Abstract
Brain metastases from breast cancer (BCBM) constitute the second most common cause of brain metastasis (BM), and the incidence of these frequently lethal lesions is currently increasing, following better systemic treatment. Patients with ER-negative and HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer (BC) are the most likely to develop BM, but if this diagnosis remains associated with a worse prognosis, long survival is now common for patients with HER2-positive BC. BCBM represents a therapeutic challenge that needs a coordinated treatment strategy along international guidelines. Surgery has always to be considered when feasible. It is now well established that stereotaxic radiosurgery allows for equivalent control and less-cognitive toxicities than whole-brain radiation therapy, which should be delayed as much as possible. Medical treatment for BCBM is currently a rapidly evolving field. It has been shown that the blood–brain barrier (BBB) is often impaired in macroscopic BM, and several chemotherapy regimens, antibody–drug conjugates and tyrosine-kinase inhibitors have been shown to be active on BCBM and can be part of the global treatment strategy. This paper provides an overview of the therapeutic option for BCBM that is currently available and outlines potential new approaches for tackling these deadly secondary tumours.
Subject terms: Breast cancer, Metastasis
Background
After lung cancer, metastatic breast cancer (MBC) is the second most common cause of brain metastases (BM) among solid malignancies.1 In a 2019 retrospective assessment of the metastatic breast cancer (MBC) cohort from the ongoing Epidemiological Strategy and Medical Economics (ESME) research programme, the risk of developing BM is estimated to be as high as 25% among patients with advanced breast cancer (BC), with a median time of BM occurrence 2–3 years after the initial BC diagnosis.2
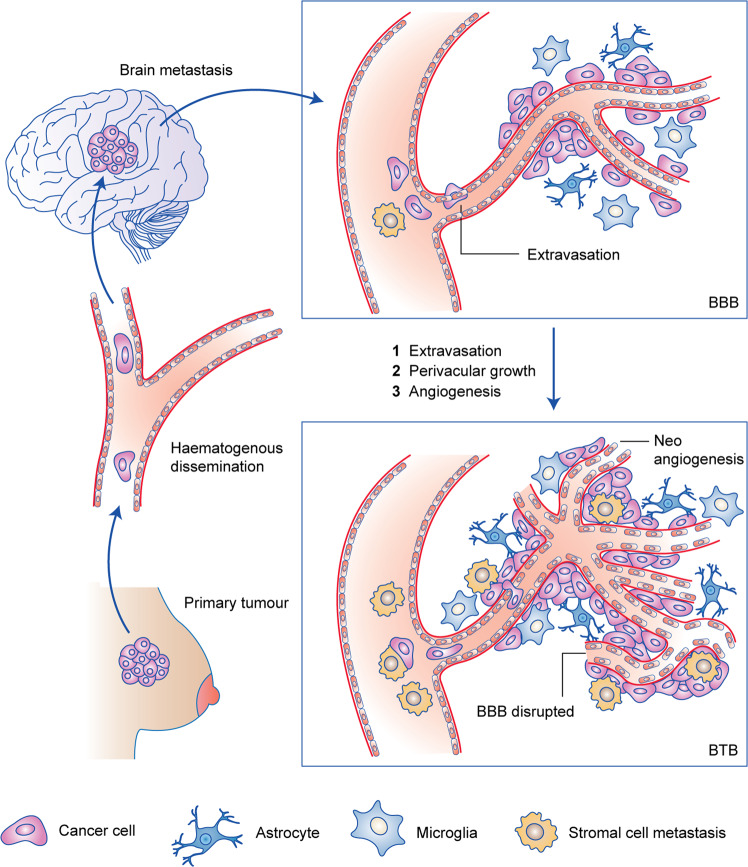
What is the history of BCBM? The main hypothesis is that cancer cells from breast parenchyma must undergo epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) to enter the bloodstream, survive haematological diffusion and implant into the CNS after extravasation and a further step of reverse mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition (MET). Thus, cancer cells metastasising to the brain must possess a distinct set of adaptations to develop effectively in this unique environment with the acquisition of several fundamental characteristics to cross the blood–brain barrier (BBB), proliferate perivascularly and begin neoangiogenesis until the creation of a brain tumour barrier (BTB). Disruption of the BBB can also be promoted by radiotherapy and a BBB disruptor (cf infra) (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1. BMBC history.
Following haematogenous dissemination, breast cancer cells invade the brain tissue by extravasation. Then they experience perivascular growth with no need of neoangiogenesis and the blood–brain barrier (BBB) is still intact. To reach macroscopic size, the new metastasis needs to stimulate neoangiogenesis. At this point, the BBB may be disrupted and is referred as the blood–tumour barrier (BTB). This Figure has been adapted from Eicher et al.29.
The microenvironment of the brain, with its unique cell types, anatomical structures, metabolic constraints and immune environment, differs radically from the microenvironments of extracranial lesions, imposing a distinct selective pressure. Each metastatic localisation has particular characteristics in favour or not of the metastatic process, but patients with MBC are highly susceptible to bone, liver or lung metastasis as well, showing the high level of selection and advancement of metastatic disease when cancer cells are able to penetrate the central nervous system (CNS). Furthermore, breast cancer cells tend to metastasise preferentially in the cerebellum, suggesting that differences in the surface properties of tumour cells and vascular endothelium should exist even within brain areas.3,4
The microenvironment of the brain is characterised by unique anatomical structures,5 cell types, metabolic pathways6 and local immune environments7 in comparison with the microenvironment of the breast and of other extracranial lesions,8 which means that cells metastasising to the brain must possess a distinct set of characteristics to not only cross the BBB but also to grow effectively in this unique environment.9 Shifts in the levels of hormone receptors and the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) status have been reported in intracranial metastases compared with primary breast cancer cells and extracranial metastases.10–12
The branched evolution and selection pressure during blood dissemination and brain implantation of metastasis could explain these shifts. As a direct consequence, the usual treatment may not be adapted to the new-known subtype and may be completely useless against BCBM. BM was also found to harbour genetic changes that were not detected in the primary tumour, including actionable mutations that were eligible for targeted therapy although, beyond HER2 and oestrogen receptor (ER) status, the therapeutic implication(s) of such mutations remain to be established.13
Current therapeutic options for patients with BCBM include surgical resection, stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS), whole-brain radiation therapy (WBRT), chemotherapy and targeted therapy. Conventional systemic therapy has been considered a challenge for BCBM treatment as complex molecules are theoretically not capable of crossing the BBB. Nevertheless, this concept has been challenged as the results from some clinical trials indicate that systemic therapies can be effective for the treatment of BM, as discussed in this paper.
We begin this review by providing an epidemiological overview of BCBM before outlining the potential influence of the BBB on drug delivery and efficacy. After a full description of the current therapeutic strategy regarding surgery, radiotherapy and systemic treatments in the main breast cancer subtypes, we present the possible new avenues for future research. A selection of ongoing clinical trials discussed throughout this review, the results of which could change practices in the future, is detailed in Table 1.
Table 1.
Selection of ongoing clinical trials for BCBM.
| Treatment | Clinical trial number | Official title | Phase | Study population | Number of patients | Study intervention | Primary outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Local treatment | |||||||
| Pre- vs post-operative SRS | NCT03741673 | A Phase 3 trial of pre-operative stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) vs post-operative SRS for brain metastases | 3 | ≤ 4-cm BM for single fraction or ≤7 cm for multifraction therapy | 86 | Pre-operative SRS vs post-operative SRS | Leptomeningeal disease (LMD)-free rate |
| Pre-operative single-fraction SRS | NCT03368625 | A Phase 2 study of neoadjuvant stereotactic radiosurgery for large brain metastases | 2 (one arm) | 1–6 BM, 2–4 cm | 30 | One pre-operative fraction of SRS | Radiation toxicity |
| Fractionated SRS alone | NCT04061408 | A Phase 2 pilot study of fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy (FSRT) in breast cancer patients with 1–10 brain metastases | 2 (one arm) | 1–10 BM HER2+ | 170 | 3–5 fractions of 8 Gy | Intracranial local tumour control rate |
| WBRT alone | NCT03075072 | Whole-brain radiation vs stereotactic radiation (SRS) in patients with 5–20 brain metastases: a Phase 3, randomised clinical trial | 3 | 5–20 BM | 196 | WBRT vs SRS | Quality of life |
| Chemotherapy agents | |||||||
| Etirinotecan pegol | NCT02915744 | A Phase 3 open-label, randomised, multicenter study of NKTR-102 vs treatment of physician’s choice (TPC) in patients with metastatic breast cancer who have stable brain metastases and have been previously treated with an anthracycline, a taxane and capecitabine | 3 | Non-progressing BM | 178 | NKTR-102 vs TPC (eribuline, ixabepilone, vinorelbine, gemcitabine, docetaxel and (nab)-paclitaxel) | OS |
| Nal-IRI (MM-398) | NCT03328884 | Multicenter open-label, Phase 2 trial, to evaluate the efficacy and safety of nal-iri for progressing brain metastases in patients with HER2-negative breast cancer (the phenomenal study) | 2 (one arm) | HER2+ excluded with BM | 63 | Nal-IRI 60 mg/m2 on D1 of a 14-day cycle | CNS ORR |
| New-generation TKIs | |||||||
| Neratinib + T-DM1 | NCT01494662 | A Phase 2 trial of HKI-272 (neratinib), neratinib and capecitabine and ado-trastuzumab–emtansine for patients HER2-positive breast cancer and brain metastases | 2 (four cohorts) | HER2+ with BM | 168 |
* Previously untreated * Progressive BM * Progressive BM after T-DM1 |
ORR (CNS ORR) |
| Tucatinib + T-DM1 | NCT03975647 | Randomised, double-blind, Phase 3 study of tucatinib or placebo in combination with ado-trastuzumab–emtansine (T-DM1) for subjects with unresectable locally advanced or metastatic HER2 + breast cancer (HER2CLIMB-02) | 3 | HER2+ with or without BM | 460 | Tucatinib + TDM1 vs placebo + TDM1 | PFS |
| New drugs | |||||||
| PARPi | |||||||
| Veliparib + cisplatin | NCT02595905 | Phase 2 randomised placebo-controlled trial of cisplatin with or without ABT-888 (veliparib) in metastatic triple-negative breast cancer and/or BRCA-mutation-associated breast cancer, with or without brain metastases | 2 (randomised, two arms) | TN and/or BRCA-mutated mBC with or without BM | 333 | Cisplatin + placebo vs cisplatin + veliparib | PFS |
| Immuno-oncology therapy | |||||||
| SHR-1316 | NCT04303988 | A prospective, single-arm, single-center, multi-cohort Phase 2 clinical study of HER2-positive and triple-negative breast cancer brain metastases | 2 (HR−/HER2− and HR+/HER2+ ) | HR−/HER2− with BM | 59 | SHR-1316 or bevacizumab or platin | CNS ORR |
| Nivolumab + SRS | NCT03807765 | Phase 1b study of stereotactic radiation and nivolumab in the management of metastatic breast cancer brain metastases | 1b | 1–10 BM largest ≤ 4 cm | 12 | Nivolumab + SRS the week after initial dose of Nivolumab | Number of patients experiencing DLTs |
| Atezolizumab + SRS | NCT03483012 | A Phase 2 study of atezolizumab in combination with stereotactic radiation for patients with triple-negative breast cancer and brain metastasis | 2 | TN BCBM largest ≤ 3 cm | 45 | Atezolizumab + SRS within 14 days after MRI | CNS-PFS |
| Pembrolizumab + SRS | NCT03449238 | Pembrolizumab and stereotactic radiosurgery (Srs) of selected brain metastases in breast cancer patients | 1/2 (one arm) | 2 BM minimum largest ≤ 4 cm | 41 | Pembrolizumab infused one day before SRS | Tumour-response for non-irradiated BM at 8 weeks |
| Intrathecal trastuzumab | |||||||
| Weekly dose (French study) | NCT01373710 | Phase 1/2 study of safety and efficacy of intrathecal trastuzumab administration in metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer patients developing carcinomatous meningitis | 1/2 | HER2+ carcinomatous meningitis | 34 | Trastuzumab weekly Phase 2 dose: 150 mg | Weekly MTD |
| Twice-weekly dose (US study) | NCT01325207 | Phase 1/2 dose escalation trial to assess safety of intrathecal trastuzumab for the treatment of leptomeningeal metastases in HER2-positive breast cancer | 1/2 | HER2+ leptomeningeal metastases | 34 | 10 mg or 20 mg or 30 mg or 40 mg twice-weekly for 4 weeks, then once-weekly 4 weeks then every 2 weeks | Number of DLTs |
