Abstract
Heterotrimeric G-proteins are key elements of signal transduction pathways, which participate in regulating multiple biological processes in fungi including growth, conidiation, antagonism, and mycoparasitism. Among G protein subunits, Gα3 showed diverse regulatory functions in different fungi. In this study, we cloned a Gα3 subunit coding gene thga3 from T. harzianum Th33 that can antagonize Rhizoctonia solani and some other plant pathogenic fungi. A thga3 deletion strain Δthga3 was generated using the double-crossover homologous recombination strategy, and Rthga3 was generated by transforming thga3-expressing vector into the protoplasts of Δthga3 by the PEG/CaCl2-mediated method. The biological characteristics of wild-type Th33, Δthga3 and Rthga3 were evaluated. Compared with wild-type Th33, Δthga3 showed 15%, 94%, and 23% decrease in hyphal growth, conidia yield, and chitinase activity, respectively, and Δthga3 showed lower antagonistic and mycoparasitism abilities, while there were no significant differences between wild-type Th33 and Rthga3. The hyphal surface hydrophobicity of Δthga3 significantly decreased compared with those of the wild-type Th33 and Rthga3. qRT-PCR analysis revealed that transcript abundance of the hydrophobin gene (tha_09745) of Δthga3 decreased by 80% compared with that of wild-type Th33 and Rthga3. The results showed that thga3 positively regulates the growth, conidiation, hydrophobicity, chitinase activities, and mycoparasitism of Th33 towards R. solani. We hence deduced that the expression level of Tha_09745 is correlated to the hyphal hydrophobicity of Th33 and therefore affects the other biological characteristics of Th33. The findings of this report provide a foundation for elucidating the G-protein signal regulatory mechanisms of fungi.
Keywords: Thga3, Trichoderma harzianum, Conidiation, Mycoparasitism, Chitinase, Hydrophobicity
Introduction
Trichoderma spp. are widely used as biocontrol agents. Understanding their genetic regulation of biocontrol activities is beneficial to their genetic improvement and application as biofungicides. The biocontrol effects of Trichoderma preparations against plant pathogenic microorganisms are affected by a variety of factors, including development stage, environmental temperature, humidity, light, and nutrition. The current understanding of how Trichoderma senses external signals, transmits the external signals to the cells, and regulates growth and development is limited. G proteins play key roles in regulating the growth, development, reproduction, pathogenesis, and secondary metabolite biosynthesis in filamentous fungi (Nogueira et al. 2015; Lei et al. 2019). Heterotrimeric G-protein complexes consist of alpha (α), beta (β), and gamma (γ) subunits. Most filamentous fungi have three Gα subunits, namely, Gα1, Gα2, and Gα3. Different Gα subunits regulate different biological processes in fungi (Lei et al. 2019). Gα1 subunits are found more frequently and regulate vegetative growth, conidiation, and mycoparasitic responses in fungi (Rocha-Ramírez et al. 2002; Sun et al. 2016; Reithner et al. 2005). The function of Gα2 in fungi is rarely reported (Lei et al. 2019), and Gα3 subunits possess different regulatory functions, the understanding of which is based on studies on Gα3 subunits from Trichoderma spp. (Schmoll et al. 2009; Susanne et al. 2005), Penicillium spp. (García-Rico et al. 2017; Hu et al. 2013), Valsa mali (Song et al. 2017), and Fusarium spp. (Yu et al. 2008; Guo et al. 2016). These regulate the growth, conidiation, cellulase, and chitinase activities of fungi. Several Gα3 subunits from various Trichoderma strains exhibit relatively different functions. For example, GNA3 (Gα3) from T. reesei (do Nascimento et al. 2009) and GNA3 (Gα3) in T. reesei (Schmoll et al. 2009) are related to cellulase activity, while Tga3 (Gα3) in T. viride affects chitinase gene expression (Susanne et al. 2005) and Tga3 (Gα3) in T. atroviride and GNA3 (Gα3) in T. viride negatively regulate conidiation. Light seems to play a role in regulating functions of Gα3 subunits in Trichoderma (Schmoll et al. 2009; Susanne et al. 2005). Studying the functions of Ga3 subunits of different Trichoderma strains may further clarify their functions and regulatory mechanisms.
This study cloned a Th33 Gα3 gene, thga3, that can antagonize multiple plant pathogenic fungi, including Rhizoctonia solani, Fusarium spp. and Phytophthora spp. In addition, we observed that the function of this gene differs from that of previously reported Gα3. It positively regulates the growth, conidiation, and chitinase activities as well as the mycoparasitism ability of Th33 on R. solani. Both hyphal hydrophobicity and the expression of a type II hydrophobin gene Tha_09745 in Th33 are positively regulated by Thga3. These findings indicate that the hydrophobicity of Th33 is correlated to the expression of Tha_09745 and therefore influences the biological characteristics of Th33.
Materials and methods
Strains and culture conditions
The strains used in this study include wild-type T. harzianum Th33 (CGMCC No. 19906), mutant Δthga3 (thga3 deletion strain), mutant Rthga3 (thga3 complemented strain), and pathogenic fungi R. solani (ACCC No. 36124). For microscopic observation and mycelial biomass determination, strains were inoculated into potato dextrose agar (PDA) and incubated at 25 °C for 4 days. Escherichia coli Trans1-T1 competent cells were purchased from TransGen (TransGen Biotech, Beijing, China) and used for cloning and propagation of plasmids. Hygromycin B (hyg, 200 mg/mL) was added to PDA to screen Δthga3, and geneticin (G418 sulfate, 100 mg/mL) was used for screening Rthga3.
