Abstract
Brown seaweed polysaccharides (BSPs) are one of the primary active components from brown seaweed that has a range of pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. However, the quality control of BSPs is a challenge due to their complicated structure and macromolecule. In this study, saccharide mapping based on high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), multi-angle laser light scattering, viscometer, and refractive index detector (HPSEC-MALLS-Vis-RID), and Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) were used to discriminate the polysaccharides from nine different species of brown algae (BA1-9). The results showed that BSPs were composed of β-D-glucans and β-1,3−1,4-glucan linkages. The molecular weight, radius of gyration, and intrinsic viscosity of BSPs were ranging from 1.718 × 105 Da to 6.630 × 105 Da, 30.2 nm to 51.5 nm, and 360.99 mL/g to 865.52 mL/g, respectively. Moreover, α values of BSPs were in the range of 0.635 to 0.971, which indicated a rigid rod chain conformation. The antioxidant activities of BSPs exhibited substantial radical scavenging activities against DPPH (1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl) and ABTS (2, 2’-azino-bis-3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) radicals, which indicated that the use of BSPs might be a potential approach for antioxidant supplements. Thus, this study gives insights about the structure-function relationship of BSPs, which will be beneficial to improve the quality of polysaccharides derived from marine algae.
Keywords: Brown seaweed, Polysaccharide, Saccharide mapping, Chromatographic analysis, Antioxidant activity
Introduction
Brown seaweed is a potentially renewable resource in the marine environment. It is one of the significantly farmed alga species along with the Asia coast, which has been used in traditional medicine for a long time [1]. As an excellent source of bioactive compounds such as carotenoids, dietary fibre, protein, essential fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals, brown seaweed is potentially exploited as functional ingredients for both human and animal health applications [2, 3]. This seaweed contains a large amount of carbohydrate as structural, storage, and functional polysaccharide, with the total carbohydrate content ranging from 50 to 60% of dry weight [4].
Brown seaweed polysaccharides (BSPs) have become the focus of interest. They are known to be an excellent resource with valuable biological activities finding applications as functional foods, pharmaceuticals, and cosmeceuticals. These polysaccharides pose an extensive array of biological activities, most notably antioxidant, anti-viral, anti-cancer, prebiotics, and immune-modulatory effects [5–7]. Structural features of polysaccharides such as molecular weight (Mw), glycosidic linkages, and chain conformation, play an important role that affects their functional property [8, 9]. To promote further exploitation and full utilization of BSPs for functional food and pharmaceutical applications, a basic understanding of BSPs’physicochemical properties and biological activities need to be investigated.
The linkage type or feature analysis of BSPs is conventionally done by two-step characterisation process, the first involving gas chromatography mass-spectrometry analysis that requires samples to be methylated by derivatization followed by further confirmation by one dimension and two dimensions of nuclear magnetic resonance [10]. Owing to the complexities associated with these techniques, it is necessary to develop a specific and straight forward method to characterise the polysaccharides derived from different species of brown seaweed. Recently, specific enzymatic digestion called saccharide mapping has been proved to be a valuable technique for the identification of polysaccharides from natural resources [11]. Saccharide mapping based on enzymatic hydrolysis has been used for comparison of polysaccharides derived from natural and cultured Cordyceps sinensis [12] and different species of Panax [2]. As the polysaccharides present in different species of brown seaweed as well as marine algae is still unclear, saccharide mapping could be the right choice for comprehensive profiling of enzymatic hydrolysates of BSPs.
In the present study, “one-factor-at-a-time” approach was implemented to optimize PMP (1-phenyl-3-methyl-5-pyrazolone) conditions (PMP concentration, reaction time, and temperature of PMP derivates) on oligosaccharide derivatization, in order to improve the detection efficiency of HPLC based on PMP derivatization. Then saccharide mapping based on chromatographic analysis was developed to characterise and compare the polysaccharides in different species of brown seaweed. Besides, the Mw, radius of gyration, intrinsic viscosity, and chain conformation of BSPs were investigated by high-performance size-exclusion chromatography coupled with multi-angle laser light scattering, viscometry, and refractive index detector (HPSEC-MALLS-Visc-RID). Furthermore, the antioxidant activities of BSPs were also investigated. We propose that the procedures used in this study could give more information about the structural and functional relationship of BSPs.
Material and methods
Materials and reagents
Nine batches of dried brown algae spices (BA1-9) were collected from different areas in China (Table 1). The corresponding author identified them, and the voucher specimens were deposited at the Institute of Marine Sciences, Shantou University, China.
Table 1.
