination behavior, including what appears to be some incontinence.
We next asked if this observed urinary dysfunction in knockout animals led to long-term consequences. Chronic urinary tract dysfunction typically causes tissue remodeling as the bladder wall grows thicker to compensate for inefficient voiding20,21. This remodeling can eventually result in “decompensation”, which is marked by a flaccid, ineffective bladder with sequelae of incomplete voiding, vesicoureteral reflux and increased UTI frequency. Bladder wall thickening was observed by H&E staining in Piezo2-deficient animals (Fig. 3q,r,s). The weight of freshly excised bladders also revealed bladder wall remodeling, as knockout bladders were significantly heavier than wildtype littermates (Fig. 3t, Extended Data Fig. 2m). Thus, impaired urinary reflexes in knockout mice lead to detrusor hypertrophy, an indicator of chronic voiding dysfunction.
We next investigated in which cell types PIEZO2 was required. We tested whether lacking PIEZO2 in urothelial cells changed the pressure threshold required to initiate micturition. We used UPKIICre allele to abrogate functional PIEZO2 in urothelial cells (Extended Data Fig. 3a), which have been proposed to act as stretch sensors and communicate to underlying neurons via ATP7,9,22–24. We found that UPKIICre+;Piezo2f/f knockout animals displayed similar phenotypes to the Hoxb8Cre+;Piezo2f/f knockout animals, with higher bladder stretch thresholds, greater bladder pressure during micturition and attenuated urethral reflexes (Fig. 4a–h). In combination with expression data from RNAscope (Fig. 2b), these data indicate that PIEZO2 is acting in umbrella cells to help set bladder stretch sensitivity and initiate appropriate micturition reflexes. These data confirm the proposed role for umbrella cells as mechanosensory cells that participate in initiating micturition8.
Figure 4. PIEZO2 functions in both bladder urothelium and sensory neurons.
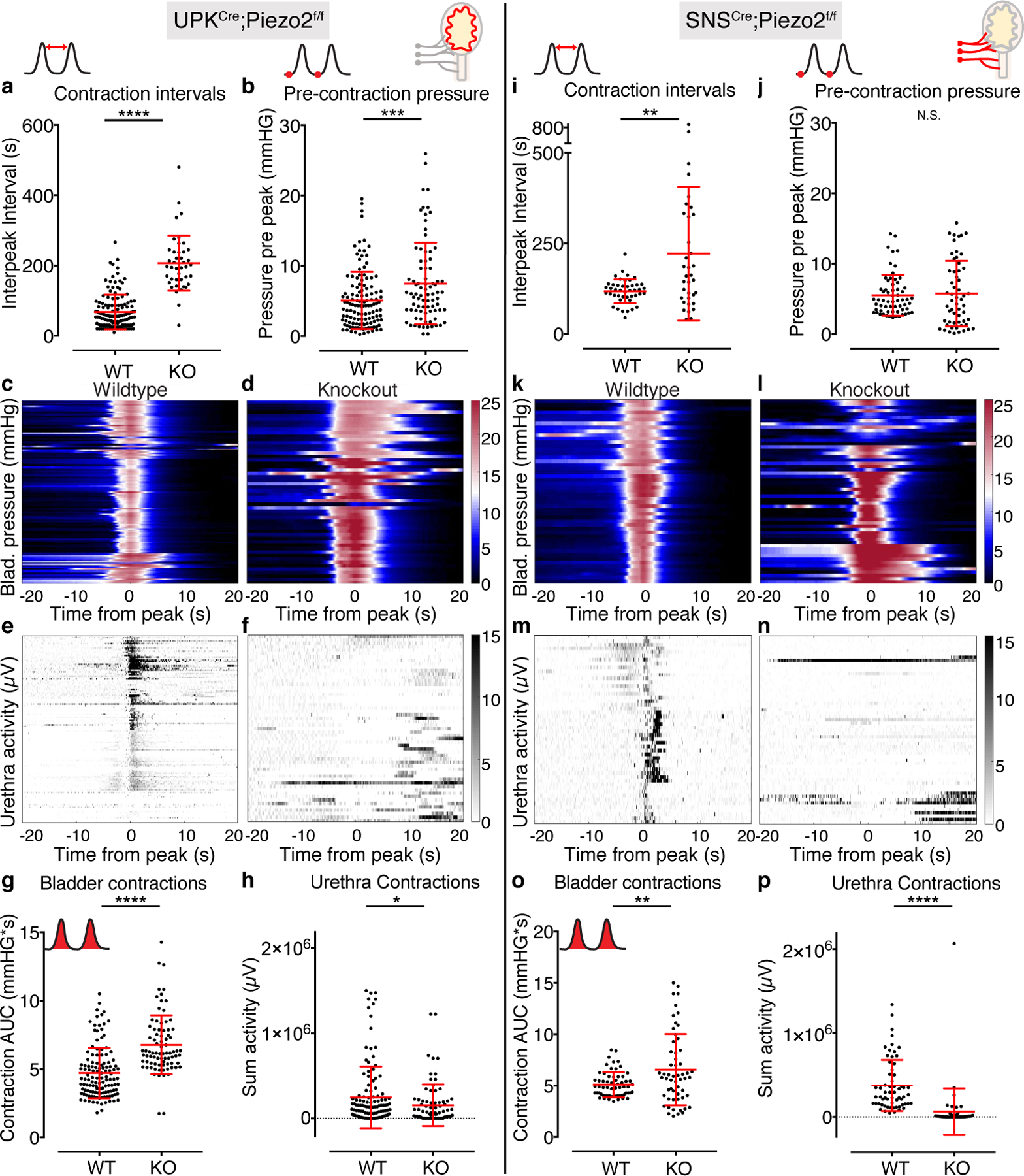
a-h, Cystometry data from UPKIICre;Piezo2f/f animals, N=5 WT and 4 KO female mice, N=18–49 bladder contractions analyzed per mouse.and i-p, SNSCre;Piezo2f/f animals, N=3 WT and 3 KO female mice, 11–24 contractions per mouse. Cartoons in the top right depict the lower urinary tract, with Piezo2 KO tissue in red. a, Intervals between bladder contraction voids (P<0.0001) and b, bladder pressures five seconds before peak contraction (P=0.001) in UPKIICre;Piezo2f/f knockout mice and wildtype littermates. c, Bladder pressure events during continuous filling cystometry in wildtype and d, UPKIICre;Piezo2f/f knockout mice. Color scale in d also applies to c. e, Urethra activity recorded during the bladder contraction events shown in c. f, Urothelial Piezo2 KO urethra activity during bladder contraction events shown in d. g, Bladder pressure during micturition events (P<0.0001) and h, urethral reflex responses during micturition (P=0.03). i, Intervals between bladder contractions in SNSCre;Piezo2f/f and wildtype littermates (P=0.002). j, Bladder pressures five seconds before peak contraction. k, Bladder pressure events during continuous filling cystometry in wildtype and l, SNSCre;Piezo2f/f knockout mice. Color scale in l also apply to k. m, Urethra activity recorded during the bladder contraction events shown in k. n, Urethra activity during bladder contraction events shown in l. o, Bladder pressure during micturition events (P=0.004) and p, urethral reflex responses during micturition (P<0.0001). Red horizontal lines indicate means, vertical red bars indicate +/− standard deviation. All P values are from two-sided Student’s t test with Welch’s correction. * is P≤0.05, ** is P≤0.01, *** is P≤0.001, **** is P≤0.0001.
