Abstract
Background
Macrophage-stimulating protein (MSP; also known as macrophage stimulating 1 and hepatocyte growth factor-like protein) has been shown to play a crucial role in calcium homeostasis and skeletal mineralization in zebrafish. However, the precise role of MSP in osteoblasts has not been elucidated. In this study, we investigated the effect of MSP on osteoblast differentiation of pre-osteoblast cells.
Methods
Osteoblast differentiation upon MSP treatment was evaluated by analyzing the osteogenic gene expression, alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity, and mineralized nodule formation. To assess changes in the MSP-RON signaling pathway, knockdown of Ron gene was performed using siRNA and pharmacological inhibitor treatment.
Results
Expression of the tyrosine kinase receptor RON, a receptor of MSP, was found to be significantly increased during osteoblast differentiation. MSP treatment significantly upregulated the expression of osteogenic marker genes and remarkably increased ALP activity and mineralized nodule formation. Conversely, knockdown of Ron significantly attenuated the expression of osteogenic marker genes and ALP activity that were induced upon MSP treatment. Mechanistically, MSP treatment significantly enhanced the phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK); however, additional treatment with the selective ERK inhibitor PD98059 attenuated the effect of MSP on osteoblast differentiation.
Conclusions
Altogether, these results indicate that the MSP-RON axis is involved in promoting osteoblast differentiation via activation of the ERK signaling pathway.
Keywords: Cell differentiation, Extracellular signal-regulated MAP kinases, Macrophage stimulating protein, Osteoblasts, Recepteur d’Origine Nantais
INTRODUCTION
Bone mass is regulated by a balance between bone-forming osteoblasts and bone-resorbing osteoclasts.[1] Osteoclasts originate from hematopoietic cells of the macrophage/monocyte lineage, while osteoblast precursors are derived from mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) that commit and differentiate into osteoblast, adipocytes, and chondrocytes.[2] Numerous signaling pathways within osteoblasts/osteoclasts or intercellular cross-talk maintain homeostasis, including osteoblastogenesis and osteoclastogenesis. An imbalance between osteoblast and osteoclast activity results in skeletal abnormalities, such as osteoporosis.[3] Therefore, bone disease drug development has focused on identifying specific regulatory signaling molecules.[4]
Macrophage-stimulating protein (MSP; also known as macrophage stimulating 1 (MST1) and hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)-like protein) is an 80-kDa serum protein that is synthesized in the liver and is secreted as a biologically inactive pro-MSP with plasma concentrations around 2–5 nM (about 160–400 ng/mL),[5] which is then cleaved by serum protease to form active protein.[6,7] Thus, MSP has a chance to meet various cells via blood stream and exhibits multiple biological effects. The receptor RON (MST1R, also known as STK) is a transmembrane tyrosine kinase that belongs to the HGF receptor family.[8] RON is a receptor for MSP that induces various physiological processes of macrophages and epithelial cells, such as cell spreading and chemotactic migration.[9] After binding to MSP, RON is activated by autophosphorylation of its kinase catalytic domain, leading to an array of pleiotropic effects, including tumor progression, adhesion, proliferation, and apoptosis.[9–11]
Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) belong to a family of proteins that consists of 3 family members: c-JUN N-terminal kinase (JNK), p38-MAPK, and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK1/2).[12] MAPK pathways are essential for bone homeostasis, mediating the response to a wide range of extracellular ligands relevant to osteoblast activity, such as bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), wingless-related integration site proteins, insulin-like growth factor (IGF), and fibroblast growth factors (FGFs).[13–15] In particular, ERK phosphorylates a range of substrates critical to osteoblast differentiation, and the MSP-RON axis mediates cellular responses through the ERK pathway.[16,17] MSP-RON signaling plays an important role in calcium homeostasis and skeletal mineralization in zebrafish.[18] Moreover, MSP activates the RON receptor on osteoclasts and facilitates bone resorption in mammals.[19,20] However, the role of the MSP-RON axis in osteoblast differentiation has not been identified. Specifically, the signaling pathway by which MSP regulates skeletal mineralization remains unknown. This study explored the effects of MSP on osteoblast differentiation and the underlining signaling pathways.
METHODS
1. Materials
Recombinant mouse MSP was purchased from R&D Systems (Minneapolis, MN, USA). Recombinant human BMP2 protein was obtained from Cowellmedi (Busan, Korea). For the MAPK inhibition assay, the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MEK)1/2 inhibitor (PD98059) was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Molecular biology-grade reagents were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich unless stated otherwise.
2. Tissue isolation
C57BL/6J mouse pups (Damool Science, Daejeon, Korea) were sacrificed at post-natal day 0. Bone, liver, and testis tissues were aseptically isolated from 3 pups. Each tissue was pooled for gene expression analysis. All protocols were reviewed and approved by the Animal Use and Care Committee of Chonnam National University (CNU IACUC-YB-2017-73).
3. Cell cultures
The murine MSC lineage C3H10T1/2 was purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA, USA), and maintained in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (Gibco/Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS; Gibco/Thermo Fisher Scientific) with 100 U/mL penicillin and 100 μg/mL streptomycin (Gibco/Thermo Fisher Scientific) under a humidified atmospheric condition of 5% CO2 at 37°C. Mouse bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs) were isolated from the tibias and femurs of 8-week-old C57BL/6J mice, and maintained as previously described.[21] Primary calvarial cells were prepared from newborn mice by sequential collagenase digestion, and maintained as previously described.[22] BMSCs and primary calvarial cells were cultured in α-minimal essential medium (α-MEM; Gibco/Thermo Fisher Scientific) supplemented with 10% FBS, 100 U/mL penicillin, and 100 μg/mL streptomycin. To induce osteoblast differentiation, cells were cultured in an osteogenic medium containing ascorbic acid (AA; 50 μg/mL) and β-glycerophosphate (β-GP; 5 mM) in the presence or absence of MSP (100 μg/mL). Osteogenic medium was replaced every 3 days.