Deletion of thga3 in T. harzianum Th33
The Gα3 gene thga3 of T. harzianum Th33 was cloned from the Th33 genomic DNA (GenBank Accession Number PRJNA272949) (Sun et al. 2016). The thga3 deletion strain Δthga3 was generated by the double-crossover homologous recombination strategy. The deletion strategy is shown in Fig. 1a using the primers listed in Additional file 1: Table S1. Plasmid pKH-KO (Wang et al. 2014) was used as a transformation vector containing two uracil-specific excision reagent (USER) cloning sites, USC1 and USC2, on either side of the hygromycin B gene hyg (Wang et al. 2014). The 5′ flanking region (1,110 bp) of the thga3 coding sequence was cloned from genomic DNA of Th33 and cloned into the USC2 sites of HindIII/XhoI-digested pKH-KO using Clontech In-Fusion®HD Cloning Kit (TaKaRa). The 3′ flanking region (1036 bp) was cloned into the USC1 sites of SpeI/EcoRI-digested pKH-KO in the same orientation as that of the 5′ flanking region to generate the Thga3 disruption vector pKH-KO-thga3. The PEG/CaCl2-mediated method (Aragona and Valente, 2015) was used to generate the Δthga3 by transforming pKH-KO-thga3 into the protoplasts of wild-type Th33, and the genotypes of Δthga3 mutants were confirmed by amplifying internal fragments of thga3 (no PCR product generated), and the hyg fragment (PCR product was 1221 bp in size).
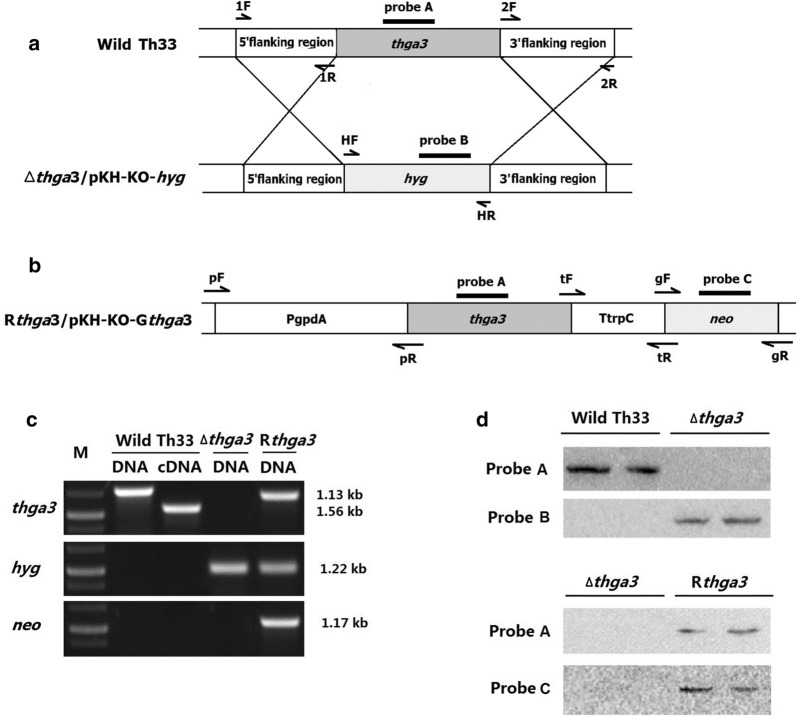
Fig. 1.
Construction of thga3 deletion and complemented mutants. a Thga3 gene deleting strategy. b Thga3 gene complementing vector pKH-KO-Gthga3. c PCR and RT-PCR identification of thga3, hyg, and neo genes in Δthga3 and Rthga3. M, 250-bp ladder. PCR templates were genomic DNA and cDNA of wild-type Th33, genomic DNAs of Δthga3 and Rthga3. d Southern hybridization analysis. Probe A. Thga3 ORF; Probe B. Hyg gene; ProbeC. Neo gene. DNAs of wild-type Th33, Δthga3 and Rthga3 were digested by EcoRI/XhoI
Complementation of thga3
To generate the complemented strain of the thga3 deletion mutant, a thga3 complementation cassette containing the promoter PgpdA, terminator TtrpC, and the coding region of thga3 was constructed. PgpdA and TtrpC fragments were amplified from the plasmid pAN7-1. The TtrpC fragment was first fused to the genome of wild-type Th33 and ligated with thga3 to produce chimeras using gene splicing by overlap extension (SOE) (Shevchuk et al. 2004). The derived chimeras were used as a template for amplifying the fragment containing thga3 and TtrpC sequences, which was then fused with the PgpdA using SOE and generated the thga3 complementation cassette, which was then cloned into SpeI/EcoRI-digested pKH-KO-G using a Clontech In-Fusion®HD cloning kit. The resulting complementing vector was designated as pKH-KO-Gthga3 (Fig. 1b). pKH-KO-Gthga3 was then transferred into Δthga3 protoplasts. The thga3 complemented strain Rthga3 was screened by G418 resistance (100 mg/mL), and the genotypes were confirmed by PCR amplifying internal fragments of thga3 and neo (G 418 resistance gene).
Reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was used to confirm the transcription of thga3 in wild-type Th33 and the mutants. Total RNA was isolated using TransZol Up Plus RNA. cDNA was prepared from total RNA using FastQuant RT kit (With gDnase) (Tiangen). R-Taq polymerase (TaKaRa) was used for PCR amplification of thga3 from cDNAs.
Southern blotting
Southern hybridization was performed using a DIG-High prime DNA labeling and detection starter kit II (Roche, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Fragments of thga3 [Probe A, 371 bp], hyg [selective marker gene, probe B (426 bp)], and neo [selective marker gene, probe C] were amplified for use as probes. DNAs of wild-type Th33 and mutants Δthga3 and Rthga3 were digested by EcoRI/XhoI. The primers used in this assay are listed in Additional file 1: Table S1.
Growth, conidiation, and hydrophobicity
Wild-type Th33, Δthga3, and Rthga3 were respectively inoculated at the center of PDA plates and cultured for 5 days at 25 °C. The colony morphology of each strain was monitored, and radial hyphal growth rates were measured daily. Twenty culture discs were collected from each culture using a cork borer (5-mm diameter) after 6 days of incubation and placed into 10 mL of sterile distilled water and vortexed. The number of spores was counted under microscope with a hemacytometer.
The hydrophobicity of hyphal surface of colonies was tested by dropping 15 μL of 0.5% aqueous aniline blue on fully grown (6 d) colonies of wild-type Th33, Δthga3, and Rthga3, and observing the disappearance of the water or dye over an 8-h period (Mukherjee and Kenerley 2010).
Antagonism and mycoparasitism assays
A dual culture technique (Dennis and Webster, 1971) was used for assessing the antagonistic activities of wild-type Th33 and its mutants against R. solani. Five-millimeter discs of Trichoderma and R. solani from 3-day-old cultures were placed in a PDA plate (90-mm diameter) 50 mm apart. A control plate was maintained with R. solani alone and incubated at room temperature (25 °C). Growth rate and colony morphology were assessed daily for six days. The percentage of growth inhibition was calculated using the equation RI = 100 × (R2—R1)/R2 (Li et al. 2019), where RI is the percentage of reduction in mycelial growth, R1 is the mycelial growth of R. solani in dual plates, and R2 is the mycelial growth of R. solani in the control. Three replicates were prepared for each treatment.
The slide culture method was used to investigate mycoparasitism of Trichoderma against R. solani. A glass microscope slide covered with a thin layer of 0.8% water agar (WA) was inoculated with 5-mm diameter mycelial discs of T. harzianum and R. solani, 10 mm apart from each other, and cultured at 25 °C. The regions where the hyphae of the two strains met were periodically observed under a light microscope as described previously (Jiang et al. 2016).
Chitinase assays
The chitinase activities of Trichoderma strains were tested on colloidal chitin agar and liquid induced medium. The composition of colloidal chitin agar was MgSO4·7H2O (3 g/L), (NH4)2SO4 (3 g/L), KH2PO4 (2 g/L), citric acid (1 g/L), Tween-80 (200 μL/L), agar (15 g/L), and 5% colloidal chitin (5.25 g/L), pH 4.7. Colloidal chitin was prepared by the method of Sakai et al. (1998). Wild-type Th33, Δthga3, and Rthga3 were inoculated independently at the center of colloidal chitin agar plates and cultured for 5 days at 25 °C. The colony growth and culture medium color changes were observed; the chitinase activity was proportional to the increasingly dark color of the medium. The chitinase activities of the wild type Th33, Δthga3, and Rthga3 in culture filtrates were determined as described elsewhere (Fernandes et al. 2013). The absorbance was measured at a wavelength of 585 nm, and one unit of enzyme (U) was defined as the amount of enzyme necessary to produce 1 mg of N-acetylglucosaminidase per gram dry weight hyphae in 1 h. The test was repeated three times.
Quantitative real-time PCR for detection of hydrophobin gene expression
Total RNA extraction and cDNA synthesis were performed as earlier described (Song et al. 2017). Primers were designed by Prime Express Software v2.0, and are listed in Additional file 2: Table S2. Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme (UCE) gene (KX686115) was used for internal standard. Quantitative real-time PCR was performed on an ViiA 7 Real time system (ABI) system using a QuantiFast SYBR Green PCR Kit (400) (Qiagen). Three parallel experiments were performed of each sample in a total volume of 16 μL. The instrument was programmed for 2 min at 95 °C, followed by 40 cycles of 10 s at 94 °C, 10 s at 60 °C, and 40 s at 72 °C.
Statistical analysis
The statistical software SAS 8.0 (SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, NC, USA) was used for ANOVA. Normality assumptions of the measured variables were checked, and no data transformation was required. Duncan's multiple range tests were used to compare the means obtained after each experiment. A value of P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. The software Origin 8 was used for drawing.
