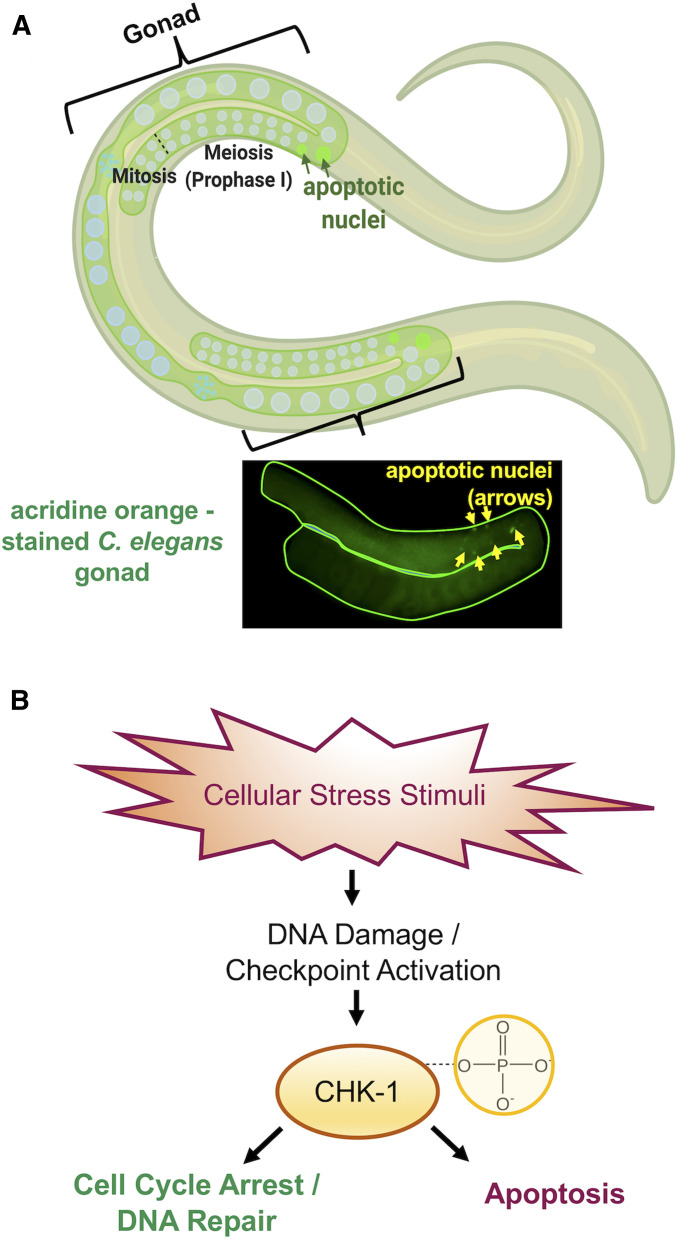
Figure 3.
Causes and consequences of DNA damage in the C. elegans germ line. (A) Top: graphic showing apoptotic nuclei (depicted as fluorescent green circles) detected in the late pachytene stage of prophase I near the bend of the C. elegans gonads. Bottom: dissected C. elegans gonad stained with acridine orange; yellow arrowheads indicate apoptotic nuclei. (B) Cellular stress stimuli, such as BPA exposure, is a source of DNA damage that signals checkpoint proteins, such as the kinase CHK-1. This is activated by phosphorylation and leads to either DNA repair or the culling of damaged cells by apoptosis.