Abstract
Hyperuricemia and gout have been linked to an increased risk for cardiovascular (CV) disease, stroke, hypertension, heart failure, and chronic kidney disease, possibly through a proinflammatory milieu. However, not all the drugs used in gout treatment improve CV outcomes; colchicine has shown improved CV outcomes in patients with recent myocardial infarction and stable coronary artery disease independent of lipid-lowering effects. There is resurging interest in colchicine following publication of the COLCOT, LoDoCo, LoDoCo2, LoDoCo-MI trials, and COLCORONA trial which will shed light on its utility in COVID-19. Our aim is to review the CV use of colchicine beyond pericardial diseases, as well as CV outcomes of the available gout therapies, including allopurinol and febuxostat. The CARES trial and its surrounding controversies, which lead to the US FDA ‘black box’ warning on febuxostat, in addition to the recent FAST trial which contradicts this and finds febuxostat to be non-inferior, are discussed in this paper.
Key Points
| Several anti-inflammatory and urate-lowering drugs used in gout have been found to have a favorable effect on cardiovascular (CV) outcomes. |
| Colchicine is first-line therapy in both gout and pericarditis. It has also demonstrated benefit in the prevention of ischemic events in patients with stable coronary artery disease (CAD) and recent myocardial infarction (MI), postpericardiotomy syndrome and postoperative atrial fibrillation. |
| Allopurinol may have a potential cardioprotective effect, particularly in the reduction of blood pressure and prevention of MI. |
| CV outcomes with febuxostat are non-inferior to allopurinol and the long-term use of febuxostat is not associated with increased death or CV mortality. |
| The CV effects of newer gout drugs such as arhalofenate, verinurad, and rilonacept need to be evaluated. |
Introduction
Gout is a chronic inflammatory arthritis that affects 9.2 million adults in the US and is characterized by monosodium urate crystal deposition in the joints, secondary to elevated urate levels [1]. Evidence suggests that hyperuricemia and gout are independently linked to an increased risk of coronary artery disease (CAD), heart failure (HF), and cardiovascular (CV) mortality [2]. Patients with recent myocardial infarction (MI) and active gout have worse survival compared with patients with MI who are receiving treatment for gout [3]. Interestingly, not all urate-lowering therapies (ULTs) improve CV outcomes. The URic acid Right for heArt Health Study Group (URRAH) confirmed the independent association of serum uric acid levels and fatal MI. Indeed, they demonstrated a prognostic uric acid cut-off of 5.26 as a predictor for fatal MI in women [4]. Colchicine, which is a commonly used gout medication, has long been used in various pericardial diseases, including pericarditis, pericardial effusion, and effusive constrictive pericarditis. It has shown reductions in long-term CV adverse events in patients with recent MI and stable ischemic heart disease (SIHD). While the outcomes of the COLCOT (Colchicine Cardiovascular Outcomes Trial) trial generated interest, more research is required to fully incorporate colchicine into clinical practice [5–7]. Similarly, allopurinol and febuxostat have shown conflicting evidence with respect to CV outcomes.
Literature Search
We searched two databases—PubMed and Cochrane—for English-language studies from database inception until June 2020, using the keywords ‘colchicine’, ‘cardiovascular’, ‘allopurinol’, ‘febuxostat’, ‘gout therapy’, ‘heart failure’, and ‘major adverse cardiovascular events’. We also searched for meta-analyses, observational studies, practice guidelines, and reviews. Importance was given to randomized controlled trials and recent high-quality reviews.
Inflammation and Uric Acid in Atherosclerosis
Initially thought to be primarily cholesterol-induced, the atherosclerotic process is now known to be the result of a complex interplay between endothelial injury, inflammation, and conventional metabolic risk factors such as dyslipidemia, hypertension, and diabetes (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
A brief outline of inflammation in atherosclerosis. IFN interferon, IL interleukin, LDL low-density lipoprotein, ROS reactive oxygen species, Th1 T-helper 1, VCAM-1 vascular cell adhesion molecule 1, NLRP3 nucleotide oligomerization domain-, leucine-rich repeat-, pyrin domain-containing protein
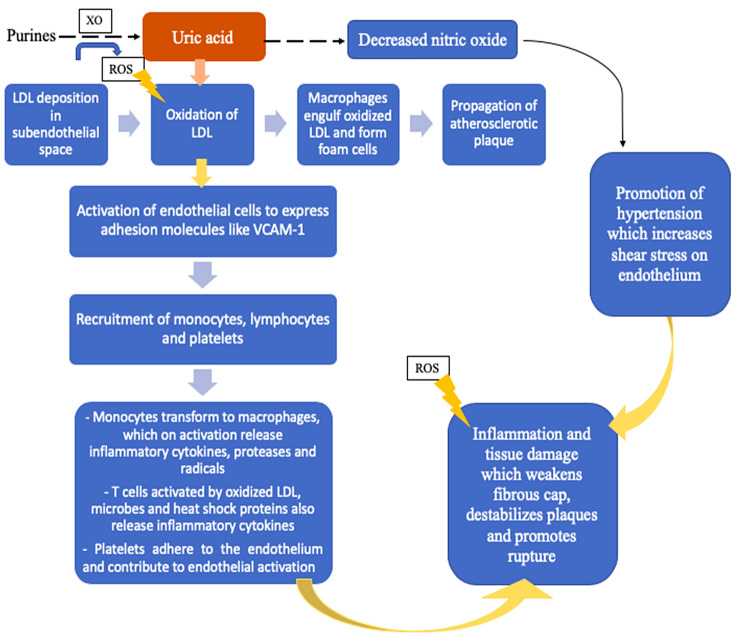
Hyperuricemia is prevalent in CV diseases such as hypertension, ischemic heart disease (IHD) and HF. However, it is unclear whether hyperuricemia is responsible for CV morbidity or is a marker of a more advanced disease. Uric acid itself has antioxidant and oxidizing properties, and its production from purines is catalyzed by xanthine oxidase (XO), which generates reactive oxygen species during the reaction, as shown in Fig. 2 [8]. Uric acid also promotes oxidation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL), which has an important role in plaque initiation and propagation. Additionally, decreased nitric oxide (which effects vasodilation, platelet aggregation inhibition, and intimal proliferation) levels have been demonstrated with elevated uric acid, possibly due to uric acid-mediated inhibition of insulin-induced nitric oxide synthase [9].