4. RNA extraction and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis
Total cellular RNA was prepared using the TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, lnc., Waltham, MA, USA), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Reverse transcription was performed using a cDNA synthesis kit (iNtRON Biotechnology, Seoul, Korea). Conventional RT-PCR was performed using 0.8 mg of total RNA. Each reaction consisted of an initial denaturation at 94°C for 1 min followed by 3-step cycling: denaturation at 94°C for 30 sec, annealing at a temperature optimized for each primer pair for 30 sec, and extension at 72°C for 30 sec. After the requisite number of cycles (25–27 cycles), the reactions underwent a final extension at 72°C for 5 min. For quantitative comparison, quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) was performed using the SYBR Green kit (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) in an ABI Prism 7000 sequence detection system (ABI, Abilene, TX, USA). The reaction conditions comprised a 3 min denaturation step at 95°C for 3 min, followed by 40 cycles of 95°C for 30 sec, 55°C for 20 sec, and 60°C for 20 sec. After amplification, melting curve analysis was performed. Samples were normalized to β-actin expression. Sense and antisense primers were as follows: Ron: (forward, 5′-CTCTCCAGTGCCATCCATTT-3′; reverse 5′-ACGGAGACCTGCTTCATTTC-3′), alkaline phosphatase (Alp): (forward, 5′-ATCTTTGGTCTGGCTCCCAT-3′; reverse 5′-TTTCCCGTTCACCGTCCAC-3′), osteocalcin (Ocn): (forward, 5′-GCAATAAGGTAGTGAACAGACTC-3′; reverse, 5′-GTTTGTAGGCGGTCTTCAAGC-3′), bone sialoprotein (Bsp): (forward 5′-TTTCCCGTTCACCGTCCAC-3′; reverse 5′-ATCTTTGGTCTGGCTCCCATG-3′, osterix (Osx): (forward 5′-GTCAAGAGTCTTAGCCAAACTC-3′; reverse 5′-AAATGATGTGAGGCCAGATGG-3′), and β-actin: (sense, 5′-ACTGCTGCGACTCTG-3′; reverse, 5′-TGATGGCGAGAACAG-3′).
5. Small interfering RNA (siRNA) against Ron and transfection
To knockdown expression of the RON receptor, an RNA interference method was employed. AccuTargetTM genome-wide predesigned Ron-specific siRNA (#19882-1) and AccuTarget negative control siRNA were purchased from Bioneer (Daejeon, Korea). Cells were transfected with Ron-siRNA or control siRNA using the Lipofectamine RNAiMAX reagent (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.), according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
6. Western blot analysis
Cells were rinsed with ice-cold phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and lysed with lysis buffer containing 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), 150 mM NaCl, 1% Triton X-100, 0.1% sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), 0.5 mM ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, 10% glycerol, and protease and phosphatase inhibitors. After centrifugation at 13,000 rpm for 15 min at 4°C, protein concentrations in the supernatants were determined using a DC Protein Assay Kit (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA), and 20 μg of the total proteins was separated by SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and transferred to a polyvinylidene difluoride membranes (Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA). Membranes were blocked with 5% skim milk and incubated with anti-RON (sc-374626), anti-OSX (sc-22536), and anti-β-actin antibodies (sc-4778) (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, USA), or anti-ERK1/2 (#9102), anti-phospho-ERK1/2 (#9101), anti-p38 (#9212), anti-phospho-p38 (#9211), anti-Smad1 (#9743), and anti-phospho-Smad1/5/9 (#13820) antibodies (Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA), followed by incubation with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.). Signals were visualized using an enhanced chemiluminescence reagent (Millipore) in a LAS-4000 lumino-image analyzer system (Fujifilm, Tokyo, Japan). Blotting results are representative of 3 independent experiments.
7. Cell proliferation
Proliferation of cells cultured in the presence or absence of MSP was measured using the water-soluble tetrazolium-based assay kit (WST-1; Dojindo Laboratories, Kumamoto, Japan), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, cells were plated at a density of 2.5×103 cells/well in a 96-well microplate. Exogenous MSP was added to the microplate wells at the following concentrations; 25, 50, or 100 ng/mL, and incubated for 2 or 3 days at 37°C. After aspiration of the culture medium, α-MEM medium containing 10% FBS was placed into each well and 10 μL of the WST-1 reagent was added. Cells were incubated at 37°C for 1 hr, and the absorbance at 450 nm of the samples was measured using a multiplate reader spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.).
8. ALP activity assay
Cells were cultured in an osteogenic medium as described above. For ALP staining, cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 min at room temperature, washed with PBS, and stained with 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-phosphate/nitro blue tetrazolium solution (Sigma-Aldrich) for 20 min. For quantitative determination of ALP activity, cultured cells were washed with PBS and lysed with 0.1% Triton X-100 in 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 9.0) and then incubated with p-nitrophenyl phosphate as a substrate. The absorbance was determined at 405 nm. ALP activity was normalized to the amount of total protein.
9. Alizarin red staining (AR-S)
Cells were washed with PBS, fixed with 70% ethanol, and treated with a 40 mM AR-S solution (pH 4.2) for 10 min to visualize calcium deposits. The stained cultures were photographed, and the AR-S was then extracted using 10% (w/v) cetylpyridinium chloride in 10 mM sodium phosphate (pH 7.0) for quantification. AR-S concentrations were compared by measuring the absorbance of the samples at 540 nm on a multiplate reader spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.).
