Abstract
Three families of RNA viruses, the Coronaviridae, Flaviviridae and Filoviridae, collectively have great potential to cause epidemic disease in human populations. The current SARS-CoV-2 (Coronaviridae) responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic, underscores the lack of effective medications currently available to treat these classes of viral pathogens. Similarly, the Flaviviridae which includes such viruses as Dengue, West Nile and Zika and the Filoviridae with the Ebola-type viruses as examples, all lack effective therapeutics. In this review, we present fundamental information concerning the biology of these three virus families, including their genomic makeup, mode of infection of human cells, and key proteins that may offer targeted therapies. Further, we present the natural products and their derivatives that have documented activities to these viral and host proteins, offering hope for future mechanism-based antiviral therapeutics. By arranging these potential protein targets and their natural product inhibitors by target type across these three families of virus, new insights are developed, and crossover treatment strategies are suggested. Hence, natural products, as is the case for other therapeutic areas, continue to be a promising source of structurally diverse new anti-RNA virus therapeutics.
Graphical Abstract

Introduction
Deadly outbreaks caused by viruses have occurred periodically throughout human history. Several endemic infections evolved into pandemics that threatened the entire global population. The last pandemic of the 19th century, known as La Grippe or the Russian Flu, occurred between 1889–1890 and caused approximately one million deaths.1 This outbreak was caused by an influenza A virus, subtype H2N2.2 The 1918 Spanish flu epidemic arrived on the heels of World War I and killed mainly small children, young adults, and the elderly.3 It is generally felt that this was the deadliest pandemic ever recorded with an estimated 50 million fatalities. The Spanish flu epidemic was also caused by an influenza virus subtype H1N1. Other notable pandemics are the 1957 and 1968 influenza infections. These were widespread and the 1957 influenza epidemic killed roughly one million people. Thanks to extensive research and development spanning decades, pandemics caused by influenza viruses are now able to be abated and at times prevented by vaccines, although few truly effective drug treatments are available.
For decades, natural products (NPs) have been an inspiration for the development of new pharmaceuticals; approximately 50% of all small molecule drugs have a NP derivation or inspiration.4 Due to the vast diversity of natural products in nature made by microbes, plants, and fungi, these compounds have been a useful reservoir of structural information from which to draw from in drug discovery campaigns. As Frank Lovering laid out in his treatise on stereochemical complexity in drug development, the complexity that natural products tend to possess is a testament to their usefulness in this area.5,6 As we search for new answers to the threat of global pandemics, where better to begin looking than to nature?
The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) has been endemic for the last 40 years. It was present in human populations at a low rate since the 1950s, but in the late 1970s and early 1980s, more cases of immunodeficiency occurred with an unknown cause. The human immunodeficiency virus was identified in 1983 by Luc Montagnier (Pasteur Institute, Paris, France) and Robert Gallo (NIH, Bethesda, Maryland).7–11 HIV infections led to the acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) epidemic that claimed approximately 30 million lives worldwide.12 There is currently no cure for AIDS, but disease progression can be mitigated with a variety of antiviral treatments, where roughly 23 million treatments are prescribed each year. The most common of these treatments are integrase inhibitors such as dolutegravir and raltegravir. Another common drug class is the nucleoside/nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs). The combination of dolutegravir/rilpivirine, a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor, can be given as a once-daily tablet, which improves compliance.13 One reason why it has been so difficult to make an AIDS vaccine is that the virus infects the very cells of the immune system that a vaccine should induce; hence, HIV is a good example of why vaccines can’t always be developed, and thus anti-viral treatments are needed.
The term hepatitis is used to describe the infection of the liver by any of the hepatitis A through E viruses. However, hepatitis viruses are fairly heterogeneous; hepatitis (Hep) A is an unenveloped symmetrical RNA virus whereas Hep B is a double-stranded DNA virus. The most common strategy for controlling different hepatitis viruses has been through the development of vaccines (e.g. to Hep A and B), though there are some drug treatments as well. Vaccines are under development for Hep C and Hep E, and Hep D only occurs as a co-infectant with Hep B. Hence, immunization against Hep B also provides protection against Hep D.14 Antiviral therapeutics have also been developed for treating Hep C,15 and are highly effective such that the virus can be completely eradicated.16
In this review, we focus on three virus families; the Coronaviridae, Flaviviridae, and Filoviridae, because these three families have been responsible for causing a number of endemic and pandemic outbreaks, including the current COVID-19 pandemic (Table 1.). Examples belonging to the Coronaviridae are SARS-CoV-1, SARS-CoV-2, and MERS-CoV. The family Flaviviridae contains the Dengue, Yellow fever, Japanese encephalitis virus, Zika, and tick-borne encephalitis (TBV) viruses. Lastly, the filoviruses considered in this review include those causing Ebola and Marburg diseases. Unfortunately, many of these viruses have inadequate or completely absent treatment options. Because of this deficiency, we have focused this review on identifying potential druggable protein targets that have been or could be used in the development of small molecule treatments, with an emphasis on natural products and their derivatives.
Table 1.
Viruses discussed in this review and associated information.
| Virus | Taxonomy | Emergence | Source/Transmission | Type | Genome Size | Treatments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SARS-CoV | Order: Nidovirales Family: Coronaviridae Genus: Betacoronavirus | Foshan, China 2002 | Bats -- > Intermediate mammal host -- > Human | Positive-sense RNA virus | ~30 kilobases | No |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Order: Nidovirales Family: Coronaviridae Genus: Betacoronavirus | Wuhan, China 2019 | Bats -- > Intermediate mammal host -- > Human | Positive-sense RNA virus | ~30 kilobases | No |
| MERS-CoV | Order: Nidovirales Family: Coronaviridae Genus: Betacoronavirus | Jeddah, Saudi Arabia 2012 | Bats -- > Intermediate mammal host -- > Human | Positive-sense RNA virus | ~30 kilobases | No |
| Ebola virus | Order: Mononegavirales Family: Filoviridae Genus: Ebolavirus | Sudan & Zaire 1976 | Bats ---> Humans Mammal hosts --- > Humans Humans --->Humans | Negative-sense RNA virus | 19 kb | Vaccine: rVSV-ZEBOV |
| Marburg virus | Order: Mononegavirales Family: Filoviridae Genus: Marburgvirus | Marburg 1967 | Bats ---> Humans Mammal hosts --- > Humans Humans --->Humans | Negative-sense RNA virus | 19 kb | No |
| Dengue | Order: Amarillovirales Family: Flaviviridae Genus: Flavivirus | Endemic since WWII. Subtropics and tropics where the aedes sp mosquito exist | Primates -- > Mosquito Vector -- > Humans | Positive-sense RNA virus | 10.7kb | No |
| West Nile | Order: Amarillovirales Family: Flaviviridae Genus: Flavivirus | Africa 1937 United States 1999 | Birds -- > Mosquito Vector -- > Human | Positive-sense RNA virus | 11kb | No |
| Zika | Order: Amarillovirales Family: Flaviviridae Genus: Flavivirus | Unknown -- > Mosquito Vector -- > Humans | Positive-sense RNA virus | 11kb | Vaccines in development, no other treatments available | |
| Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus | Order: Amarillovirales Family: Flaviviridae Genus: Flavivirus | Virus isolated in 1937. Endemic in Russia, Europe | Ticks -- > Humans | Positive-sense RNA virus | 11kb | Vaccine available, but not outside of endemic areas. |
| Japanese Encephilitis Virus | Order: Amarillovirales Family: Flaviviridae Genus: Flavivirus | Southeast Asia 1930’s | Unknown -- > Mosquito Vector -- > Humans | Positive-sense RNA virus | 10.9kb | Vaccine available, but no other pharmaeutical treatments available. |
Viral life cycles
Coronaviridae
The current outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 represents the third documented spillover of an animal coronavirus to humans in the last 20 years that has resulted in a major epidemic of global proportions.17 As of this writing, the virus has infected worldwide almost 65 million people and claimed over 1.5 million lives.18 The Coronaviridae Study Group of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses has assessed the placement of this current human pathogen within the Coronaviridae family. They have recognized this virus as forming a sister clade to the prototype human and bat severe acute respiratory syndrome coronaviruses (SARS-CoVs) and designated it as SARS-CoV-2.19 Coronaviruses are enveloped, positive-sense RNA viruses that are distributed broadly among humans, other mammals, and birds, and are known to cause respiratory, enteric, hepatic, and neurologic diseases.20,21 The Coronaviridae family of viruses contain the largest known RNA genomes, 30–32 kb,22 and is divided into four genera (alpha, beta, gamma, and delta coronaviruses). While most coronavirus infections cause common cold symptoms in humans, SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and SARS-CoV-2, the three coronaviruses covered in this review, have the potential to cause more serious disease, including death. These three viruses have emerged relatively recently, all in the 21st century, and have been the focus of extensive research in an urgent response to their global occurrence and impact. SARS-CoV appeared first in late 2002 and was characterized by rapid human-to-human transmission with various degrees of morbidity and mortality ranging from moderate to high. The zoonotic origin of these outbreaks was linked to bat coronaviruses (>90% sequence identity) with possible intermediate transmission through other mammals such as civets20 or pangolins.23 These infections tended to disproportionately affect older populations, with SARS mortality reaching 50% of those infected over 60 years of age.20 To date there are no clinically approved treatments for these viruses, and therefore we provide this review with the goal of providing insight into these viruses, their vulnerabilities, and past and ongoing natural product-based drug discovery efforts to curb these deadly pathogens.
Coronaviruses infect their hosts through a number of pathways, exploiting host receptors and transmembrane proteases to facilitate their entry into cells and delivery of viral RNA into the cytoplasm (Figure 1, Table 2). In overview, the viral spike glycoprotein (S) facilitates entry into target cells by binding to cellular receptors and is subsequently primed by host cellular proteases that promote fusion of viral and cellular membranes and internalization. Trimers of the S protein form peplomers embedded in the viral envelope, giving the virus its characteristic crown-like morphology. Due to their highly homologous S proteins (96% sequence identity), both SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 make use of the mammalian angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) as a means of initial contact.20,24,25 The MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV-1/2 spike proteins share a high degree of structural similarity in their core subdomains, but are notably divergent in the receptor-binding subdomain. For this reason, MERS-CoV utilizes a different surface protein for entry, namely the dipeptidyl peptidase 4 receptor (DPP-4 or CD26).26 It has been posited that the more widespread distribution of SARS-CoV-2 is facilitated by a stronger binding affinity to the ACE2 receptor.27 Once contact is made, host proteases TMPRSS2/4 (co-localized with ACE2 or DPP-4 on the cell surface) or endosomal cathepsin L cleave at two or more sites on the S protein to facilitate a conformational rearrangement and fusion with the host membrane, releasing viral RNA into the host cytoplasm.24,28–30 Mechanistically, it appears that the coronavirus S protein undergoes a receptor-mediated conformational change that reveals cryptic cleavage sites within the viral envelope glycoprotein.31 Proteolysis by host proteases is then necessary to fully activate the viral glycoprotein’s membrane-fusion potential. Inhibiting activity of either host protease partially blocks infection, and inhibiting both efficiently prevents cell entry and replication in vitro.29,32 Temporary blockage of these host proteases by small molecules is non-lethal to mammalian cells, and thus they are active targets of investigation for prophylactic treatment. Following entry, the replicase gene is translated by host machinery and co-translationally processed by the Mpro and PLpro into 16 non-structural proteins encoded in orf1a/1ab. These proteins are assembled into the replicase-transcriptase complex to create an environment suitable for viral RNA synthesis and is responsible for RNA replication and transcription of the genomic and sub-genomic RNAs. A comprehensive list of these proteins and their known functions has been assembled by Fehr and Perlman.33 Viral RNA synthesis by the replicase complex produces RNAs that serve as mRNAs for production of the structural and accessory proteins. This process is currently the focus of active drug discovery efforts to prevent viral replication. For example, remdesivir (1) (Gilead Sciences; Fig. 7) is a promising candidate targeting the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp).34,35
Figure 1.
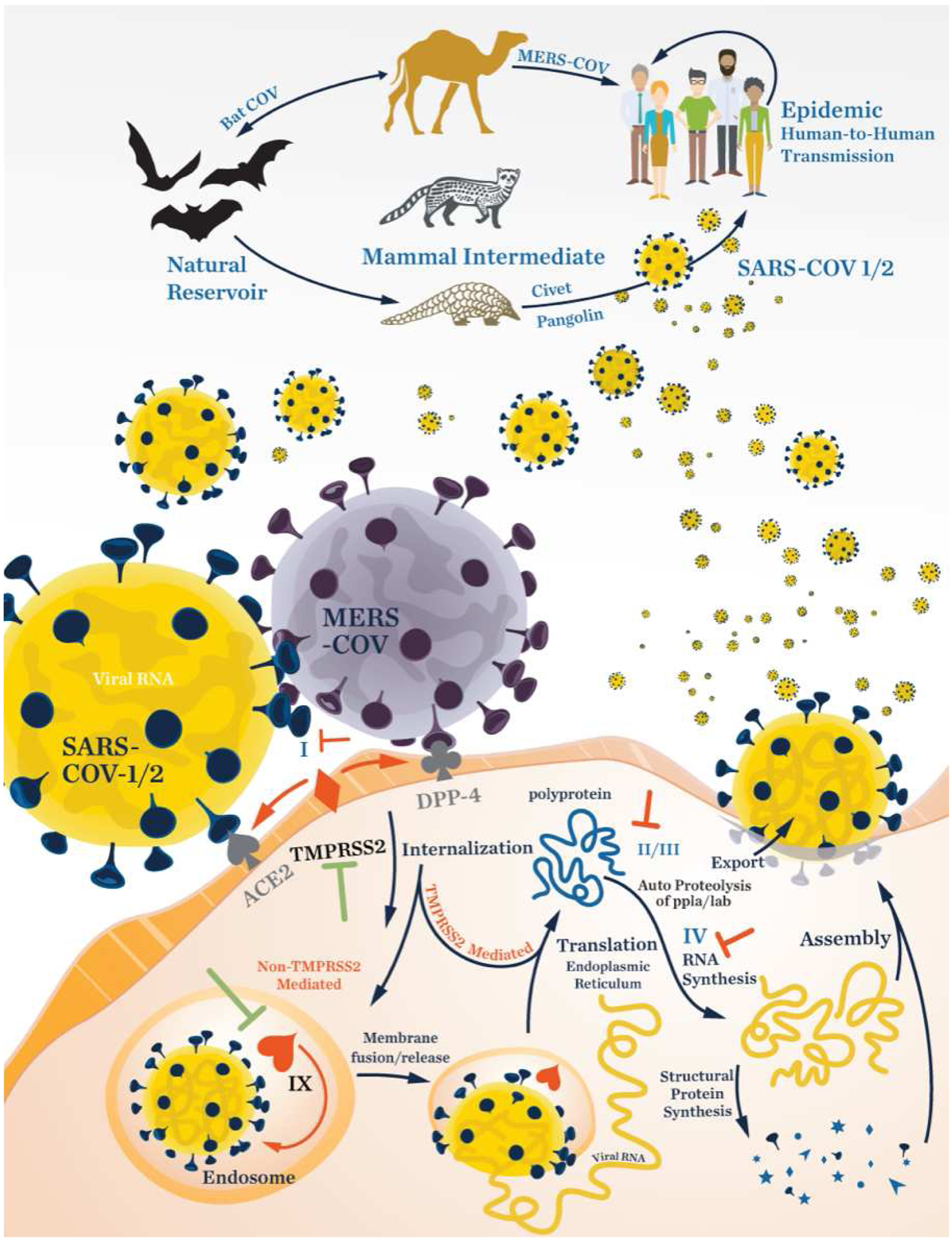
Life cycle of coronaviruses as represented by the SARS-CoV-1/2 and MERS-COV viruses. The Roman numerals in the figure refer to entries in Table 2. The “T” symbol indicates a target with potential for developing an inhibitor.
Table 2.
Validated and potential drug targets and known NP inhibitors against Coronaviridae. Roman numbering corresponds to numbering in Figure1. Numbers in parenthesis corresponds to structures in Figures 5–10
| Viral Proteins | l | Spike Glycoprotein | Host cell recognition | Griffithsin (2), Emodin (3) |
| II | Main Protease (Mpro/3CLpro) | Viral protein mauration | Herbacetin (13), Rhoifolin (15), & other flavonoids | |
| Tomentin A-E (16), Hirsutenone (17), | ||||
| lll | Papain-Like Protease (PLpro) | Viral protein mauration | Tanshinones (19), Psoralidin (18), and | |
| Others | ||||
| IV | RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) | Viral RNA replication | Inhibitors Needed | |
| V | NSP1 | Obstructs host cell protein synthesis and innate immune response | Inhibitors Needed | |
| VI | NSP13 | Vrial helicase | Myricetin (26), Scutellarein (27) | |
| VII | Orf8b | Obstructs innate immune response | Inhibitors Needed | |
| Host Proteins | VIII | TMPRSS2 | Cell membrane protease. Cleaves viral spike protein facilitating membrane fusion & entry | Aprotinin (34) |
| IX | Cathepsin L | Endosomal protease. Cleaves spike protein facilitating membrane fusion | Gallinamide A (35), Nicolaidesin C (36), Grassypeptolide (37), E-64, Leupeptin (38) |
Figure 7.
