Abstract
Cognitive side effects of anticholinergic medications in older adults are well documented. Whether these poor cognitive outcomes are observed in children has not been systematically investigated. We aimed to conduct a systematic review and meta-analysis on the associations between anticholinergic medication use and cognitive performance in children. Systematic review was conducted using Medline, PsychInfo, and Embase, identifying studies testing cognitive performance relative to the presence versus absence of anticholinergic medication(s) in children. We assessed effects overall, as well as relative to drug class, potency (low and high), cognitive domain, and duration of administration. The systematic search identified 46 articles suitable for meta-analysis. For the most part, random effects meta-analyses did not identify statistically significant associations between anticholinergic exposure and cognitive performance in children; the one exception was a small effect of anticholinergic anti-depressants being associated with better cognitive function (Hedges’ g = 0.24, 95% CI 0.06–0.42, p = 0.01). Anticholinergic medications do not appear to be associated with poor cognitive outcomes in children, as they do in older adults. The discrepancy in findings with older adults may be due to shorter durations of exposure in children, differences in study design (predominantly experimental studies in children rather than predominantly epidemiological in older adults), biological ageing (e.g. blood brain barrier integrity), along with less residual confounding due to minimal polypharmacy and comorbidity in children.
Subject terms: Outcomes research, Cognitive ageing, Paediatric research
Introduction
Anticholinergic medications are commonly prescribed1–3 yet a growing body of evidence has demonstrated that their use is associated with a higher risk of incident cognitive impairment4–6. This literature has been reviewed multiple times in older adults, whereby anticholinergic medications have been consistently associated with cognitive decline and dementia7–9. There has been no systematic synthesis of the cognitive effects of anticholinergic medications in children.
There are few population-based studies that have assessed the extent to which children are exposed to anticholinergic medicines1. Most studies examining anticholinergic medicines in children have focussed on the use of medicine classes for specific indications, for example, asthma or overactive bladder, rather than providing population-based estimates for the use of anticholinergic medicines like the studies in older adults. Approximately 11% of Australian children have a current diagnosis of asthma10 and up to 20% of children experience bedwetting11 so there is potential for a high prevalence of use of anticholinergic medicines to treat these conditions in children. One population based study from Slovenia reported that 20% of children using prescription medicines were dispensed anticholinergic medicines, most commonly antihistamines1.
Anticholinergic medications refer to a broad class of medicines which block the neurotransmitter acetylcholine12. These medications are used in the treatment of many conditions such as depression, vertigo, asthma, cardiac arrhythmias and incontinence. High potency anticholinergic medications appear to most detrimentally affect cognition in older adults (as compared to low potency)13. Further, the class of anticholinergic medication differentially associates with cognitive decline in late-life, with anti-depressants (amitriptyline, dosulepin, paroxetine), urologicals (oxybutynin, tolterodine), and antiparkinsonian drugs showing the strongest associations with incident dementia4. Neurobiologically, the cholinergic system primarily mediates attentional processes14–17 and therefore could be expected to be primarily impaired by anticholinergic medications, although cognitive domain specific effects have not been investigated.
The current study aims to quantitively synthesise the literature on associations between anticholinergic medications and cognitive performance in children. Findings from this review will inform medical practitioners of any risks (or lack thereof) associated with anticholinergic use in children, and subsequently help to inform the safe prescribing of anticholinergics. It is critical to identify whether anticholinergics should be prescribed with restraint in children. We hypothesise that in children (1) exposure to anticholinergic medications will be significantly negatively associated with performance on cognitive tests, and that associations will be strongest for (2) antidepressant and urological drug classes (as compared to other drug classes), (3) high-potency anticholinergics (as compared to low-potency), (4) those exposed long-term (as opposed to short-term) and (5), within the cognitive domain of attention.
Methods
Search strategy
This study adhered to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines (see Supplementary Table 1 for PRISMA Checklist)18,19. A systematic literature search was conducted in December 2019 using the electronic databases Medline, PsychInfo, and Embase. The search strategy used a combination of keywords for anticholinergic medications (see Supplementary Material), cognition terms (cognit* OR neuropsych* OR learn* OR memory OR "executive function" OR "executive functions") and demographic terms (children OR childhood OR youth* OR teen*). No published review protocol exists for the current study.
Anticholinergic medications were defined as medicines with clinically significant anticholinergic properties as listed in a systematic review by Duran et al.12. Medications assessed by the Duran systematic review to be of either high or low anticholinergic potency, but not ambiguous potency, were included. Studies were screened and assessed for eligibility by two independent reviewers, first by title and abstract, then by full text, according to inclusion and exclusion criteria described below (MC, TJR, DC, CS and JNH). Any conflicts were resolved through consensus.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Studies of either within- or between-groups design were included if they reported at least one cognitive outcome for both children exposed and unexposed to anticholinergic medications; reported data for a sample of children (< 18 years old); were published in English; and were published in peer-reviewed journal articles. Studies from all publication years were accepted. “On” medication participants included children exposed to at least one anticholinergic medication. “Off” medication participants included matched controls unexposed to any other medication, participants treated with placebo, participants undergoing withdrawal from the medication, or the baseline measurements of the exposed group. To be eligible for inclusion, studies needed to report cognitive outcomes based on objective cognitive measures; subjective behavioural reports were not included (e.g. self, parent or teacher reports of cognitive functioning). Studies were excluded if the control group did not share the same disorder or symptom (i.e. healthy control group) of the experimental group. Studies which only compared the effects of anticholinergic medication versus non-anticholinergic medication, rather than anticholinergic medication versus no medication, were excluded. Studies were also excluded if they involved non-human (animal) participants; if they assessed in-utero anticholinergic exposure; or if they were a case report, case series, thesis or conference abstract.
Data extraction
Data were extracted from eligible studies independently by one reviewer (EG, MC, TJR) and then checked by a second reviewer, with any discrepancies resolved through discussion or checked again (by a third reviewer). Extracted data include country of publication, study design, sample size (and number of male/female participants), age, diagnoses of sample, name of medication, duration of administration, and cognitive domains assessed. The extracted medication name was then classified by potency and drug class by an academic pharmacist (LE). Data required for meta-analysis were also extracted. This included any data for which an effect size (standardised mean difference) could be calculated for differences between on and off medication groups (e.g., means and standard deviations, Cohen’s d and confidence intervals (CIs), sample size and correlation statistic, means and correlation statistic, or means and p-value).
Quality assessment
A quality assessment tool was developed for this study, adapted from a critical appraisal tool for randomised controlled trials from the Joanna Briggs Institute20, see Supplementary Material—Quality Assessment Tool. The Joanna Briggs Institute is a highly regarded organization with recommended21 and well-used critical appraisal checklists22–24. The quality assessment tool comprised an eight-point checklist. All studies were screened using this tool by two independent reviewers (MC and TJR) and any conflicts in scoring were resolved through discussion.
Statistical approach
Some included studies reported data for both within- and between-groups designs. For example, they may include two groups: one that experiences a period of on and off medication, and one non-medicated control group. In these cases, the between-group design (i.e. medication versus control) was preferentially selected in order to minimise the effect of cognitive development (over time). Where one study reported both within- and between-group comparisons for two distinct participant samples (i.e. one group both on and off medication, along with a second group on medication and a third no-medication control group) both within- and between-groups data were extracted. In cases where one study reported both (within and between) comparisons over multiple time-points, within-groups data were extracted for any time-points where between-groups data were unavailable.
All outcome measures were standardised using Hedges’ g for difference between on- and off-medication groups. A positive Hedges’ g represents a better cognitive score for the on-medication group compared to the off-medication group, regardless of the direction of the original cognitive test. Small, medium, and large effect sizes were classified using the Hedges and Olkin25 method, as 0.20, 0.50, and 0.80 respectively. Comprehensive Meta-Analysis software (version 3) was used to calculate effect sizes, where calculations of Hedge’s g are dependent on study design (within- or between-groups). Statistical analyses were conducted using the meta package26 for R (Version 4.0.2). Dependency was present in analyses due to included studies reporting multiple cognitive outcomes or time-points for follow-up based on the same, or largely overlapping, participant samples. This was accounted for by averaging across effect sizes within studies, so one effect size was used per study within each analysis. The data and script associated with this analysis are publicly available (https://github.com/ericaghezzi/anticholinergic_med_metaanalysis).
Outcomes across studies were pooled using a random-effects model. The commonly used DerSimonian and Laird27 estimator of between-study variance has been criticised due to its propensity to underestimate true between-study variance, leading to narrow CIs and potential false-positive estimations28,29. Hence, we followed the recommendation of Veroniki et al.30 and employed the Paule and Mandel31 method, which has been shown to be less biased29,32 when estimating between-study variance. Sensitivity analyses revealed no substantial differences in outcomes when analyses were run using common between-groups estimators. The Hartung-Knapp method for random effects meta-analysis33,34 was also applied to all analyses. A result was considered statistically significant when p < 0.05. We considered this an exploratory study and did not correct for multiple comparisons. Between-study variance was quantified using τ2. The proportion of between-study heterogeneity out of total variance was assessed using the I2 statistic. Values of I2 were classified as low (25%), moderate (50%), or high (75%)35.
