Abstract
Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) fruits are typically red at ripening, with high levels of carotenoids and a low content in flavonoids. Considerable work has been done to enrich the spectrum of their health-beneficial phytochemicals, and interspecific crosses with wild species have successfully led to purple anthocyanin-colored fruits. The Aft (Anthocyanin fruit) tomato accession inherited from Solanum chilense the ability to accumulate anthocyanins in fruit peel through the introgression of loci controlling anthocyanin pigmentation, including four R2R3 MYB transcription factor-encoding genes. Here, we carried out a comparative functional analysis of these transcription factors in wild-type and Aft plants, and tested their ability to take part in the transcriptional complexes that regulate the biosynthetic pathway and their efficiency in inducing anthocyanin pigmentation. Significant differences emerged for SlAN2like, both in the expression level and protein functionality, with splicing mutations determining a complete loss of function of the wild-type protein. This transcription factor thus appears to play a key role in the anthocyanin fruit pigmentation. Our data provide new clues to the long-awaited genetic basis of the Aft phenotype and contribute to understand why domesticated tomato fruits display a homogeneous red coloration without the typical purple streaks observed in wild tomato species.
Key words: Solanum lycopersicum, tomato, Aft, anthocyanin, R2R3 MYB transcription factors, MBW complex
The Anthocyanin fruit (Aft) tomato line accumulates anthocyanins in fruit peel through the introgression of R2R3 MYB genes from Solanum chilense. A comparative functional analysis of these genes revealed important differences for one of them, SlAN2like, between wild-type and Aft plants. Remarkably, splicing mutations in the wild-type allele determine a loss of function of the protein, explaining why domesticated tomato does not synthesize anthocyanins in its fruits.
Introduction
Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) is the most consumed vegetable worldwide, contributing 14% of global vegetable production (FAO, 2010). It belongs to the Solanaceae family, and is the only domesticated species within the 14 of the tomato clade (Solanum genus, section Lycopersicon) (Bedinger et al., 2011). It was first cultivated in the pre-Columbian era in Central–South America, where it originated. In the 16th century it was introduced to Europe as an ornamental plant, and only two centuries later did its cultivation for human consumption gradually spread (Peralta and Spooner, 2007). The domestication of tomato experienced repeated bottlenecks, which strongly reduced its genetic diversity. Today it represents only 5% of the genetic diversity in the wild relative Solanum species (Bai and Lindhout, 2007), which thus constitute an invaluable reserve of genetic variability. Although there may be reproductive barriers (Bedinger et al., 2011), interspecific crosses can be carried out to improve tomato performance with new genes and allelic variants.
Human selection has progressively changed many of the original traits of tomato plants, also producing a wide variation in fruit size, morphology, and color. S. lycopersicum, as well as Solanum pimpinellifolium, Solanum galapagense, and Solanum cheesmaniae, bear orange/red fruits, with carotenoids as major pigments. The other Solanum species produce green fruits, which under favorable conditions display purple pigmentation on the peel (Bedinger et al., 2011). The purple color is conferred by the accumulation of anthocyanins, polyphenolic secondary metabolites belonging to the class of flavonoids (Liu et al., 2018).
Cultivated tomato cannot produce purple fruits: flavonoid biosynthesis is interrupted with the accumulation of intermediate compounds (mainly naringenin chalcone and the flavonol glycosides rutin and kaempferol-3-O-rutinoside) (Bovy et al., 2002), probably due to an inefficient activation of the pathway (Povero et al., 2011). However, due to their increasingly recognized health-promoting effects (Martin et al., 2011, Liu et al., 2017), considerable work has been done in recent years to enrich tomatoes with anthocyanins (Gonzali et al., 2009, Martí et al., 2016). Along with transgenic approaches (Butelli et al., 2008), biodiversity has been exploited with positive results (Mes et al., 2008, Gonzali et al., 2009).
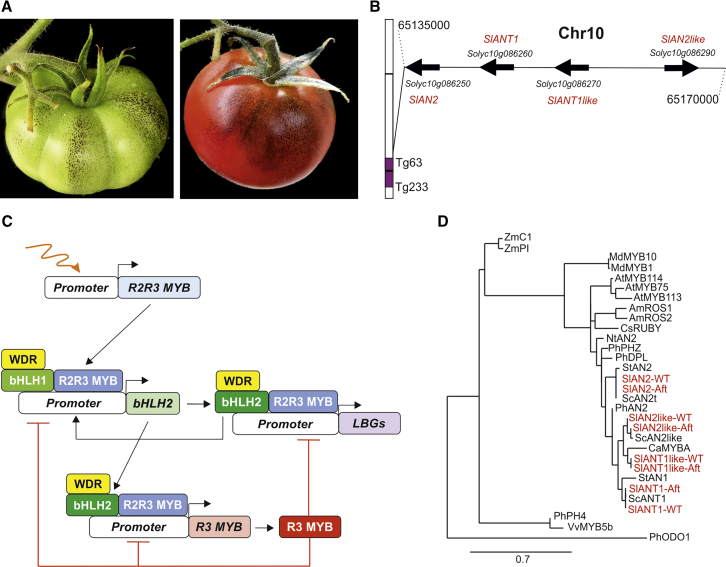
The Aft (Anthocyanin fruit) line, selected in a segregant progeny from a cross between S. lycopersicum and Solanum chilense (Georgiev, 1972), is one of the genotypes mostly commonly used in tomato breeding to obtain purple-peel fruits (Mes et al., 2008, Gonzali et al., 2009, Myers, 2012). In Aft, anthocyanin-spotted fruits are produced upon intense light exposure (Figure 1A). The phenotype is associated with a genomic region mapped on the distal part of the long arm of chromosome 10 (Mes et al., 2008, Sapir et al., 2008) (Figure 1B), introgressed from S. chilense. In this genomic region there therefore needs to be a major locus controlling fruit anthocyanin pigmentation. Interestingly, a major quantitative trait locus responsible for most of the phenotypic variations in fruit anthocyanin content is already known to be in chromosome 10 of eggplant, and both the flower and tuber skin color of potato have been associated with genes mapped on chromosome 10 (Doganlar et al., 2002). Genetic mapping studies in pepper have identified a major region in chromosome 10 containing genes related to the accumulation of anthocyanins in the fruit (Wang et al., 2018). The association of fruit anthocyanin pigmentation with chromosome 10 observed in Aft tomato thus appears to be strongly conserved in domesticated Solanaceae.
Figure 1.
Anthocyanin Synthesis in Aft Tomato Is Associated with Four R2R3 MYB Genes Introgressed into Chromosome 10.
(A)Aft tomato fruit at mature green (left) and red ripening (right) stages.
(B) Location of the four R2R3 MYB encoding genes in the distal part of the long arm of chromosome 10 introgressed into Aft from Solanum chilense.
(C) Model describing the regulatory mechanism controlling anthocyanin synthesis in dicots. Wavy orange arrow represents inductive environmental or developmental stimuli that trigger anthocyanin production. Black arrows indicate activation. Red lines indicate repression. Adapted from Albert et al. (2014) and Liu et al. (2018).
(D) Phylogenetic tree showing the relatedness of the tomato R2R3 MYB proteins under study with other plant R2R3 MYB factors involved in anthocyanin synthesis. Protein sequences were identified on the SOL Genomics Network and NCBI websites. The relative accession numbers were as follows: SlAN2 (Solyc10g086250.1.1), SlAN2_Aft (ACT36608.1), SlANT1 (Solyc10g086260.1.1), SlANT1_Aft (ABO26065.1), SlANT1like (Solyc10g086270.1.1), SlANT1like_Aft (MN242013), SlAN2like (Solyc10g086290.1.1), SlAN2like_Aft (MN242011), ScAN2like (MN242012), StAN1 (AAX53089.1), StAN2 (AAX53091.1), PhAN2 (ABO21074.1), PhDPL (HQ116169), PhPHZ (HQ116170), PhPH4 (BAP28594.1), PhODO1 (Q50EX6.1), NtAN2 (ACO52470.1), AmROS1 (ABB83826.1), AmROS2 (ABB83827.1), AtMYB75 (AAG42001.1), AtMYB113 (NM_105308), AtMYB114 (NM_105309), ZmC1 (AAA33482), ZmPl (AAA19819), MdMYB10 (ABB84753), ScANT1 (ABO26065.1), ScAN2 (ACT36604.1), CsRuby (NP_001275818.1), CaMYBA (BBJ25251.1), MdMYB1 (ADQ27443.1), VvMYB5b (NP_001267854.1).