Fig. 2.
A simplified representation of the role of uric acid in atherogenesis and cardiovascular disease. Other proposed mechanisms, not represented here, are activation of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system and insulin resistance. LDL low-density lipoprotein, ROS reactive oxygen species, VCAM-1 vascular cell adhesion molecule 1, XO xanthine oxidase
Management and Pharmacotherapies in Gout
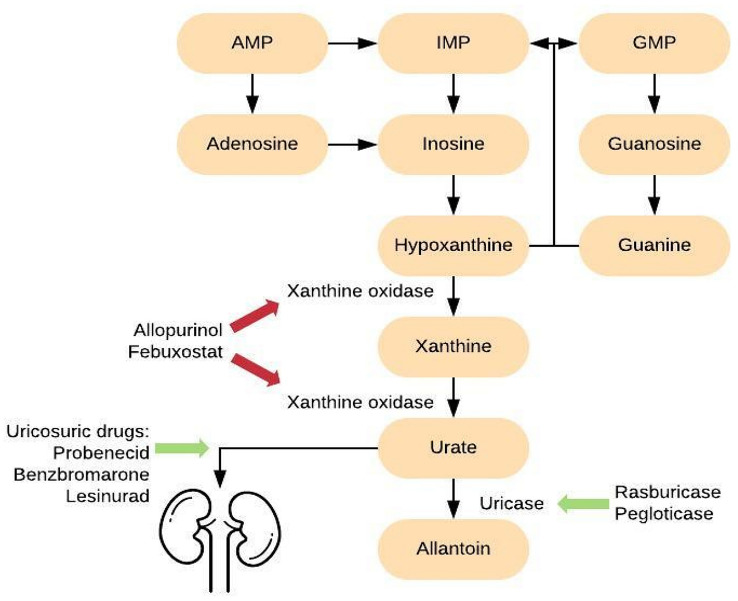
The treatment of a gout flare involves monotherapy with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) or cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors, colchicine, or corticosteroids individualized for each patient (American College of Rheumatology [ACR] level A recommendation). These drugs target synovial neutrophil infiltration and suppress the acute inflammatory response. Colchicine is recommended for use within 36 h of a flare and a loading dose of 1.2 mg followed by 0.6 mg 1 h later effectively reduces pain by about 50%. For severe gout flares, colchicine can be used in combination with NSAIDs, oral corticosteroids, or intralesional corticosteroid injections. Thereafter, it can be continued prophylactically at a dose of 0.6 mg one to two times daily. Pharmacological properties of colchicine are detailed in Table 1 [6]. Patients presenting with frequent flares, history of urolithiasis, glomerular filtration rate < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 or higher, or presence of tophi should be started on ULT; however, all patients with gout should be made aware of the benefits of, and offered, ULT at diagnosis. The current ACR level A-recommended ULTs include the XO inhibitors, allopurinol, and febuxostat. Probenecid, a uricosuric, is a level B-recommended ULT in patients with intolerance to allopurinol or febuxostat. In refractory gout, a recombinant uricase (pegloticase) is the level A ACR-recommended drug [7]. Pharmacotherapies in gout are summarized in Tables 1 and 2, with mechanism outlined in Fig. 3 [9, 10].
Table 1.
Pharmacology of colchicinea
| Drug for acute flarea | Colchicine |
|---|---|
| Route of administration | Oral |
| Metabolism and excretion | Metabolized by CYP3A4 to 2- and 3-demethylcolchicine; gastrointestinal absorption is limited by enterocyte P-glycoprotein; renally excreted |
| Dosing |
1.2 mg at onset of gout flare, followed by 0.6 mg after 1 h For prophylaxis: 0.6 mg once to twice daily The dose used in the COLCOT trial was 0.5 mg once daily |
| Important adverse effects | Gastrointestinal, most commonly diarrhea, in up to 10%. Other important adverse effects are myelosuppression and neuromuscular toxicity |
| Important drug interactions | Avoid coadministration with P-glycoprotein or CYP3A4 inhibitors (such as cyclosporine or clarithromycin, respectively) as they inhibit colchicine metabolism |
| Monitoring | Blood counts, and liver and renal function |
| Contraindications | Patients with liver or renal dysfunction should not be administered colchicine along with CYP or P-glycoprotein inhibitors |
CYP cytochrome P450 enzyme, COLCOT Colchicine Cardiovascular Outcomes Trial
aNSAIDs and glucocorticoids are also first-line agents that are not included here
Table 2.
