Abstract
An 84-year-old man developed motor aphasia and right hemiparesis on postoperative day 1 after orchiectomy for suspected malignant lymphoma. He had a history of thoracic endovascular aortic repair for aortic aneurysm using a bypass graft from the right subclavian artery to the left common carotid artery (CCA); however, the graft had become occluded six months later. Brain magnetic resonance imaging revealed acute cerebral infarctions in the left frontal lobe. Carotid ultrasonography revealed a stump at the left CCA, just below the bifurcation, formed by the occluded graft with an oscillating thrombus. This case was rare in that a CCA stump was identified as the embolic source of ischemic stroke.
Keywords: ischemic stroke, carotid stump syndrome, common carotid artery, ultrasonography
Introduction
Carotid stump syndrome (CSS) is a cause of ischemic stroke due to thrombus forming at the site of an arterial stump (1). Most CSS cases are caused by thrombus at an internal carotid artery (ICA) stump, although it can also very occasionally form at a common carotid artery (CCA) stump (2,3).
We herein report a case of ischemic stroke that occurred in a patient with a CCA stump diagnosed by ultrasonography.
Case Report
An 84-year-old man who had a history of thoracic endovascular aortic repair (TEVAR) with a bypass graft from the right subclavian artery to the left CCA for an aortic aneurysm 7 years earlier underwent orchiectomy for suspected malignant lymphoma on postoperative day (POD) 0. Computed tomography (CT) before the orchiectomy showed swelling of the testis and suspected lymphadenopathy in the para-aorta, mesentery, right iliac region and right inguinal canal. Although complete occlusion of the bypass graft had been identified by contrast CT six months after TEVAR, he had been medicated with warfarin and clopidogrel for seven years, and these antithrombotic drugs were discontinued two weeks before the orchiectomy procedure.
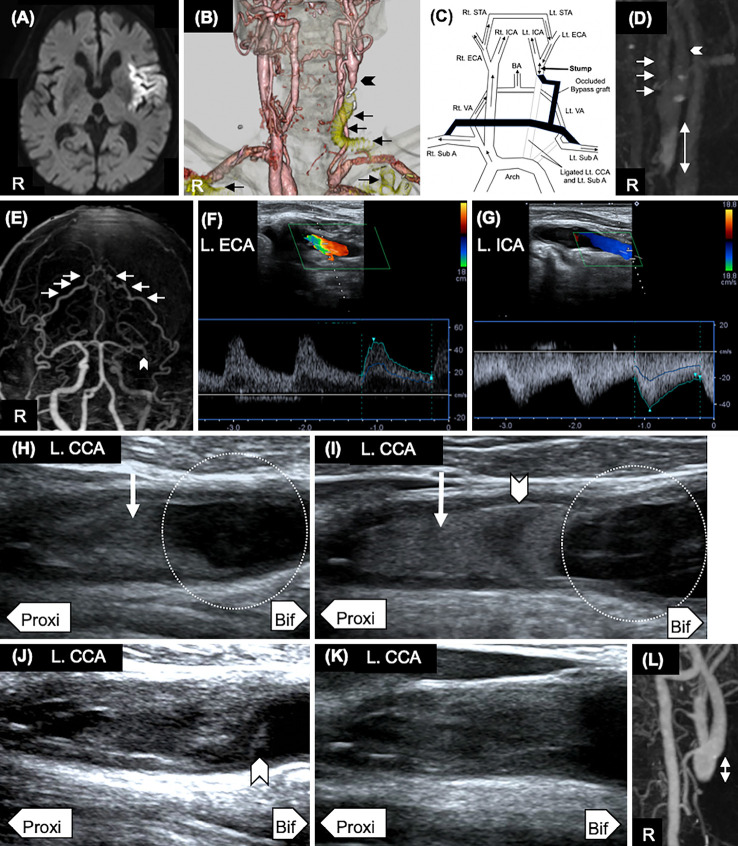
He developed motor aphasia and right hemiparesis on POD 1. His blood pressure was 145/74 mmHg, and he weighed 64.5 kg. Blood findings of electrolytes and his hepatic function were unremarkable, but creatinine was 1.72 mg/dL, and coagulation tests showed high plasma D-dimer (9.3 μg/dL, Table). Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed a fresh ischemic lesion at the left middle cerebral artery territory that appeared as high- and low-intensity signals on diffusion-weighted and apparent diffusion coefficient images, respectively (Figure A). Cervical CT angiography showed the left CCA and left subclavian artery ligated by TEVAR and complete occlusion of the bypass graft connecting the right subclavian artery to the left CCA and left subclavian artery. Thus, the stump was formed at distal side of the left CCA, just below the bifurcation (Figure B, C).
Table.