The genetic nature of the Aft trait is still an open issue. Several studies have proposed putative candidates among the four R2R3 MYB encoding genes (Solyc10g086250 = SlMYB75 = SlAN2, Solyc10g086260 = anthocyanin 1 = SlANT1, Solyc10g086270 = SlMYB28 = SlANT1like, Solyc10g086290 = SlMYB114 = SlAN2like) identified in this chromosome region (Figure 1B) (Sapir et al., 2008, Schreiber et al., 2011, Kiferle et al., 2015, Cao et al., 2017, Qiu et al., 2019). R2R3 MYB proteins are transcription factors (TFs) involved in the regulation of many aspects of cell identity and fate, including the control of secondary metabolism (Stracke et al., 2001, Liu et al., 2015). They can participate with subgroup IIIf basic helix–loop–helix (bHLH) and WD40 repeat (WDR) factors in the MYB–bHLH–WDR (MBW) transcriptional complexes that regulate the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway (Xu et al., 2015, Liu et al., 2018), and their expression patterns may impact on the pigmentation patterns of a plant.
Activation of the anthocyanin synthesis is a consequence of a transcriptional regulatory cascade (Albert et al., 2014, Montefiori et al., 2015) (Figure 1C). The first MBW complex is composed of an R2R3 MYB protein, developmentally or environmentally regulated, and the constitutively expressed WDR and bHLH1 factors. This complex transcriptionally activates an inducible bHLH2-encoding gene, thus producing a second complex composed of the same MYB and WDR proteins as well as the new bHLH2 partner. Thanks to the MYB DNA-binding domains, the second MBW complex finally activates the transcription of the “late biosynthetic genes” (LBGs). This produces the enzymes involved in the steps of the flavonoid pathway that lead to anthocyanins and are differently regulated from the “early biosynthetic genes,” which encode the enzymes that act in earlier reactions of the pathway (Liu et al., 2018). The second complex also induces other positive regulators, including the same bHLH2 factor (“reinforcement mechanism”), and repressor MYB proteins, in a feedback loop finely titrating the accumulation of anthocyanins (Albert et al., 2014).
In this work, we carried out a functional characterization of the Aft R2R3 MYB TFs, which contribute, individually or in combination, to the pigmentation of the fruit, compared with the wild-type (WT) protein variants. We found some key differences in transcript levels and protein activities for one of these MYB factors, which thus appeared to be primarily involved in the Aft phenotype. We believe that our identification of splicing mutations in the WT allele of its gene finally contributes to the understanding of the lack of anthocyanin pigmentation in cultivated tomato.
Results and Discussion
Structural and Functional Analyses of R2R3 MYBs Encoded by the Genes Located in the Introgressed Genomic Region of Aft
The R2R3 MYB genes identified in the long arm of chromosome 10, where Aft was mapped (Sapir et al., 2008), encode proteins phylogenetically correlated with many other plant MYBs involved in anthocyanin synthesis (Figure 1D). They also show very similar sequences: the R2/R3 MYB domains, which specify DNA binding (Lin-Wang et al., 2010), are highly conserved, whereas the C-terminal regions, which influence the strength of the promoter activation (Heppel et al., 2013), are more variable (Supplemental Figure 1). In Aft, the four R2R3 MYB genes show sequence polymorphisms compared with the WT counterparts, which produce amino acid variants in the relative polypeptides (Supplemental Figure 2).
Anthocyanins are synthesized in tomato vegetative tissues upon different environmental stimuli, such as cold or intense light, with the R2R3 MYB TF SlAN2 representing the key MYB activator of the pathway (Kiferle et al., 2015). Similarly to other dicots, a ternary MBW complex constitutes the key transcriptional regulator of the structural LBGs of the biosynthetic pathway, and SlAN2, as well as the bHLH factors SlJAF13 (bHLH1) (Nukumizu et al., 2013, Montefiori et al., 2015) and SlAN1 (bHLH2) (Qiu et al., 2016, Colanero et al., 2018, Gao et al., 2018), and the WDR protein SlAN11 (Gao et al., 2018), have been proved to interact with each other and to be essential for the synthesis of anthocyanins. SlAN2 shows the conserved [DE]Lx2[RK] x3Lx6Lx3R motif containing the bHLH-binding site (Zimmermann et al., 2004) in the R3 domain, the amino acidic signature [A/S/G]NDV and the KPRPR[ST]F motif typical of dicot R2R3 MYBs involved in anthocyanin synthesis (Stracke et al., 2001, Lin-Wang et al., 2010, Heppel et al., 2013) (Supplemental Figure 2A). All these features are also present in the other three WT and four Aft R2R3 MYB factors (Supplemental Figure 2A–2D). On the basis of their strict sequence similarities, all these MYB TFs should therefore be able to activate the synthesis of anthocyanins. For SlANT1 this has already been demonstrated (Mathews et al., 2003, Schreiber et al., 2011, Kiferle et al., 2015).
To directly compare all these TFs, either from the WT or from Aft, in the activation of the anthocyanin pathway, we tested them in a transactivation assay in tomato protoplasts. We used a reporter luciferase gene driven by the promoter of Dihydroflavonol 4-reductase (SlDFR), a marker LBG (Kiferle et al., 2015). Each MYB protein was expressed starting from its genomic sequence and in combination with the bHLH2 factor SlAN1. An ectopic WDR protein was not included in the test, as SlAN11 is constitutively expressed (Gao et al., 2018). Whereas all four Aft MYB TFs were able to strongly transactivate the reporter gene, only three WT MYBs activated it, with SlAN2like being ineffective (Figure 2A). This incapacity was also verified in combination with the bHLH1 factor SlJAF13 (Figure 2B). The WT SlAN2like protein (hereafter SlAN2likeWT) thus behaved very differently from the Aft SlAN2like (hereafter SlAN2likeAft), with only the latter being active with both bHLHs (Figure 2B).
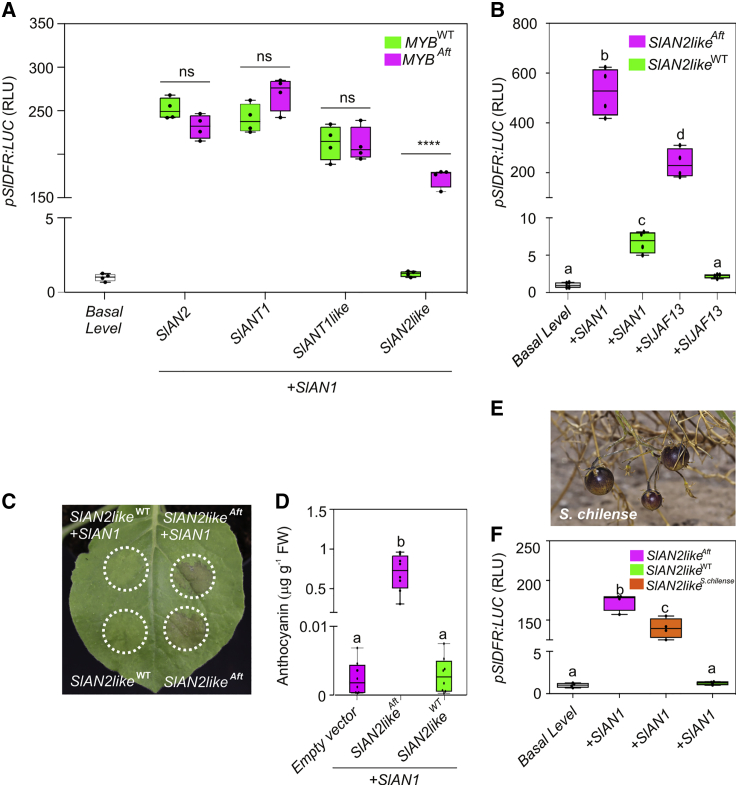
Figure 2.
Functional Analysis of the R2R3 MYB Proteins from WT and Aft Plants.
(A) Transactivation of the SlDFR promoter driving firefly luciferase in protoplasts with effector plasmids containing the MYB SlAN2, SlANT1, SlANT1like, or SlAN2like genomic sequences from WT or Aft plants, in combination with the effector plasmid containing the bHLH factor SlAN1. Data are expressed as relative luciferase activity (RLU) (FireflyLuc/RenillaLuc) with the value of the promoter basal level set to 1 and are means of four biological replicates ± SE. One-way ANOVA with Tukey's HSD post hoc test was performed. ns, P > 0.5; ****P ≤ 0.0001.
(B) Transactivation of the SlDFR promoter driving firefly luciferase in protoplasts with effector plasmids containing the MYB SlAN2like genomic sequence from WT or Aft plants, in combination with effector plasmids containing the bHLH factor SlAN1 or SlJAF13. Data are expressed as RLU with the value of the promoter basal level set to 1 and are means of four biological replicates ± SE. One-way ANOVA with Tukey's HSD post hoc test was performed. Different letters indicate significant differences at P ≤ 0.05.