10. Statistical analysis
All data were analyzed using Prism 5 statistical software (GraphPad, La Jolla, CA, USA), and values are expressed as the mean±standard deviation (SD) of triplicate independent samples. Differences between groups were evaluated using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey post hoc test. P values less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
1. Expression of the RON receptor increases in the process of osteoblast differentiation
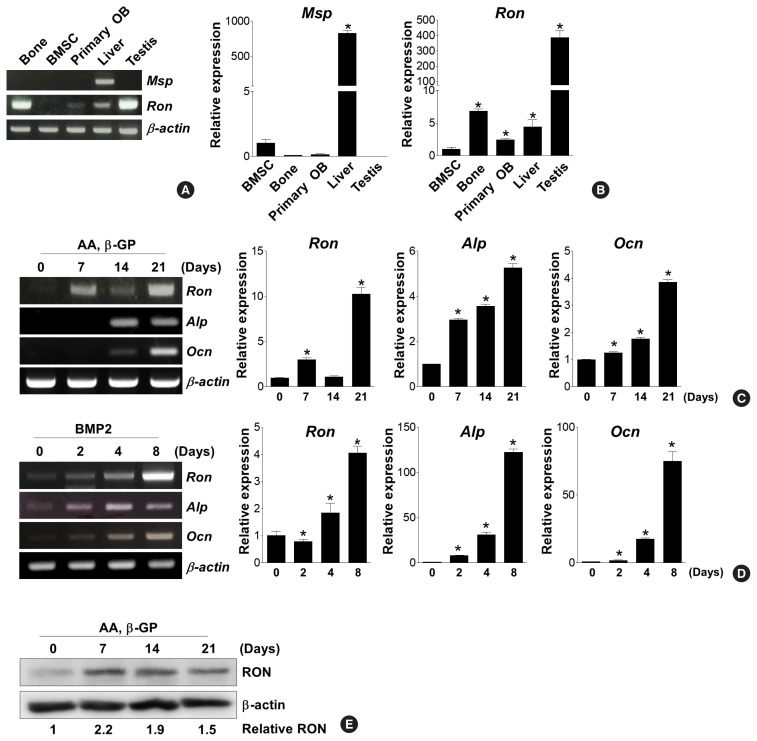
To understand whether the MSP-RON signaling axis might play a role in osteoblast differentiation, the expression profile of MSP and its receptor RON in bone tissue, primary BMSCs, and primary calvarial-derived pre-osteoblasts were investigated using both RT-PCR and qRT-PCR analyses (Fig. 1A, B). Msp mRNA expression was very low in bone tissue, BMSCs, and primary pre-osteoblasts, while Msp was highly expressed in the liver. Ron was highly expressed in bone tissue, moderately expressed in primary pre-osteoblasts, and showed very low expression in BMSCs. Tissues of the testis was used as a positive control.
Fig. 1.
Expression levels of macrophage-stimulating protein (MSP) and the RON receptor during osteoblast differentiation. (A, B) Expression profiles of MSP and its receptor RON mRNA in bone, liver, and testis, bone marrow stromal cells (BMSC), calvarial pre-osteoblasts (primary OB) from mice. Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) (A) and quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) (B) analyses were performed. Results are expressed with fold changes compared to the levels of the genes in BMSCs. (C, D) Changes in RON mRNA expression during osteoblast differentiation. Primary calvarial pre-osteoblasts were cultured with osteogenic medium, containing ascorbic acid (AA, 50 μg/mL) and β-glycerophosphate (β-GP, 5 mM) (C), or bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP2; 200 ng/mL) (D). At the indicated time points, total RNA was harvested, and then RT-PCR (left panel) and qRT-PCR (right 3 panels) were performed. Results of the qRT-PCR analysis are expressed as fold change over the control group. *P<0.05. (E) RON protein expression was evaluated using Western blotting analysis with an anti-RON antibody in AA-and β-GP-treated cells. β-actin expression is used as a loading control. Ocn, osteocalcin.
Next, we examined changes in RON expression during osteoblastic differentiation of primary pre-osteoblasts following ascorbic acid/β-GP or BMP2 stimulation. Both osteogenic stimuli significantly increased Ron mRNA expression, along with the increased of Alp and Ocn expression (Fig. 1C, D). Treatment of ascorbic acid/β-GP consistently also increased RON protein expression (Fig. 1E). These results suggest that the MSP-RON signaling pathway might be involved in osteoblast differentiation.
2. MSP treatment increases osteoblast-specific gene expression and mineralization
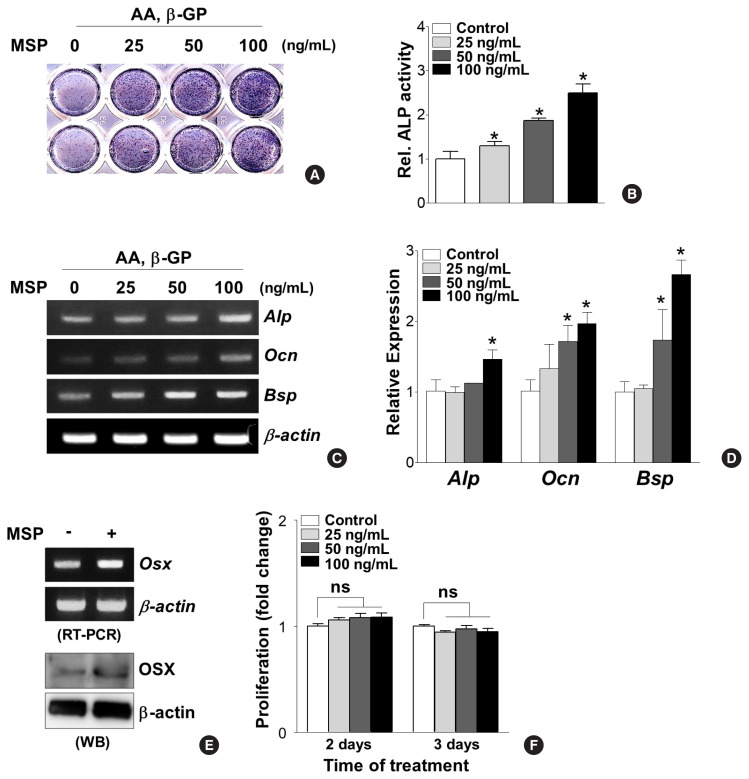
To decipher the effects of the MSP-RON pathway on osteoblast differentiation, primary pre-osteoblasts were cultured in the absence or presence of recombinant MSP (25, 50, and 100 ng/mL) and then tested for ALP activity and osteoblast-specific gene expressions. MSP treatment for 7 days dose-dependently increased ALP enzyme activity (Fig. 2A, B). Consistently, MSP treatment significantly increased Alp, Ocn, and Bsp mRNA expression (Fig. 2C, D). In addition, 100 ng/mL of MSP enhanced mRNA and protein levels of the osteoblast-specific transcription factor OSX in primary pre-osteoblasts (Fig. 2E). However, use of less than 100 ng/mL of MSP did not affect cell proliferation of primary pre-osteoblasts (Fig. 2F).