Interestingly, we again observed these phenotypes in animals that lacked PIEZO2 only in sensory neurons (Fig 4i–p). Deleting PIEZO2 in all sensory neurons is lethal, so we used SNSCre mice25 to delete PIEZO2 in the Aδ- and c-fiber subsets, which are the primary sensory neuron types described in the bladder10,26. This line does not induce recombination in urothelial cells (Extended Data Fig 3b–e). Sensory neuron knockout animals displayed longer intervals between contractions (Fig. 4i), but interestingly, the pressure before contractions was not different from wildtypes as it was in urothelial and full caudal knockout animals (Fig. 4j). This implies that mechanosensory stimuli activate PIEZO2 in umbrella cells to initiate bladder relaxation during filling (Fig 4b), but neuronal mechanosensing is dispensable for this process. Alternatively, it is possible that bladders become fibrotic and less compliant in UPKIICre and HoxB8Cre Piezo2 knockouts, but not SNSCre Piezo2 knockouts. Neuronal PIEZO2 knockout animals do require more bladder pressure for micturition and have highly attenuated urethral reflex responses (Fig. 4o,p). These data implicate PIEZO2 in mediating neuronal stretch responses that are critical for downstream urethral reflexes. Interestingly, individual tissue knockout animals did not display the dramatic bladder remodeling that was observed in full caudal knockout animals (Fig 3s,t, Extended Data Fig. 3f,g), suggesting that urothelial or neuronal PIEZO2 alone could still contribute to urinary function. These data indicate that there is a two-part signaling mechanism that utilizes PIEZO2 in umbrella cells and sensory neurons to set bladder sensitivity and promote micturition reflexes. Future work is required to address how these cell types communicate.
We have used evidence from mice and humans to determine that the mechanotransduction channel PIEZO2 is a critical mediator of urinary tract function. Nonetheless, lacking Piezo2 in mice does not result in urinary tract paralysis and death, and PIEZO2-deficient humans are still able to urinate. This indicates that mechanotransduction proteins beyond PIEZO2 are present in the urothelium and LUT sensory neurons. For example, the mechanotransduction ion channels TMEM63b and PIEZO1 are widely expressed in the urothelium, and PIEZO1 partially mediates urothelial stretch responses in vitro27.
Our data puts forth a two-part model of mechanosensory signaling in the urinary tract, which is reminiscent of epithelial cell-neuronal sensory machinery in the skin (Merkel cell-neurite complexes), lung (neuro-epithelial bodies) and intestine (enterochromaffin cells)15,17,28,29. Our data also implicate umbrella cells in mediating bladder relaxation during filling, perhaps by signaling to bladder muscle and/or through stretch-induced cellular changes30. Future studies will address how urothelial cells and sensory neurons collaborate to control urinary function.