Blood Examination Findings on Stroke Onset.
| Hematology | ALT | 44 | U/L | |||||
| Leukocytes | 13,700 | /μL | BUN | 27 | mg/dL | |||
| Erythrocytes | 389 | ×106/μL | Creatinine | 1.72 | mg/dL | |||
| Hemoglobin | 11.9 | g/dL | Sodium | 134 | mEq/L | |||
| Hematocrit | 32.9 | % | Potassium | 4.5 | mEq/L | |||
| Platelets | 26.9 | ×103/μL | Cloride | 98 | mEq/L | |||
| Coagulation | T-chol | 104 | mg/dL | |||||
| PT-INR | 1.10 | LDL-chol | 48 | mg/dL | ||||
| APTT | 28.1 | sec. | HDL-chol | 36 | mg/dL | |||
| D-dimer | 9.3 | μg/mL | Glucose | 93 | mg/dL | |||
| Biochemistry | HbA1c (NGSP) | 5.7 | % | |||||
| Total protein | 6.8 | g/dL | C-reactive protein | 3.83 | mg/dL | |||
| Albumin | 3.7 | g/dL | BNP | 32.6 | pg/mL | |||
| AST | 51 | U/L | Soluble interleukin-2 recepter | 3,537 | U/mL | |||
PT-INR: international normalized ration for prothrombin time, APTT: activated partial thromboplastin time, AST: aspartate aminotransferase, ALT: alanine aminotransferase, BUN: blood urea nitrogen, T-chol: total cholesterol, LDL-chol: low density lipoprotein cholesterol, HDL-chol: high density lipoprotein cholesterol, HbA1c (NGSP): hemoglobin A1c (National Glycohemoglobin Standardization Program), BNP: brain natriuretic peptide
Figure.
Imaging findings. (A) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging showed high-intensity lesions in the left middle cerebral artery (POD1). R: right side. (B) By total arch replacement, the origin of the left common carotid artery (CCA) and left subclavian artery was ligated. Cervical CT angiography (POD 1) showed complete occlusion of the bypass graft connecting the right subclavian artery to the left CCA and left subclavian artery (arrow). Thus, a stump was formed at the distal side of the left CCA (arrowhead). (C) Schematic illustration of the arterial hemodynamics based on cervical contrast CT in this patient. Rt: right, Lt: left, Sub A: subclavian artery, VA: vertebral artery, ECA: external carotid artery, STA: superficial temporal artery, ICA: internal carotid artery, BA: basilar artery, CCA: common carotid artery. (D) Cervical four-dimensional (4-D) contrast CT (POD 1) showed a stump at the distal side of the left CCA. Blood flow stasis was observed at the stump of the left CCA in the venous phase. The length of the stump at the CCA from the bifurcation (2-way arrow) was 19 mm. The arrow indicates the left external carotid artery (ECA), and the arrowhead indicates the left internal carotid artery (ICA). (E) Head 4-D contrast CT (POD 2) showed that the left ECA flow was mainly supplied from the left superficial temporal artery (STA) via the right STA (D). In addition, the left middle cerebral artery was occluded (arrowhead), which caused ischemic stroke. (F) The flow of the left ECA (L. ECA) was retrograde according to carotid ultrasonography (CU) on POD 1. (G) The flow of the left ICA (L. ICA) was anterograde according to CU on POD 1. (H) Oscillating thrombus (arrow) and spontaneous echo contrast (SEC, circle) were detected by CU on POD 1. Proxi: proximal side, Bif: bifurcation side. (I) The thrombus with oscillating thrombus (arrow) detected at the time of the stroke onset was gradually extended with central echolucency (arrowhead) on POD 4. SEC was still observed (circle). (J) Ultrasonography on POD 42 revealed a new low-echoic thrombus (arrowhead) even though the oscillating thrombus had stabilized. (K) The low-echoic thrombus had disappeared by POD 42. (L) The length of the stump from the bifurcation (2-way arrow) was 10 mm on POD 45.
Four-dimensional (4-D) contrast CT indicated blood flow stasis at the stump of the left CCA (Figure D). The length of the stump from the bifurcation was 19 mm. The left ICA mainly flowed from the external carotid artery via the right superficial temporal artery (Figure E-G). Ultrasonography revealed a stump with oscillating thrombus and spontaneous echo contrast (SEC) at the distal side of the left CCA (Figure H). A Holter electrocardiography (ECG), transthoracic echocardiography and transesophageal echocardiography did not reveal any other significant embolic sources. We therefore diagnosed him with CSS caused by the stump at the CCA and treated the patient with warfarin and clopidogrel.
The thrombus detected at the time of the stroke onset gradually extended with central echolucency on POD 4 (Figure I). Finally, he was diagnosed with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (germinal center B-cell-like phenotype, Ann Arbor stage IV, International Prognostic Index: high-intermediate risk). Thus, he was treated with chemotherapy (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin and prednisone: CHP) from POD 12. Stroke did not recur after the index stroke following the administration of warfarin and clopidogrel. However, ischemic stroke recurred in the left frontal lobe on POD 42 when warfarin was less effective (prothrombin time-international normalized ratio: 1.58). Ultrasonography on POD 42 revealed a new low-echoic thrombus even though the oscillating thrombus had stabilized (Figure J). Adding heparin erased the low-echoic thrombus on POD 45 without further ischemic stroke recurrence (Figure K). The length of the stump from the bifurcation (2-way arrow) was 10 mm on POD 45 (Figure L). However, motor aphasia and severe right hemiparesis persisted. The lymphadenopathy increased on CT, and the malignant lymphoma was unresponsive to chemotherapy unfortunately. Although additional chemotherapy (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisone: R-CHOP) was administered, the lymphadenopathy did not decrease on CT on POD 49. Considering his age and activity of daily living (performance status: 4, modified Rankin Scale: 5), he was transferred to a palliative care hospital on POD 61.