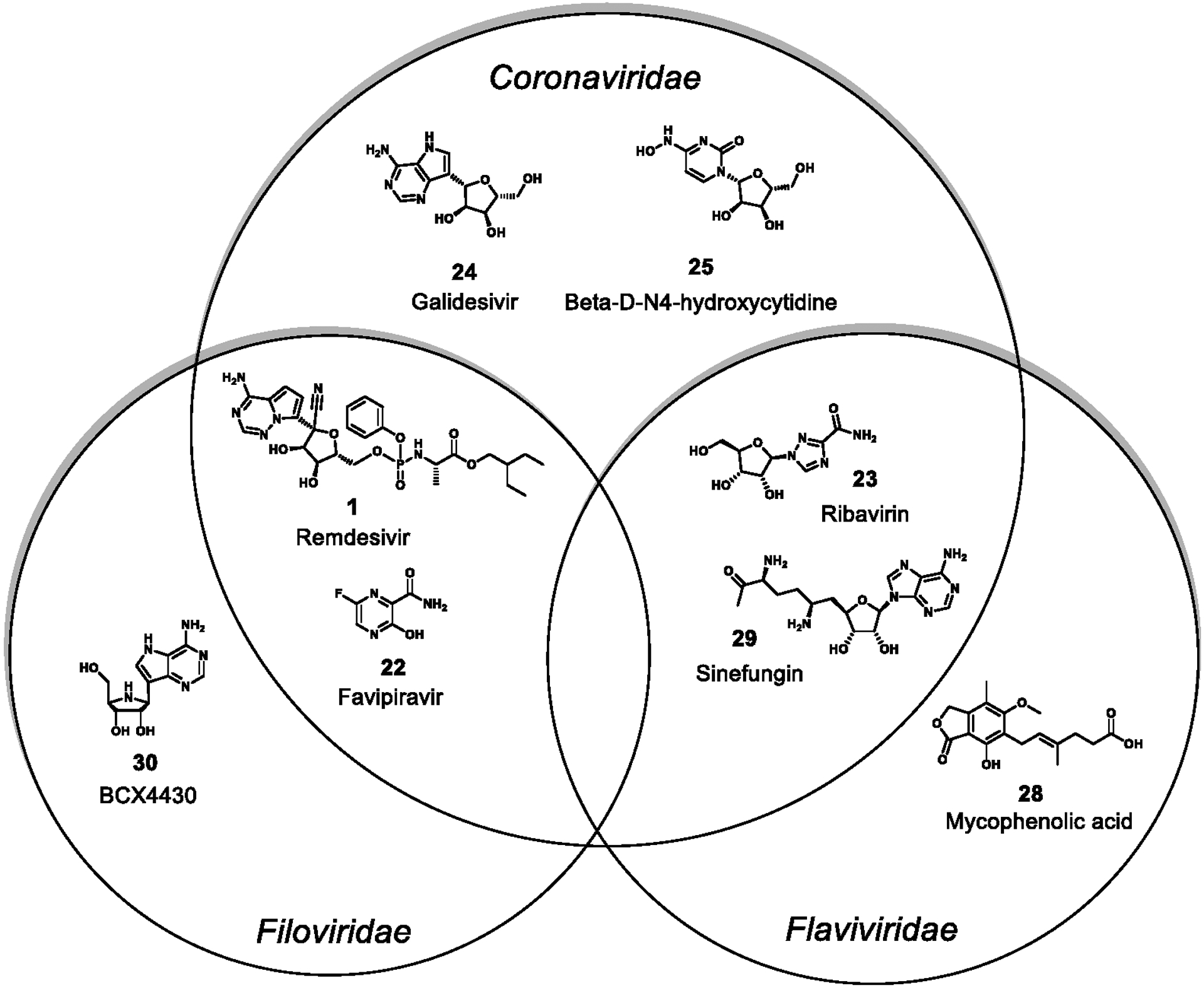
Inhibitors of viral replicase complex component RdRp. Shown here are compounds that are inhibitors of Coronaviridae, Flaviviridae, Filoviridae, or of multiple families. The following are natural products: mycophenolic acid and sinefungin and natural product derivatives: Remdesivir, Favipiravir, Ribavirin, Galdesivir, 3-D-N4-hydroxycytidine, BCX4430.
The main pillars of drug discovery against these recently emergent coronaviruses has been inhibition of viral entry or prevention of replication once infection has occurred. There are several routes by which the virus can escape the cell, including exocytosis or by inducing apoptosis, and this makes the targeting of packaging or export mechanisms much more challenging drug targets. However, by targeting the spike glycoprotein, host recognition by the virus is prevented and entry nullified. Alternatively, inhibition of polyprotein processing by the viral proteases or targeting the RdRp can partly or wholly prevent replication. A list of repurposed or investigational agents against SARS-CoV-2 was recently reported36, and several studies have been published identifying new inhibitors of SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV.37,38
FLAVIVIRIDAE
Several well-known endemics are caused by flaviviruses, for example, West Nile, Dengue, Zika, Japanese encephalitis (JEV), and Tick-borne encephalitis (TBV). Most Flaviviridae infections involve an intermediate host before transmission to humans. West Nile, Zika, Dengue and JEV viruses are all transmitted by mosquitoes whereas TBV involves spread by ticks; humans are typically the end host. Intermediate animal hosts include monkeys, birds, and pigs, with transfers to mosquitos that pass the infection to humans (Figure 2, Table 3. However, Dengue is common in human populations around the world with around 4.2 million cases reported to WHO in 2019; however the true number of infections is estimated to be much higher. Because of its prevalence, human to mosquito to human transmission of Dengue is the most common route (Figure 2).39 The tick-borne flaviviruses are commonly transmitted from deer and sheep to ticks and then to humans.40 Because there are many different flaviviruses that can cause potential pandemics, after a brief review of the diversity of disease-causing Flaviviridae, this review focuses on Dengue virus. This is appropriate and representative as all flaviviruses have similar genome sizes (10–11 kb) as well as similar gene organization in their positive RNA strand genomes.
Figure 2.
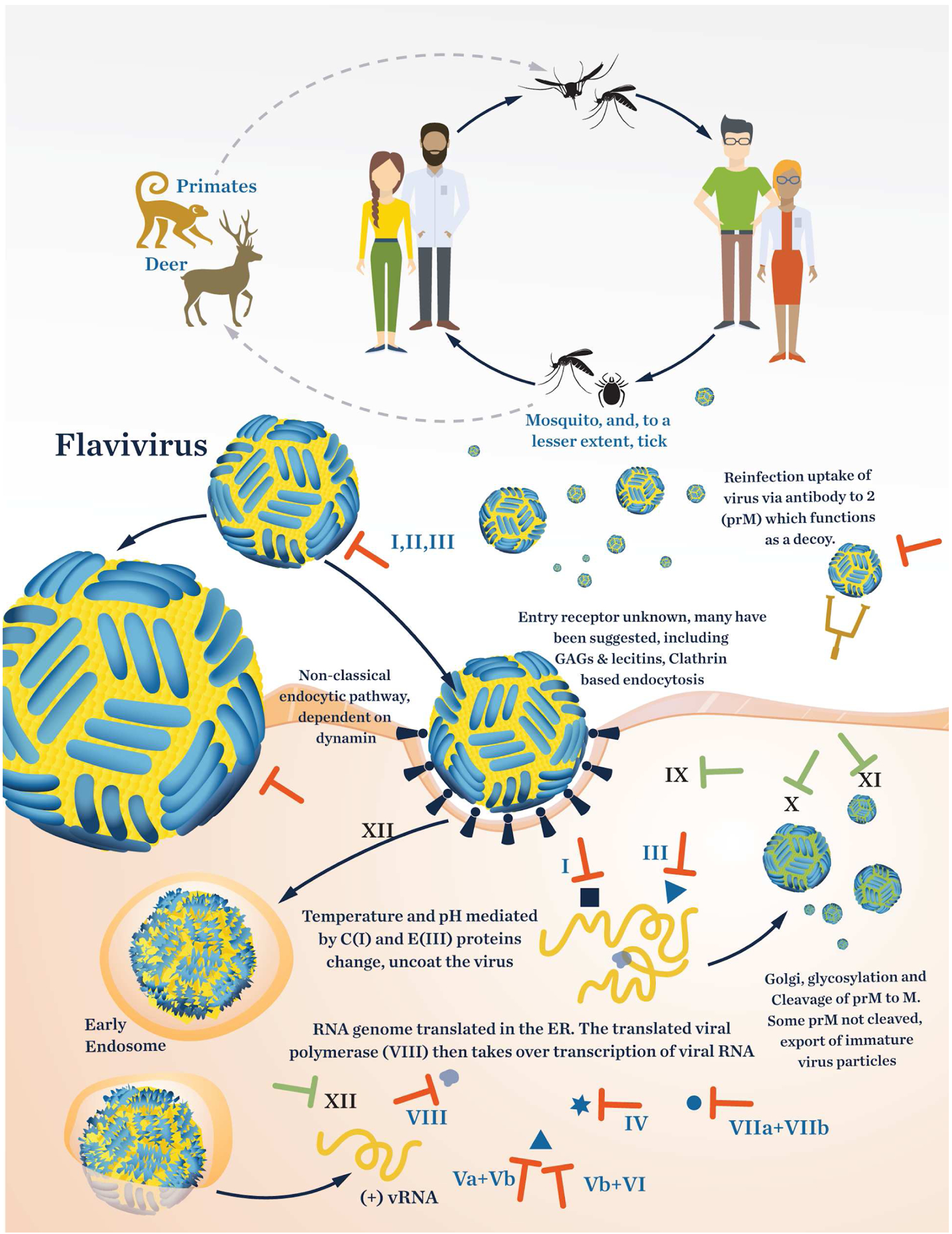
Life cycle of Flaviviridae as represented by the dengue virus. The roman numerals in the figure refer to entries in Table 3. The “T” symbol indicates a target with potential for developing an inhibitor.
Table 3.
Validated and potential drug targets in Flaviviridae and NP inhibitors (dengue virus shown). Roman numbering corresponds to numbering in Figure1. Numbers in parenthesis corresponds to structures in Figures 5–10
| Viral Proteins | Capsid protein | Binds to viral nucleotide strand. Forms viral capsid. | Nordihydroguaiaretic acid (NDGA) | |
| II | prM/M protein | Membrane protein | Inhibitors Needed | |
| III | E protein | E nvelope protein | Inhibitors needed | |
| IV | NS 1 | Anti-host factor glycoprotein | Castanospermine (32) | |
| Va | NS2A | Membrane protein, interacts with calmodulin (Ca-influx) | Inhibitors Needed | |
| Vb | NS2B | NS 3 cofactor / part of the replication complex | Inhibitors Needed | |
| VI | NS 3 | Protease/Helicase | G anoderma lucidum triterpenoid Ganodermanontriol (20) | |
| VIIa | NS4A | ER membrane protein/also part of replication complex | Inhibitors Needed | |
| VIIb | NS4B | ER membrane protein/also part of replication complex | Inhibitors Needed | |
| VIII | NS 5 | R dR p / methyltransferas e / helicase | Mycophenolic acid (28) | |
| Host Proteins | IX | Calmodulin | Ca-influx. Interacts with NS2A | Inhibitors N e ede d |
| X | Signal peptidase / Signalase | Cleaves signal peptides. In Dengue Four cleavages (prM, E, NS1, and NS4B) | Cavinafungin (44) | |
| XI | Alpha-glucosidase | Aids in E R release of glycoproteins E and NS 1 | deoxynojirimycin (46) | |
| XII |
Dengue is the most prevalent mosquito-borne viral disease in the world.41 The dengue virus consists of four serotypes, which introduces considerable complication in the disease and its clinical course. Infection with one serotype does not confer immunity to another serotype. Rather, infection with a different serotype can create an antibody-dependent enhancement of the disease. This makes it very difficult to develop a universal vaccine for all the Dengue serotypes41 and makes imperative the development of small molecule therapeutics.
West Nile virus infections first appeared in the United States in 1999. The most common route of human infection is by a mosquito bite with the natural reservoir mainly being in birds. Since 1999 an estimated 7 million humans have been infected; this makes the West Nile virus the most common mosquito-borne virus infection and also the virus that is responsible for the most cases of viral encephalitis in the United States.42 According to the CDC there are no currently approved treatments for West Nile virus, other than standard supportive care.43
The Zika virus was first isolated from a monkey in Uganda in 1947 and transmission to humans was first detected in 1952. So far, only 12 cases in Puerto Rico and one case in Virginia have been recorded in the United States (CDC.gov). It is, like many other Flaviviridae, transmitted by mosquitoes and is widespread in Africa and Asia Pacific countries. In 2015, reports of the virus spreading to Brazil started circulating and several thousand babies were born with microcephaly.44 The virus has since spread through South America and the Caribbean.
The Japanese Encephalitis Virus (JEV) was first discovered in the 1870s in Japan. It is widespread throughout Asia with about 69,000 cases per year.45 Several different genotypes and the unpredictable spread of the JEV makes developing specific pharmaceutical treatments very attractive. Several vaccines exist against different genotypes, and one manufactured by IXIARO must be given as two doses with 28 days between followed by a yearly booster.46 This elaborate vaccination schedule can be prohibitive for travelers, and thus there is an unmet medical need for specific agents to treat JEV infections.
Several flaviviruses are transmitted via ticks; an example being Tick-borne encephalitis (TBE). TBE is endemic to Eurasia and is becoming more widespread. A recent review provides details on the viral life cycle, and viral and host proteins involved in transmission.47
Viruses of the family Flaviviridae have a positive RNA strand that can, upon entry into the cell, immediately hijack the ribosome for translation. The size of the RNA genome varies from about 10.6 to 10.9 kb. The RNA encodes for 10 proteins, 3 of which are structural and 7 are non-structural (Figure 4). The orfs for the structural proteins contain the nucleocapsid protein (C), the envelope protein (M), and the major spike (envelope) glycoprotein (E) of the capsid. The seven remaining orfs encode for non-structural proteins (NSP). NS1, in at least the Zika virus, appears to ubiquitinate Arg63 of the metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9) to increase its stability. MMP9 degrades structural proteins and tight junctions between cells such that the virus can invade more easily.48 Involvement of MMP9 in West Nile infection has also been reported, but there is no experimental data to support NS1 ubiquitination. Instead, some evidence exists that the interferon pathway is downregulated by this protein.49 The Dengue virus NS1 was examined by Glasner50 and was reported to break down extracellular glycocalyx and cause cell-intrinsic vascular leakage. Regardless of the mechanism of action of NS1, it appears to be an important virulence factor that may be targeted for potential drug development. The NS2 orf encodes for two proteins; NS2A is a transmembrane protein and in Dengue has been shown to bind directly to calmodulin, the protein involved in calcium influx.51 There have been no efforts to date to develop inhibitors of NS2A; however, a known calmodulin inhibitor has been shown to inhibit the dengue virus.51,52 The NS2B protein is a hydrophobic protein that serves as a cofactor to the NS3 protease.53 NS2B has not been validated as an independent drug target, but only when in combination with NS3.54 The Dengue virus NS4 orf encodes for a membrane protein in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. It consists of NS4A (127 aa) and NS4B (248 aa). These two are connected by a 23-residue linker from the C terminal of NS4A.47 After integration into the membrane, the 23 aa linker is cleaved by a host signal peptidase (signalase). NS4 has 11 helices, and the C-terminal containing helices 9 and 9’ flip from the ER membrane to the cell membrane where it interacts with the RNA dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) NS5, also a key drug target in Flaviviridae.55,56
Figure 4.
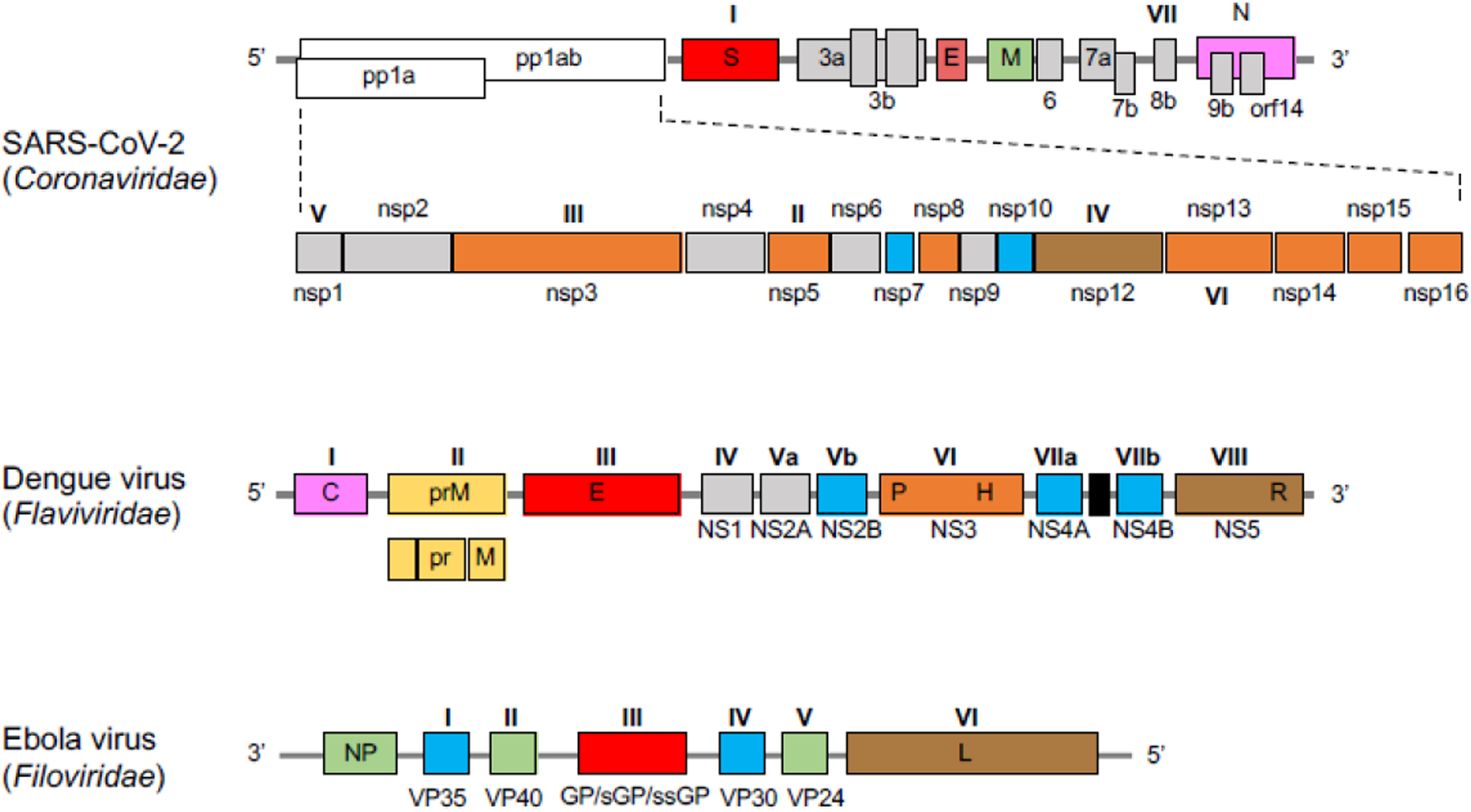
Schematic diagrams for the genomes of coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 (Coronaviridae), Dengue virus (Flaviviridae), and Ebola virus (Filoviridae). The genomes of Coronaviridae and Flaviviridae are composed of single-strand positive-sense RNA whereas those of the Filoviridae are composed of a single-strand of negative-sense RNA. Genes labeled by Roman numerals encode potential druggable protein targets mentioned in this review, and accord to the same Roman numerals used in Figures 1–3 and Tables 2–4. Capsid protein (pink), spike protein (red), polymerase (brown), enzyme (orange), structural protein (green), envelope protein (yellow), cofactor/activator (blue), others/undefined protein (grey).
