Haemostatic complications are commonly observed in patients undergoing blood or marrow transplantation (BMT), and are related to thrombocytopenia and immunological complications. In allogeneic transplant recipients, the cumulative incidence of bleeding was higher than venous thromboembolism (VTE) (30% vs 11.8%) at 14 years after transplant. Development of bleeding was associated with inferior survival but not thrombosis, though the median follow-up in this study was only 20 months.(Labrador, et al 2013) A comprehensive analysis of sociodemographics, therapeutic exposures and comorbidities, and their impact on the risk of mortality in long-term BMT survivors with a history of VTE has not been performed. We hypothesized that a longer follow-up is needed to study this effect. We addressed this gap in knowledge using the resources offered by the Blood or Marrow Transplant Survivor Study (BMTSS).
Eligible participants included patients who received BMT at City of Hope or the University of Minnesota between 1 January 11974 and 31 December 1998, survived ≥2 years after transplantation, were alive and aged ≥18 years at study participation. BMT survivors were approached to complete a BMTSS survey between 2000 and 2004. The BMTSS survey covered sociodemographics, access to and use of medical care, diagnosis of physical health conditions by a healthcare provider with age at diagnosis and medication use. Institutional transplant databases were used to obtain information regarding primary diagnosis, transplant preparative regimens, stem cell source and graft type. The BMTSS questionnaire identified patients with a history of VTE diagnosed by their health care providers. Patients were categorized into those with and without a past history of VTE, irrespective of the time of onset with respect to BMT. National Death Index (https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/ndi/index.htm, accessed 31 December 2015) and/or medical records provided information regarding the date and cause of death until 31 December 2015. Additional information from Accurint databases (www.accurint.com, accessed 31 December 2016) was used to extend the vital status information up to 31 December 2016. This enabled a near-complete ascertainment of follow-up of this cohort and enhanced accuracy of mortality status. All patients were assigned a primary and, if present, a secondary cause of death. In the analyses of relapse-related mortality (RRM) and non-relapse-related mortality (NRM), all patients with primary disease as a primary or secondary cause of death were assigned relapse-related cause of death.
A total of 1,022 BMT survivors completed the survey. Demographic and clinical characteristics of these patients are summarized in Table S1. Median (interquartile range [IQR]) age at BMT was 34.9 (25.1-45.0) years, and median (IQR) length of follow-up after completion of the survey was 15.1 (12.6-16.0) years. Seventy-one patients (6.9%) had a history of VTE in this cohort. Subsequent to completion of the survey, 309 (30.3%) deaths were observed. The overall survival (OS) among patients with and without VTE was 77.5% vs. 91.1% at five years and 50.4% vs. 72.3% at 15 years after survey completion, p<0.0001 (Figure 1A; Table S2). Cox regression analysis, adjusting for age, sex, race/ethnicity, income, insurance, education, co-morbidities, use of hormonal therapy, primary diagnosis, conditioning regimen, stem cell source, transplant type, history of graft-versus-host disease, and relapse of primary cancer or development of subsequent neoplasm, showed that patients with a history of VTE were at a 59% higher risk of subsequent all-cause mortality compared to those without (hazard ratio [HR]=1.59, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.09-2.31, p=0.015) (Table I).
Figure 1.