| High-dose trastuzumab | |||||||
| Intra-arterial cerebral infusion | NCT02571530 | Phase 1 trial of super-selective intra-arterial cerebral infusion of trastuzumab after blood–brain barrier disruption for the treatment of cerebral metastases of HER2/Neu positive breast cancer | 1 | HER2+ with BM | 48 | Intra-arterial cerebral infusion of trastuzumab | MTD |
| Blood–brain barrier disruption | |||||||
| ExAblate Neuro System | NCT03714243 | A study to evaluate the safety and feasibility of blood–brain barrier disruption using MRI-guided focused ultrasound in the treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer brain metastases | Not applicable | HER2+ with BM | 10 | ExAblate Model 4000 type-2 temporarily | Adverse events |
| Targeted therapy | |||||||
| Entrectinib or abemaciclib or GDC-0084 | NCT03994796 | Genomically-guided treatment trial in brain metastases | 2 (three arms) | CDK or PI3K or NTRK/ROS1 mutation with BM | 150 |
Arm1: Abemaciclib Arm2: GDC-0084 Arm3: Entrectinib |
CNS ORR |
| Palbociclib + trastuzumab | NCT02774681 | A Phase 2 single-arm study of palbociclib in patients with metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer with brain metastasis | 2 (one arm) | HER2+ with BM | 12 | Palbociclib + trastuzumab IV | CNS radiographic response rate |
| Palbociclib + trastuzumab + lapatinib + fuvelstrant | NCT04334330 | Palbociclib, trastuzumab, lapatinib and fulvestrant treatment in patients with brain metastasis from ER positive, HER2 positive breast cancer: a multicenter, prospective study in China | 2 (one arm) | HER2+/ER+ with BM | 48 | Palbociclib + trastuzumab + lapatinib + fuvelstrant | CNS ORR |
| Tucatinib + abemaciclib + trastuzumab + AI | NCT03846583 | Phase 1b trial of tucatinib in combination with abemaciclib and trastuzumab for patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer | 1b | ER+/HER2+ with or without BM | 53 | Tucatinib + abemaciclib + trastuzumab + AI | MTD |
| Afatinib | NCT02423525 | A Phase 1 dose escalation and central nervous system (CNS) pharmacokinetic study of the ErbB family inhibitor afatinib in patients with recurrent or progressive brain cancer | 1 |
Cohort f: BM Cohort h: leptomeningeal metastases |
24 | Afatinib: 80 mg/4d or 120 mg/4d or 180 mg/4d or 280 mg/7d | Rate of DLTs of pulsatile afatinib |
| Afatinib | NCT02768337 | Cambridge brain mets trial 1: a proof-of-principle Phase 1b/randomised Phase 2 study of afatinib penetration into cerebral metastases for patients undergoing neurosurgical resection, both with and without prior low-dose, targeted radiotherapy | 1b/2 (two arms randomised) | Operable BCBM | 70 |
Afatinib + /− radiation Arm 1: no radiotherapy Arm 2: 2 Gy Arm 3: 4 Gy |
Ratio of fatinib concentration in resected BM vs plasma |
| Afatinib + TDM1 | NCT04158947 | A randomised study of HER2-positive breast cancer patients with active refractory brain metastases treated with afatinib in combination with T-DM1 vs T-DM1 alone | 1/2 (two arms randomised) | HER2+ with BM | 130 | Afatinib + TDM1 vs TDM1 | Safety and tolerability of TDM1 and Afatinib RP2D |
| Pyrotinib + vinorelbine | NCT03933982 | Pyrotinib plus vinorelbine in patients with brain metastases from HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer: a prospective, single-arm, open-label study | 2 (one arm) | HER2+ with BM | 30 | Pyrotinib daily + vinorelbine weekly | CNS ORR |
| Pyrotinib + temozolomide | NCT04303988 | A prospective, single-arm, single-center, multi-cohort Phase 2 clinical study of HER2-positive and triple-negative breast cancer brain metastases | 2 (HR−/HER2− and HR+/HER2+ ) | HR+/HER2+ with BM | 59 | Pyrotinib + temozolomide IV | CNS ORR |
| Pyrotinib + capecitabine | NCT03691051 | Pyrotinib plus capecitabine in patients with brain metastases from HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer: a single-arm, open-label, ahead study | 2 | HER2+ with BM | 102 | Pyrotinib + capecitabine | intracranial-lesion-ORR |
| Sorafenib + WBRT | NCT01724606 | Whole-brain radiotherapy (WBRT) with sorafenib for breast cancer brain metastases (BCBM): a Phase 1 study | 1 | New and/or progressive BM WBRT indication | 21 | Sorafenib 200 mg, 400 mg or 600 mg + WBRT | MTD |
| AZD1390 + WBRT | NCT03423628 | A Phase 1, multicentre study to assess the safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of ascending doses of AZD1390 in combination with radiation therapy in patients with glioblastoma multiforme and brain metastases from solid tumours | 1 | Arm B: BCBM eligible | 132 | 1–3 cycles of AZD1390 + WBRT or PBRT | Incidence of DLTs |
| GDC-0084 + trastuzumab | NCT03765983 | Phase 2 trial of GDC-0084 in combination with trastuzumab for patients with HER2-positive breast cancer brain metastases | 2 | HER2+ new and/or progressive BM | 47 | GDC-0084 + trastuzumab | CNS ORR |
| MRI screening | |||||||
| MRI every 4 months | NCT03881605 | Routine MRI screening vs symptom-directed surveillance for brain metastases among patients with triple-negative and HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer (MBC): a single-centre randomised pilot study | 2 (randomised pilot study) | HER2+ BCBM and triple-negative BCBM | 50 | MRI screening vs clinical symptoms every 4 months during 1 year | Proportion of eligible patients agree to enroll and complete protocol |
| Histology-adapted (Dana-Farber) | NCT04030507 | Screening magnetic resonance imaging of the brain in patients with metastatic breast cancer managed with first/second-line chemotherapy or inflammatory breast cancer managed with definitive intent: a prospective study | 2 |
BCBM cohort 1: TNBC cohorts 2 + 3: HR+/HER2− and HER2+ cohort 4: inflammatory BC |
214 |
Cohort 1: MRI/6 months Cohorts 2 + 3: MRI at diagnosis or not Cohort 4: MRI at diagnosis |
Neurological quality of life at 12 months |
| Observational study | NCT03617341 | Brain monitoring for high risk of brain metastases in metastatic breast cancer | Cohort |
HER2+ and TNBC BCBM |
200 | MRI at diagnosis, first- and second-line treatment failure | BM incidence rates |
| Every 4 months vs every 12 months | NCT00398437 | Role of gadolinium enhanced brain magnetic resonance in the follow-up of metastatic breast cancer patients overexpressing HER2 Neu. A randomised prospective study | Prospective randomised study | HER2+ No CNS metastases | 96 | MRI every 4 months vs every 12 months | Survival without neurological symptoms due to BM and/or leptomeningeal involvement |
OS overall survival, PFS progression-free survival, SRS stereotactic radiosurgery, ORR overall response rate, DLT dose-limiting toxicity, MTD maximum tolerated dose, CNS central nervous system, BM brain metastasis, TN triple negative, AI aromatase inhibitor.
BCBM epidemiology
Incidence and prevalence
The incidence of BCBM has increased in in the last few years following improved survival rates of patients with MBC (particularly those with the HER2+ subtype) and increased detection of metastatic disease through advanced imaging techniques.14,15 Identified risk factors for BM are common risk and prognostic factors for metastatic disease: diagnosis of breast cancer before age 40,16,17 ER negativity,16,17 triple-negative status (ER–, progesterone receptor (PR)− and HER2−),18 high histological grade,19 overexpression of HER2,16,20 presence of extracerebral metastases (pulmonary, hepatic and lymphatic), number of extracerebral metastatic sites and location of extracerebral metastases,16,17 short time from diagnosis of cancer to metastatic disease21 and elevated lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels prior to treatment.22
In the ESME cohort, 4118 patients with BM among 16,701 MBC patients were screened between 2008 and 2014 and followed up for a median of 42.8 months. The overall BM prevalence was 24.6% (7.2% at MBC diagnosis and 17.5% during follow-up). BM was diagnosed based on symptom occurrence in 70.7% of patients, and through systematic imaging examination in 29.3% of patients. Due to the lack of data demonstrating a clinical benefit, brain screening for patients with MBC is not currently recommended in the US National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) and European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) guidelines.23 This explains why for 70.7% of patients, symptoms lead to diagnostic brain imaging. The ESME cohort is a real-life cohort that illustrates the daily practice in French cancer centres and hospitals. The prevalence of BM varied according to initial histological subtype of BC, with increased BM risk for ductal carcinoma, Scarff–Bloom–Richardson (SBR) grade III, ER+/HER2+, ER–/HER2+ and triple-negative (ER–, PR– and HER2–) subtypes. At initial BC diagnosis, BM was detected in 4.3% of ER+/HER2–, 9.2% of ER+/HER2+, 17% of ER–/HER2+ and 13% of triple-negative subtypes. Patients presented BM during their metastatic disease in 19% of ER+/HER2–, 34% of ER+/HER2+, 49% of ER–/HER2+ and 38% of triple-negative metastatic breast cancers.2 The development of BM in triple-negative BC patients frequently occurs with concurrent extracranial disease progression,18 in contrast with HER2-overexpressed BM, which often occurs with a stable extracranial status.24 BM-free survival (BM-FS) rates at 5 years were 68%, 50% and 30% for ER+/HER2–, ER+/HER2+ and ER– subtypes, respectively. A direct correlation between the time from first relapse and the incidence of BM existed for all three subgroups. For patients with ER– disease (HER– or HER2+), the prevalence of BM is 70% 5 years after metastatic diagnosis.
Survival and prognosis
During a 30-month follow-up, the median overall survival (OS) after BM diagnosis was 7.9 months. OS was independently associated with subtypes: the median OS after BM diagnosis was 18.9 months for ER+/HER2+, 13.1 months for ER–/HER2+, 7.1 months for ER+/HER2– and 4.4 months for ER–/HER2– (P < 0.0001).2 These differences in OS following BM diagnosis are mostly due to available and efficient systemic treatment—before the anti-HER2 therapy revolution, survival outcomes were comparable between patients with HER2+ and HER2– MBC. In a retrospective study, Dawood et al. showed that patients with HER2+ disease and CNS metastases treated with the recombinant humanised IgG1 monoclonal anti-HER2 antibody trastuzumab had better survival (11.6 months) compared with patients with HER2+ disease who had never received trastuzumab (6.1 months; hazard ratio (HR) for death 1.34, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.78–2.30, P = 0.28) and patients with HER2– breast cancer (6.3 months, HR for death 1.66, 95% CI 1.31–2.12, P < 0.0001).24
The poorer prognosis of patients with ER+/HER2– disease compared with patients with HER2+ disease is most likely due to the fact that BM is a late event in metastatic disease evolution in this subtype. Factors identified as conferring a good prognosis at the time of diagnosis of BM are young age (<60 years), good ECOG-performance status, molecular subtype (ER+ and/or HER2+), single BM and controlled systemic disease.25,26
The blood–brain barrier
As well as presenting a potential barrier to metastasising cells, the BBB can hinder the delivery of systemic therapies into brain tumours, thus decreasing intracranial response rates to treatment27 (Box 1).