Methods
All experiments were performed within the protocols and guidelines approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees of The Scripps Research Institute in compliance with regulatory standards established by the Association for Assessment and Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care International (AAALAC).
Statistics
Unless otherwise noted in the legends, groups were compared using two-tailed Student’s t-test with Welch’s correction, as groups did not have equal variances. For comparisons of groups with an N less than 15, we used the non-parametric Mann-Whitney test to assess differences, as we could not assess distributions. These tests were indicated in the figure legends. No statistical test was used to pre-determine sample size. Instead, sample size was determined by animal availability and previous studies in the field, which found these sample sizes sufficient to detect deficits.
Study Design
We established exclusion criteria prior to collecting cystometry data: data from the first 30 minutes of cystometry recording was not used because bladder muscle activity has often not stabilized. Moreover, animals that displayed bladder leaking during recording were excluded from analysis, as leaking indicated a flawed seal and thus inaccurate filling responses. To verify the reproducibility of experimental findings, we restricted the time of day that cystometry recordings were done (Zeitgeber 8–14) and we performed every experiment in a cohort of male and female mice to compare to their wildtype littermates. The order of recordings for different genotypes was randomized. The experimenter was blind to genotype when possible. HoxB8Cre+;Piezo2f/f knockout mice have obvious motor impairments, so the experimenter was never blind to genotype for these groups.
Mice
Mice were kept in standard housing with 12 h light/dark cycle set with lights on from 6 AM to 6 PM, with room temperature kept around 72 degrees Fahrenheit, with humidity between 30–80 % (not controlled). Adult male and female mice were used as indicated in the text. Age-matched knockout and wildtype littermates were tested at the same age in each cohort, but ages tested ranged from 5–8 months for HoxB8Cre;Piezof/f, 6–12 months for SNSCre and 4–6 months for UPKIICre). The HoxB8Cre;Piezof/f mouse line has been previously described11. GCaMP6f+/+ mice (B6;129S-Gt(ROSA)26Sortm95.1(CAG-GCaMP6f)Hze/J, Jackson Laboratory: Ai95, #024105) were bred to Piezo2f/f mice as described previously13,31 . Piezo2f/f mice were mated with SNSCre mice25 or UPKIICre mice (B6(129)-Tg(Upk2-cre)1Rkl/WghJ , Jackson Laboratory: #029281) to create sensory-neuron specific and urothelial specific Piezo2 knockout animals, respectively. Each of these Cre lines was also crossed with Ai9 mice (B6.Cg-Gt(ROSA)26Sortm9(CAG-tdTomato)Hze/J, Jackson Laboratory: # 07909) to assess Cre expression. Genotyping was performed using guidelines from Jackson Laboratory.
Retrograde labeling of sensory neurons
Mice were anesthetized with isoflurane. Their lower abdomen was de-haired using Nair (Fisher Scientific: NC0132811), and sterilized with ethanol and iodine, cleaned, and a midline laparotomy was performed to expose the bladder. Three to five injections of 1–2 μl of Cholera Toxin B–Alexa 488 (Fisher Scientific: C22841) were made in the bladder wall using a Hamilton syringe. Care was taken to avoid puncturing through to the bladder lumen. The abdominal wall and skin were sutured separately, and mice were given subcutaneous flunixin (0.1 ml / g bw) for post-operative care. We waited three to five days before taking tissue to allow the dye to reach the cell soma.
Fluorescent in situ hybridization
Bladder and DRG tissues were removed immediately from euthanized animals, and flash frozen in liquid nitrogen. The protocol for RNAscope Multiplex Fluorescent Reagent Kit V2 (ACDBio: 323100) was followed according to instructions for fresh frozen tissue. A gentler protease (III) was applied for only 25 min to lessen CTB-fluorophore degradation in DRG tissue and delicate bladder tissue. Probes for Piezo2 (ACDBio: 400191 or 439971), Krt20 (ACDBio: 402301), Piezo1 (ACDBio: ) or Tmem63b (ACDBio: 431531) were applied to detect transcript. Quantification of was performed in ImageJ using regions of interest to define quantification area and then by measuring mean pixel intensity. Only DRG cells with nuclei visible were quantified to prevent double-counting of the same cells in different sections. Multinucleated umbrella cell borders could not always be defined, so quantification was done per nucleus, with a set ROI size used for all nuclei (roughly 2X the diameter of the nucleus). ROIs were centered on each nucleus and used to measure mean pixel intensity. Control area intensity was measured from tissue background to define an intensity cutoff for negative cells.