Pharmacology of drugs used for the chronic management of gout
| Urate-lowering therapy | Xanthine oxidase inhibitors | Uricosuric drugs | Uricase | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allopurinol | Febuxostat | Probenecid | Lesinurad | Rasburicase | Pegloticase | |
| Route of administration | Oral | Oral | Oral | Oral | IV infusion | IV infusion |
| Metabolism and excretion | Metabolized to oxypurinol, which is excreted renally | Undergoes hepatic metabolism by CYP1A2, CYP2C8, and CYP2C9 to active metabolites; excreted renally | Undergoes oxidation of alkyl side chains and glucuronide conjugation; excreted renally | Moderate CYP3A4 inducer; up to 40% excreted renally | Undergoes peptide hydrolysis | Renal excretion |
| Dosing | 50–800 mg/day | 40 or 80 mg once daily | 500–1000 mg twice daily | Moderate CYP3A4 inducer; up to 40% excreted renally | 0.2 mg/kg as an infusion over 30 min daily for up to 5 days (single course only, not repeated) | 8 mg every 2 weeks |
| Important adverse effects | Rash, allopurinol hypersensitivity and gout flare on initiation of treatment | Liver impairment and gout flare on initiation of treatment. US FDA added a boxed warning for possible increased CV mortality | Kidney stones and gout flare on initiation of treatment | 200 mg/day in combination with an xanthine oxidase inhibitor | Headache, abdominal pain, mucositis. Uncommon adverse effects are anaphylaxis, hemolytic anemia, and methemoglobinemia. | Infusion reactions, immunogenic effects and gout flare on initiation of treatment |
| Important drug interactions | Potentiates action of azathioprine and warfarin | Coadministration with drugs that are xanthine oxidase substrates, azathioprine or mercaptopurine, could increase plasma concentrations with resultant severe toxicity | Can increase methotrexate toxicity | Renal failure and urate kidney stones, more common when used as monotherapy; adverse CV events |
Does not have any significant drug interactions Interferes with laboratory measurement of serum uric acid. Therefore, blood is collected in heparinized prechilled tubes, maintained in an ice-water bath and tested within 4 h |
Other urate-lowering drugs can mask the absence of response to pegloticase and thus raise the risk of infusion reaction |
| Monitoring | Renal and liver function and serum urate | Renal and liver function and serum urate | Renal function and serum urate | Renal function | Serum urate | Serum urate |
| Contraindications | Allopurinol hypersensitivity |
1. Ischemic heart disease and cardiac failure 2. Patients taking azathioprine or mercaptopurine |
1. Uric acid kidney stones 2. Blood dyscrasias |
1. Serum creatinine level < 30 mL/min, or kidney transplant 2. Tumor lysis syndrome 3. Lesh–Nyhan syndrome 4. Prior cardiac disease |
1. Hypersensitivity to, or hemolysis/methemoglobinemia with, rasburicase 2. G6PD deficiency |
1. G6PD deficiency 2. If serum urate response is absent |
CYP cytochrome P450 enzyme, CV cardiovascular, G6PD glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, IV intravenous
Fig. 3.
Mechanism of urate-lowering drugs. AMP adenosine monophosphate, GMP guanosine monophosphate, IMP inosine monophosphate
Cardiovascular Outcome and Expanded Use of Colchicine
Colchicine
Colchicine is widely used in the management of pericarditis. Colchicine for 3 months is recommended as first-line therapy along with NSAIDs (European Society of Cardiology [ESC] class IA recommendation) for acute pericarditis. The addition of colchicine results in a lower rate of symptom persistence at 72 h, effective reduction in pericarditis recurrence, and rates of hospitalization due to pericarditis. Colchicine is also indicated in the setting of pericardial effusion (with systemic inflammation) and effusive constrictive pericarditis (ESC recommendation class I, level of evidence C) [10].
Recent evidence suggests potential benefit of colchicine in atherogenesis and secondary prevention of CAD via inhibition of cytokine production. The anti-inflammatory action of colchicine is summarized in Fig. 4 [11]. The COLCOT trial demonstrated a significant reduction in the primary composite endpoint of death from CV causes, resuscitated cardiac arrest, MI, stroke, or urgent rehospitalization for angina leading to coronary revascularization in patients with recent MI (mean of 13.5 days after MI), when treated with low-dose colchicine (0.5 mg once daily) compared with the placebo group (hazard ratio [HR] 0.77, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.61–0.96; p = 0.02) at a median follow-up of 22.6 months [5]. Another study noted colchicine significantly reduced coronary artery plaque volume (− 40.9% vs. − 17.0% in placebo; p = 0.008) and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP; − 37.3% vs. 14.6% in placebo; p < 0.001) in patients with recent acute coronary syndrome (ACS) [12]. In contrast, the results of the Low-Dose Colchicine (LoDoCo)-MI trial did not demonstrate a significantly increased likelihood of achieving a CRP level < 2 mg/L or lower absolute levels of CRP 30 days after an acute MI in the colchicine group compared with the placebo group [13]. Emerging evidence is encouraging considering the cost effectiveness and safety profile of colchicine. Larger trials with a longer follow-up period in other patient subgroups could potentially solidify the role of colchicine as add-on therapy in the secondary prevention of MI (Fig. 5).
Fig. 4.
Schematic representation of the mechanism of the anti-inflammatory effects of colchicine. IL interleukin, MMP matrix metalloproteinase, NLRP3 nucleotide oligomerization domain-, leucine-rich repeat-, pyrin domain-containing protein
Fig. 5.
Summary of major cardiovascular outcomes of the drugs. ACS acute coronary syndrome, CAD coronary artery disease, AF atrial fibrillation, MI myocardial infarction, BP blood pressure, CV cardiovascular, SGLT 2 sodium glucose transporter-2
Nascent data on colchicine in ACS are also available; in vitro, colchicine has been shown to have antiplatelet activity, while, in vivo, reduced rates of in-stent stenosis and stabilization of coronary plaques post-ACS have been demonstrated [14]. Use of colchicine in ST elevation MI presenting within 12 h of symptom onset and treated with primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) demonstrated a smaller infarct size (18.3 vs. 23.2 mL/1.73 m2 in placebo; p = 0.019), lower neutrophil level, and lower hsCRP level [15]. Additionally, decreased cytokine levels in coronary sinus, right atrium, and aortic root was demonstrated in ACS patients (treated with PCI) after administration of colchicine 1.5 mg [16]. In another study evaluating 400 patients undergoing PCI, the administration of colchicine 1.8 mg prior to PCI improved the levels of hsCRP and IL-6 but did not reduce the risk of PCI-induced myocardial injury [17].
