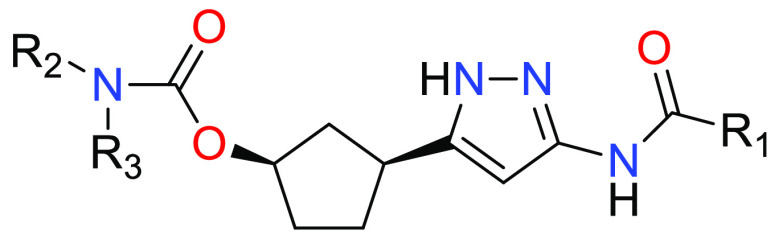
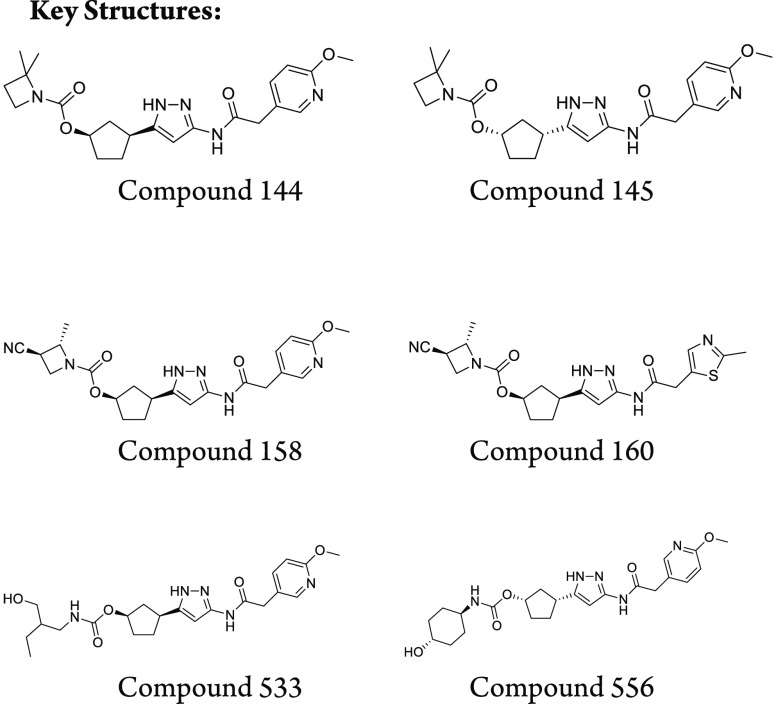
Important Compound Classes
Title
CDK2 Inhibitors
Patent Publication Number
WO 2020/157652 A2
Publication Date
August 6, 2020
Priority Application
US 62/799,455 and US 62/959,042
Priority Date
January 31, 2019 and January 9, 2020
Inventors
Behenna, D. C.; Freeman-Cook, K. D.; Hoffman, R. L.; Nagata, A.; Ninkovic, S.; Sutton, S. C.
Assignee Company
Pfizer Inc., USA
Disease Area
Cancer
Biological Target
CDK2
Summary
Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) and related serine/threonine protein kinases are important cellular enzymes that perform essential functions in regulating cell division and proliferation. CDKs 1–4, 6, 10, and 11 have been reported to play a direct role in cell cycle progression, while CDKs 3, 5, and 7–9 may play an indirect role. The CDK catalytic units are activated by binding to regulatory subunits, known as cyclins, followed by phosphorylation. Cyclins can be divided into four general classes (G1, G1/S, S, and M cyclins) whose expression levels vary at different points in the cell cycle.
Overexpression of CDK2 is associated with abnormal regulation of the cell-cycle. Cyclin E, the regulatory cyclin for CDK2, is frequently overexpressed in cancer. Cyclin E amplification or overexpression has long been associated with poor outcomes in breast cancer. Amplification or overexpression of cyclin E1 (CCNE1) is associated with poor outcomes in ovarian, gastric, endometrial, and other cancers.
The small molecule inhibitor dinaciclib inhibits CDK1, CDK2, CDK5, and CDK9 and is currently in clinical development for breast and hematological cancers. Seliciclib, which inhibits CDK2, CDK7, and CDK9 was studied in nasopharyngeal cancer. CYCO65, which inhibits CDK2 and CDK9, is in early clinical development. Despite significant efforts, there are no approved agents selectively targeting CDK2 to date. The present application describes a series of novel CDK2 inhibitors that are useful for treatment of cancer. Further, the application discloses compounds, their preparation, use, pharmaceutical composition, and treatment.