Results
Construction and validation of thga3 deleted and complemented mutants
The Thga3 gene was cloned from wild-type Th33 genome, which contains six exons and five introns and encoding 355 amino acids (GenBank Acc. No. KY937956). There was a single copy of thga3 in the wild-type Th33 genome (data not shown). The thga3 single-deleted strain Δthga3 with resistance to hygromycin B and thga3 complemented mutant Rthga3 with resistance to G418 were obtained (Fig. 1c, d). For the Δthga3 strain, the PCR analysis confirmed the existence of the hyg sequence and the absence of the thga3 sequence. Southern hybridization showed a single copy of the hyg sequence in Δthga3. For the Rthga3 strain, PCR analysis confirmed the existence of thga3, hyg, and neo sequences. Southern hybridization showed a single copy of the thga3 and neo sequence in the Rthga3 (Fig. 1c, d). The primers used for PCR, RT-PCR, and the probes for southern hybridization are listed in Additional file 1: Table S1.
Morphology, growth, and conidiation
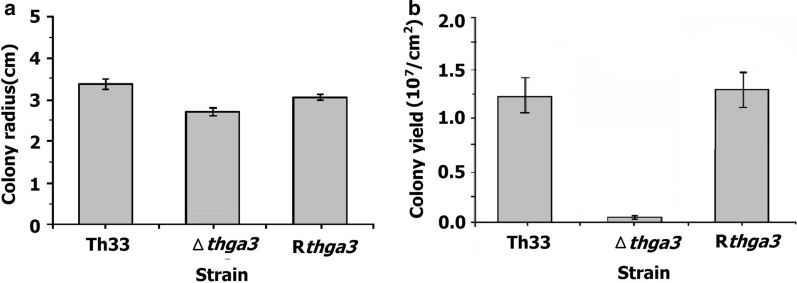
When incubated on PDA medium, there were no significant differences in colony morphology, growth, and conidiation between wild-type Th33 and Rthga3. ΔThga3 showed a 15% reduction (P < 0.001) in growth rate compared with wild-type Th33 (1.4 cm/day linear growth, compared with wild-type Th33 growth of 1.7 cm/day), when grown on PDA plates at 25 °C for 48 h (Fig. 2a), and the formation of aerial hyphae and conidia significantly decreased compared with wild-type Th33. The conidia yield of wild-type Th33, Δthga3, and Rthga3 was 1.26 ± 0.17 × 107 spores/cm2, 7.7 ± 0.58 × 105 spores/cm2, and 1.32 ± 0.01 × 107 spores/cm2, respectively, after culturing on PDA for 6 d. ΔThga3 conidia yield was approximately 94% lower (P < 0.001) than that of wild-type Th33 and Rthga3 (P < 0.0001) (Fig. 2b).
Fig. 2.
Growth and conidiation of the T. harzianum wild-type Th33, Δthga3, and Rthga3. a Growth of wild-type Th33, Δthga3, and Rthga3 on PDA for 48 h at 25 °C. b Conidia yield of wild-type Th33, Δthga3, and Rthga3, on PDA for 6 d at 25 °C. Error bars represent the SD of three determinations for two independent experiments
Antagonistic activities against R. solani
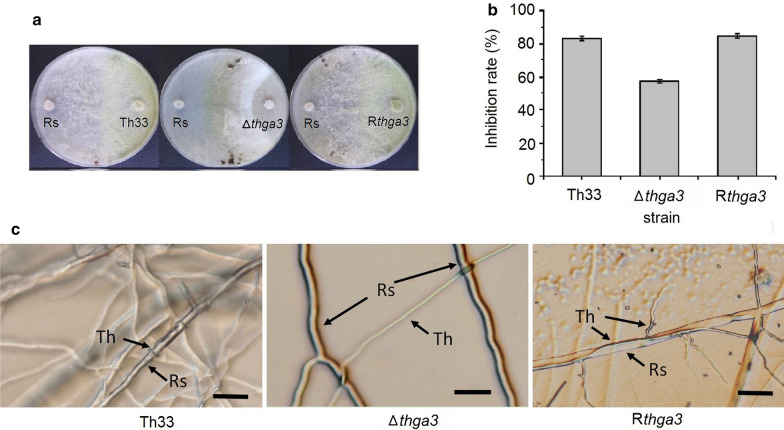
When confront cultured with R. solani, all the wild-type Th33, Δthga3, and Rthga3 could overgrow the colony of R. solani and further produce clusters of spores with different inhibitory effects (Fig. 3a). The growth inhibition ratios of wild-type Th33 and Rthga3 against R. solani were 83.83 ± 1.01% and 84.79 ± 0.90%, respectively, which were significantly higher than 58.24 ± 0.19% of Δthga3 after confront culturing for 6 d (P < 0.0001). The inhibition rate of Δthga3 decreased by about 31% compared to those of wild-type Th33 and Rthga3. The hyphae of the wild-type Th33 and Rthga3 grew around the hyphae of R. solani (Fig. 3a, c), and part of the hyphae of R. solani underwent fragmentation. In Δthga3, the hyphae of Δthga3 and R. solani grew independently and were not affected by each other, even when the hyphae of Δthga3 and R. solani came into contact, showing that Δthga3 lost its mycoparasitism ability against R. solani (Fig. 3b).
Fig. 3.