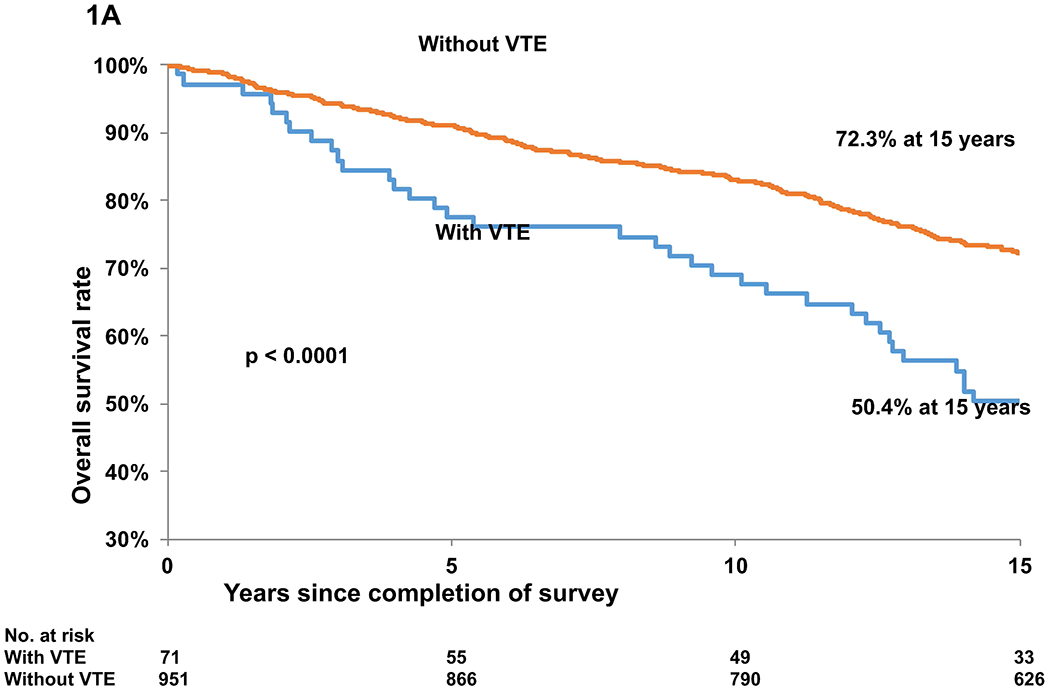
A. Overall Survival in blood and marrow transplant (BMT) survivors with and without a past history of venous thromboembolism (VTE)
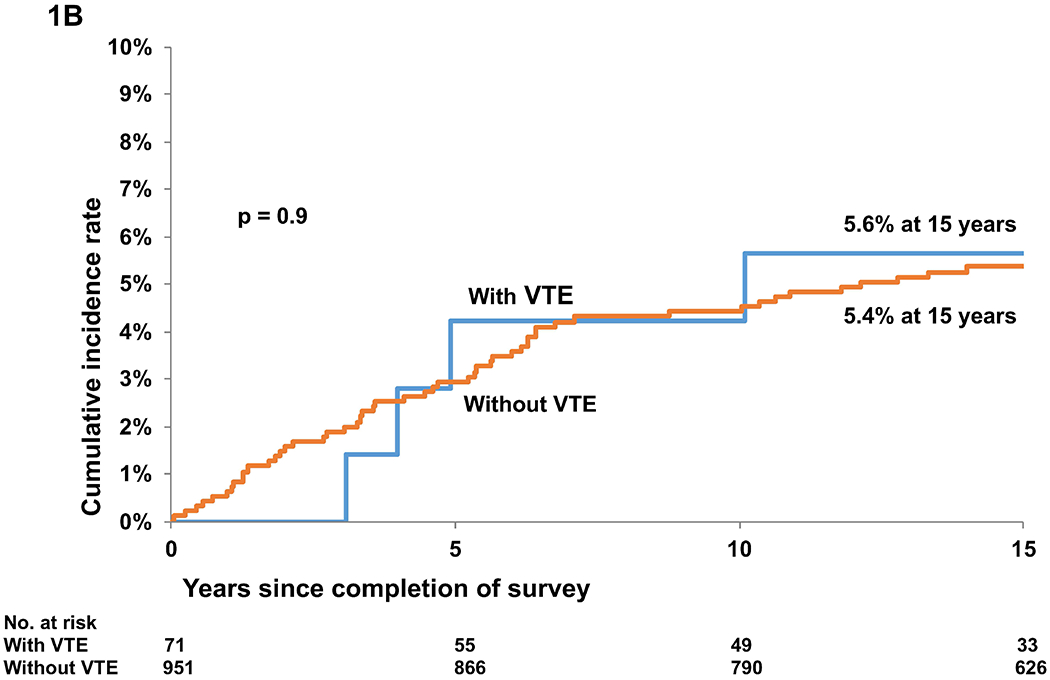
B. Cumulative incidence of relapse-related mortality in BMT survivors with and without a history of VTE
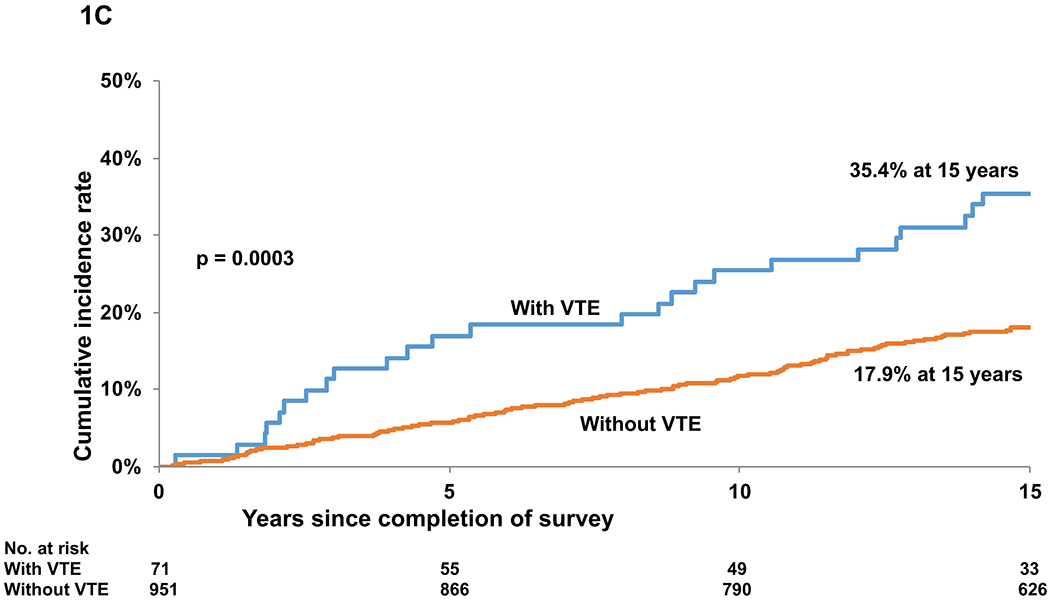
C. Cumulative incidence of non-relapse-related mortality in BMT survivors with and without a history of VTE
Table I:
Cox regression analysis for all-cause mortality in BMT survivors
| Variable | Univariable | Multivariable | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Ratio | 95% CI | P | Hazard Ratio | 95% CI | P | |
| VTE | ||||||
| Yes vs. No | 2.09 | (1.47,2.95) | <0.0001 | 1.59 | (1.09,2.31) | 0.015 |
| Age at survey participation | 1.06 | (1.05,1.07) | <0.0001 | 1.05 | (1.04,1.07) | <0.0001 |
| Body Mass Index | 1.00 | (0.98,1.02) | 0.872 | 0.96 | (0.93,0.98) | 0.001 |
| Sex | ||||||
| Male | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Female | 0.74 | (0.59,0.93) | 0.009 | 0.68 | (0.53,0.87) | 0.002 |
| Race/Ethnicity | ||||||
| Whites | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Hispanics | 1.06 | (0.75,1.49) | 0.738 | 1.15 | (0.77,1.73) | 0.499 |
| Blacks | 1.38 | (0.68,2.79) | 0.372 | 1.35 | (0.62,2.95) | 0.447 |
| Asian | 0.62 | (0.33,1.16) | 0.132 | 0.81 | (0.4,1.6) | 0.536 |
| Other | 1.20 | (0.45,3.23) | 0.715 | 3.24 | (1.16,9.02) | 0.025 |
| Education | ||||||
| 1: ≤High School | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| 2: High School + College | 0.98 | (0.71,1.35) | 0.906 | 1.13 | (0.79,1.61) | 0.517 |