FILOVIRIDAE
Filoviruses, such as Ebola virus (EBOV) and Marburg virus (MARV), are known as zoonotic pathogens which cause rare yet severe diseases affecting humans and other primates. Ebola virus disease (EVD) was first discovered in 1976 as a result of consecutive outbreaks in two areas of central Africa, in South Sudan and Zaire.57 EVD is often a deadly disease, and typical symptoms include fever, headache, vomiting, and diarrhea. Some people in severe cases can suffer internal and external bleeding. It was later discovered that these outbreaks were caused by genetically distinct EBOVs, Sudan ebolavirus and Zaire ebolavirus. Many outbreaks of EVD have occurred since 1976, primarily in Africa.58 Today, there are five characterized species of the genus Ebolavirus: Sudan ebolavirus (SUDV), Zaire ebolavirus (EBOV), Reston ebolavirus (RESTV), Taï Forest ebolavirus (TAFV), and Bundibugyo ebolavirus (BDBV). RESTV is the only known filovirus which does not cause severe disease in humans; however, it can be fatal in monkeys and pigs.59,60
Marburg virus disease (MVD) was first observed in 1967 in Marburg, Germany and is caused by the filovirus Marburg Marburgvirus (MARV). The symptoms of MVD are similar to those of EVD.61 MVD appears in sporadic outbreaks in African countries as well.62 The family of Filoviridae is a member of the order Mononegavirales and generally have a filamentous morphology (about 1,000 nm in length with a diameter of 80 nm). It has been reported that fruit bats serve as a wildlife reservoir in nature for EBOV and MARV.63,64 Bats carrying the virus transmit it to other animals such as monkeys65 and chimpanzees,66 as well as to humans. Human-to-human transmission can occur through contact with a patient’s blood and bodily fluids.67 In December 2019, the first vaccine, rVSV-ZEBOV, was approved for the prevention of EVD by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States,68 and other vaccines are now in development.69
Figure 3 shows the generalized life cycle of filoviruses.62 The filovirus infects its host by the GP protein binding to several host molecules on the cell membrane, including the T-cell immunoglobulin mucin receptor 1 (TIM1), also known as hepatitis A virus cellular receptor 1 (HAVCR1), C-type lectins such as dendritic cell-specific intercellular adhesion molecule 3-grabbing non-integrin (DC-SIGN), and β-integrins.70–72 The virus is then incorporated into the cell through macropinocytosis.73 Next, two host cell cysteine proteases, cathepsin B and cathepsin L, cleave the surface GP protein, and the processed GP binds to the Niemann–Pick C1 (NPC1) cholesterol transporter.74,75 This interaction leads to the fusion of the virus with the endosomal membrane and release of the viral RNA into the cytoplasm for transcription and replication in the inclusion body. Viral mRNAs produced by an RdRp are translated into proteins associated with VP30, VP35, and L by host ribosomes (primary transcription). The synthesized viral proteins are used in secondary transcription and vRNA replication. Following transcription, the GP protein, a type I transmembrane glycoprotein, is produced as a precursor protein known as GP0; this is then cleaved post-translationally by a furin-like protease to yield the ectodomains GP1 and GP2. These proteins form dimers, which in turn form trimers to produce the mature and functional heterotrimeric GP.76,77 The mature GP protein is transported to the cell membrane in secretory vesicles. vRNA is replicated through a complementary positive sense RNA (cRNA) along with VP35 and L.78 After translation, viral proteins are assembled to form the nucleocapsid, then transported to the plasma membrane. Finally, budding to form new virus particles is mediated by VP40 and GP at the membrane (Figure 3, Table 4)79
Figure 3.
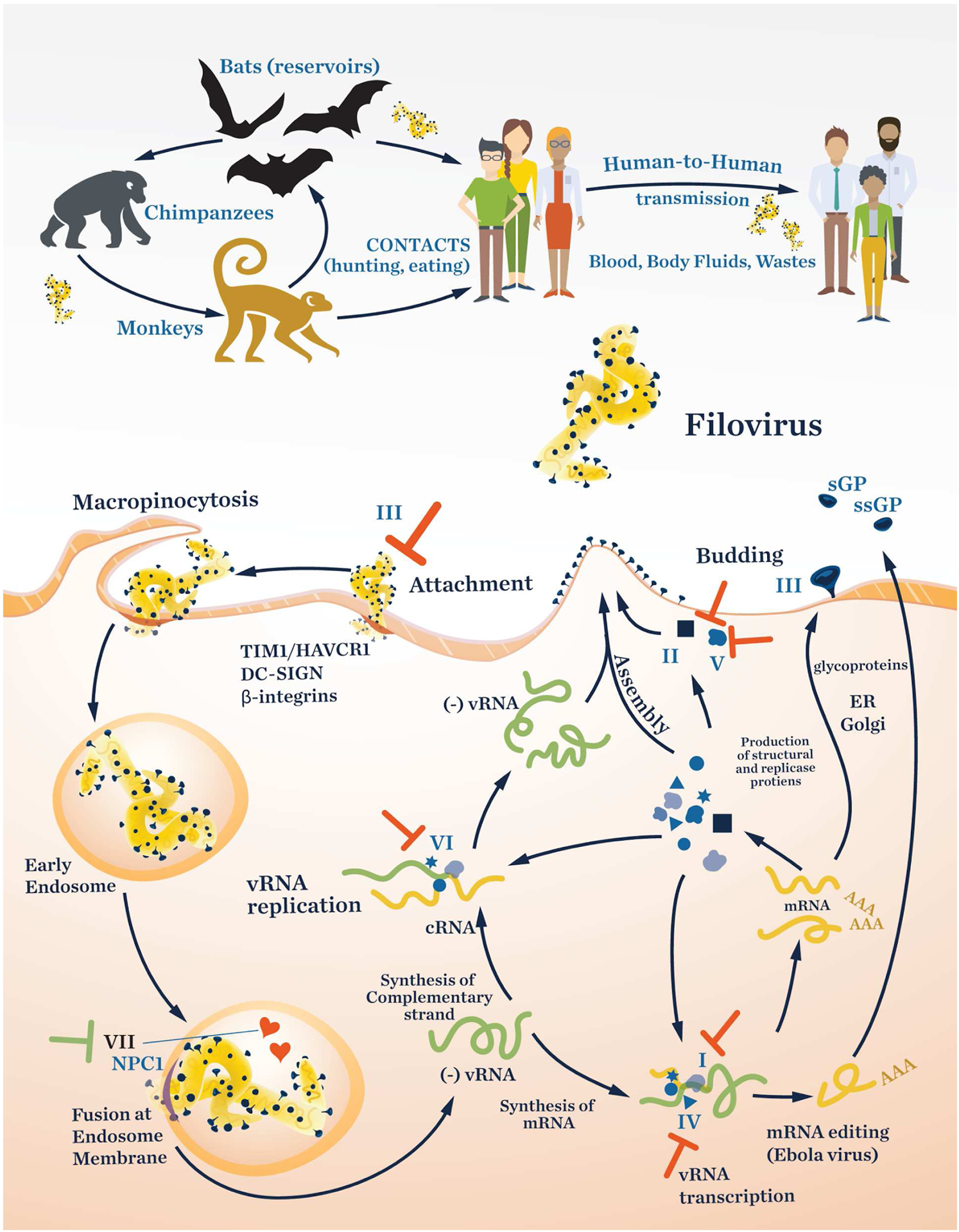
Life cycle of filoviruses as represented by the Ebola virus. The Roman numerals in the figure refer to the entries in Table 4. The “T” symbol indicates a target with potential for developing an inhibitor.
Table 4.
Validated and potential drug targets in Filoviridae and NP Inhibitors. Numbering corresponds to numbering in Figure 2. Roman numbering corresponds to numbering in Figure1. Numbers in parenthesis corresponds to structures in Figures 5–10
| Viral Proteins | I | VP35 | Polymerase cofactor responsible for transcription and replication with L protein | myricetin (26), epigallocatechingallate (31) |
| II | VP40 | Matrix protein involved in budding | Inhibitors Needed | |
| III | GP | Host cell recognition | ellagic acid (6), gallic acid (7), cyanovirin-N (11) | |
| IV | VP30 | Transcriptional activator | Inhibitors Needed | |
| V | VP24 | Structural protein. Important role in nucleocapsid formation | Inhibitors Needed | |
| VI | L protein | RNA-dependent RNA polymerase | Inhibitors Needed | |
| Host Proteins | VII | Cathepsin B / Cathepsin L | Endosomal protease. Cleaves spike protein facilitating membrane fusion & entry | gallinamide A (35), tokaramide A (39), miraziridine A (40) |
Genome Structures
Schematic diagrams for the genomes of coronaviruses (Coronaviridae), Dengue virus (Flaviviridae), and Ebola virus (Filoviridae) are provided in Figure 4. The genes labeled by Roman numerals are encoding for potential druggable protein targets, and accord to the same Roman numerals in Figures 2–4 and Tables 1–3. The coronavirus genome is one of the larger known viral genomes at over 30 kb, with the viral replicase gene cassette comprising roughly two-thirds of these nucleotides (orf1a/orf1ab); the remaining one-third contains structural and accessory proteins.33,80,81 The replicase is translated as two large polyproteins 1a and 1ab which are auto-proteolytically cleaved22 into the 16 proteins that form the replicase/transcriptase complex (Figures 1 and 4A). The family of Flaviviridae viruses, characterized by a positive-sense RNA single-strand, upon cellular immediately hijack the host’s ribosome to translate its viral RNA. Flaviviridae RNA genomes vary in size from about 10.6 to 10.9 kb. The RNA encodes for 10 proteins: 3 structural and 7 non-structural (Figure 4B). The orfs for the structural proteins contain the nucleocapsid protein (C), the envelope protein (M), and the major spike (envelope) glycoprotein (E) of the capsid. The seven remaining orfs encode for non-structural proteins (NS). The Filoviridae genome is a single-strand negative-sense RNA approximately 19 kb in length.82,83 Seven viral proteins are encoded in this genome: the nucleoprotein (NP), a polymerase cofactor protein (VP35), matrix protein (VP40), a glycoprotein (GP), a transcriptional activator (VP30), a nucleocapsid- associated protein (VP24), and an RdRp (L) (Figure 4C).62,78 EBOV produces some secreted GPs, soluble GP (sGP) and small soluble GP (ssGP) via a transcriptional editing event derived from the same GP gene, whereas MARV does not. It has reported that sGP may act as a decoy antigen to disturb the host immune response as a result of developing antibodies against GPs.76
In this review, we discuss both validated as well as prospective protein targets under investigation for the potential treatment of Coronaviridae, Flaviviridae and Filoviridae viral infections. We focus this analysis on natural products and NP-like or inspired inhibitors of viral infection or replication, and modulators of immune evasion. We opted to organize our treatment of potential therapeutic targets for the three classes of RNA viruses by biochemical target rather than by virus. The arrangement by virus family was rejected, as very similar targets would contribute to repetitive discussions of the same agents. Additionally, we conceived that insights would be gained by comparison and contrast of the same or similar targets in different virus families and their therapeutic modulators. Finally, therapeutics effective against a given target in one family may have as yet unrealized application to a comparable target in another viral family. For this combination of reasons, we have chosen to arrange and present the natural product inhibitors of these RNA-containing viruses by respective biochemical target. Reviews covering synthetic or other natural product inhibitors have appeared elsewhere and are largely excluded from this review, as are compounds reported with only in silico data that have not been further validated.37,84–86In addition to the more well-studied targets, we also discuss prospective targets based on recent reports characterizing some of these lesser-known viral proteins and their functions.
Protein Targets & Drug Development
Across viral diversity there are several biochemical themes and mechanisms that are conserved. For example, different families of viruses exploit different host surface proteins to gain entry into target cells, and the general mechanisms employed show great similarity to one another. Similarly, the viral replication cycle has points of commonality across different viral families, including: 1) exploiting host proteins to gain entry into cells, 2) commandeering a host’s protein manufacturing machinery, 3) manipulating a host’s innate immune system to evade detection, and 4) siphoning the host’s resources to replicate, mature, and export new virions so as to propagate infection. The proteins responsible for carrying out these biochemical steps, both those of viral and host origin, are presented in some detail, and then used to organize this perspective review by target across viral families so as to emphasize similarities and differences. In so doing, we present new connections and present a fresh approach for potential antiviral drug discovery.
As we search for new answers to the threat of global pandemics, where better to begin looking than to nature? In this discussion, we will review natural products and natural product-inspired compounds that have activities reported against viruses of the Coronaviridae, Flaviviridae, and Filoviridae outlined above. We have chosen to focus on these families of RNA viruses because of their potential to cause pandemics in human populations. Here we reveal gaps and shortcomings in past drug development efforts, and hope to inspire a renewed vigor in antiviral natural product discovery. Generally, the individual protein targets that we discuss are homologous between viral families; however that is not to say that every compound discussed therein will be universally applicable. Additional investigation and careful structural analysis of each protein target should be pursued in any drug development campaign.
A. Viral Proteins
Viruses have many nuanced mechanisms for promoting infection and propagation. They exploit host receptors and proteases to enter undetected into cells, then suppress the innate immune response, and ultimately manipulate the host to manufacture new virions for export, all with only a handful of viral proteins at their disposal. There are four main classes of proteins that cover the majority of druggable space of these viral genomes: structural proteins such as the spike protein, non-structural proteins such as viral proteases, proteins involved in replication, and accessory proteins that perform a variety of functions non-essential for replication but important for propagation. This latter class of protein may prove to be useful targets as well.
Structural Proteins
Structural proteins make up a smaller portion of the viral genome, however it is well known that the spike glycoproteins facilitate host recognition and endocytosis. Therefore, spike proteins have been an active target for drug discovery and have focused on disrupting binding to host receptors to prevent entry into cells. Indeed, a number of vaccine and convalescent plasma efforts have focused on developing antibodies against spike proteins.57,87 However, in this section we will review small molecule NPs and their inspired agents that inhibit the function of these receptor-binding proteins and thus block viral uptake into cells (Figure 5).
Figure 5.
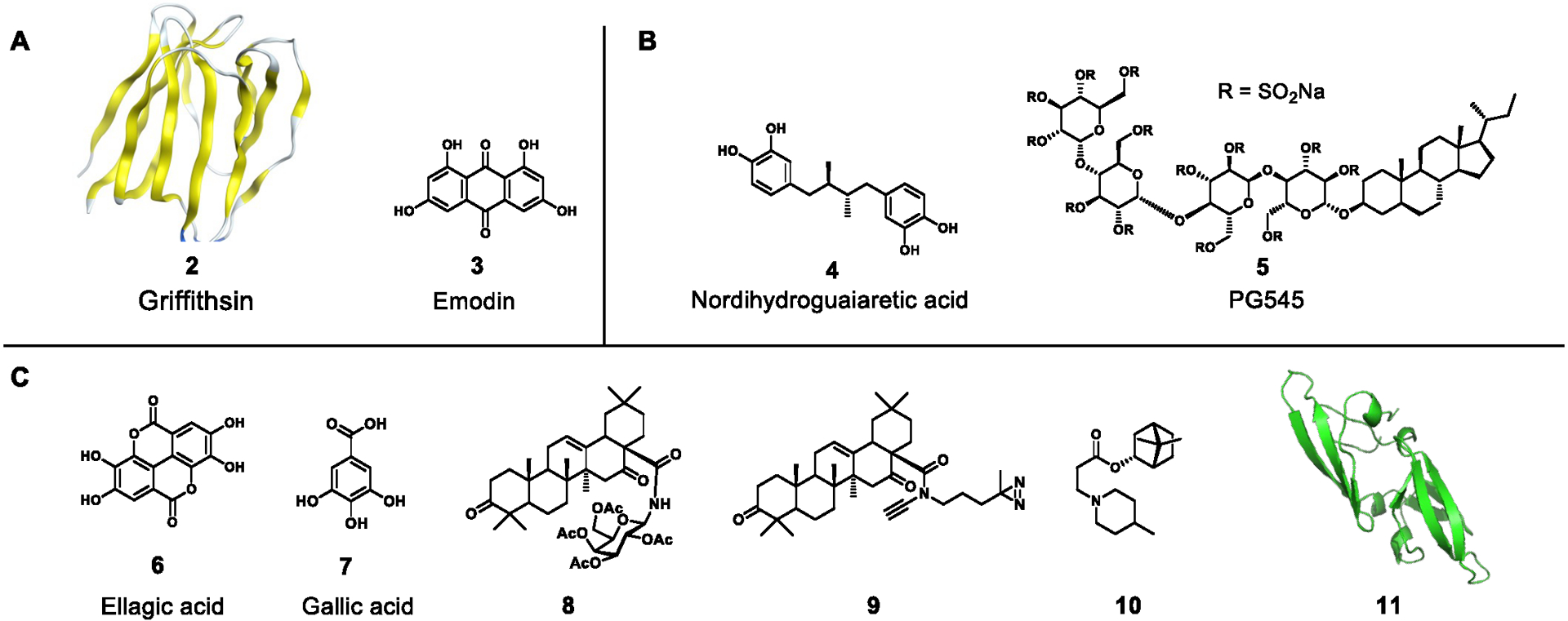
Inhibitors of viral structural proteins of A) Coronaviridae, B) Flaviviridae, or C) Filoviridae. The following are natural products: griffithsin (PDB: 2GTY), emodin, nordihydroguaiaretic acid, ellagic acid, gallic acid, cyanovirin-N (11, PDB: 2EZM) and natural product derivatives: PG545, 8, 9, 10
The Coronaviridae have 5 structural proteins in their genomes including an S protein responsible for cellular recognition, a small envelope (E) protein that is essential for proper virion assembly in most coronaviruses and is implicated in inducing apoptosis, a membrane (M) protein that comprises the majority of the virus envelope, an RNA-binding nucleocapsid (N) protein that complexes with genome RNA to form the viral capsid and is also known to be an interferon antagonist, and in some betacoronaviruses, a hemagglutinin-esterase (HE) protein that forms a second, smaller spike on the envelope. This second spike protein may serve to enhance virus attachment via binding to sialic acid-containing molecules. These proteins provide a vessel for the viral RNA and perform critical functions during assembly, though they are seldom the target of drug discovery efforts because of the late-stage nature of their existence in viral replication. After the emergence of SARS in 2002, there has been an ongoing effort to develop inhibitors for these viruses with an emphasis on preventing viral entry via inhibition of S binding. Inhibitors of this spike-receptor binding interaction have largely been based on peptide fragments of the S protein88,89 or variations thereof.90 Although these showed efficacy in vitro, the translation of these peptides into the clinic may be arduous and as of yet, none have been approved for treatment for coronavirus infections.
Two natural products, griffithsin (2) and emodin (3), have been validated as disruptors of viral receptor binding to date, inhibiting SARS-CoV S at 48 nM and 200 μΜ respectively.91,92 Compound 2, a small protein isolated from the red algae Griffithsia, has demonstrated broad spectrum ability to bind to viral glycoproteins and prevent binding to cellular receptors including HIV and EBOV with minimal toxicity.93 The activity of 2 appears to be due to several binding sites for monosaccharides such as mannose and glucose, and it is currently under development for use in the clinic. Compound 3 is a small plant-derived anthraquinone that was found to specifically inhibit S protein interaction of SARS-CoV1/2 with host-derived ACE2 in a dose-dependent manner.