(C) Anthocyanin accumulation in tobacco leaves agroinfiltrated with effector plasmids containing the SlAN2like genomic sequence cloned in WT or Aft plants expressed with or without the effector plasmid containing the bHLH factor SlAN1. White dotted circles indicate the agroinfiltrated areas.
(D) Quantification of the anthocyanins produced in the areas of tobacco leaves agroinfiltrated with WT or Aft SlAN2like in combination with SlAN1. Anthocyanins are expressed in μg petunidin-3-(p-coumaroyl rutinoside)-5-glucoside g−1 fresh weight (FW). Data are means of eight biological replicates ± SE. One-way ANOVA with Tukey's HSD post hoc test was performed. Different letters indicate significant differences at P ≤ 0.05.
(E)Solanum chilense mature fruits (picture reproduced with the permission of the author from https://giorgetta.ch/fl_solanaceae_solanum_chilense.htm).
(F) Transactivation of the SlDFR promoter driving the firefly luciferase gene in protoplasts transfected with effector plasmids containing SlAN2like genomic sequences from WT or Aft plants or ScAN2like genomic sequence from S. chilense, in combination with the effector plasmid containing the bHLH factor SlAN1. Data are expressed as RLU with the value of the promoter basal level set to 1 and are means of four biological replicates ± SE. One-way ANOVA with Tukey's HSD post hoc test was performed. Different letters indicate significant differences at P ≤ 0.05.
To obtain an in vivo confirmation of the different functionality of the two SlAN2like variants, we agroinfiltrated tobacco leaves with vectors expressing SlAN2likeWTor SlAN2likeAft. Again, whereas SlAN2likeAft induced ectopic anthocyanin synthesis both by interacting with or without its partner SlAN1 (likely engaging a tobacco bHLH factor), SlAN2likeWT was non-functional (Figure 2C and 2D).
The fruits of S. chilense, the wild progenitor of Aft (Georgiev, 1972), show anthocyanin pigmentation when exposed to light (Figure 2E). Therefore, if SlAN2likeAft is involved in the Aft phenotype, the corresponding protein of S. chilense, ScAN2like, whose sequence differs from SlAN2likeWT in relation to many amino acid variants already found in SlAN2likeAft (Supplemental Figure 3), should be functional. In fact, when expressed in tomato protoplasts, ScAN2like activated the SlDFR promoter similarly to SlAN2likeAft (Figure 2F). Both in vitro and in vivo analyses thus indicated that, among the R2R3 MYB factors encoded by the genes identified in chromosome 10, the WT TF SlAN2like was non-functional (Figure 2A and 2B), unlike its Aft and S. chilense orthologous proteins (Figure 2F).
SlAN2likeAft Plays a Primary Role in Aft Fruit Pigmentation
The previous results prompted us to focus on the possible role of SlAN2like in the pigmentation of the fruit. We then grew Aft and WT plants under light conditions that induce anthocyanin production. In Aft, anthocyanins were synthesized from the green stage in the part of the fruit peel developed directly under light, corresponding to the stem end of the epicarp, whereas the stylar end remained green (Figure 3A and 3B). By contrast, anthocyanins were not produced in WT fruits, not even in the stem end of the epicarp, when developed directly under light (Figure 3B).
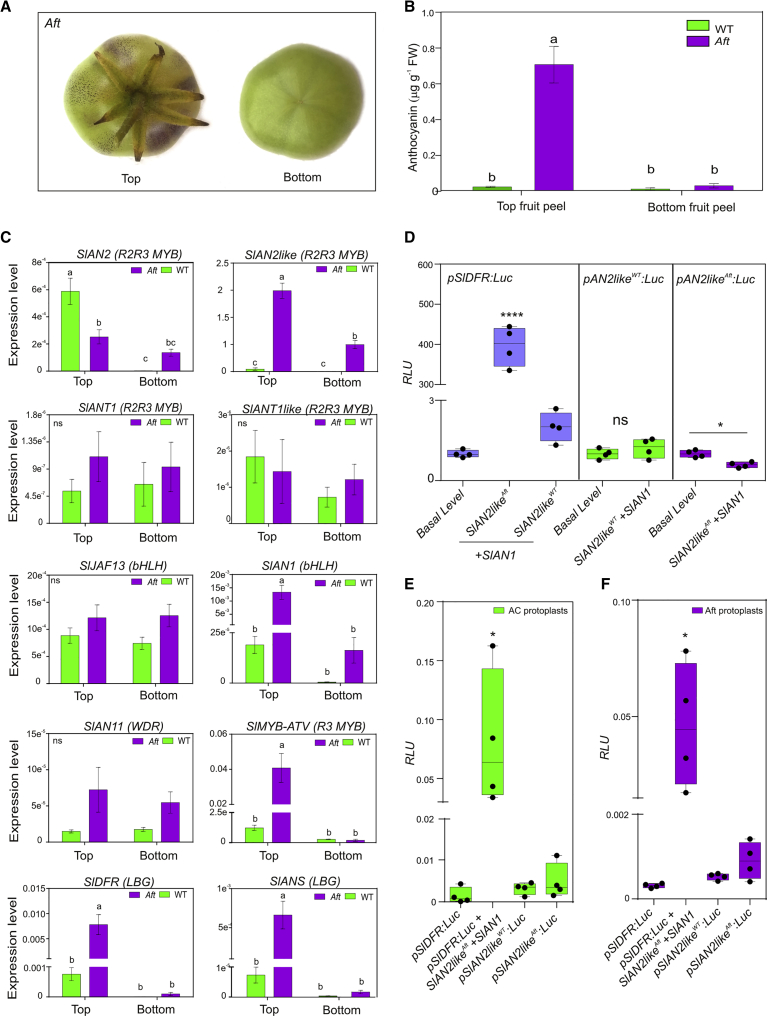
Figure 3.
SlAN2likeAft Is the Major R2R3 MYB Factor Promoting Anthocyanin Synthesis in Aft Fruit Peel.
(A) Top half (stem end) and bottom half (stylar end) of Aft fruit developed under permissive light conditions and photographed at the mature green stage.
(B) Anthocyanin content measured in the peel sampled from top and bottom halves of WT and Aft fruits at the mature green stage. Anthocyanins are expressed in μg petunidin-3-(p-coumaroyl rutinoside)-5-glucoside g−1 fresh weight (FW). Data are means of three biological replicates ± SE. One-way ANOVA with Tukey's HSD post hoc test was performed. Different letters indicate significant differences at P ≤ 0.05.
(C) qPCR analysis of regulatory R2R3 MYB (SlAN2, SlAN2like, SlANT1, SlANT1like), bHLH (SlJAF13, SlAN1), WDR (SlAN11), and R3 MYB (SlMYB-ATV) genes performed in the skin from top and bottom halves of WT and Aft fruits at the mature green stage. Data are means of eight biological replicates ± SE. One-way ANOVA with Tukey's HSD post hoc test was performed. Different letters indicate significant differences at P ≤ 0.05.
(D) Transactivation of the SlAN2like promoters from WT and Aft plants and of the SlDFR promoter, all of them driving the firefly luciferase gene, in leaf protoplasts. As positive control, transactivation of the SlDFR promoter in protoplasts transfected with the effector plasmids containing the SlAN2likeAft genomic sequence and the bHLH factor SlAN1 is shown. Data are expressed as relative luciferase activity (RLU) (FireflyLuc/RenillaLuc) with the value of the promoter basal level set to 1 and are means of four biological replicates ± SE. One-way ANOVA with Tukey's HSD post hoc test was performed. ns, P > 0.5; *P ≤ 0.05; ****P ≤ 0.0001.
(E) Transactivation of the SlAN2like promoters from WT and Aft plants and of SlDFR promoter, all of them driving the firefly luciferase gene, in fruit peel protoplasts isolated from WT fruits at the mature green stage. As positive control, transactivation of the SlDFR promoter in protoplasts transfected with the effector plasmids containing the SlAN2likeAft genomic sequence and the bHLH factor SlAN1 is shown. Data are expressed as RLU and are means of four biological replicates ± SE. One-way ANOVA with Tukey's HSD post hoc test was performed. “∗” P ≤ 0.05.
(F) Transactivation of the SlAN2like promoters from WT and Aft plants and of SlDFR promoter, all of them driving the firefly luciferase gene, in fruit peel protoplasts isolated from Aft fruits at the mature green stage. As positive control, transactivation of the SlDFR promoter in protoplasts transfected with the effector plasmids containing the SlAN2likeAft genomic sequence and the bHLH factor SlAN1 is shown. Data are expressed as RLU and are means of four biological replicates ± SE. One-way ANOVA with Tukey's HSD post hoc test was performed. ∗P ≤ 0.05.