| 3: College graduate + post | 0.97 | (0.71,1.32) | 0.822 | 1.13 | (0.78,1.64) | 0.507 |
| Household Income (US$) | ||||||
| ≥60k | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| 20-60k | 1.17 | (0.9,1.51) | 0.233 | 1.25 | (0.95,1.65) | 0.108 |
| ≤20k | 1.62 | (1.17,2.24) | 0.003 | 1.69 | (1.17,2.44) | 0.005 |
| Current Insurance | ||||||
| Yes vs. No | 1.13 | (0.73,1.76) | 0.582 | 0.95 | (0.57,1.57) | 0.831 |
| BMT Type | ||||||
| Allo + no GvHD | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Allo + GvHD | 1.60 | (1.14,2.26) | 0.007 | 1.33 | (0.91,1.93) | 0.136 |
| Auto | 2.17 | (1.59,2.97) | <0.0001 | 1.34 | (0.86,2.1) | 0.197 |
| Stem cell source | ||||||
| PBSC vs. Other | 2.06 | (1.64,2.58) | <0.0001 | 1.82 | (1.29,2.56) | 0.0006 |
| Primary diagnosis | ||||||
| CML | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| AML | 0.96 | (0.68,1.36) | 0.824 | 1.25 | (0.86,1.83) | 0.246 |
| HL | 1.18 | (0.76,1.83) | 0.456 | 1.20 | (0.67,2.12) | 0.543 |
| NHL | 1.48 | (1.07,2.07) | 0.02 | 0.89 | (0.57,1.39) | 0.603 |
| ALL | 1.11 | (0.72,1.7) | 0.649 | 1.97 | (1.23,3.18) | 0.005 |
| Other* | 1.21 | (0.83,1.77) | 0.322 | 1.10 | (0.68,1.77) | 0.713 |
| Conditioning regimen | ||||||
| Cy + Radiation | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Cy + BU | 1.22 | (0.8,1.86) | 0.361 | 1.05 | (0.63,1.74) | 0.864 |
| Other | 0.96 | (0.75,1.23) | 0.753 | 1.15 | (0.86,1.54) | 0.349 |
| History of smoking | ||||||
| Yes vs. No | 1.61 | (1.29,2.01) | <0.0001 | 1.31 | (1.02,1.68) | 0.033 |
| Hypertension | ||||||
| Yes vs. No | 1.68 | (1.34,2.11) | <0.0001 | 1.36 | (1.05,1.77) | 0.02 |
| Diabetes | ||||||
| Yes vs. No | 2.58 | (1.92,3.47) | <0.0001 | 2.51 | (1.8,3.52) | <0.0001 |
