Abstract
We describe a case of chronic coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in a patient with lymphoma and associated B-cell immunodeficiency. Viral cultures and sequence analysis demonstrate ongoing replication of infectious severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) for at least 119 days. The patient had 3 admissions related to COVID-19 over a 4-month period and was treated twice with remdesivir and convalescent plasma with resolution of symptoms. The patient’s lack of seroconversion and prolonged course illustrate the importance of humoral immunity in resolving SARS-CoV-2 infection. This case highlights challenges in managing immunocompromised hosts, who may act as persistent shedders and sources of transmission.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2, COVID-19, immunocompromise, evolution, antibody
A detailed study of chronic COVID-19 in a patient with hematologic malignancy. The patient shed infectious virus for >119 days. This case highlights unique challenges in infection control and the clinical management of immunocompromised hosts.
Since the emergence of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the causative agent of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), there has been an ongoing effort to define viral kinetics, host immune responses, and transmission dynamics. In individuals who develop symptoms, the average incubation period is approximately 5 days (interquartile range, 2–7 days). The viral load in the respiratory tract peaks around the time of symptom onset and shedding of infectious virus occurs for 2–3 more days [1]. While peak viral loads in asymptomatic and symptomatic individuals are similar, those with symptoms appear to shed viral RNA in greater quantities for longer periods. Individuals can test positive for nucleic acid for up to 6 weeks after symptom onset [2]. When evaluated, infectious virus is generally not detected after 7 days or more after symptom onset and contact tracing studies suggest that individuals are most infectious within 5 days of symptoms [3, 4]. The majority of infected individuals experience an illness lasting 1–2 weeks. The resolution of symptoms often coincides with seroconversion, with immunoglobulin G (IgG) levels increasing between 7 and 14 days postinfection.
Immunocompromised individuals are underrepresented in most of these studies, and patients with primary or secondary immunodeficiencies may differ in their degree of shedding, kinetics of immune clearance, and disease severity. There is also likely to be considerable variability based on the type and severity of underlying immune deficit. Here, we describe the clinical and virological course of a patient with functional B-cell immunodeficiency and COVID-19.
CASE REPORT
A 60-year-old man with a history of refractory mantle cell lymphoma (immunohistochemistry positive for CD20, CD5, BCL2, cyclin D1, and SOX11; lambda-restricted, CD5-positive B-cell population by flow cytometry) presented to the emergency department with a 1-week history of epistaxis and a cough productive of blood-streaked sputum. Immunochemotherapy for his lymphoma was ongoing and included a CD20 bispecific antibody and a second B-cell directed antibody in combination with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone. He was afebrile and did not require supplemental oxygen. His chest radiograph was without abnormality. A nasopharyngeal (NP) swab was positive for SARS-CoV-2 by reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR, Diasorin assay; all Ct values are shown in Figure 1A).
Figure 1.