Subgroup analysis
Subgroup analyses were stratified by anticholinergic potency, cognitive domain, drug class, and duration of medication administration. Anticholinergic potency was classified as low or high according to Durán et al.12. Cognitive domain was based on Lezak et al.36: attention, psychomotor functioning, concept formation and reasoning, perception, memory, executive function, language, and intelligence. The anticholinergic drugs administered were categorised by class as antiepileptics (WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical code N03), antiparkinsonian medicines (N04B), antipsychotics (N05A), antidepressants (N06A), respiratory medicines (R), opioid analgesics (N02A), or urological medicines (G04B). Only one study37 reported results based on an antiparkinsonian anticholinergic, so subgroup meta-analysis of this medication class was not conducted (note: the study was included in the overall meta-analysis). Total volume of exposure or dose has been shown to be important in assessing risk of cognitive impairment associated with use of anticholinergic medicines in adults; however, dose was inconsistently reported, or not reported at all, in many of the studies included in the meta-analysis. Duration of exposure, which was consistently reported in the studies, was therefore analysed. Duration of medication administration was categorised as either (1) current and long-term (> 1-month), (2) current and acute (≤ 1-month) and (3) historical administration. Each subgroup analysis was based on a random-effects model, where calculations of within-subgroup variance and comparisons between subgroups were both made using a random-effects model. Fixed effects comparisons of differences between subgroups were not made due to the risk of false positives38. The Q statistic was calculated as a test of between subgroups differences.
Publication bias. Funnel plots of effect size versus standard error for the primary outcome were visually examined for symmetry to assess for bias across studies due to the small-study effect39. As the whole meta-analysis contained at least 10 studies, small-study effect was formally tested using Egger’s test of the intercept40. If evidence of asymmetry was found (one-tailed p < 0.1 on the Egger’s test), Duval and Tweedie’s41 trim and fill method would have been used to quantify the magnitude of potential bias.
Results
Summary of studies
A total of 7,645 articles were identified, of which 6,283 were screened by title and abstract following duplicate removal. Full-text review was conducted on 323 articles, and 46 of these were included for final review and meta-analysis (Fig. 1). The 46 included studies were published across 6 decades, with 1, 2, 7, 10, 13, and 13 studies published in ascending decades from the 1960s. Of the included studies, 37 were conducted in developed countries, 7 in developing countries, and 2 included children from both developing and developed countries (classified according to the UN42). For a complete overview of the characteristics of included studies, see Table 1.
Figure 1.
PRISMA flow diagram of the article selection and screening process. The databases searched were Medline, PsychInfo, and Embase.
Table 1.
Demographic, sample, anticholinergic medication and cognitive outcome characteristics for included studies within meta-analysis for cognitive outcomes on and off anticholinergic medication.
| Author | Year | Country | Design | Sample | Anticholinergic medication | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (M/F) | Age in years* | Diagnoses | Name | Potency | Class/function | Length of administration | Medication duration | Cognitive domain(s) | ||||
| Aldenkamp et al.43 | 1993 | Sweden | NRCT (Within) | 83 (47/36) | 12.8 (2.4) | Epilepsy | Carbamazepine | Low | Antiepileptic | Long | > 1 year | Att., PM |
| Aman et al.44 | 2008 | USA | RCT (Between**) | 38 (29/9) | 9.4 (3.0) | Autism + Severe behavioural disturbance | Risperidone | Low | Antipsychotic | Acute, Long | 4 weeks, 8 weeks | Att., CF + R, Mem., Perc., PM, |
| Aman et al.45 | 2009 | USA | RCT (Crossover) | 16 (14/2) | 8.6 (2.6) | DBD/ADHD/High-functioning autism | Risperidone | Low | Antipsychotic | Acute | 2 weeks | Att., PM |
| Barrickman et al.46 | 1991 | USA | NRCT (Within) | 19 (16/3) | 11.0 (2.3) | ADHD | Fluoxetine | Low | Antidepressant | Long | 6 weeks | Att., EF, Int |
| Beers et al.37 | 2005 | USA | RCT (Between**) | 13 | 11.9 (3.0) | TBI | Amantadine | Low | Antiparkinsonian | Long | 12 weeks | Att., CF + R, EF |
| Bender and Milgrom47 | 2004 | USA | RCT (Between) | 60 | [8–17] | SAR | Loratadine | Low | Respiratory | Acute | 2 weeks | Att., Mem |
| Bender et al.48 | 1991 | USA | NRCT (Between) | 63 | 11.7 (2.1) | Asthma | Theophylline | Low | Respiratory | Acute | 1 week, 1 month, 3 months, 6 months | Att |
| Carlson et al.49 | 1992 | USA | NRCT (Crossover) | 11 (8/3) | 8.7 (2.4) | CD with manic symptoms/CD with family BPD history/Aggressive behaviour | Lithium | Low | Antipsychotic | Acute, Long | 4 weeks, 8 weeks | Att., EF + R, Mem |
| Chen et al.50 | 2001 | Taiwan | NRCT (Within) | 25 (13/12) | 11.2 (2.0) | Epilepsy | Carbamazepine | Low | Antiepileptic | Long | > 1 year | Int |
| de Graaf et al.51 | 2011 | Netherlands | RCT (Between) | 90 (51/39) | < 3d at exposure; 5 at follow up | Pain | Morphine | Low | Opioid analgesic | History | NR | Int., PM |
| de Graaf et al.52 | 2013 | Netherlands | RCT (Between) | 89 (56/33) | < 3d at exposure; 8 – 9 at follow-up | Pain | Morphine | Low | Opioid analgesic | History | NR | Att., CF + R, EF, Int., PM |
| Donati et al.53 | 2007 | Europe (7 countries) | RCT (Within) | 83 (37/46) | 10 [6–16] | Partial seizures |
Oxcarbazepine, Carbamazepine |
Low | Antiepileptic | Long | 6 months | Att., Mem, Perc., PM |
| Erickson et al.54 | 1984 | USA | RCT (Within) | 11 | 14.2 (12.9–18.6) | Schizophrenia/Schizophreniform disorder | Thioridazine, Thiothixene | High | Antipsychotic | Long | 35 days | Att |
| Eun et al.55 | 2012a | South Korea | RCT (Within) | 41 (24/17) | 8.3 (2.1) | Epilepsy | Carbamazepine | Low | Antiepileptic | Long | 32 weeks | Int |
| Eun et al.56 | 2012b | South Korea | NRCT (Within) | 168 (98/70) | 8.4 (2.7) | Epilepsy | Oxcarbazepine | Low | Antiepileptic | Long | 26–32 weeks | Att., Int., CF + R, Lan., PM |
| Farmer et al.57 | 2017 | USA | RCT (Between) | 165 (128/3) | 8.9 (2.0) | ADHD + Severe physical aggression | Risperidone | Low | Antipsychotic | Acute | 3 weeks | Att |
