Figure 4.
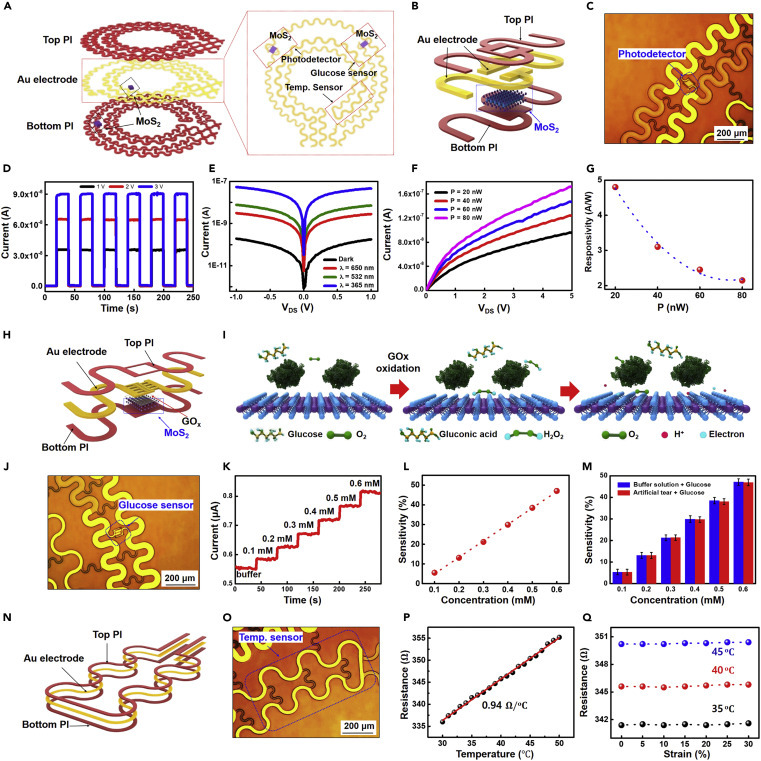
The characteristics of the multifunctional sensor system
(A) Schematic illustration of the multifunctional sensor structure.
(B and C) 3D schematic illustration (B) and optical image (C) of the two-terminal MoS2 photodetector.
(D) Photoswitching behavior under pulsed illumination by 365 nm wavelength UV light with different VDS values.
(E) Drain-source characteristics in the dark and under illumination with different wavelengths of light.
(F) Drain-source characteristics of the photodetector under different illuminating light intensities.
(G) The photoresponsivity of the MoS2 phototransistor, exhibiting a high photoresponsivity of 4.8 A/W for a UV power of 20 nW.
(H) Schematic illustration of ac MoS2 glucose sensor.
(I) Illustration of the sensing mechanism of the device with oxidation of glucose.
(J) Optical image of the MoS2 glucose sensor.
(K) Time versus current curve based on changes in glucose levels.
(L) The sensitivity (|R|/R0) of the glucose sensor with a buffer solution, where R0 is the initial resistance at zero glucose concentration.
(M) Sensitivity of the sensors with the PBS buffer solution (blue) and the artificial tear solution (red). Five devices with each solution were tested and the standard deviation is represented by error bars.
(N and O) Schematic illustration (N) and optical image (O) of the temperature sensor.
(P) The temperature-dependent resistance curve for the Au thermal resistor.
(Q) The resistance of the temperature sensor versus strain under different temperatures.