Because there are many Flaviviridae that pose a risk of endemic disease, we opted to use the dengue virus as a proxy for all Flaviviridae (Figure 2, Table 3) as discussing all memers of this family would become highly repetitive. In general, the Flaviviridae have three structural proteins, the capsid (C), M, and E proteins (Figure 2, Table 3). The C protein forms the capsid that becomes unraveled inside the endosome during endocytosis. Few efforts have been directed towards inhibiting C. One example is the dissociation of C from lipid droplets by the compound nordihydroguaiaretic acid (4) isolated from the creosote brush. Fat metabolism and lipid droplets play a role in Dengue viral replication.94 The M protein is initially translated as a pro-protein (prM) and the precursor portion is cleaved in the trans Golgi network by a host furin protease. However, the precursor portion is often not cleaved, and many immature viral particles are secreted. It remains to be determined if furin is a good drug target; however, Imran et al. developed a peptide that inhibits furin cleavage of prM, and Braun and Sauter in their 2019 review argue that a furin inhibitor could be useful for both combating infectious diseases as well as cancer.95 The major envelope protein (E) is essential for the virus to enter the cell via clathrin-mediated endocytosis. There are several host receptor candidates, but one suggestion appears to be the glycosaminoglycan (GAG) receptor. The E protein binds to GAGs, some of which contain heparin sulfates, and a heparin sulfate mimic PG545 (5) disrupts that binding by acting as a decoy receptor.96
The structural proteins in Filoviridae include the nucleoprotein (NP) which encapsulates the viral genome, glycoprotein (GP), nucleocapsid-associated protein (VP24), and matrix protein (VP40). The GP is an essential spike protein that, like many other viruses, interacts with a receptor expressed on the host cell to facilitate entry. A screening program evaluated 373 extracts from 128 traditional Chinese medicines for activity as EBOV inhibitors. The extract of Rhodiola rosea (Crassulaceae) was identified as a specific inhibitor at 12.5 μg/mL using a pseudotyped EBOV screening test.97 Furthermore, ellagic acid (6) and gallic acid (7) of R. rosea were the most effective compounds in this assay system. Compound 6 had an IC50 value of 1.4 μM and 6.4 μM against EBOV and MARV pseudovirions, respectively, while 7 showed an approximately four-fold lesser activity against each pseudovirion. It should be noted that 6 and 7 are often classified as Pan-assay interference compounds (PAINS) in that they give false-positive results in a wide range of biological screening assays. The mechanism by which these compounds (6 and 7) block viral entry is not clear; however, it was suggested that they act at a similar post-binding step in the endosome as the cathepsin B inhibitor CA074, or as the entry inhibitor benztropine that binds to the EBOV-GP and interferes with GP-mediated fusion in the endosome.98
Two triterpenoid derivatives (8 and 9), derived from the naturally occurring oleanane-type triterpene echinocystic acid, were found to inhibit EBOV-host fusion.99 The IC50 values for 8 and 9 against the EBOV pseudotyped viruses were 59.2 nM and 467.3 nM, respectively, as evaluated in A549 and 293T cells. Heptad repeat-2 (HR2), a prevalent heptad repeat sequence comprising an alpha-helical coil in the GP, was identified as a site accessible to these triterpenoid analogues, and results in antagonizing EBOV-cell fusion. This results from interacting with the hydrophobic helix and blocking of the HR1-HR2 interaction critical to common trimer-of-hairpins formation. In addition, compounds 8 and 9 were able to inhibit the infection of MARV using a Marburg pseudo-particle entry assay with IC50 values of 2.29 μM and 5.52 μM, respectively.
Kononova et al. reported that an N-heterocyclic borneol derivative exhibited antiviral activity via inhibition of MARV-GP-dependent virus entry.100 Borneol is a bicyclic monoterpenoid found in essential oils of numerous medicinal plants. An N-heterocyclic bornyl ester 10 containing a methylpiperidine moiety showed an IC50 value of 4 μM using a MARV GP-mediated VSIV pseudotype system.
The natural product cyanovirin-N (11) is an 11-kDa protein that was isolated from cultures of the cyanobacterium Nostoc ellipsosporum.101 It has been reported that 11 inhibits HIV infection by binding to the surface envelope glycoprotein (gp120) through an interaction between 11 and high-mannose oligosaccharides on gp120. In 2003, Barrientos et al. reported that 11 also binds with high specificity to the EBOV GP and shows antiviral activity in vitro with an EC50 value of 100 nM.102 Similar to its inhibitory mechanism of HIV infection, oligosaccharide-mediated 11–GP interaction plays an important role in the inhibition of EBOV infection.
Proteases
Although there are only one to three proteases in each of the virus families we discuss here, they are absolutely essential for replication. Importantly, after initial translation of the viral RNA into large polyproteins, these proteases, from within the polyprotein, fold into active form and cleave the polyprotein into its individual components.16 These cleaved proteins in turn form the replicase complex that allows the virus to reproduce. Inhibition of these proteases has proven to be an effective way to mitigate replication and spread of the viruses. Because they are so few and so essential, a large amount of effort has gone into drug discovery efforts to screen and generate new protease inhibitors (Figure 6). In this section we cover recent reports of viral protease inhibitor discovery, and outline suggestions for future success in this area. Interestingly, the filoviruses do not possess their own proteases and rely completely on the host proteases for replication.
Figure 6.
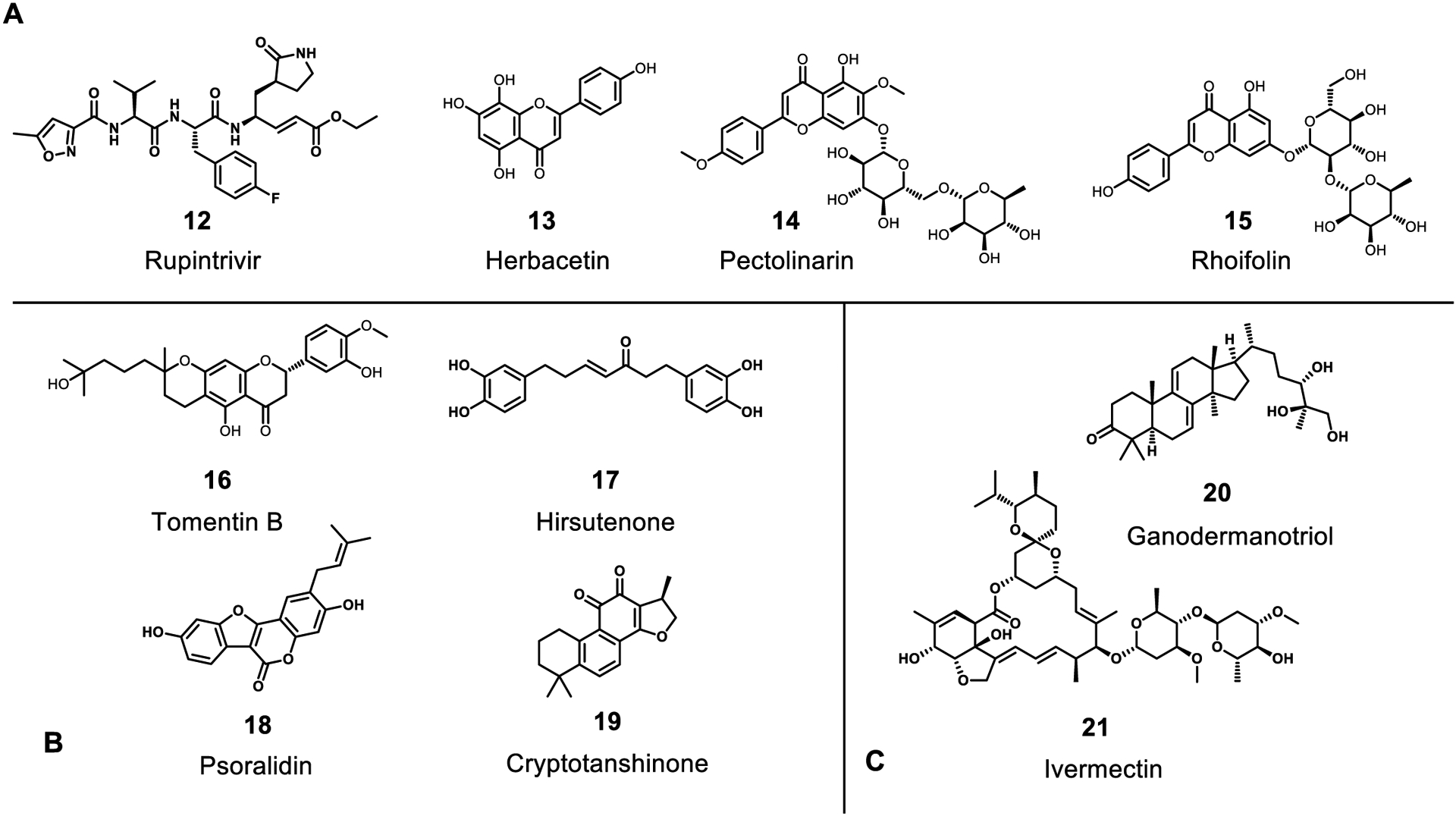
Inhibitors of viral proteases 3CLpro (A), PLpro (B), or NS3 (C). The following are natural products: herbacetin, pectolinarin, rhoifolin, tomentin B, hirsutenone, cryptotanshinone, psoralidin, ganodermanotriol, ivermectin and natural product derivatives: Rupintrivir.
Coronaviruses, with the exception of SARS-CoV-1/2, possess 3 proteases including 2 papain-like proteases and a chymotrypsin-like protease (3CLpro or Mpro); this latter protease does not have a known human homolog. SARS-CoV-1/2 lack one of the papain-like proteases, although this does not appear to have any impact on its ability to replicate and is likely redundant in other coronaviruses. These proteases are responsible for viral protein maturation after translation and have been at the center of drug discovery efforts against coronaviruses. That they are each essential for viral replication makes them especially attractive for targeting with small molecules. A large body of work exists in the literature of synthetic compounds targeting these proteases and has been reviewed previously.36,37,103 Because of their inherent peptidase activity, much effort has been put toward designing peptidomimetic inhibitors of these proteases. The main protease sequence is quite conserved across the Coronaviridae family and beyond, and inhibitors designed for 3CLpro have found use against other viruses as well. Extensive structure-activity relationships have been established for this enzyme and several crystal structures have been reported with bound inhibitors (PDB: 1UK4, 4YOG, 6Y2F, & others). One of the most important features of these inhibitors is the absolute requirement for a Gln or Gln-like residue at P1 followed by a generally hydrophobic side chain at P2; the latter pocket has been shown to be quite flexible. Interestingly, this specificity is not seen in any human enzyme, thus making the 3CLpro a prime target for peptidomimetic inhibition without competing off-target effects. A number of compounds with micromolar to nanomolar in vitro activity are depicted in Figure 6, most notably the approved drug rupintrivir (12) that was developed earlier to target the rhinovirus 3C protease. Some natural products, mainly flavonoids, have been reported to have mild inhibitory activity against 3CLpro as well including herbacetin (13), pectolinarin (14), and rhoifolin (15) with IC50 values of 33, 38, and 27 μm respectively.104 Interestingly, there have been very few efforts to screen natural products against this promising target.105 However, there have been several screening studies that have identified natural product inhibitors of Coronaviridae propagation without identifying a target; some of these may target the 3CLpro protease, and we will cover these in a later section.
The papain-like protease cleaves the viral polyprotein at fewer sites than the main protease, though inhibition is still effective at preventing replication. As a whole, this protease is less sought after as a drug target due to closer homology to human enzymes that may lead to off-target effects. As a result, there has been little development of peptidomimetic molecules designed against this protease. In contrast, there have been a number of reports of natural products inhibiting its activity including tomentin B at 6.1 μm106 (16), hirsutenone at 4.1 μm107 (17), tanshinones from 14.4–226.7 μm108 (18), psoralidin at 4.2 μm109 (19), and others depicted in Figure 6.110 Many of these phytochemicals were identified from extract screening, and like the 3CLpro, there has not been a large scale effort to explore a wider diversity of natural product scaffolds against it. With most compounds reported eliciting low micromolar activity and inherently nonspecific nature of planar, aromatic phytochemicals, there remains much to be desired. Nevertheless, these studies may provide a good starting point for a medicinal chemistry campaign.
The Flaviviridae genome is smaller than the Coronaviridae and only contains one orf that encodes for a protease, the NS3 orf (Figure 4B). NS3 belongs to the S7 serine protease family and requires NS2b as a cofactor for full activity.111 The NS2B-NS3 protease was virtually screened and triterpenoids from Ganoderma lucidum were suggested to be active. When tested in an in vitro Dengue virus inhibition assay, ganodermanontriol (20) (Figure 6) was found to inhibit the virus by 25% at 25 μM.112 The NS2B-NS3 complex is crucial for cleavage of the polypeptide as well as providing helicase activity during replication. Ivermectin (21) (Figure 6), isolated from Streptomyces avermitilis, is a well-known anti-parasitic drug. By molecular modeling it was determined that it could also bind effectively to the helicase portion of NS3 where the single stranded RNA is bound. Compound 20 also inhibits Dengue helicase (IC50 = 500 nM) using a FRET-based helicase assay, and completely inhibits virus propagation at 25 μM. NS2B-NS3 is an important target and continued investigation and identification of inhibitors for the NS2B-NS3 complex is warranted.
Replicase / Transcriptase Complex Proteins
The viral replicase complex consists of several key proteins including the RdRp and helicase that are solely responsible for generating new genomic as well as sub-genomic viral RNAs; these in turn are responsible for the production of structural proteins which assemble into new virions. Several critical features exist in this assortment of proteins, especially the RdRp, that can be targeted with small molecules to disrupt replication, and considerable effort has been expended to discover inhibitors of RdRp activity. Approved drugs such as favipiravir (22), ribavirin (23), and remdesivir (1) were all developed to target this polymerase, and its highly conserved nature across viral families has made it a promising target for drug development. In this section we discuss the various NP-inspired RdRp inhibitors that have been discovered to date (Figure 7).
In the Coronaviridae, the majority of the known effective inhibitors of RdRp are derived from its natural nucleotide substrates. These NP-inspired RdRp inhibitors include favipiravir (22), remdesivir (1), ribavirin (23), galdesivir (24), and β-d-N4-hydroxycytidine (25).36,113 While these nucleotide analogs were developed as inhibitors of RdRp activity in other viruses, they also have activity to these more newly emergent coronaviruses. Coronaviridae helicase NSP13 is also instrumental for viral replication, and two flavonoid natural products, myricetin (26) and scutellarein (27), have shown inhibitory activity with IC50 values of 2.71 μM and 0.86 μM, respectively (Figure 8).114
Figure 8.
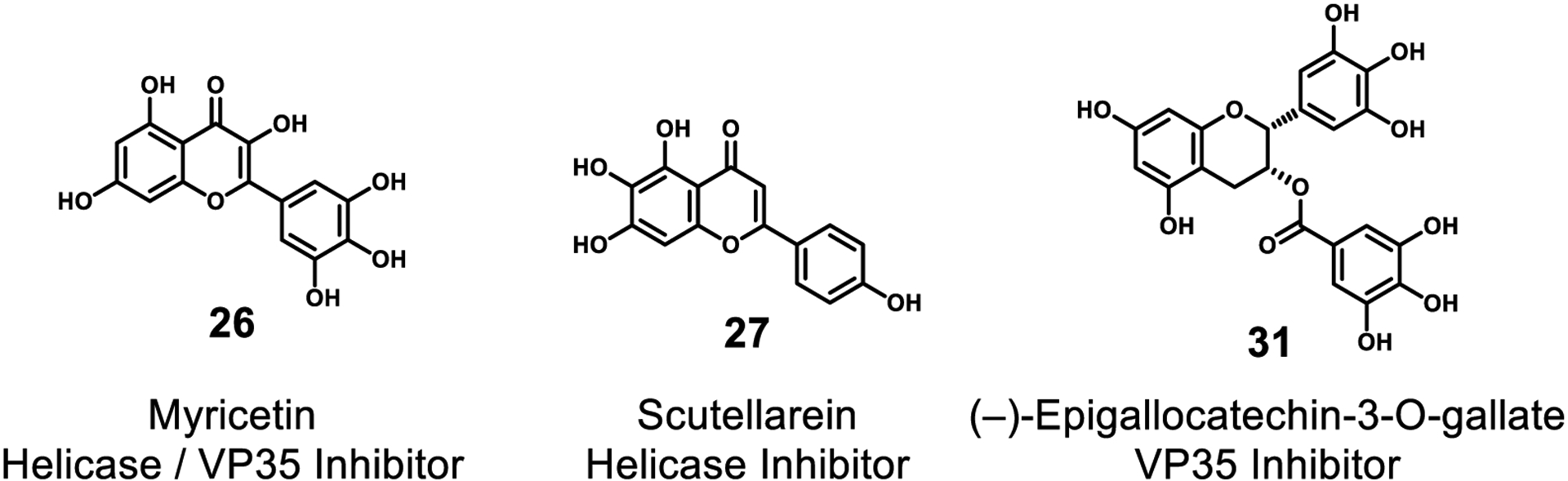
Inhibitors of viral helicase. All of these are natural products.
In the Flaviviridae, the NS2b-NS3 complex confers helicase activity as well as protease activity; the NS5 protein has been designated as the RdRp. NS5 is indirectly inhibited by mycophenolic acid (MPA) (28)(Figure 7), a natural product originally isolated from Penicillium glaucum in 1896. MPA as well as 23 inhibit inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase, and in so doing limit the amount of guanosine available to the RNA polymerase for RNA synthesis.115 Several synthetic compounds have been designed as direct inhibitors of NS5.116 The NS4 orf produces two full-length membrane proteins, NS4A and NS4B. They are linked by a 23-residue C-terminal region of NS4A, and the full length NS4 is cleaved by the NS2B-NS3 protease into NS4A and 2K-NS4B. The 2k fragment is a signal peptide that traffics NS4B to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). NS4A also inserts into the ER membrane and is quite hydrophobic due to its eight transmembrane regions. NS4A stabilizes the membrane-associated replication machinery.51 Reddey et al. have identified several possible inhibitors to both NS4A and NS4B.51
Methyltransferase (MTase) is an important enzyme for replication of Coronaviridae and Flaviviridae and is crucial for their RNA cap formation. The natural product sinefungin (29) was first isolated as an antibiotic from a strain of Streptomyces griseolus in 1973.117 This compound has a potent interaction with the MTases of SARS-CoV-2118, ZIKV119, and DENV (Figure 7)120.
Natural products have inspired the discovery of additional L protein (e.g. RNA-dependent RNA polymerase; see Table 4, Figure 4) inhibitors. Compound 22 mimics the structure of nucleic acids and has a broad-spectrum activity against a wide variety of both negative-strand and positive-strand RNA viruses. It is first converted to its phosphoribosyl derivative and subsequently to the triphosphate before it inhibits the RNA polymerase, principally through direct competition with GTP.121 Oestereich et al. reported that 22 suppressed replication of EBOV in cell cultures with IC50 and IC90 values of 67 μM and 110 μM, respectively.122 Remdesivir (1), a prodrug, is also converted to its triphosphate metabolite and interferes with viral RdRp activity. In cell-based assays, it has a potency against a broad range of filoviruses including MARV and several variants of EBOV.123 Compound 1 also inhibited EBOV replication in multiple relevant human cell types with EC50 values of 0.06–0.14 μM. Another synthetic adenosine analogue, BCX4430 (30), inhibits RNA polymerase function by inducing RNA chain termination which occurs two bases after the incorporation of 30 monophosphate, perhaps as a result of inhibitory stereochemical distortions of the nascent RNA chain.124 Moderate antiviral activity of 30 has been reported against members of the Filoviridae; EC50 values were 11.8 μM for EBOV, 3.4 μM for SUDV, and 4.4–6.7 μM for MARV, respectively. Weak activity against positive-sense RNA viruses has also been reported: DENV-2 (EC50 32.8 μM), SARS-CoV (EC50 57.7 μM), and MERS-CoV (EC50 68.4 μM).