DRG calcium imaging
Viral strategy is previously described13. Animals were anesthetized with isoflurane and the bladder was exposed (described above). The bladder apex was opened and phlanged PE20 tubing was filled with saline and inserted as a catheter (Stoelting: 51154) into the bladder, and tied off using silk suture (Fisher Scientific: NC9140103). A syringe and lines filled with saline that were connected to the catheter was used to fill the bladder and test for leaking. The abdomen was sewn shut with the catheter extending out. The animal was flipped to prone position, and the vertebral column was exposed. A microdrill was used to open a window in the bone above the first sacral DRG. Epifluorescence imaging was performed using an upright microscope (FVMPE-RS, Olympus) equipped with a 4X, 0.28–numerical aperture air objective. Illumination was provided with a 130-W halogen light source (U-HGLGPS, Olympus), using a standard green excitation/emission filter cube. Images were acquired using an ORCA-Flash 4.0 CMOS camera (Hamamatsu, Japan) at a frame rate of 5 Hz using MetaMorph (Molecular Devices. Analysis was previously described13.
Cystometry and electromyography
Male and female mice were anesthetized by isoflurane (5% induction, 1–2% maintenance, Kent Scientific SomnoSuite) and the bladder was catheterized and connected to saline lines (described above). Tungsten electrodes were inserted directly into the urethral muscle (A-M systems: 795500). Saline lines were connected to a pressure sensor (Biopac: RX104A-MRI) which connected via pressure transducer (TSD104A) to an MP160 Biopac system amplifier (DA100C). EMG electrodes were connected to a differential amplifier (EMG100C: gain = 1000, sample rate = 10kHz, low pass filter = 5kHz, 60Hz notch filter and 100Hz high pass filter). Bladder was continuously filled at 20 μl/min using a syringe pump until regular urination cycles began. Data was not collected until the mouse had been stably cycling (30–40 min after beginning of recording), at which point filling rate was increased to 30 μl/min. Data was logged with Acqknowledge software (version 4.4.2) and processed in MATLAB (version 2018b).
Behavioral assays
Female mice were placed in normal home cages that were bottomless, set on filter paper (Fisher Scientific: 05-714-4) and left in a darkened room for 4 hours. Mice did not have access to water to prevent the water leaks from disturbing urine marks. Paper was imaged using a widefield camera (Logitech C930e) while illuminated by UV light. Images were thresholded and converted to B&W binary in ImageJ (version 2.0.0-rc-49/1.51d), and total number of black pixels was counted. A region of interest corresponding to the middle 50% of the image area was used to count the number of black pixels in the middle of the cage.
Bladder Histology
Bladders used for histology were the same bladders used for the bladder weight measurements. Wildtype and knockout littermate male bladders were collected, opened and blotted on kimwipes before weighing. After recording their freshly excised weight, they were fixed in 10% Neutral Buffered Formalin for 24 hours, and then stored in 70% ethanol. Bladders were paraffin embedded, and central cross-sections were used for Hematoxylin & Eosin staining. Processing and staining was performed by Scripps Histology Core services. Muscle layer thickness was measured in ImageJ at 7–11 different places along the muscle wall per animal perpendicular to the muscle surface, and an average thickness value is shown per mouse.
Clinical assessment
Twelve patients with PIEZO2 loss-of-function mutations from 11 families (N=4 males and 8 females, ranging in age from 4 to 43) were evaluated at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) under research protocol approved by the Institutional Review Boards of National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS, protocol 12-N-0095) between April of 2015 and May of 2020. Written informed consent and/or assent (for minor patients) was obtained from each participant in the study. All of the patients had biparentally inherited bi-allelic homozygous or compound heterozygous nonsense variants that are expected to result in a ‘null’ status for protein expression. Patients with PIEZO2 loss-of-function either found us or were referred to our group through our network of international collaborators. Genotype information can be found in Extended Data Table 1, along with past treatments and diagnoses. One patient, P10, carried a nonsense and a deleterious splice site variant in compound heterozygosity. Also as stated above, all subjects presented with a profound congenital ubiquitous lack of proprioception, vibration, and specific loss of touch discrimination on glabrous skin. Detailed history, clinical evaluation and testing were conducted including an in-depth review of urinary function, urologic history, review of previous evaluations and non-invasive bladder ultrasound. Patients were recruited from all over the world and their age ranged between 5 to 43 years (see table). 4 adult patients (3 females and 1 male) provided their own history. None of the subjects were taking any medications that could affect urinary function at the time of the questionnaire. Parents assisted with information gathering from their children.
Data Availability
The raw data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Code Availability Statement
Code for calcium imaging analysis is previously published13. Matlab (version 2018b) code used for cystometry analysis is available at: https://github.com/PatapoutianLab/cystometry.
Extended Data
Extended Data Figure 1.
