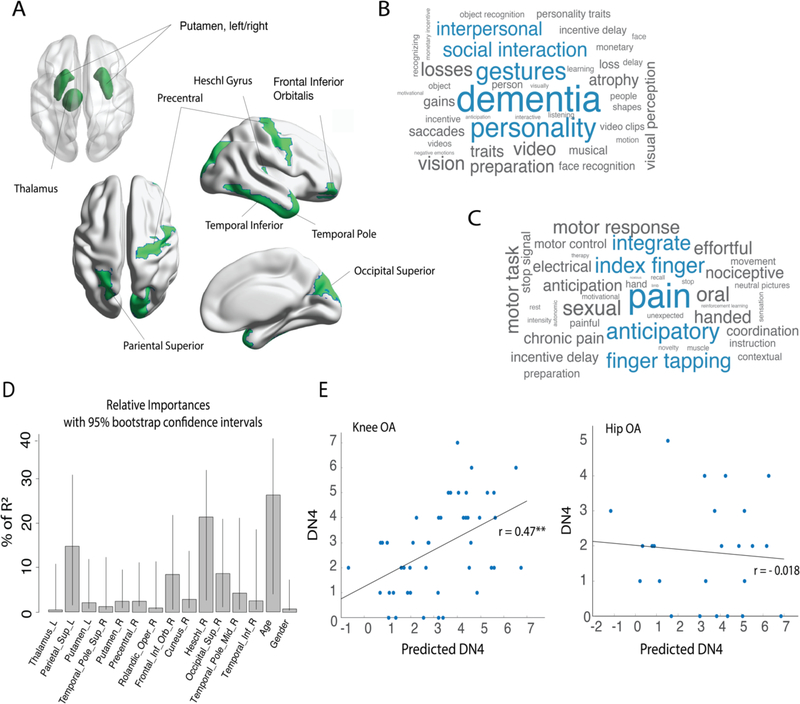
Figure 4. Neuropathic pain profile was associated with KOA multivariable brain volume changes.
A. Graphic representation of the AAL ROIs identified in the multivariable analysis (flipped brain). B. and C. plots show the top 40 (of about 1700) correlated psychological/task terms using Neurosynth reverse inference decoder for the brain regions (B) and weighted regions, given the model estimate coefficients (C). The size of a term in each word cloud is proportional to the correlation strength of term/region. Blue color represents top 5 correlations. D-E: A multiple regression model using the logistic regression/LASSO results for flipped brain KOA classification predicted neuropathic pain score (DN4) in a subsample of KOA patients (training sample, n=45). This result was validated on a KOA holdout sample (test sample, n=46), but not in the HOA group. C. shows the relative importance of all predictive variables where % of R2 is normalized to sum 100%. Bars correspond to 1000 bootstrap confidence intervals at 95%. E. shows the validation of the obtained regression model in KOA testing sample and HOA groups. Predicted neuropathic pain scale (DN4) strongly and significantly correlated with the actual score in the KOA test group, but not in the HOA. DN4 (Douleur Neuropathique en 4 questions); **p<0.001.