| Ferguson et al.58 | 2012 | USA | RCT (Between) | 19 (12/7) | Neonate exposure; 6.2 (0.3) at follow-up | Pain | Morphine | Low | Opioid analgesic | History | ≤ 14 days | Att., CF + R, Int., Lan |
| Forsythe et al. 59 | 1991 | UK | RCT (Within) | 14 (7/7) | 10 | Epilepsy | Carbamazepine | Low | Antiepileptic | Acute, Long | 1 month, 6 months, 12 months | Att., Mem |
| Freibergs et al.60 | 1968 | Canada | RCT (Between**) | 36 (36/0) | 8.7 (6–12) | Hyperactivity | Chlorpromazine | High | Antipsychotic | Long | 74.8 days | CF + R |
| Giramonti et al.61 | 2008 | USA | RCT (Crossover) | 14 (9/5) | 7.7 (2.0) | Incontinence | Oxybutynin, Tolterodine | High | Urological | Acute | 2 weeks | Att., Mem |
| Gualtieri and Evans 62 | 1988 | USA | RCT (Crossover) | 9 (6/3) | 9.5 (1.3) | ADHD | Imipramine | High | Antidepressant | Acute | 2–3 days | Att., PM |
| Gualtieri et al.63 | 1991 | USA | RCT (Crossover) | 12 (11/1) | [6–12] | ADHD | Desipramine | High | Antidepressant | Acute | 2–3 days | Att., Mem, PM |
| Gunther et al.64 | 2006 | Germany | NRCT (Within) | 23 (21/2) | 11.9 (2.1) | ADHD + DBD | Risperidone | Low | Antipsychotic | Acute | 4 weeks | Att., EF |
| Jung et al.65 | 2015 | South Korea | RCT (Within) | 40 | [4–16] | Epilepsy | Carbamazepine | Low | Antiepileptic | Long | 52 weeks | Int |
| Klein66 | 1990 | USA | RCT (Within & Between) | 36 (33/3) | 8.5 (1.6) | ADHD + Hyperactivity | Thioridazine | High | Antipsychotic | Acute, Long | 4 weeks, 12 weeks | Att., CF + R, EF, Int., Lan., Mem., PM |
| Kwon et al.67 | 2013 | South Korea | NRCT (Between**) | 29 (17/15) | 8.4 (2.3) | Epilepsy | Oxcarbazepine | Low | Antiepileptic | Long | 6 months | Att., CF + R, EF, Int |
| O'Dougherty et al.68 | 1987 | USA | NRCT (Within) | 11 (4/7) | 9.8 (3.1) | Epilepsy | Carbamazepine | Low | Antiepileptic | Long | 3 weeks–10 months | Att., Mem, PM |
| Operto et al.69 | 2020 | Italy | NRCT (Within) | 46 (16/20) | 9.8 (2.3) | Epilepsy | Oxcarbazepine, Carbamazepine | Low | Antiepileptic | Long | 9 months | Comp |
| Pandina et al.70 | 2009 | Europe (6 countries), Israel, South Africa | RCT (Within & Between) | 284 (248/36) | 10.8 (2.9) | DBD | Risperidone | Low | Antipsychotic | Long | 6 weeks, 6 months | Att., Mem |
| Piccinelli et al.71 | 2010 | Italy | NRCT (Within) | 43 (21/22) | 10.4 (3.1) | Epilepsy | Carbamazepine | Low | Antiepileptic | Long | 12 months | CF + R, Int |
| Platt et al.72 | 1981 | USA | RCT (Between**) | 30 (28/2) | 9.0 (5.8–12.9) | CD | Haloperidol, Lithium | Low | Antipsychotic | Acute | 4 weeks | Att., EF |
| Platt et al.73 | 1984 | USA | RCT (Between**) | 61 (57/4) | 9.0 (5.2–12.9) | CD | Haloperidol, Lithium | Low | Antipsychotic | Acute | 4 weeks | Att., EF |
| Rappaport et al.74 | 1989 | USA | RCT (Crossover) | 17 (11/6) | [6–12] | Asthma | Theophylline | Low | Respiratory | Acute | 3.5 days | Att., EF, Mem., PM |
| Robles et al.75 | 2011 | Spain | RCT (Within) | 49 (38/11) | 15.9 (1.4) | Psychosis | Quetiapine, Olanzapine | Low | Antipsychotic | Long | 6 months | Att., CF + R, Comp., EF, Mem., Perc., PM |
| Schlieper et al.76 | 1991 | Canada | RCT (Crossover) | 31 (21/10) | 9.8 (1.6) | Asthma | Theophylline | Low | Respiratory | Acute | 10 days | Att., EF Mem |
| Seidel and Mitchell77 | 1999 | USA | NRCT (Crossover) | 10 (6/4) | 9.7 (2.0) | Epilepsy | Carbamazepine | Low | Antiepileptic | Long | 2.2 months–2.1 years | Att., CF + R, Int., Lan., Mem., PM |
| Shehab et al.78 | 2016 | Lebanon | NRCT (Within) | 24 (8/16) | 14.8 (1.6) | MDD | Fluoxetine | Low | Antidepressant | Long | 6 weeks, 12 weeks | Att., EF |
| Sommer et al.79 | 2005 | USA | NRCT (Between**) | 25 (11/14) | 7.2 (1.8) | Incontinence | Oxybutynin | High | Urological | Acute | 4 weeks | Att., Mem |
| Stevenson et al.80 | 2002 | Europe (12 countries), Brazil, Canada | RCT (Between) | 165 | 2.92 | Dermatitis | Cetrizine | Low | Respiratory | Long | 8 weeks | Comp |
| Tonnby et al.81 | 1994 | Sweden | NRCT (Within) | 100 (56/44) | 12.5 (2.1) | Epilepsy | Carbamazepine | Low | Antiepileptic | Long | Approx. 3.7 years | Att., Mem., PM |
| Troost et al.82 | 2006 | Netherlands | RCT (Within) | 24 (22/2) | 9.3 (2.6) | PDD | Risperidone | Low | Antipsychotic | Acute, Long | 4 weeks, 8 weeks, 24 weeks | Att |
| Tzitiridou et al.83 | 2005 | Greece | NRCT (Within) | 70 (45/25) | 8.4 (1.2) | Epilepsy | Oxcarbazepine | Low | Antiepileptic | Long | 18 months | Att, CF + R, Lan., PM |
| Werry et al.84 | 1975 | New Zealand | RCT (Crossover) | 21 (21/0) | 8.7 (1.7) | Incontinence | Imipramine | High | Antidepressant | Acute | 3 weeks | Att |
| Wilson and Staton85 | 1984 | USA | NRCT (Within) | 75 (55/20) | 10.8 (5.5–16.0) | MDD | Amitriptyline, Imipramine | High | Antidepressant | Long | > 3 months | Att., CF + R, EF, Int., Lan., PM |
| Yepes et al.86 | 1977 | USA | RCT (Crossover) | 22 (21/1) | 9.2 (7.3–12.3) | Hyperactivity/aggressive behaviour | Amitriptyline | High | Antidepressant | Acute | 2 weeks | Att., EF |
| Yuan et al.87 | 2018 | China | RCT (Between**) | 124 (85/39) | 6.5 (2.0) | ID | Lithium | Low | Antipsychotic | Long | 3 months | Int |
*Age reported as mean (SD or range) or median [range].
**Sufficient data available for both within- and between-groups design. Selection was made using protocol outlined in “Methods”.
Studies without description of gender split did not report this information in their original study.
ADHD attention deficit hyperactive disorder, Att. attention, BPD bipolar disorder, CD conduct disorder, CF + R concept formation and reasoning, Comp. composite score, DBD disruptive behaviour disorder, EF executive function, ID intellectual disability, Int. intelligence, IQ intelligence quotient, Lan. language, MDD major depressive disorder, Mem. memory, NRCT non-randomized controlled trial, NR not reported, PDD pervasive developmental disorder, Perc. perception, PM psychomotor functioning, RCT randomized controlled trial, SAR seasonal affective rhinitis, TBI traumatic brain injury.
Overall cognition
Overall, the 46 studies included reported a total of 536 effect sizes. The pooled effect size of the difference between cognition on and off medication across the 46 studies was negligible and non-significant (g = 0.05, 95% CI − 0.02 to 0.11, p = 0.16; see Fig. 2), with no heterogeneity between studies (τ2 = 0, I2 = 0%, Q = 42.36). The funnel plot did not reveal significant asymmetry (Egger’s intercept = − 0.5, p = 0.14; see Fig. 3).
Figure 2.
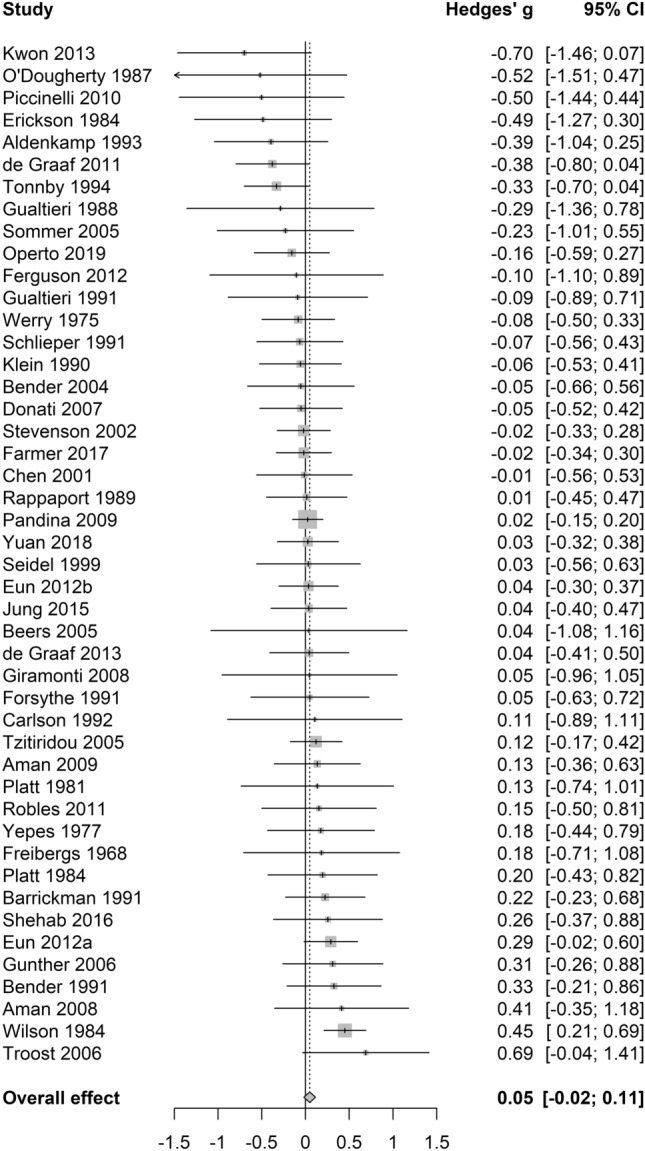
Forest plot for overall cognition analysis.
