Abstract
Background
Esophageal cancer is the eighth most common cause of cancer mortality in Japan. More than 11,000 people had died from esophageal cancer in 2018. The Japan Esophageal Society has collected the data on patients' characteristics, performed treatment, and outcomes annually.
Methods
We analyzed the data of patients who had first visited the participating hospitals in 2013. In 2019, the data collection method was changed from an electronic submission to a web-based data collection using the National Clinical Database (NCD). Japanese Classification of Esophageal Cancer 10th by the Japan Esophageal Society (JES) and UICC TNM Classification 7th were used for cancer staging
Results
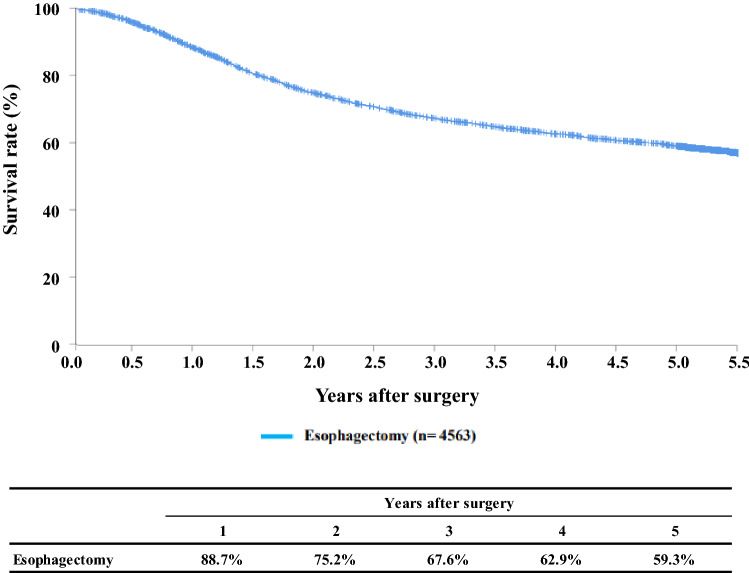
A total of 8019 cases were registered from 334 institutions in Japan. Squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma accounted for 87.8% and 6.3%, respectively. The 5-year survival rates of patients treated using endoscopic resection, concurrent chemoradiotherapy, radiotherapy alone, or esophagectomy were 88.3%, 32.4%, 24.4%, and 59.3%, respectively. Esophagectomy was performed in 4910 cases. The operative and the hospital mortality rates were 0.77% and 1.98%, respectively. The survival curves showed a good discriminatory ability both in the clinical and pathologic stages by the JES system. The 5-year survival rate of patients with pStage IV in the UICC classification that included patients with supraclavicular node metastasis was better than that of patients with pStage IVb in JES classification.
Conclusion
We hope this report contributes to improving all aspects of the diagnosis and treatment of esophageal cancer in Japan.
Keywords: Esophageal cancer, Esophagectomy, Endoscopic resection, Chemotherapy, Chemoradiotherapy
Preface 2013
We deeply appreciate the great contributions of many physicians in the registry of esophageal cancer cases. The Comprehensive Registry of Esophageal Cancer in Japan, 2013, was published here. In 2019, the data collection method was changed from an electronic submission to a web-based data collection using the National Clinical Database (NCD). Personal information was replaced with individual management code inside each institute, and the NCD collected only anonymized information. The registry complies with the Act for the Protection of Personal Information.
We briefly summarized the Comprehensive Registry of Esophageal Cancer in Japan, 2013. Japanese Classification of Esophageal Cancer 10th by the Japan Esophageal Society (JES) [1] and UICC TNM Classification 7th [2] were used for cancer staging according to the subjected year. A total of 8019 cases were registered from 334 institutions in Japan. Tumor locations were cervical: 4.8%, upper thoracic: 12.1%, middle thoracic: 46.5%, lower thoracic: 28.2% and EG junction: 7.9%. Superficial carcinomas (Tis, T1a, T1b) were 38.6%. As for the histologic type of biopsy specimens, squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma accounted for 87.8% and 6.3%, respectively. Regarding clinical results, the 5-year survival rates of patients treated using endoscopic resection, concurrent chemoradiotherapy, radiotherapy alone, or esophagectomy were 88.3%, 32.4%, 24.4%, and 59.3%, respectively. The endoscopic submucosal dissection accounted for 91.6% of endoscopic resection. Esophagectomy was performed in 4910 cases. Concerning the approach used for esophagectomy, 43.0% of the cases were treated thoracoscopically. The operative mortality (within 30 days after surgery) was 0.77%, and the hospital mortality was 1.98%. The Kaplan–Meier survival curves diverged according to the N-grade both in the JES and the UICC classifications. The survival curves showed a good discriminatory