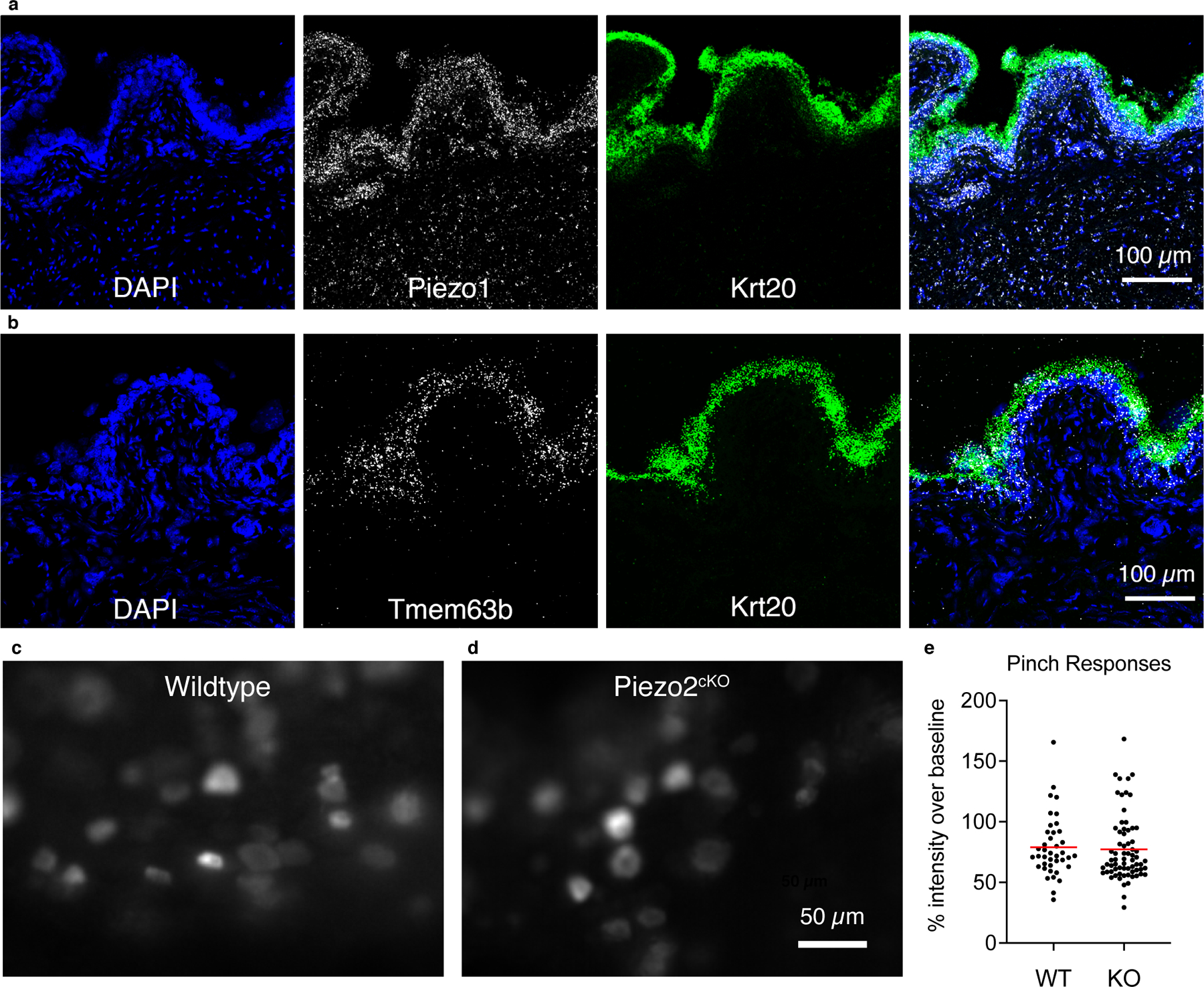
a, FISH in bladder tissue with probes against Krt20 (green) and Piezo1 (white). DAPI in blue. b, FISH in bladder tissue with probes against Krt20 (green) and Tmem63b (white). DAPI in blue. c, z-projection of the standard deviation of responses from genital pinch in WT and d, Piezo2cKO DRG. e, quantification of peak responses during pinch shown as percent of baseline (each data point is one cell). N=3 DRGs, 40 cells for WT, 4 DRGs and 69 cells for Piezo2cKO DRGs.
Extended Data Figure 2.