Fig. 2.
Macrophage-stimulating protein (MSP) treatment stimulates osteoblastic differentiation in primary pre-osteoblasts. (A, B) Effect of MSP treatment on alkaline phosphatase (Alp) activity. Primary pre-osteoblasts were cultured with MSP (25–100 ng/mL) in osteogenic medium, containing ascorbic acid (AA) (50 μg/mL) and β-glycerophosphate (β-GP) (5 mM) for 9 days. The cells were subjected to analyzing ALP staining analysis (A) and quantitative ALP activity (B). *P<0.05 vs. control. (C, D) Effect of MSP treatment on expression of osteoblast specific genes. Cells were cultured with MSP (25–100 ng/mL) for 6 days. Total RNA was isolated, and reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) or quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) was performed with ALP, osteocalcin (Ocn), bone sialoprotein (Bsp) primers. Their relative expression is calculated after normalization to the levels of β-actin. *P<0.05 vs. control. (E) Effect of MSP treatment on the expression of osterix (Osx). Cells were cultured with MSP (100 ng/mL) for 3 days. RT-PCR (upper panel) and Western blotting analyses (lower panel) were performed. (F) Effect of MSP on proliferation of primary pre-osteoblasts. The cells were cultured with MSP (25–100 ng/mL) for 2 and 3 days, and cell proliferation was evaluated using WST-1 assay reagents. ns, not significant.
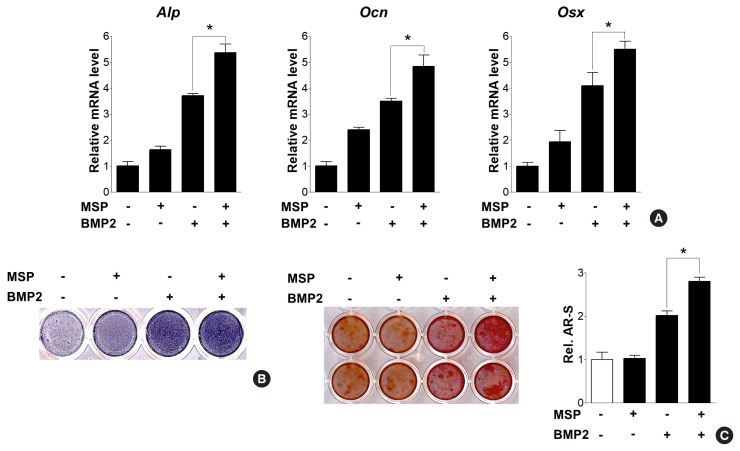
We next examined whether the addition of MSP, along with BMP2 treatment, could potentiate BMP2-induced osteoblast differentiation. Combined treatment of BMP2 and MSP further increased expression of Alp, Ocn, and Osx, and also increased ALP activity and calcium deposits, compared to treatment of each alone (Fig. 3A–C). These results suggest MSP might enhance BMP2-downstream signaling pathways and subsequent osteoblast differentiation.
Fig. 3.
Macrophage-stimulating protein (MSP) enhanced bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP2)-induced osteoblast differentiation and calcium deposition. (A) Quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) of primary osteoblasts were treated with MSP (100 ng/mL) in the presence or absence of BMP2 (50 ng/mL) for 3 days. (B) Alkaline phosphatase (Alp) staining of cells were treated with MSP or/and BMP2 for 5 days, as described above. (C) After 9 days, the cells were stained with alizarin red staining solution. To quantify calcium deposition, the stained samples were treated with 10% cetylpyridinium chloride, and the absorbance of the eluting solution was measured at 540 nm using a spectrophotometer. *P<0.05.