Definitions
R1 = -L1-(5–10 membered heteroaryl) or -L1-(C6–C12 aryl), where 5–10 membered heteroaryl or C6–C12 aryl is optionally substituted by one or more R4;
R2 and R3 are independently H, C1–C6 alkyl, C1–C6 fluoroalkyl, -L2-(C3–C7 cycloalkyl) or -L2-(4–7 membered heterocyclyl), where each C1–C6 alkyl and C1–C6 fluoroalkyl is optionally substituted by one or more R5 and C3–C7 cycloalkyl and 4–7 membered heterocyclyl is optionally substituted by one or more R6; or
R2 and R3 are taken together with the N atom to which they are attached to form a 4–6 membered heterocyclyl optionally containing an additional heteroatom selected from O, N(R7), and S(O)q as a ring member, where 4–6 membered heterocyclyl is optionally substituted by one or more R8;
L1 and L2 is independently a bond or a C1–C2 alkylene optionally substituted by one or more R9;
R4 = F, Cl, OH, CN, NR10R11, C1–C4 alkyl, C1–C4 fluoroalkyl, C1–C4 alkoxy, C1–C4 fluoroalkoxy, C3–C8 cycloalkyl, C(O)NR10R11, SO2R12, SO(=NH)R12 or SO2NR10R11, where each C1–C4 alkyl and C1–C4 fluoroalkyl is optionally substituted by one or more R13;
R5 = OH, C1–C4 alkoxy or NR10R11;
R6 = F, OH, C1–C4 alkyl, C1–C4 fluoroalkyl, C1–C4 alkoxy, C1–C4 fluoroalkoxy or NR10R11 where each C1–C4 alkyl, C1–C4 fluoroalkyl is optionally substituted by one or more R13;
R7 = H, C1–C4 alkyl or C(O)-C1–C4 alkyl;
R8 = F, OH, C1–C4 alkyl, C1–C4 alkoxy or CN;
R9 = F, OH, or C1–C2 alkyl;
R10 and R11 are independently H, or C1–C2 alkyl;
R12 = C1–C4 alkyl or C3–C6 cycloalkyl;
R13 = OH, C1–C4 alkoxy or NR14R15;
R14 and R15 are independently H, or C1–C2 alkyl; and
q = 0, 1 or 2.
Key Structures
Biological Assay
The CDK2/cyclin E1 and GSK3β assays were performed. The compounds described in this application were tested using a fluorescence-based microfluidic mobility shift assays to test the ability of the compounds to inhibit CDK2/cyclin E1 and GSK3β. The CDK2/cyclin E1 Ki (nM) and GSK3β Ki (nM) inhibition are shown in the following Table.
Biological Data
The Table below shows representative
compounds were tested for CDK2/cyclin E1 and GSK3β inhibition.
The biological data obtained from testing representative examples
are listed in the following table.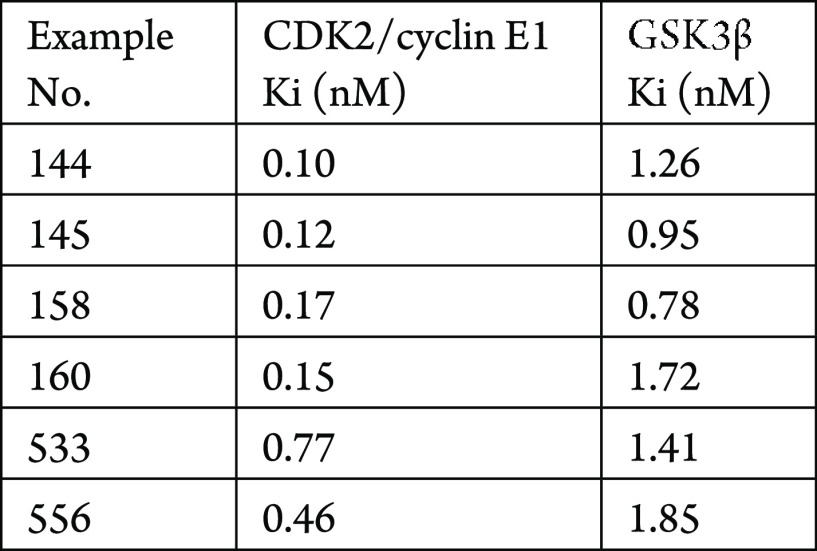
Claims
Total claims: 20
Compound claims: 18
Pharmaceutical composition claims: 1
Method of treatment claims: 1
Recent Review Articles
-
1.
Tadesse S.; Anshabo A. T.; Portman L.; Lim E.; Tilley W.; Caldon C. E.; Wang S.. Drug Discovery Today 2020, 25, 406.
-
2.
Liu Q.; Gao J.; Zhao C.; Guo Y.; Wang S.; Shen F.; Xing X.; Luo Y.. DNA Repair 2020, 85, 102702.
-
3.
Marak B. N.; Dowarah J.; Khiangte L.; Singh V. P.. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 203, 112571.
-
4.
Leal-Esteban L. C.; Fajas L.. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165715.
The author declares no competing financial interest.