The LoDoCo trial studied the effect of low-dose colchicine as an add-on therapy to statins and antiplatelet agents in 532 patients with stable CAD followed for a median of 3 years. A significant reduction in the primary outcome (ACS, cardiac arrest, and ischemic stroke) was observed in the colchicine group compared with the placebo group (HR 0.33, 95% CI 0.18–0.59; p < 0.001) [18]. The potential benefit of colchicine in the prevention of future ischemic events was confirmed by the results of the LoDoCo2 trial. The trial randomized 5522 patients with catheterization or imaging-proven chronic CAD to receive daily colchicine or placebo and followed them for a median of 28.6 months. They demonstrated a significant reduction in primary outcome measures, including CV mortality, MI, ischemia-driven revascularization and stroke, for colchicine compared with placebo (6.8% vs. 9.6%; HR 0.69, 95% CI 0.57–0.83; p < 0.001). The caveat is a trend towards increased non-cardiac mortality in the colchicine group that warrants further investigation [19]. Two retrospective observational studies found a significantly lower risk of CV events in people with gout treated with colchicine compared with those who did not receive colchicine [20, 21].
In addition, colchicine is efficacious for prophylaxis in postoperative or postablative atrial fibrillation (AF) [22]. A meta-analysis evaluated five RCTs with 1412 patients and found that compared with placebo, prophylactic colchicine reduced the incidence of postoperative AF by 30%, as well as decreased the length of stay [23]. Colchicine is also beneficial in postpericardiotomy syndrome, with supportive evidence from major trials [24, 25]. Furthermore, Colchicine Coronavirus SARS-CoV2 Trial (COLCORONA) is an ongoing phase 3 RCT with an aim to evaluate the effect of 30-day treatment with colchicine on the mortality rate and pulmonary complications of COVID-19. The results of this trial would shed light on the potential utility of colchicine in the pandemic [26]. COVID-19 is associated with elevated inflammatory mediators, including IL-6, IL-8, IL-10 and tumor necrosis factor-α [27]. In addition, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV2) virus is thought to stimulate NLRP3 inflammasome activation, and the anti-inflammatory action of colchicine has been hypothesized to be from NLRP3 inhibitions. Previous studies have demonstrated a beneficial effect of colchicine on CRP, IL-1b, and IL-6 in chronic inflammatory conditions [27]. An open-label RCT evaluated the role of colchicine in COVID-19 patients by assessing time to clinical deterioration, time to CRP elevation, and differences in maximum high-sensitivity cardiac troponin (hs-cTn) recorded in the control and colchicine groups. They found that hs-cTn and CRP levels were comparable in the two groups, however time to clinical deterioration was improved (14% in controls vs. 1.8% in colchicine; odds ratio [OR] 0.11, 95% CI 0.01–0.96; p = 0.046). Major study limitations were the open-label design and a small population size [28].
Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors
Allopurinol
This urate-lowering agent has several observed CV effects. In an RCT in 65 patients with CAD, allopurinol resulted in increased exercise capacity, time to ST depression, and time to chest pain [29]. In another trial, allopurinol reduced the left ventricular mass by a mean of 5.2 g, compared with 1.3 g in the placebo group [30]. Larger population-based and case–control studies have corroborated these findings, indicating a possible cardioprotective benefit of allopurinol. The study by de Abajo et al. found that the protective effect of allopurinol appeared to increase with greater duration of treatment and higher dose (> 300 mg compared with < 300 mg) [31–33]. The observational study by Singh et al. also found increasing duration of colchicine to be protective for MI in the elderly, as seen from analysis of Medicare claims [34]. In addition to its protective role in CAD, allopurinol has also been shown to reduce blood pressure. In a meta-analysis including 738 participants, the allopurinol group had significantly lower systolic and diastolic blood pressure (by 3.3 mmHg and 1.3 mmHg, respectively) compared with controls [35]. Another meta-analysis compared XO inhibitors with placebo/no treatment and found that allopurinol ≤ 300 mg daily did not significantly reduce the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) and mortality, but reduced the risk of hypertension (OR 0.54, 95% CI 0.37–0.80) and total events (OR 0.60, 95% CI 0.44–0.82) [36]. Moreover, it is suggested that XO inhibition with allopurinol may improve endothelial function, leading to vasodilation and improved blood flow in HF. Since this effect is seen in patients with both hyperuricemia and normouricemia, it may be related to a direct reduction in XO-mediated oxidative stress rather than its hypouricemic effect [37]. The ALL HEART trial is a current trial studying MACE in 5215 patients in the UK with IHD treated with allopurinol 600 mg daily compared with the placebo group, and will further help determine the role of allopurinol in CV disease [38].
Febuxostat
In animal studies, another XO inhibitor, febuxostat, demonstrated potential scavenger-like activity for oxidative radicals, with improvement in myocardial structure and a reduction in the expression of inflammatory markers on myocytes [39]. Pretreatment with febuxostat was noted to interrupt mitochondria-dependent apoptosis and subsequent cardiomyocyte injury with reduced endothelial dysfunction in the left atrium [40]. However, Hays et al. found no benefit on coronary endothelial function in patients with prior CAD after 6 weeks of treatment with febuxostat [41].