3. RON receptor-mediated MSP signaling enhances osteogenic differentiation
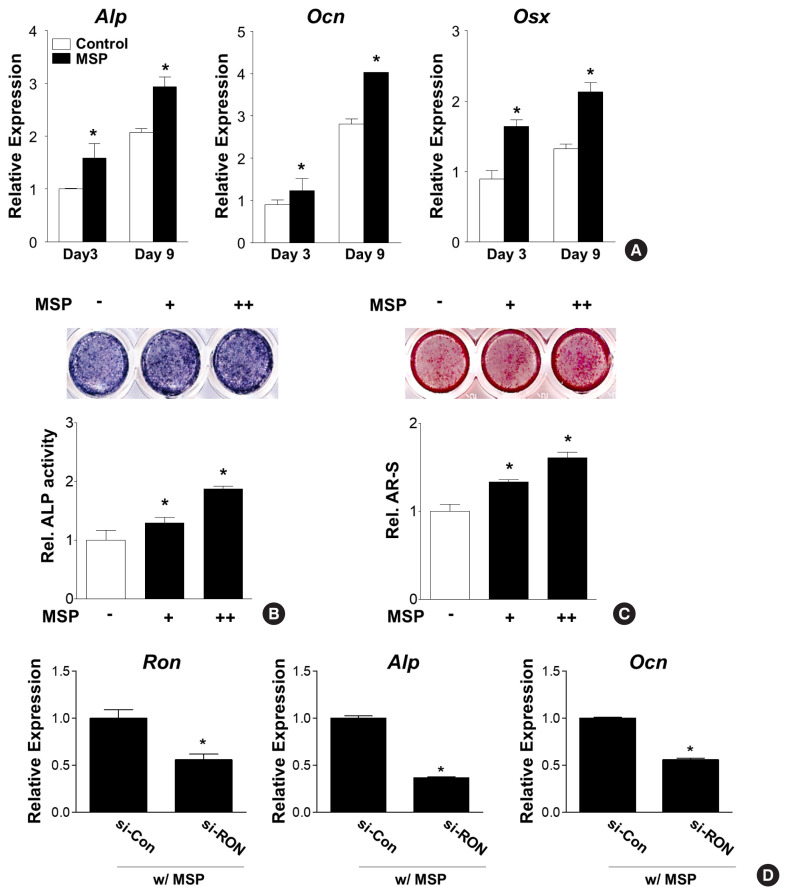
To understand the involvement of the RON receptor in MSP-treated osteoblast differentiation, a silencing experiment using Ron-specific siRNA (si-Ron) was performed. Because primary pre-osteoblasts exhibited very low transfection efficiency of si-Ron (data not shown), the silencing experiment was performed using C3H10T1/2 cells. As observed in case of primary pre-osteoblasts, C3H10T1/2 cells stimulated with MSP also showed increased expression of Alp, Ocn, and Osx (Fig. 4A), increased ALP enzyme activity (Fig. 4B), and increased calcium deposits (Fig. 4C). However, MSP-mediated Alp and Ocn gene expression were significantly suppressed in Ron-silenced cells (Fig. 4D). These results suggest that the MSP-RON signaling axis might have a stimulatory role in osteoblast differentiation.
Fig. 4.
Macrophage-stimulating protein (MSP) may stimulate osteoblast differentiation via the RON receptor in the mesenchymal lineage C3H10T1/2 cells. (A) Effects of MSP on osteoblast-specific gene expression in C3H10T1/2 cells. Cells were cultured with MSP (100 ng/mL) for 3 or 9 days. Quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was performed with alkaline phosphatase (Alp), osteocalcin (Ocn), and osterix (Osx) primers. (B) Effects of MSP on ALP activity. C3H10T1/2 cells were cultured in an osteogenic medium in the absence or presence of MSP (+:50 and ++:100 ng/mL). After 10 days, the cells were subjected to ALP staining (upper panel) and ALP activity was quantified (lower panel). (C) Effects of MSP on calcium deposition. C3H10T1/2 cells were cultured as described above. After 3 weeks, the cell cultures were stained with alizarin red solution (upper panel). For quantitative analysis, the stained samples were treated with 10% cetylpyridinium chloride solution, and absorbance was measured by spectrophotometry (lower panel). (D) Effects of si-RON on MSP-induced gene expression. C3H10T1/2 cells were transfected with si-RON (50 nM) or control siRNA, and then MSP (100 ng/mL) was added. After 48 hr, cells were harvested, and qRT-PCR analysis was performed. *P<0.05 vs. control.
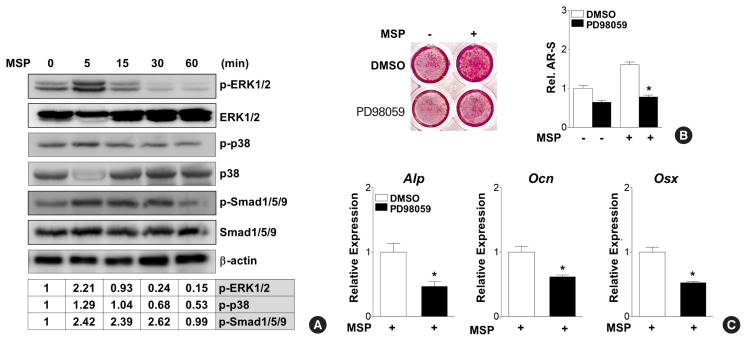
4. MSP treatment enhances osteoblast differentiation with the increased of ERK phosphorylation
The RON receptor tyrosine kinase activates numerous intracellular signaling pathway, including MAPK/ERK and β-catenin. For example, MSP activation of RON phosphorylates ribosomal S6 kinase-2 and MAPK/ERK to induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition in Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells expressing RON.[17,23] MAPK signaling pathways also play an important role in cytokine/receptor-mediated osteoblast differentiation.[24,25] Therefore, we examined whether MSP could modulate osteoblast differentiation through MAPK signaling pathways. Western blot analysis showed that MSP treatment enhanced the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and Smad1/5/9, but not p38 (Fig. 5A). In addition, pre-treatment with the ERK-specific inhibitor PD98059 significantly inhibited the MSP-induced calcium deposition (Fig. 5B). Consistent with these results, the gene expression of Alp, Ocn, and Osx with MSP exposure was attenuated by PD98059 pretreatment (Fig. 5C). These results suggest that MSP might stimulate the osteoblast differentiation, at least in part, via the ERK signaling pathway.
Fig. 5.