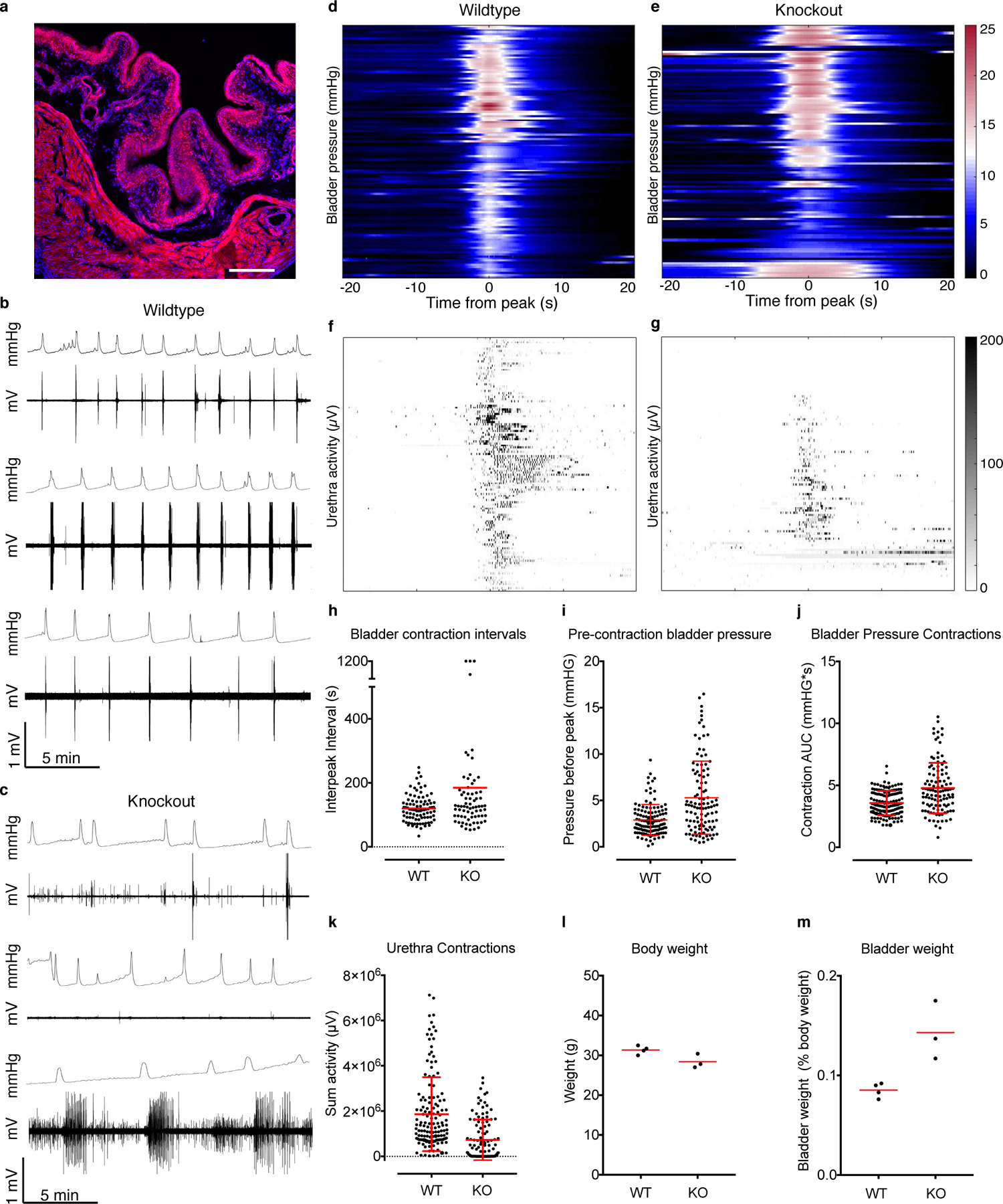
a, HoxB8Cre;Ai9 bladder tissue, fixed, frozen and mounted to show tdTomato (red) throughout the tissue, labeled with DAPI (blue). Scale is 100 μm. Expression was evaluated in two mice. b, Example pressure and urethra activity traces from three wildtype males and c, three HoxB8Cre;Piezo2f/f knockout male littermates. d, heatmap of individual bladder contraction events in wildtype and e, knockout male mice, with corresponding urethra activity below in f and g respectively. h, Bladder contraction intervals for males. i, bladder pressures five seconds before peak contraction for males. Note: 1200 s was the length of one recording. These dots represent recording periods where the animal had no successful urination events. j, Total bladder pressure for males and k, sum of urethra activity during bladder contractions. N = 6 males per group. P<0.0001 for graphs in h, i, j and k, two-sided Student’s t test with Welch’s correction. l, body weights from a subset of mice whose bladder weights are shown in Figure 2t, and m, bladder weights from animals in l, shown as a percentage of body weight. Red horizontal lines indicate means, vertical red bars indicate +/− standard deviation (shown where possible).
Extended Data Figure 3.