In the early trials that compared febuxostat and allopurinol for the treatment of gout, there were a numerically greater incidence of CV events in the febuxostat arms compared with the allopurinol arms, although the differences were not statistically significant [42–45]. As a result, the US FDA mandated the CARES trial, a postmarketing RCT in which 6190 patients were randomized to either febuxostat or allopurinol, and followed for a median of 32 months. Although the primary endpoint of composite of CV death, non-fatal MI, non-fatal stroke, and unstable angina requiring revascularization was similar in both groups (10.8% in the febuxostat group and 10.4% in the allopurinol group), CV mortality was significantly higher in the febuxostat group (HR 1.34, CI 95% 1.03–1.73) [46]. In response to these observations, the FDA issued a black-box warning that restricted the use of febuxostat to people with gout who have failed or cannot tolerate maximally titrated allopurinol doses. It is essential that health care professionals counsel patients about CV risk with febuxostat prior to prescribing [47]. However, the CARES trial had several limitations that make interpretation challenging; for example, a high attrition rate (45%), high medication discontinuation rate (57%), lack of a placebo-control group, and the majority of deaths (85%) occurred after study medication had been discontinued. Rheumatologists have commented that the findings of the CARES trial do not support first-line use of febuxostat, and remind practitioners that there is evidence to support efficacy of both allopurinol dose escalation in the majority of patients with gout and uricosuric therapy [48]. The biological plausibility of the febuxostat increasing risk has also been questioned and raises the possibility that the findings could be explained by allopurinol reducing risk rather than febuxostat increasing risk. In a recently published European trial—the Febuxostat versus Allopurinol Streamlined Trial (FAST)—6128 patients followed for a median period of 1467 days were randomized to either allopurinol or febuxostat to study the primary endpoint of major adverse cardiovascular events. In contrast to the CARES trial, febuxostat was found to be non-inferior to allopurinol (HR 0·85; 95% CI 0.70–1.03; p < 0.0001) [49].
Some of the subsequent studies however have shown variable outcomes. A recent observational study comparing febuxostat and allopurinol with controls showed a similar incidence of major adverse CV events in both groups, while patients receiving febuxostat had a lower incidence of HF hospitalization [50]. Further information from the LEAF-CHF (Effect of urate LowEring Agent Febuxostat in Chronic Heart Failure patients with hyperuricemia) trial, in which patients with HF (left ventricular ejection fraction < 40%) and hyperuricemia (7.0–10.0 mg/day) are randomized to febuxostat or placebo, with a primary endpoint of difference in plasma B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) from baseline to 24 weeks, may help elucidate the effect of febuxostat in HF [51]. A population-based cohort study evaluated febuxostat versus allopurinol in 99,744 elderly patients (≥ 65 years of age) and found that the primary outcome of composite of hospitalization for MI or stroke was similar in both groups at 1 year. However, there was a trend towards increased all-cause mortality in the group that used febuxostat for more than 3 years [52]. Additionally, a meta-analysis in a Taiwanese population showed no significant difference in CV outcome and mortality with febuxostat versus allopurinol [53]. In a recent study, febuxostat failed to show a halt in the progression of atherosclerosis, as measured by the carotid intimal thickness, after 24 months of treatment [54].
Future Directions
Newer drugs are emerging for the treatment of gout and it is too early to comment on their effect on CV morbidity or mortality. A phase I study has shown that a selective uric acid reabsorption inhibitor called verinurad lowered serum urate without any major adverse effects in healthy males, but unclear CV safety [55].
Another potential drug class, IL-1 antagonist therapy, is being evaluated in current trials. A recent animal study showed beneficial cardiac effects of anakinra on the myocardium, while rilonacept, a newer IL-1 antagonist, has limited data regarding the CV safety [56]. Arhalofenate, a partial agonist on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-γ was initially developed as an antidiabetic drug and was serendipitously found to have modest uric acid-lowering properties in addition to anti-ILβ activity. A randomized, double-blind study on arhalofenate did not reveal any specific CV adverse effect, but more research is required [57]. Several ongoing studies on gout therapies are listed in Tables 3 and 4.
Table 3.
Recent cardiovascular outcomes trials of drugs used in the management of gout
| Drug name | Official title of the trial | Abbreviated name of the trial | Median duration for observed effect | Phase of the trial | NCT identifier | Primary outcomes | Key points |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Colchicine (patients who had suffered from an MI in the last 30 days) |
Colchicine Cardiovascular Outcomes Trial | COLCOT | 22.6 months | III | NCT02551094 | CV death, recurrent MI, stroke, resuscitated cardiac arrest and hospitalization for unstable angina requiring coronary revascularization |
1. Absolute reduction of 1.6% in ischemic events in the colchicine group compared with placebo (primary endpoint was 5.5% vs. 7.1%, respectively; HR 0.77. 95% CI 0.61–0.96) 2. Pneumonia was higher with colchicine, but diarrhea rates did not significantly differ in either group |
| Colchicine | Effect of ColchiciNe on the InciDence of Atrial Fibrillation in Open Heart Surgery Patients: END-AF Trial | END-AF | Variable: range was 2–56 days | III | NCT03021343 | Rate of AF lasting more than 5 min |
1. There was no significant difference in rates of AF in the group administered colchicine prior to cardiac surgery compared with the no colchicine group (overall rates of AF were 14.5% vs. 20.5%, respectively; RRR 29.3%, p = 0.14). No net benefit in composite of primary endpoint 2. Diarrhea lead to colchicine discontinuation in about half of the patients with this adverse effect. |
|
Allopurinol (patients undergoing cardiac surgery and no prior history of AF or supraventricular arrhythmias) |
Xanthine Oxidase Inhibition for Hyperuricemic Heart Failure Patients | EXACT-HF | 24 weeks | II | NCT00987415 | Improvement, worsening, or unchanged clinical status of patients with heart failure |
1. There was no significant difference in clinical status or left ventricular ejection fraction between the allopurinol- and placebo-treated patients 2. Rash was more common with allopurinol but there was no significant difference in serious adverse event rates compared with placebo |
| Febuxostat vs. allopurinol | A multicenter, randomized, active-control, phase 3B study to evaluate the cardiovascular safety of febuxostat and allopurinol in subjects with gout and cardiovascular comorbidities | CARES | 7 years | III | NCT01101035 | Percentage of patients with a composite of non-fatal MI, non-fatal stroke, CV death, and unstable angina requiring coronary revascularization |
1. A primary endpoint event occurred in 10.8% in the febuxostat group compared with 10.4% in the allopurinol group 2. All-cause and CV mortality were higher in the febuxostat group than in the allopurinol group |
AF atrial fibrillation, CI confidence interval, CV cardiovascular, HR hazard ratio, LDL low-density lipoprotein, MI myocardial infarction, RRR relative risk reduction
Table 4.