However, with the growth of new, abnormal, vessels during tumour progression, the BBB can become disrupted and is referred to as the blood–tumour barrier (BTB).28,29 The BTB is more leaky than the BBB and heterogeneous, including in such permeability, which results in the uneven distribution of drugs in mouse models of brain metastasis.28 These characteristics could explain the discordant results from preclinical studies, some of which clearly favour a lower concentration of drug in experimental BM, while others have shown that some chemotherapy drugs can penetrate experimental BM as efficiently as they can for extracerebral metastatic disease.27,28,30–32 Furthermore, pharmacokinetics particularity might not be the only barrier to drug efficacy in BM. Preclinical studies have shown that trastuzumab penetrates experimental BM as efficiently as it does extracerebrally localised metastases, but nevertheless shows decreased activity in the brain.32 These results have led some authors to reconsider whether mechanisms beyond inadequate drug penetration across the BBB, such as brain-specific drug resistance, might be operative in BM.33 Translational clinical diffusion studies of patients with CNS metastatic disease have also shown that chemotherapy and trastuzumab can accumulate in BM. Fine et al. report that patients who receive an infusion of paclitaxel prior to BM surgery show a significant concentration of taxane in the metastatic tissue, particularly at the centre of the metastases:34 2507 ng/gm tumour for an estimated therapeutic level of >1000 ng/gm.27 Dijkers et al. have shown that [89Zr]-trastuzumab can be detected in BM at the same median concentration than in bone metastasis of patients with HER2+ MBC.35 However, the results of Lockman et al. and Dijkers et al. in humans revealed a large variability of concentrations in BMs. Taken together, these studies show that the BTB is more permeable to chemotherapy than the BBB, at least in the case of macrometastatic disease with established neovascularisation.28 The difference between these two entities (BBB and BTB) might explain the observed activity of most medical treatment on established BM (see below).
However, BBB-generated ‘sanctuary’ might be more relevant with regard to micrometastatic deposits in the adjuvant setting and for meningeal carcinomatosis. Neovascularisation plays a key role in the BBB disruption. It occurs in response to central hypoxia in large nodular metastases. Micrometastases and meningeal carcinomatosis are therefore less neovascularised and therefore their BBB is theoretically less permeable than macrometastases’ one. Indeed, large positive adjuvant trials of HER2-targeted therapy repeatedly failed to show any significant decrease in CNS relapse in the experimental arm compared with the control arm.36,37 Furthermore, in patients receiving standard intravenous trastuzumab, pharmacokinetic analysis showed infra-therapeutic concentrations in the lateral cephalometric radiograph.
Box 1 (see Fig. 1).
Blood–brain barrier (BBB)
Highly selective semipermeable border of endothelial cells that prevents non-selectively crossing from blood into the extracellular fluid of the central nervous system.
Selectivity is due to the tight junctions between the endothelial cells of brain capillaries.
Astrocyte cell projections provide biochemical support to endothelial cells.
Microglial cells, primary immune cells of the CNS, involved in immune response and homoeostasis by scavenging, phagocytosis and extracellular signalling.
Mesenchymal stroma cells protect the blood–brain barrier.
Blood–tumour barrier (BTB)
Highly heterogeneous with non-uniform permeability and active efflux of molecules.
Tumoral invasion, perivascular growth and neoangiogenesis disrupted BBB creating BTB.
Epithelial cells and tight junctions are disconnected and allow non-selectively crossing from blood into the extracellular fluid.
Tumoral mesenchymal stroma cells could metastasise with cancer cells and support tumoral development.
Current treatment options for BMBC
Current therapeutic options for BM include both local (surgery and radiotherapy) and systemic treatments (chemotherapy, therapeutic antibodies and tyrosine-kinase inhibitors) or a combination of several modalities.38–40 Regardless of the initial BC subtype, if the estimated life expectancy is greater than 3 months and extra-CNS disease is controlled, it is recommended that cases of up to 10 BM be systematically discussed by multidisciplinary staff. If the estimated life expectancy is less than 3 months, appropriate supportive care, whole-brain radiotherapy (WBRT) or exclusive systemic treatment will be proposed.41 Given that not only breast cancer but other cancer types were included in the radiotherapy studies detailed in the following paragraphs, the results cannot discard the influence of this variable in the results.
Surgery followed by radiotherapy
The use of surgery is most often reserved for patients with good performance status, few lesions or large symptomatic lesions (≥3 cm). Surgery followed by radiation therapy has been shown to improve OS and symptom control vs radiation therapy alone.42,43 Patchell et al. demonstrated that, in patients with a single BM (comprising 9.5% of cases of BMBC), WBRT after complete surgical resection reduced the rate of recurrence at both the initial metastatic site (10% vs 46%, P < 0.001) and other brain sites (14% vs 37%, P < 0.01), and reduced death due to intracranial progression (14% vs 44%, P = 0.003). However, OS was similar between the WBRT and the control arm.44 In addition, WBRT has short- and long-term toxicities, including neurocognitive side effects and decreased quality of life.45,46
Two randomised clinical trials compared post-operative WBRT to post-operative stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS), a precise form of radiotherapy that delivers highly conformal high-dose radiation to restricted areas to kill small groups of cells with minimal damage to the surrounding normal tissues.47,48 One of these studies included patients with up to three lesions. In both studies, local control was equivalent or better with SRS and there was a lower risk of cognitive impairment; no differences in OS were seen between the radiotherapeutic approaches. Therefore, after surgical resection, the use of SRS is the recommended option whenever feasible.47,48
Pre-operative SRS
In a multi-institutional retrospective analysis with 180 patients receiving pre-operative SRS or postoperative SRS, Patel et al. demonstrated a significantly lower rate of symptomatic radionecrosis (16.4% vs 4.9%) and leptomeningeal disease (cancer in the leptomeninges, 16.6% vs 3.2%) using the neoadjuvant approach, but similar rates of local recurrence, distant brain recurrence and OS occurred between the two arms (37.5% BMBC).49 A two-arm trial in which patients are randomised to receive SRS before or after surgical removal aims to investigate whether 1-year leptomeningeal disease-free survival will be increased using the neoadjuvant approach (NCT03741673). The neoadjuvant SRS (NaSRS) non-randomised Phase 2 study is investigating the outcome of patients with 1–6 BCBMs treated with a single fraction of SRS before surgical removal of the metastases (NCT03368625).
SRS alone
When surgical resection is not feasible, SRS alone is the recommended approach. Given the short- and long-term neurological toxicities associated with the use of WBRT, its use should be delayed as long as possible in favour of SRS. A retrospective trial carried out in Japan has shown that patients with up to ten metastases can be safely treated using SRS without increased toxicities (20.6% BMBC). Patients with 2–4 BM and patients with 5–10 BM had similar OS (10.8 months in both arms). Each treatment group had excellent local control (89% vs 90%) and required low rates of salvage WBRT (10 vs 8%). Two-year neurological death, new brain-lesion incidence and neurocognitive outcome were also similar between the two groups. However, the risk of leptomeningeal dissemination was significantly higher in the 5–10 BM arm than in the 2–4 BM arm (22% vs 13%, respectively).50,51 As there are more metastases, either the diffusion process is more advanced or the cancer cell seeds have a greater affinity for the brain tissue. Consequently, the probability of minimal initial carcinomatous meningitis or secondary diffusion is greater.
Grandhi et al. demonstrated a high rate of local control in patients with ≥10 BM receiving SRS alone (24.6% BMBC) but observed a median OS of only 4 months.52 A Phase 2 trial in China examined whether fractionated doses of SRS were safer (reducing necrosis) and more effective (increasing local control) than single-dose SRS for patients with 1–10 BM (NCT04061408). In any case, the global volume of BM, rather than the total number of BM, seemed to be an important factor to take into account.50 In patients with up to ten metastases and a volume of less than or equal to 30 cc, SRS is the recommended treatment option.41
WBRT alone
The use of WBRT alone is indicated only in patients with more than ten BM for whom local treatment is not appropriate and in patients with new lesions on which additional SRS cannot be performed.41 Repeat SRS twice or more time on progressive BM is an increasingly used therapeutic option, although little data are available to support this practice. The tumour control following repeat SRS for locally recurring metastatic brain tumours after a previous SRS is relatively lower than that for primary SRS. However, both low tumour volume and high-prescription radiation dose were significantly related to the tumour control following repeat SRS for these tumours after previous SRS, which is a general understanding of primary SRS for metastatic brain tumours.53 In asymptomatic patients, a systemic therapy approach, based on the BC subtype, might be preferred. In the absence of cerebral symptomatology, the urgency is to systemic control and the best treatment for brain metastasis remains the treatment of cancer. WBRT should be limited to symptomatic patients without feasible systemic therapy options and with an urgent need of symptom relief. In particular for HER2+ BCBM patients, the late-onset toxicities of WBRT should be weighed up against the favourable prognosis as indicated by different prognostic scores.54 It remains unknown whether SRS improves the quality of life of patients with 5–20 BM relative to WBRT—SRS avoids whole-brain radiation, but the potential risk of recurrence is increased. A randomised trial that compares WBRT to SRS for patients with 5–20 metastases who have received no prior radiation is ongoing, with quality of life as the primary endpoint (NCT03075072).
A notable development in WBRT is the use of intensity-modulated radiotherapy techniques—termed hippocampal avoidance WBRT (HA-WBRT)—that avoid hippocampal neural stem cells, which are essential for new memory formation.55 Encouraging data on toxicity were reported in Phase 2 studies of HA-WBRT when compared with the historical control, WBRT without hippocampal avoidance.56 A large, randomised clinical trial of 518 patients (18.5% BMBC) assigned to HA-WBRT or WBRT revealed no difference in clinical progression between the two arms, but the HA-WBRT group experienced a significantly lower risk of cognitive function deterioration (HR, 0.74, P = 0.02). This result favours the use of HA-WBRT over classical WBRT.57 When SRS is not possible, HA-WBRT is the recommended option.57
Chemotherapy agents
For systemic therapies, various drugs, including older chemotherapy agents such as capecitabine, cyclophosphamide, 5-fluorouracil, methotrexate, vincristine, cisplatin, etoposide, vinorelbine and gemcitabine, have shown activity in the treatment of BM, with an objective response rate (ORR) of over 30%, a median duration of neurological remission for responder patients of up to 30 weeks and a median OS of up to 31 weeks, similar to the systemic response rates usually observed similar to the systemic response rates commonly observed with the same drug molecules.34,58,59 Combinations such as cisplatin–etoposide, capecitabine–temozolomide and cisplatin–temozolomide have been analysed in retrospective Phase 1 and Phase 2 studies, with an ORR of up to 40%, a median progression-free survival (PFS) of up to 2.9 months and a median OS of up to 5.5 months.59–61 However, the results of these slightly older studies might be affected by incomplete diagnostic imaging (cranial CT scan instead of MRI, for example) and non-standard chemotherapy regimens. Consequently, the evidence for the efficacy of chemotherapeutic agents for patients with BCBM remains limited. Furthermore, owing to the limited number of patients with BCBM, none of these protocols has been approved for the treatment of this indication. Furthermore, the PFS and OS figures are dismal, and traditional chemotherapy alone cannot be considered to be a satisfactory treatment for BCBM. Nevertheless, these studies do support the fact that the BTB is at least partially permeable to systemic treatment.