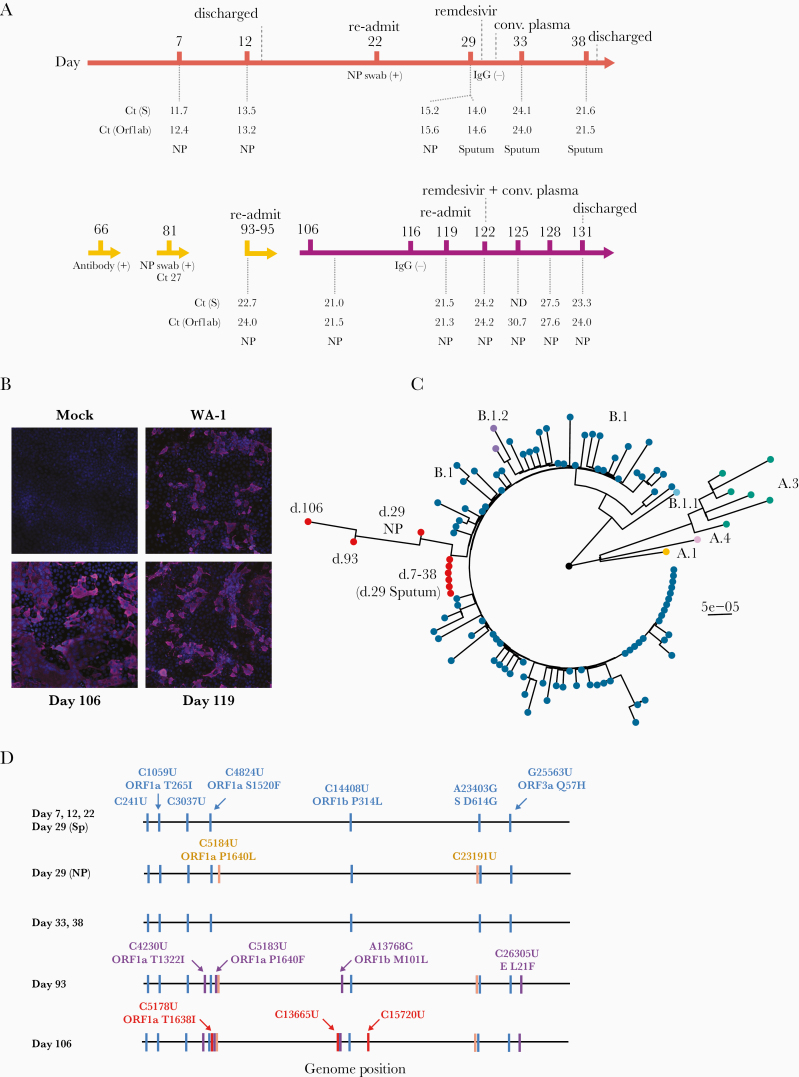
A, Timeline of case. Color is by stage of infection, orange (initial presentation); yellow (largely outpatient); purple (recrudescence and readmission). Key events and treatments are shown above the timeline and key laboratory values are shown below it. B, Immunofluorescence microscopy of viral cultures. The patient’s samples (days 106 and 119) and a positive control (WA-1 strain) viral stock were cultured on Vero E6 cells until cytopathic effect was observed. Huh-7 cells were infected with cell-free supernatants from the Vero E6 cultures and stained 48 hours later with Hoechst (blue, nuclei) and an anti–severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 nucleocapsid antibody (magenta). C, Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree of whole genome consensus sequences for 9 samples from this case (red tips) and 100 other samples from inpatients at the same hospital (see Supplementary Table 1, color coded by lineage). Tree is rooted to Wuhan-Hu-1. Bootstrap support (1000 replicates) at nodes for the samples from the case and for all lineages is >90. D, Consensus mutations in the 9 samples sequenced. All nucleotide substitutions are shown. Amino acid substitutions are indicated for all nonsynonymous substitutions. Mutations in blue were in the original day 7 sample and persisted. Mutations in orange were detected in 1 of 2 day 29 samples and then at days 93 and 106. Mutations in purple were first detected in the day 93 sample and persisted at day 106. Mutations in red were fixed in the day 106 sample only. Abbreviations: Ct, cycle threshold; E, envelope; IgG, immunoglobulin G; ND, not detected; NP, nasopharyngeal; ORF, open reading frame; S, spike.
He was admitted to the hospital (day 7 of illness) for monitoring in the setting of chemotherapy-associated neutropenia and severe thrombocytopenia. He received a platelet transfusion and his presenting symptoms improved. With resolution of his cytopenias, he was discharged to his home 6 days later (day 13; Figure 1A).
Over the following week, he continued to have fatigue and a mild cough, but remained afebrile. He began to experience mild shortness of breath and returned to the emergency department on day 22. He was afebrile and did not require supplemental oxygen. Computed tomography of the chest revealed multiple bilateral lung nodules with bibasilar atelectasis and a ground glass opacity at the right lung base. An NP swab was again positive for SARS-CoV-2 by RT-PCR. He was admitted for intravenous fluid hydration and monitoring, but soon became persistently febrile and required 1–3 L of supplemental oxygen. A sputum culture and PCR panel for 18 respiratory pathogens (BioFire FilmArray) were negative. On day 29, repeat NP and sputum samples were both positive for SARS-CoV-2 by RT-PCR.