Discussion
Ischemic stroke due to CSS is caused by thrombus that forms at the stump of an occluded vessel. Most CSS cases are caused by thrombus at an ICA stump (2,3). The mechanism is thought to involve a thrombus at the ICA stump forming due to large plaque flows into the intracranial ICA via collateral circulation from the external carotid artery (4). Our patient was unique in that ischemic stroke was induced by thrombus that formed at the CCA stump after a bypass vessel became occluded and anticoagulant therapy was discontinued. In addition, lymphoma may have induced thrombus formation due to hypercoagulation, since tumor cells and stimulation of tumor-associated inflammatory cells activate the clotting cascade (5).
Only one case report has described CSS caused by a CCA stump that formed due to chronic occlusion of the CCA along with a thrombus detected by carotid ultrasonography synchronously oscillating with the cardiac cycle (6). Just as in that case, an oscillating thrombus with high echo was also found at the onset of ischemic stroke in our patient. Furthermore, the thrombus extended gradually with central echolucency, which was the low-echoic portion, thus indicating that liquid rapidly formed within the thrombus (7). This shift from low- to high-echoic content stabilized the thrombus and reduced the risk of recurrent ischemic stroke (8).
Our patient also had SEC, which is blood flow with a slowly moving, cloud-like swirling pattern of "smoke" that is considered to indicate a risk of thrombus (9,10). This is a rouleaux formation caused by low shear rates and is associated with the formation of consecutive local thrombi (9). Indeed, a new, low-echoic thrombus formed at the site of SEC when warfarin was ineffective in our patient. Warfarin does not affect SEC, although hematocrit, fibrinogen and other factors do, so SEC persisted despite the administration of antithrombotic therapy (10).
The treatment for CSS is antithrombotic agents, surgical ligature of the stump or endovascular therapy with stenting (11). However, the priority of surgery or endovascular therapy compared with medication has not been fully investigated. Both surgery and endovascular therapy were considered difficult to perform in the present patient because of the complex vascular structure or focal adhesions due to stasis after bypass-graft surgery. Total anticoagulation therapy might be needed for secondary prevention even after confirming that a thrombus has stabilized.
We described a patient with ischemic stroke caused by rare thrombus formation at the stump of the CCA. CSS should be considered when other embolic sources are undetectable and a stump is evident.
The authors state that they have no Conflict of Interest (COI).
References
- 1.Quill DS, Colgan MP, Sumner DS. Carotid stump syndrome: a colour-coded doppler flow study. Eur J Vasc Surg 3: 79-83, 1989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Zhang XU, Shao S, Zheng X, Gao X, Zhang Y. Carotid stump syndrome: a case report. Exp Ther Med 10: 1161-1164, 2015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cassidy L, Grace PA, Bouchier-Hayes DJ. The carotid stump syndrome. Eur J Vasc Surg 6: 368-370, 1992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lakshminarayan R, Scott PM, Robinson GJ, Ettles DF. Carotid stump syndrome: pathophysiology and endovascular treatment options. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 34 (Suppl 2): S48-S52, 2011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Liu B, Li B, Zhou P, et al. Prognostic value of pretreatment plasma D-dimer levels in patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Clin Chim Acta 482: 191-198, 2018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Omoto S, Hasegawa Y, Sakai K, et al. Common carotid artery stump syndrome due to mobile thrombus detected by carotid duplex ultrasonography. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 25: e205-e207, 2016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Haugland JM, Asinger RW, Mikell FL, Elsperger J, Hodges M. Embolic potential of left ventricular thrombi detected by two-dimensional echocardiography. Circulation 70: 588-598, 1984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Meissner MH, Moneta G, Burnand K, et al. The hemodynamics and diagnosis of venous disease. J Vasc Surg 46: 4S-24S, 2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kawabori M, Yoshimoto T, Ito M, et al. Spontaneous echo contrast and thrombus formation at the carotid bifurcation after carotid endarterectomy. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 52: 885-891, 2012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ito T, Suwa M, Nakamura T, Miyazaki S, Hirota Y, Kawamura K. Influence of Warfarin therapy on left atrial spontaneous echo contrast in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol 84: 857-859, 1999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hrbac T, Benes V, Sirucek P, et al. Safety and efficacy of surgical treatment of carotid stump syndrome: pilot study. Ann Vasc Surg 26: 797-801, 2012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]