A qPCR analysis carried out in Aft skin at the mature green stage showed differences between the top and the bottom halves of the fruit. In the peel directly exposed to light (top epicarp), we observed the expression of several genes involved in the anthocyanin pathway, including R2R3 MYBs SlAN2 and SlAN2like, bHLH SlJAF13 and SlAN1, and WDR SlAN11 (Figure 3C). Both SlAN2 and SlAN2like responded to light intensity, showing a higher expression in the top than in the bottom half of the fruit; however, SlAN2like was much more expressed than SlAN2 (Figure 3C). The expression of the other two MYBs, SlANT1 and SlANT1like, was barely detectable (Figure 3C). SlAN1, along with the LBGs, SlDFR and SlANS, only showed high expression levels in the top peel (Figure 3C). The same was found for SlMYB-ATV (Figure 3C), encoding an R3 MYB repressor of the pathway, which has been recently characterized (Cao et al., 2017, Colanero et al., 2018).
In WT fruit peel, the transcript analysis showed a low expression of all four MYBs in both the stem end and stylar end of the fruit (Figure 3C). However, in the part of the fruit developed under light, SlAN2 was more expressed in WT than in Aft fruit, whereas SlAN2like was much less expressed (Figure 3C). SlJAF13 and SlAN11 were expressed in both halves of the fruit at similar levels, confirming their constitutive expression, whereas very few transcripts were measured for SlAN1, SlMYB-ATV, SlDFR, and SlANS in all the fruit (Figure 3C).
Transcript qPCR data clearly indicated that the actors of the activation mechanism were present in Aft peel under light, with SlAN2likeAft as the major R2R3 MYB expressed gene. The interaction among this light-induced MYB activator and the bHLH1 and WDR factors, SlJAF13 and SlAN11, thus produced the first MBW complex, hierarchically activating the transcription of the inducible bHLH2 gene, SlAN1. The SlAN1 protein then participated with SlAN2likeAft and SlAN11 in the second MBW complex, inducing the LBGs and the anthocyanin accumulation. In WT fruits, based on transcript analyses, the absence of anthocyanins was due to a scarce activation of the LBGs, which, in turn, could be attributed to the failure of the assembly of the MBW complexes, particularly the second one, which could have been formed only at negligible concentrations given the very low expression levels of SlAN1 (Figure 3C).
On the whole, the qPCR analysis indicated that: (1) in fruit peel at the mature green stage, SlANT1 and SlANT1like levels appeared insignificant in both Aft and WT fruits; (2) whereas in WT, SlAN2 was the most expressed MYB gene, in Aft SlAN2like was the main MYB, while its expression was very low in WT; and (3) the expression of the MYB gene SlAN2 in WT fruit peel was not sufficient to trigger anthocyanin synthesis. The high expression of SlAN2like that we observed in Aft fruit confirmed findings in other tomato lines expressing the Aft gene (Cao et al., 2017, Qiu et al., 2019).
It is known from other species, particularly Arabidopsis (Nesi et al., 2000, Zhang et al., 2003, Ramsay and Glover, 2005), that R2R3 MYBs determine the pathway specificity of the MBW complexes, whereas bHLH and WDR factors can control different aspects of cell identity participating in different MBW complexes. It is thus possible that the global level of the R2R3 MYBs promoting anthocyanins and expressed in fruit peel need to reach a certain threshold to be able to recruit enough bHLH and WDR partners to produce sufficient MBW complexes to activate the anthocyanin pathway. If this holds true, in Aft fruits, under appropriate light conditions, the SlAN2likeAft level may become high enough to activate anthocyanin synthesis. By contrast, in WT fruits, SlAN2like is poorly expressed and, most importantly, SlAN2like proteins are not functional, while SlAN2 cannot reach an adequate level to activate a significant transcription of SlAN1. Overexpression of SlAN2 (as well as SlANT1) in tomato WT plants can lead to purple fruit pigmentation (Kiferle et al., 2015). The level of expression of this R2R3 MYB TF in fruit peel is therefore crucial in activating the anthocyanin pathway. As a consequence of the insufficient transcription of SlAN2 and the inefficiency of SlAN2like, all the genes that are under the transcriptional control of the second MBW complex cannot be properly expressed in WT fruit peel. This is the case for the LBGs and for the same bHLH2 gene, SlAN1, whose weak induction makes its final protein level insufficient for the sufficient activation of the pathway. In line with this, the repressor R3 MYB protein, SlMYB-ATV, whose transcription is stimulated through a feedback mechanism by the same MBW complex activating SlAN1 and the LBGs (Colanero et al., 2018), was much less expressed in WT than in the Aft fruit peel (Figure 3C).
To understand whether the differences in the expression levels of SlAN2like in Aft and WT fruits depended on the different activation of the gene, we cloned the promoter regions. The sequence amplified in WT plants overlapped with the one deposited in the SOL Genomics database. The promoter of the Aft gene was instead cloned thanks to the data available with the recent publication of the reference genome of S. chilense (Stam et al., 2019). In fact, the Aft promoter was very similar to the region upstream of the ScAN2like gene, although, as with the coding sequence (CDS), a few polymorphisms between them were found (Supplemental Figure 4).
R2R3 MYB TFs are often prone to autoactivation, which has also been found to characterize MYB proteins involved in anthocyanin synthesis (Brendolise et al., 2017). We found MYB cis-regulatory elements in both WT and Aft promoters of SlAN2like (Supplemental Figure 4). Therefore, to test whether they could be transactivated by the MYB proteins produced by their respective genes and involved in the MBW complex, we expressed the promoters of SlAN2like fused to the luciferase gene in protoplasts transfected with the components of the MBW complex. We found similar basal expression levels of the two reporter genes and no activation for either the WT or the Aft promoters (Figure 3D). On the other hand the promoter of SlDFR, included in the test as a control, was transactivated by the complex including the SlAN2likeAft MYB protein (Figure 3D), as already observed (Figure 2A and 2B). This result indicated that the higher expression of SlAN2likeAft in Aft fruit peel was not due to autoactivation by the MBW complex that induces anthocyanin synthesis. Finally, to test whether the two promoters showed different activation states in the respective fruits, we also expressed them fused to the luciferase reporter gene in protoplasts isolated from the fruit peel sampled from mature green WT (Figure 3E) and Aft fruits (Figure 3F). Again, no significant differences were measured between the basal activities of the promoter of SlAN2likeWT and of SlAN2likeAft either in WT or in Aft fruit protoplasts (Figure 3E and 3F). Moreover, in both of them a very low basal activation of the SlAN2like promoters was observed compared with the activity of the promoter of SlDFR transactivated by the MBW complex including the SlAN2likeAft protein and included in the test as a control (Figure 3E and 3F).
Splicing Mutations Affect the Transcripts of SlAN2like Produced in Tomato Fruit Peel
To understand why SlAN2likeWT is non-functional, we amplified the SlAN2like transcripts from the top epicarp of WT and Aft fruits (Figure 4A). Whereas the CDS of SlAN2likeAft was well aligned with the tomato SlAN2like CDS bioinformatically predicted (Solyc10g086290.1.1) (Supplemental Figure 5A and 5B), in WT fruit peel we amplified two slightly different shorter sequences, lacking one or two nucleotide strings, at the end of the first or second exon (Supplemental Figure 5C–5E). As the genomic sequence of SlAN2likeWT from our plants was identical to the reference sequence (Solyc10g086290.1), an alternative processing of the pre-mRNA should have occurred before leading to these transcript arrangements. To verify whether this was linked to the variety Ailsa Craig that we used as WT, we also cloned the SlAN2like transcript from another variety, Heinz 1706, the one used as a reference for the tomato genome (Tomato Genome Consortium, 2012). Again, from the fruit peel at the mature green stage, we obtained a shorter sequence than the expected one, lacking the same nucleotide string at the end of the second exon already identified in one of the transcripts of Ailsa Craig fruits (Supplemental Figure 6A).