| Relapse/SMN | ||||||
| Yes vs. No | 1.76 | (1.35,2.30) | <0.0001 | 1.93 | (1.44,2.59) | <0.0001 |
Includes aplastic anaemia, multiple myeloma, myelofibrosis, breast cancer, immunodeficiency disorders and sarcoma.
ALL, acute lymphocytic leukaemia; Allo, allogeneic; AML, acute myeloid leukaemia; Auto, autologous;BMT, blood or marrow transplant; BU, busulfan; CI, confidence interval; CML, chronic myeloid leukaemia; Cy, cyclophosphamide; GvHD, graft-versus-host disease; HL, Hodgkin lymphoma; NHL, non-Hodgkin lymphoma; PBSC, peripheral blood stem cells; SD, standard deviation; SMN, second malignant neoplasm; VTE, venous thromboembolism
Cumulative incidence of RRM was similar among those with and without VTE (5.6% vs. 5.4% at 15 years, p=0.9) (Figure 1B, Table S2). On the other hand, the cumulative incidence of NRM was higher among those with VTE (35.4% vs. 17.9% at 15 years, p=0.0003) (Figure 1C, Table S2). Proportional sub-distribution hazards model (Fine-Gray) for competing risks was used for determining the association between VTE and subsequent RRM and NRM. The adjusted hazard of death from RRM was not significantly different between those with and without VTE (HR=0.69, 95%CI, 0.2-1.8, p=0.54). In contrast, patients with VTE were more likely to die from NRM (HR=1.68, 95%CI: 1.1-2.5, p=0.018). In analysis restricted to patients with VTE and adjusted for socio-demographics, a history of diabetes was associated with a significantly higher hazard of all-cause late mortality (HR=3.28, 95%CI: 1.31-8.21, p=0.011). All analyses were performed with SAS software version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, North Carolina, USA).