ability both in the clinical and pathologic stages by the JES system. However, the survival of cStage IIB was better than those of IB and IIA, while the survival curves were almost identical between cStage IIIc and IV in the UICC system. Also, the survival curve of pStage IIA merged with that of IIB, and the survival of pStage IV was better than that of IIIC. The 5-year survival rate of patients with pStage IV in the UICC classification that included patients with supraclavicular node metastasis was better than that of patients with pStage IVb in JES classification.
We hope that this Comprehensive Registry of Esophageal Cancer in Japan for 2013 will help to improve all aspects of the diagnosis and treatment of esophageal cancer in Japan.
Contents
-
I.Clinical factors of esophageal cancer patients treated in 2013
- Institution-registered cases in 2013
- Patient background
-
II.Results of endoscopically treated patients in 2013
- Table 9Details of endoscopic treatment for curative intent
- Table 10Complications of EMR/ESD
- Table 11Pathological depth of tumor invasion of EMR/ESD specimens
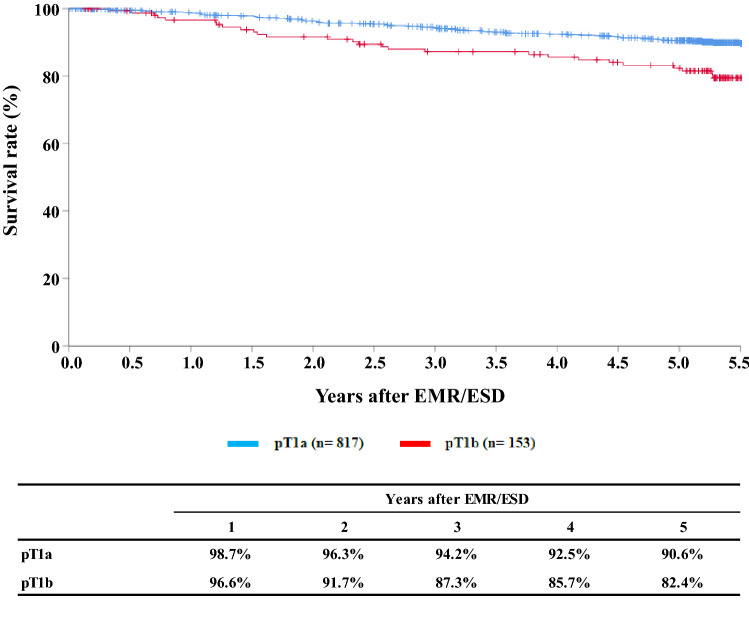
- Figure 1Survival of patients treated with EMR/ESD
- Figure 2Survival of patients treated with EMR/ESD according to the pathological depth of tumor invasion, pT (JES 10th)
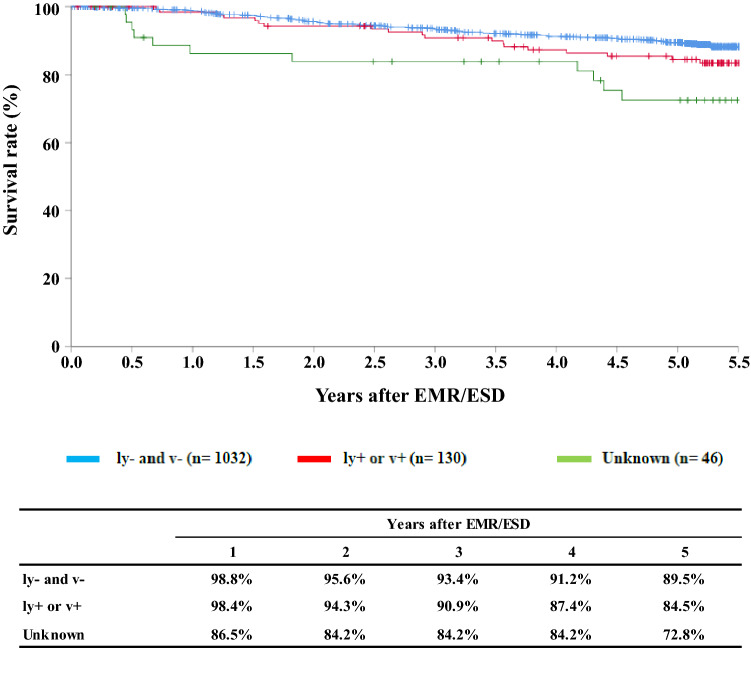
- Figure 3Survival of patients treated with EMR/ESD according to the lymphatic and venous invasion
-
III.Results in patients treated with chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy in 2013
- Table 12Dose of irradiation (non-surgically treated cases)
- Table 13Dose of irradiation (surgically treated cases)
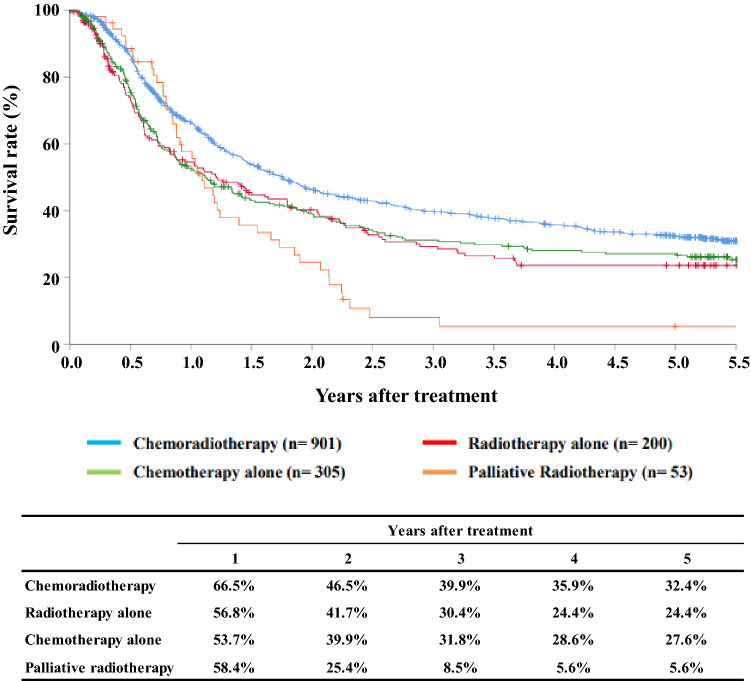
- Figure 4Survival of patients treated with chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy
- Figure 5Survival of patients treated with definitive chemoradiotherapy according to clinical stage (UICC TNM 7th)
- Figure 6Survival of patients underwent radiotherapy alone according to clinical stage (UICC TNM 7th)
-
IV.Results in patients who underwent esophagectomy in 2013
- Table 14Treatment modalities of esophagectomy
- Table 15Tumor location
- Table 16Approaches to tumor resection
- Table 17Video-assisted surgery
- Table 18Fields of lymph node dissection according to the location of the tumor
- Table 19Reconstruction route
- Table 20Organs used for reconstruction
- Table 21Histological classification
- Table 22Depth of tumor invasion, pT (JES 10th)
- Table 23Pathological grading of lymph node metastasis, pN (JES 10th)
- Table 24Pathological findings of lymph node metastasis, pN (UICC TNM 7th)
- Table 25Pathological findings of distant organ metastasis, pM (JES 10th)
- Table 26Residual tumor
- Table 27Causes of death
- Figure 7Survival of patients who underwent esophagectomy
- Figure 8Survival of patients who underwent esophagectomy according to clinical stage (JES 10th)
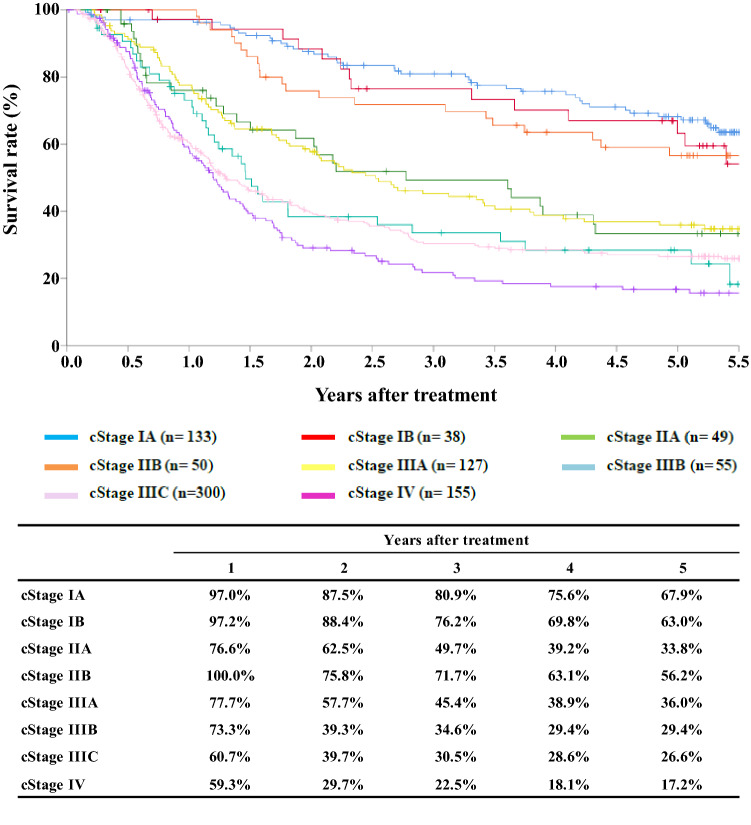
- Figure 9Survival of patients who underwent esophagectomy according to clinical stage (UICC TNM 7th)
- Figure 10Survival of patients who underwent esophagectomy according to the depth of tumor invasion, pT (JES 10th)
- Figure 11Survival of patients who underwent esophagectomy according to lymph node metastasis (JES 10th)
- Figure 12Survival of patients who underwent esophagectomy according to lymph node metastasis (UICC TNM 7th)
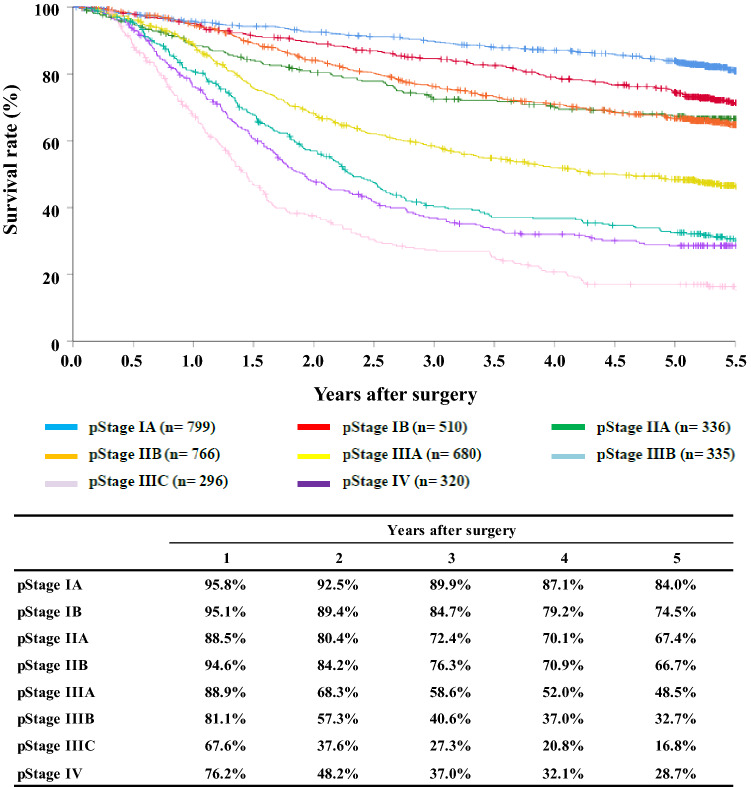
- Figure 13Survival of patients who underwent esophagectomy according to pathological stage (JES 10th)
- Figure 14Survival of patients who underwent esophagectomy according to pathological stage (UICC TNM 7th)
- Figure 15Survival of patients who underwent esophagectomy according to residual tumor (R)
Table 1.