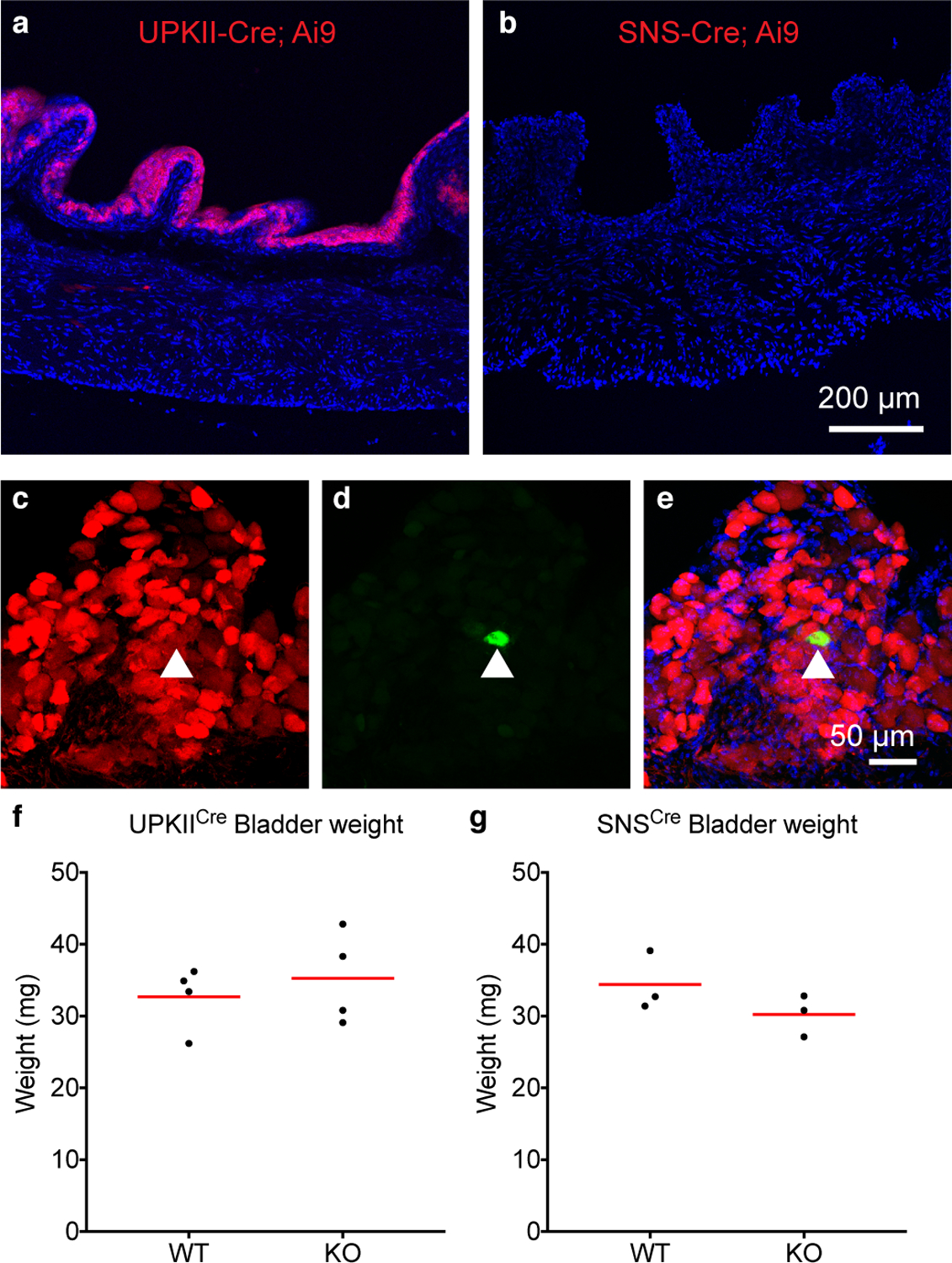
a, UPKIICre; Ai9 bladder tissue fixed, frozen and mounted to show tdTomato (red) throughout the urothelium, labeled with DAPI (blue). Expression was evaluated in two mice. b, SNSCre: Ai9 bladder tissue fixed, frozen and mounted to show tdTomato (red) is not present. Expression was evaluated in two mice. Thin cryosections made neuronal endings difficult to visualize. Scale: 200 μm, applies to a and b. c, SNSCre: Ai9 DRG tissue showing tdTomato (red) in the majority of neurons, and d, a cell backlabled with CTB-Alexa 488 injected into bladder. e, merge of c and d, DAPI in blue. 9/9 backlabeled bladder cells analyzed from two mice were tdTomato positive. f, Quantification of freshly excised bladder weights from four UPKIICre; Piezo2f/f knockout and wildtype littermates. Age-matched littermates were 10–11 months old, which could account for greater variability. g, Bladder weights from age-matched SNSCre;Piezo2f/f knockout mice and wildtype littermates, 7–8 months old. Red lines indicate mean values.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Diana Bharucha Goebel, Reghan Foley and Sandra Donkervoort for help with the clinical assessments. We also thank Dr. Shang Ma and Dr. Sierra Simpson-Dworschak for early work on the project and Dr. Evan Lacefield for helpful discussions. We thank the Scripps Histology Core for sample preparation.
Footnotes
The authors declare no competing interests.
Supplementary Information is available for this paper.