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling pathway mediates macrophage-stimulating protein (MSP)-induced osteoblast differentiation. (A) Western blot analysis using the indicated antibodies shows effects of MSP on several signaling molecules. C3H10T1/2 cells were treated with MSP (100 ng/mL) in non-osteogenic medium for the indicated time. Relative levels of phosphorylation of ERK1/2, p38, and Smad1/5/9 are expressed as the ratio of phosphorylated forms to total protein levels normalized to untreated control. (B) Effects of the ERK inhibitor, PD98059, on MSP induction of calcium deposition. Cells were pre-treated with the PD98059 (10 μM) in osteogenic medium, and then MSP (100 ng/mL) was added. After 21 days, the cells were stained with alizarin red solution (left panel). To quantify calcium deposition, the stained samples were reacted with 10% cetylpyridinium chloride, and the absorbance of elution solution was measured by spectrophotometry (right panel). Each bar shows 3 independent experiments. *P<0.05 vs. control. (C) Effects of an ERK specific inhibitor on MSP-treated gene expression. Cells were pre-treated with the ERK1/2 specific inhibitor PD98059 (10 μM) in osteogenic medium, and then MSP (100 ng/mL) was added. After 7 days, cells were harvested and quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was performed. Alp, alkaline phosphatase; Ocn, osteocalcin; Osx, osterix.
DISCUSSION
In this study, MSP was identified as a novel factor involved in osteoblast differentiation. The expression of the RON receptor, a tyrosine kinase receptor for MSP, was increased during osteoblast differentiation of pre-osteoblast cells, and MSP treatment dose-dependently stimulated osteoblast-specific gene expression and calcium deposition by activating the ERK pathway. Furthermore, the combination of MSP with BMP2 further increased osteoblast differentiation more than single treatment with each alone. From these findings, we hypothesized that the MSP-RON axis had a stimulatory role in osteoblast differentiation.
The RON receptor is highly expressed in bone tissue, especially in mature osteoclasts and in pre-osteoclast cells during differentiation, whereas MSP is not detected in bone tissue.[19,20,26,27] We confirmed that Msp and Ron expression patterns were consistent with previous reports; Msp was only detected in liver tissue and Ron expression was high in bone tissue. Since the RON receptor has not been detected in osteoblasts,[19] research has been focused on the role of RON in osteoclast function. This study provides the first evidence of the osteogenic function of RON by demonstrating that the expression of RON receptors was increased during osteoblast differentiation, and when MSP was present, osteoblast differentiation was promoted. MSP is mainly synthesized and secreted in liver tissue, but it is overexpressed in certain cancer types associated with bone metastasis.[19,28,29] To date, the role of the MSP-RON axis has been recognized as an important causative factor in inducing bone destruction by activating osteoclasts when cancer cells overexpressing MSP reside in bone tissue.[8, 19,20] Combining our findings with this fact, we suggest that not only bone resorption by osteoclasts but also bone formation by osteoblasts can be operated simultaneously under bone metastasis conditions. We surmise that the operation of MSP-RON axis in both cell types is an intrinsic mechanism of bone tissue for maintaining bone homeostasis. In a normal condition, the bone continuously undergoes remodeling by the process that bone-resorbing osteoclasts excavate bone and bone-depositing osteoblasts synthesize osteoid matrix that forms new bone, with no net gain or loss of bone. However, in the case of bone metastasis, this bone homeostasis is disrupted due to an out-of-balance between osteoclasts and osteoblasts actions. Here, we are speculating that this imbalance may be caused by the superiority of operation of the MSP-RON axis in osteoclasts at some point in the development of bone metastasis cancer. Based on this study, we believe that the proposed method targeting for RON inhibition to control bone destruction could lead to affect osteoblasts functions in bone microenvironment. Relevant research has recently been reported to support our concern. Osteoblasts stimulated by breast cancer cells that are metastasized to bone can inhibit the proliferation of cancer cells in the bone microenvironment depending on the stage of the bone metastasis.[30] Combined, we surmise that MSP-RON-osteoblasts actions have the potential to act as a mechanism to inhibit cancer progression as well as maintain bone homeostasis through osteoid matrix synthesis in the early stage of bone metastasis. Therefore, we would like to suggest that reconsideration and careful attention to therapeutic strategies using RON receptors as therapeutic targets are required to control bone destruction in bone metastasis.
MSP is a growth factor-like protein that has multiple biological roles, such as cell proliferation and differentiation, although the responses are dependent on the cell type and/or the expression of RON.[18] MSP treatment upregulated genes responsible for the bone formation process, while MSP treatment did not affect cell proliferation of pre-osteoblasts. Thus, MSP might stimulate osteoblasts to be mature and function by accelerating osteogenic gene expression, but not increase the osteoblast number.
Various extracellular stimuli, such as BMP2 and FGF2, stimulate osteoblast differentiation of uncommitted mesenchymal precursors and matrix mineralization via activating the ERK signaling pathway.[31–33] MSP also activates the ERK signaling pathway through the activation of the RON receptor in MDCK cells.[17] As demonstrated in this study, the MSP-RON axis activated the ERK signaling pathway in osteogenic progenitor cells and inhibition of ERK with PD98059 significantly decreased MSP-induced matrix mineralization and expression of osteoblastic marker gene. Together with the effect of silencing of the RON receptor during MSP-induced osteogenic gene expression, these findings suggest that the MSP-RON-ERK signaling pathway might be a newly discovered mechanism responsible for regulating osteoblast differentiation. Activation of the ERK signaling pathway promotes osteogenesis through the direct regulation of the stability and transcriptional activity of OSX.[31] OSX is a zinc-finger domain-containing transcription factor that regulates osteogenesis and bone formation.[34] This study also showed that MSP stimulation robustly increased OSX expression, and ERK inhibition with PD98059 significantly decreased the expression of the transcription factor Osx. These results suggested that MSP might stimulate osteoblast differentiation via ERK-OSX signal transduction, but further studies are needed to determine the direct relevance of MSP regulation of OSX expression and activity.