In the general population, individuals with VTE experience inferior survival compared to age-, sex- and race-matched individuals without VTE; the mortality risk remains elevated up to 30 years.(Sogaard, et al 2014) Older age, male sex, lower body mass index, confinement to a hospital/nursing home, congestive heart failure, chronic lung disease, neurological disease and active cancer are independent predictors of early mortality after VTE.(Gussoni, et al 2013, Heit 2015) Age is an independent risk factor for VTE; in our cohort, patients with VTE were older at BMT and at the time of study participation. This difference in age between the two groups would not affect the results as mortality analysis was performed after adjusting for this. Cancer patients with VTE have lower survival compared to those without VTE matched for cancer type, age and sex; in fact, thromboembolic complications are the second leading cause of death in cancer patients.(Khorana, et al 2007, Sorensen, et al 2000) Previous studies describing the risk of VTE in BMT recipients were limited by small sample sizes and short duration of follow-up. In a retrospective analysis of 2,276 allogenic transplant recipients, VTE was associated with increased NRM, but not RRM, progression-free survival or OS. (Kekre, et al 2017) This study did not include autologous BMT recipients, and the median follow-up at 4 years was shorter than our study. With a longer follow-up of >15 years, our study showed inferior OS in BMT survivors with VTE, primarily due to increased NRM. History of diabetes is predictive of late mortality in patients with VTE. This cohort of 1,022 BMT survivors represents the largest analysis of the risk of mortality in BMT survivors with a history of VTE. As our intention was to study the impact of VTE on late mortality in BMT survivors, we excluded events occurring in the first two years after transplant, and a considerable number of patients with VTE might have died within two years. In conclusion, BMT survivors with a history of VTE have a higher overall mortality, primarily due to non-relapse related causes. Further studies aimed at identifying the high-risk population, continued assessment for risk factors and secondary thromboprophylaxis may reduce the mortality associated with VTE.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by grants from the National Cancer Institute (R01 CA078938), and the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society (R6502-16) (SB).
Footnotes
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
References:
- Gussoni G, Frasson S, La Regina M, Di Micco P & Monreal M (2013) Three-month mortality rate and clinical predictors in patients with venous thromboembolism and cancer. Findings from the RIETE registry. Thromb Res, 131, 24–30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heit JA (2015) Epidemiology of venous thromboembolism. Nat Rev Cardiol, 12, 464–474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kekre N, Kim HT, Ho VT, Cutler C, Armand P, Nikiforow S, Alyea EP, Soiffer RJ, Antin JH, Connors JM & Koreth J (2017) Venous thromboembolism is associated with graft-versus-host disease and increased non-relapse mortality after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Haematologica, 102, 1185–1191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khorana AA, Francis CW, Culakova E, Kuderer NM & Lyman GH (2007) Thromboembolism is a leading cause of death in cancer patients receiving outpatient chemotherapy. J Thromb Haemost, 5, 632–634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labrador J, Lopez-Anglada L, Perez-Lopez E, Lozano FS, Lopez-Corral L, Sanchez-Guijo FM, Vazquez L, Perez Rivera JA, Martin-Herrero F, Sanchez-Barba M, Guerrero C, del Canizo MC, Caballero MD, San Miguel JF, Alberca I & Gonzalez-Porras JR (2013) Analysis of incidence, risk factors and clinical outcome of thromboembolic and bleeding events in 431 allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation recipients. Haematologica, 98, 437–443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogaard KK, Schmidt M, Pedersen L, Horvath-Puho E & Sorensen HT (2014) 30-year mortality after venous thromboembolism: a population-based cohort study. Circulation, 130, 829–836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen HT, Mellemkjaer L, Olsen JH & Baron JA (2000) Prognosis of cancers associated with venous thromboembolism. N Engl J Med, 343, 1846–1850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