Daino et al. have tested the extract from Limonium morisianum (Plumbaginaceae) in a fluorescence-based rVP35-dsRNA interaction assay.125 The extract was shown to inhibit VP35-dsRNA binding at a concentration of 19 μg/mL, and two flavonoid compounds, myricetin (26) and (–)-epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate (31), were identified as the active inhibitors (IC50 values were 2.7 μM and 43.5 μM respectively). In addition, molecular docking studies revealed that 26 binds to the highly conserved region of the VP35 RNA binding pocket. However, compounds 26 and 31 may also be considered PAINS due to their wide spread biological activity.
Accessory Proteins
Accessory proteins are typically not considered essential for replication but play other roles in the viral life cycle such as immune evasion, targeting degradation of host RNAs, and inducing apoptosis. Some viruses have few accessory proteins whereas others have many, such as the coronaviruses. Several have been characterized and their biochemical function is known; for others they remain to be investigated. In this section we cover a collection of known accessory proteins and their functions and discuss opportunities for drug discovery.
Two notable accessory proteins from the Coronaviridae include NSP1126 and orf8b127, and a comprehensive review of the full list of accessory proteins and their role in pathogenesis was reported in 2012.128 Both of these proteins were found to take part in immune evasion by two distinct mechanisms. NSP1 was reported to promote host mRNA degradation and thus suppress host gene expression, including proteins involved in the host innate immune system. Alternatively, orf8b has been observed to trigger intracellular stress pathways via formation of insoluble aggregates that induce ER stress, lysosomal damage, and subsequent activation of transcription factor EB involved in lysosomal biogenesis, leading to cell death. However, there have been no reports of inhibitors targeting these proteins to date, and clarification of the mechanisms by which these viruses evade immune detection is still needed.
The Flaviviridae NS1 protein appears to be an anti-host factor; however, it has many attributed functions and mechanisms. As indicated above, the Zika virus NS1 has been shown to stabilize metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9). A higher concentration of MMP9 aids viral entry into cells by breaking down tight intercellular junctions and cellular structural proteins.48 However, in the West Nile virus it appears that NS1 downregulates interferon and in Dengue it breaks down the glycocalyx. Another function appears to be as a GAG-binding protein. Regardless of mechanism, NS1 inhibitors could be promising candidates for development. An effort to inhibit NS1 binding was achieved with a synthetic heparan sulfate mimetic 8. This mimic blocked NS1 binding completely and decreased viremia in mice.96 NS1 is also indirectly inhibited by the bicyclic alkaloid castanospermine (32) as well as its prodrug ester celgosivir (33) (Figure 9). These compounds interfere with the glycosylation of NS1 and creates misfolding of the protein.129,130
Figure 9.
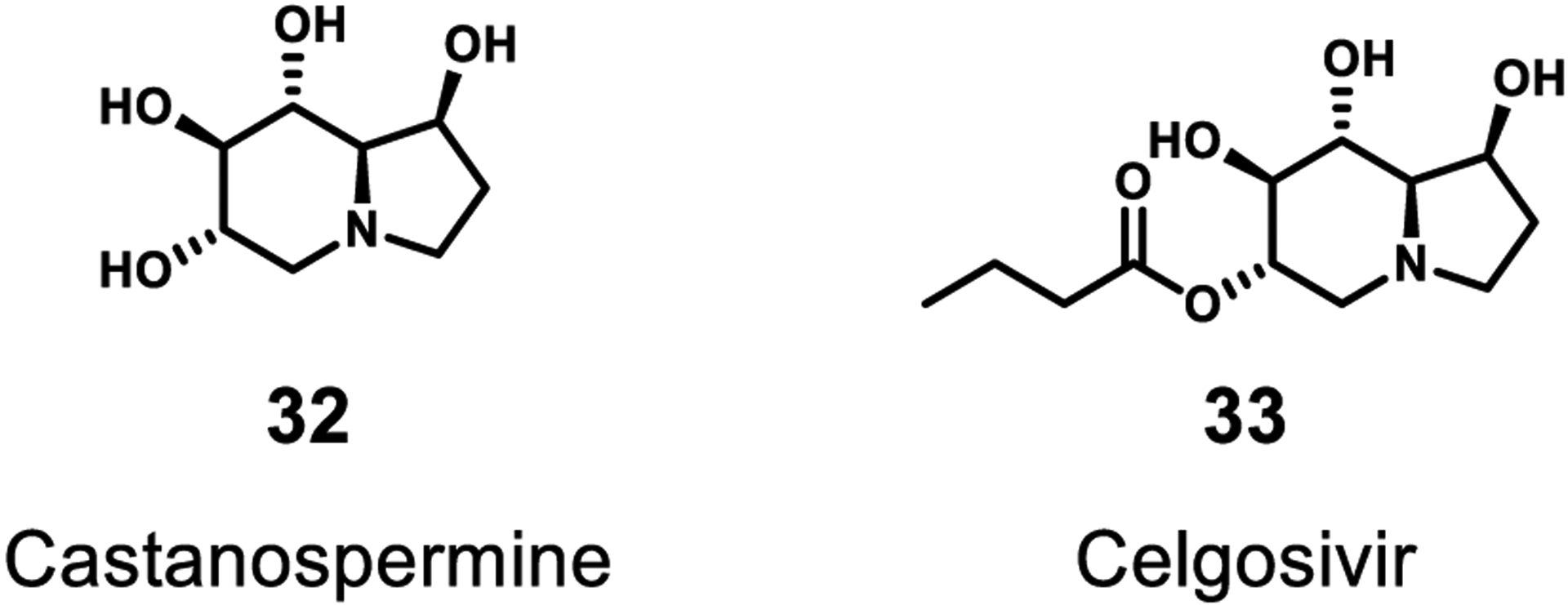
Inhibitors of selected accessory proteins. Celgosivir is a derivative of the natural product castanospermine.
B. Host Proteins
Viruses often utilize host proteins, such as cathepsin L (CatL) or TMPRSS2/4 in the case of SARS-CoV-1/2, for cellular recognition, entry, and translation. Thus, these host proteins can also be targeted to hinder viral infections. In this section we cover the host proteins of interest in antiviral drug discovery, their functions, and efforts to find suitable inhibitors among natural products and their derivatives. It should be noted that the compounds discussed in this section are preclinical agents, and toxicity and other side effects will need to be assessed when targeting host proteins.
Proteases
After receptor binding, host proteases either at the cell surface or in endosomes are responsible for critical cleavage events that induce fusion of the viral capsid with the cell or endosome membrane, and the subsequent release of its genetic material into the cell cytoplasm. Across the three families of viruses in this review, it appears that only a few host proteases are implicated, none of which are completely essential for viability. There have been a number of drug discovery campaigns targeting these proteases in the context of other diseases, and more recently, a recognition that they may be viable antiviral drug targets as well. In this section, we will cover a number of inhibitors of host proteases that prevent viral entry by blocking processing of the spike glycoproteins and membrane fusion (Figure 10).
Figure 10.
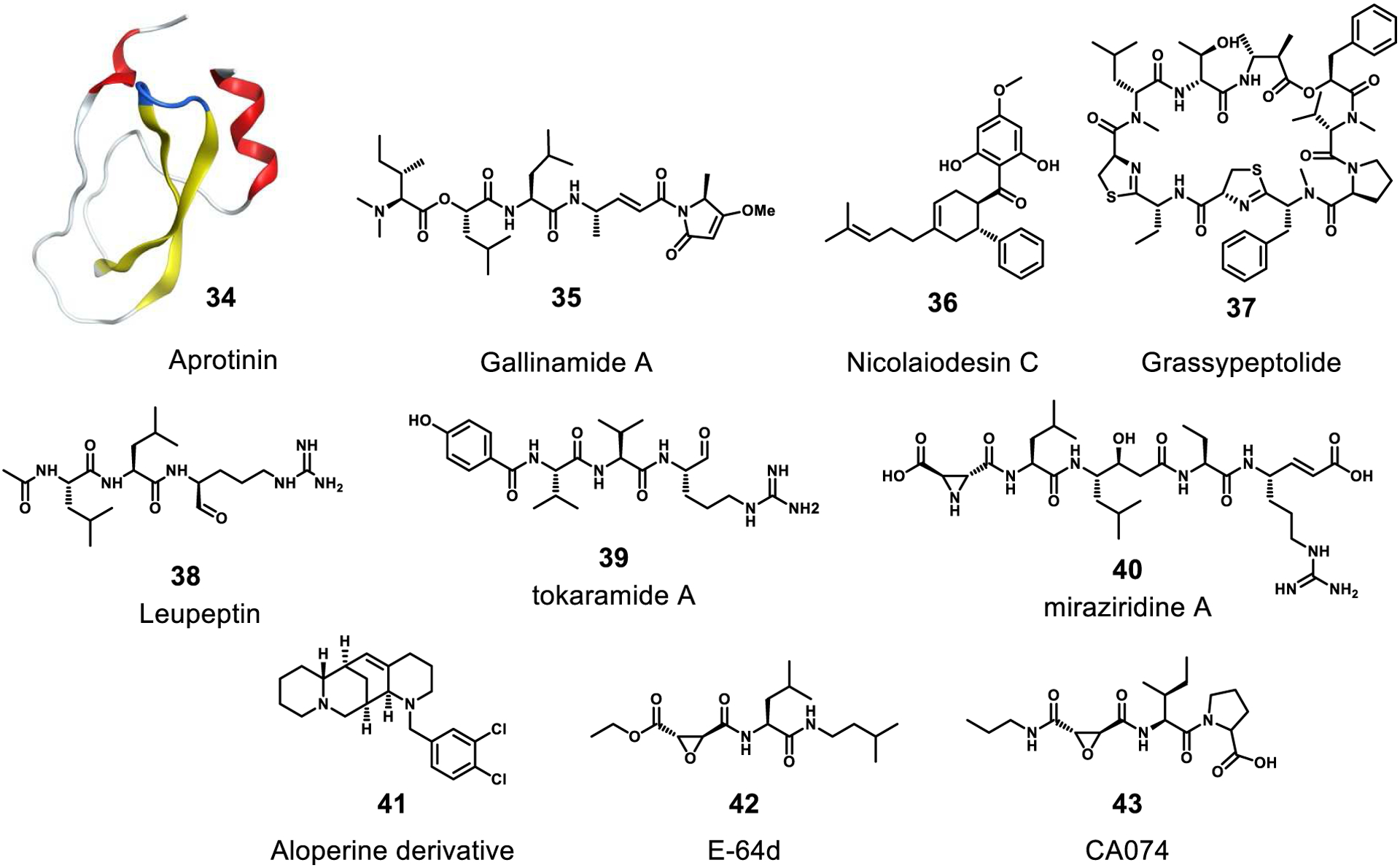
Inhibitors of host cysteine proteases cathepsin L/B or serine proteases TMPRSS2/4. The following are natural products: aprotinin, gallinamide A, nicolaiodesin C, grassypeptolide, leupeptin, tokoramide A, miraziridine A, E-64d and natural product derivatives: 41, CA074.
TMPRSS2 and TMPRSS4 are transmembrane serine proteases located on the surface of human cells. They have been shown to cleave the coronavirus extracellular spike protein S after the virus has bound to surface ACE2 receptors, and this allows viral fusion to the cell membrane. These proteases are essential for viral entry in several different tissues.24,28 Despite the essentiality of this process, there are very few known inhibitors, and only one is a natural product. Aprotinin (34), is a small protein that is marketed as a bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor; it has also shown inhibitory activity against TMPRSS2.131 In addition to these surface proteases, cathepsin L and B (CatL/B), promote membrane fusion of the virus via an endocytic pathway. Unlike TMPRSS2/4, there are a number of reviews describing the activity and role in human physiology and disease of CatL and B.132,133 Furthermore, a number of natural products have been reported with inhibitory activity against these important enzymes, such as gallinamide A (35), nicolaiodesin C (36), grassypeptolide (37), and leupeptin (38) against CatL. The wide variety of natural products effective and selective against these proteases raises hopes that useful antiviral therapeutics may emerge from continued investigation.
CatL was also reported to be involved in the entry of JEV into cells.134 It was shown that a CatL inhibitor could decrease shedding of the Flaviviridae anti-host factor protein NS1 with a subsequent decrease in endothelial permeability. It would be worthwhile to continue to explore cathepsin L inhibitors for use in treatment of dengue, JEV, and other Flaviviridae viruses.135
The mostly linear lipopeptide gallinamide A (35), isolated from a Schizothrix sp. cyanobacterium, selectively inhibited CatL with an IC50 value of 5.0 nM.136 It was also shown that 35 was remarkably selective for Cat L as it was only modestly active to CatB with an IC50 value of 11.7 μM. From a marine sponge Theonella aff. mirabilis, tokaramide A (39) and miraziridine A (40) were isolated. These selectively inhibited CatB with IC50 values of 29 ng/mL and 1.4 μg/mL, respectively.137–139 Zhang et al. reported that a new aloperine derivative (41) that exhibited activity against EBOV and MARV with EC50 values of 4.8 μM and 7.1 μM, respectively. Aloperine was reported as a component of the seeds and leaves of Sophora alopecuroides (Fabaceae). Aloperine was shown to selectively inhibit CatB but had no activity towards CatL.140 This remarkable selectivity of 41 for CatB over CatL was subsequently explained through a molecular docking analysis.
Chandran et al. measured the antiviral effects of the peptide derivatives E-64d (42) and CA074 (43) using EBOV. Vero cells were pretreated with 42 (300 μM) or 43 (80 μM) and exposed to EBOV. Yields of infectious EBOV progeny and expression of cell-associated GP1 were markedly reduced, suggesting that EBOV multiplication in Vero cells is sensitive to these inhibitors of endosomal cysteine proteases in general and of CatB in particular.75 Compound 42, also known as EST, is a synthetic analogue of E-64 that was first isolated from the extract of a solid media culture of Aspergillus japonicus.141,142 Additionally, 43, a new epoxysuccinyl peptide with a structure similar to 42, was designed as a specific inhibitor of CatB.143
Furin is a protease located in the trans golgi apparatus. It belongs to the subtilisin-like proprotein convertase family and it aids in cleaving precursor proteins into mature proteins. During viral infections, furin cleaves a precursor spike protein into mature spike S proteins.95 As discussed above for the Flaviviridae, furin is also responsible for cleavage of the the prM protein to the M protein, however, some prM-coated viral particles escape from the cell before furin cleavage. These immature virus particles are known to generate antibodies, and these antibodies are proposed to enhance the disease if an individual is infected with a different serotype of the dengue virus.144 Therefore, furin is not likely a good drug target as it may increase the severity of subsequent infection with dengue.
Others
There are a handful of other targets that show promise in additional areas of the viral life cycle and may be used in combination with direct inhibitors of viral proteases or RdRp. Here we discuss these targets and their potential for inhibition by natural products to hinder virus reproduction and distribution (Figure 11).
Figure 11.
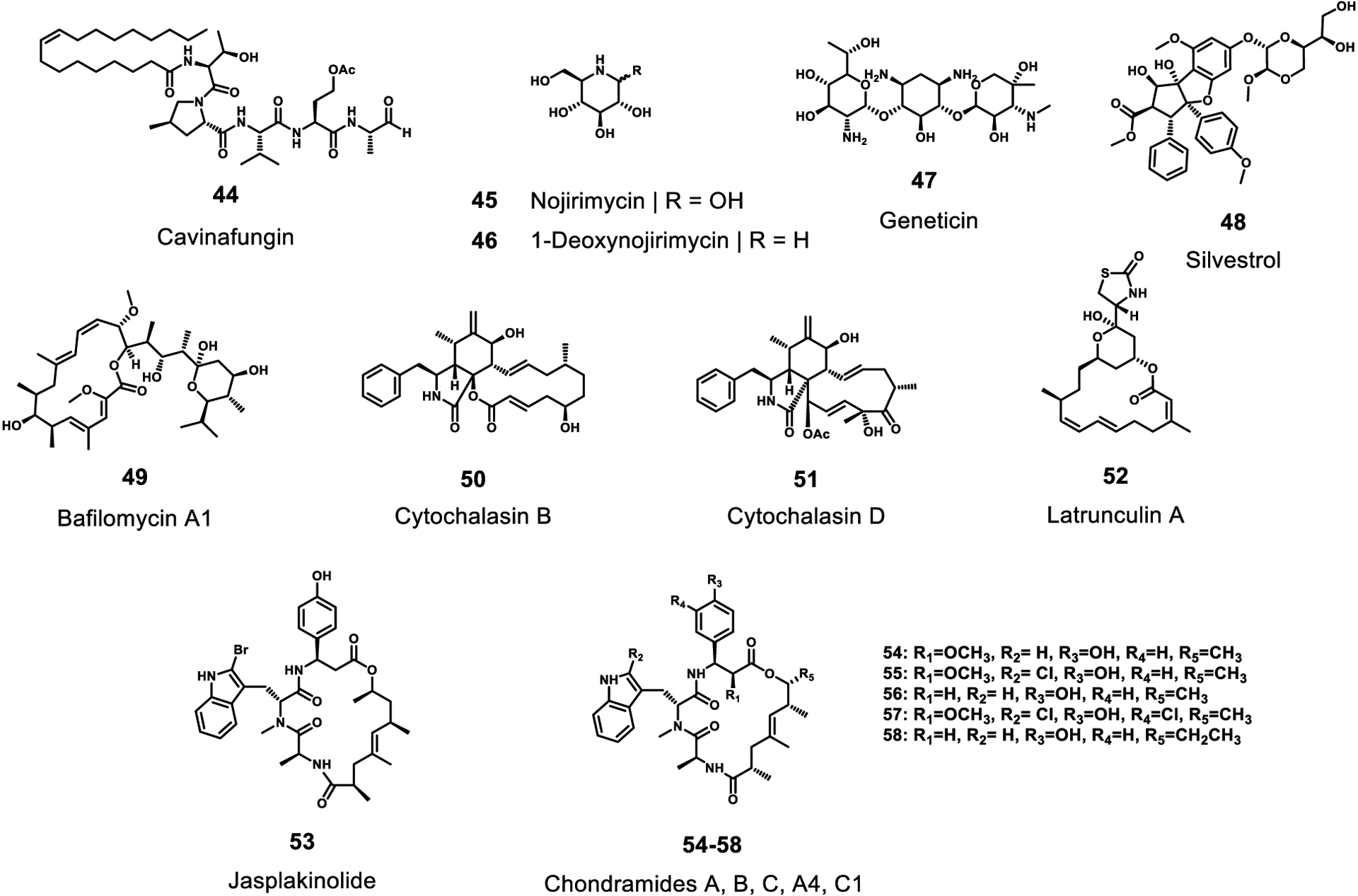
Inhibitors of other selected targets with activity to RNA viruses. All of these compounds are natural products.
Calmodulin (calcium-modulated protein) in normal cells senses calcium levels and regulates calcium flux into the cells. During Dengue infection the viral protein NS2A interacts with calmodulin. A synthetic calmodulin inhibitor was shown to inhibit virus production,52 suggesting that natural products that are calmodulin inhibitors could also be useful. In fact, plants and fungi have been a rich source of structurally diverse calmodulin inhibitors, and these should be further evaluated for their anti-Dengue effects.
