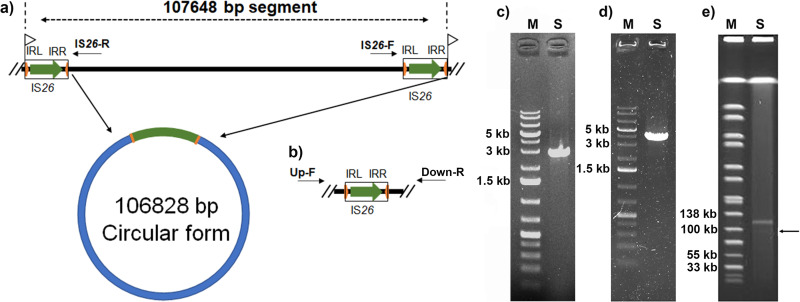
FIG 2.
Formation of a circular intermediate by circularization of the insertion segment in the chromosome of strain 16HN-263. (a) Genetic structure of the transposon and its circular intermediate. IS26 elements are shown as open boxes. Green arrows indicate the position and orientation of tnp26. Orange arrows refer to the left and right terminal inverted repeats (IRL and IRR) of the IS26 element. Flags indicate the position and direction of the identified target site duplication (TSD). (b) Genetic structure of the chromosomal fragment after excision of the transposon. (c) Gel electrophoresis of PCR amplicons corresponding to the circular intermediate generated using the reverse primers IS26-F and IS26-R. S depicts the PCR product. (d) Gel electrophoresis of PCR amplicons corresponding to the excision of Tn7074 using the primers Up-F and Up-R. S depicts the PCR product. (e) S1-PFGE profile of strain 16HN-263. S indicates strain 16HN-263.