Figure 3.
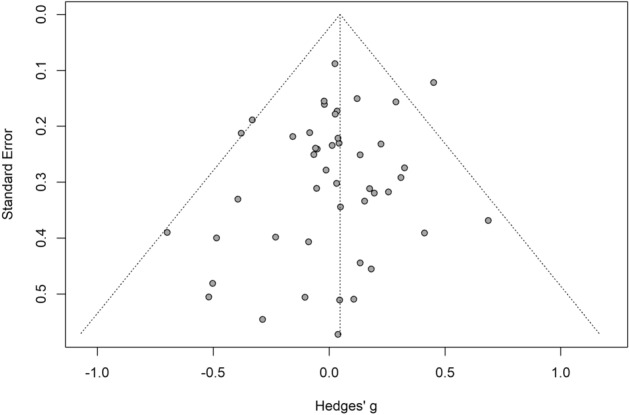
Funnel plot for overall cognition analysis.
Subgroup analyses
Pooled estimates for subgroup analyses by anticholinergic drug class, potency, length of administration and cognitive domain are presented in Table 2. The number of studies within individual sub-analyses ranged from 2 to 37. Varying levels of heterogeneity were present across analyses, ranging from null to high (τ2 range: 0–0.13, I2 range: 0–76.2, Q = 0.18–54.70).
Table 2.
Pooled estimates for subgroup analyses by anticholinergic drug class, potency, length of administration and cognitive domains.
| Subgroup analysis | Pooled estimate | Heterogeneity | Test of between-subgroups differences | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k | g | 95% CI | p value | Tau2 | I2 | Q | Q | df | p value | |
| Drug class | 9.98 | 5 | 0.08 | |||||||
| Antiepileptic | 14 | − 0.03 | − 0.17–0.11 | 0.63 | 0 | 9.67 | 14.39 | |||
| Antipsychotic | 14 | 0.06 | − 0.03–0.16 | 0.19 | 0 | 0 | 7.44 | |||
| Antidepressant | 7 | 0.24 | 0.01–0.47 | 0.04 | 0 | 13.22 | 6.91 | |||
| Respiratory | 5 | 0.02 | − 0.15–0.19 | 0.75 | 0 | 0 | 1.48 | |||
| Opioid analgesic | 3 | − 0.18 | − 0.79–0.44 | 0.34 | 0 | 0 | 1.84 | |||
| Urological | 2 | − 0.13 | − 1.83–1.58 | 0.52 | 0 | 0 | 0.18 | |||
| Potency | 0.71 | 1 | 0.40 | |||||||
| Low | 36 | 0.02 | − 0.05–0.09 | 0.50 | 0 | 0 | 27.40 | |||
| High | 10 | 0.11 | − 0.11–0.33 | 0.29 | 0.01 | 28.02 | 12.50 | |||
| Length of administration | 2.62 | 2 | 0.27 | |||||||
| Current and long-term | 29 | 0.07 | − 0.03–0.17 | 0.19 | 0.01 | 23.39 | 36.55 | |||
| Current and acute | 20 | 0.05 | − 0.04–0.14 | 0.25 | 0 | 0 | 8.06 | |||
| Historical | 3 | − 0.18 | − 0.79–0.44 | 0.34 | 0.00 | 0 | 1.84 | |||
| Cognitive domain | 5.59 | 7 | 0.59 | |||||||
| Attention | 37 | 0.04 | − 0.04–0.12 | 0.32 | 0 | 0 | 35.49 | |||
| Psychomotor functioning | 17 | − 0.10 | − 0.32–0.11 | 0.32 | 0.10 | 63.24 | 43.52 | |||
| Concept formation and reasoning | 13 | 0.14 | − 0.02–0.30 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 15.96 | 14.28 | |||
| Perception | 3 | 0.25 | − 0.90–1.39 | 0.45 | 0.11 | 50.18 | 4.01 | |||
| Memory | 16 | 0.04 | − 0.06–0.14 | 0.40 | 0 | 0 | 9.05 | |||
| Executive function | 15 | − 0.01 | − 0.27–0.24 | 0.91 | 0.12 | 48.50 | 27.19 | |||
| Intelligence | 14 | 0.08 | − 0.18–0.33 | 0.53 | 0.13 | 76.23 | 54.70 | |||
| Language | 6 | 0.11 | − 0.07–0.29 | 0.17 | 0 | 0 | 4.54 | |||
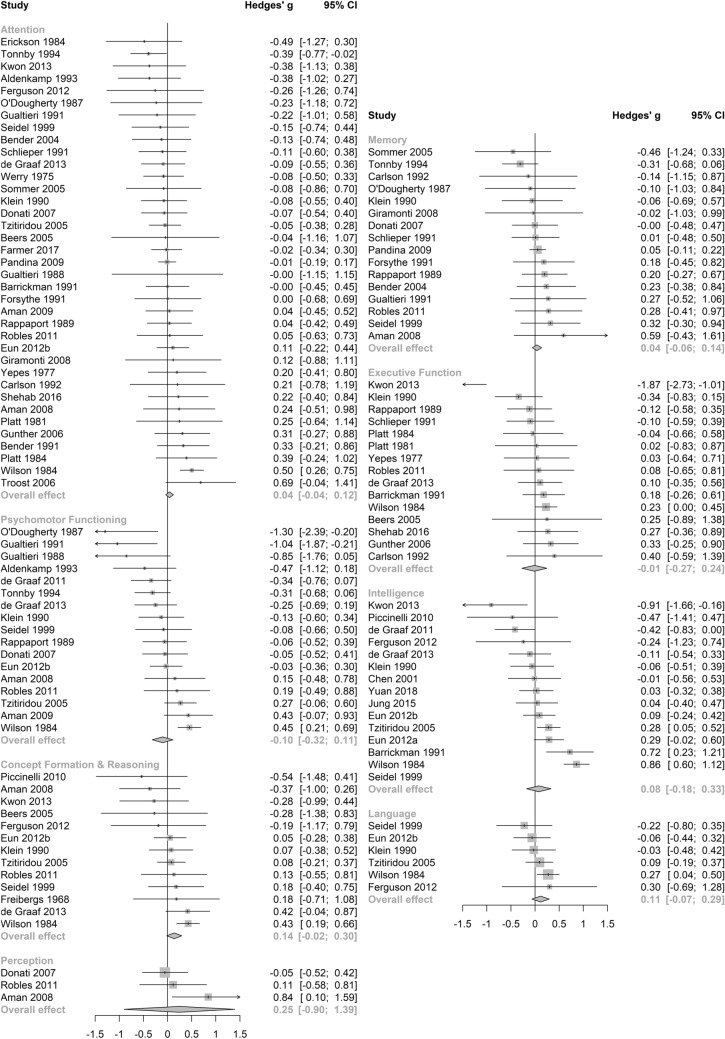
No significant differences between subgroups were revealed through a test of between-subgroup differences using the random-effects model (see Table 2). The pooled effect size for cognitive outcomes on antidepressant medications was small and statistically significant (see Table 2 and Fig. 4), with negligible heterogeneity between studies (τ2 = 0, I2 = 13.2%, Q = 6.91). Notably, this effect was not significant in a sensitivity analysis (Supplementary Table 3) which included only studies of high quality. Pooled estimates were non-significant across the remaining anticholinergic drug class (see Fig. 4), potency (see Fig. 5), length of administration (see Fig. 6), and cognitive domain (see Fig. 7) subgroup analyses. All null results were replicated within the sensitivity analysis of high-quality studies, except the memory cognitive domain analysis, which had a small positive significant effect (g = 0.09, 95% CI 0.01–0.17, p = 0.02).
Figure 4.
