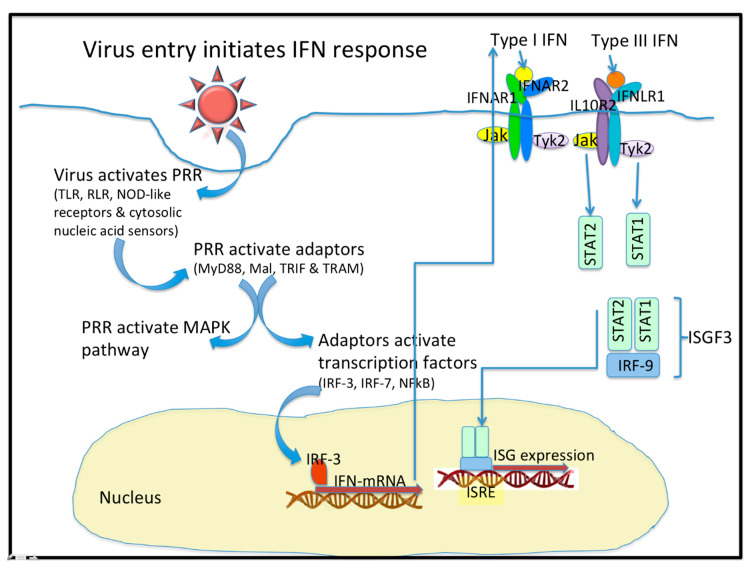
Figure 1.
Virus entry initiates the interferon (IFN) response. Upon entering a cell, virus activates Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRR) that include the Toll-like receptors (TLR), the RIG-I-like receptors (RLR), the NOD-like receptors, and some cytosolic nucleic acid receptors. These PRR activate adaptor molecules like MyD88, Mal, TRIF, and TRAM. PRR also activate the MAPK pathway. The Adaptor molecules activate Transcription factors like IRF-3, IRF-7 and NF-kB. IFN mRNA are transcribed and they express the type I, type II (not shown), and type III IFN. Type I and Type III IFN bind to distinct receptors that activate similar signaling pathways and transcriptional responses. The heterodimeric IFN receptors signal through the JAK/STAT pathways to form a complex with IRF-9 to initiate the expression of hundreds of Interferon stimulated genes (ISG). The ISG are peptidic antivirals that interfere with virus replication.