On day 30, serological testing did not detect antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 (EUROIMMUN anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay), and remdesivir was initiated (10-day course). He received convalescent plasma therapy on day 31 and defervesced soon thereafter. His sputum remained positive for SARS-CoV-2 by RT-PCR on days 33 and 38. His condition continued to improve and he was discharged to home on day 39 of his illness.
The patient was without significant complaints at a follow-up telemedicine visit on day 60. Repeat serologic testing 66 days after his initial symptoms detected IgG antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 (Roche Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2, outside hospital report). He also had 3 outpatient NP swabs at another institution on days 46, 57, and 66 that were all positive (Roche assay). While the patient remained positive for SARS-CoV-2 RNA on day 81 (Abbott assay), the decision was made to reinitiate lymphoma treatment given his relatively high Ct values, apparent seroconversion, and progression of his underlying disease. Chemotherapy was started on day 85 and completed on day 106. He had mild upper respiratory symptoms on day 106. A sputum culture, urine Legionella antigen, Pneumocystis jirovecii PCR, and respiratory pathogen PCR panel were negative. An NP swab was positive for SARS-CoV-2 by RT-PCR (Diasorin assay).
On day 119, the patient presented to the emergency department with fever, cough, and shortness of breath. A chest radiograph showed new bilateral air space opacities. Two days after admission, he had a worsening chest radiograph and increasing oxygen requirement. On day 122, due to worsening symptoms and persistent fevers, the patient was given a second course of remdesivir (10 days) and convalescent plasma. He defervesced within 24 hours and was slowly weaned off of oxygen. He was discharged on day 131 of his illness.
The patient was readmitted on day 156 due to progression of his lymphoma. His admission NP swab was positive for SARS-CoV-2 (Ct value 22.5). He remained afebrile and his chest radiograph was improved from prior evaluations. The patient decided to pursue home hospice care.
LABORATORY INVESTIGATION
Residual respiratory tract specimens from days 7, 12, 22, 29 (1 NP swab and 1 sputum), 33, 38, 81, 93, 106, and 119 (Figure 1) were recovered from the hospital clinical microbiology laboratory and cultured on Vero E6 cells. Cultures of all samples except day 81 produced a cytopathic effect. Cells infected with supernatants from these primary cultures were positive for the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein (Figure 1B), demonstrating the presence of infectious virus from days 7 through 119 of the patient’s illness.
We amplified and sequenced SARS-CoV-2 from RNA in the original NP and sputum specimens. A whole genome phylogenetic analysis with 100 SARS-CoV-2 sequences (Supplementary Table 1) from the same hospital revealed clustering of all 9 sequences from this patient, which essentially rules out reinfection (Figure 1C). Six of the 7 sequences from days 7–38 had an identical consensus. The NP sample from day 29 had 2 additional substitutions, 1 synonymous and 1 nonsynonymous (C5184U, ORF1a P1640L; Figure 1D). Given that the other day 29 sample was from sputum, these differences might reflect 2 different subpopulations present within the same host on that particular day. Four additional nonsynonymous substitutions were fixed by day 93. One of the nonsynonymous changes, ORF1a P1640F, actually had 2 mutations in the same codon—C5184U, which was fixed in the day 29 NP specimen, and C5183U, which was a minority variant in the day 29 and day 33 sputum samples (Supplementary Figure 1). The day 106 sample had 1 additional nonsynonymous substitution (C5178U, ORF1a T1368I), which was also present as a minority variant in the day 29 and 33 sputum samples. These data demonstrate the within-host evolution, and therefore replication, of SARS-CoV-2 over a 4-month period.