Age and gender
| Age | Male | Female | Cases (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ≤ 29 | 12 | 1 | 13 (0.2%) |
| 30–39 | 16 | 6 | 22 (0.3%) |
| 40–49 | 164 | 59 | 223 (2.8%) |
| 50–59 | 917 | 174 | 1091 (13.6%) |
| 60–69 | 2675 | 431 | 3106 (38.7%) |
| 70–79 | 2403 | 437 | 2840 (35.4%) |
| 80–89 | 570 | 133 | 703 (8.8%) |
| 90 ≤ | 10 | 11 | 21 (0.3%) |
| Total | 6767 | 1252 | 8019 |
Table 2.
Performed treatment
| Treatments | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| Surgery | 5038 (62.8%) |
| Esophagectomy | 4910 (61.2%) |
| Palliative surgery | 128 (1.6%) |
| Chemotherapy and/or Radiotherapy | 4062 (50.7%) |
| Endoscopic treatment | 1421 (17.7%) |
Table 3.
Tumor location
| Location of tumor | Endoscopic treatment | Surgery | Chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy (%) | Total (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | Esophagectomy (%) | Palliative surgery (%) | |||
| Cervical | 48 (3.4%) | 163 (3.3%) | 10 (7.8%) | 256 (6.3%) | 384 (4.8%) |
| Upper thoracic | 142 (10.0%) | 525 (10.7%) | 25 (19.5%) | 597 (14.7%) | 969 (12.1%) |
| Middle thoracic | 775 (54.5%) | 2188 (44.6%) | 61 (47.7%) | 1864 (45.9%) | 3726 (46.5%) |
| Lower thoracic | 369 (26.0%) | 1544 (31.4%) | 26 (20.3%) | 1118 (27.5%) | 2264 (28.2%) |
| EG | 61 (4.3%) | 356 (7.3%) | 5 (3.9%) | 165 (4.1%) | 470 (5.9%) |
| E = G | 14 (1.0%) | 66 (1.3%) | 23 (0.6%) | 88 (1.1%) | |
| GE | 6 (0.4%) | 61 (1.2%) | 15 (0.4%) | 72 (0.9%) | |
| Unknown | 6 (0.4%) | 7 (0.1%) | 1 (0.8%) | 45 (0.6%) | 46 (0.6%) |
| Total | 1421 | 4910 | 128 | 4062 | 8019 |
E esophageal, G gastric
Table 4.
Histologic type of biopsy specimens
| Histologic types | Endoscopic treatment | Surgery | Chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy (%) | Total (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | Esophagectomy (%) | Palliative surgery (%) | |||
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 1101 (77.5%) | 4291 (87.4%) | 116 (90.6%) | 3733 (91.9%) | 6911 (86.2%) |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 867 (61.0%) | 2442 (49.7%) | 74 (57.8%) | 2330 (57.4%) | 4377 (54.6%) |
| Well differentiated | 100 (7.0%) | 387 (7.9%) | 9 (7.0%) | 259 (6.4%) | 565 (7.0%) |
| Moderately differentiated | 117 (8.2%) | 1093 (22.3%) | 24 (18.8%) | 805 (19.8%) | 1448 (18.1%) |
| Poorly differentiated | 17 (1.2%) | 369 (7.5%) | 9 (7.0%) | 339 (8.3%) | 521 (6.5%) |
| Adenocarcinoma | 38 (2.7%) | 340 (6.9%) | 4 (3.1%) | 133 (3.3%) | 419 (5.2%) |
| Barrett's carcinoma | 33 (2.3%) | 91 (1.9%) | 1 (0.8%) | 25 (0.6%) | 133 (1.7%) |
| Adenosquamous carcinoma | 2 (0.1%) | 11 (0.2%) | 4 (0.1%) | 14 (0.2%) | |
| Mucoepidermoid carcinoma | 1 (0.0%) | 1 (0.0%) | |||
| Basaloid carcinoma | 2 (0.1%) | 31 (0.6%) | 16 (0.4%) | 39 (0.5%) | |
| Neuroendocrine tumor | 1 (0.0%) | 1 (0.0%) | 2 (0.0%) | ||
| Neuroendocrine carcinoma | 4 (0.3%) | 21 (0.4%) | 27 (0.7%) | 34 (0.4%) | |
| Undifferentiated carcinoma | 6 (0.1%) | 4 (0.1%) | 9 (0.1%) | ||
| Malignant melanoma | 15 (0.3%) | 6 (0.1%) | 19 (0.2%) | ||
| Carcinosarcoma | 16 (0.3%) | 1 (0.8%) | 8 (0.2%) | 19 (0.2%) | |
| GIST | 1 (0.0%) | 1 (0.0%) | |||
| Adenoid cystic carcinoma | 1 (0.0%) | 1 (0.0%) | |||
| Nonepithelial tumors | 2 (0.1%) | 3 (0.0%) | |||
| Other epithelial tumors | 17 (1.2%) | 4 (0.1%) | 8 (0.2%) | 27 (0.3%) | |
| Other tumors | 51 (3.6%) | 16 (0.3%) | 13 (0.3%) | 79 (1.0%) | |
| Unknown | 171 (12.0%) | 64 (1.3%) | 6 (4.7%) | 84 (2.1%) | 308 (3.8%) |
| Total | 1421 | 4910 | 128 | 4062 | 8019 |
Table 5.
Depth of tumor invasion, cT (UICC TNM 7th)
| Clinical T | Endoscopic treatment | Surgery | Chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy (%) | Total (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | Esophagectomy (%) | Palliative surgery (%) | |||
| cTX | 12 (0.8%) | 11 (0.2%) | 1 (0.8%) | 34 (0.8%) | 80 (1.0%) |
| cT0 | 6 (0.6%) | 4 (0.1%) | 3 (0.1%) | 14 (0.2%) | |
| cT1a | 1139 (80.2%) | 247 (5.0%) | 102 (2.5%) | 1426 (17.8%) | |
| cT1b | 196 (13.8%) | 1319 (26.9%) | 9 (7.0%) | 515 (12.7%) | 1658 (20.7%) |
| cT2 | 4 (0.3%) | 832 (16.9%) | 4 (3.1%) | 609 (15.0%) | 1006 (12.5%) |
| cT3 | 41 (2.9%) | 2223 (45.3%) | 49 (38.3%) | 2036 (50.1%) | 2895 (36.1%) |
| cT4a | 4 (0.3%) | 133 (2.7%) | 17 (13.3%) | 257 (6.3%) | 341 (4.3%) |
| cT4b | 19 (1.3%) | 141 (2.9%) | 48 (37.5%) | 506 (12.5%) | 599 (7.5%) |
| Total | 1421 | 4910 | 128 | 4062 | 8019 |
Table 6.
Lymph node metastasis, cN (UICC TNM 7th)
| Clinical N | Endoscopic treatment | Surgery | Chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy (%) | Total (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | Esophagectomy (%) | Palliative surgery (%) | |||
| cN0 | 1351 (95.1%) | 2278 (46.4%) | 31 (24.2%) | 1117 (27.5%) | 4047 (50.5%) |
| cN1 | 38 (2.7%) | 1704 (34.7%) | 37 (28.9%) | 1663 (40.9%) | 2318 (28.9%) |
| cN2 | 22 (1.5%) | 800 (16.3%) | 43 (33.6%) | 1009 (24.8%) | 1301 (16.2%) |
| cN3 | 10 (0.7%) | 128 (2.6%) | 17 (13.3%) | 273 (6.7%) | 353 (4.4%) |
| Total | 1421 | 4910 | 128 | 4062 | 8019 |
Table 7.
Distant metastasis, cM (UICC TNM 7th)
| Clinical M | Endoscopic treatment | Surgery | Chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy (%) | Total (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | Esophagectomy (%) | Palliative surgery (%) | |||
| cM0 | 1406 (98.9%) | 4753 (96.8%) | 103 (80.5%) | 3513 (86.5%) | 7350 (91.7%) |
| cM1 | 15 (1.1%) | 157 (3.2%) | 25 (19.5%) | 549 (13.5%) | 669 (8.3%) |
| Total | 1421 | 4910 | 128 | 4062 | 8019 |
Table 8.