Antagonistic activities of the T. harzianum wild-type Th33, Δthga3, and Rthga3 against R. solani (Rs). a Confrontation assay of wild-type Th33, Δthga3, and Rthga3 against Rs. Cultures were grown on PDA plates for 10 d at 25 °C. b Inhibition ratio of the wild-type Th33, Δthga3, and Rthga3 on the growth of Rs (grown on PDA plates for 6 d at 25 °C); error bars represent the SD of five determinations for two independent experiments. c Mycoparasitism of wild-type Th33, Δthga3, and Rthga3 against Rs. For wild-type Th33 and Rthga3, the hyphae grew along and coiled the hyphae of Rs; for Δthga3, no coiled growth of the hyphae to the Rs was observed. Bars = 40 μm
Thga3 regulates the hyphal hydrophobicity and the expression of the hydrophobin gene
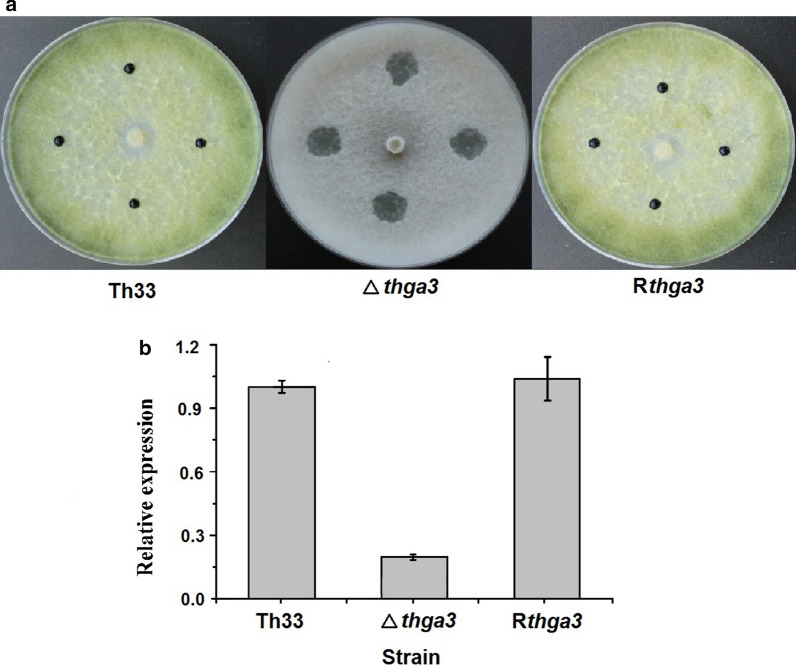
Wild-type Th33 and Rthga3 were highly hydrophobic, but Δthga3 was hydrophilic (Fig. 4a). The transcript level of the hydrophobin gene (tha_09745) of Δthga3 decreased by 80% compared with that of wild-type Th33 and Rthga3 as detected by qRT-PCR (Fig. 4b), whereas no significant differential expression of the other five hydrophobin genes was observed in Δthga3 compared with wild-type Th33 (Additional file 3: Fig. S1). The results showed that both the hydrophobicity and expression of Tha_09745 were positively regulated by Thga3, and we deduced that the expression level of Tha_09745 is correlated to the hyphal hydrophobicity of Th33.
Fig. 4.
Hydrophobicity and expression of hydrophobin gene Tha_09745 of wild-type T. harzianum Th33, Δthga3, and Rthga3. a Hydrophobicity of wild-type T. harzianum Th33, Δthga3, and Rthga3. Fifteen microliters of 0.5% aqueous aniline blue was spotted onto colonies and imaged after 8 h. b Relative expression levels of Tha_09745 in wild-type Th33, Δthga3, and Rthga3 grown on PDA plates for 7 days at 25 °C (fold-changes in mRNA expression relative to that of reference gene UCE). Error bars represent the SD of three determinations from two independent experiments
Thga3 regulates chitinase activities
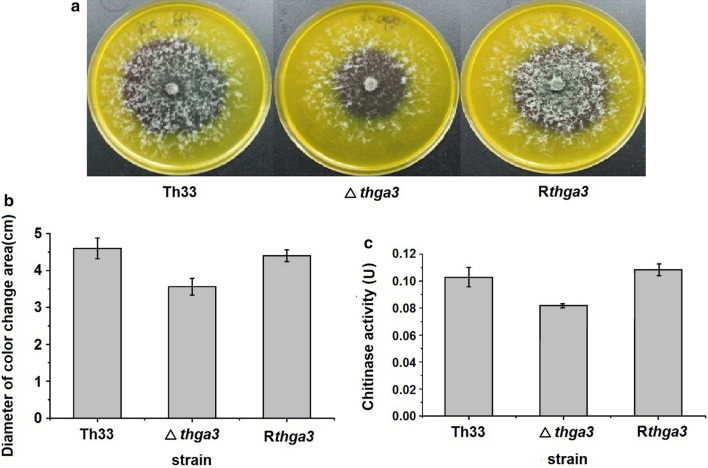
When wild-type Th33, Δthga3, and Rthga3 were growing on chitinase-inducing medium, the medium turned to dark purple with different discoloration ranges 5 days later (Fig. 5a). The diameters of purple areas of wild-type Th33 (4.6 ± 0.3 cm) and Rthga3 (4.4 ± 0.2 cm) were significantly greater than that of Δthga3 (3.6 ± 0.2 cm) (Fig. 5b). The corresponding activities of Δthga3 (82 ± 1.3 ug/h/mL) reduced by 23% compared with that of wild-type Th33 (100 ± 6.5 ug/h/mL) and Rthga3 (110 ± 5.1 ug/h/mL), showing that Thga3 positively regulated chitinase activity of Th33.