The normal function of signalase/signal peptidase is to cleave signal peptides when they are trafficked to the endoplasmic reticulum.145 In Dengue, the host cell signalase is used to cleave the viral polyprotein between the prM, E, NS1, and NS4B proteins. In a phenotypic screen the fungal natural product cavinafungin (44) was shown to inhibit replication of all four serotypes of dengue virus, as well as Zika virus, with an IC50 in the low nanomolar range. Compound 44 was initially isolated in 2015 from the fungus Colispora cavincola, and subsequently, the antiviral target was identified as signalase by using a CRISPR/Cas9-based chemogenomic profiling where the subunits of the signal peptidase were identified.146
Alpha-glucosidase, located in the ER, adds N-linked sugars to proteins. Inhibitors that block this addition have been shown to decrease the production of several ER-budding viruses, such as Dengue and Japanese encephalitis virus.147 In particular, these inhibitors affect the glycosylation of the NS1 and the E proteins. Oral administration of glucose mimics such as nojirimycin (45) and its derivative 1-deoxynojirimycin (46) to mice were effective at inhibiting viral replication.147 Compound 46 (duvoglustat or moranolin) was first reported in mulberry leaves.148 Medicinal chemistry efforts starting with derivative CM-10–18 of deoxynojirimycin resulted in potent inhibitors of alpha-glucosidase. Moreover, they were shown to inhibit bovine viral diarrhea virus (a proxy for dengue virus) at high nanomolar or low micromolar ranges while not showing any overt cytotoxicity.149 Furthermore, miglitol (a derivative of 1-deoxynojirimycin) and acarbose, approved type-II diabetes drugs that target alpha-glucosidase, have also shown antiviral properties to Filoviruses and Flaviviruses.150,151
The 80S ribosome is a very general target that, when inhibited, blocks all translation including production of viral polyproteins. Geneticin (47), an analog of neomycin, was tested for its ability to inhibit Dengue virus, and found to inhibit the cytopathic effect resulting from Dengue virus infection with an EC50 of 3.0 μg/mL in BHK cells. Curiously, the closely related analogs kanamycin, gentamycin and guanidylated geneticin showed no protective effect in this cytopathic assay.152
Silvestrol (48), isolated from the fruits and twigs of Aglaia silvestris (Meliaceae)153, is a potent inhibitor of the ATP-dependent DEAD-box RNA helicase eIF4A. This helicase activity appears to be essential for 5’-cap-dependent translation of mRNAs with highly structured 5’-UTRs to enable binding of the translation preinitiation complex in eukaryotes.154 Biedenkopf et al. reported inhibition of viral propagation by treatment with 10 nM of silvestrol.
It has been suggested that EBOV GP-mediated entry and fusion requires acidification within the endosome. This acidification is produced by vacuolar ATPases that create a proton gradient. Yonezawa et al. pretreated target cells with the vacuolar ATPase inhibitor bafilomycin A1 (49), a macrolide antibiotic isolated from mycelia of Streptomyces griseus.155 They evaluated the effects of incubation of 49 in a virion pseudotyped with EBOV GP.156 As a result, treatment with compound 49 at 5–500 nM nearly completely blocked detection of viral entry and fusion mediated by EBOV GP.
Yonezawa et al. also reported that compounds that impair microfilament function inhibit EBOV GP-mediated entry and fusion. They demonstrated that cytochalasin B (50) and D (51), obtained from the molds Helminthosporium dematiodeum and Metarrhizium anisopliae,157 latrunculin A (52) from the marine sponge Latrunculia magnifica,158 and jasplakinolide (53) from the marine sponge Jaspis johnstoni,159 were all active inhibitors of EBOV cell entry. They suggested that microtubules and actin filaments play key roles in these antiviral events. Similarly, Beck et al. reported that the chondramides (54–58), antifungal and cytostatic depsipeptides, inhibited EBOV GP-mediated cell entry with IC50 values of 24–42 nM. The chondramides are known to exert modulatory effects on the actin cytoskeleton.160 Chondramides A (54), B (55), C (56), A4 (57), and propionyl chondramide C1 (58) were isolated from two myxobacterial strains, Chondromyces crocatus and Chondromyces sp. MSr9030.161,162
C. Unknown Targets
During the course of drug discovery there have been a number of reports that do not specify a target or investigate a mechanism by which a compound acts. Although the compounds reported in this section were shown to have antiviral activity, the nature of their effect is unknown and requires more investigation (Figure 12). A small screening effort revealed several disparate micromolar inhibitors of SARS-CoV infection including existing natural product drugs reserpine (59) (an indole alkaloid from Indian snakeroot Rauvolfia serpentina), aescin (60) (saponins from the horse chestnut Aesculus hippocastanum), and valinomycin (61) (a cyclic depsipeptide from Streptomyces spp.).105 In a recent study, the FDA-approved cyclic alkaloid cepharanthine (62), and a veterinary product related to 21, selamectin (63), were found to completely inhibit the cytopathic effects of betacoronaviruses in cell culture at 10 μM, however, no target nor mechanism was proposed.163 The alkaloid lycorine (64) was also found to inhibit viral replication with an EC50 15.7 nM.164 Eugenol (65), a ubiquitous phenolic compound in plants, was found to have activity against EBOV with an EC50 value of 1.3 μM.165 Further exploration of the targets and mechanisms of these reported natural product inhibitors would be invaluable for future antiviral drug development.
Figure 12.
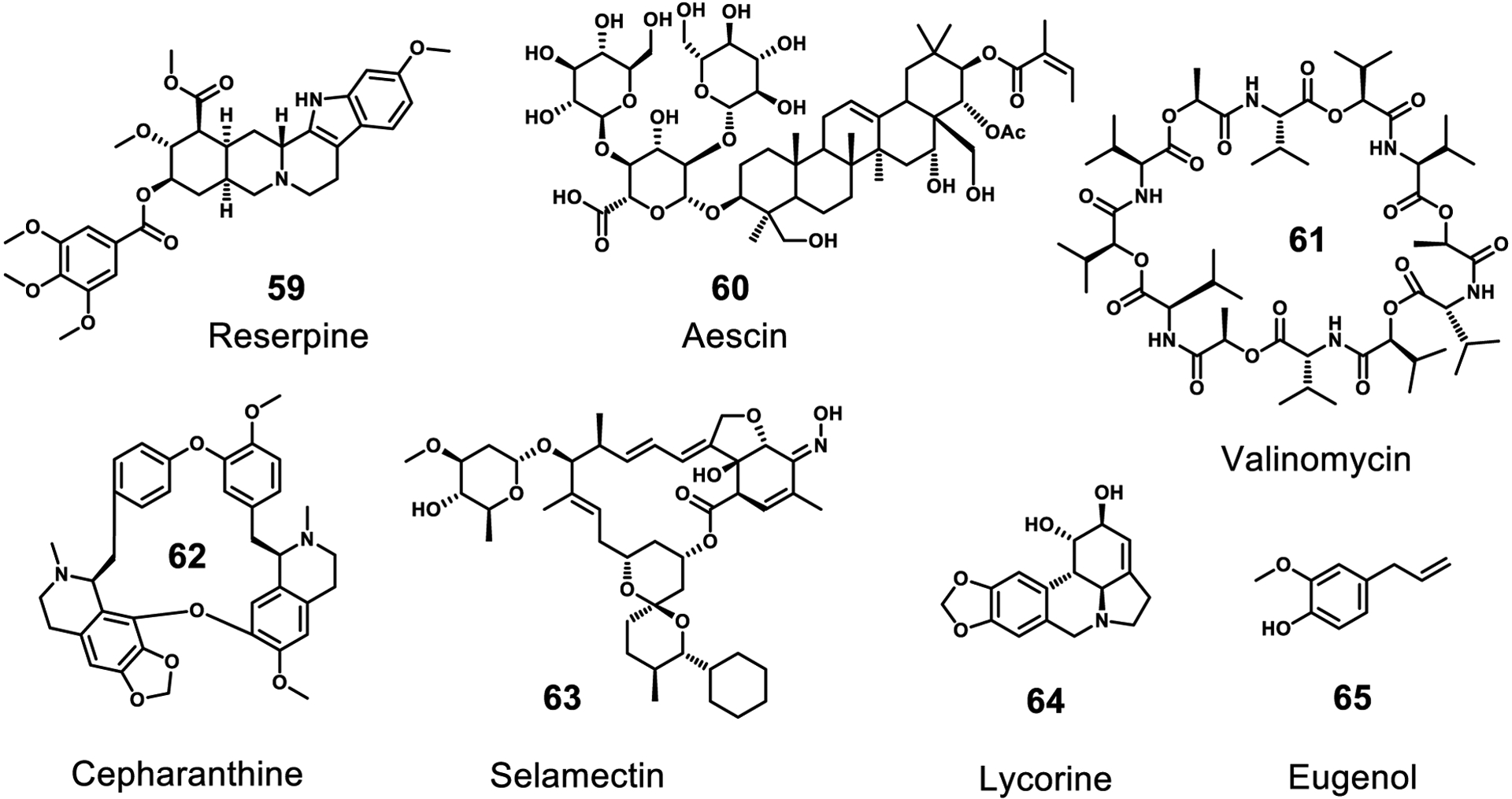
Inhibitors with demonstrated antiviral activity without a known target or mechanism of action. All of these compounds are natural products.
Summary and Outlook
Natural products have been underexplored for their potentially useful antiviral activity, especially to RNA viruses causing endemic and pandemic infections. Nevertheless, several useful compounds based on natural products have emerged from these efforts, most notably in the purine-based inhibitors of the viral replicase complex component, the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), and protease inhibitors, including those that target proteases that are virally encoded and those that are host derived. Another broad class of natural product with anti-RNA virus activity include those with polyphenolic structures; however, these are generally considered to be PAINS and non-selective to these viral targets. From a broad perspective, this review covers anti-RNA virus natural products that illustrate a large number of different molecular architectures, suggesting a variety of enzymatic protein targets and a range of inhibitory mechanisms. This foreshadows an even richer potential for the conribution that natural products can make to our antiviral pharmacopeia as more thorough and broader screening occurs in the future.
It is clear that human populations will continue to see more endemics and pandemics in the future, be they caused by viruses, bacteria or other infectious agents. Thus, it is simply common sense that we should put into place the infrastructure necessary to more rapidly develop treatments when future pandemics occur. One such recommendation is to create and maintain international compound libraries with substances that possess antiviral, antibacterial, or antiparasitic activity. These could be rapidly deployed into relevant biological screening systems as new pandemics arise. This resource could be internationally housed, and a logical entity might be the World Health Organization. But to accomplish this, new types of international treaties and agreements need to be drawn up in advance to cover the evolving concepts of intellectual property and inherent national ownership of genetic resources. Similarly, new international legislation needs to be written in advance of the next pandemic so as to cover the rights and responsibilities of international scientific teams so that they may form quickly and with a transparent sharing of data and results. Because the private sector is likely the segment of society that will bring new therapeutics to people, laws and policies that protect economic interests while simultaneously promoting openness and collaboration need to be put in place. Ultimately, the discovery and development of new pharmaceuticals from nature provides a justification for biodiversity preservation that is very understandable by the lay public, and thus, is ultimately good for human society, the planet, and the valuation of our rich biodiversity.
Acknowledgments
We thank J. Matthews for creating figures 1-3, and R. Rex and NIH R01 NS109075 for generous financial assistance used in the construction of this manuscript. We further dedicate this review to R. Rex, a believer in the multidimensional value of scientific research.
Footnotes
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
References
- (1).Shally-Jensen Michael, ed. (2010). “Influenza”. Encyclopedia of Contemporary American Social Issues 2. ABC-CLIO. p. 1510. ISBN 0–31339205-6. [Google Scholar]
- (2).Hilleman MR Realities and Enigmas of Human Viral Influenza: Pathogenesis, Epidemiology and Control. Vaccine 2002, 20 (25), 3068–3087. 10.1016/S0264-410X(02)00254-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (3).Monto AS Influenza: Quantifying Morbidity and Mortality. Am. J. Med 1987, 82 (6, Supplement 1), 20–25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (4).Newman DJ; Cragg GM Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs over the Nearly Four Decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J. Nat. Prod 2020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (5).Lovering F; Bikker J; Humblet C Escape from Flatland: Increasing Saturation as an Approach to Improving Clinical Success. J. Med. Chem 2009, 52 (21), 6752–6756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (6).Lovering F Escape from Flatland 2: Complexity and Promiscuity. MedChemComm 2013, 4 (3), 515–519. [Google Scholar]
- (7).Barre-Sinoussi F; Chermann JC; Rey F; Nugeyre MT; Chamaret S; Gruest J; Dauguet C; Axler-Blin C; Vezinet-Brun F; Rouzioux C; Rozenbaum W; Montagnier L Isolation of a T-Lymphotropic Retrovirus from a Patient at Risk for Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS). Science 1983, 220 (4599), 868–871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (8).Popovic M; Sarngadharan MG; Read E; Gallo RC Detection, Isolation, and Continuous Production of Cytopathic Retroviruses (HTLV-III) from Patients with AIDS and Pre-AIDS. Science 1984, 224 (4648), 497–500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (9).Gallo RC; Salahuddin SZ; Popovic M; Shearer GM; Kaplan M; Haynes BF; Palker TJ; Redfield R; Oleske J; Safai B; Et A Frequent Detection and Isolation of Cytopathic Retroviruses (HTLV-III) from Patients with AIDS and at Risk for AIDS. Science 1984, 224 (4648), 500–503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (10).Schupbach J; Popovic M; Gilden RV; Gonda MA; Sarngadharan MG; Gallo RC Serological Analysis of a Subgroup of Human T-Lymphotropic Retroviruses (HTLV-III) Associated with AIDS. Science 1984, 224 (4648), 503–505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (11).Sarngadharan MG; Popovic M; Bruch L; Schupbach J; Gallo RC Antibodies Reactive with Human T-Lymphotropic Retroviruses (HTLV-III) in the Serum of Patients with AIDS. Science 1984, 224 (4648), 506–508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (12). https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/fact-sheet .
- (13).Blair HA Dolutegravir/Rilpivirine: A Review in HIV-1 Infection. Drugs 2018, 78 (16), 1741–1750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (14).Zuckerman JN; Powell L; Lequin RM; Zuckerman AJ Determination of Hepatitis A Antibody Response to Vaccination by an Enzyme Immunoassay. J. Virol. Methods 1996, 56 (1), 27–31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (15).Deutsch L; Houri I; Ben-Ari Z; Shlomai A; Veitsman E; Cohen-Ezra O; Issachar A; Mor O; Gozlan Y; Bruck R; Menachem Y; Zelber-Sagi S; Katchman H; Shibolet O Ombitasvir/Paritaprevir/Ritonavir & Dasabuvir ± Ribavirin Following Protease Inhibitors Failure - a Prospective Multi-Centre Trial. BMC Infect. Dis 2020, 20 (1), 264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (16).Pol S; Lagaye S The Remarkable History of the Hepatitis C Virus. Genes Immun. 2019, 20 (5), 436–446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (17).Perlman S Another Decade, Another Coronavirus. N. Engl. J. Med 2020, 382 (8), 760–762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (18).Dong E; Du H; Gardner L An Interactive Web-Based Dashboard to Track COVID-19 in Real Time. Lancet Infect. Dis 2020, 20 (5), 533–534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (19).Gorbalenya AE; Baker SC; Baric RS; de Groot RJ; Drosten C; Gulyaeva AA; Haagmans BL; Lauber C; Leontovich AM; Neuman BW; Penzar D; Perlman S; Poon LLM; Samborskiy DV; Sidorov IA; Sola I; Ziebuhr J; Coronaviridae Study Group of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. The Species Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Related Coronavirus: Classifying 2019-NCoV and Naming It SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Microbiol 2020, 5 (4), 536–544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (20).Weiss SR; Leibowitz JL Chapter 4 - Coronavirus Pathogenesis. In Advances in Virus Research; Maramorosch K, Shatkin AJ, Murphy FA, Eds.; Academic Press, 2011; Vol. 81, pp 85–164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (21).Zhu N; Zhang D; Wang W; Li X; Yang B; Song J; Zhao X; Huang B; Shi W; Lu R; Niu P; Zhan F; Ma X; Wang D; Xu W; Wu G; Gao GF; Tan W A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med 2020, 382 (8), 727–733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (22).Muramatsu T; Takemoto C; Kim Y-T; Wang H; Nishii W; Terada T; Shirouzu M; Yokoyama S SARS-CoV 3CL Protease Cleaves Its C-Terminal Autoprocessing Site by Novel Subsite Cooperativity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci 2016, 113 (46), 12997–13002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (23).Zhang T; Wu Q; Zhang Z Probable Pangolin Origin of SARS-CoV-2 Associated with the COVID-19 Outbreak. Curr. Biol 2020, 30 (7), 1346–1351.e2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (24).Hoffmann M; Kleine-Weber H; Schroeder S; Krüger N; Herrler T; Erichsen S; Schiergens TS; Herrler G; Wu N-H; Nitsche A; Müller MA; Drosten C; Pöhlmann S SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181 (2), 271–280.e8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (25).Yan R; Zhang Y; Li Y; Xia L; Guo Y; Zhou Q Structural Basis for the Recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by Full-Length Human ACE2. Science 2020, 367 (6485), 1444–1448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (26).Lu G; Hu Y; Wang Q; Qi J; Gao F; Li Y; Zhang Y; Zhang W; Yuan Y; Bao J; Zhang B; Shi Y; Yan J; Gao GF Molecular Basis of Binding between Novel Human Coronavirus MERS-CoV and Its Receptor CD26. Nature 2013, 500 (7461), 227–231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (27).Wrapp D; Wang N; Corbett KS; Goldsmith JA; Hsieh C-L; Abiona O; Graham BS; McLellan JS Cryo-EM Structure of the 2019-NCoV Spike in the Prefusion Conformation. Science 2020, 367 (6483), 1260–1263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (28).Zang R; Castro MFG; McCune BT; Zeng Q; Rothlauf PW; Sonnek NM; Liu Z; Brulois KF; Wang X; Greenberg HB; Diamond MS; Ciorba MA; Whelan SPJ; Ding S TMPRSS2 and TMPRSS4 Promote SARS-CoV-2 Infection of Human Small Intestinal Enterocytes. Sci. Immunol 2020, 5 (47). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (29).Simmons G; Gosalia DN; Rennekamp AJ; Reeves JD; Diamond SL; Bates P Inhibitors of Cathepsin L Prevent Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Entry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci 2005, 102 (33), 11876–11881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (30).Gierer S; Bertram S; Kaup F; Wrensch F; Heurich A; Krämer-Kühl A; Welsch K; Winkler M; Meyer B; Drosten C; Dittmer U; Hahn T. von; Simmons G; Hofmann H; Pöhlmann S The Spike Protein of the Emerging Betacoronavirus EMC Uses a Novel Coronavirus Receptor for Entry, Can Be Activated by TMPRSS2, and Is Targeted by Neutralizing Antibodies. J. Virol 2013, 87 (10), 5502–5511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (31).Yuan M; Wu NC; Zhu X; Lee C-CD; So RTY; Lv H; Mok CKP; Wilson IA A Highly Conserved Cryptic Epitope in the Receptor-Binding Domains of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV. Science 2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (32).Kawase M; Shirato K; Hoek L.van der; Taguchi F; Matsuyama S Simultaneous Treatment of Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells with Serine and Cysteine Protease Inhibitors Prevents Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Entry. J. Virol 2012, 86 (12), 6537–6545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (33).Fehr AR; Perlman S Coronaviruses: An Overview of Their Replication and Pathogenesis. In Coronaviruses: Methods and Protocols; Maier HJ, Bickerton E, Britton P, Eds.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, 2015; pp 1–23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (34).Yin W; Mao C; Luan X; Shen D-D; Shen Q; Su H; Wang X; Zhou F; Zhao W; Gao M; Chang S; Xie Y-C; Tian G; Jiang H-W; Tao S-C; Shen J; Jiang Y; Jiang H; Xu Y; Zhang S; Zhang Y; Xu HE Structural Basis for Inhibition of the RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase from SARS-CoV-2 by Remdesivir. Science 2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (35).Gordon CJ; Tchesnokov EP; Woolner E; Perry JK; Feng JY; Porter DP; Gotte M Remdesivir Is a Direct-Acting Antiviral That Inhibits RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase from Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 with High Potency. J. Biol. Chem 2020, jbc.RA120.013679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (36).Sanders JM; Monogue ML; Jodlowski TZ; Cutrell JB Pharmacologic Treatments for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review. JAMA 2020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (37).Pillaiyar T; Manickam M; Namasivayam V; Hayashi Y; Jung S-H An Overview of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome–Coronavirus (SARS-CoV) 3CL Protease Inhibitors: Peptidomimetics and Small Molecule Chemotherapy. J. Med. Chem 2016, 59 (14), 6595–6628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (38).Lee H; Lei H; Santarsiero BD; Gatuz JL; Cao S; Rice AJ; Patel K; Szypulinski MZ; Ojeda I; Ghosh AK; Johnson ME Inhibitor Recognition Specificity of MERS-CoV Papain-like Protease May Differ from That of SARS-CoV. ACS Chem. Biol 2015, 10 (6), 1456–1465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (39).Salles TS; da Encarnação Sá-Guimarães T; de Alvarenga ESL; Guimarães-Ribeiro V; de Meneses MDF; de Castro-Salles PF; dos Santos CR; do Amaral Melo AC; Soares MR; Ferreira DF; Moreira MF History, Epidemiology and Diagnostics of Dengue in the American and Brazilian Contexts: A Review. Parasit. Vectors 2018, 11 (1), 264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (40).Michelitsch A; Tews BA; Klaus C; Bestehorn-Willmann M; Dobler G; Beer M; Wernike K In Vivo Characterization of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus in Bank Voles (Myodes Glareolus). Viruses 2019, 11 (11), 1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (41).Aguas R; Dorigatti I; Coudeville L; Luxemburger C; Ferguson NM Cross-Serotype Interactions and Disease Outcome Prediction of Dengue Infections in Vietnam. Sci. Rep 2019, 9 (1), 9395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (42).Hadfield J; Brito AF; Swetnam DM; Vogels CBF; Tokarz RE; Andersen KG; Smith RC; Bedford T; Grubaugh ND Twenty Years of West Nile Virus Spread and Evolution in the Americas Visualized by Nextstrain. PLOS Pathog. 2019, 15 (10), e1008042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (43). https://www.cdc.gov/westnile/healthcareproviders/healthCareProviders-TreatmentPrevention.html .