Clinical Stage (UICC TNM 7th)
| Clinical stage | Endoscopic treatment | Surgery | Chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy (%) | Total (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | Esophagectomy (%) | Palliative surgery (%) | |||
| Stage IA | 1317 (92.7%) | 1268 (25.8%) | 7 (5.5%) | 388 (9.6%) | 2712 (33.8%) |
| Stage IB | 3 (0.2%) | 417 (8.5%) | 3 (2.3%) | 252 (6.2%) | 492 (6.1%) |
| Stage IIA | 8 (0.6%) | 523 (10.7%) | 10 (7.8%) | 356 (8.8%) | 629 (7.8%) |
| Stage IIB | 15 (1.1%) | 522 (10.6%) | 389 (9.6%) | 609 (7.6%) | |
| Stage IIIA | 19 (1.3%) | 1169 (23.8%) | 14 (10.9%) | 952 (23.4%) | 1375 (17.1%) |
| Stage IIIB | 9 (0.6%) | 514 (10.5%) | 14 (10.9%) | 488 (12.0%) | 642 (8.0%) |
| Stage IIIC | 17 (1.2%) | 325 (6.6%) | 55 (43.0%) | 667 (16.4%) | 821 (10.2%) |
| Stage IV | 15 (1.1%) | 157 (3.2%) | 25 (19.5%) | 549 (13.5%) | 669 (8.3%) |
| Unknown | 18 (1.3%) | 15 (0.3%) | 21 (0.5%) | 70 (0.9%) | |
| Total | 1421 | 4910 | 128 | 4062 | 8019 |
Table 9.
Details of endoscopic treatment for curative intent
| Treatment details | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| EMR | 108 (8.0%) |
| EMR + YAG laser | 1 (0.1%) |
| EMR + MCT/RFA | |
| ESD | 1224 (90.2%) |
| ESD + EMR | 4 (0.3%) |
| ESD + PDT | |
| ESD + YAG laser | 5 (0.4%) |
| PDT | 2 (0.1%) |
| YAG laser | 13 (1.0%) |
| Total | 1357 |
EMR endoscopic mucosal resection, PDT photodynamic therapy, YAG yttrium aluminum garnet, MCT microwave coagulation therapy, ESD endoscopic submucosal dissection
Table 10.
Complications of EMR/ESD
| Complications of EMR/ESD | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| None | 1298 (92.7%) |
| Perforation | 10 (0.7%) |
| Bleeding | 1 (0.1%) |
| Mediastinitis | 1 (0.1%) |
| Stenosis | 23 (1.7%) |
| Others | |
| Unknown | 2 (0.1%) |
| Total | 1335 |
Table 11.
Pathologic depth of tumor invasion of MER/ESD specimens
| Pathological depth of tumor invasion (pT) | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| pTX | 22 (1.6%) |
| pT0 | 7 (0.5%) |
| pT1a | 1111 (82.8%) |
| pT1b | 201 (15.0%) |
| pT2 | |
| pT3 | 1 (0.1%) |
| Total | 1342 |
Fig. 1.
Survival of patients treated with EMR/ESD
Fig. 2.
Survival of patients treated with EM/ESD according to the pathological depth of tumor invasion, pT(JES 10th)
Fig. 3.
Survival of patients treated with EMR/ESD according to the lymphatic and venous invasion
Table 12.
Dose of irradiation (non-surgically treated cases)
| Dose of irradiation (Gy) | Definitive | Palliative (%) | Recurrence (%) | Others (%) | Total (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radiation alone (%) | With chemotherapy (%) | |||||
| –29 | 2 (1.5%) | 20 (2.4%) | 23 (11.7%) | 2 (5.9%) | 1 (10.0%) | 48 (4.0%) |
| 30–39 | 4 (3.0%) | 16 (1.9%) | 33 (16.8%) | 1 (2.9%) | 2 (20.0%) | 56 (4.7%) |
| 40–49 | 7 (5.3%) | 33 (4.0%) | 40 (20.4%) | 1 (2.9%) | 3 (30.0%) | 84 (7.0%) |
| 50–59 | 15 (11.4%) | 233 (28.2%) | 35 (17.9%) | 10 (29.4%) | 2 (20.0%) | 295 (24.6%) |
| 60–69 | 98 (74.2%) | 505 (61.1%) | 63 (32.1%) | 19 (55.9%) | 2 (20.0%) | 687 (57.3%) |
| 70– | 6 (4.5%) | 18 (2.2%) | 1 (0.5%) | 1 (2.9%) | 26 (2.2%) | |
| Unknown | 2 (0.2%) | 1 (0.5%) | 3 (0.3%) | |||
| Total | 132 | 827 | 196 | 34 | 10 | 1199 |
| Median (min–max) | 60.0 (5.4–80.0) | 60.0 (2.0–99.0) | 50.0 (2.0–70.0) | 60.0 (11.0–70.0) | 43.2 (26.0–66.0) | 60.0 (2.0–99.0) |
Table 13.
Dose of irradiation (surgically treated cases)
| Dose of irradiation (Gy) | Preoperative irradiation (%) | Postoperative irradiation (%) |
|---|---|---|
| –29 | 4 (1.4%) | 6 (10.0%) |
| 30–39 | 62 (22.2%) | 3 (5.0%) |
| 40–49 | 177 (63.4%) | 5 (8.3%) |
| 50–59 | 19 (6.8%) | 19 (31.7%) |
| 60–69 | 10 (3.6%) | 24 (40.0%) |
| 70– | 4 (1.4%) | 2 (3.3%) |
| Unknown | 3 (1.1%) | 1 (1.7%) |
| Total | 279 | 60 |
| Median (min–max) | 40.0 (2.0–99.0) | 55.0 (16.0–75.9) |
Fig. 4.
Survival of patients treated with chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy
Fig. 5.
Survival of patients treated with definitive chemoradiotheraphy according to clinical stage (UICC TNM 7th)
Fig. 6.
Survival of patients underwent radiotherapy alone according to clinical stage (UICC TNM 7th)
Table 14.
Treatment modalities of esophagectomy
| Treatment modalities | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| Esophagectomy alone | 2336 (47.6%) |
| Esophagectomy + postoperative chemotherapy | 385 (7.8%) |
| Esophagectomy + postoperative chemoradiotherapy | 109 (2.2%) |
| Esophagectomy + postoperative radiotherapy | 34 (0.7%) |
| Preoperative chemotherapy + esophagectomy | 1558 (31.7%) |
| Preoperative chemoradiotherapy + esophagectomy | 286 (5.8%) |
| Definitive radiotherapy + esophagectomy | 6 (0.1%) |
| Definitive chemoradiotherapy + esophagectomy | 101 (2.1%) |
| Others | 95 (1.9%) |
| Total | 4910 |
Table 15.
Tumor location
| Locations | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| Cervical | 166 (3.4%) |
| Upper thoracic | 536 (10.9%) |
| Middle thoracic | 2165 (44.1%) |
| Lower thoracic | 1507 (30.7%) |
| EG | 368 (7.5%) |
| E = G | 85 (1.7%) |
| GE | 72 (1.5%) |
| Unknown | 11 (0.2%) |
| Total | 4910 |
Table 16.
Approaches to tumor resection
| Approaches | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| Cervical | 135 (2.7%) |
| Right thoracic | 4171 (84.9%) |
| Left thoracic | 63 (1.3%) |
| Left thoracoabdominal | 115 (2.3%) |
| Abdominal | 171 (3.5%) |
| Transhiatal lower esophagectomy | 94 (1.9%) |
| Transhiatal thoracic esophagectomy | 100 (2.0%) |
| Sternotomy | 2 (0.0%) |
| Others | 46 (0.9%) |
| Unknown | 13 (0.3%) |
| Total | 4910 |
Thoracic includes thoracotomy and thoracoscopic
Abdominal includes laparotomy and laparoscopic
Table 17.
Video-assisted surgery
| Video-assisted surgery | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| None | 2444 (49.8%) |
| Thoracoscopy | 1072 (21.8%) |
| Thoracoscopy + laparoscopy | 1037 (21.1%) |
| Thoracoscopy + laparoscopy + mediastinoscopy | 5 (0.1%) |
| Thoracoscopy + laparoscopy + other | |
| Thoracoscopy + mediastinoscopy | |
| Thoracoscopy + other | 1 (0.0%) |
| Laparoscopy | 237 (4.8%) |
| Laparoscopy + mediastinoscopy | 11 (0.2%) |
| Laparoscopy + mediastinoscopy + other | 11 (0.3%) |
| Mediastinoscopy | 57 (1.2%) |
| Laparoscopy + other | 2 (0.0%) |
| Others | 30 (0.6%) |
| Unknown | 3 (0.1%) |
| Total | 4910 |
Table 18.
