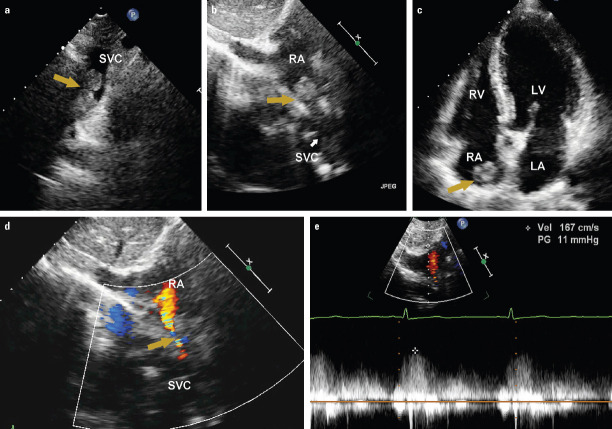
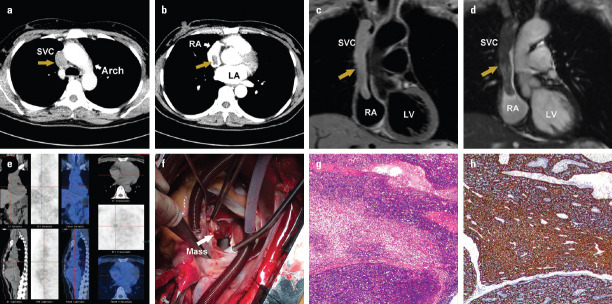
A 44-year-old female with facial edema and dizziness for six months was admitted to our hospital. Transthoracic echocardiogram showed the dilated superior venae cava (SVC) occluded by a mass. The mass in the SVC was extending into the right atrium (RA) (Fig. 1a–1c, Videos 1-2). Color Doppler flow imaging indicated a narrowed blood flow in the SVC with an increased velocity of 1.6 m/s (Fig. 1d, 1e, Video 3). Contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) scan revealed a soft tissue density mass measuring 9.0×3.3 cm within the SVC extending into the RA (Fig. 2a, 2b). Cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging demonstrated a heterogeneous mass within the SVC extending into the RA. The mass appeared isointense on the T1-weighted images and slightly hyperintense on the T2-weighted images (Fig. 2c, 2d). Positron emission tomography (PET)/CT scan showed a mass with no significant uptake of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) (Fig. 2e). She underwent the surgical resection of the tumor and a reconstruction of SVC. During the operation, a soft and ashen mass, measuring 10×3×2.5 cm, was found to be located within the SVC extending into the RA (Fig. 2f). Histopathological examination revealed a thymoma (Fig. 2g, 2h). At the six-year follow-up, the patient is well without any evidence of tumor recurrence.
Figure 1.
(a) Transthoracic echocardiogram showing a mass within the SVC. (b) The subcostal view revealing the mass extending into the right atrium via the SVC. (c) The apical four-chamber view demonstrating the mass extending into the right atrium. (d) Color Doppler flow imaging indicating a narrowed blood flow in the SVC. (e) Continuous-wave Doppler echocardiography showing an increased blood flow velocity
SVC - superior vena cava; RA - right atrium; RV - right ventricle; LV - left ventricle; LA - left atrium
Figure 2.
Contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) showing a mass within the (a) superior vena cava and (b) right atrium. The mass appears to be isointense on the (c) T1-weighted images and hyperintense on the (d) T2-weighted images of cardiac magnetic resonance scans. (e) Positron emission tomography (PET)/CT scan indicating a mass with no significant uptake of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose. (f) Intra-operative photograph showing the mass in the right atrium. (g, h) Histopathological examination of the mass revealing a thymoma
SVC - superior vena cava; RA - right atrium; LA - left atrium; LV - left ventricle
Thymoma is a rare epithelial tumor and its overall prevalence is approximately 0.15 cases per 100.000 population. Although thymoma may involve the pleura, pericardium, and great vessels, its extension into the RA via the SVC is exceptionally rare. Our case emphasizes that multimodality imaging is crucial in characterizing the thymoma and determining the surgical plan.
Video 1
Transthoracic echocardiogram showing a mass within the superior vena cava.
Video 2
An apical four-chamber view demonstrating the mass extending into the right atrium.
Video 3
Color Doppler flow imaging indicating a narrowed blood flow in the superior vena cava.
Footnotes
Informed consent: The informed consent was obtained from the patient for this study.
Funding: The study was funded by National Key R&D Program of China (Grant Nos. 2018YFC0114600) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 81727805, 81401432).
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.