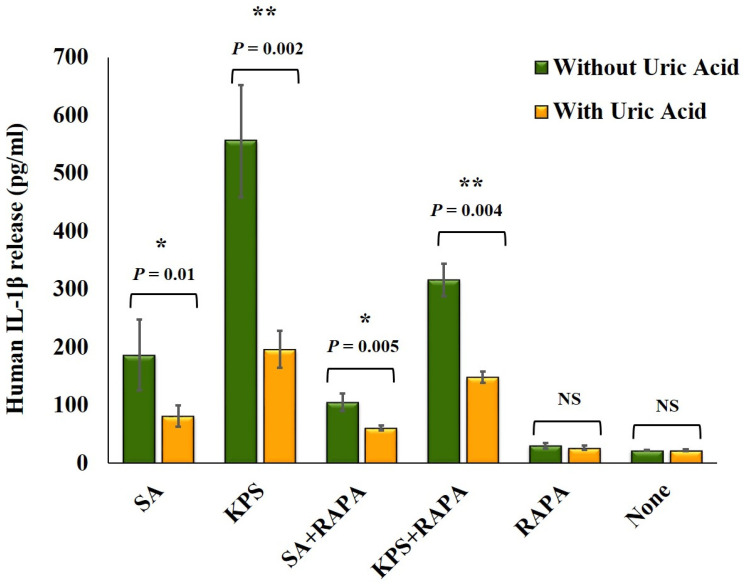
Figure 4.
Soluble uric acid attenuates IL-1β released from macrophages infected with live bacteria. IL-1β release from human THP-1 monocytic cells infected with live bacteria at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 10 in presence and absence of soluble uric acid (19 mg/dL) and Rapamycin for three hours prior to the addition of Gentamycin, Penicillin, and Streptomycin, then incubated overnight. IL-1β released in the supernatants was quantitated using ELISA method. These data represent the mean of two independent experiments with bars showing the standard error of the mean. SA: S. aureus; KPS: K. pneumoniae sensitive to antibiotics; RAPA: Rapamycin; UA: uric acid; ns: not significant. p value < 0.05 are significant, * in comparison to SA without Rapamycin, ** in comparison to KPS without Rapamycin.