Fields of lymph node dissection according to the location of tumor
| Field of lymphadenectomy | Cervical | Upper thoracic | Middle thoracic | Lower thoracic | Abdominal | E = G | GE | Unknown | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| None | 5 (3.0%) | 15 (2.8%) | 24 (1.1%) | 31 (2.1%) | 6 (1.6%) | 2 (2.4%) | 2 (2.8%) | 3 (27.3%) | 88 (1.8%) |
| C | 36 (21.7%) | 8 (1.5%) | 16 (0.7%) | 10 (0.7%) | 70 (1.4%) | ||||
| C + UM | 21 (12.7%) | 1 (0.2%) | 1 (0.0%) | 4 (0.3%) | 1 (9.1%) | 28 (0.6%) | |||
| C + UM + MLM | 10 (6.0%) | 14 (2.6%) | 47 (2.2%) | 15 (1.0%) | 1 (0.3%) | 87 (1.8%) | |||
| C + UM + MLM + A | 69 (41.6%) | 336 (62.7%) | 1098 (50.7%) | 532 (35.3%) | 62 (16.8%) | 10 (11.8%) | 1 (1.4%) | 5 (45.5%) | 2113 (43.0%) |
| C + UM + A | 5 (3.0%) | 4 (0.7%) | 17 (0.8%) | 7 (0.5%) | 1 (0.3%) | 1 | 35 (0.7%) | ||
| C + MLM | 1 (0.1%) | 1 (0.0%) | |||||||
| C + MLM + A | 3 (1.8%) | 6 (1.1%) | 14 (0.6%) | 9 (0.6%) | 1 (0.3%) | 33 (0.7%) | |||
| C + A | 3 (1.8%) | 3 (0.6%) | 4 (0.2%) | 6 (0.4%) | 1 (1.4%) | 17 (0.3%) | |||
| UM | 1 (0.6%) | 2 (0.4%) | 9 (0.4%) | 1 (0.1%) | 1 (0.3%) | 14 (0.3%) | |||
| UM + MLM | 3 (1.8%) | 8 (1.5%) | 41 (1.9%) | 24 (1.6%) | 5 (1.4%) | 1 (1.2%) | 82 (1.7%) | ||
| UM + MLM + A | 3 (1.8%) | 124 (23.1%) | 792 (36.6%) | 668 (44.3%) | 116 (31.5%) | 16 (18.8%) | 10 (13.9%) | 1729 (35.2%) | |
| UM + A | 2 (0.4%) | 12 (0.6% | 9 (0.6%) | 2 (0.5%) | 25 (0.5%) | ||||
| MLM | 3 (0.6%) | 8 (0.4%) | 8 (0.5%) | 4 (1.1%) | 1 1.2%) | 2 (2.8%) | 26 (0.5%) | ||
| MLM + A | 3 (1.8%) | 4 (0.7%) | 62 (2.9%) | 154 (10.2%) | 141 (38.3%) | 43 (50.6%) | 39 (54.2%) | 446 (9.1%) | |
| A | 4 (2.4%) | 6 (1.1%) | 20 (0.9%) | 28 (1.9%) | 28 (7.6%) | 12 (14.1%) | 16 (22.0%) | 2 (18.2%) | 116 (2.4%) |
| Total | 166 | 536 | 2165 | 1507 | 368 | 85 | 72 | 11 | 4910 |
C bilateral cervical nodes, UM upper mediastinal nodes, MLM middle-lower mediastinal nodes, A abdominal nodes
Table 19.
Reconstruction route
| Route | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| None | 62 (1.3%) |
| Subcutaneous | 353 (7.2%) |
| Retrosternal | 1971 (40.1%) |
| Posterior mediastinal | 1972 (40.2%) |
| Intrathoracic | 462 (9.4%) |
| Cervical | 49 (1.0%) |
| Others | 26 (0.5%) |
| Unknown | 15 (0.3%) |
| Total | 4910 |
Table 20.
Organs used for reconstruction
| Organs | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| None | 88 (1.3%) |
| Whole stomach | 215 (4.3%) |
| Gastric tube | 4114 (83.1%) |
| Jejunum | 249 (5.0%) |
| Free jejunum | 85 (1.7%) |
| Colon | 162 (3.3%) |
| Free colon | 8 (0.2%) |
| Others | 32 (0.6%) |
| Total organs | 4953 |
| Total cases | 4822 |
Table 21.
Histological classification
| Histological classification | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 4086 (83.2%) |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 756 (15.4%) |
| Well differentiated | 750 (15.3%) |
| Moderately differentiated | 1989 (40.5%) |
| Poorly differentiated | 591 (12.0%) |
| Adenocarcinoma | 306 (6.2%) |
| Barrett's carcinoma | 118 (2.4%) |
| Adenosquamous carcinoma | 22 (0.4%) |
| Mucoepidermoid carcinoma | 1 (0.0%) |
| Basaloid carcinoma | 86 (1.8%) |
| Neuroendocrine tumor | 1 (0.0%) |
| Neuroendocrine carcinoma | 32 (0.7%) |
| Undifferentiated carcinoma | 8 (0.2%) |
| Malignant melanoma | 16 (0.3%) |
| Carcinosarcoma | 43 (0.9%) |
| GIST | 2 (0.0%) |
| Adenoid cystic carcinoma | 3 (0.1%) |
| Sarcoma | 2 (0.0%) |
| Other carcinomas | 3 (0.1%) |
| Other tumors | 41 (0.8%) |
| Unknown | 140 (2.9%) |
| Total | 4910 |
Table 22.
Pathological depthe of tumor invasion, pT (JES 10th)
| Pathological depth of tumor invasion | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| pTx | 72 (1.5%) |
| pT0 | 161 (3.3%) |
| pT1a | 589 (12.0%) |
| pT1b | 1339 (27.3%) |
| pT2 | 607 (12.4%) |
| pT3 | 1898 (38.7%) |
| pT4a | 138 (0.8%) |
| pT4b | 106 (2.2%) |
| Total | 4910 |
Table 23.
Pathological grading of lymph node metastasis, pN (JES 10th)
| Lymph node metastasis | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| pN0 | 2335 (47.6%) |
| pN1 | 936 (19.1%) |
| pN2 | 1000 (20.4%) |
| pN3 | 354 (7.2%) |
| pN4 | 254 (5.2%) |
| Unknown | 31 (0.6%) |
| Total | 4910 |
Table 24.
Pathological grading of lymph node metastasis, pN (UICC TNM 7th)
| Lymph node metastasis | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| pN0 | 2361 (48.1%) |
| pN1 (1–2) | 1374 (28.0%) |
| pN2 (3–6) | 757 (15.4%) |
| pN3 (7–) | 366 (7.5%) |
| Unknown | 52 (1.1%) |
| Total | 4910 |
Table 25.
Pathological findings of distant organ metastasis, pM (JES 10th)
| Distant metastasis (M) | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| MX | 125 (2.5%) |
| M0 | 4715 (96.0%) |
| M1 | 70 (1.4%) |
| Total | 4910 |
Table 26.
Residual tumor
| Residual tumor (R) | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| RX | 126 (2.6%) |
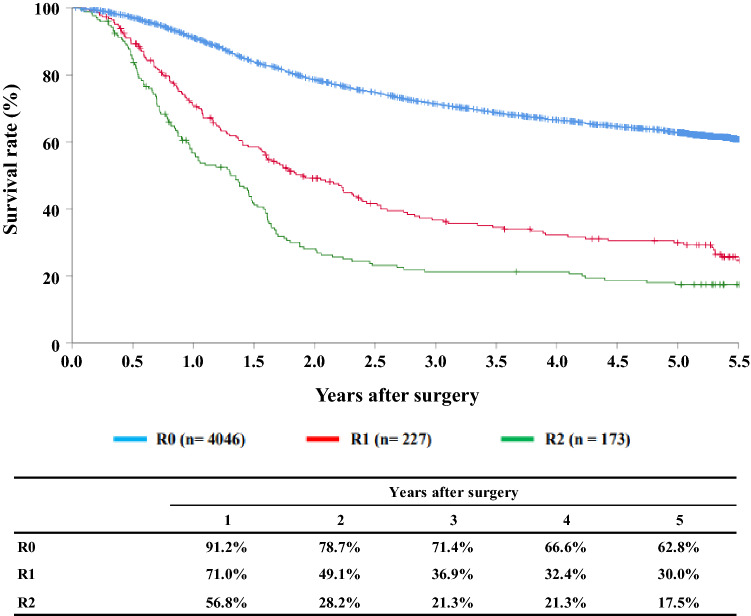
| R0 | 4359 (88.8%) |
| R1 | 239 (4.9%) |
| R2 | 186 (3.8%) |
| Total | 4910 |
Table 27.