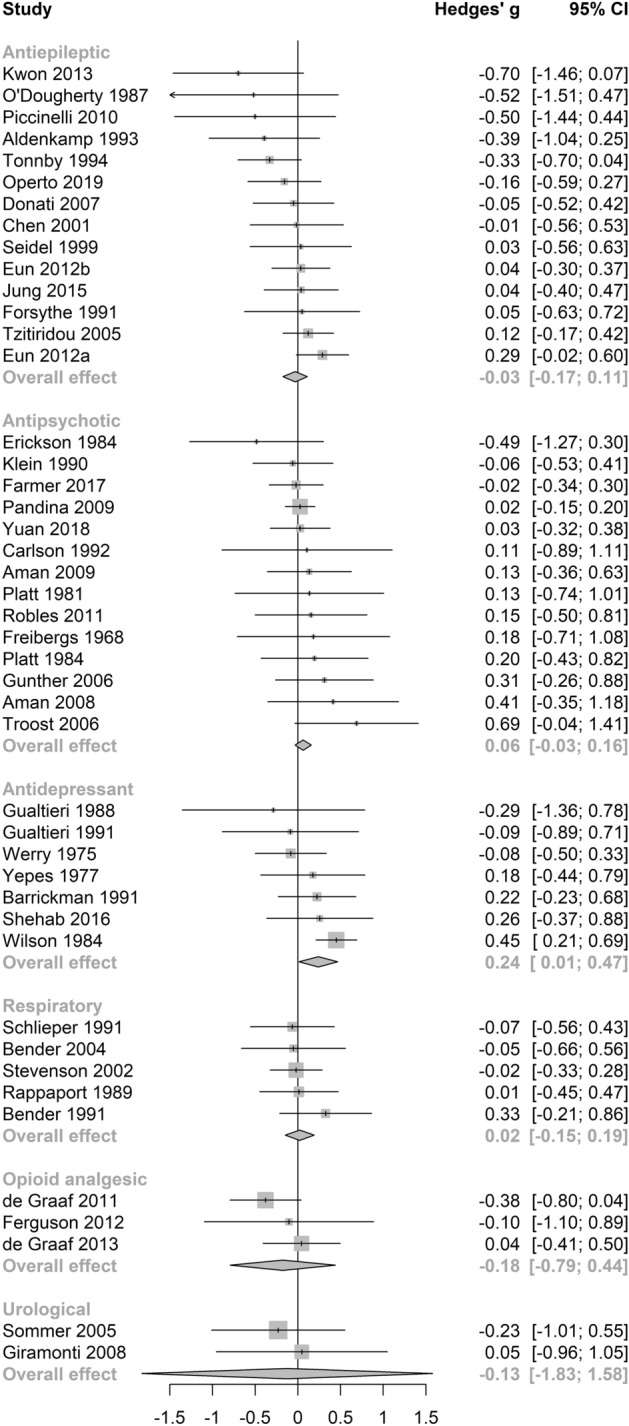
Forest plot for medication class sub-analysis.
Figure 5.
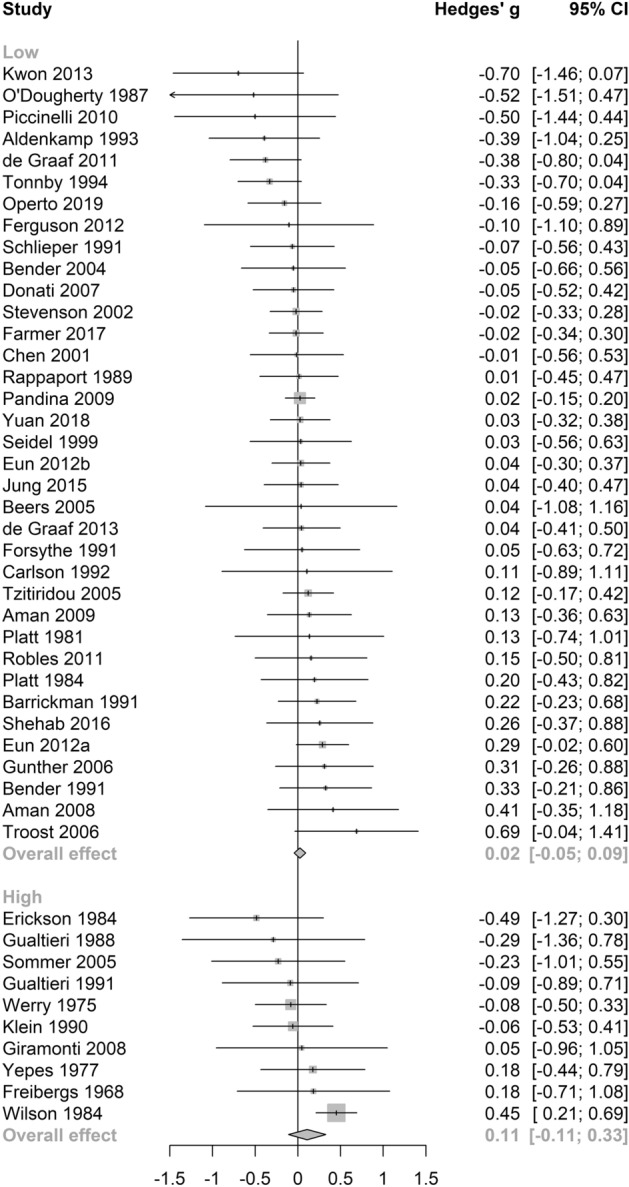
Forest plot for anticholinergic potency sub-analysis.
Figure 6.
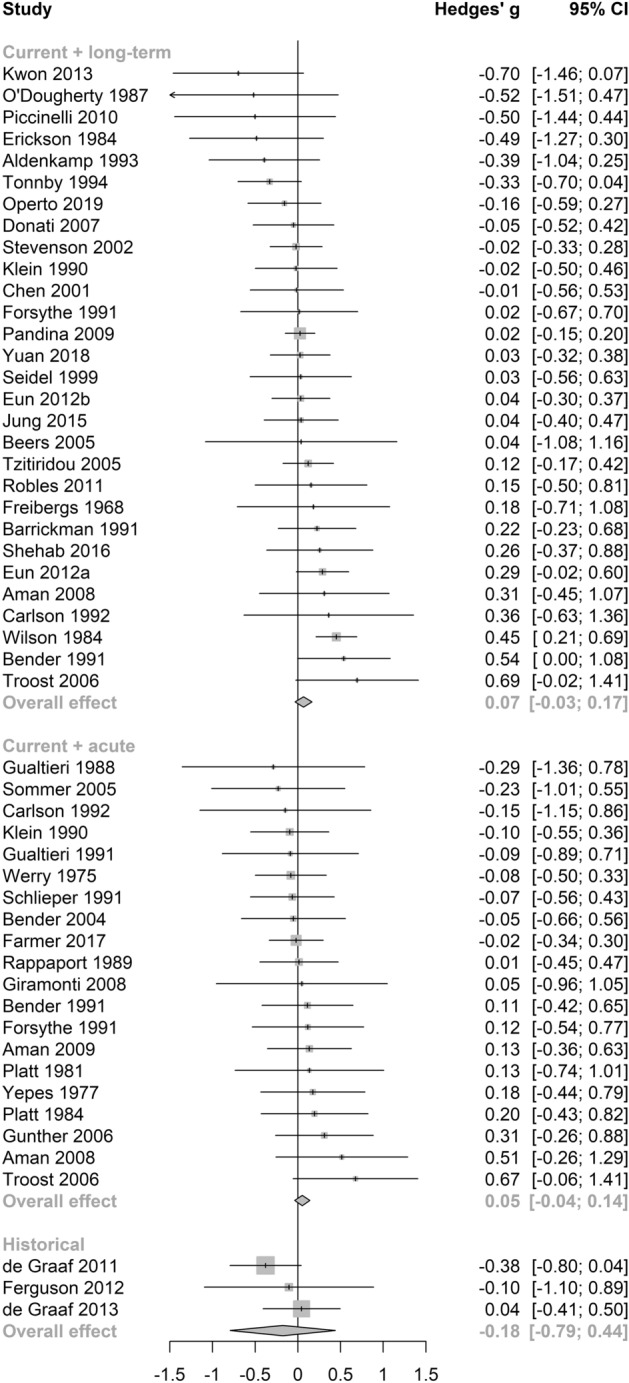
Forest plot for length of administration sub-analysis.
Figure 7.
Forest plot for cognitive domain sub-analysis.
Discussion
We quantified the effects of anticholinergic medications on cognition in children systematically across the literature. We report that, unlike older adult samples7–9, anticholinergic medications are not associated with cognitive impairments in children. This finding was regardless of the classification approach used: drug class, potency, duration of use, and cognitive domain. The discrepancy between child and older adult samples may be due to shorter lengths of exposure in children, higher rates of polypharmacy in older adults88, residual confounding, study design, or biological ageing processes.