- (44).Rodrigues LC Microcephaly and Zika Virus Infection. The Lancet 2016, 387 (10033), 2070–2072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (45).Turtle L; Solomon T Japanese Encephalitis — the Prospects for New Treatments. Nat. Rev. Neurol 2018, 14 (5), 298–313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (46). https://www.cdc.gov/japaneseencephalitis/vaccine/index.html .
- (47).Velay A; Paz M; Cesbron M; Gantner P; Solis M; Soulier E; Argemi X; Martinot M; Hansmann Y; Fafi-Kremer S Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus: Molecular Determinants of Neuropathogenesis of an Emerging Pathogen. Crit. Rev. Microbiol 2019, 45 (4), 472–493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (48).Hui L; Nie Y; Li S; Guo M; Yang W; Huang R; Chen J; Liu Y; Lu X; Chen Z; Yang Q; Wu Y Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 Facilitates Zika Virus Invasion of the Testis by Modulating the Integrity of the Blood-Testis Barrier. PLOS Pathog. 2020, 16 (4), e1008509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (49).Wang P; Dai J; Bai F; Kong K-F; Wong SJ; Montgomery RR; Madri JA; Fikrig E Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 Facilitates West Nile Virus Entry into the Brain. J. Virol 2008, 82 (18), 8978–8985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (50).Glasner DR; Ratnasiri K; Puerta-Guardo H; Espinosa DA; Beatty PR; Harris E Dengue Virus NS1 Cytokine-Independent Vascular Leak Is Dependent on Endothelial Glycocalyx Components. PLOS Pathog. 2017, 13 (11), e1006673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (51).Gopala Reddy SB; Chin W-X; Shivananju NS Dengue Virus NS2 and NS4: Minor Proteins, Mammoth Roles. Biochem. Pharmacol 2018, 154, 54–63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (52).Bautista-Carbajal P; Soto-Acosta R; Angel-Ambrocio AH; Cervantes-Salazar M; Loranca-Vega CI; Herrera-Martínez M; del Angel RM The Calmodulin Antagonist W-7 (N-(6-Aminohexyl)-5-Chloro-1-Naphthalenesulfonamide Hydrochloride) Inhibits DENV Infection in Huh-7 Cells. Virology 2017, 501, 188–198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (53).Falgout B; Pethel M; Zhang YM; Lai CJ Both Nonstructural Proteins NS2B and NS3 Are Required for the Proteolytic Processing of Dengue Virus Nonstructural Proteins. J. Virol 1991, 65 (5), 2467–2475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (54).Timiri AK; Sinha BN; Jayaprakash V Progress and Prospects on DENV Protease Inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem 2016, 117, 125–143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (55).Miller S; Sparacio S; Bartenschlager R Subcellular Localization and Membrane Topology of the Dengue Virus Type 2 Non-Structural Protein 4B. J. Biol. Chem 2006, 281 (13), 8854–8863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (56).Li Y; Wong YL; Lee MY; Li Q; Wang Q-Y; Lescar J; Shi P-Y; Kang C Secondary Structure and Membrane Topology of the Full-Length Dengue Virus NS4B in Micelles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2016, 55 (39), 12068–12072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (57).Feldmann H; Klenk H-D Marburg and Ebola Viruses. In Advances in Virus Research; Maramorosch K, Murphy FA, Shatkin AJ, Eds.; Academic Press, 1996; Vol. 47, pp 1–52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (58).Di Paola N; Sanchez-Lockhart M; Zeng X; Kuhn JH; Palacios G Viral Genomics in Ebola Virus Research. Nat. Rev. Microbiol 2020, 1–14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (59).Miranda MEG; Miranda NLJ Reston Ebolavirus in Humans and Animals in the Philippines: A Review. J. Infect. Dis 2011, 204 (suppl_3), S757–S760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (60).Barrette RW; Metwally SA; Rowland JM; Xu L; Zaki SR; Nichol ST; Rollin PE; Towner JS; Shieh W-J; Batten B; Sealy TK; Carrillo C; Moran KE; Bracht AJ; Mayr GA; Sirios-Cruz M; Catbagan DP; Lautner EA; Ksiazek TG; White WR; McIntosh MT Discovery of Swine as a Host for the Reston Ebolavirus. Science 2009, 325 (5937), 204–206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (61).Brauburger K; Hume AJ; Mühlberger E; Olejnik J Forty-Five Years of Marburg Virus Research. Viruses 2012, 4 (10), 1878–1927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (62).Messaoudi I; Amarasinghe GK; Basler CF Filovirus Pathogenesis and Immune Evasion: Insights from Ebola Virus and Marburg Virus. Nat. Rev. Microbiol 2015, 13 (11), 663–676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (63).Leroy EM; Kumulungui B; Pourrut X; Rouquet P; Hassanin A; Yaba P; Délicat A; Paweska JT; Gonzalez J-P; Swanepoel R Fruit Bats as Reservoirs of Ebola Virus. Nature 2005, 438 (7068), 575–576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (64).Towner JS; Amman BR; Sealy TK; Carroll SAR; Comer JA; Kemp A; Swanepoel R; Paddock CD; Balinandi S; Khristova ML; Formenty PBH; Albarino CG; Miller DM; Reed ZD; Kayiwa JT; Mills JN; Cannon DL; Greer PW; Byaruhanga E; Farnon EC; Atimnedi P; Okware S; Katongole-Mbidde E; Downing R; Tappero JW; Zaki SR; Ksiazek TG; Nichol ST; Rollin PE Isolation of Genetically Diverse Marburg Viruses from Egyptian Fruit Bats. PLOS Pathog. 2009, 5 (7), e1000536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (65).Jahrling PB; Geisbert TW; Johnson ED; Peters CJ; Dalgard DW; Hall WC Preliminary Report: Isolation of Ebola Virus from Monkeys Imported to USA. The Lancet 1990, 335 (8688), 502–505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (66).Le Guenno B; Formenty P; Wyers M; Gounon P; Walker F; Boesch C Isolation and Partial Characterisation of a New Strain of Ebola Virus. The Lancet 1995, 345 (8960), 1271–1274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (67).Dowell SF; Mukunu R; Ksiazek TG; Khan AS; Rollin PE; Peters CJ Transmission of Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever: A Study of Risk Factors in Family Members, Kikwit, Democratic Republic of the Congo, 1995. J. Infect. Dis 1999, 179 (Supplement_1), S87–S91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (68).U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA news release, December 19, 2019. First FDA-approved vaccine for the prevention of Ebola virus disease, marking a critical milestone in public health preparedness and response. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/first-fda-approved-vaccine-prevention-ebola-virus-disease-marking-critical-milestone-public-health (accessed May 21, 2020) [Google Scholar]
- (69).Suschak JJ; Schmaljohn CS Vaccines against Ebola Virus and Marburg Virus: Recent Advances and Promising Candidates. Hum. Vaccines Immunother 2019, 15 (10), 2359–2377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (70).Kondratowicz AS; Lennemann NJ; Sinn PL; Davey RA; Hunt CL; Moller-Tank S; Meyerholz DK; Rennert P; Mullins RF; Brindley M; Sandersfeld LM; Quinn K; Weller M; McCray PB; Chiorini J; Maury W T-Cell Immunoglobulin and Mucin Domain 1 (TIM-1) Is a Receptor for Zaire Ebolavirus and Lake Victoria Marburgvirus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci 2011, 108 (20), 8426–8431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (71).Takada A; Watanabe S; Ito H; Okazaki K; Kida H; Kawaoka Y Downregulation of B1 Integrins by Ebola Virus Glycoprotein: Implication for Virus Entry. Virology 2000, 278 (1), 20–26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (72).Takada A; Fujioka K; Tsuiji M; Morikawa A; Higashi N; Ebihara H; Kobasa D; Feldmann H; Irimura T; Kawaoka Y Human Macrophage C-Type Lectin Specific for Galactose and N-Acetylgalactosamine Promotes Filovirus Entry. J. Virol 2004, 78 (6), 2943–2947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (73).Nanbo A; Imai M; Watanabe S; Noda T; Takahashi K; Neumann G; Halfmann P; Kawaoka Y Ebolavirus Is Internalized into Host Cells via Macropinocytosis in a Viral Glycoprotein-Dependent Manner. PLOS Pathog. 2010, 6 (9), e1001121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (74).Carette JE; Raaben M; Wong AC; Herbert AS; Obernosterer G; Mulherkar N; Kuehne AI; Kranzusch PJ; Griffin AM; Ruthel G; Cin PD; Dye JM; Whelan SP; Chandran K; Brummelkamp TR Ebola Virus Entry Requires the Cholesterol Transporter Niemann–Pick C1. Nature 2011, 477 (7364), 340–343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (75).Chandran K; Sullivan NJ; Felbor U; Whelan SP; Cunningham JM Endosomal Proteolysis of the Ebola Virus Glycoprotein Is Necessary for Infection. Science 2005, 308 (5728), 1643–1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (76).Zhu W; Banadyga L; Emeterio K; Wong G; Qiu X The Roles of Ebola Virus Soluble Glycoprotein in Replication, Pathogenesis, and Countermeasure Development. Viruses 2019, 11 (11), 999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (77).Volchkov VE; Feldmann H; Volchkova VA; Klenk H-D Processing of the Ebola Virus Glycoprotein by the Proprotein Convertase Furin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci 1998, 95 (10), 5762–5767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (78).Mühlberger E Filovirus Replication and Transcription. Future Virol. 2007, 2 (2), 205–215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (79).Noda T; Sagara H; Suzuki E; Takada A; Kida H; Kawaoka Y Ebola Virus VP40 Drives the Formation of Virus-Like Filamentous Particles Along with GP. J. Virol 2002, 76 (10), 4855–4865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (80).Coleman CM; Frieman MB Coronaviruses: Important Emerging Human Pathogens. J. Virol 2014, 88 (10), 5209–5212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (81).Wu A; Peng Y; Huang B; Ding X; Wang X; Niu P; Meng J; Zhu Z; Zhang Z; Wang J; Sheng J; Quan L; Xia Z; Tan W; Cheng G; Jiang T Genome Composition and Divergence of the Novel Coronavirus (2019-NCoV) Originating in China. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27 (3), 325–328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (82).Sanchez A; Rollin PE Complete Genome Sequence of an Ebola Virus (Sudan Species) Responsible for a 2000 Outbreak of Human Disease in Uganda. Virus Res. 2005, 113 (1), 16–25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (83).Feldmann H; Mühlberger E; Randolf A; Will C; Kiley MP; Sanchez A; Klenk H-D Marburg Virus, a Filovirus: Méssenger RNAs, Gene Order, and Regulatory Elements of the Replication Cycle. Virus Res. 1992, 24 (1), 1–19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (84).Hoenen T; Groseth A; Feldmann H Therapeutic Strategies to Target the Ebola Virus Life Cycle. Nat. Rev. Microbiol 2019, 17 (10), 593–606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (85).García LL; Padilla L; Castaño JC Inhibitors Compounds of the Flavivirus Replication Process. Virol. J 2017, 14 (1), 95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (86).Islam MT; Sarkar C; El-Kersh DM; Jamaddar S; Uddin SJ; Shilpi JA; Mubarak MS; Natural products and their derivatives against coronavirus: A review of the non-clinical and pre-clinical data. Phytotherapy Res. 2020, 34, 2471–2492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (87).Ehrhardt SA; Zehner M; Krähling V; Cohen-Dvashi H; Kreer C; Elad N; Gruell H; Ercanoglu MS; Schommers P; Gieselmann L; Eggeling R; Dahlke C; Wolf T; Pfeifer N; Addo MM; Diskin R; Becker S; Klein F Polyclonal and Convergent Antibody Response to Ebola Virus Vaccine RVSV-ZEBOV. Nat. Med 2019, 25 (10), 1589–1600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (88).Bosch BJ; Martina BEE; Zee R. van der; Lepault J; Haijema BJ; Versluis C; Heck AJR; Groot R. de; Osterhaus ADME; Rottier PJM Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (SARS-CoV) Infection Inhibition Using Spike Protein Heptad Repeat-Derived Peptides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci 2004, 101 (22), 8455–8460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (89).Sainz B; Mossel EC; Gallaher WR; Wimley WC; Peters CJ; Wilson RB; Garry RF Inhibition of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Associated Coronavirus (SARS-CoV) Infectivity by Peptides Analogous to the Viral Spike Protein. Virus Res. 2006, 120 (1), 146–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (90).Xia S; Liu M; Wang C; Xu W; Lan Q; Feng S; Qi F; Bao L; Du L; Liu S; Qin C; Sun F; Shi Z; Zhu Y; Jiang S; Lu L Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 (Previously 2019-NCoV) Infection by a Highly Potent Pan-Coronavirus Fusion Inhibitor Targeting Its Spike Protein That Harbors a High Capacity to Mediate Membrane Fusion. Cell Res. 2020, 30 (4), 343–355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (91).Ho T-Y; Wu S-L; Chen J-C; Li C-C; Hsiang C-Y Emodin Blocks the SARS Coronavirus Spike Protein and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Interaction. Antiviral Res. 2007, 74 (2), 92–101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (92).O’Keefe BR; Giomarelli B; Barnard DL; Shenoy SR; Chan PKS; McMahon JB; Palmer KE; Barnett BW; Meyerholz DK; Wohlford-Lenane CL; McCray PB Broad-Spectrum In Vitro Activity and In Vivo Efficacy of the Antiviral Protein Griffithsin against Emerging Viruses of the Family Coronaviridae. J. Virol 2010, 84 (5), 2511–2521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (93).Lee C Griffithsin, a Highly Potent Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Lectin from Red Algae: From Discovery to Clinical Application. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17 (10), 567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (94).Soto-Acosta R; Bautista-Carbajal P; Syed GH; Siddiqui A; Del Angel RM Nordihydroguaiaretic Acid (NDGA) Inhibits Replication and Viral Morphogenesis of Dengue Virus. Antiviral Res. 2014, 109, 132–140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (95).Braun E; Sauter D Furinmediated Protein Processing in Infectious Diseases and Cancer. Clin. Transl. Immunol 2019, 8 (8). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (96).Modhiran N; Gandhi NS; Wimmer N; Cheung S; Stacey K; Young PR; Ferro V; Watterson D Dual Targeting of Dengue Virus Virions and NS1 Protein with the Heparan Sulfate Mimic PG545. Antiviral Res. 2019, 168, 121–127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (97).Cui Q; Du R; Anantpadma M; Schafer A; Hou L; Tian J; Davey RA; Cheng H; Rong L Identification of Ellagic Acid from Plant Rhodiola Rosea L. as an Anti-Ebola Virus Entry Inhibitor. Viruses 2018, 10 (4), 152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (98).Cheng H; Lear-Rooney CM; Johansen L; Varhegyi E; Chen ZW; Olinger GG; Rong L Inhibition of Ebola and Marburg Virus Entry by G Protein-Coupled Receptor Antagonists. J. Virol 2015, 89 (19), 9932–9938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (99).Si L; Meng K; Tian Z; Sun J; Li H; Zhang Z; Soloveva V; Li H; Fu G; Xia Q; Xiao S; Zhang L; Zhou D Triterpenoids Manipulate a Broad Range of Virus-Host Fusion via Wrapping the HR2 Domain Prevalent in Viral Envelopes. Sci. Adv 2018, 4 (11), eaau8408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (100).Kononova AA; Sokolova AS; Cheresiz SV; Yarovaya OI; Nikitina RA; Chepurnov AA; Pokrovsky AG; Salakhutdinov NF N-Heterocyclic Borneol Derivatives as Inhibitors of Marburg Virus Glycoprotein-Mediated VSIV Pseudotype Entry. MedChemComm 2017, 8 (12), 2233–2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (101).Boyd MR et al. Discovery of cyanovirin-N, a novel human immunodeficiency virus-inactivating protein that binds viral surface envelope glycoprotein gp120: potential applications to microbicide development. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother 1997, 41, 1521–1530 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (102).Barrientos LG et al. Cyanovirin-N binds to the viral surface glycoprotein, GP1,2 and inhibits infectivity of Ebola virus. Antivairal Res. 2003, 58, 47–56 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (103).Báez-Santos YM; St. John SE; Mesecar AD The SARS-Coronavirus Papain-like Protease: Structure, Function and Inhibition by Designed Antiviral Compounds. Antiviral Res. 2015, 115, 21–38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (104).Jo S; Kim S; Shin DH; Kim M-S Inhibition of SARS-CoV 3CL Protease by Flavonoids. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem 2020, 35 (1), 145–151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (105).Wu C-Y; Jan J-T; Ma S-H; Kuo C-J; Juan H-F; Cheng Y-SE; Hsu H-H; Huang H-C; Wu D; Brik A; Liang F-S; Liu R-S; Fang J-M; Chen S-T; Liang P-H; Wong C-H Small Molecules Targeting Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Human Coronavirus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci 2004, 101 (27), 10012–10017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (106).Cho JK; Curtis-Long MJ; Lee KH; Kim DW; Ryu HW; Yuk HJ; Park KH Geranylated Flavonoids Displaying SARS-CoV Papain-like Protease Inhibition from the Fruits of Paulownia Tomentosa. Bioorg. Med. Chem 2013, 21 (11), 3051–3057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (107).Park J-Y; Jeong HJ; Kim JH; Kim YM; Park S-J; Kim D; Park KH; Lee WS; Ryu YB Diarylheptanoids from Alnus Japonica Inhibit Papain-Like Protease of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus. Biol. Pharm. Bull 2012, advpub. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (108).Park J-Y; Kim JH; Kim YM; Jeong HJ; Kim DW; Park KH; Kwon H-J; Park S-J; Lee WS; Ryu YB Tanshinones as Selective and Slow-Binding Inhibitors for SARS-CoV Cysteine Proteases. Bioorg. Med. Chem 2012, 20 (19), 5928–5935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (109).Kim DW; Seo KH; Curtis-Long MJ; Oh KY; Oh J-W; Cho JK; Lee KH; Park KH Phenolic Phytochemical Displaying SARS-CoV Papain-like Protease Inhibition from the Seeds of Psoralea Corylifolia. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem 2014, 29 (1), 59–63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (110).Sayed AM; Khattab AR; AboulMagd AM; Hassan HM; Rateb ME; Zaid H; Abdelmohsen UR Nature as a Treasure Trove of Potential Anti-SARS-CoV Drug Leads: A Structural/Mechanistic Rationale. RSC Adv. 2020, 10 (34), 19790–19802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (111).Luo D; Vasudevan SG; Lescar J The Flavivirus NS2B–NS3 Protease–Helicase as a Target for Antiviral Drug Development. Antiviral Res. 2015, 118, 148–158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (112).Bharadwaj S; Lee KE; Dwivedi VD; Yadava U; Panwar A; Lucas SJ; Pandey A; Kang SG Discovery of Ganoderma Lucidum Triterpenoids as Potential Inhibitors against Dengue Virus NS2B-NS3 Protease. Sci. Rep 2019, 9 (1), 19059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (113).Sheahan TP; Sims AC; Zhou S; Graham RL; Pruijssers AJ; Agostini ML; Leist SR; Schäfer A; Dinnon KH; Stevens LJ; Chappell JD; Lu X; Hughes TM; George AS; Hill CS; Montgomery SA; Brown AJ; Bluemling GR; Natchus MG; Saindane M; Kolykhalov AA; Painter G; Harcourt J; Tamin A; Thornburg NJ; Swanstrom R; Denison MR; Baric RS An Orally Bioavailable Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in Human Airway Epithelial Cell Cultures and Multiple Coronaviruses in Mice. Sci. Transl. Med 2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (114).Yu M-S; Lee J; Lee JM; Kim Y; Chin Y-W; Jee J-G; Keum Y-S; Jeong Y-J Identification of Myricetin and Scutellarein as Novel Chemical Inhibitors of the SARS Coronavirus Helicase, NsP13. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett 2012, 22 (12), 4049–4054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (115).Botta L; Rivara M; Zuliani V; Radi M Drug Repurposing Approaches to Fight Dengue Virus Infection and Related Diseases. Front. Biosci. Landmark Ed 2018, 23, 997–1019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (116).Shimizu H; Saito A; Mikuni J; Nakayama EE; Koyama H; Honma T; Shirouzu M; Sekine S; Shioda T Discovery of a Small Molecule Inhibitor Targeting Dengue Virus NS5 RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis 2019, 13 (11), e0007894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (117).Hamill RL; Hoehn MM A9145, A new adenine-containing antifungal antibiotic I. Discovery and isolation. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 1973, 26 (8), 463–465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (118).Krafcikova P; Silhan J; Nencka R; Boura E Structural Analysis of the SARS-CoV-2 Methyltransferase Complex Involved in RNA Cap Creation Bound to Sinefungin. Nat. Commun 2020, 11 (1), 3717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (119).Hercik K; Brynda J; Nencka R; Boura E Structural Basis of Zika Virus Methyltransferase Inhibition by Sinefungin. Arch. Virol 2017, 162 (7), 2091–2096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (120).Noble CG; Li S-H; Dong H; Chew SH; Shi P-Y Crystal Structure of Dengue Virus Methyltransferase without S-Adenosyl-L-Methionine. Antiviral Res. 2014, 111, 78–81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (121).De Clercq E Ebola Virus (EBOV) Infection: Therapeutic Strategies. Biochem. Pharmacol 2015, 93 (1), 1–10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (122).Oestereich L; Lüdtke A; Wurr S; Rieger T; Muñoz-Fontela C; Günther S Successful Treatment of Advanced Ebola Virus Infection with T-705 (Favipiravir) in a Small Animal Model. Antiviral Res. 2014, 105, 17–21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (123).Warren TK; Jordan R; Lo MK; Ray AS; Mackman RL; Soloveva V; Siegel D; Perron M; Bannister R; Hui HC; Larson N; Strickley R; Wells J; Stuthman KS; Van Tongeren SA; Garza NL; Donnelly G; Shurtleff AC; Retterer CJ; Gharaibeh D; Zamani R; Kenny T; Eaton BP; Grimes E; Welch LS; Gomba L; Wilhelmsen CL; Nichols DK; Nuss JE; Nagle ER; Kugelman JR; Palacios G; Doerffler E; Neville S; Carra E; Clarke MO; Zhang L; Lew W; Ross B; Wang Q; Chun K; Wolfe L; Babusis D; Park Y; Stray KM; Trancheva I; Feng JY; Barauskas O; Xu Y; Wong P; Braun MR; Flint M; McMullan LK; Chen S-S; Fearns R; Swaminathan S; Mayers DL; Spiropoulou CF; Lee WA; Nichol ST; Cihlar T; Bavari S Therapeutic Efficacy of the Small Molecule GS-5734 against Ebola Virus in Rhesus Monkeys. Nature 2016, 531 (7594), 381–385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (124).Warren TK; Wells J; Panchal RG; Stuthman KS; Garza NL; Van Tongeren SA; Dong L; Retterer CJ; Eaton BP; Pegoraro G; Honnold S; Bantia S; Kotian P; Chen X; Taubenheim BR; Welch LS; Minning DM; Babu YS; Sheridan WP; Bavari S Protection against Filovirus Diseases by a Novel Broad-Spectrum Nucleoside Analogue BCX4430. Nature 2014, 508 (7496), 402–405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (125).Daino GL; Frau A; Sanna C; Rigano D; Distinto S; Madau V; Esposito F; Fanunza E; Bianco G; Taglialatela-Scafati O; Zinzula L; Maccioni E; Corona A; Tramontano E Identification of Myricetin as an Ebola Virus VP35–Double-Stranded RNA Interaction Inhibitor through a Novel Fluorescence-Based Assay. Biochemistry 2018, 57 (44), 6367–6378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (126).Kamitani W; Narayanan K; Huang C; Lokugamage K; Ikegami T; Ito N; Kubo H; Makino S Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Nsp1 Protein Suppresses Host Gene Expression by Promoting Host MRNA Degradation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci 2006, 103 (34), 12885–12890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (127).Shi C-S; Nabar NR; Huang N-N; Kehrl JH SARS-Coronavirus Open Reading Frame-8b Triggers Intracellular Stress Pathways and Activates NLRP3 Inflammasomes. Cell Death Discov. 2019, 5 (1), 1–12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (128).McBride R; Fielding BC The Role of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS)-Coronavirus Accessory Proteins in Virus Pathogenesis. Viruses 2012, 4 (11), 2902–2923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (129).Whitby K; Pierson TC; Geiss B; Lane K; Engle M; Zhou Y; Doms RW; Diamond MS Castanospermine, a Potent Inhibitor of Dengue Virus Infection In Vitro and In Vivo. J. Virol 2005, 79 (14), 8698–8706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (130).Watanabe S; Rathore APS; Sung C; Lu F; Khoo YM; Connolly J; Low J; Ooi EE; Lee HS; Vasudevan SG Dose- and Schedule-Dependent Protective Efficacy of Celgosivir in a Lethal Mouse Model for Dengue Virus Infection Informs Dosing Regimen for a Proof of Concept Clinical Trial. Antiviral Res. 2012, 96 (1), 32–35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (131).Shen LW; Mao HJ; Wu YL; Tanaka Y; Zhang W TMPRSS2: A Potential Target for Treatment of Influenza Virus and Coronavirus Infections. Biochimie 2017, 142, 1–10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (132).Dana D; Pathak SK A Review of Small Molecule Inhibitors and Functional Probes of Human Cathepsin L. Molecules 2020, 25 (3), 698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (133).Vidal-Albalat A; González FV Chapter 6 - Natural Products as Cathepsin Inhibitors. In Studies in Natural Products Chemistry; Atta-ur-Rahman, Ed.; Elsevier, 2016; Vol. 50, pp 179–213. [Google Scholar]
- (134).Mori Y; Yamashita T; Tanaka Y; Tsuda Y; Abe T; Moriishi K; Matsuura Y Processing of Capsid Protein by Cathepsin L Plays a Crucial Role in Replication of Japanese Encephalitis Virus in Neural and Macrophage Cells. J. Virol 2007, 81 (16), 8477–8487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (135).Puerta-Guardo H; Glasner DR; Harris E Dengue Virus NS1 Disrupts the Endothelial Glycocalyx, Leading to Hyperpermeability. PLOS Pathog. 2016, 12 (7), e1005738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (136).Miller B; Friedman AJ; Choi H; Hogan J; McCammon JA; Hook V; Gerwick WH The Marine Cyanobacterial Metabolite Gallinamide A Is a Potent and Selective Inhibitor of Human Cathepsin L. J. Nat. Prod 2014, 77 (1), 92–99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (137).Brosius AD; Overman LE Aloperine: Stereocontrolled Synthesis of Two Stereoisomers and Determination of Absolute Configuration. J. Org. Chem 1997, 62 (3), 440–441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (138).Fusetani N; Fujita M; Nakao Y; Matsunaga S; van Soest RWM Tokaramide A,a New Cathepsin B Inhibitor from the Marine Sponge Theonella Aff. Mirabilis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett 1999, 9 (24), 3397–3402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (139).Nakao Y; Fujita M; Warabi K; Matsunaga S; Fusetani N Miraziridine A, a Novel Cysteine Protease Inhibitor from the Marine Sponge Theonella Aff. Mirabilis1. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2000, 122 (42), 10462–10463. [Google Scholar]
- (140).Zhang X; Liu Q; Zhang N; Li Q; Liu Z; Li Y; Gao L; Wang Y; Deng H; Song D Discovery and Evolution of Aloperine Derivatives as Novel Anti-Filovirus Agents through Targeting Entry Stage. Eur. J. Med. Chem 2018, 149, 45–55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (141).Hanada K; Tamai M; Yamagishi M; Ohmura S; Sawada J; Tanaka I Isolation and Characterization of E–64, a New Thiol Protease Inhibitor. Agric. Biol. Chem 1978, 42 (3), 523–528. [Google Scholar]
- (142).Tamai M; Matsumoto K; Omura S; Koyama I; Ozawa Y; Hanada K In Vitro and in Vivo Inhibition of Cysteine Proteinases by Est, a New Analog of E-64. J. Pharmacobiodyn 1986, 9 (8), 672–677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (143).Murata M; Miyashita S; Yokoo C; Tamai M; Hanada K; Hatayama K; Towatari T; Nikawa T; Katunuma N Novel Epoxysuccinyl Peptides Selective Inhibitors of Cathepsin B, in Vitro. FEBS Lett. 1991, 280 (2), 307–310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (144).Smith SA; Nivarthi UK; Alwis R. de; Kose N; Sapparapu G; Bombardi R; Kahle KM; Pfaff JM; Lieberman S; Doranz BJ; Silva A. M. de; Crowe JE Dengue Virus PrM-Specific Human Monoclonal Antibodies with Virus Replication-Enhancing Properties Recognize a Single Immunodominant Antigenic Site. J. Virol 2016, 90 (2), 780–789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (145).Dalbey RE; von Heijne G Signal Peptidases in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes - a New Protease Family. Trends Biochem. Sci 1992, 17 (11), 474–478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (146).Estoppey D; Lee CM; Janoschke M; Lee BH; Wan KF; Dong H; Mathys P; Filipuzzi I; Schuhmann T; Riedl R; Aust T; Galuba O; McAllister G; Russ C; Spiess M; Bouwmeester T; Bonamy GMC; Hoepfner D The Natural Product Cavinafungin Selectively Interferes with Zika and Dengue Virus Replication by Inhibition of the Host Signal Peptidase. Cell Rep. 2017, 19 (3), 451–460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (147).Wu S-F; Lee C-J; Liao C-L; Dwek RA; Zitzmann N; Lin Y-L Antiviral Effects of an Iminosugar Derivative on Flavivirus Infections. J. Virol 2002, 76 (8), 3596–3604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (148).Yagi M; Kouno T; Aoyagi Y; Murai H The Structure of Moranoline, a Piperidine Alkaloid from Morus Species. Nippon Nōgeikagaku Kaishi 1976, 50 (11), 571–572. [Google Scholar]
- (149).Yu W; Gill T; Wang L; Du Y; Ye H; Qu X; Guo J-T; Cuconati A; Zhao K; Block TM; Xu X; Chang J Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of N-Alkylated Deoxynojirimycin (DNJ) Derivatives for the Treatment of Dengue Virus Infection. J. Med. Chem 2012, 55 (13), 6061–6075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (150).Wang H; Shen Y; Zhao L; Ye Y 1-Deoxynojirimycin and its Derivatives: A Mini Review of the Literature. Current Medicinal Chemistry 2020, 27, 1–15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (151).Chang J; Warren TK; Zhao X; Gill T; Guo F; Wang L; Comunale MA; Du Y; Alonzi DS; Yu W; Ye H; Liu F; Guo J-T; Mehta A; Cuconati A; Butters TD; Bavari S; Xu X; Block TM Small Molecule Inhibitors of ER #-Glucosidases Are Active against Multiple Hemorrhagic Fever Viruses. Antiviral Res. 2013, 98 (3), 432–440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (152).Zhang XG; Mason PW; Dubovi EJ; Xu X; Bourne N; Renshaw RW; Block TM; Birk AV Antiviral Activity of Geneticin against Dengue Virus. Antiviral Res. 2009, 83 (1), 21–27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (153).Hwang BY; Su B-N; Chai H; Mi Q; Kardono LBS; Afriastini JJ; Riswan S; Santarsiero BD; Mesecar AD; Wild R; Fairchild CR; Vite GD; Rose WC; Farnsworth NR; Cordell GA; Pezzuto JM; Swanson SM; Kinghorn AD Silvestrol and Episilvestrol, Potential Anticancer Rocaglate Derivatives from Aglaia Silvestris. J. Org. Chem 2004, 69 (10), 3350–3358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (154).Biedenkopf N; Lange-Grünweller K; Schulte FW; Weißer A; Müller C; Becker D; Becker S; Hartmann RK; Grünweller A The Natural Compound Silvestrol Is a Potent Inhibitor of Ebola Virus Replication. Antiviral Res. 2017, 137, 76–81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (155).Werner G; Hagenmaier H; Albert K; Kohlshorn H The Structure of the Bafilomycins, a New Group of Macrolide Antibiotics. Tetrahedron Lett. 1983, 24 (47), 5193–5196. [Google Scholar]
- (156).Yonezawa A; Cavrois M; Greene WC Studies of Ebola Virus Glycoprotein-Mediated Entry and Fusion by Using Pseudotyped Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Virions: Involvement of Cytoskeletal Proteins and Enhancement by Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha. J. Virol 2005, 79 (2), 918–926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (157).Aldridge DC; Armstrong JJ; Speake RN; Turner WB The Cytochalasins, a New Class of Biologically Active Mould Metabolites. Chem. Commun. Lond 1967, No. 1, 26–27. [Google Scholar]
- (158).Kashman Y; Groweiss A; Shmueli U Latrunculin, a New 2-Thiazolidinone Macrolide from the Marine Sponge Latrunculia Magnifica. Tetrahedron Lett. 1980, 21 (37), 3629–3632. [Google Scholar]
- (159).Crews P; Manes LV; Boehler M Jasplakinolide, a Cyclodepsipeptide from the Marine Sponge, Jaspis SP. Tetrahedron Lett. 1986, 27 (25), 2797–2800. [Google Scholar]
- (160).Beck S; Henß L; Weidner T; Herrmann J; Müller R; Chao Y-K; Grimm C; Weber C; Sliva K; Schnierle BS Identification of Entry Inhibitors of Ebola Virus Pseudotyped Vectors from a Myxobacterial Compound Library. Antiviral Res. 2016, 132, 85–91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (161).Kunze B; Jansen R; Sasse F; Höfle G; Reichenbach H Chondramides A-D, New Antifungal and Cytostatic Depsipeptides from Chondromyces Crocatus (Myxobacteria). J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 1995, 48 (11), 1262–1266.. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (162).Herrmann J; Hüttel S; Müller R Discovery and Biological Activity of New Chondramides from Chondromyces Sp. ChemBioChem 2013, 14 (13), 1573–1580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (163).Fan H-H; Wang L-Q; Liu W-L; An X-P; Liu Z-D; He X-Q; Song L-H; Tong Y-G Repurposing of Clinically Approved Drugs for Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in a 2019-Novel Coronavirus-Related Coronavirus Model. Chin. Med. J. (Engl.) 2020, 133 (9), 1051–1056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (164).Li S; Chen C; Zhang H; Guo H; Wang H; Wang L; Zhang X; Hua S; Yu J; Xiao P Identification of Natural Compounds with Antiviral Activities against SARS-Associated Coronavirus. Antiviral Res. 2005, 67 (1), 18–23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (165).Lane T; Anantpadma M; Freundlich JS; Davey RA; Madrid PB; Ekins S The Natural Product Eugenol Is an Inhibitor of the Ebola Virus In Vitro. Pharm. Res 2019, 36 (7), 104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