We evaluated the patient’s serological response with banked sera from days 30, 88, 120, and 122 (Supplementary Table 2). On day 30, he was negative for total antibodies against nucleocapsid (Roche), total antibodies against the spike receptor binding domain (Siemens), IgG against spike S1/S2 (Diasorin), and IgG against S1 (EUROIMMUN). He was categorically positive for nucleocapsid antibodies on day 60 (outside report) and only marginally positive on day 88 (index value of 2.1, threshold of 1.0 where values during natural infection are often >100); he remained negative for anti-spike antibodies, although the Siemens index value after receiving plasma was numerically greater than baseline. It is not clear whether this represents seroconversion or decay of antibodies administered in the convalescent plasma. He was negative for all antibodies on day 120 and then again became marginally positive for nucleocapsid antibodies after the second administration of convalescent plasma.
DISCUSSION
Persistence of viral RNA and long-term replication are increasingly recognized as sequelae of acute viral infections [5]. In most cases, these phenomena are attributable to incomplete immune clearance and/or ongoing viral replication in immune-privileged sites. For example, persistence of measles virus in the central nervous system has been well documented months after infection, and Ebola virus replication has been found in the testes and retina [6, 7]. There are many examples of chronic infections with norovirus and influenza virus in individuals with adaptive immune deficits [8, 9], and patients with common variable immune deficiency or agammaglobulinemia have been found to shed the oral poliovirus vaccine for many years [10, 11].
Our patient’s mantle cell lymphoma, cancer chemotherapy, and associated immunosuppression are likely the reason for his protracted clinical course. While his regimen included broadly active, cytotoxic agents that would affect multiple aspects of immune function (eg, doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide), we hypothesize that antibody-mediated ablation of B-cell precursors by two B-cell directed antibodies was primarily responsible for his prolonged viral shedding. The impact of both agents is expected to be greater on naive—as opposed to memory—B cells, which would be required for the initial response against a new pathogen, such as SARS-CoV-2. This humoral defect explains the absence of detectable seroconversion and recrudescence with reinitiation of his lymphoma treatment. While he clinically improved with each course of convalescent plasma, the coadministration of remdesivir makes it difficult to know whether this was related to antibody-mediated viral clearance.
Repeated sampling over a prolonged infectious period allowed us to examine the evolutionary dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 in a human host. Studies of noroviruses and influenza viruses in immunocompromised hosts suggest that these individuals may be reservoirs of antigenically novel viruses and that within-host selection may parallel evolutionary dynamics on larger scales [12, 13]. Prior to the first course of remdesivir and convalescent plasma (days 7–31), we observed a steady accumulation of minority single-nucleotide variants (Supplementary Figure 1). Mutations accumulated over the next 2 months, and 9 mutations fixed between days 93 and 106. None of these mutations have been observed at >0.25% frequency in >88 000 sequences available in GISAID (Supplementary Table 3). Notably, there were no new mutations in the spike protein between days 7 and 106, despite early treatment with convalescent plasma. The ORF1b M101L substitution (day 93 and 106 samples) maps to NiRAN domain of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, but is not known to mediate remdesivir resistance.
At this early stage of the pandemic, decisions regarding patient isolation and cohorting have largely been based on the results of nucleic acid testing. However, it is increasingly clear that SARS-CoV-2 RNA can be detected in clinical specimens long after a patient becomes culture negative, and culture positivity has not been identified past 20 days [4, 14]. Because RT-PCR positivity appears to persist for several weeks, national guidelines have suggested that viral RNA detected after 2 weeks of illness is of unclear significance and favor basing isolation decisions on time since symptom onset (www.cdc.gov). Our case highlights the unresolved issue of immunocompromised hosts, who may shed infectious virus for longer periods of time and may require alternative criteria. While routine use of viral culture is currently not feasible, it may be reasonable to use Ct thresholds, RT-PCR for replicative subgenomic RNA, or seroconversion with titer as surrogates for the presence or absence of infectious virus.