Older adults have the opportunity for years or decades of anticholinergic exposure88, with polypharmacy common, whereas studies included here from child samples typically had short exposure durations (6 months or less in most studies) and little polypharmacy. It may be that the detrimental effect of anticholinergic medications on cognition in late-adulthood is driven by long exposure and polypharmacy89,90, factors not observed in children. Further, in late-life, the class of antidepressant appears to differentially affect cognition, with anti-depressants, urologicals, and antiparkinsonian drugs showing the strongest associations with incident dementia risk4. We did not see this pattern of effects in children. It may be that duration of exposure and polypharmacy again drives this difference, however residual confounding in late-life samples cannot be ruled out. It may be that incontinence and mood symptoms, for which anticholinergic medications are prescribed, are early clinical indicators of dementia-related neuropathologies4 (which accrue decades prior to a dementia diagnosis91) and that early, undiagnosed dementia is driving the associations between use of anticholinergic medicines and poor cognition in adults.
Interestingly, all study designs included in this review were experimental, whereas those included in reviews of older adults are typically longitudinal epidemiological cohort studies7–9. Standards of reporting cognitive performance also differ between children and adults. Cognitive performance in children is typically reported as test scores on a continuum, while in adults (especially those in late-life), a dichotomous classification of Neurocognitive Disorders is primarily used (e.g. presence versus absence of mild cognitive impairment or dementia). Study designs and differences in classification of cognition therefore may also underlie differences in the patterns of effects observed in children versus older adults, including the finding that anticholinergic antidepressants displayed a positive association with cognition (albeit with a small effect size, which was not significant when only high-quality studies were included). This small positive effect may be due to the short-term nature of the studies included here and is consistent with a meta-analysis of randomised control trials in adult samples92. We do not know the effects of the long-term use anticholinergic antidepressants in children. Notably, a small positive effect of anticholinergic medication on memory was found when only including studies of high quality. Whether this is a true effect, which is counter to that found in adults93, needs to be replicated in future studies. Lastly, there are important biological differences between children and adults that would modify the psychopharmacological effects of anticholinergic medications, particularly blood brain permeability94,95.
This study is not without limitations. The included studies were biased in terms of geographical representativeness. Fourteen studies were excluded at the full-text stage as they were not in English (of 323) and we do not know if any would have met inclusion criteria; although, given the low number, they would unlikely have changed the conclusions. Authors of papers were contacted, but we either had no response or the author was unable to provide us with the necessary data where it was not presented in text. We assessed the effect of duration of exposure on cognitive outcomes, when total dose or volume of exposure may have been more appropriate. However, this information was inconsistently reported or not reported at all in many of the studies. Therefore, duration of use was used as the best proxy for volume of exposure, with the assumption that longer duration of use would equate to higher volume of exposure. Only 21 of the 100 high- or low-potency anticholinergics identified in a systematic review of anticholinergic medications by Duran et al.12 were used in the studies included in this meta-analysis. It may be that different results would be seen had children been exposed to a wider range of anticholinergic medicines. Positively, the vast majority of studies (all but two) utilised valid and reliable cognitive outcome measures, as catalogued specifically or adapted from those detailed in Lezak et al.96.
Conclusion
By pooling effects across previous literature, anticholinergic medications do not appear to detrimentally affect cognitive function in children. In fact, there may be a small positive cognitive benefit of anticholinergic antidepressants, at least in the short-term. Our findings appear to conflict with reviews in older adults, and future studies will have to disentangle the reasons for this.
Supplementary Information
Acknowledgement
HADK is supported by a NHMRC Dementia Research Leadership Fellowship (GNT1135676). LMKE is supported by an NHMRC-ARC Dementia Research Development Fellowship (APP1101788). KR is supported by the UK Alzheimer's Society.
Author contributions
H.A.D.K. and L.M.E.K. conceptualised the study in consultation with K.R. H.A.D.K. and M.C. wrote the first draft of the manuscript. E.G. carried out the statistical analyses. M.C., T.J.R., D.C., C.S. and J.N.H. carried out the systematic review. All authors provided intellectual input to the manuscript and approved the final version for submission.
Data availability
All data and code available at https://github.com/ericaghezzi/anticholinergic_med_metaanalysis.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
These authors contributed equally: Erica Ghezzi and Michelle Chan.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1038/s41598-020-80211-6.
References
- 1.Cebron Lipovec N, Jazbar J, Kos M. Anticholinergic burden in children, adults and older adults in Slovenia: A Nationwide database study. Sci. Rep. 2020;10(1):9337. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-65989-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Santos JD, Lopes RI, Koyle MA. Bladder and bowel dysfunction in children: An update on the diagnosis and treatment of a common, but underdiagnosed pediatric problem. Can. Urol. Assoc. J. 2017;11(1–2 Suppl):S64–S72. doi: 10.5489/cuaj.4411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Rhee TG, Choi YC, Ouellet GM, Ross JS. National prescribing trends for high-risk anticholinergic medications in older adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2018;66(7):1382–1387. doi: 10.1111/jgs.15357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Richardson K, Fox C, Maidment I, Steel N, Loke YK, Arthur A, Myint PK, Grossi CM, Mattishent K, Bennett K, et al. Anticholinergic drugs and risk of dementia: Case-control study. BMJ. 2018;361:k1315. doi: 10.1136/bmj.k1315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Campbell NL, Lane KA, Gao S, Boustani MA, Unverzagt F. Anticholinergics influence transition from normal cognition to mild cognitive impairment in older adults in primary care. Pharmacotherapy. 2018;38(5):511–519. doi: 10.1002/phar.2106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Coupland CAC, Hill T, Dening T, Morriss R, Moore M, Hippisley-Cox J. Anticholinergic drug exposure and the risk of dementia: A nested case-control study. JAMA Intern. Med. 2019;179(8):1084–1093. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2019.0677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Fox C, Smith T, Maidment I, Chan WY, Bua N, Myint PK, Boustani M, Kwok CS, Glover M, Koopmans I, et al. Effect of medications with anti-cholinergic properties on cognitive function, delirium, physical function and mortality: A systematic review. Age Ageing. 2014;43(5):604–615. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afu096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ruxton K, Woodman RJ, Mangoni AA. Drugs with anticholinergic effects and cognitive impairment, falls and all-cause mortality in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015;80(2):209–220. doi: 10.1111/bcp.12617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Pieper NT, Grossi CM, Chan W-Y, Loke YK, Savva GM, Haroulis C, Steel N, Fox C, Maidment ID, Arthur AJ, et al. Anticholinergic drugs and incident dementia, mild cognitive impairment and cognitive decline: A meta-analysis. Age Ageing. 2020;49:939–947. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afaa090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Australian Centre for Asthma Monitoring: Asthma in Australian children: findings from Growing Up in Australia, the Longitudinal Study of Australian Children. Cat. No. ACM 17. AIHW, Canberra (2009).
- 11.Caldwell P, Edgar D, Hodson E, Craig J. Bedwetting and toileting problems in children. MJA. 2005;182(4):190–195. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.2005.tb06653.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Durán CE, Azermai M, Vander Stichele RH. Systematic review of anticholinergic risk scales in older adults. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013;69(7):1485–1496. doi: 10.1007/s00228-013-1499-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Gray SL, Anderson ML, Dublin S, Hanlon JT, Hubbard R, Walker R, Yu O, Crane PK, Larson EB. Cumulative use of strong anticholinergics and incident dementia: A prospective cohort study. JAMA Intern. Med. 2015;175(3):401–407. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2014.7663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.McKeith I, Del Ser T, Spano P, Emre M, Wesnes K, Anand R, Cicin-Sain A, Ferrara R, Spiegel R. Efficacy of rivastigmine in dementia with Lewy bodies: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled international study. Lancet. 2000;356(9247):2031–2036. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)03399-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Klinkenberg I, Sambeth A, Blokland A. Acetylcholine and attention. Behav. Brain Res. 2011;221(2):430–442. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2010.11.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Parikh V, Sarter M. Cholinergic mediation of attention: Contributions of phasic and tonic increases in prefrontal cholinergic activity. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008;1129:225–235. doi: 10.1196/annals.1417.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Gill TM, Sarter M, Givens B. Sustained visual attention performance-associated prefrontal neuronal activity: Evidence for cholinergic modulation. J. Neurosci. 2000;20(12):4745–4757. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-12-04745.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. BMJ. 2009;339:b2535. doi: 10.1136/bmj.b2535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Shamseer L, Moher D, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, Shekelle P, Stewart LA. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: Elaboration and explanation. BMJ. 2015;349:g7647. doi: 10.1136/bmj.g7647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Tufanaru C, Munn Z, Aromataris E, Campbell J, Hopp L: Chapter 3: Systematic reviews of effectiveness. In: Joanna Briggs Institute Reviewer's Manual. edn. Edited by Aromataris E, Munn Z: The Joanna Briggs Institute; 2017.