Ongoing trials on drugs used in gout and other rheumatological diseases
| Drug studied | Official title (acronym) | NCT identifier | Primary outcome measure | Status, expected completion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colchicine | A 2 × 2 factorial randomized controlled trial of colchicine and spironolactone in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI)/SYNERGY Stent Registry (CLEAR SYNERGY) | NCT03048825 | Major adverse cardiovascular effects | Recruiting, December 2021 |
| The Canadian study of Arterial inflammation in patients with Diabetes and recent vascular events: EvaluatioN of Colchicine Effectiveness (CADENCE) | NCT04181996 | Change in the FDG uptake of tissue-to-blood ratio as a marker of arterial plaque inflammation in the maximally diseased segment of imaged vasculature (carotid or aorta) over a period of 6 months | Not yet recruiting, December 2023 | |
| Impact of Short-course Colchicine Versus Placebo After Pulmonary Vein Isolation: A Pilot Study, (IMPROVE-PVI Pilot) | NCT04160117 | Average monthly number of patients enrolled | Recruiting, January 2022 | |
| Colchicine Prevents Myocardial Injury After Non-Cardiac Surgery Pilot Study (COPMAN) | NCT04139655 | Number of patients included in 3 months after the run-in period | Recruiting, October 2021 | |
| Colchicine for the Prevention Of Perioperative Atrial Fibrillation in Patients Undergoing Thoracic Surgery (COP-AF) | NCT03310125 | Atrial fibrillation within 14 days of randomization | Recruiting, June 2022 | |
| Hypouricemic agents | A phase 2, MulticEnter, double-blind, THree-arm, placebo and active control efficacy and safetY STudy to evaluate verinurad combined with allopurinol in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (AMETHYST) | NCT04327024 | Effect of verinurad and allopurinol on exercise capacity by measurement of VO2 change over 28 weeks | Not yet recruiting, September 2021 |
| Anti-inflammatory agents | Phase 3, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized withdrawal study with open-label extension, to assess the efficacy and safety of rilonacept treatment in subjects with recurrent pericarditis (RHAPSODY) | NCT03737110 | Time to recurrence of pericarditis | Active but not recruiting, June 2021 |
| Treatment of Acute Pericarditis with Anakinra (none) | NCT03224585 | Change in pain, measured by Visual Analog Score, within 6–12 h | Active, not recruiting, March 2021 |
Sodium glucose cotransporter (SGLT)-2 inhibitors, a prominent antidiabetic drug class with extended benefit in HF patients, have also shown a reduction in serum uric acid levels, which could contribute to the CV mortality benefit seen with this class of drugs. By increasing renal urate losses, this drug class decreases serum uric by about 0.60–0.75 mg/dL, making it a potential add-on agent for use in patients with diabetes and hyperuricemia. Several randomized studies have reported a decrease in MACE and HF rehospitalization with SGLT-2 inhibitors [58].
Conclusion
The recent advancements in atherosclerosis pathophysiology indicate that inflammation plays a significant role. With trials such as COLCOT and LoDoCo showing benefit of colchicine in CAD, there is a possibility of expansion of our current armamentarium in secondary prevention of CAD. However, further study is needed to change practice and to evaluate the utility of colchicine in ACS. Early data have shown CV benefits of certain other gout medications, but there are no current FDA-approved indications in cardiology. Febuxostat, earlier thought to have a poor cardiovascular outcome compared with allopurinol, was found to be non-inferior to allopurinol and with no increase in mortality in the recent FAST trial. Overall, more evidence is required to definitively endorse clinical use of these drug classes in CAD.
Declarations
Conflicts of interest
Dr. Fonarow discloses the following relationships: consultant for Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Janssen, Medtronic, Merck, and Novartis, and Associate Section Editor for the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) Cardiology. Subuhi Kaul, Manasvi Gupta, Dhrubajyoti Bandyopadhyay, Adrija Hajra, Prakash Deedwania, Edward Roddy, Mamas Mamas, Allan Klein, Carl J. Lavie, and Raktim K. Ghosh have no disclosures to declare.
Funding
No sources of funding were used to assist in the preparation of this article.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Footnotes
Subuhi Kaul and Manasvi Gupta contributed equally to this work and are considered as first co-authors.