Our case illustrates that some patients with defective immune responses can shed infectious virus for many more weeks than originally thought. This has important public health and infection control implications. A major limitation of our study is that it describes a single individual whose clinical course may not be broadly generalizable to other immunocompromised populations. Nevertheless, we expect that additional cases such as the one described above will continue to elucidate important aspects of SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis, evolution, and immunity.
Supplementary Data
Supplementary materials are available at The Journal of Infectious Diseases online. Consisting of data provided by the authors to benefit the reader, the posted materials are not copyedited and are the sole responsibility of the authors, so questions or comments should be addressed to the corresponding author.
Notes
Financial support. This work was supported by a coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Response Innovation Grant from the University of Michigan. Additional support for the enrollment of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 was provided by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (U01 IP000974).
Potential conflicts of interest. The authors: No reported conflicts of interest. All authors have submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest.
Presented in part: Preprint publication, medRxiv, 22 September 2020.
References
- 1. Wiersinga WJ, Rhodes A, Cheng AC, Peacock SJ, Prescott HC. Pathophysiology, transmission, diagnosis, and treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a review. JAMA 2020; 324:782–93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Xiao AT, Tong YX, Zhang S. Profile of RT-PCR for SARS-CoV-2: a preliminary study from 56 COVID-19 patients [manuscript published online ahead of print 19 August 2020]. Clin Infect Dis 2020. doi:10.1093/cid/ ciaa460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Bullard J, Dust K, Funk D, et al. Predicting infectious SARS-CoV-2 from diagnostic samples [manuscript published online ahead of print 22 May 2020]. Clin Infect Dis 2020. doi:10.1093/cid/ ciaa638.32442256 [Google Scholar]
- 4. Rhee C, Kanjilal S, Baker M, Klompas M. Duration of SARS-CoV-2 infectivity: when is it safe to discontinue isolation? [manuscript published online ahead of print August 25 2020]. Clin Infect Dis 2020. doi:10.1093/cid/ ciaa1249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Randall RE, Griffin DE. Within host RNA virus persistence: mechanisms and consequences. Curr Opin Virol 2017; 23:35–42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Deen GF, Broutet N, Xu W, et al. Ebola RNA persistence in semen of Ebola virus disease survivors—final report. N Engl J Med 2017; 377:1428–37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Jacobs M, Rodger A, Bell DJ, et al. Late Ebola virus relapse causing meningoencephalitis: a case report. Lancet 2016; 388:498–503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Bok K, Prevots DR, Binder AM, et al. Epidemiology of norovirus infection among immunocompromised patients at a tertiary care research hospital, 2010–2013. Open Forum Infect Dis 2016; 3:ofw169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Lumby CK, Zhao L, Oporto M, et al. Favipiravir and zanamivir cleared infection with influenza B in a severely immunocompromised child [manuscript published online ahead of print 3 March 2020]. Clin Infect Dis 2020. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Dunn G, Klapsa D, Wilton T, Stone L, Minor PD, Martin J. Twenty-eight years of poliovirus replication in an immunodeficient individual: impact on the Global Polio Eradication Initiative. PLoS Pathog 2015; 11:e1005114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. DeVries AS, Harper J, Murray A, et al. Vaccine-derived poliomyelitis 12 years after infection in Minnesota. N Engl J Med 2011; 364:2316–23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Debbink K, Lindesmith LC, Ferris MT, et al. Within-host evolution results in antigenically distinct GII.4 noroviruses. J Virol 2014; 88:7244–55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Xue KS, Stevens-Ayers T, Campbell AP, et al. Parallel evolution of influenza across multiple spatiotemporal scales. eLife 2017; 6:e26875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. van Kampen JJA, van de Vijver DAMC, Fraaij PLA, et al. Shedding of infectious virus in hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19): duration and key determinants. medRxiv [Preprint]. Posted online 9 June 2020. http://medrxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2020.06.08.20125310. Accessed 9 July 2020.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.