Cause of death
| Cause of death | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| Death due to recurrence | 1584 (63.8%) |
| Death due to other cancer | 193 (7.8%) |
| Death due to other disease (with recurrence) | 50 (2.0%) |
| Death due to other disease (without recurrence) | 330 (13.3%) |
| Death due to other disease (recurrence unknown) | 15 (0.6%) |
| Operative deatha | 38 (1.5%) |
| Postoperative hospital deathb | 59 (2.4%) |
| Unknown | 213 (8.6%) |
| Total of death cases | 2482 |
aOperative death means death within 30 days after operation in or out of hospital. Operative mortality rate: 0.77%
bHospital death is defined as death during the same hospitalization, regardless of department at time of death. Hospital mortality rate: 1.98%

Fig. 7.
Survival of patients who underwent esophagectomy
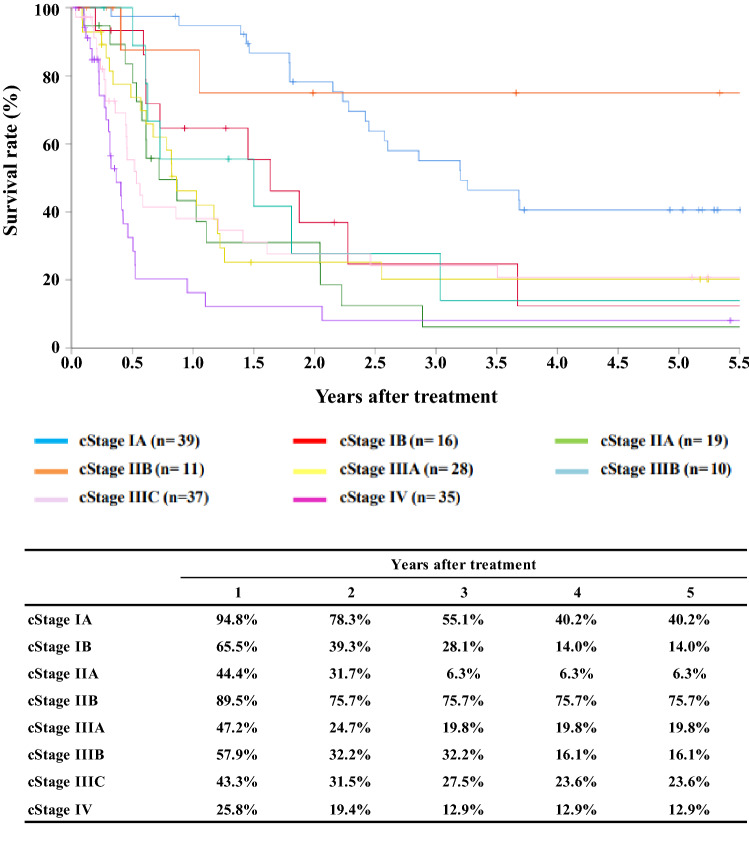
Fig. 8.
Survival of patients who underwent eseophagectomy according to clinical stage (JES 10th)
Fig. 9.
Survival of patients who underwent esophagectomy according to clinical stage (UICC TNM 7th)
Fig. 10.
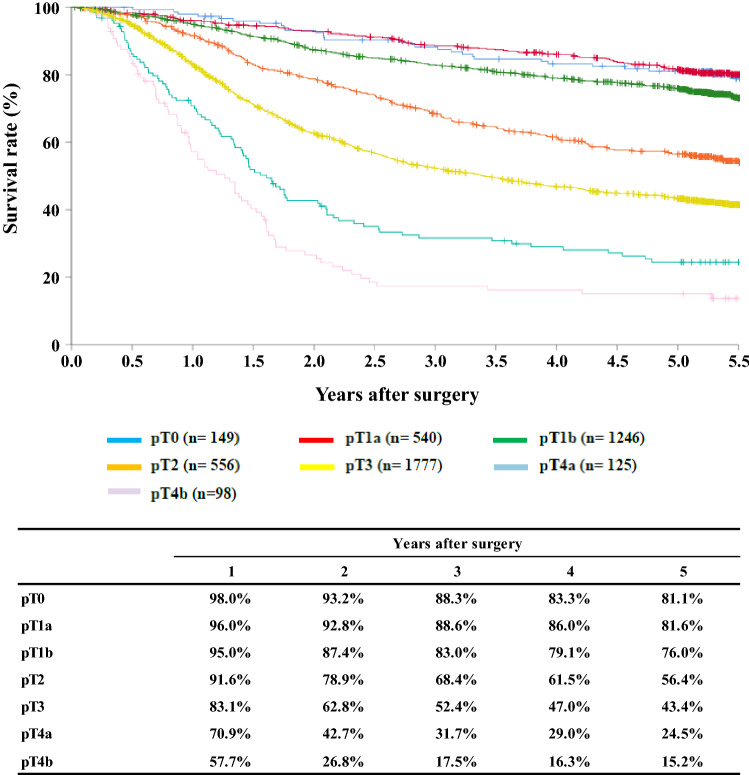
Survival of patients who underwent esophagectomy according to the depth of tumor invasion, pT (JES 10th)
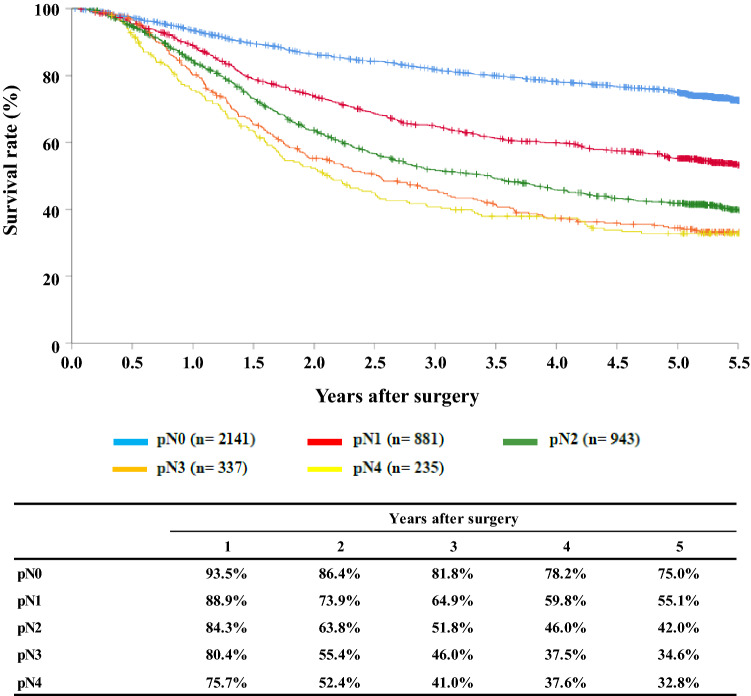
Fig. 11.
Survival of patients who underwent esophagectomy according to lymph node metastasis (JES 10th)
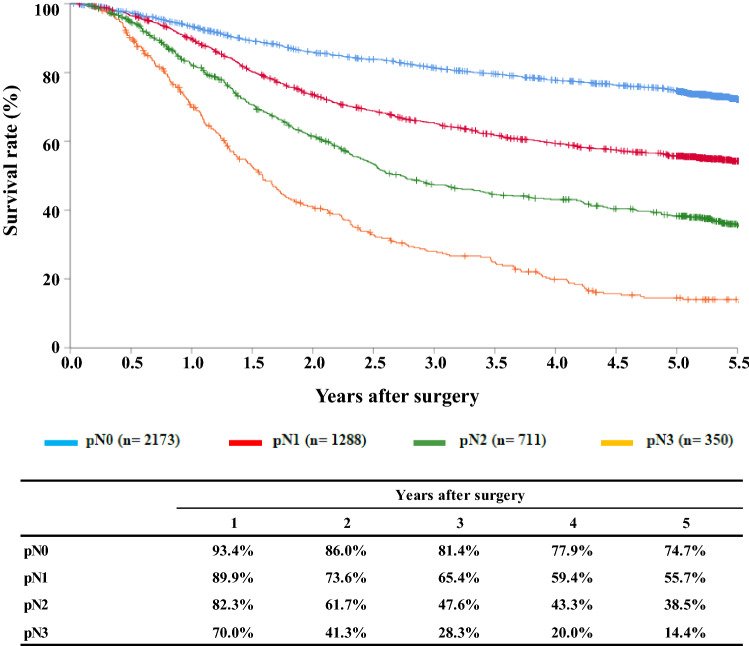
Fig. 12.