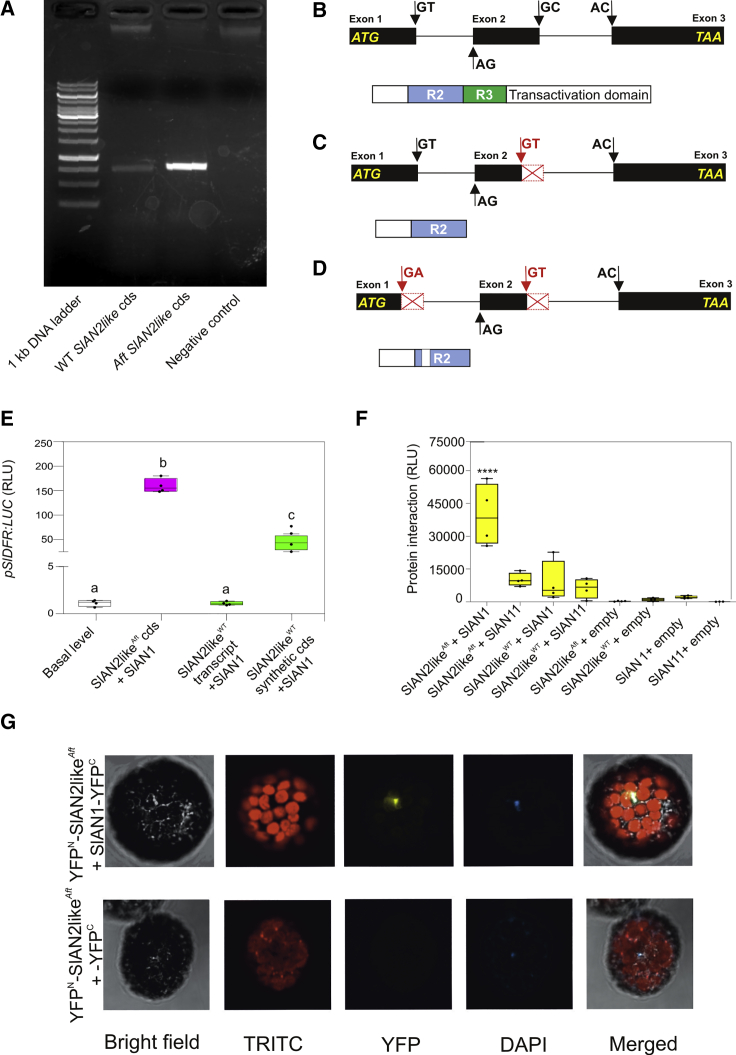
Figure 4.
Structural and Functional Analysis of the SlAN2like Factors Produced from the Transcripts Identified in WT and Aft Fruit Peel.
(A) Agarose gel electrophoresis of the RT–PCR products showing the SlAN2like transcripts amplified from WT and Aft fruit peel cDNAs. The expected length of the WT SlAN2like CDS (Solyc10g086290.1.1) is 798 bp.
(B) Schematic representation of intron–exon structure of the WT genomic sequence of SlAN2like with the positions of the “canonical” splicing sites (black arrows), which produce the theoretical transcript registered in the SOL Genomics Network database (Solyc10g086290.1.1) (above), and protein produced from its mature mRNA with major functional domains (below). Gene and protein sequences are shown at different scales.
(C) Schematic representation of intron–exon structure of the WT genomic sequence of SlAN2like with the positions of the “canonical” splicing sites (black arrows) and the alternative ones (red arrows), which produce the first shorter transcript identified in fruit peel (above), and protein produced from its mature mRNA with major functional domains (below). Gene and protein sequences are shown at different scales.
(D) Schematic representation of intron–exon structure of the WT genomic sequence of SlAN2like with the positions of the “canonical” splicing sites (black arrows) and the alternative ones (red arrows), which produce the second shorter transcript identified in fruit peel, and protein produced from its mature mRNA with major functional domains (below). Gene and protein sequences are shown at different scales.
(E) Transactivation of the SlDFR promoter driving the firefly luciferase gene in protoplasts with effector plasmids containing the SlAN2like transcripts cloned in WT and Aft fruit peel and the SlAN2like synthetic CDS (corresponding to the theoretical transcript produced from the WT pre-mRNA using the “canonical” splicing sites used in the processing of the pre-mRNA of SlAN2likeAft). MYB proteins were expressed in combination with SlAN1. Data are expressed as relative luciferase activity (RLU) (FireflyLuc/RenillaLuc) with the value of the promoter basal level set to 1 and are means of four biological replicates ± SE. One-way ANOVA with Tukey's HSD post hoc test was performed. Different letters indicate significant differences at P ≤ 0.05.
(F) Split-luciferase complementation assay in WT protoplasts expressing the fusion proteins NLuc-SlAN2likeWT or NLuc-SlAN2likeAft with CLuc-SlAN1 or CLuc-SlAN11. Combinations of each construct with the empty vectors expressing the complementary half of the luciferase gene represent negative controls. Data are expressed as RLU and are means of four biological replicates ± SE. One-way ANOVA with Tukey's HSD post hoc test was performed. Each box was compared with the first one, with significant difference at ****P ≤ 0.0001.
(G) Bimolecular fluorescence complementation assay analyzing the interaction between SlAN2likeAft and SlAN1 in tomato protoplasts expressing the fusion proteins YFPN-SlN2likeAft and YFPC-SlAN1. As a control, YFPC-half protein was expressed in combination with YFPN-SlAN2likeAft fusion protein.
The SlAN2likeWT polypeptide bioinformatically predicted from the reference gene sequence (Solyc10g086290, Supplemental Figures 1 and 2) derives from a mature mRNA assembled by using the splicing sites, which are indeed recognized by the splicing machinery in the sequence of the primary transcript of SlAN2likeAft (Figure 4B; Supplemental Figure 5B and 5C). These splicing sites can be considered as “canonical,” since they produce a mature mRNA translated into a functional protein. By contrast, in the WT pre-mRNA, alternative 5′ splicing sites in the first and second introns are recognized by the spliceosome, thus producing shorter transcripts (Figure 4C and 4D; Supplemental Figure 5D and 5E). Interestingly, in these transcripts the loss of various nucleotides led to a frameshift, which produced an early stop codon at the beginning of the third exon (Supplemental Figure 5D and 5E). The corresponding proteins should thus present a premature truncation resulting in a much lower size than the theoretical one, with the loss of most of the residues downstream of the R2 domain (Figure 4C and 4D; Supplemental Figure 7A).
By directly comparing the WT and Aft SlAN2like transcript variants in protoplasts, we confirmed that the WT proteins derived from the fruit peel transcripts were non-functional, whereas the Aft activated the SlDFR promoter (Figure 4E), similarly to its corresponding genomic sequence (Figure 2A and 2B). We also found transactivation of the reporter gene by expressing a synthetic CDS corresponding to the version of SlAN2likeWT produced through the canonical splicing (Figure 4E). The “correctly spliced” version of this MYB TF was able to transactivate the SlDFR promoter. Its efficiency was lower than that of SlAN2likeAft (Figure 4E), probably due to the presence of polymorphisms in the C-terminal region (Supplemental Figure 7B), which is part of the activation domain of the TF. The alternative splicing leading to the fruit peel transcripts of SlAN2likeWT thus prevented the translation of a functional protein.
By examining the structure of the truncated SlAN2likeWT protein, it seems evident that the absence of the R3 domain, containing the bHLH-binding signature, prevents it from forming MBW complexes. In fact, a split-luciferase complementation assay carried out in protoplasts showed that SlAN2likeWT did not interact with the bHLH factor SlAN1, unlike SlAN2likeAft, which showed a clear interaction with the bHLH partner (Figure 4F). On the contrary, the WDR protein SlAN11 did not bind either SlAN2likeWT or SlAN2likeAft (Figure 4F), confirming previous data indicating that WDR proteins can only bind bHLH factors and not MYBs (An et al., 2012, Montefiori et al., 2015, Gao et al., 2018). A bimolecular fluorescence complementation assay confirmed the interaction between SlAN2likeAft and SlAN1, taking place in the nucleus (Figure 4G), the cellular compartment where transcription occurs. Protein–protein interaction assays thus demonstrated that SlAN2likeWT is unable to associate with bHLH partners, and thus to participate in the MBW complexes that induce anthocyanin synthesis.
Non-canonical splicing events are becoming more and more frequently identified in plants, and over 60% of intron-containing genes are estimated to be prone to alternative splicing (AS) (Syed et al., 2012). AS can affect transcript levels and stability. Aberrant transcripts, containing premature termination codons, may induce a nonsense-mediated decay leading to degradation of the same mRNAs (Syed et al., 2012, Sibley et al., 2016). If a similar mechanism affected SlAN2likeWT transcripts, it would explain why we found very low expression levels in WT fruits (Figure 3C). Interestingly, tomato fruits of the Heinz 1706 variety not only produced aberrant SlAN2like transcripts such as Ailsa Craig, but also displayed similar low expression levels in fruit peel compared with Aft (Supplemental Figure 6B). Also in this variety, therefore, the red color of the fruit peel is associated with an AS of SlAN2like and a low expression of this gene. Heinz 1706 fruits also showed a low transcription of the other R2R3 MYB gene, SlAN2 (Supplemental Figure 6B). These data suggest that what we observed was not peculiar to the variety chosen in the study, but may be a general feature of domesticated tomato. The AS of SlAN2likeWT, preventing the translation of a functional MYB TF, thus would impede WT tomatoes from responding to excess light and to synthesize anthocyanins.