New chemotherapy agents, such as third-generation taxanes, are in development for the specific indication of BCBM. Several polymeric conjugates of irinotecan and SN-38 (the active metabolite of irinotecan) are also being investigated. These include etirinotecan pegol and MM-398.62 Etirinotecan pegol is a long-acting derivative of irinotecan that prolongs exposure to SN-38 while reducing its toxicity. In a predefined sub-study of the BEACON study, in which 67 patients with BCBM were randomised to etirinotecan pegol or a treatment of physician’s choice—eribulin, vinorelbine, gemcitabine, nab-paclitaxel, paclitaxel, ixabepilone or docetaxel—longer survival was observed in the etirinotecan pegol group (10.0 months vs 4.8 months, HR 0.51, P < 0.01).63 This molecule is currently being evaluated against the treatment of the investigator’s choice in a randomised trial in patients with stable brain dissemination (ATTAIN Phase 3 NCT02915744). Another Phase 2 international trial is currently evaluating the efficiency and safety of MM-398, a nanoliposomal irinotecan thought to penetrate the BBB, in patients with HER2– MBC (The Phenomenal Study, NCT03328884).
Trastuzumab-based regimens for patients with HER2+ BM
To date, evidence for the direct efficacy of HER2-targeting monoclonal antibodies trastuzumab, trastuzumab–emtansine (T-DM1) and pertuzumab on BMBC is based on the retrospective subgroup analysis of clinical trials or on small cohorts. Nevertheless, evidence mostly argues in favour of the clinical efficacy of these molecules on BM.
Park et al.64 demonstrated that BC patients receiving trastuzumab had a significantly longer median time to BCBM (15 months vs 10 months, P = 0.035) and median time to death (14.9 vs 4.0 months, P = 0.0005) than patients who were not treated with trastuzumab. Similarly, Rostami et al.65 also demonstrated that the mean survival of patients with HER2+ BCBM was prolonged when treated with trastuzumab (17.5 vs 11 months). In a retrospective study, Dawood et al.24 showed that patients with HER2+ disease treated with trastuzumab had longer median time to CNS metastasis (13.1 months) compared with patients with HER2+ disease who had never received trastuzumab (2.1 months, HR 2.13, 95% CI 1.51–3.00, P = 0.28) and patients with HER2– breast cancer (8.9 months, HR 1.5, 95% CI 1.15–1.95, P < 0.0001).
These studies show a correlation between the use of trastuzumab and the development of less aggressive BM. However, it is impossible from these results to conclude whether trastuzumab had a direct effect on BM or an indirect one (perhaps fewer secondary BM was formed following new systemic lesions).
Trastuzumab–emtansine (T-DM1) is an antibody–drug conjugate that has been approved for the second-line treatment of HER2+ MBC after the failure of trastuzumab and pertuzumab, following the results of the randomised Phase 3 EMILIA trial.66 T-DM1 was associated with a statistical and clinically meaningful improvement of PFS and OS (HR for OS = 0,68, P < 0,001) compared with a combination of the tyrosine-kinase inhibitor (TKI) lapatinib and capecitabine. An exploratory analysis of second-line T-DM1 focusing on patients with treated and asymptomatic BM at baseline showed improved OS in the T-DM1 group over the lapatinib–capecitabine group (26.8 vs 12.9 months, HR = 0.38, P = 0.008). Otherwise, the incidence of BM progression was similar between the T-DM1 arm and the capecitabine–lapatinib arm.67 Bartsch et al. investigated the intracranial response rates to T-DM1 treatment in BCBM patients. T-DM1 was administered at a dose of 3.6 mg once every 3 weeks as a primary systemic therapy for BM or upon documented CNS progression after initial local treatment. At 8.5 months median follow-up, intracranial PFS was 5 months and median OS from initiation of T-DM1 was not reached.68 Direct efficacy of T-DM1 on BM has also been shown in several retrospective analyses.69 A subgroup analysis of 398 patients with BM included in the KAMILLA single-arm open-label, Phase 3b study published in 2020, confirms the efficacy and safety of T-DM1 in this situation, with a BM response rate of 21%, a median PFS of 6 months and a median OS of 19 months.70
Pertuzumab–trastuzumab combination for patients with HER2+ BM
Pertuzumab is a recombinant humanised monoclonal antibody targeting the dimerisation domain II of HER2 that was approved for the first-line treatment of patients with HER2+ MBC following the randomised Phase 3 placebo-controlled CLEOPATRA trial. This study showed that the combination of pertuzumab with trastuzumab and a taxane was superior to the standard trastuzumab plus taxane combination (HR for PFS 0.68, P < 0.001; HR for OS: 0.68, P < 0.001).71 Although the patients reportedly did not have BM at diagnosis, disease relapse occurred in the brain in 13% of patients. As these latter patients did not develop systemic disease before brain progression, it is likely that this progression actually resulted from pre-existing small BM that was undetected at diagnosis. In this subpopulation, the median BM-PFS increased from 11.9 to 15 months with the addition of pertuzumab (HR = 0.58, P = 0.0049).72 Furthermore, median OS tended to be longer in the pertuzumab arm (34.4 months) compared with the control arm (26.3 months). These results suggest that the pertuzumab–trastuzumab and taxane combination shows comparable activity on BM and systemic disease. Nevertheless, a specific prospective study is warranted to confirm this hypothesis.
First-generation TKIs for the treatment of HER2+ BM
Small-molecule tyrosine-kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are promising agents for the treatment of Her2+ BCBM as they cross the BBB and can block several receptors of the ErbB2 family. Lapatinib, a first-generation TKI, is a dual inhibitor of HER1 and HER2 kinases. Used as a monotherapy, this agent has shown poor results for BM,73 but better results were obtained in combination with capecitabine. The lapatinib–capecitabine combination is associated with a brain-response rate of up to 38% after radiotherapy.73–75 In the LANDSCAPE trial, lapatinib–capecitabine given at the time of BM diagnosis led to a response rate of 66%; the median time to progression (TTP) was 5.5 months and the median time to brain radiotherapy was 8.3 months.76 These results are consistent with the efficacy of this therapeutic combination on extracerebral diseases such as BC,77 but remain modest in terms of clinical benefits. In this trial, half of the patients had asymptomatic BM, and therefore intracranial response rates might have been overestimated. However, the results indicate a better outcome for patients diagnosed at an early stage of intracranial disease and therefore raise the question of implementing a standard screening procedure in a high-risk population (discussed later). In 2011, Lin et al. published the results from a randomised Phase 2 trial comparing the efficacy and safety of lapatinib–capecitabine with lapatinib–topotecan in patients pretreated with trastuzumab and cranial radiotherapy for BCBM.78 This study was discontinued early because the lapatinib–topotecan arm was too toxic and no objective response was observed. However, the response rate in the lapatinib–capecitabine arm was 38%.
Despite these important results, it has not been shown that the lapatinib–capecitabine combination was superior to trastuzumab-based treatment for BM control—neither as a ‘preventive’ treatment for patients without BM at relapse in the first-line CEREBEL study comparing lapatinib–capecitabine with trastuzumab–capecitabine (3% vs 5%, P = 0.36),79 nor for established BM when compared with T-DM1 in the subgroup analysis of the EMILIA study.67 Notably, these results provide additional evidence that the BTB is generally permeable to common systemic treatment, resulting in comparable results on BM and systemic disease in most randomised trials.
New-generation TKIs for the treatment of HER2+ BM
New TKIs with a specific BM endpoint, particularly neratinib, a new irreversible pan-HER TKI and tucatinib, a HER2-specific TKI,80,81 have been developed.
Neratinib has been tested in combination with capecitabine in patients with HER2+ BCBM.82 Of the 37 patients, 89%, 22% and 14% were previously treated with trastuzumab, T-DM1 and another investigational HER2-directed agent, respectively, and most had received previous radiotherapy (65% WBRT and 32% SRS) and several chemotherapy agents. Freedman et al. reported 18 partial responses, with a BM volumetric response of 49%, 6-month PFS of 38% and a median time-to-BM progression of 5.5 months. Fifty-one percent (51%) of patients experienced grade 3 toxicities, of which 32% were gastrointestinal events, mostly diarrhoea, requiring specific prophylactic management. This result was supported by the NALA -randomised second-/third-line trial, including 130 patients with non-progressive BM at study entry.83 The overall cumulative incidence of intervention for BM was reduced from 29.2% with lapatinib–capecitabine to 22.8% with neratinib–capecitabine (P = 0.043).83 Cohort 4 of the Phase 2 trial NCT01494662 will study the combination of neratinib and T-DM1 for patients with untreated or progressive HER2+ BCBM with or without prior treatment with T-DM1.
The activity of tucatinib on BM was a prespecified secondary endpoint of the large pivotal HER2CLIMB trial,84 which analysed the addition of tucatinib to trastuzumab plus capecitabine in patients with pretreated HER2+ MBC. Patients with BM could be included even if BM was not pretreated or if they were active after local treatment. For patients with a history of BM (291 patients), the risk of progression or death was reduced by 68% with the addition of tucatinib vs placebo (HR 0.32, P < 0.00001), with a median PFS of 9.9 months vs 4.2 months, respectively. Impressively, median OS was 18.1 months in the tucatinib arm vs 12.0 months in the placebo arm (HR, 0.58, 95% CI, 0.40–0.85, P = 0.005). In fact, the efficacy of tucatinib on this BM population is consistent with the efficacy of tucatinib on the whole population (HR for PFS 0.54, P < 0.001; HR for OS: 0.66, P = 0.005). The main toxicity was diarrhoea, with 12.9% of grade 3 in the tucatinib arm vs 8.6% in the placebo arm.84 This study is the largest randomised trial to date with a specific BM endpoint and consequently provides the highest levels of evidence regarding medical treatment of patients with HER2+ BCBM. Interestingly, it shows that, once again, the effects of medical treatment on the progression of brain disease are mostly equivalent to those observed in extracerebral diseases. The HER2CLIMB2 trial comparing T-DM1 associated with tucatinib vs T-DM1 alone is ongoing (NCT03975647).
Treatment for patients with HER2– BM
For the treatment of patients with ER+/HER2– BCBM, some responses have been observed with tamoxifen,85 aromatase inhibitors86,87 and fulvestrant88, and therefore, in the absence of therapeutic alternatives, these low-toxicity treatments have a place in paucisymptomatic ER+ patients.
Studies assessing late-line agents that target cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) 4 and 6 have been published. In an open-label, Phase 2 trial, abemaciclib was proposed for the treatment of patients with ER+/HER2− (Part A) or ER+/HER2+ (Part B) BCBM. Patients in Part B did not reach the primary endpoint, the investigator-assessed objective response rate (ORR). Patients in Part A (n = 58) had an intracranial ORR of 5.2%, an intracranial clinical benefit rate of 24% and a median PFS of 4.9 months with some long responses (n = 11). A subgroup of 8 patients in this study had surgical resection of BM while undergoing treatment, and it was shown in the resected samples that therapeutic levels of abemaciclib were reached in BM, demonstrating abemaciclib and its active metabolites penetrated the BBB.89
For patients with triple-negative BCBM, two chemotherapy regimens seem to show specific CNS activity: the anti-vascular endothelial growth factor agent bevacizumab plus paclitaxel in a small Phase 2 study (70% ORR but only 6 patients with triple-negative MBC)90 and the microtubule inhibitor eribulin in case reports.91 A Phase 2 trial presented at ASCO 2013 highlighted a combination of bevacizumab plus carboplatin in the treatment of BCBM.92 In this study, 38 patients were treated with bevacizumab plus carboplatin, and trastuzumab was added if the tumour was HER2+. The composite brain ORR was 63% and the global ORR was 45%. For these HER2– patients, therefore, standard chemotherapy comprising capecitabine, eribulin or carboplatin plus bevacizumab can be used for progressive BM after local treatment.