To date, RON has been reported as the only receptor for MSP. Despite the fact that MSP and HGF are highly homologous in sequence and structure, MSP and HGF signals to RON and c-MET, respectively.[35] The HGF-c-MET axis plays a negative role in osteoblast differentiation, and overexpression of c-MET is known to be associated with osteosarcoma,[36] implying that MSP and HGF exert opposite effects on osteoblasts. To our knowledge, it has not been examined whether MSP can substitute for HGF or whether MSP-RON and HGF-c-MET signaling separately contributes to ERK activation in in pre-osteoblast cells. Previously, our study has revealed that inhibition of c-MET potentiates osteogenic differentiation of precursor cells [37]; this suggests the possibility that the MSP-RON and HGF-c-MET axes may have a distinctly different role in pre-osteoblast cells. It was found that single MSP treatment acutely increased Smad1/5/9 phosphorylation, as well as ERK phosphorylation. ERK-mediated phosphorylation of Smad1 inhibits Smad1 activity,[38] raising the question of what the actual active state of Smad1-mediated signaling under MSP-treated conditions is. Moreover, the mechanism of how MSP treatment induces Smad1 phosphorylation is questionable. Given that Smad1 phosphorylation is induced by BMP2-activated BMP receptor, further experiments are needed to examine whether MSP affects induction of BMP2 expression or may directly stimulate BMP receptors. Related to this issue, it was shown that treatment of MSP further activated BMP2-induced osteogenic differentiation, which was likely to be an additive effect, not a synergistic effect. These results implied that MSP might affect Smad1 signaling independently of BMP2. Thus, future work will be needed to further understand the signaling mechanism of MSP in pre-osteoblast cells.
The limitations of this study are that the anabolic effects of MSP and its cellular mechanism were investigated only in the culture of osteoblasts, without understanding the physiologic role of MSP in animal studies. In other studies, global Msp-deficient mice have been found to be viable and fertile, with no apparent growth defects at birth.[39] However, mutation in the gene encoding MSP (Mst1) causes a phenotype of delayed skeletal mineralization in zebrafish.[18] Thus, to better understand the role of MSP in bone metabolism in animal models, extensive studies are needed further.
Several reports have suggested decreased bone formation as a critical mechanism of osteoporosis in liver disease.[40] Patients with cirrhosis and osteoporosis showed low levels of IGF and reduced bone formation,[41] implying that this might be the result of decreased osteoblast function. Given that MSP is mainly expressed in the liver and the potential role of MSP on osteoblast differentiation, it is possible that MSP may contribute to bone reduction in patients with liver disease. To our knowledge, however, there are no reports showing decreased MSP expression in these liver diseases. Although the expression of MSP is increased in human hepatocellular carcinoma,[42] no studies have been conducted on the effect of MSP on bone in liver cancer to date. Thus, we believe that the study on MSP-RON signaling in liver disease will provide insight into the treatment of liver disease-related bone disorders.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Korea government (MSIP) to J.T. Koh (No. 2019R1A5A2027521).
Footnotes
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All protocols were reviewed and approved by the Animal Use and Care Committee of Chonnam National University (CNU IACUC-YB-2017-73).
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
REFERENCES
- 1.Sims NA, Martin TJ. Coupling the activities of bone formation and resorption: a multitude of signals within the basic multicellular unit. Bonekey Rep. 2014;3:481. doi: 10.1038/bonekey.2013.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hu L, Yin C, Zhao F, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells: Cell fate decision to osteoblast or adipocyte and application in osteoporosis treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19 doi: 10.3390/ijms19020360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Feng X, McDonald JM. Disorders of bone remodeling. Annu Rev Pathol. 2011;6:121–45. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-011110-130203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Harada S, Rodan GA. Control of osteoblast function and regulation of bone mass. Nature. 2003;423:349–55. doi: 10.1038/nature01660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Wang MH, Ronsin C, Gesnel MC, et al. Identification of the ron gene product as the receptor for the human macrophage stimulating protein. Science. 1994;266:117–9. doi: 10.1126/science.7939629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wang MH, Gonias SL, Skeel A, et al. Proteolytic activation of single-chain precursor macrophage-stimulating protein by nerve growth factor-gamma and epidermal growth factor-binding protein, members of the kallikrein family. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:13806–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Yoshimura T, Yuhki N, Wang MH, et al. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of human macrophage stimulating protein (MSP, MST1) confirms MSP as a member of the family of kringle proteins and locates the MSP gene on chromosome 3. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:15461–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kurihara N, Iwama A, Tatsumi J, et al. Macrophage-stimulating protein activates STK receptor tyrosine kinase on osteoclasts and facilitates bone resorption by osteoclast-like cells. Blood. 1996;87:3704–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Yao HP, Zhou YQ, Zhang R, et al. MSP-RON signalling in cancer: pathogenesis and therapeutic potential. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13:466–81. doi: 10.1038/nrc3545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Iwama A, Yamaguchi N, Suda T. STK/RON receptor tyrosine kinase mediates both apoptotic and growth signals via the multifunctional docking site conserved among the HGF receptor family. EMBO J. 1996;15:5866–75. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Santoro MM, Collesi C, Grisendi S, et al. Constitutive activation of the RON gene promotes invasive growth but not transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1996;16:7072–83. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.12.7072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Cargnello M, Roux PP. Activation and function of the MAPKs and their substrates, the MAPK-activated protein kinases. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2011;75:50–83. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.00031-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ge C, Xiao G, Jiang D, et al. Critical role of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase-MAPK pathway in osteoblast differentiation and skeletal development. J Cell Biol. 2007;176:709–18. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200610046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Greenblatt MB, Shim JH, Zou W, et al. The p38 MAPK pathway is essential for skeletogenesis and bone homeostasis in mice. J Clin Invest. 2010;120:2457–73. doi: 10.1172/jci42285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Shim JH, Greenblatt MB, Zou W, et al. Schnurri-3 regulates ERK downstream of WNT signaling in osteoblasts. J Clin Invest. 