- 21.Ma L-L, Wang Y-Y, Yang Z-H, Huang D, Weng H, Zeng X-T. Methodological quality (risk of bias) assessment tools for primary and secondary medical studies: What are they and which is better? Milit. Med. Res. 2020;7(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s40779-020-00238-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Sakiris N, Berle D. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the Unified Protocol as a transdiagnostic emotion regulation based intervention. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2019;72:101751. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2019.101751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ashdown-Franks G, Williams J, Vancampfort D, Firth J, Schuch F, Hubbard K, Craig T, Gaughran F, Stubbs B. Is it possible for people with severe mental illness to sit less and move more? A systematic review of interventions to increase physical activity or reduce sedentary behaviour. Schizophr. Res. 2018;202:3–16. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2018.06.058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ge S, Zhu Z, Wu B, McConnell ES. Technology-based cognitive training and rehabilitation interventions for individuals with mild cognitive impairment: a systematic review. BMC Geriatr. 2018;18(1):213. doi: 10.1186/s12877-018-0893-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hedges LV, Olkin I. Statistical Methods for Meta-Analysis. Cambridge: Academic Press; 2014. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Schwarzer G: Meta. CRAN 2020: Version 4.13–10.
- 27.DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control. Clin. Trials. 1986;7(3):177–188. doi: 10.1016/0197-2456(86)90046-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Cornell JE, Mulrow CD, Localio R, Stack CB, Meibohm AR, Guallar E, Goodman SN. Random-effects meta-analysis of inconsistent effects: A time for change. Ann. Intern. Med. 2014;160(4):267–270. doi: 10.7326/M13-2886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Novianti PW, Roes KC, van der Tweel I. Estimation of between-trial variance in sequential meta-analyses: A simulation study. Contemp. Clin. Trials. 2014;37(1):129–138. doi: 10.1016/j.cct.2013.11.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Veroniki AA, Jackson D, Viechtbauer W, Bender R, Bowden J, Knapp G, Kuss O, Higgins JP, Langan D, Salanti G. Methods to estimate the between-study variance and its uncertainty in meta-analysis. Res. Synth. Methods. 2016;7(1):55–79. doi: 10.1002/jrsm.1164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Paule RC, Mandel J. Consensus values and weighting factors. J. Res. Natl. Bureau Standards. 1982;87(5):377–385. doi: 10.6028/jres.087.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Panityakul T, Bumrungsup C, Knapp G. On estimating residual heterogeneity in random-effects meta-regression: A comparative study. J. Stat. Theory Appl. 2013;12(3):253–265. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Hartung J, Knapp G. On tests of the overall treatment effect in meta-analysis with normally distributed responses. Stat. Med. 2001;20(12):1771–1782. doi: 10.1002/sim.791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Hartung J, Knapp G. A refined method for the meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials with binary outcome. Stat. Med. 2001;20(24):3875–3889. doi: 10.1002/sim.1009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003;327(7414):557–560. doi: 10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lezak MD, Howieson DB, Loring DW, Fischer JS: Neuropsychological assessment: Oxford University Press, USA; 2004.
- 37.Beers SR, Skold A, Dixon CE, Adelson PD. Neurobehavioral effects of amantadine after pediatric traumatic brain injury: A preliminary report. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 2005;20(5):450–463. doi: 10.1097/00001199-200509000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Higgins JPT, Thompson SG. Controlling the risk of spurious findings from meta-regression. Stat. Med. 2004;23(11):1663–1682. doi: 10.1002/sim.1752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Sterne JA, Sutton AJ, Ioannidis JP, Terrin N, Jones DR, Lau J, Carpenter J, Rücker G, Harbord RM, Schmid CH. Recommendations for examining and interpreting funnel plot asymmetry in meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials. BMJ. 2011;343:1. doi: 10.1136/bmj.d4002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Egger M, Smith GD, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997;315(7109):629–634. doi: 10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Duval S, Tweedie R. Trim and fill: a simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics. 2000;56(2):455–463. doi: 10.1111/j.0006-341X.2000.00455.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs. World Economic Situation and Prospects. (2020).
- 43.Aldenkamp A, Alpherts W, Blennow G, Elmqvist D, Heijbel J, Nilsson H, Sandstedt P, Tonnby B, Wåhlander L, Wosse E. Withdrawal of antiepileptic medication in children–effects on cognitive function: The Multicenter Holmfrid Study. Neurology. 1993;43(1):41. doi: 10.1212/WNL.43.1_Part_1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Aman MG, Hollway JA, McDougle CJ, Scahill L, Tierney E, McCracken JT, Arnold LE, Vitiello B, Ritz L, Gavaletz A. Cognitive effects of risperidone in children with autism and irritable behavior. J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2008;18(3):227–236. doi: 10.1089/cap.2007.0133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Aman MG, Hollway JA, Leone S, Masty J, Lindsay R, Nash P, Arnold LE. Effects of risperidone on cognitive-motor performance and motor movements in chronically medicated children. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2009;30(2):386–396. doi: 10.1016/j.ridd.2008.07.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Barrickman L, Noyes R, Kuperman S, Schumacher E, Verda M. Treatment of ADHD with fluoxetine: A preliminary trial. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry. 1991;30(5):762–767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Bender BG, Milgrom H. Comparison of the effects of fluticasone propionate aqueous nasal spray and loratadine on daytime alertness and performance in children with seasonal allergic rhinitis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2004;92(3):344–349. doi: 10.1016/S1081-1206(10)61573-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Bender BG, Lerner JA, Ikle D, Comer C, Szefler S. Psychological change associated with theophylline treatment of asthmatic children: A 6-month study. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 1991;11(3):233–242. doi: 10.1002/ppul.1950110309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Carlson GA, Rapport MD, Pataki CS, Kelly KL. Lithium in hospitalized children at 4 and 8 weeks: Mood, behavior and cognitive effects. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry. 1992;33(2):411–425. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.1992.tb00876.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Chen Y-J, Chow JC, Lee I-C. Comparison the cognitive effect of anti-epileptic drugs in seizure-free children with epilepsy before and after drug withdrawal. Epilepsy Res. 2001;44(1):65–70. doi: 10.1016/S0920-1211(00)00204-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.De Graaf J, van Lingen RA, Simons SH, Anand KJ, Duivenvoorden HJ, Weisglas-Kuperus N, Roofthooft DW, Jebbink LJG, Veenstra RR, Tibboel D. Long-term effects of routine morphine infusion in mechanically ventilated neonates on children’s functioning: Five-year follow-up of a randomized controlled trial. Pain. 2011;152(6):1391–1397. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2011.02.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.de Graaf J, van Lingen RA, Valkenburg AJ, Weisglas-Kuperus N, Groot Jebbink L, Wijnberg-Williams B, Anand KJS, Tibboel D, van Dijk M. Does neonatal morphine use affect neuropsychological outcomes at 8 to 9years of age? Pain. 2013;154(3):449–458. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2012.12.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Donati F, Gobbi G, Campistol J, Rapatz G, Daehler M, Sturm Y, Aldenkamp AP, Group OCS The cognitive effects of oxcarbazepine versus carbamazepine or valproate in newly diagnosed children with partial seizures. Seizure. 2007;16(8):670–679. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2007.05.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Erickson, W., Yellin, A., Hopwood, J., Realmuto, G., Greenberg, L. The effects of neuroleptics on attention in adolescent schizophrenics. Biol. Psychiatry (1984). [PubMed]
- 55.Eun S-H, Eun B-L, Lee JS, Hwang YS, Kim KJ, Lee Y-M, Lee IG, Lee M, Ko T-S, Kim JT. Effects of lamotrigine on cognition and behavior compared to carbamazepine as monotherapy for children with partial epilepsy. Brain Develop. 2012;34(10):818–823. doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2012.03.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Eun S-H, Kim HD, Chung HJ, Kang H-C, Lee JS, Kim JS, You SJ, Moon HK, Lee Y-M, Kim DW. A multicenter trial of oxcarbazepine oral suspension monotherapy in children newly diagnosed with partial seizures: A clinical and cognitive evaluation. Seizure. 2012;21(9):679–684. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2012.07.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Farmer CA, Epstein JN, Findling RL, Gadow KD, Arnold LE, Kipp H, Kolko DJ, Butter E, Schneider J, Bukstein OG. Risperidone added to psychostimulant in children with severe aggression and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: Lack of effect on attention and short-term memory. J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2017;27(2):117–124. doi: 10.1089/cap.2016.0040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Ferguson SA, Ward WL, Paule MG, Hall RW, Anand KJS. A pilot study of preemptive morphine analgesia in preterm neonates: Effects on head circumference, social behavior, and response latencies in early childhood. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2012;34(1):47–55. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2011.10.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Forsythe I, Butler R, Berg I, McGuire R. Cognitive impairment in new cases of epilepsy randomly assigned to carbamazepine, phenytoin and sodium valproate. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 1991;33(6):524–534. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1991.tb14917.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Freibergs V, Douglas VI, Weiss G. The effect of chlorpromazine on concept learning in hyperactive children under two conditions of reinforcement. Psychopharmacologia. 1968;13(4):299–310. doi: 10.1007/BF00414341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Giramonti KM, Kogan BA, Halpern LF. The effects of anticholinergic drugs on attention span and short-term memory skills in children. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2008;27(4):315–318. doi: 10.1002/nau.20507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Gualtieri CT, Evans RW. Motor performance in hyperactive children treated with imipramine. Percept. Mot. Skills. 1988;66(3):763–769. doi: 10.2466/pms.1988.66.3.763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Gualtieri, C. T., Keenan, P., Chandler, M. Clinical and neuropsychological effects of desipramine in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. (1991). [PubMed]