Potential new drugs for the treatment of BM
According to the ClinicalTrial.gov site (accessed May 2020), there are 108 studies on BCBM, of which 24 are recruiting to test new drugs, including poly-ADP ribose polymerase (PARP) inhibitors (4 studies), immuno-oncology therapy (4), CDK4/6 inhibitors (2), TKIs (7), phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitors (1), ATM inhibitors (1) and BBB disruptors (1).
PARP inhibitors
Inhibitors of the enzyme PARP are approved for the treatment of germline BRCA-mutated MBC. In the Phase 3 EMBRACA trial of patients with BRCA-mutated advanced and/or MBC, 15% of patients in the talazoparib treatment arm had stable/treated CNS disease at baseline. In this subgroup analysis, the benefit in terms of PFS was even more significant than it was for patients without BM (HR 0.32, 95% CI 0.15–0.68 and HR 0.58, CI 95%, 0.43–0.78, respectively), suggesting the possibility of a CNS effect of the drug.93 In the OLYMPIAD study, the benefit of olaparib vs practitioner’s choice among patients with HER2– germline BRCA-mutated BCBM appeared to be comparable with the benefit observed in the whole study population, for both PFS (8.3 months vs 2.8 months) and ORR (64.7% vs 20.0%). The study was not designed to detect differences between subgroups, with a small number of patients and insufficient power, and so the results should be interpreted with caution.94 In BROCADE 3 with veliparib, only 4% of patients had a history of CNS metastases; the evidence of efficacy on BCBMs is therefore limited.95
Veliparib is the first PARP inhibitor to be tested specifically in BCBM; it was used in combination with WBRT in a Phase 1 trial recruiting patients with BM from primary solid tumours.96 Median OS in the breast cancer group was 8 months (2.8–15.0 months) vs an OS of 4.9 months predicted by nomogram modelling. A nomogram represents the relations between three or more quantitative variables by means of several scales, arranged in such a way that the value of a variable can be found by a simple geometric construction, for example by drawing a straight line intersecting the other scales at the appropriate values. The main toxicities associated with this treatment approach were asthenia (30%) and nausea (20%), with no new toxicities observed.96 Additional studies with PARP inhibitors are ongoing: SWOG S1416 is a Phase 2 study of cisplatin with or without veliparib in patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer and/or BRCA-mutation-associated breast cancer, with or without brain metastases (NCT02595905).
Immuno-oncology therapy
The development of immuno-oncology drugs for the treatment of BM was initially slow owing to the concept that the brain is ‘immunologically privileged’—that is, antigens present in the brain do not elicit an inflammatory immune response. However, there is some evidence that immune infiltrates are present in melanoma-derived BM,97 and clinical trials in metastatic melanoma patients reported comparable ORR and OS in patients with or without asymptomatic BM at inclusion treated with the immune-checkpoint inhibitors nivolumab (which targets the programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1)) and ipilimumab (which targets CTLA-4).98 Immuno-oncology therapy could therefore be effective against BM as it is against other metastatic sites.
Atezolizumab (an antibody that targets the PD-1 ligand, PD-L1) has been approved in combination with nab-paclitaxel for the treatment of triple-negative MBC. Subgroup analyses showed a benefit for patients without BM (HR 0.80, 95% CI 0.69–0.93) but not for patients with BM (HR 0.86, 95% CI 0.50–1.49). However, the HRs were similar, and the absence of statistical significance could be explained by the small population size with BM, as only 6.3% of the study population had a history of BM (61 patients).99 As with other tumour locations, if immunotherapy proves effective for MBC, patients with BCBM could also benefit from an intracerebral response. A Phase 2 study is underway to evaluate the efficacy and safety of a new anti-PD-L1 antibody (SHR-1316) in combination with cisplatin/carboplatin and bevacizumab for triple-negative BCBM. The primary endpoint will be CNS ORR (NCT04303988).
The combination of immuno-oncology therapy using nivolumab (anti-PD-1, Phase 1 NCT03807765), atezolizumab (anti-PD-L1, Phase 2 NCT03483012) or pembrolizumab (anti-PD-1, Phase 1/2 NCT03449238) plus SRS is also under investigation. This latter trial is recruiting patients with at least two BM who are eligible to receive SRS in order to evaluate the potential abscopal effect of irradiating one lesion on other, non-irradiated lesions.
Other targeted therapy
A genomic-guided Phase 2 trial (Alliance A071701, NCT03994796) in which biopsies of intracranial and extracranial lesions are performed on patients with progressive BM to allow targeted sequencing on specific pathways (neurotrophic tropomyosin receptor kinase (NTRK), ROS1 fusions, CDK and PI3K pathways) is ongoing. In the event of actionable mutations, a matched targeted therapeutic agent known to have CNS penetrance will be proposed (entrectinib for NTRK and ROS1, abemaciclib for CDKs or GDC-0084 for PI3K). The objective is to determine whether targeting specific BM mutations will improve clinical outcomes.
Several studies are ongoing to further analyse targeted therapies such as CDK4/6 inhibitors, TKIs, PI3K inhibitors and ATM inhibitors. CDK4/6 inhibitors, which are able to cross the BBB, have generated a lot of interest. As well as the study with abemaciclib,89 a single-arm Phase 2 pilot trial with palbociclib monotherapy is currently enrolling patients with HER2+ BCBM (ER+ and ER) (NCT02774681). Furthermore, a single-arm trial in China will evaluate the efficacy of combining palbociclib, trastuzumab and lapatinib with fulvestrant in ER+/HER2+ BCBM (NCT04334330). For patients with ‘triple positive’ MBC, another original combination of tucatinib, abemaciclib and trastuzumab is currently being tested, with specific CNS secondary endpoints (NCT03846583).
With regard to TKIs, afatinib, an inhibitor of HER2 and other EGFRs, is currently being analysed: a Phase 1 study will determine the appropriate dose and safety for patients with HER2+ BM (NCT02423525) and a Phase 2 study will analyse afatinib penetrance into BM for patients having undergone BM surgery, with or without low-dose targeted radiation (NCT02768337). Afatinib is also being tested in combination with T-DM1 vs T-DM1 alone in a Phase 1/2 study (HER2BAT NCT04158947). Pyrotinib, an inhibitor of HER1, HER2 and HER4, is being tested in combination with vinorelbine in a single-arm Phase 2 trial for women with HER2+ BM (NCT03933982). Pyrotinib is also to be tested in combination with temozolomide injection (NCT04303988 cohort HR+/HER2+) and in combination with capecitabine (NCT03691051) in two Phase 2 single-arm trials, with CNS ORR as the primary endpoint. The anti-angiogenic TKI sorafenib and AZD1390, an ATM inhibitor, are both being tested in combination with WBRT in Phase 1 clinical trials (NCT01724606 and NCT03423628). Finally, the safety and efficacy of the combination of the PI3K inhibitor GDC-0084 with trastuzumab is being trialled in a single-arm Phase 2 trial for HER2+ BM (NCT03765983).
Intrathecal trastuzumab
Another emerging area of interest is the use of intrathecal trastuzumab for patients with leptomeningeal metastases. Numerous case reports and retrospective cohorts have compared intrathecal trastuzumab, intrathecal chemotherapy and WBRT, and shown intrathecal trastuzumab to be efficacious for some patients.100,101 The Phase 1 part of the study NCT01373710 has been published,102 and suggests a Phase 2 weekly dose of intrathecal trastuzumab of 150 mg. The Phase 2 trial using this dose regimen is ongoing. In another Phase 1 trial (NCT01325207), intrathecal trastuzumab was administrated twice a week for 1 month, then once a week for another month and then every week until progression.103 The maximum tolerated dose was 80 mg. In Phase 2, 5 patients (19.2%) showed partial response, 13 patients (50%) had stable disease and 8 patients (30.8%) showed disease progression. Median PFS was 2.4 months and median OS was 12.1 months. The primary endpoint of a 25% response rate has not yet been met. However, 69% of patients showed clinical benefit (stable disease or better).103
High-dose trastuzumab
The use of high-dose trastuzumab (6 mg/w) with pertuzumab to increase the intracerebral trastuzumab concentration has also been tested in patients with progressive BM after radiotherapy.104 This study was based on the fact that preclinical data supported the dose-dependent activity of trastuzumab in intracranial tumour models.32 Lin et al. demonstrated a modest clinical benefit with a pertuzumab–high-dose-trastuzumab combination in a Phase 2, open-label, single-arm study of 40 patients; CNS 0RR was 11% and 6-month CBR was 51%. No excess cardiotoxicity was observed but there was an increased incidence of limited grade 1–2 diarrhoea. Another way to increase trastuzumab concentration is to use a super-selective intra-arterial cerebral infusion of trastuzumab. A trial using such an approach is underway in patients with HER2+ BCBM (NCT02571530).
Blood–brain barrier disruption (BBBD)
As the BBB could, in theory, hinder drug delivery to the brain, three different strategies—involving chemical and mechanical means—are being developed to transiently disrupt the BBB to deliver higher concentrations of anti-HER2 drugs to the brain (Fig. 2). Obviously, such strategies will be of interest in the clinical situation where the BBB is indeed effective, and future clinical trials will have to assess this point.105 The first approach uses osmotic BBBD with certain drugs such as mannitol to open the blood vessels around the brain to enable methotrexate and carboplatin with or without trastuzumab to penetrate. However, a clinical trial using this method was discontinued prematurely owing to lack of evidence of efficacy (NCT00397501). Other, more promising, strategies are currently still at the preclinical stage. One technology currently undergoing testing is microbubble-assisted focused ultrasound (FUS), which uses oscillating microbubbles to generate micrometre-scale mechanofluidic effects to enhance drug transport. The combination of trastuzumab and FUS showed anticancer activity in the rat brain: after six weekly trastuzumab treatments with FUS, the mean tumour volume was significantly reduced, and survival was significantly prolonged.106 The combination of trastuzumab, pertuzumab and FUS also delayed the progression of experimental brain metastases.107 The Exablate Neuro system (INSIGHTEC), which serially disrupts the BBB temporarily and locally with MRI-guided FUS, will be tested in patients with HER2+ BCBM (NCT03714243). The third technology tested involves the use of nanoparticles conjugated with anticancer agents. Patil et al. demonstrated that, compared with the phosphate-buffered saline control, tumour-targeted nanoconjugates carrying molecular inhibitors of EGFR or HER2 significantly prolonged the survival of mice with Her2+ BCBM.108 Hamilton et al. also showed that nanoparticles coated with a tumour-penetrating peptide (iRGD) strongly inhibited tumour progression when applied in the early stages of metastasis development, indicating that this technology might provide a promising treatment for the prevention of BM.109
Fig. 2.