2013;123:4010–22. doi: 10.1172/jci69443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Teal HE, Craici A, Paulson RF, et al. Macrophage-stimulating protein cooperates with erythropoietin to induce colony formation and MAP kinase activation in primary erythroid progenitor cells. J Hematother Stem Cell Res. 2003;12:165–77. doi: 10.1089/152581603321628313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Xiangming X, Yun Q, Guoliang Z, et al. Mechanisms of RON-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in MDCK cells through the MAPK pathway. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2011;44:634–41. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x2011007500070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Huitema LF, Renn J, Logister I, et al. Macrophage-stimulating protein and calcium homeostasis in zebrafish. FASEB J. 2012;26:4092–101. doi: 10.1096/fj.11-202663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Andrade K, Fornetti J, Zhao L, et al. RON kinase: A target for treatment of cancer-induced bone destruction and osteoporosis. Sci Transl Med. 2017;9 doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aai9338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kurihara N, Tatsumi J, Arai F, et al. Macrophage-stimulating protein (MSP) and its receptor, RON, stimulate human osteoclast activity but not proliferation: effect of MSP distinct from that of hepatocyte growth factor. Exp Hematol. 1998;26:1080–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Jeong BC, Kang IH, Hwang YC, et al. MicroRNA-194 reciprocally stimulates osteogenesis and inhibits adipogenesis via regulating COUP-TFII expression. Cell Death Dis. 2014;5:e1532. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Jeong BC, Lee YS, Bae IH, et al. The orphan nuclear receptor SHP is a positive regulator of osteoblastic bone formation. J Bone Miner Res. 2010;25:262–74. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.090718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ma Q, Guin S, Padhye SS, et al. Ribosomal protein S6 kinase (RSK)-2 as a central effector molecule in RON receptor tyrosine kinase mediated epithelial to mesenchymal transition induced by macrophage-stimulating protein. Mol Cancer. 2011;10:66. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-10-66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Mukherjee A, Rotwein P. Akt promotes BMP2-mediated osteoblast differentiation and bone development. J Cell Sci. 2009;122:716–26. doi: 10.1242/jcs.042770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Xiao G, Jiang D, Thomas P, et al. MAPK pathways activate and phosphorylate the osteoblast-specific transcription factor, Cbfa1. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:4453–9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.6.4453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Gaudino G, Avantaggiato V, Follenzi A, et al. The proto-oncogene RON is involved in development of epithelial, bone and neuro-endocrine tissues. Oncogene. 1995;11:2627–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Yang G, Zaidi M, Zhang W, et al. Functional grouping of osteoclast genes revealed through microarray analysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;366:352–9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.11.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Welm AL, Sneddon JB, Taylor C, et al. The macrophage-stimulating protein pathway promotes metastasis in a mouse model for breast cancer and predicts poor prognosis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104:7570–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0702095104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sugie S, Mukai S, Yamasaki K, et al. Plasma macrophage-stimulating protein and hepatocyte growth factor levels are associated with prostate cancer progression. Hum Cell. 2016;29:22–9. doi: 10.1007/s13577-015-0123-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kolb AD, Shupp AB, Mukhopadhyay D, et al. Osteoblasts are “educated” by crosstalk with metastatic breast cancer cells in the bone tumor microenvironment. Breast Cancer Res. 2019;21:31. doi: 10.1186/s13058-019-1117-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Choi YH, Gu YM, Oh JW, et al. Osterix is regulated by Erk1/2 during osteoblast differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;415:472–8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.10.097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Jun JH, Yoon WJ, Seo SB, et al. BMP2-activated Erk/MAP kinase stabilizes Runx2 by increasing p300 levels and histone acetyltransferase activity. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:36410–9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.142307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Park OJ, Kim HJ, Woo KM, et al. FGF2-activated ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase enhances Runx2 acetylation and stabilization. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:3568–74. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.055053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Nakashima K, Zhou X, Kunkel G, et al. The novel zinc finger-containing transcription factor osterix is required for osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Cell. 2002;108:17–29. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00622-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Follenzi A, Bakovic S, Gual P, et al. Cross-talk between the proto-oncogenes Met and Ron. Oncogene. 2000;19:3041–9. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sampson ER, Martin BA, Morris AE, et al. The orally bioavailable met inhibitor PF-2341066 inhibits osteosarcoma growth and osteolysis/matrix production in a xenograft model. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26:1283–94. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kim JW, Lee MN, Jeong BC, et al. Chemical inhibitors of c-Met receptor tyrosine kinase stimulate osteoblast differentiation and bone regeneration. Eur J Pharmacol. 2017;806:10–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.03.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Sapkota G, Alarcón C, Spagnoli FM, et al. Balancing BMP signaling through integrated inputs into the Smad1 linker. Mol Cell. 2007;25:441–54. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Bezerra JA, Carrick TL, Degen JL, et al. Biological effects of targeted inactivation of hepatocyte growth factor-like protein in mice. J Clin Invest. 1998;101:1175–83. doi: 10.1172/jci1744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Patel N, Muñoz SJ. Bone disease in cirrhosis. Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken) 2015;6:96–9. doi: 10.1002/cld.498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.George J, Ganesh HK, Acharya S, et al. Bone mineral density and disorders of mineral metabolism in chronic liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2009;15:3516–22. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.3516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Zhu M, Paddock GV. Expression of the hepatocyte growth factor-like protein gene in human hepatocellular carcinoma and interleukin-6-induced increased expression in hepatoma cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999;1449:63–72. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4889(98)00171-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]