Fig. 5.
Chitinase activities of wild-type Th33, Δthga3, and Rthga3. a Discoloration of chitinase-inducing medium cultured with wild-type Th33, Δthga3, and Rthga3 at 28 °C 5 days later. b Diameter of discolored area of chitinase-inducing medium cultured with wild-type Th33, Δthga3, and Rthga3 at 28 °C 5 days later. c Chitinase activities of the culture filtrates of wild-type Th33, Δthga3, and Rthga3. Error bars represent the SD of three determinations from two independent experiments
Discussion
Gα3 subunits in various fungi possess multiple different regulatory functions. Thga3 in this study positively regulates the hyphal growth, which is similar with that of PGA3 (Gα3) in Penicillium camemberti (Hu et al. 2013), Gvm3 (Gα3) in Valsa mali (Song et al. 2017), and GanB (Gα3) in Aspergillus nidulans (Chang et al. 2004). Furthermore, FGA3 (Gα3) in Fusarium oxysporum shows no influence on vegetative growth (Guo et al. 2016). Gα3 subunits in T. viride, T. atroviride, and Rhodospirillum sp. negatively regulate conidiation (Schmoll et al. 2009; Zeilinger et al. 2005), and GanB (Gα3) in Aspergillus nidulans positively regulates conidial germination (Chang et al. 2004). Thga3 in this study positively regulates conidiation in Th33 and does not show influence on the conidial germination (data not shown).
GNA3 (Gα3) from T. reesei participates in cellulase activity and antimicrobial peptide synthesis (do Nascimento et al. 2009). Tga3 (Gα3) in T. viride and GzGPA2 (Gα3) in F. graminearum affect chitinase gene expression (Susanne et al. 2005), and PGA3 in P. decumbens regulates amylase and cellulase synthesis (Hu et al. 2013). In this study, the thga3 knockout mutant shows a lower chitinase activity than those of the wild-type Th33 and thga3-complemented mutant Rthga3, meaning that it positively regulates the chitinase activity of Th33, which is similar to Tga3 (Gα3) in T. viride and GzGPA2 (Gα3) in F. graminearum, but Thga3 shows no significant effect on cellulase and amylase activities (data not shown).
The regulatory functions of Gα3 in fungi are apparently affected by light. For example, Tga3 in T. atroviride shows hyper-conidiation in the dark with loss of tga3 (Susanne et al. 2005), and GNA3 in T. reesei itself is induced by light exposure and regulates the expression of cellulase that is in response to light (Schmoll et al. 2009). However, the regulatory functions of Thga3 on the growth, conidiation, and chitinase activity of Th33 in this study seem to have no correlation with light (data not shown).
Based on aforementioned comparison and analysis, we speculated that the role of Ga3 is diverse and complicated in different fungi species, which could influence growth, sporulation, chitinase and cellulase activities, as well as their responses to light in different strains. However, the reports concerning the function of Ga3 in fungi are still limited, and its regulation mechanism is not revealed yet. Therefore, study on the regulatory mechanisms of Ga3 will help us to uncover the difference of its function in different strains”.
T. harzianum Th33 in this study is a biocontrol fungi used in controlling plant fungal diseases caused by R. solani, Sclerotium rolfsii, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, F. oxysporum, and Pythium spp. (Sun et al. 2016). Deleting thga3 resulted in a significant decrease in antagonistic and mycoparasitic ability, which is similar to GzGPA2 in F. graminearum, wherein deletion of GzGPA2 caused reduced pathogenicity and increased chitin accumulation in the cell wall (Yu et al. 2008). Chitinase was reported to have antifungal activities (Lorito et al. 1993). We thus deduced that the reduced chitinase activities of Δthga3 reduces the antagonistic and mycoparasitic ability of Trichoderma against R. solani.
Hydrophobins are small cysteine-rich surface active proteins produced by fungi on the outer surface of cell walls. The roles of hydrophobins in surface hydrophobicity, conidiation, fruit body formation, recognition, and adhesion onto the host surface and virulence have been investigated (Dubey et al. 2014; Minenko et al. 2014; Zhang et al. 2011). In this study, wild-type Th33 and Rthga3 are hydrophobic, whereas the hyphae of Δthga3 is hydrophilic. The Th33 genome (GenBank Acc. No. PRJNA272949) harbors six hydrophobin-encoding genes. We detected the expressions of all of the six hydrophobin genes in wild-type Th33, Δthga3, and Rthga3 (data not shown). Only the expression of Tha_09745 significantly decreased in Δthga3 compared with wild-type Th33 and Rthga3, and there was no significant difference between wild-type Th33 and Rthga3, which corresponded with the hydrophobicity phenotype of the strains. We deduced that the expression level of Tha_09745 is correlated to the hyphal hydrophobicity of Th33, and loss of hydrophobicity may affect the surface recognition and mycoparasitism of Th33 against R. solani, although this requires further investigation.