References
- 1.Dalbeth N, Merriman TR, Stamp LK. Gout. Lancet. 2016;388:2039–2052. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00346-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Colantonio LD, Saag KG, Singh JA, et al. Gout is associated with an increased risk for incident heart failure among older adults: the REasons for Geographic And Racial Differences in Stroke (REGARDS) cohort study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2020;22:86. doi: 10.1186/s13075-020-02175-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Krishnan E, Pandya BJ, Lingala B, Hariri A, Dabbous O. Hyperuricemia and untreated gout are poor prognostic markers among those with a recent acute myocardial infarction. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012;14:R10. doi: 10.1186/ar3684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Casiglia E, Tikhonoff V, Virdis A, et al. Serum uric acid and fatal myocardial infarction: detection of prognostic cut-off values: the URRAH (Uric Acid Right for Heart Health) study. J Hypertens. 2020;38:412–419. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000002287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Tardif J-C, Kouz S, Waters DD, et al. Efficacy and safety of low-dose colchicine after myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:2497–2505. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1912388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Khanna D, Khanna PP, Fitzgerald JD, et al. American College of Rheumatology guidelines for management of gout. Part 2: therapy and antiinflammatory prophylaxis of acute gouty arthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2012;64:1447–1461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 7.Khanna D, Fitzgerald JD, Khanna PP, et al. American College of Rheumatology guidelines for management of gout. Part 1: systematic nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic therapeutic approaches to hyperuricemia. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2012;64:1431–1446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 8.Hansson GK. Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:1685–1695. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra043430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Libby P, Ridker PM, Hansson GK, Leducq transatlantic network on atherothrombosis. Inflammation in atherosclerosis: from pathophysiology to practice. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;54:2129–2138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 10.Adler Y, Charron P, Imazio M, et al. ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of pericardial diseases: the Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Pericardial Diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Endorsed by: The European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS) Eur Heart J. 2015;36:2921–2964. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Tong DC, Wilson AM, Layland J. Colchicine in cardiovascular disease: an ancient drug with modern tricks. Heart. 2016;102:995–1002. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2015-309211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Vaidya K, Arnott C, Martínez GJ, et al. Colchicine therapy and plaque stabilization in patients with acute coronary syndrome: a CT coronary angiography study. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018;11:305–316. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2017.08.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hennessy T, Soh L, Bowman M, et al. The Low Dose Colchicine after Myocardial Infarction (LoDoCo-MI) study: a pilot randomized placebo controlled trial of colchicine following acute myocardial infarction. Am Heart J. 2019;215:62–69. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2019.06.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Deftereos S, Giannopoulos G, Raisakis K, et al. Colchicine treatment for the prevention of bare-metal stent restenosis in diabetic patients. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;61:1679–1685. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.01.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Deftereos S, Giannopoulos G, Angelidis C, et al. Anti-inflammatory treatment with colchicine in acute myocardial infarction: a pilot study. Circulation. 2015;132:1395–1403. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.017611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Tucker B, Kurup R, Barraclough J, et al. Colchicine as a novel therapy for suppressing chemokine production in patients with an acute coronary syndrome: a pilot study. Clin Ther. 2019;41:2172–2181. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2019.07.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Shah B, Pillinger M, Zhong H, et al. Effects of acute colchicine administration prior to percutaneous coronary intervention: COLCHICINE-PCI randomized trial. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2020;13:e008717. doi: 10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.119.008717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Nidorf SM, Eikelboom JW, Budgeon CA, Thompson PL. Low-dose colchicine for secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;61:404–410. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2012.10.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Nidorf SM, Fiolet ATL, Mosterd A, et al. Colchicine in patients with chronic coronary disease. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:1838–1847. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2021372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Solomon DH, Liu C-C, Kuo I-H, Zak A, Kim SC. Effects of colchicine on risk of cardiovascular events and mortality among patients with gout: a cohort study using electronic medical records linked with Medicare claims. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75:1674–1679. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-207984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Crittenden DB, Lehmann RA, Schneck L, et al. Colchicine use is associated with decreased prevalence of myocardial infarction in patients with gout. J Rheumatol. 2012;39:1458–1464. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.111533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Deftereos SG, Vrachatis DA, Angelidis C, et al. The role of colchicine in treating postoperative and post-catheter ablation atrial fibrillation. Clin Ther. 2019;41:21–29. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2018.08.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lennerz C, Barman M, Tantawy M, Sopher M, Whittaker P. Colchicine for primary prevention of atrial fibrillation after open-heart surgery: systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Cardiol. 2017;249:127–137. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2017.08.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Imazio M, Brucato A, Ferrazzi P, et al. Colchicine for prevention of postpericardiotomy syndrome and postoperative atrial fibrillation: the COPPS-2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2014;312:1016–1023. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.11026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Imazio M, Trinchero R, Brucato A, et al. COlchicine for the prevention of the post-pericardiotomy Syndrome (COPPS): a multicentre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Eur Heart J. 2010;31:2749–2754. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehq319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.NIH US National Library of Medicine. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04322682. Accessed 12 Dec 2020.