- 64.Günther T, Herpertz-Dahlmann B, Jolles J, Konrad K. The influence of risperidone on attentional functions in children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and co-morbid disruptive behavior disorder. J Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2006;16(6):725–735. doi: 10.1089/cap.2006.16.725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Jung D, Yu R, Yoon J-R, Eun B-L, Kwon S, Lee Y, Eun S-H, Lee J, Kim H, Nam S. Neuropsychological effects of levetiracetam and carbamazepine in children with focal epilepsy. Neurology. 2015;84(23):2312–2319. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000001661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Klein RG. Thioridazine effects on the cognitive performance of children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 1990;1(4):263–270. doi: 10.1089/cap.1990.1.263. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Kwon S, Hwang TG, Lee J, Kim D-K, Seo H-E. Benign childhood epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes: To treat or not to treat. J. Epilepsy Res. 2013;3(1):1. doi: 10.14581/jer.13001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.O'Dougherty M, Wright FS, Cox S, Walson P. Carbamazepine plasma concentration: Relationship to cognitive impairment. Arch. Neurol. 1987;44(8):863–867. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1987.00520200065021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Operto FF, Pastorino GMG, Mazza R, Carotenuto M, Roccella M, Marotta R, di Bonaventura C, Verrotti A. Effects on executive functions of antiepileptic monotherapy in pediatric age. Epilepsy Behav. 2020;102:106648. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2019.106648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Pandina GJ, Zhu Y, Cornblatt B. Cognitive function with long-term risperidone in children and adolescents with disruptive behavior disorder. J Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2009;19(6):749–756. doi: 10.1089/cap.2008.0159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Piccinelli P, Beghi E, Borgatti R, Ferri M, Giordano L, Romeo A, Termine C, Viri M, Zucca C, Balottin U. Neuropsychological and behavioural aspects in children and adolescents with idiopathic epilepsy at diagnosis and after 12 months of treatment. Seizure. 2010;19(9):540–546. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2010.07.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Platt JE, Campbell M, Green WH, Perry R, Cohen I. Effects of lithium carbonate and haloperidol on cognition in aggressive hospitalized school-age children. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 1981;1(1):8–13. doi: 10.1097/00004714-198101000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Platt JE, Campbell M, Green WH, Grega DM. Cognitive effects of lithium carbonate and haloperidol in treatment-resistant aggressive children. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry. 1984;41(7):657–662. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1984.01790180027003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Rappaport L, Coffman H, Guare R, Fenton T, DeGraw C, Twarog F. Effects of theophylline on behavior and learning in children with asthma. Am. J. Dis. Child. 1989;143(3):368–372. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1989.02150150126032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Robles O, Zabala A, Bombín I, Parellada M, Moreno D, Ruiz-Sancho A, Arango C. Cognitive efficacy of quetiapine and olanzapine in early-onset first-episode psychosis. Schizophr. Bull. 2011;37(2):405–415. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbp062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Schlieper A, Alcock D, Beaudry P, Feldman W, Leikin L. Effect of therapeutic plasma concentrations of theophylline on behavior, cognitive processing, and affect in children with asthma. J. Pediatr. 1991;118(3):449–455. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3476(05)82167-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Seidel WT, Mitchell WG. Cognitive and behavioral effects of carbamazepine in children: data from benign rolandic epilepsy. J. Child Neurol. 1999;14(11):716–723. doi: 10.1177/088307389901401106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Shehab AAS, Brent D, Maalouf FT. Neurocognitive changes in selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors—treated adolescents with depression. J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2016;26(8):713–720. doi: 10.1089/cap.2015.0190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Sommer BR, O'Hara R, Askari N, Kraemer HC, Kennedy WA. The effect of oxybutynin treatment on cognition in children with diurnal incontinence. J. Urol. 2005;173(6):2125–2127. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000157685.83573.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Stevenson J, Cornah D, Evrard P, Vanderheyden V, Billard C, Bax M, Van Hout A. On behalf of the Etac Study G: Long-term evaluation of the impact of the H1-receptor antagonist cetirizine on the behavioral, cognitive, and psychomotor development of very young children with atopic dermatitis. Pediatr. Res. 2002;52(2):251–257. doi: 10.1203/00006450-200208000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Tonnby B, Nilsson H, Aldenkamp A, Alpherts W, Blennow G, Elmqvist D, Heijbel J, Sandstedt P, Wåhlander L, Wosse E. Withdrawal of antiepileptic medication in children correlation of cognitive function and plasma concentration—The multicentre ‘Holmfrid’study. Epilepsy Res. 1994;19(2):141–152. doi: 10.1016/0920-1211(94)90024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Troost PW, Althaus M, Lahuis BE, Buitelaar JK, Minderaa RB, Hoekstra PJ. Neuropsychological effects of risperidone in children with pervasive developmental disorders: ABlinded discontinuation study. J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2006;16(5):561–573. doi: 10.1089/cap.2006.16.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Tzitiridou M, Panou T, Ramantani G, Kambas A, Spyroglou K, Panteliadis C. Oxcarbazepine monotherapy in benign childhood epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes: A clinical and cognitive evaluation. Epilepsy Behav. 2005;7(3):458–467. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2005.07.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Werry JS, Dowrick PW, Lampen EL, Vamos MJ. Imipramine in enuresis—psychological and physiological effects. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry. 1975;16(4):289–299. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.1975.tb00363.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Wilson H, Staton RD. Neuropsychological changes in children associated with tricyclic antidepressant therapy. Int. J. Neurosci. 1984;24(3–4):307–312. doi: 10.3109/00207458409089823. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Yepes L, Balka EB, Winsberg BG, Bialer I. Amitriptyline and methylphenidate treatment of behaviorally disordered children. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry. 1977;18(1):39–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.1977.tb00415.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Yuan J, Song J, Zhu D, Sun E, Xia L, Zhang X, Gao C, Agam G, Wang X, Blomgren K. Lithium treatment is safe in children with intellectual disability. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018;11:425. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Cai X, Campbell N, Khan B, Callahan C, Boustani M. Long-term anticholinergic use and the aging brain. Alzheimer Dement. 2013;9(4):377–385. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2012.02.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Carrière I, Fourrier-Reglat A, Dartigues J-F, Rouaud O, Pasquier F, Ritchie K, Ancelin M-L. Drugs with anticholinergic properties, cognitive decline, and dementia in an elderly general population: The 3-city study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2009;169(14):1317–1324. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2009.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Kalisch Ellett LM, Pratt NL, Ramsay EN, Barratt JD, Roughead EE. Multiple anticholinergic medication use and risk of hospital admission for confusion or dementia. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2014;62(10):1916–1922. doi: 10.1111/jgs.13054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Jack CR, Jr, Knopman DS, Jagust WJ, Petersen RC, Weiner MW, Aisen PS, Shaw LM, Vemuri P, Wiste HJ, Weigand SD, et al. Tracking pathophysiological processes in Alzheimer's disease: An updated hypothetical model of dynamic biomarkers. Lancet Neurol. 2013;12(2):207–216. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(12)70291-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Rosenblat JD, Kakar R, McIntyre RS. The cognitive effects of antidepressants in major depressive disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015;19:2. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyv082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Ziad A, Olekhnovitch R, Ruiz F, Berr C, Bégaud B, Goldberg M, Zins M, Mura T. Anticholinergic drug use and cognitive performances in middle age: Findings from the CONSTANCES cohort. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry. 2018;89(10):1107–1115. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2018-318190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Farrall AJ, Wardlaw JM. Blood–brain barrier: Ageing and microvascular disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurobiol. Aging. 2009;30(3):337–352. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2007.07.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Popescu BO, Toescu EC, Popescu LM, Bajenaru O, Muresanu DF, Schultzberg M, Bogdanovic N. Blood-brain barrier alterations in ageing and dementia. J. Neurol. Sci. 2009;283(1):99–106. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2009.02.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Lezak MD, Howieson DB, Bigler ED, Tranel D, editors. Neuropsychological Assessment. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2012. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
All data and code available at https://github.com/ericaghezzi/anticholinergic_med_metaanalysis.