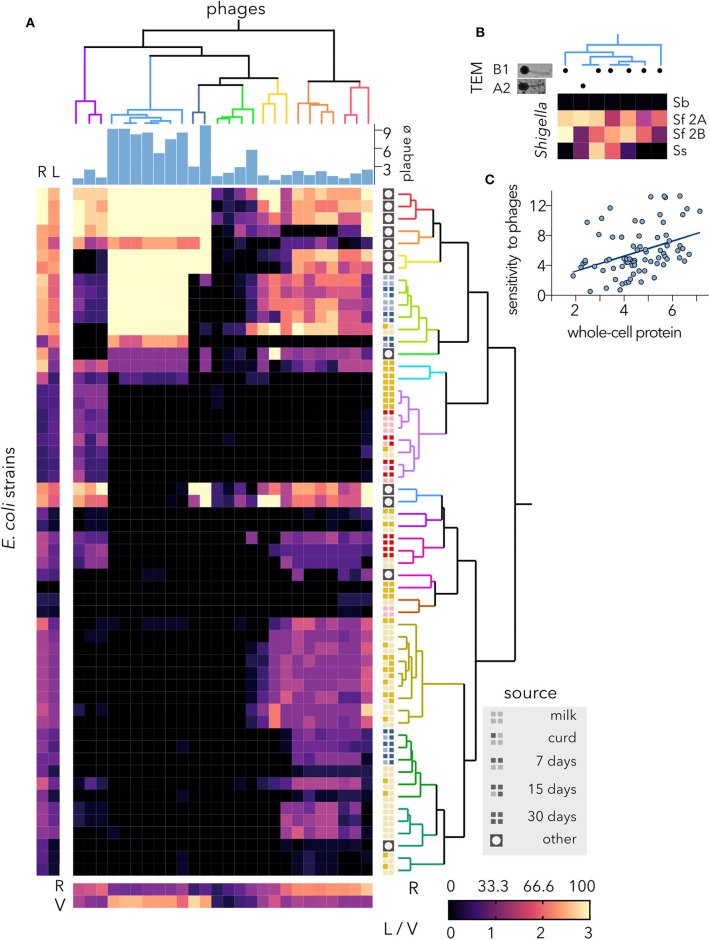
In the original article, there was a mistake in Figure 3 as published. An outdated version of the figure was published instead of the final version. Thus, panel C was wrongly labeled as B and the actual panel B was missing. The corrected Figure 3 appears below.
Figure 3.
Host range of virulent isolated phages. (A) The heatmap represents the lysis profiles of phages versus host E. coli strains. Phage infection is indicated after calculating the average clearing values of several experiments (6 > N > 2), where clearing varies between 1 and 3; 0 = no lysis. The average values for each strain are shown on the left (bacteria) and bottom (phages). The hierarchical classifications of Escherichia coli strains and coliphages were performed using Ward's method. The source of each bacterial strain is shown. The plaque diameter (mm) measured after infecting strain MG1655 is shown for each phage. R, % host range. The clearing is indicated as L (lysis) for the bacteria and V (virulence) for the phages. (B) Characterization of the coliphage cluster with the lowest infectivity variance. TEM, transmission electron microscopy; B1, Siphoviridae; A2, Myoviridae with elongated head. Lysis profiles of Shigella spp. strains. Sb, Shigella boydii; Sf 2A, Shigella flexneri 2A; Sf 2B, Shigella flexneri 2B; Ss, Shigella sonnei. (C) Correlation of SDS-PAGE and lysis profiles of cheese-isolated E. coli strains. Using the distance matrices, the correlation (r = 0.401) and statistical significance (p-value = 0.001) at an alpha of 0.05 were computed by performing a Mantel test.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.