Both G proteins and hydrophobin in fungi have a variety of regulatory functions, and numerous studies on this property have been conducted (Huang et al. 2015; Espino-rammer et al. 2013; Khalesi et al. 2015). However, studies on the correlation between the G proteins and hydrophobin in fungi are limited, Segers and Nuss (2003) reported that Gα negatively regulated hydrophobin gene expression in the chestnut blight fungus Cryphonectria parasitica. In this study, we found for the first time that Gα in Trichoderma positively regulates the expression of the hydrophobin gene and hyphal hydrophobicity, which is also correlated to the growth, conidiation, and mycoparasitism of Th33. Our findings may be used in future studies on the regulatory mechanism of the G signal system in fungi.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Table S1. Primers used for deletion and complementation of Thga3.
Additional file 2: Table S2. Primers for qRT-PCR detection the expression of six hydrophobin genes and UCE (ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme) gene as reference gene in wild-type Th33 and thga3 deletion strain Δthga3.
Additional file 3: Figure S1. The relative expression of the five hydrophobin genes in wild-type Th33 and Δthga3.
Acknowledgments
We thank LetPub (https://www.letpub.com) for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
Authors’ contributions
Experimental design and planning were performed by ML. Experiments were executed and data was processed by JD, JM, PH, YT and YL. Data analysis was done by ML and XJ. The article was written by ML. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31371983) and the National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFD0200900).
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Jie Mei, Email: limei@caas.cn.
Yao Liang, Email: jiangxiliang@caas.cn.
Xiliang Jiang, Email: jiangxiliang@caas.cn.
Mei Li, Email: limei@caas.cn.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s13568-020-01162-9.
References
- Aragona M, Valente MT. Genetic transformation of the tomato pathogen Pyrenochaeta lycopersici allowed gene knockout using a split-marker approach. Curr Genet. 2015;61:1–10. doi: 10.1007/s00294-014-0461-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang MH, Chae KS, Han DM. The GanB Gα-protein negatively regulates asexual conidiation and plays a positive role in conidial germination in Aspergillus nidulans. Genetics. 2004;167:1305–1315. doi: 10.1534/genetics.103.025379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis C, Webster J. Antagonistic properties of species groups of Trichoderma: 1. Production of non volatile metabolites. Trans Br Mycol Soc. 1971;57:25–39. doi: 10.1016/S0007-1536(71)80077-3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- do Nascimento Silva R, Steindorff AS, Ulhoa CJ, Félix CR. Involvement of G-alpha protein GNA3 in production of cell wall-degrading enzymes by Trichoderma reesei (Hypocrea jecorina) during mycoparasitism against Pythium ultimum. Biotechnol Lett. 2009;31:531–536. doi: 10.1007/s10529-008-9900-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubey MK, Jensen DF, Karlsson M. Hydrophobins are required for conidial hydrophobicity and plant root colonization in the fungal biocontrol agent Clonostachys rosea. BMC Microbiol. 2014;14:18. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-14-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espino-rammer L, Ribitsch D, Przylucka A, Marold A, Greimel KJ, Acero H. Two novel class II hydrophobins from Trichoderma spp. stimulate enzymatic hydrolysis of poly (ethylene terephthalate) when expressed as fusion proteins. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013;79:4230–4238. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01132-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes KF, Cortijotriviño D, Batista KA, Ulhoa CJ, Garcíaruiz PA. Chitin hydrolysis assisted by cell wall degrading enzymes immobilized of Trichoderma asperellum on totally cinnamoylated d-sorbitol beads. Mat Sci Eng C. 2013;33:3077–3081. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2013.03.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Rico RO, Gil-Duran C, Rojas-Aedo JF, Vaca I, Figueroa L, Levican G, Chávez R. Heterotrimeric G protein alpha subunit controls growth, stress response, extracellular protease activity, and cyclopiazonic acid production in Penicillium camemberti. Fungal Biol. 2017;121:754–762. doi: 10.1016/j.funbio.2017.05.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo L, Yang Y, Yang L, Wang F, Wang G, Huang J. Functional analysis of the G-protein α subunits FGA1 and FGA3 in the banana pathogen Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol. 2016;94:75–82. doi: 10.1016/j.pmpp.2016.04.003. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Y, Liu G, Li Z, Qin Y, Qu Y, Song X. G protein-cAMP signaling pathway mediated by PGA3 plays different roles in regulating the expressions of amylases and cellulases in Penicillium decumbens. Fungal Genet Biol. 2013;59:62–70. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2013.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Y, Mijiti G, Wang Z, Yu W, Fan H, Zhang R, Liu Z. Functional analysis of the class II hydrophobin gene HFB2-6 from the biocontrol agent Trichoderma asperellum ACCC30536. Microbiol Res. 2015;171:8–20. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2014.12.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang H, ZhangL ZJZ, Ojaghian MR, Hyde KD. Antagonistic interaction between Trichoderma asperellum and Phytophthora capsici in vitro. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2016;17:271–281. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1500243. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Khalesi M, Gebruers K, Derdelinckx G. Recent advances in fungal hydrophobin towards using in industry. Protein J. 2015;34:243–255. doi: 10.1007/s10930-015-9621-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lei M, Liu J, Fang Y, Shao Y, Li L, Yu J, Chen F. Effects of different G-protein α-subunits on growth, development and secondary metabolism of Monascus ruber M7. Front Microbiol. 2019;10:1555. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li M, Ma G, Lian H, Su X, Tian Y, Huang W, Mei J, Jiang X. The effects of Trichoderma on preventing cucumber fusarium wilt and regulating cucumber physiology. J Integr Agric. 2019;18:607–617. doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(18)62057-X. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Lorito M, Harman GE, Hayes CK, Broadway RM, Tronsmo A, Woo SL, Pietro AD. Chitinolytic enzymes produced by Trichoderma harzianum: antifungal activity of purified endochitinase and chitobiosidase. Mol Plant Pathol. 1993;83:303–307. [Google Scholar]