Survival of patients who underwent esophagectomy according to lymph node metastasis (UICC TNM 7th)
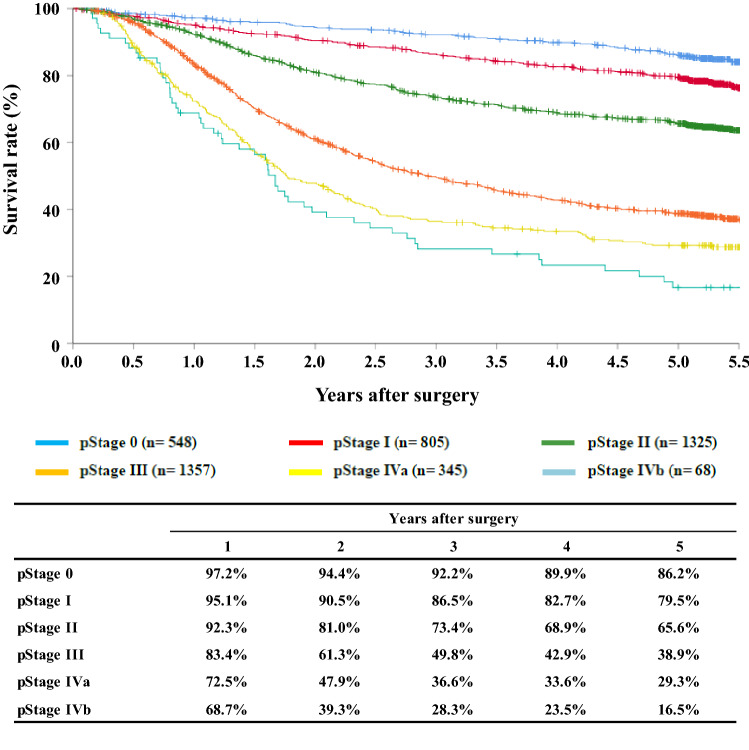
Fig. 13.
Survival of patients who underwent esophagectomy according to pathological stage (JES 10th)
Fig. 14.
Survival of patients who underwent esophagectomy according to pathological stage (UICC TNM 7th)
Fig. 15.
Survival of patients who underwent esophagectomy according to residual tumor (R)
I. Clinical features of esophageal cancer patients treated in 2013
Institution-registered cases in 2013.
| Institutions |
|---|
| Ageo Central General Hospital |
| Aichi Cancer Center |
| Aichi Medical University Hospital |
| Aizawa Hospital |
| Akita University Hospital |
| Aomori Prefectural Central Hospital |
| Arao Municipal Hospital |
| Asahikawa Medical University Hospital |
| Cancer Institute Hospital of JFCR |
| Chiba Cancer Center |
| Chiba University Hospital |
| Chibaken Saiseikai Narashino Hospital |
| Chiba-Nishi General Hospital |
| Chigasaki Municipal Hospital |
| Chugoku Rosai Hospital |
| Dokkyo Medical University Hospital |
| Ehime Prefectural Central Hospital |
| Eijyu General Hospital |
| Fuchinobe General Hospital |
| Fuchu Hospital |
| Fujinomiya City General Hospital |
| Fujioka General Hospital |
| Fujisaki Hospital |
| Fujita Health University Hospital |
| Fukaya Red Cross Hospital |
| Fukui Prefectural Hospital |
| Fukui University Hospital |
| Fukui-ken Saiseikai Hospital |
| Fukuoka City Hospital |
| Fukuoka Shin Mizumaki Hospital |
| Fukuoka University Chikushi Hospital |
| Fukuoka University Hospital |
| Fukuoka Wajiro Hospital |
| Fukushima Medical University Hospital |
| Fukuyama City Hospital |
| Gifu Prefectural General Center |
| Gifu University Hospital |
| Gunma Prefectural Cancer Center |
| Gunma Saiseikai Maebashi Hospital |
| Gunma University Hospital |
| Hachinohe City Hospital |
| Hakodate City Hospital |
| Hakodate Goryokaku Hospital |
| Hakodate National Hospital |
| Hamamatsu University Hospital |
| Heartlife Hospital |
| Higashiosaka City Medical Center |
| Hiraka General Hospital |
| Hiratsuka City Hospital |
| Hiratsuka Kyosai Hospital |
| Hirosaki University Hospital |
| Hiroshima City Asa Hospital |
| Hiroshima City Hospital |
| Hiroshima Red Cross Hospital & Atomic-bomb Survivors Hospital |
| Hiroshima University Hospital |
| Hitachi General Hospital |
| Hofu Institute of Gastroenterology |
| Hokkaido University Hospital |
| Hospital of the University of Occupational and Environmental Health, Japan |
| Hyogo Cancer Center |
| Hyogo Prefectural Amagasaki General Medical Center |
| Ibaraki Prefectural Central Hospital |
| Iizuka Hospital |
| International Goodwill Hospital |
| International University of Health and Welfare Atami Hospital |
| International University of Health and Welfare Hospital |
| International University of Health and Welfare Ichikawa Hospital |
| International University of Health and Welfare Mita Hospital |
| Isehara Kyodo Hospital |
| Ishikawa Prefectural Central Hospital |
| Itami City Hospital |
| Iwata City Hospital |
| Iwate Medical University Hospital |
| Iwate Prefectural Central Hospital |
| Iwate Prefectural Chubu Hospital |
| JA Hiroshima General Hospital |
| JA Kouseiren Enshu Hospital |
| JA Onomichi General Hospital |
| Japanese Red Cross Ashikaga Hospital |
| Japanese Red Cross Fukuoka Hospital |
| Japanese Red Cross Ishinomaki Hospital |
| Japanese Red Cross Kitami Hospital |
| Japanese Red Cross Kyoto Daiichi Hospital |
| Japanese Red Cross Maebashi Hospital |
| Japanese Red Cross Medical Center |
| Japanese Red Cross Musashino Hospital |
| Japanese Red Cross Nagasaki Genbaku Hospital |
| Japanese Red Cross Nagoya Daiichi Hospital |
| Japanese Red Cross Saitama Hospital |
| Japanese Red Cross Society Nagano Hospital |
| Japanese Red Cross Tottori Hospital |
| Japanese Red Cross Wakayama Medical Center |
| JCHO Gunma Chuo Hospital |
| JCHO Kyushu Hospital |
| JCHO Miyazaki Konan Hospital |
| JCHO Osaka Hospital |
| JCHO Saitama Medical Center |
| JCHO Tokuyama Central Hospital |
| JCHO Yokohama Chuo Hospital |
| Jichi Medical University Hospital |
| Jichi Medical University Saitama Medical Center |
| Juntendo University Hospital |
| Juntendo University Shizuoka Hospital |
| Juntendo University Urayasu Hospital |
| Junwakai Memorial Hospital |
| Kagawa Prefectural Central Hospital |
| Kagawa Rosai Hospital |
| Kagawa University Hospital |
| Kagoshima University Hospital |
| Kaizuka City Hospital |
| Kakogawa Central City hospital |
| Kanagawa Cancer Center |
| Kanazawa Medical University Hospital |
| Kanazawa University Hospital |
| Kansai Denryoku Hospital |
| Kansai Medical University Hospital |
| Kansai Medical University Medical Center |
| Kansai Rosai Hospital |
| Kanto Central Hospital |
| Kashiwa Kousei General Hospital |
| Kasugai Municipal Hospital |
| Kawasaki Hospital |
| Kawasaki Medical School Hospital |
| Kawasaki Medical School Kawasaki Hospital |
| Kawasaki Municipal Hospital |
| Kawasaki Municipal Ida Hospital |
| Kawasaki Saiwai Hospital |
| Keio University Hospital |
| Keiyukai Sapporo Hospital |
| Kindai University Hospital |
| Kindai University Nara Hospital |
| Kinki Central Hospital |
| Kiryu Kousei General Hospital |
| Kitaakita Municipal Hospital |
| Kitaharima Medical Center |
| Kitakyushu General Hospital |
| Kitakyushu Municipal Medical Center |
| Kitano Hospital |
| Kitasato University Hospital |
| Kobe City Medical Center General Hospital |
| Kobe University Hospital |
| Kochi Health Science Center |
| Kochi University Hospital |
| Kokura Memorial Hospital |
| Kouseiren Takaoka Hospital |
| Kumagai General Hospital |
| Kumamoto University Hospital |
| Kummoto Regional Medical Center |
| Kurashiki Central Hospital |
| Kurume University Hospital |
| Kyorin University Hospital |
| Kyoto University Hospital |
| Kyoto-Katsura Hospital |
| Kyushu Central Hospital |
| Kyushu University Hospital |
| Machida Municipal hospital |
| Matsudo City General Hospital |
| Matsushita Memorial Hospital |
| Matsuyama Red Cross Hospital |
| Mie University Hospital |
| Minamiosaka Hospital |
| Minoh City Hospital |
| Mito Red Cross Hospital |
| Mitsui Memorial Hospital |
| Miyazaki University Hospital |
| Mizushima Kyudo Hospital |
| Moriguchi Keijinkai Hospital |
| Murakami General Hospital |
| Nagahama City Hospital |
| Nagahama Red Cross Hospital |
| Nagano Municipal Hospital |
| Nagaoka Chuo General Hospital |
| Nagasaki University Hospital |
| Nagoya City University Hospital |
| Nagoya City West Medical Center |
| Nagoya University Hospital |
| Nanpuh Hospital |
| Nara City Hospital |
| Nara Medical University Hospital |
| Nasu Red Cross Hospital |
| National Cancer Center Hospital |