- 27.Papadopoulos C, Patoulias D, Teperikidis E, et al. Colchicine as a potential therapeutic agent against cardiovascular complications of COVID-19: an exploratory review. SN Compr Clin Med. Epub 4 Aug 2020. 10.1007/s42399-020-00421-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 28.Deftereos SG, Giannopoulos G, Vrachatis DA, et al. Effect of colchicine vs standard care on cardiac and inflammatory biomarkers and clinical outcomes in patients hospitalized with coronavirus disease 2019: the GRECCO-19 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3:e2013136. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.13136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Grunfeld C, Feingold KR. The metabolic effects of tumor necrosis factor and other cytokines. Biotherapy. 1991;3:143–158. doi: 10.1007/BF02172087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Rekhraj S, Gandy SJ, Szwejkowski BR, et al. High-dose allopurinol reduces left ventricular mass in patients with ischemic heart disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;61:926–932. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2012.09.066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Grimaldi-Bensouda L, Alpérovitch A, Aubrun E, et al. Impact of allopurinol on risk of myocardial infarction. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74:836–842. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.de Abajo FJ, Gil MJ, Rodríguez A, et al. Allopurinol use and risk of non-fatal acute myocardial infarction. Heart. 2015;101:679–685. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2014-306670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Larsen KS, Pottegård A, Lindegaard HM, Hallas J. Effect of allopurinol on cardiovascular outcomes in hyperuricemic patients: a cohort study. Am J Med. 2016;129(299–306):e2. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2015.11.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Singh JA, Yu S. Allopurinol reduces the risk of myocardial infarction (MI) in the elderly: a study of Medicare claims. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016;18:209. doi: 10.1186/s13075-016-1111-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Agarwal V, Hans N, Messerli FH. Effect of allopurinol on blood pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2013;15:435–442. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-7176.2012.00701.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Bredemeier M, Lopes LM, Eisenreich MA, et al. Xanthine oxidase inhibitors for prevention of cardiovascular events: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2018;18:24. doi: 10.1186/s12872-018-0757-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Doehner W, Schoene N, Rauchhaus M, et al. Effects of xanthine oxidase inhibition with allopurinol on endothelial function and peripheral blood flow in hyperuricemic patients with chronic heart failure: results from 2 placebo-controlled studies. Circulation. 2002;105:2619–2624. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000017502.58595.ED. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Mackenzie IS, Ford I, Walker A, et al. Multicentre, prospective, randomised, open-label, blinded end point trial of the efficacy of allopurinol therapy in improving cardiovascular outcomes in patients with ischaemic heart disease: protocol of the ALL-HEART study. BMJ Open. 2016;6:e013774. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-013774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Krishnamurthy B, Rani N, Bharti S, et al. Febuxostat ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats. Chem Biol Interact. 2015;237:96–103. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2015.05.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Wang S, Li Y, Song X, et al. Febuxostat pretreatment attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via mitochondrial apoptosis. J Transl Med. 2015;13:209. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0578-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Hays AG, Iantorno M, Schär M, et al. The influence of febuxostat on coronary artery endothelial dysfunction in patients with coronary artery disease: a phase 4 randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, crossover trial. Am Heart J. 2018;197:85–93. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2017.11.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Becker MA, Schumacher HR, Wortmann RL, et al. Febuxostat, a novel nonpurine selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase: a twenty-eight-day, multicenter, phase II, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-response clinical trial examining safety and efficacy in patients with gout. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52:916–923. doi: 10.1002/art.20935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Becker MA, Schumacher HR, MacDonald PA, Lloyd E, Lademacher C. Clinical efficacy and safety of successful longterm urate lowering with febuxostat or allopurinol in subjects with gout. J Rheumatol. 2009;36:1273–1282. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.080814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Schumacher HR, Becker MA, Wortmann RL, et al. Effects of febuxostat versus allopurinol and placebo in reducing serum urate in subjects with hyperuricemia and gout: a 28-week, phase III, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;59:1540–1548. doi: 10.1002/art.24209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Schumacher HR, Becker MA, Lloyd E, MacDonald PA, Lademacher C. Febuxostat in the treatment of gout: 5-yr findings of the FOCUS efficacy and safety study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2009;48:188–194. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ken457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.White WB, Saag KG, Becker MA, et al. Cardiovascular safety of febuxostat or allopurinol in patients with gout. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:1200–1210. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1710895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Abeles AM, Pillinger MH. Febuxostat and the black box blues. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2019;1:343–344. doi: 10.1002/acr2.11047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Choi H, Neogi T, Stamp L, Dalbeth N, Terkeltaub R. New perspectives in rheumatology: implications of the cardiovascular safety of febuxostat and allopurinol in patients with gout and cardiovascular morbidities trial and the associated food and drug administration public safety alert. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70:1702–1709. doi: 10.1002/art.40583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Mackenzie IS, Ford I, Nuki G, Hallas J, Hawkey CJ, Webster J, Ralston SH, Walters M, Robertson M, De Caterina R, Findlay E, Perez-Ruiz F, McMurray JJV, MacDonald TM. FAST Study Group. Long-term cardiovascular safety of febuxostat compared with allopurinol in patients with gout (FAST): a multicentre, prospective, randomised, open-label, non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2020;396(10264):1745–1757. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32234-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Ju C, Lai RWC, Li KHC, et al. Comparative cardiovascular risk in users versus non-users of xanthine oxidase inhibitors and febuxostat versus allopurinol users. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2020;59(9):2340–2349. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kez576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Yokota T, Fukushima A, Kinugawa S, Okumura T, Murohara T, Tsutsui H. Randomized trial of effect of urate-lowering agent febuxostat in chronic heart failure patients with hyperuricemia (LEAF-CHF) Int Heart J. 2018;59:976–982. doi: 10.1536/ihj.17-560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Zhang M, Solomon DH, Desai RJ, et al. Assessment of cardiovascular risk in older patients with gout initiating febuxostat versus allopurinol: population-based cohort study. Circulation. 2018;138:1116–1126. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.033992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Chen C-H, Chen C-B, Chang CJ, et al. Hypersensitivity and cardiovascular risks related to allopurinol and febuxostat therapy in Asians: a population-based cohort study and meta-analysis. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2019;106:391–401. doi: 10.1002/cpt.1377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Tanaka A, Taguchi I, Teragawa H, et al. Febuxostat does not delay progression of carotid atherosclerosis in patients with asymptomatic hyperuricemia: a randomized, controlled trial. PLoS Med. 2020;17:e1003095. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1003095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Strilchuk L, Fogacci F, Cicero AF. Safety and tolerability of available urate-lowering drugs: a critical review. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2019;18:261–271. doi: 10.1080/14740338.2019.1594771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Van Tassell BW, Lipinski MJ, Appleton D, et al. Rationale and design of the Virginia Commonwealth University-Anakinra Remodeling Trial-3 (VCU-ART3): a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blinded, multicenter study. Clin Cardiol. 2018;41:1004–1008. doi: 10.1002/clc.22988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Poiley J, Steinberg AS, Choi Y-J, et al. A randomized, double-blind, active- and placebo-controlled efficacy and safety study of arhalofenate for reducing flare in patients with gout. Arthritis Rheumatology. 2016;68:2027–2034. doi: 10.1002/art.39684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Zou C-Y, Liu X-K, Sang Y-Q, Wang B, Liang J. Effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on cardiovascular outcomes and mortality in type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 2019;98:e18245. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000018245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]