- Minenko E, Vogel RF, Niessen L. Significance of the class II hydrophobin FgHyd5p for the life cycle of Fusarium graminearum. Fungal Biol. 2014;118:385–393. doi: 10.1016/j.funbio.2014.02.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee PK, Kenerley CM. Regulation of morphogenesis and biocontrol properties in Trichoderma virens by a VEL. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010;76:2345–2352. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02391-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira KMV, Costa MdN, de Paula RG, Mendonça-Natividade FC, Ricci-Azevedo R, Silva RN. Evidence of cAMP involvement in cellobiohydrolase expression and secretion by Trichoderma reesei in presence of the inducer sophorose. BMC Microbiol. 2015;15:195. doi: 10.1186/s12866-015-0536-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reithner B, Brunner K, Schuhmacher R, Peissl I, Seidl V, Krska R, Zeilinger S. The G protein α subunit tga1 of Trichoderma atroviride is involved in chitinase formation and differential production of antifungal metabolites. Fungal Genet Biol. 2005;42:749–760. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2005.04.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocha-Ramírez V, Omero C, Chet I, Horwitz BA, Herrera-Estrella A. Trichoderma atroviride G-protein α-subunit gene tga1 is involved in mycoparasitic coiling and conidiation. Eukaryot Cell. 2002;1:594–605. doi: 10.1128/EC.1.4.594-605.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai K, Yokota A, Kurokawa H, Wakayama M, Moriguchi M. Purification and characterization of three thermostable endochitinases of a noble bacillus strain, mh-1, isolated from chitin. Appl Environ Microb. 1998;64:3397–3402. doi: 10.1128/AEM.64.9.3397-3402.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmoll M, Schuster A, Silva R, Kubicek CP. The G-alpha protein GNA3 of Hypocrea jecorina (Anamorph Trichoderma reesei) regulates cellulase gene expression in the presence of light. Commun Integr Biol. 2009;8:410–420. doi: 10.1128/EC.00256-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segers GC, Nuss DL. Constitutively activated Gα negatively regulates virulence, reproduction and hydrophobin gene expression in the chestnut blight fungus Cryphonectria parasitica. Fungal Genet Biol. 2003;38:198–208. doi: 10.1016/S1087-1845(02)00534-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shevchuk NA, Bryksin AV, Nusinovich YA, Cabello FC, Sutherland M, Ladisch S. Construction of long DNA molecules using long PCR-based fusion of several fragments simultaneously. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;32:e19. doi: 10.1093/nar/gnh014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song N, Dai Q, Zhu B, Wu Y, Xu M, Voegele RT, Gao X, Kang Z, Huang L. Gα proteins Gvm2 and Gvm3 regulate vegetative growth, asexual development, and pathogenicityon apple in Valsa mali. PLoS ONE. 2017;7:e0173141. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0173141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun Q, Jiang X, Pang L, Wang L, Li M. Functions of thga1 gene in Trichoderma harzianum based on transcriptome analysis. BioMed Res Int. 2016 doi: 10.1155/2016/8329513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Susanne Z, Barbara R, Valeria S, Isabel P, Matteo L, Robert LM. Signal transduction by Tga3, a novel G protein subunit of Trichoderma atroviride. Appl Environ Microb. 2005;71:1591–1597. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.3.1591-1597.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X, Zhang H, Pan Y, Xu J, Xu J, Feng J. Effective universal vectors building for gene knockout and fluorescent expression in Fusarium graminearum. Plant Protect. 2014;40:106–112. [Google Scholar]
- Yu HY, Seo JA, Kim JE, Han KH, Shim WB, Yun SH, Lee YW. Functional analyses of heterotrimeric G protein G alpha and G beta subunits in Gibberella zeae. Microbiol. 2008;154:392–401. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2007/012260-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeilinger S, Reithner B, Scala V, Peissl I, Lorito M, Mach RL. Signal transduction by Tga3, a novel G protein α subunit of Trichoderma atroviride. Appl Environ Microb. 2005;71:1591–1597. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.3.1591-1597.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang S, Yu X, Kim B, Nemat OK. Two hydrophobins are involved in fungal spore coat rodlet layer assembly and each play distinct roles in surface interactions, development and pathogenesis in the entomopathogenic fungus, Beauveria bassiana. Mol Microbiol. 2011;80:811–826. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07613.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1: Table S1. Primers used for deletion and complementation of Thga3.
Additional file 2: Table S2. Primers for qRT-PCR detection the expression of six hydrophobin genes and UCE (ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme) gene as reference gene in wild-type Th33 and thga3 deletion strain Δthga3.
Additional file 3: Figure S1. The relative expression of the five hydrophobin genes in wild-type Th33 and Δthga3.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.