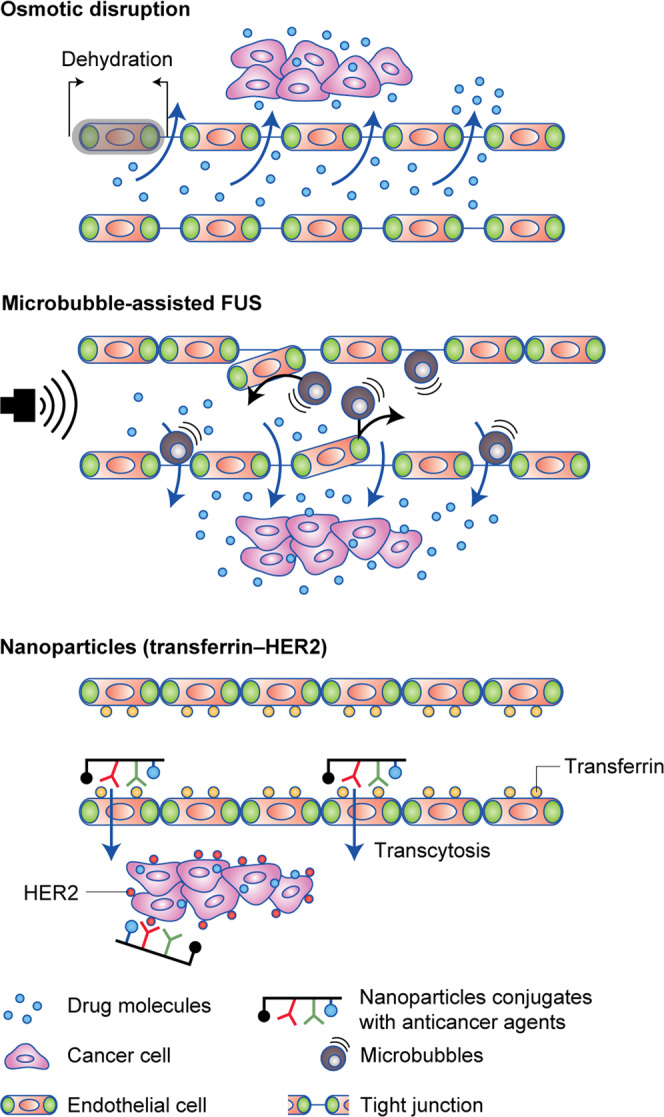
Main blood–brain barrier (BBB) disrupting strategies under development: osmotic disruption, microbubble-assisted focused ultrasound (FUS) and nanoparticules conjugated with cancer agent.
Systematic screening for the detection of BM?
Due to the lack of data demonstrating a clinical benefit, brain screening for patients with MBC is not currently recommended in the US NCCN and ESMO guidelines.23 Nevertheless, patients at high risk of developing BM could potentially benefit from screening strategies, as an earlier diagnosis could lead to a reduction in WBRT use and enable localised, less toxic and more effective BM treatment in a higher proportion of cases.23,110,111 Four studies are exploring the value of systematic radiological screening.
In the SYMPToM trial (NCT03881605), 50 women with HER2+ or triple-negative MBC will be randomised to receive either MRI or clinical surveillance for BM every 4 months for 1 year, although any patient under clinical surveillance who develops symptoms will receive an MRI. The Dana-Farber Cancer Institute trial (NCT04030507) will contain four patient cohorts: patients with triple-negative breast cancer will undergo screening MRI of the brain (single arm, one cohort), patients with ER+/HER2– and HER2+ subtypes will be randomised between screening MRI of the brain or not (two cohorts) and patients with inflammatory BC will undergo screening MRI of the brain (one cohort). The primary endpoints will be quality of life at 12 months, incidence of symptomatic BM and incidence of BM. Another trial, NCT03617341, comprises an observational cohort of 200 patients with TNBC or HER2+ BC in which MRI of the brain will be undertaken at the time of initial diagnosis, first- and second-line treatment failure. Finally, a randomised trial will analyse the survival outcome (without neurological symptoms owing to BM) in patients with HER+ MBC who undergo a brain MRI once every 4 months vs once every 12 months (NCT00398437).
Conclusions
The increased survival rates of breast cancer patients who have metastatic disease mean that an increasing incidence of BCBM, alongside the associated impairment of quality of life and OS, has become a problem that requires improved solutions. Local treatment, with surgery when possible, and SRS, remains central in the current treatment strategy. With regard to medical treatment, multiple studies have shown that the results obtained with conventional chemotherapy and targeted therapies are mostly consistent with the systemic efficacy observed with these same molecules. Thus, the intrinsic efficacy on tumour type appears to be more important than the issue of BBB diffusion to predict treatment usefulness, owing to the fact that the BTB is more permeable to systemic molecules than the intact BBB. Nevertheless, when patients with progressive BM after radiation therapy are treated with systemic treatment, prognosis remains poor, which has been recently suggested to correlate with additional organ-specific genomic alterations.13 The best results published to date have been obtained in patients with BM from HER2+ MBC, for whom all currently used combinations of chemotherapy and anti-HER2 therapy have shown some efficacy, with particularly impressive results obtained with the tucatinib–trastuzumab–capecitabine combination. Patients with BM from luminal or triple-negative MBC have fewer medical options currently, but CDK inhibitors, PARP inhibitors, PI3K inhibitors and immuno-oncology therapy are promising therapeutic candidates.
The individuality of patients with BCBM, in terms of clinical characteristics and treatment resistance, makes it necessary to develop specific clinical trials to generate new treatment strategies.105 In the near future, brain-specific therapies that target crosstalk with the microenvironment and brain-specific genomic alterations could provide significant benefits for patients. New therapeutic strategies with combinations of immunotherapy, radiotherapy and targeted therapies could increase efficacy while limiting the side effects. Finally, preventing the development of BM in the adjuvant setting using molecules that can cross the intact BBB is a particularly attractive option.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge George MORGAN for the translation of this paper.
Author contributions
Drafting the paper: C.B. and T.B.; revising the paper content: C.B., T.B. and L.E.; approving the final version of the paper: C.B., T.B. and L.E.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Data availability
Not applicable.
Competing interests
C.B. and L.E. declare no conflict of interest. T.B. reports personal fees and non-financial support from Roche, grants, personal fees and non-financial support from Novartis, grants, personal fees and non-financial support from AstraZeneca, grants, personal fees and non-financial support from Pfizer, personal fees from SeattleGenetics, outside the submitted work.
Funding information
None.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Weil RJ, Palmieri DC, Bronder JL, Stark AM, Steeg PS. Breast cancer metastasis to the central nervous system. Am. J. Pathol. 2005;167:913–920. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)61180-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Darlix A, Louvel G, Fraisse J, Jacot W, Brain E, Debled M, et al. Impact of breast cancer molecular subtypes on the incidence, kinetics and prognosis of central nervous system metastases in a large multicentre real-life cohort. Br. J. Cancer. 2019;121:991–1000. doi: 10.1038/s41416-019-0619-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Quattrocchi CC, Errante Y, Gaudino C, Mallio CA, Giona A, Santini D, et al. Spatial brain distribution of intra-axial metastatic lesions in breast and lung cancer patients. J. Neurooncol. 2012;110:79–87. doi: 10.1007/s11060-012-0937-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Schroeder T, Bittrich P, Kuhne JF, Noebel C, Leischner H, Fiehler J, et al. Mapping distribution of brain metastases: does the primary tumor matter. J. Neurooncol. 2020;147:229–235. doi: 10.1007/s11060-020-03419-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Valiente M, Ahluwalia MS, Boire A, Brastianos PK, Goldberg SB, Lee EQ, et al. The evolving landscape of brain metastasis. Trends Cancer. 2018;4:176–196. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2018.01.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Neman J, Termini J, Wilczynski S, Vaidehi N, Choy C, Kowolik CM, et al. Human breast cancer metastases to the brain display GABAergic properties in the neural niche. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2014;111:984–989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1322098111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sevenich L, Bowman RL, Mason SD, Quail DF, Rapaport F, Elie BT, et al. Analysis of tumour- and stroma-supplied proteolytic networks reveals a brain-metastasis-promoting role for cathepsin S. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014;16:876–888. doi: 10.1038/ncb3011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bonneh-Barkay D, Wiley CA. Brain extracellular matrix in neurodegeneration. Brain Pathol. 2009;19:573–585. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2008.00195.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Boire A, Zou Y, Shieh J, Macalinao DG, Pentsova E, Massagué J. Complement component 3 adapts the cerebrospinal fluid for leptomeningeal metastasis. Cell. 2017;168:1101–1113.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.02.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Brastianos PK, Carter SL, Santagata S, Cahill DP, Taylor-Weiner A, Jones RT, et al. Genomic characterization of brain metastases reveals branched evolution and potential therapeutic targets. Cancer Discov. 2015;5:1164–1177. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-15-0369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Priedigkeit N, Hartmaier RJ, Chen Y, Vareslija D, Basudan A, Watters RJ, et al. Intrinsic subtype switching and acquired ERBB2/HER2 amplifications and mutations in breast cancer brain metastases. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3:666–671. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.5630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sperduto, P. W., Mesko, S., Li, J., Cagney, D., Aizer, A., Lin, N. U. et al. Estrogen, progesterone and HER2 receptor discordance between primary tumor and brain metastases in breast cancer and its effect on treatment and survival. Neuro-oncology. 10.1093/neuonc/noaa025 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 13.Hu Z, Li Z, Ma Z, Curtis C. Multi-cancer analysis of clonality and the timing of systemic spread in paired primary tumors and metastases. Nat. Genet. 2020;52:701–708. doi: 10.1038/s41588-020-0628-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gobbini E, Ezzalfani M, Dieras V, Bachelot T, Brain E, Debled M, et al. Time trends of overall survival among metastatic breast cancer patients in the real-life ESME cohort. Eur. J. Cancer. 2018;96:17–24. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2018.03.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lin NU, Bellon JR, Winer EP. CNS metastases in breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004;22:3608–3617. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2004.01.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Slimane K, Andre F, Delaloge S, Dunant A, Perez A, Grenier J, et al. Risk factors for brain relapse in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2004;15:1640–1644. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdh432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Evans AJ, James JJ, Cornford EJ, Chan SY, Burrell HC, Pinder SE, et al. Brain metastases from breast cancer: identification of a high-risk group. Clin. Oncol. (R. Coll. Radio.) 2004;16:345–349. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2004.03.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lin NU, Claus E, Sohl J, Razzak AR, Arnaout A, Winer EP. Sites of distant recurrence and clinical outcomes in patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer: high incidence of central nervous system metastases. Cancer. 2008;113:2638–2645. doi: 10.1002/cncr.23930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Chow L, Suen D, Ma KK, Kwong A. Identifying risk factors for brain metastasis in breast cancer patients: Implication for a vigorous surveillance program. Asian J. Surg. 2015;38:220–223. doi: 10.1016/j.asjsur.2015.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kennecke H, Yerushalmi R, Woods R, Cheang MC, Voduc D, Speers CH, et al. Metastatic behavior of breast cancer subtypes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010;28:3271–3277. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.25.9820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pestalozzi BC, Zahrieh D, Price KN, Holmberg SB, Lindtner J, Collins J, et al. Identifying breast cancer patients at risk for Central Nervous System (CNS) metastases in trials of the International Breast Cancer Study Group (IBCSG) Ann. Oncol. 2006;17:935–944. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdl064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ryberg M, Nielsen D, Osterlind K, Andersen PK, Skovsgaard T, Dombernowsky P. Predictors of central nervous system metastasis in patients with metastatic breast cancer. A competing risk analysis of 579 patients treated with epirubicin-based chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2005;91:217–225. doi: 10.1007/s10549-005-0323-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Cardoso F, Senkus E, Costa A, Papadopoulos E, Aapro M, André F, et al. 4th ESO-ESMO international consensus guidelines for advanced breast cancer (ABC 4)†. Ann. Oncol. 2018;29:1634–1657. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdy192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Dawood S, Broglio K, Esteva FJ, Ibrahim NK, Kau SW, Islam R, et al. Defining prognosis for women with breast cancer and CNS metastases by HER2 status. Ann. Oncol. 2008;19:1242–1248. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdn036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Altundag K, Bondy ML, Mirza NQ, Kau SW, Broglio K, Hortobagyi GN, et al. Clinicopathologic characteristics and prognostic factors in 420 metastatic breast cancer patients with central nervous system metastasis. Cancer. 2007;110:2640–2647. doi: 10.1002/cncr.23088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Sperduto PW, Kased N, Roberge D, Xu Z, Shanley R, Luo X, et al. Effect of tumor subtype on survival and the graded prognostic assessment for patients with breast cancer and brain metastases. Int J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012;82:2111–2117. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.02.027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lockman PR, Mittapalli RK, Taskar KS, Rudraraju V, Gril B, Bohn KA, et al. Heterogeneous blood-tumor barrier permeability determines drug efficacy in experimental brain metastases of breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010;16:5664–5678. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-1564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Arvanitis CD, Ferraro GB, Jain RK. The blood-brain barrier and blood-tumour barrier in brain tumours and metastases. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2020;20:26–41. doi: 10.1038/s41568-019-0205-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Eichler AF, Chung E, Kodack DP, Loeffler JS, Fukumura D, Jain RK. The biology of brain metastases-translation to new therapies. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011;8:344–356. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2011.58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Monsky WL, et al. Role of host microenvironment in angiogenesis and microvascular functions in human breast cancer xenografts: mammary fat pad versus cranial tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002;8:1008–1013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Pitz MW, Desai A, Grossman SA, Blakeley JO. Tissue concentration of systemically administered antineoplastic agents in human brain tumors. J. Neurooncol. 