There is increasing evidence that AS represents a way of further regulating gene expression and at the same time increasing the protein-coding capacity of a genome. It thus contributes to the adaptation of plants to the environment (Syed et al., 2012). Wild tomato species mainly come from the Andean regions of South America (Chetelat et al., 2009), environments where high altitudes are common and there is ultraviolet radiation-enriched light. In these conditions, it is plausible that the capacity to synthesize protective anthocyanins not only in vegetative tissues but also in fruit peel is common, and in fact most of the wild species still found in these areas (e.g. S. chilense, Solanum peruvianum, Solanum lycopersicoides) show green/purple fruits. With gradual diffusion in low-altitude areas, also as a consequence of domestication and cultivation, it is possible that such a characteristic was progressively lost or counter-selected, perhaps because of a more appealing uniform red color. Interestingly, the AN2like CDS is very conserved in S. lycopersicum, its more direct ancestor species, S. pimpinellifolium, and other more distant wild species, such as S. chilense, Solanum pennellii, and S. lycopersicoides (Supplemental Figure 8), and all of these CDS can be translated into functional proteins. The intronic regions of the gene appear more variable, and S. lycopersicum and S. pimpinellifolium, which both bear red fruits, are considerably more interrelated in terms of their intronic sequences than the other green/purple-fruited species (Supplemental Figure 8). Transcriptomic data related to the expression levels of the gene AN2like in wild species are not available. However, an RNA-sequencing experiment carried out in S. pimpinellifolium indicated a level of expression of AN2like in the fruit not so different from that of S. lycopersicum (Supplemental Figure 9). It is tempting to speculate that intronic mutations in the SlAN2like gene could lead to the production of those cis elements that force the spliceosome to recognize the non-canonical splicing sites with a consequent reduction in splicing fidelity. Further studies are needed, however, to verify how much this process has spread among tomato varieties and when it originated.
Methods
Plant Material and Growth Conditions
Seeds of S. lycopersicum cv. Ailsa Craig (LA2838A), representing WT tomato, Aft/Aft (LA1996), cv Heinz 1706 (LA 4345), and S. chilense (LA1930), were provided by the Tomato Genetic Resource Center (https://tgrc.ucdavis.edu/). Accession LA1930 was chosen, as the line of S. chilense that was originally crossed with S. lycopersicum (Georgiev, 1972) is not known. Seeds were germinated in rock-wool plugs (Grodan, https://www.grodan.com/) soaked in a nutritive solution (Kiferle et al., 2013). Two-week-old seedlings were transplanted in pots containing a 70:30 soil (Hawita Flor, https://www.hawita-gruppe.de/en/)/expanded clay mixture, and placed in a growth chamber with 12 h daylight, 300 μmol photons m−2 s−1, 28°C/21°C day/night temperature, and 50% relative humidity. Fruits were sampled at the mature green stage, divided into two halves, the peel removed from the top and bottom parts, frozen in liquid nitrogen, and stored at −80°C until use.
Plasmid Construction
The genes Solyc10g086250 (SlAN2), Solyc10g086260 (SlANT1), Solyc10g086270 (SlANT1like), Solyc10g086290 (SlAN2like), Solyc09g065100 (SlAN1), Solyc08g081140 (SlJAF13), and Solyc03g097340 (SlAN11) (SOL Genomics Network, https://sgn.cornell.edu) were amplified by PCR starting from WT and/or Aft genomic DNAs using Phusion High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase (Thermo Fisher Scientific, https://corporate.thermofisher.com) and the oligonucleotide primers reported in Supplemental Table 1. The promoters of SlAN2likeWT and SlAN2likeAft were amplified by PCR as described above and using the primers reported in Supplemental Table 1. The S. chilense AN2like was amplified from DNA extracted from dry seeds. The CDS of WT (Ailsa Craig and Heinz 1706) or Aft SlAN2like was amplified from RNA extracted from fruit peel using the Spectrum Plant Total RNA Kit (Sigma-Aldrich, https://www.sigmaaldrich.com), treated with DNase, and reverse transcribed with SuperScript IV Reverse Transcriptase (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The “synthetic” SlAN2likeWT CDS was purchased from GeneArt Gene Synthesis (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The amplified sequences were cloned into pENTR/D-TOPO vector (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and the entry clones were recombined with different destination vectors, as described below, via Invitrogen Gateway recombination cloning technology (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Multiple sequence alignments were performed using ClustalW (www.genome.jp/tools-bin/clustalw) and DNAMAN sequence analysis software.
Phylogenetic Analysis
The analysis was performed on the Phylogeny.fr platform (Dereeper et al., 2008). R2R3 MYB protein sequences were aligned with MUSCLE (v3.8.31) configured for highest accuracy (MUSCLE with default settings). Ambiguous regions (i.e., containing gaps and/or poorly aligned) were removed with Gblocks (v0.91b) using the following parameters: minimum length of a block after gap cleaning: 10; no gap positions were allowed in the final alignment; all segments with contiguous non-conserved positions bigger than 8 were rejected; minimum number of sequences for a flank position: 85%. The phylogenetic tree was reconstructed using the maximum-likelihood method implemented in the PhyML program (v3.1/3.0 aLRT). The WAG substitution model was selected assuming an estimated proportion of invariant sites (of 0.145) and four γ-distributed rate categories to account for rate heterogeneity across sites. The γ shape parameter was estimated directly from the data (γ = 1.135). Reliability for internal branch was assessed using the aLRT test (SH-Like). Graphical representation and edition of the phylogenetic tree were performed with TreeDyn (v198.3).
Anthocyanin Quantification
Anthocyanins were extracted and quantified as described in Colanero et al. (2018), and finally expressed as micrograms of petunidin-3-(p-coumaroyl rutinoside)-5-glucoside per gram fresh weight (Kiferle et al., 2015).
Tomato Protoplast Isolation
Leaf protoplasts were isolated following the protocol in Shi et al. (2012) from 3-week-old tomato plants, cv. Micro-Tom, grown as reported above. Fruit peel protoplasts were isolated from mature green WT and Aft fruits using the same protocol. Polyethylene glycol-mediated protoplast transformation was carried out as in Yoo et al. (2007).
Transactivation Assays
Transactivation assays by dual-luciferase system were performed by exploiting the Renilla reniformis (Renilla) and Photinus pyralis (Firefly) luciferase (Luc) enzymes. The effector constructs 35S:SlAN2, 35S:SlANT1, 35S:SlANT1like, 35S:SlAN2like, 35S:ScAN2like, 35S:SlJAF13, and 35S:SlAN1, with R2R3 MYB genomic sequences and bHLH CDS, as well as the promoter SlDFR:FireflyLuc and SlAN2like:FireflyLuc reporter constructs, were produced as reported in Colanero et al. (2018). A 35S:RenillaLuc vector was used to normalize luminescence values detected in protoplasts (Weits et al., 2014). Effector and reporter plasmids were co-transfected in protoplasts, and luminescence relative levels were measured as described in Kiferle et al. (2015). In each assay, data were expressed as relative luciferase activity (RLU) (FireflyLuc/RenillaLuc). Each experiment was repeated three times with similar results.
Agroinfiltration Assay
Transient expression assay was performed using Nicotiana benthamiana plants placed in a growth chamber with 16 h daylight, 100 μmol photons m−2 s−1, and 23°C/20°C day/night temperature. Overexpression vectors were generated by recombining the entry clones containing the genomic sequences of SlAN2likeWT, SlAN2likeAft, and the CDS of SlAN1 with the Gateway compatible binary vector pK7WG2 (Karimi et al., 2002). Agrobacterium tumefaciens GV3101 (MP90) strains hosting the different constructs were infiltrated in Nicotiana leaves following the protocol of Li (2011). Each leaf was infiltrated in four different points with different constructs, as shown in Figure 2C. Non-recombined pK7WG2 vectors were used as negative controls. Three different leaves in three tobacco plants were analyzed as biological replicates for each combination of plasmids. Anthocyanins were quantified in single portions sampled from leaves in relation to the infiltrated areas at 4 days after infiltration. The experiment was repeated twice with similar results.
