Figure 7:
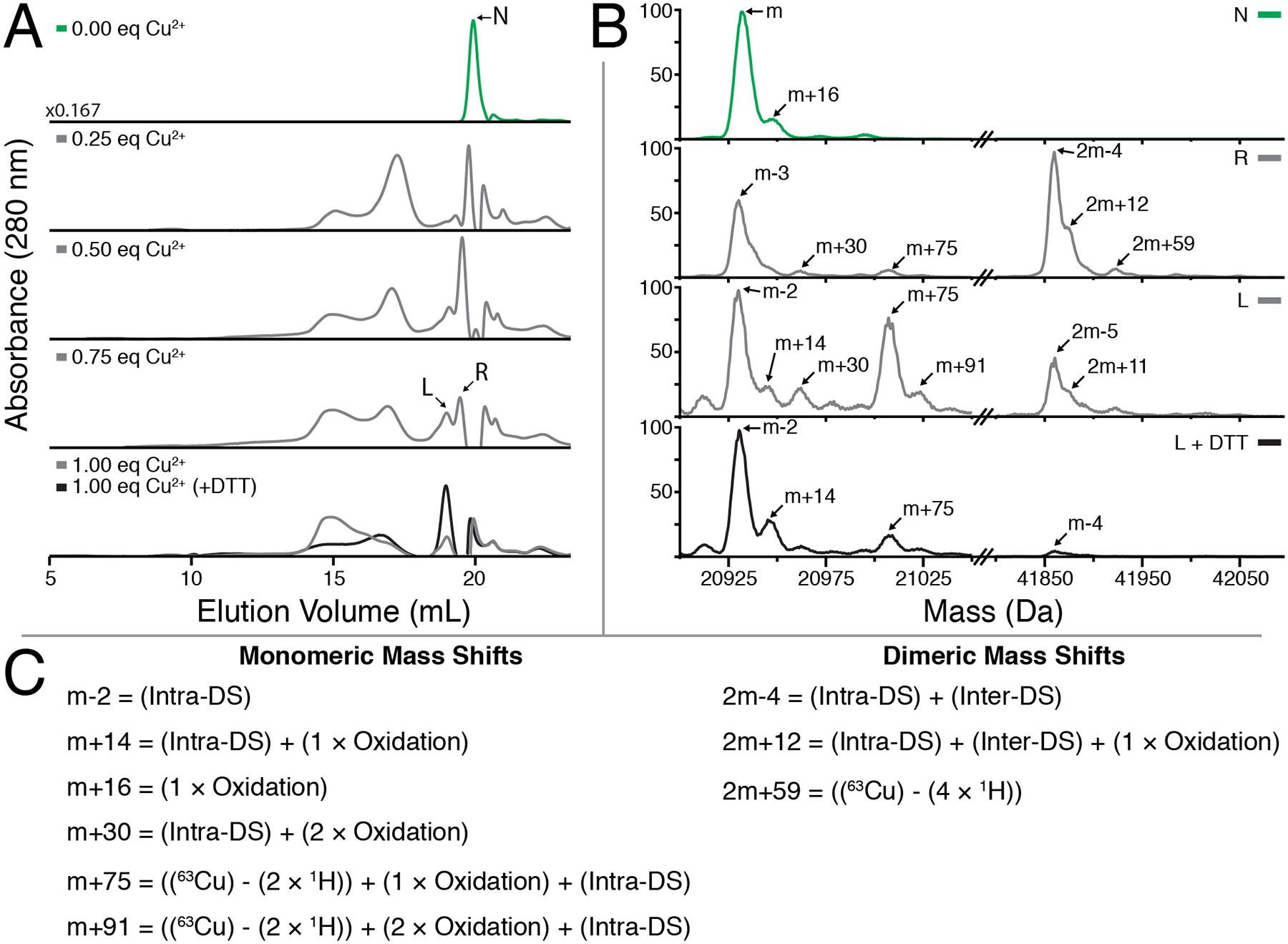
(A) Analytical SEC measurements of γS-WT treated with increasing equivalents of CuCl2 followed by excess EDTA. The addition of CuCl2 results in dimerization of γS-WT, with a shift towards high molecular weight species with increasing concentration. Formation of these larger species is partly reversible upon DTT reduction. (bottom panel). (B) Protein masses reconstructed using MaxEnt1 for individual peaks collected in (A). The untreated γS-WT (U) is strictly monomeric, whereas the fractions eluting at the same time (R) and just before (L) following Copper treatment exhibit dimer character. Reduction via DTT considerably increases the total monomeric content of the L peak. (C) Modifications accounting for the observed mass shifts observed in part (B).
