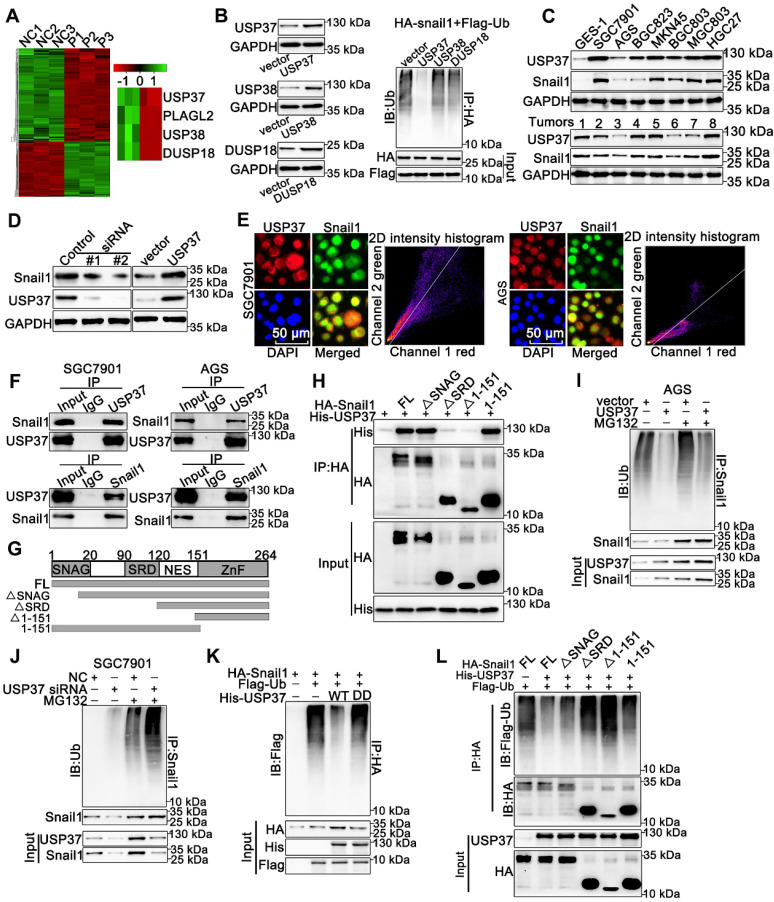
Figure 4.
USP37 interacts with and deubiquitinates Snail1 directly. (A) Microarray analysis for mRNAs was performed with RNA extracted from SGC7901 NC and SGC7901 shRNA cells. (B) Ubiquitination assays of endogenous Snail1 in HEK293T cell, which was cotransfected with HA-Snail1, Flag-Ubi, and one of the three DUBs (USP37, USP38, and DUSP18). (C) WB analysis of protein levels of USP37 and Snail1 in clinical GC specimens and human GC cell lines. (D) WB analysis of protein levels of Snail1 and USP37 in SGC7901 cells transfected with two independent USP37 siRNAs and AGS cells expressing USP37 plasmid. (E) The representative images of IF staining of Snail1 (green) and USP37 (red) were shown in SGC7901 and AGS cells. Scale bars, 50 µm. (F) Reciprocal Co-IP and WB assays indicated the interaction between endogenous USP37 and Snail1 in AGS and SGC7901 cells. (G) Schematic diagram of the Snail1 full-length and deletion mutant plasmid. (H) HEK293T cells were cotransfected with USP37-His and the full length or truncation mutants of HA-Snail1. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-HA antibody, and its production was analyzed by WB analysis with anti-His antibody (I-J) Ubiquitination assays of endogenous Snail1 in the lysates from AGS cells transfected with the USP37 plasmid (I) or AGC7901 cells transfected with the USP37 siRNA (J). (K) Ubiquitination assays of endogenous Snail1 in the lysates from HEK293T cells, which were cotransfected with the His-USP37-WT or His-USP37-DD, HA-Snail1 and Flag-Ub expressing plasmids. (L) Ubiquitination assays of endogenous Snail1 in the lysates from HEK293T cells, which were cotransfected with USP37-His and the full length or truncation mutants of HA-Snail1.