Split-Luciferase Complementation Assay
The Gateway compatible bait vector pDuEx-Dn6 and prey vector pDuEx-Ac6 (Fujikawa and Kato, 2007), containing the C-terminal half and the N-terminal half of the Renilla luciferase gene, respectively, were used for the recombination of SlAN2likeWT, SlAN2likeAft, SlAN1, and SlJAF13 entry clones. Leaf protoplasts were transfected with mixtures of two different recombined bait and prey vectors. As the control, the NLuc-half protein was expressed in combination with each of the two CLuc-SlAN2likeWT or CLuc-SlAN2likeAft fusion proteins, and the CLuc-half protein was expressed in combination with each of the two SlAN1-NLuc or SlAN11-NLuc fusion proteins. Luciferase activity was analyzed as described in Colanero et al. (2018). Data were expressed as RLU (RenillaLuc/protein content). The experiment was repeated twice with similar results.
RNA Isolation, cDNA Synthesis, and Real-Time PCR Analysis
Total RNA, extracted from fruit peel as described above, was subjected to DNase treatment and then reverse transcribed into cDNA using the Maxima First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit for qRT–PCR, with dsDNase (Thermo Fisher Scientific). qRT–PCR was performed with an ABI Prism 7300 Sequence Detection System (Thermo Fisher Scientific) using PowerUp SYBR Green Master Mix (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and the primers listed in Supplemental Table 2. Elongation Factor 1-alpha (SlEF1A) (Kiferle et al., 2015) and Abscisic stress ripening gene 1 (SlASR1) (Bovy et al., 2002) were used as reference genes. Expression levels relative to the geometric averaging of the reference genes were quantified for each target gene.
Bimolecular Fluorescence Complementation Assay
The Gateway compatible destination vectors used were pDH51-GW-YFPN and pDH51-GW-YFPC (Zhong et al., 2008), enabling the fusion of the N terminus or C terminus of the yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) moieties, respectively, to the C terminus of the protein of interest. Control vectors were pDH51-YFPC and pDH51-YFPN (Zhong et al., 2008). Protoplasts were isolated as described, transformed with 1 μg of DNA for each plasmid, and incubated in the dark at 25°C for 16 h before subsequent analysis. Fluorescence of YFP was analyzed with a Zeiss LSM 880 with Airyscan microscope. Yellow fluorescence was excited with 488 nm laser light and collected at 497-546 nm wavelength range. Chlorophyll autofluorescence was excited with 640 nm laser light and collected at 656-700 nm wavelength range. Nuclei were stained with 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylidone (DAPI, Sigma-Aldrich), fluorescence was excited at 405 nm and collected at 410-470 nm.
Statistics
Statistical analyses were performed with GraphPad Prism 6.01 (www.graphpad.com/scientific-software/prism/). Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA, and differences were tested using the Tukey honest significant difference (HSD) multiple-comparisons test.
Author Contributions
P.P. and S.G. conceived and designed the project. S.C. performed molecular cloning, transactivation assays, split-luciferase complementation and bimolecular fluorescence complementation assays, and anthocyanin measurements. S.G. performed gene-expression analysis and sequence analyses. A.T. carried out microscopic analysis. S.C., P.P., and S.G. wrote the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr. Remko Stam for his assistance in the analysis of the ScAN2like promoter sequence. The authors acknowledge funding by Scuola Superiore Sant’Anna. No conflict of interest declared.
Published: January 13, 2020
Footnotes
Published by the Plant Communications Shanghai Editorial Office in association with Cell Press, an imprint of Elsevier Inc., on behalf of CSPB and IPPE, CAS.
Supplemental Information is available at Plant Communications Online.
Contributor Information
Pierdomenico Perata, Email: p.perata@santannapisa.it.
Silvia Gonzali, Email: s.gonzali@santannapisa.it.
Accession Numbers
Genomic sequences of AN2like from Aft and S. chilense as well as genomic ANT1like sequence from Aft were deposited in the GenBank database with the following accession numbers: SlAN2likeAft, MN242011; ScAN2like, MN242012; SlANT1likeAft, MN242013.
Supplemental Information
References
- Albert N.W., Davies K.M., Lewis D.H., Zhang H., Montefiori M., Brendolise C., Boase M.R., Ngo H., Jameson P.E., Schwinn K.E. A conserved network of transcriptional activators and repressors regulates anthocyanin pigmentation in eudicots. Plant Cell. 2014;26:962–980. doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.122069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- An X.H., Tian Y., Chen K.Q., Wang X.F., Hao Y.J. The apple WD40 protein MdTTG1 interacts with bHLH but not MYB proteins to regulate anthocyanin accumulation. J. Plant Physiol. 2012;169:710–717. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2012.01.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bai Y., Lindhout P. Domestication and breeding of tomatoes: what have we gained and what can we gain in the future? Ann. Bot. 2007;100:1085–1094. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcm150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedinger P.A., Chetelat R.T., McClure B., Moyle L.C., Rose J.K., Stack S.M., van der Knaap E., Baek Y.S., Lopez-Casado G., Covey P.A. Interspecific reproductive barriers in the tomato clade: opportunities to decipher mechanisms of reproductive isolation. Sex. Plant Reprod. 2011;24:171–187. doi: 10.1007/s00497-010-0155-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bovy A., de Vos R., Kemper M., Schijlen E., Almenar Pertejo M., Muir S., Collins G., Robinson S., Verhoeyen M., Hughes S. High-flavonol tomatoes resulting from the heterologous expression of the maize transcription factor genes LC and C1. Plant Cell. 2002;14:2509–2526. doi: 10.1105/tpc.004218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brendolise C., Espley R.V., Lin-Wang K., Laing W., Peng Y., McGhie T., Dejnoprat S., Tomes S., Hellens R.P., Allan A.C. Multiple copies of a simple MYB-binding site confers trans-regulation by specific flavonoid-related R2R3 MYBs in diverse species. Front. Plant Sci. 2017;8:1864. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butelli E., Titta L., Giorgio M., Mock H.P., Matros A., Peterek S., Schijlen E.G., Hall R.D., Bovy A.G., Luo J. Enrichment of tomato fruit with health-promoting anthocyanins by expression of select transcription factors. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008;26:1301–1308. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao X., Qiu Z., Wang X., Van Giang T., Liu X., Wang J., Wang X., Gao J., Guo Y., Du Y. A putative R3 MYB repressor is the candidate gene underlying atroviolacium, a locus for anthocyanin pigmentation in tomato fruit. J. Exp. Bot. 2017;68:5745–5758. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erx382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chetelat R.T., Pertuzé R.A., Faúndez L., Graham E.B., Jones C.M. Distribution, ecology and reproductive biology of wild tomatoes and related nightshades from the Atacama Desert region of northern Chile. Euphytica. 2009;167:77–93. [Google Scholar]
- Colanero S., Perata P., Gonzali S. The atroviolacea gene encodes an R3-MYB protein repressing anthocyanin synthesis in tomato plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2018;9:830. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dereeper A., Guignon V., Blanc G., Audic S., Buffet S., Chevenet F., Dufayard J.F., Guindon S., Lefort V., Lescot M. Phylogeny.fr: robust phylogenetic analysis for the non-specialist. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36:W465–W469. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doganlar S., Frary A., Daunay M.C., Lester R.N., Tanksley S.D. .Conservation of gene function in the Solanaceae as revealed by comparative mapping of domestication traits in eggplant. Genetics. 2002;161:1713–1726. doi: 10.1093/genetics/161.4.1713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAO . Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations; Rome: 2010. Plant Genetic Resource for Food and Agriculture. [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa Y., Kato N. Split luciferase complementation assay to study protein-protein interactions in Arabidopsis protoplasts. Plant J. 2007;52:185–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03214.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao Y., Liu J., Chen Y., Tang H., Wang Y., He Y., Ou Y., Sun X., Wang S., Yao Y. Tomato SlAN11 regulates flavonoid biosynthesis and seed dormancy by interaction with bHLH proteins but not with MYB proteins. Hortic. Res. 2018;5:27. doi: 10.1038/s41438-018-0032-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgiev C. Anthocyanin fruit (Af) Rep. Tomato Genet. Coop. 1972;22:10. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzali S., Mazzucato A., Perata P. Purple as a tomato: towards high anthocyanin tomatoes. Trends Plant Sci. 2009;14:237–241. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2009.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heppel S.C., Jaffé F.W., Takos A.M., Schellmann S., Rausch T., Walker A.R., Bogs J. Identification of key amino acids for the evolution of promoter target specificity of anthocyanin and proanthocyanidin regulating MYB factors. Plant Mol. Biol. 2013;82:457–471. doi: 10.1007/s11103-013-0074-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karimi M., Inzé D., Depicker A. GATEWAY vectors for Agrobacterium-mediated plant transformation. Trends Plant Sci. 2002;7:193–195. doi: 10.1016/s1360-1385(02)02251-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiferle C., Fantini E., Bassolino L., Povero G., Spelt C., Buti S., Giuliano G., Quattrocchio F., Koes R., Perata P. Tomato R2R3-MYB proteins SlANT1 and SlAN2: same protein activity, different roles. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0136365. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiferle C., Gonzali S., Holwerda H.T., Ibaceta R.R., Perata P. Tomato fruits: a good target for iodine biofortification. Front. Plant Sci. 2013;4:205. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2013.00205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X. Infiltration of Nicotiana benthamiana protocol for transient expression via agrobacterium. Bio Protoc. 2011 doi: 10.21769/BioProtoc.95. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Lin-Wang K., Bolitho K., Grafton K., Kortstee A., Karunairetnam S., McGhie T.K., Espley R.V., Hellens R.P., Allan A.C. An R2R3 MYB transcription factor associated with regulation of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway in Rosaceae. BMC Plant Biol. 2010;10:50. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-10-50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C., Zhu L., Fukuda K., Ouyang S., Chen X., Wang C., Zhang C.J., Martin B., Gu C., Qin L. The flavonoid cyanidin blocks binding of the cytokine interleukin-17A to the IL-17RA subunit to alleviate inflammation in vivo. Sci. Signal. 2017;10:467. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aaf8823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J., Osbourn A., Ma P. MYB transcription factors as regulators of phenylpropanoid metabolism in plants. Mol. Plant. 2015;8:689–708. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2015.03.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y., Tikunov Y., Schouten R.E., Marcelis L.F.M., Visser R.G.F., Bovy A. Anthocyanin biosynthesis and degradation mechanisms in solanaceous vegetables: a review. Front. Chem. 2018;6:52. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2018.00052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martí R., Roselló S., Cebolla-Cornejo J. Tomato as a source of carotenoids and polyphenols targeted to cancer prevention. Cancers (Basel) 2016;8:6. doi: 10.3390/cancers8060058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin C., Butelli E., Petroni K., Tonelli C. How can research on plants contribute to promoting human health? Plant Cell. 2011;23:1685–1699. doi: 10.1105/tpc.111.083279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews H., Clendennen S.K., Caldwell C.G., Liu X.L., Connors K., Matheis N., Schuster D.K., Menasco D.J., Wagoner W., Lightner J. Activation tagging in tomato identifies a transcriptional regulator of anthocyanin biosynthesis, modification, and transport. Plant Cell. 2003;15:1689–1703. doi: 10.1105/tpc.012963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mes P.J., Boches P., Myers J.R. Characterization of tomatoes expressing anthocyanin in the fruit. J. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 2008;133:262–269. [Google Scholar]
- Montefiori M., Brendolise C., Dare A.P., Lin-Wang K., Davies K.M., Hellens R.P., Allan A.C. In the Solanaceae, a hierarchy of bHLHs confer distinct target specificity to the anthocyanin regulatory complex. J. Exp. Bot. 2015;66:1427–1436. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eru494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers, J. (2012). Breeding tomatoes for increased flavonoids. In: Strengthening Community Seed Systems. Proceedings of the 6th Organic Seed Growers Conference, Port Townsend, Washington, USA, 19–21 January, pp. 50–51.
- Nesi N., Debeaujon I., Jond C., Pelletier G., Caboche M., Lepiniec L. The TT8 gene encodes a basic helix-loop-helix domain protein required for expression of DFR and BAN genes in Arabidopsis siliques. Plant Cell. 2000;12:1863–1878. doi: 10.1105/tpc.12.10.1863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nukumizu Y., Wada T., Tominaga-Wada R. Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) homologs of TRIPTYCHON (SlTRY) and GLABRA3 (SlGL3) are involved in anthocyanin accumulation. Plant Signal. Behav. 2013;8:e24575. doi: 10.4161/psb.24575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peralta I.E., Spooner D.M. History, origin and early cultivation of tomato (Solanaceae) In: Razdan M.K., Mattoo A.K., editors. Vol. 2. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL: 2007. pp. 1–24. (Genetic Improvement of Solanaceous Crops). [Google Scholar]
- Povero G., Gonzali S., Bassolino L., Mazzucato A., Perata P. Transcriptional analysis in high-anthocyanin tomatoes reveals synergistic effect of Aft and atv genes. J. Plant Physiol. 2011;168:270–279. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2010.07.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiu Z., Wang H., Li D., Yu B., Hui Q., Yan S., Huang Z., Cui X., Cao B. Identification of candidate HY5-dependent and -independent regulators of anthocyanin biosynthesis in tomato. Plant Cell Physiol. 2019;60:643–656. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcy236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiu Z., Wang X., Gao J., Guo Y., Huang Z., Du Y. The tomato Hoffman's anthocyaninless gene encodes a bHLH transcription factor involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis that is developmentally regulated and induced by low temperatures. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0151067. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay N.A., Glover B.J. MYB-bHLH-WD40 protein complex and the evolution of cellular diversity. Trends Plant Sci. 2005;10:63–70. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2004.12.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapir M., Oren-Shamir M., Ovadia R., Reuveni M., Evenor D., Tadmor Y., Nahon S., Shlomo H., Chen L., Meir A. Molecular aspects of Anthocyanin fruit tomato in relation to high pigment-1. J. Hered. 2008;99:292–303. doi: 10.1093/jhered/esm128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber G., Reuveni M., Evenor D., Oren-Shamir M., Ovadia R., Sapir-Mir M., Bootbool-Man A., Nahon S., Shlomo H., Chen L. ANTHOCYANIN1 from Solanum chilense is more efficient in accumulating anthocyanin metabolites than its Solanum lycopersicum counterpart in association with the ANTHOCYANIN FRUIT phenotype of tomato. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2011;124:295–307. doi: 10.1007/s00122-011-1705-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi X., Gupta S., Rashotte A.M. Solanum lycopersicum cytokinin response factor (SlCRF) genes: characterization of CRF domain-containing ERF genes in tomato. J. Exp. Bot. 2012;63:973–982. doi: 10.1093/jxb/err325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley C.R., Blazquez L., Ule J. Lessons from non-canonical splicing. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016;17:407–421. doi: 10.1038/nrg.2016.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stam R., Nosenko T., Hörger A.C., Stephan W., Seidel M., Kuhn J.M.M., Haberer G., Tellier A. The de novo reference genome and transcriptome assemblies of the wild tomato species Solanum chilense highlights birth and death of NLR genes between tomato species. G3 (Bethesda) 2019 doi: 10.1534/g3.119.400529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stracke R., Werber M., Weisshaar B. The R2R3-MYB gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2001;4:447–456. doi: 10.1016/s1369-5266(00)00199-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syed N.H., Kalyna M., Marquez Y., Barta A., Brown J.W. Alternative splicing in plants—coming of age. Trends Plant Sci. 2012;17:616–623. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2012.06.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomato Genome Consortium The tomato genome sequence provides insights into fleshy fruit evolution. Nature. 2012;485:635–641. doi: 10.1038/nature11119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang G., Chen B., Du H., Zhang F., Zhang H., Wang Y., He H., Geng S., Zhang X. Genetic mapping of anthocyanin accumulation-related genes in pepper fruits using a combination of SLAF-seq and BSA. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0204690. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0204690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weits D.A., Giuntoli B., Kosmacz M., Parlanti S., Hubberten H.M., Riegler H., Hoefgen R., Perata P., van Dongen J.T., Licausi F. Plant cysteine oxidases control the oxygen-dependent branch of the N-end-rule pathway. Nat. Commun. 2014;5:3425. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu W., Dubos C., Lepiniec L. Transcriptional control of flavonoid biosynthesis by MYB-bHLH-WDR complexes. Trends Plant Sci. 2015;20:176–185. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2014.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoo S.D., Cho Y.H., Sheen J. Arabidopsis mesophyll protoplasts: a versatile cell system for transient gene expression analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2007;2:1565–1572. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2007.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang F., Gonzalez A., Zhao M., Payne C.T., Lloyd A. A network of redundant bHLH proteins functions in all TTG1-dependent pathways of Arabidopsis. Development. 2003;130:4859–4869. doi: 10.1242/dev.00681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong S., Lin Z., Fray R.G., Grierson D. Improved plant transformation vectors for fluorescent protein tagging. Transgenic Res. 2008;17:985–989. doi: 10.1007/s11248-008-9199-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann I.M., Heim M.A., Weisshaar B., Uhrig J.F. Comprehensive identification of Arabidopsis thaliana MYB transcription factors interacting with R/B-like BHLH proteins. Plant J. 2004;40:22–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02183.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.