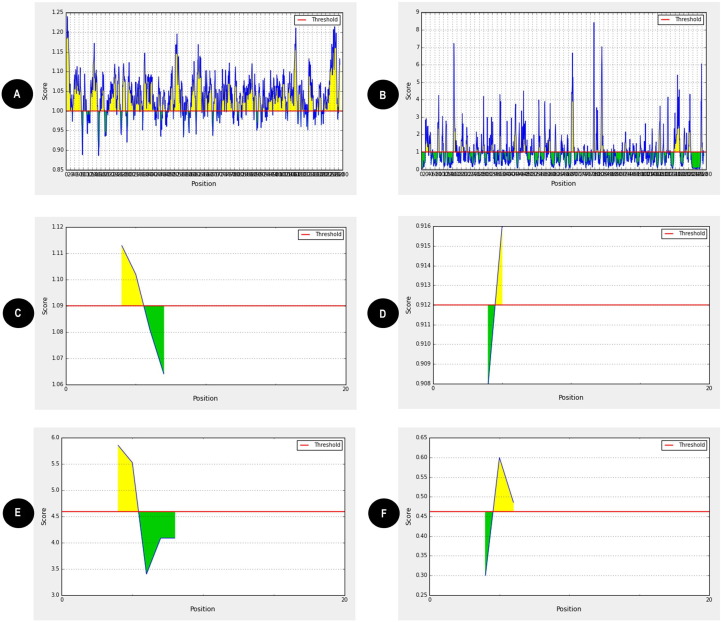
Fig. 2.
(A) The spike surface glycoprotein is highly antigenic. VaxiJen v2.0 server and Kolaskar and Tongaonkar method were used to predict the antigenic property of the given sequence. The threshold was kept at 1.00; highlighted region above the threshold are antigenic. X axis indicates the position of amino acid sequence and Y axis indicates the antigenic score of amino acid residues. (B) The spike surface glycoprotein is surface accessible. The red horizontal line indicates surface accessibility cutoff and highlighted regions above threshold line are surface accessible epitopes. The threshold was kept at 1.00 for our analysis. X axis indicates the position of amino acid sequence and Y axis indicates surface accessible epitopes indicating minimum score as 0.031 and maximum score 8.415. Emini surface accessible prediction tool of the IEDB was used to determine the surface accessibility of the epitope. (C) Representative image indicating flexibility of two B-cell epitopes SGTNGTKRFDN and ASVYAWNRK (D). With a window size of 7 amino acids and center position as 4, both epitopes were found to have flexibility above the threshold of 0.9. Flexibility predictions were determined using Karplus and Schulz (KS) flexibility online tool. Image indicating hydrophilicity of two B-cell epitopes SGTNGTKRFDN (E) and ASVYAWNRK (F). With a window size of 7 amino acids and centre position as 4, highlighted region specifies that both the epitopes were found to have hydrophilicity above the threshold of 0.40. Hydrophilicity predictions were determined using Parker hydrophilicity prediction tool. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)