2011;104:629–638. doi: 10.1007/s11060-011-0564-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Lewis Phillips GD, Nishimura MC, Lacap JA, Kharbanda S, Mai E, Tien J, et al. Trastuzumab uptake and its relation to efficacy in an animal model of HER2-positive breast cancer brain metastasis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2017;164:581–591. doi: 10.1007/s10549-017-4279-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kabraji S, Ni J, Lin NU, Xie S, Winer EP, Zhao JJ. Drug resistance in HER2-positive breast cancer brain metastases: blame the barrier or the brain. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018;24:1795–1804. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-3351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Fine RL, Chen J, Balmaceda C, Bruce JN, Huang M, Desai M, et al. Randomized study of paclitaxel and tamoxifen deposition into human brain tumors: implications for the treatment of metastatic brain tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006;12:5770–5776. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-2356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Dijkers EC, Oude Munnink TH, Kosterink JG, Brouwers AH, Jager PL, de Jong JR, et al. Biodistribution of 89Zr-trastuzumab and PET imaging of HER2-positive lesions in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2010;87:586–592. doi: 10.1038/clpt.2010.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Pestalozzi BC, Holmes E, de Azambuja E, Metzger-Filho O, Hogge L, Scullion M, et al. CNS relapses in patients with HER2-positive early breast cancer who have and have not received adjuvant trastuzumab: a retrospective substudy of the HERA trial (BIG 1-01) Lancet Oncol. 2013;14:244–248. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.von Minckwitz G, Huang CS, Mano MS, Loibl S, Mamounas EP, Untch M, et al. Trastuzumab emtansine for residual invasive HER2-positive breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019;380:617–628. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1814017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Mills MN, Figura NB, Arrington JA, Yu HM, Etame AB, Vogelbaum MA, et al. Management of brain metastases in breast cancer: a review of current practices and emerging treatments. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020;180:279–300. doi: 10.1007/s10549-020-05552-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Fecci PE, Champion CD, Hoj J, McKernan CM, Goodwin CR, Kirkpatrick JP, et al. The evolving modern management of brain metastasis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019;25:6570–6580. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-1624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Ramakrishna N, Temin S, Chandarlapaty S, Crews JR, Davidson NE, Esteva FJ, et al. Recommendations on disease management for patients with advanced human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive breast cancer and brain metastases: ASCO Clinical Practice Guideline Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018;36:2804–2807. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2018.79.2713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.ANOCEF. Métastases cérébrales de l’adulte, Référentiel ANOCEF. https://www.anocef.org/download.php?modele=anocef_referentiel_meta_cerebrales (2018).
- 42.Patchell RA, Tibbs PA, Walsh JW, Dempsey RJ, Maruyama Y, Kryscio RJ, et al. A randomized trial of surgery in the treatment of single metastases to the brain. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990;322:494–500. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199002223220802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kalkanis SN, Kondziolka D, Gaspar LE, Burri SH, Asher AL, Cobbs CS, et al. The role of surgical resection in the management of newly diagnosed brain metastases: a systematic review and evidence-based clinical practice guideline. J. Neurooncol. 2010;96:33–43. doi: 10.1007/s11060-009-0061-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Patchell RA, Tibbs PA, Regine WF, Dempsey RJ, Mohiuddin M, Kryscio RJ, et al. Postoperative radiotherapy in the treatment of single metastases to the brain: a randomized trial. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1998;280:1485–1489. doi: 10.1001/jama.280.17.1485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Sperduto PW, Wang M, Robins HI, Schell MC, Werner-Wasik M, Komaki R, et al. A phase 3 trial of whole brain radiation therapy and stereotactic radiosurgery alone versus WBRT and SRS with temozolomide or erlotinib for non-small cell lung cancer and 1 to 3 brain metastases: Radiation Therapy Oncology Group 0320. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2013;85:1312–1318. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2012.11.042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Soffietti R, Kocher M, Abacioglu UM, Villa S, Fauchon F, Baumert BG, et al. A European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer phase III trial of adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation in patients with one to three brain metastases from solid tumors after surgical resection or radiosurgery: quality-of-life results. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013;31:65–72. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.41.0639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Brown PD, Ballman KV, Cerhan JH, Anderson SK, Carrero XW, Whitton AC, et al. Postoperative stereotactic radiosurgery compared with whole brain radiotherapy for resected metastatic brain disease (NCCTG N107C/CEC·3): a multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18:1049–1060. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30441-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Kayama T, Sato S, Sakurada K, Mizusawa J, Nishikawa R, Narita Y, et al. Effects of surgery with salvage stereotactic radiosurgery versus surgery with whole-brain radiation therapy in patients with one to four brain metastases (JCOG0504): a phase III, noninferiority, randomized controlled trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018;33:3282–3289. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2018.78.6186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Patel KR, Burri SH, Asher AL, Crocker IR, Fraser RW, Zhang C, et al. Comparing preoperative with postoperative stereotactic radiosurgery for resectable brain metastases: a multi-institutional analysis. Neurosurgery. 2016;79:279–285. doi: 10.1227/NEU.0000000000001096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Yamamoto M, Serizawa T, Shuto T, Akabane A, Higuchi Y, Kawagishi J, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain metastases (JLGK0901): a multi-institutional prospective observational study. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:387–395. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70061-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Yamamoto M, Serizawa T, Higuchi Y, Sato Y, Kawagishi J, Yamanaka K, et al. A multi-institutional prospective observational study of stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain metastases (JLGK0901 Study Update): irradiation-related complications and long-term maintenance of mini-mental state examination scores. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017;99:31–40. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.04.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Grandhi R, Kondziolka D, Panczykowski D, Monaco EA, Kano H, Niranjan A, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery using the Leksell Gamma Knife Perfexion unit in the management of patients with 10 or more brain metastases. J. Neurosurg. 2012;117:237–245. doi: 10.3171/2012.4.JNS11870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Kim IY, Jung S, Jung TY, Moon KS, Jang WY, Park JY, Song TW, Lim SH. Repeat stereotactic radiosurgery for recurred metastatic brain tumors. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2018;61:633–639. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2017.0238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Sperduto PW, Kased N, Roberge D, Xu Z, Shanley R, Luo X, et al. Summary report on the graded prognostic assessment: an accurate and facile diagnosis-specific tool to estimate survival for patients with brain metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012;30:419–425. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.38.0527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Brown PD, Ahluwalia MS, Khan OH, Asher AL, Wefel JS, Gondi V. Whole-brain radiotherapy for brain metastases: evolution or revolution. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018;36:483–491. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.75.9589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Gondi V, Pugh SL, Tome WA, Caine C, Corn B, Kanner A, et al. Preservation of memory with conformal avoidance of the hippocampal neural stem-cell compartment during whole-brain radiotherapy for brain metastases (RTOG 0933): a phase II multi-institutional trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014;32:3810–3816. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.57.2909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Brown PD, Gondi V, Pugh S, Tome WA, Wefel JS, Armstrong TS, et al. Hippocampal avoidance during whole-brain radiotherapy plus memantine for patients with brain metastases: phase III trial NRG oncology CC001. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020;38:1019–1029. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.02767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Boogerd W, Dalesio O, Bais EM, van der Sande JJ. Response of brain metastases from breast cancer to systemic chemotherapy. Cancer. 1992;69:972–980. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19920215)69:4<972::aid-cncr2820690423>3.0.co;2-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Franciosi V, Cocconi G, Michiara M, Di Costanzo F, Fosser V, Tonato M, et al. Front-line chemotherapy with cisplatin and etoposide for patients with brain metastases from breast carcinoma, nonsmall cell lung carcinoma, or malignant melanoma: a prospective study. Cancer. 1999;85:1599–1605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Rivera E, Meyers C, Groves M, Valero V, Francis D, Arun B, et al. Phase I study of capecitabine in combination with temozolomide in the treatment of patients with brain metastases from breast carcinoma. Cancer. 2006;107:1348–1354. doi: 10.1002/cncr.22127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Christodoulou C, Bafaloukos D, Linardou H, Aravantinos G, Bamias A, Carina M, et al. Temozolomide (TMZ) combined with cisplatin (CDDP) in patients with brain metastases from solid tumors: a Hellenic Cooperative Oncology Group (HeCOG) Phase II study. J. Neurooncol. 2005;71:61–65. doi: 10.1007/s11060-004-9176-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Hoch U, Staschen CM, Johnson RK, Eldon MA. Nonclinical pharmacokinetics and activity of etirinotecan pegol (NKTR-102), a long-acting topoisomerase 1 inhibitor, in multiple cancer models. Cancer Chemother. Pharm. 2014;74:1125–1137. doi: 10.1007/s00280-014-2577-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Cortés J, Rugo HS, Awada A, Twelves C, Perez EA, Im SA, et al. Prolonged survival in patients with breast cancer and a history of brain metastases: results of a preplanned subgroup analysis from the randomized phase III BEACON trial. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2017;165:329–341. doi: 10.1007/s10549-017-4304-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Park YH, Park MJ, Ji SH, Yi SY, Lim DH, Nam DH, et al. Trastuzumab treatment improves brain metastasis outcomes through control and durable prolongation of systemic extracranial disease in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer patients. Br. J. Cancer. 2009;100:894–900. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6604941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Rostami R, Mittal S, Rostami P, Tavassoli F, Jabbari B. Brain metastasis in breast cancer: a comprehensive literature review. J. Neurooncol. 2016;127:407–414. doi: 10.1007/s11060-016-2075-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Verma S, Miles D, Gianni L, Krop IE, Welslau M, Baselga J, et al. Trastuzumab emtansine for HER2-positive advanced breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012;367:1783–1791. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1209124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Krop IE, Lin NU, Blackwell K, Guardino E, Huober J, Lu M, et al. Trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) versus lapatinib plus capecitabine in patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer and central nervous system metastases: a retrospective, exploratory analysis in EMILIA. Ann. Oncol. 2015;26:113–119. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdu486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Bartsch R, Berghoff AS, Vogl U, Rudas M, Bergen E, Dubsky P, et al. Activity of T-DM1 in Her2-positive breast cancer brain metastases. Clin. Exp. Metastasis. 2015;32:729–737. doi: 10.1007/s10585-015-9740-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Jacot W, Pons E, Frenel JS, Guiu S, Levy C, Heudel PE, et al. Efficacy and safety of trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer with brain metastases. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2016;157:307–318. doi: 10.1007/s10549-016-3828-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Montemurro, F., Delaloge, S., Barrios, C. H., Wuerstlein, R., Anton, A., Brain, E. et al. Trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) in patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer and brain metastases: exploratory final analysis of cohort 1 from KAMILLA, a single-arm phase IIIb clinical trial☆. Ann. Oncol.10.1016/j.annonc.2020.06.020 (2020). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 71.Swain SM, Baselga J, Kim SB, Ro J, Semiglazov V, Campone M, et al. Pertuzumab, trastuzumab, and docetaxel in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015;372:724–734. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1413513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Swain SM, Baselga J, Miles D, Im YH, Quah C, Lee LF, et al. Incidence of central nervous system metastases in patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer treated with pertuzumab, trastuzumab, and docetaxel: results from the randomized phase III study CLEOPATRA. Ann. Oncol. 2014;25:1116–1121. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdu133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Lin NU, Diéras V, Paul D, Lossignol D, Christodoulou C, Stemmler HJ, et al. Multicenter phase II study of lapatinib in patients with brain metastases from HER2-positive breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009;15:1452–1459. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Sutherland S, Ashley S, Miles D, Chan S, Wardley A, Davidson N, et al. Treatment of HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer with lapatinib and capecitabine in the lapatinib expanded access programme, including efficacy in brain metastases-the UK experience. Br. J. Cancer. 2010;102:995–1002. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Metro G, Foglietta J, Russillo M, Stocchi L, Vidiri A, Giannarelli D, et al. Clinical outcome of patients with brain metastases from HER2-positive breast cancer treated with lapatinib and capecitabine. Ann. Oncol. 2011;22:625–630. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdq434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Bachelot T, Romieu G, Campone M, Diéras V, Cropet C, Dalenc F, et al. Lapatinib plus capecitabine in patients with previously untreated brain metastases from HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer (LANDSCAPE): a single-group phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14:64–71. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(12)70432-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Geyer CE, Forster J, Lindquist D, Chan S, Romieu CG, Pienkowski T, et al. Lapatinib plus capecitabine for HER2-positive advanced breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006;355:2733–2743. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa064320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Lin NU, Eierman W, Greil R, Campone M, Kaufman B, Steplewski K, et al. Randomized phase II study of lapatinib plus capecitabine or lapatinib plus topotecan for patients with HER2-positive breast cancer brain metastases. J. Neurooncol. 2011;105:613–620. doi: 10.1007/s11060-011-0629-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Pivot X, Manikhas A, Żurawski B, Chmielowska E, Karaszewska B, Allerton R, et al. CEREBEL (EGF111438): a phase III, randomized, open-label study of lapatinib plus capecitabine versus trastuzumab plus capecitabine in patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive metastatic breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015;33:1564–1573. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.57.1794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Awada A, Colomer R, Inoue K, Bondarenko I, Badwe RA, Demetriou G, et al. Neratinib plus paclitaxel vs trastuzumab plus paclitaxel in previously untreated metastatic ERBB2-positive breast cancer: the NEfERT-T randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2016;2:1557–1564. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.0237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Murthy R, Borges VF, Conlin A, Chaves J, Chamberlain M, Gray T, et al. Tucatinib with capecitabine and trastuzumab in advanced HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer with and without brain metastases: a non-randomised, open-label, phase 1b study. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19:880–888. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30256-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Freedman RA, Gelman RS, Anders CK, Melisko ME, Parsons HA, Cropp AM, et al. TBCRC 022: a phase II trial of neratinib and capecitabine for patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive breast cancer and brain metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019;37:1081–1089. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.01511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Saura C, Oliveira M, Feng YH, Dai MS, Hurvitz SA, Kim SB, et al. Neratinib + capecitabine versus lapatinib + capecitabine in patients with HER2+ metastatic breast cancer previously treated with ≥ 2 HER2-directed regimens: findings from the multinational, randomized, phase III NALA trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019;37:1002–1002. [Google Scholar]
- 84.Lin NU, Borges V, Anders C, Murthy RK, Paplomata E, Hamilton E, et al. Intracranial efficacy and survival with tucatinib plus trastuzumab and capecitabine for previously treated HER2-positive breast cancer with brain metastases in the HER2CLIMB trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020;38:2610–2619. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.00775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Pors H, von Eyben FE, Sørensen OS, Larsen M. Longterm remission of multiple brain metastases with tamoxifen. J. Neurooncol. 1991;10:173–177. doi: 10.1007/BF00146879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Madhup R, Kirti S, Bhatt ML, Srivastava PK, Srivastava M, Kumar S. Letrozole for brain and scalp metastases from breast cancer-a case report. Breast. 2006;15:440–442. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2005.07.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Navarro Martín LM, Ocaña Fernández A, Rodríguez Sánchez CA, Ruiz Martín I, Cruz, Hernández JJ. Durable clinical benefit with exemestane in leptomeningeal metastasis of breast cancer. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2005;7:358–360. doi: 10.1007/BF02716553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Rusz O, Kószó R, Dobi Á, Csenki M, Valicsek E, Nikolényi A, et al. Clinical benefit of fulvestrant monotherapy in the multimodal treatment of hormone receptor and HER2 positive advanced breast cancer: a case series. Onco Targets Ther. 2018;11:5459–5463. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S170736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Tolaney, S. M., Sahebjam, S., Le Rhun, E., Bachelot, T., Kabos, P., Awada, A. et al. A phase 2 study of abemaciclib in patients with brain metastases secondary to hormone receptor positive breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res.10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-1764 (2020). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 90.Labidi SI, Bachelot T, Ray-Coquard I, Mosbah K, Treilleux I, Fayette J, et al. Bevacizumab and paclitaxel for breast cancer patients with central nervous system metastases: a case series. Clin. Breast Cancer. 2009;9:118–121. doi: 10.3816/CBC.2009.n.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Matsuoka H, Tsurutani J, Tanizaki J, Iwasa T, Komoike Y, Koyama A, et al. Regression of brain metastases from breast cancer with eribulin: a case report. BMC Res. Notes. 2013;6:541. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-6-541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Lin NU, Gelman RS, Younger WJ, Sohl J, Freedman RA, Sorensen AG, et al. Phase II trial of carboplatin (C) and bevacizumab (BEV) in patients (pts) with breast cancer brain metastases (BCBM) J. Clin. Oncol. 2013;31:513–513. [Google Scholar]
- 93.Litton JK, Rugo HS, Ettl J, Hurvitz SA, Gonçalves A, Lee KH, et al. Talazoparib in patients with advanced breast cancer and a germline BRCA mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018;379:753–763. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1802905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Robson ME, Tung N, Conte P, Im SA, Senkus E, Xu B, et al. OlympiAD final overall survival and tolerability results: olaparib versus chemotherapy treatment of physician’s choice in patients with a germline BRCA mutation and HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2019;30:558–566. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdz012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Diéras V, Han HS, Kaufman B, Wildiers H, Friedlander M, Ayoub JP, et al. Veliparib with carboplatin and paclitaxel in BRCA-mutated advanced breast cancer (BROCADE3): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21:1269–1282. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30447-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Mehta MP, Wang D, Wang F, Kleinberg L, Brade A, Robins HI, et al. Veliparib in combination with whole brain radiation therapy in patients with brain metastases: results of a phase 1 study. J. Neurooncol. 2015;122:409–417. doi: 10.1007/s11060-015-1733-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Fischer GM, Jalali A, Kircher DA, Lee WC, McQuade JL, Haydu LE, et al. Molecular profiling reveals unique immune and metabolic features of melanoma brain metastases. Cancer Discov. 2019;9:628–645. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-1489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Long GV, Atkinson V, Lo S, Sandhu S, Guminski AD, Brown MP, et al. Combination nivolumab and ipilimumab or nivolumab alone in melanoma brain metastases: a multicentre randomised phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19:672–681. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30139-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Schmid P, Adams S, Rugo HS, Schneeweiss A, Barrios CH, Iwata H, et al. Atezolizumab and nab-paclitaxel in advanced triple-negative breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018;379:2108–2121. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1809615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Figura NB, Rizk VT, Armaghani AJ, Arrington JA, Etame AB, Han HS, et al. Breast leptomeningeal disease: a review of current practices and updates on management. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019;177:277–294. doi: 10.1007/s10549-019-05317-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Stemmler HJ, Mengele K, Schmitt M, Harbeck N, Laessig D, Herrmann KA, et al. Intrathecal trastuzumab (Herceptin) and methotrexate for meningeal carcinomatosis in HER2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer: a case report. Anticancer Drugs. 2008;19:832–836. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0b013e32830b58b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Bonneau C, Paintaud G, Trédan O, Dubot C, Desvignes C, Dieras V, et al. Phase I feasibility study for intrathecal administration of trastuzumab in patients with HER2 positive breast carcinomatous meningitis. Eur. J. Cancer. 2018;95:75–84. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2018.02.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Kumthekar P, Gradishar W, Lin N, Pentsova E, Groves M, Jeyapalan S, et al. CMET-22. Intrathecal (IT) trastuzumab (T) for the treatment of leptomeningeal metastases (LM) in patients (PTS) with human epidermal growth factor recepor 2-positive (HER2+) cancer: a multicenter phase 1/2 study. Neuro Oncol. 2018;20:vi58. [Google Scholar]
- 104.Lin NU, Kumthekar P, Sahebjam S, Ibrahim N, Fung A, Cheng A, et al. Pertuzumab (P) plus high-dose trastuzumab (H) for the treatment of central nervous system (CNS) progression after radiotherapy (RT) in patients (pts) with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer (MBC): primary efficacy analysis results from the phase II PATRICIA study. Cancer Res. 2020;80:P1-18-03. [Google Scholar]
- 105.Camidge DR, Lee EQ, Lin NU, Margolin K, Ahluwalia MS, Bendszus M, et al. Clinical trial design for systemic agents in patients with brain metastases from solid tumours: a guideline by the Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology Brain Metastases working group. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19:e20–e32. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30693-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Park EJ, Zhang YZ, Vykhodtseva N, McDannold N. Ultrasound-mediated blood-brain/blood-tumor barrier disruption improves outcomes with trastuzumab in a breast cancer brain metastasis model. J. Control Release. 2012;163:277–284. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2012.09.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Kobus T, Zervantonakis IK, Zhang Y, McDannold NJ. Growth inhibition in a brain metastasis model by antibody delivery using focused ultrasound-mediated blood-brain barrier disruption. J. Control Release. 2016;238:281–288. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.08.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Patil R, Ljubimov AV, Gangalum PR, Ding H, Portilla-Arias J, Wagner S, et al. MRI virtual biopsy and treatment of brain metastatic tumors with targeted nanobioconjugates: nanoclinic in the brain. ACS Nano. 2015;9:5594–5608. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b01872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Hamilton AM, Aidoudi-Ahmed S, Sharma S, Kotamraju VR, Foster PJ, Sugahara KN, et al. Nanoparticles coated with the tumor-penetrating peptide iRGD reduce experimental breast cancer metastasis in the brain. J. Mol. Med. 2015;93:991–1001. doi: 10.1007/s00109-015-1279-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Miller KD, Weathers T, Haney LG, Timmerman R, Dickler M, Shen J, et al. Occult central nervous system involvement in patients with metastatic breast cancer: prevalence, predictive factors and impact on overall survival. Ann. Oncol. 2003;14:1072–1077. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdg300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Tsao MN, Rades D, Wirth A, Lo SS, Danielson BL, Gaspar LE, et al. Radiotherapeutic and surgical management for newly diagnosed brain metastasis(es): an American Society for Radiation Oncology evidence-based guideline. Pr. Radiat. Oncol. 2012;2:210–225. doi: 10.1016/j.prro.2011.12.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.