Reprints and permissions information is available at www.nature.com/reprints
References
- 1.de Groat WC & Yoshimura N Afferent nerve regulation of bladder function in health and disease. Handb Exp Pharmacol, 91–138, doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-79090-7_4 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Keller JA et al. Voluntary urination control by brainstem neurons that relax the urethral sphincter. Nat Neurosci 21, 1229–1238, doi: 10.1038/s41593-018-0204-3 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hou XH et al. Central Control Circuit for Context-Dependent Micturition. Cell 167, 73–86 e12, doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.08.073 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Garry RC, Roberts TD & Todd JK Reflex responses of the external urethral sphincter of the cat to filling of the bladder. J Physiol 139, 13–14P (1957). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cockayne DA et al. Urinary bladder hyporeflexia and reduced pain-related behaviour in P2X3-deficient mice. Nature 407, 1011–1015, doi: 10.1038/35039519 (2000). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Andersson KE, Gratzke C & Hedlund P The role of the transient receptor potential (TRP) superfamily of cation-selective channels in the management of the overactive bladder. BJU Int 106, 1114–1127, doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2010.09650.x (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Mochizuki T et al. The TRPV4 cation channel mediates stretch-evoked Ca2+ influx and ATP release in primary urothelial cell cultures. J Biol Chem 284, 21257–21264, doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.020206 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Merrill L, Gonzalez EJ, Girard BM & Vizzard MA Receptors, channels, and signalling in the urothelial sensory system in the bladder. Nat Rev Urol 13, 193–204, doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2016.13 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Apodaca G, Balestreire E & Birder LA The uroepithelial-associated sensory web. Kidney Int 72, 1057–1064, doi: 10.1038/sj.ki.5002439 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Zagorodnyuk VP, Brookes SJ, Spencer NJ & Gregory S Mechanotransduction and chemosensitivity of two major classes of bladder afferents with endings in the vicinity to the urothelium. J Physiol 587, 3523–3538, doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.172577 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Murthy SE et al. The mechanosensitive ion channel Piezo2 mediates sensitivity to mechanical pain in mice. Sci Transl Med 10, doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aat9897 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ranade SS et al. Piezo2 is the major transducer of mechanical forces for touch sensation in mice. Nature 516, 121–125, doi: 10.1038/nature13980 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Szczot M et al. PIEZO2 mediates injury-induced tactile pain in mice and humans. Sci Transl Med 10, doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aat9892 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Woo SH et al. Piezo2 is the principal mechanotransduction channel for proprioception. Nat Neurosci 18, 1756–1762, doi: 10.1038/nn.4162 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Woo SH et al. Piezo2 is required for Merkel-cell mechanotransduction. Nature 509, 622–626, doi: 10.1038/nature13251 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chesler AT et al. The Role of PIEZO2 in Human Mechanosensation. N Engl J Med 375, 1355–1364, doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1602812 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Nonomura K et al. Piezo2 senses airway stretch and mediates lung inflation-induced apnoea. Nature 541, 176–181, doi: 10.1038/nature20793 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zeng WZ et al. PIEZOs mediate neuronal sensing of blood pressure and the baroreceptor reflex. Science 362, 464–467, doi: 10.1126/science.aau6324 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Afshar K, Mirbagheri A, Scott H & MacNeily AE Development of a symptom score for dysfunctional elimination syndrome. J Urol 182, 1939–1943, doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2009.03.009 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ehrhardt A et al. Urinary Retention, Incontinence, and Dysregulation of Muscarinic Receptors in Male Mice Lacking Mras. PLoS One 10, e0141493, doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0141493 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Flum AS et al. Testosterone Modifies Alterations to Detrusor Muscle after Partial Bladder Outlet Obstruction in Juvenile Mice. Front Pediatr 5, 132, doi: 10.3389/fped.2017.00132 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Takezawa K et al. Authentic role of ATP signaling in micturition reflex. Sci Rep 6, 19585, doi: 10.1038/srep19585 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Takezawa K, Kondo M, Nonomura N & Shimada S Urothelial ATP signaling: what is its role in bladder sensation? Neurourol Urodyn 36, 966–972, doi: 10.1002/nau.23099 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ferguson DR, Kennedy I & Burton TJ ATP is released from rabbit urinary bladder epithelial cells by hydrostatic pressure changes--a possible sensory mechanism? J Physiol 505 ( Pt 2), 503–511, doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1997.503bb.x (1997). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Agarwal N, Offermanns S & Kuner R Conditional gene deletion in primary nociceptive neurons of trigeminal ganglia and dorsal root ganglia. Genesis 38, 122–129, doi: 10.1002/gene.20010 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Sengupta JN & Gebhart GF Mechanosensitive properties of pelvic nerve afferent fibers innervating the urinary bladder of the rat. J Neurophysiol 72, 2420–2430, doi: 10.1152/jn.1994.72.5.2420 (1994). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Miyamoto T et al. Functional role for Piezo1 in stretch-evoked Ca(2)(+) influx and ATP release in urothelial cell cultures. J Biol Chem 289, 16565–16575, doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.528638 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Maksimovic S et al. Epidermal Merkel cells are mechanosensory cells that tune mammalian touch receptors. Nature 509, 617–621, doi: 10.1038/nature13250 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Alcaino C et al. A population of gut epithelial enterochromaffin cells is mechanosensitive and requires Piezo2 to convert force into serotonin release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115, E7632–E7641, doi: 10.1073/pnas.1804938115 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wang EC et al. ATP and purinergic receptor-dependent membrane traffic in bladder umbrella cells. J Clin Invest 115, 2412–2422, doi: 10.1172/JCI24086 (2005). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Chen TW et al. Ultrasensitive fluorescent proteins for imaging neuronal activity. Nature 499, 295–300, doi: 10.1038/nature12354 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The raw data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.