| National Cancer Center Hospital East |
| National Center for Global Health and Medicine |
| National Defence Medical College Hospital |
| New Tokyo Hospital |
| NHO Beppu Medical Center |
| NHO Chiba Medical Center |
| NHO Fukuoka-Higashi Medical Center |
| NHO Iwakuni Clinincal Center |
| NHO Kanmon Medical Center |
| NHO Kure Medical Center |
| NHO Kyoto Medical Center |
| NHO Kyushu Cancer Center |
| NHO Matsumoto Medical Center |
| NHO Mito Medical Center |
| NHO Miyakonojo Medical Center |
| NHO Nagasaki Medical Center |
| NHO Nagoya Medical Center |
| NHO Okayama Medical Center |
| NHO Osaka Medical Center |
| NHO Saitama Hospital |
| NHO Sendai Medical Center |
| NHO Shikoku Cancer Center |
| NHO Tokyo Medical Center |
| NHO Yokohama Medical Center |
| Nihonkai General Hospital |
| Niigata Cancer Center Hospital |
| Niigata City General Hospital |
| Niigata Prefectural Central Hospital |
| Niigata Prefectural Shibata Hospital |
| Niigata University Medical & Detal Hospital |
| Nikko Memorial Hospital |
| Nippon Medical School Chiba Hokusou Hospital |
| Nippon Medical School Hospital |
| Nippon Medical School Musashi Kosugi Hospital |
| Nippon Medical School Tama Nagayama Hospital |
| Nishi Kobe Medical Center |
| Nissan Tamagawa Hospital |
| Nozaki Tokushukai Hospital |
| Numazu City Hospital |
| Obihiro Kousei Hospital |
| Ogaki Municipal Hospital |
| Ohta Hospital |
| Ohta Nishinouchi Hospital |
| Oita Red Cross Hospital |
| Oita University Hospital |
| Okayama Red Cross General Hospital |
| Okayama Saiseikai General Hospital |
| Okayama University Hospital |
| Okitama Public General Hospital |
| Onomichi Municipal Hospital |
| Osaka City General Hospital |
| Osaka City University Hospital |
| Osaka Ekisaikai Hospital |
| Osaka General Medical Center |
| Osaka International Cancer Institute |
| Osaka Medical College Hospital |
| Osaka Police Hospital |
| Osaka Red Cross Hospital |
| Osaki City Hospital |
| Otsu City Hospital |
| Rinku General Medical Center |
| Saga Prefectural Hospital Koseikan |
| Saga University Hospital |
| Sagamihara National Hospital |
| Saiseikai Fukuoka General Hospital |
| Saiseikai Karatsu Hospital |
| Saiseikai Noe Hospital |
| Saiseikai Utsunomiya Hospital |
| Saiseikai Yokohama Tobu Hospital |
| Saitama Cancer Center |
| Saitama Medical University International Medical Center |
| Saitama Medical University Saitama Medical Center |
| Sakai City Medical Center |
| Saku Central Hospital |
| Sapporo Medical University Hospital |
| Seikei-kai Chiba Medical Center |
| Sendai City Hospital |
| Shiga General Hospital |
| Shiga University of Medical Science Hospital |
| Shimane University Hospital |
| Shin Takeo Hospital |
| Shinko Hospital |
| Shinshu University Hospital |
| Shizuoka Cancer Center |
| Shizuoka City Shizuoka Hospital |
| Shizuoka General Hospital |
| Shizuoka Saiseikai General Hospital |
| Showa University Hospital |
| Southern Tohoku General Hospital |
| St. Luke's International Hospital |
| St. Marianna University School of Medicine Hospital |
| St. Mary's Hospital |
| Steel Memorial Yawata Hospital |
| Suita Municipal Hospital |
| Suzuka Chuo General Hospital |
| Tachikawa Hospital |
| Takatsuki Red Cross Hospital |
| Teikyo University Chiba Medical Center |
| Teikyo University Hospital |
| Teine Keijinkai Hospital |
| Tenri Hospital |
| The Hospital of Hyogo College of Medicine |
| The Jikei University Daisan Hospital |
| The Jikei University Hospital |
| Tochigi Cancer Center |
| Toho University Ohashi Medical Center |
| Toho University Omori Medical Center |
| Toho University Sakura Medical Center |
| Tohoku University Hospital |
| Tokai University Hachioji Hospital |
| Tokai University Hospital |
| Tokai University Tokyo Hospital |
| Tokushima Red Cross Hospital |
| Tokushima University Hospital |
| Tokyo Dental College Ichikawa General Hospital |
| Tokyo Medical and Dental University Hospital |
| Tokyo Medical University Hachioji Medical Center |
| Tokyo Medical University Hospital |
| Tokyo Metropolitan Cancer and Infectious Diseases Center Komagome Hospital |
| Tokyo Metropolitan Tama Medical Center |
| Tokyo Rosai Hospital |
| Tokyo University Hospital |
| Tokyo Women's Medical University Hospital |
| Tokyo Women's Medical University Medical Center East |
| Tokyo Women's Medical University Yachiyo Medical Center |
| Tonan Hospital |
| Toranomon Hospital |
| Tosei General Hospital |
| Toshima Hospital |
| Tottori Prefectural Central Hospital |
| Tottori University Hospital |
| Toyama Prefectural Central Hospital |
| Toyama University Hospital |
| Toyonaka Municipal Hospital |
| Toyota Memorial Hospital |
| Tsuchiura Kyodo Hospital |
| Tsukuba University Hospital |
| Tsuruoka Municipal Shonal Hospital |
| Tsuyama Chuo Hospital |
| University Hospital Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine |
| University of the Ryukyus Hospital |
| Wakayama Medical University Hospital |
| Yamagata Prefectural Central Hospital |
| Yamagata University Hospital |
| Yamaguchi University Hospital |
| Yamanashi Prefectural Central Hospital |
| Yamanashi University Hospital |
| Yao Municipal Hospital |
| Yokohama City Municipal Hospital |
| Yokohama City University Hospital |
| Yokohama City University Medical Center |
| Yokohama Sakae Kyosai Hospital |
| Yokosuka General Hospital Uwamachi |
(Total 334 institutions)
Patient background
II. Results of endoscopically treated patients in 2013
Tables 9, 10, 11, and Figs. 1, 2, 3.
III. Results in patients treated with chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy in 2013
IV. Results in patients who underwent esophagectomy in 2013
Tables 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, and Figs. 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15
Compliance with ethical standards
Conflict of interest
All authors have nothing to disclose with regard to commercial support.
Ethical statement
All procedures followed in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1964 and later versions.
Footnotes
These data were first made available on July 15, 2020, as the Comprehensive Registry of Esophageal Cancer in Japan, 2013.
The authors were members of the Registration Committee for Esophageal Cancer, the Japan Esophageal Society, and made great contribution to the preparation of this material.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Reference
- 1.Japan Esophageal Society Japanese classification of esophageal cancer, 10th edition: part 1. Esophagus. 2009;6:1–25. doi: 10.1007/s10388-009-0169-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK, Wittekind C, UICC International Union Against Cancer . TNM classification of malignant tumors. 7. New York: Wiley-Blackwell; 2009. [Google Scholar]