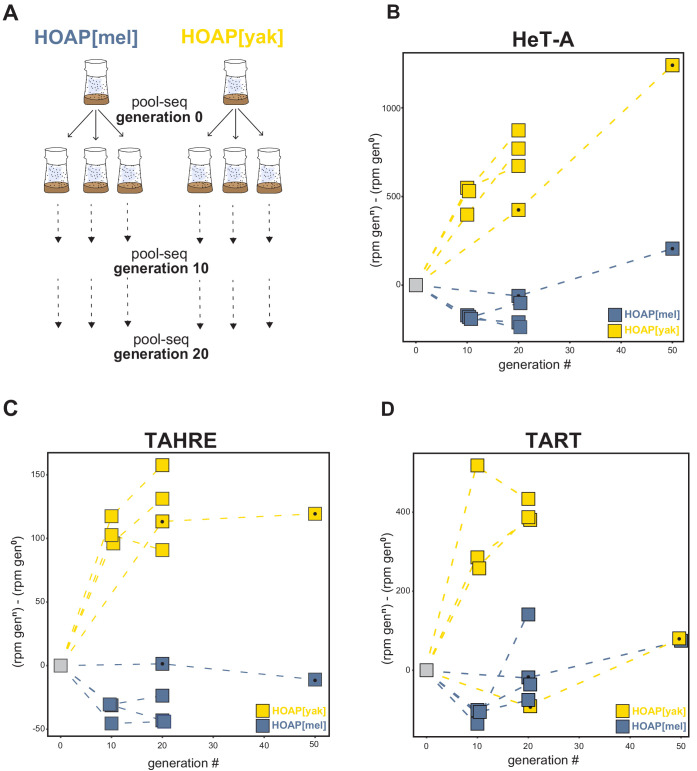
Figure 3. Retrotransposons proliferate in HOAP[yak] over experimental evolution.
(A) Replicated experimental evolution strategy that begins with an expanded population of HOAP[mel] and HOAP[yak]. We divided each founder population into three replicates and then froze down 100 females for pool-DNA-seq ('generation 0'). We flipped replicate populations until generation 20, sampling pools of females for DNA-seq at generations 10 and 20 per population. A parallel run of experimental evolution (not shown) was sampled at generations 0, 20, and 50. (B-D) DNA-seq reads mapped to the D. melanogaster HeT-A (B), TAHRE (C), and TART (D) consensus sequences, shown as reads per million (rpm) at a given generation minus the rpm at generation 0 for a given population. The long-term experimental evolution samples have a filled black circle in each square. Note the different y-axes of (B), (C), and (D).