Summary of the investigated samples of various brown seaweed species and the yield of polysaccharides
| Code | Species | Sources | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BA1 | Saccharina japonica | Lianyungang City, Jiangsu Province | 11.17 |
| BA2 | Saccharina japonica | Yantai City, Shandong Province | 5.85 |
| BA3 | Saccharina japonica | Jining City, Shandong Province | 6.71 |
| BA4 | Saccharina japonica | Ningde City, Fujian Province | 8.19 |
| BA5 | Undaria pinnatifida | Yantai City, Shandong Province | 8.36 |
| BA6 | Undaria pinnatifida | Lianyungang City, Jiangsu Province | 9.47 |
| BA7 | Undaria pinnatifida | Dalian City, Liaoning Province | 11.43 |
| BA8 | Sargassum fusiforme | Wenzhou City, Zhejiang Province | 9.62 |
| BA9 | Sargassum hemiphyllum | Jining City, Shandong Province | 12.30 |
Isomalto-oligosaccharides, 1-phenyl-3-methyl-5-pyrazolone (PMP), α-Amylase-1,4-α-D-Glucan-glucanohydrolase from hog pancreas, cellulase-1,4-β-D-glucan glucanohydrolase from Aspergillus sp., and pectinase-α-1,4-glycosidic from Aspergillus aculeatus were purchased from Sigma (St. ouis, MO, USA). Fucosidase-α-(1–2,3,4,6)-L-fucosidase from Homo sapiens and lichenase-1,3(4)-β-Glucanase from Bacillus sp. were purchased from Megazyme (Wicklow, Ireland). All the other reagents were of analytical grade.
Preparation of polysaccharides
The low Mw compounds were removed by treating 10 g pulverised brown algae samples with 200 mL methanol/dichloromethane/water (4: 2: 1; v/v/v). The mixture was placed on a shaking incubator at room temperature for 24 h. The precipitate obtained after centrifugation (4000×g, 15 min) was dried in an oven at 50 °C. The dried material was resuspended in distilled water, and kept at room temperature for 10 min. Next, the samples were heated at 90 °C on a water bath for 2 h, centrifuged (4000×g, 15 min), resuspended in 3-fold volumes of ethanol (95%) and then stored at 4 °C overnight. After centrifugation (4000×g, 15 min), the precipitate was collected and dissolved in hot water, freeze-dried for a day to obtain crude brown seaweed polysaccharides (BSPs). The yield of BSPs (%) was calculated by following equation:
Optimization of PMP on oligosaccharide derivatization
To identify the optimized condition of oligosaccharides-PMP derivatives, several conditions were performed by changing one factor at a time while keeping the others constant. The experimental variables were PMP concentration, reaction time, and temperature of PMP derivates.
Before derivatization, isomalto-oligosaccharides (5 mg) were dissolved in distilled water (1 mL) to get standard sample solution. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) based oligomers detection of PMP derivatives was performed according to a reported method with slight modifications [13]. Briefly, the standard sample solution (50 µL) was mixed with 0.1 mol/L NaOH solution (50 µL) and 0.025-0.3 mol/L PMP methanolic solution (100 µL). The mixture was reacted at 40–90 °C for 40–140 min, and washed three times with dichloromethane, then the aqueous layer was filtered through a 0.45 µm membrane. The analysis of PMP-labeled samples was carried on an Agilent 1200 HPLC system (Alltech, USA), equipped with a vacuum degasser, a binary pump, an autosampler, and a diode array detector (DAD). The analytical column was a VisionHT C18 column (250 mm × 4.6 mm, 5 µm) operated at 30 ℃. The injection volume was 20 µL. Elution was at a flow rate of 0.8 mL/min. The mobile phase A consisted of acetonitrile and mobile phase B was 0.1 mol/L phosphate buffer at pH 6.7, using an isocratic elution of 16% A and 84% B.
Saccharide mapping based on chromatographic analysis
BSPs samples were dissolved in water at a concentration of 5 mg/mL. Sample solutions (250 µL) were incubated for 12 h at 40 °C with the following enzyme (500 µL), respectively: cellulase, α-amylase, lichenase, pectinase, and α-fucosidase at a final concentration of 20 U/mL. Subsequently, the mixtures were heated at 80 °C for 20 min to stop the reaction. The hydrolysates were derived with optimized PMP conditions and then analysed by HPLC as described above.
Monosaccharide composition
Monosaccharide composition of BSPs was determined by 1-phenyl-3-methyl-5-pyrazolone (PMP) pre-column derivatization described as a published method [13]. The sample was analyzed by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) system (Shimadzu, Japan) equipped with a VisionHT C18 column (250 mm × 4.6 mm, 5 µm) and a UV detection at 245 nm.
Fourier transforms infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR)
The FT-IR (MAGNA-IR 750, Thermo Nicolet Co., USA) spectrum was determined in the frequency range of 4000 − 400 cm− 1 by pressing BSPs samples (1 mg) and KBr (100 mg) into a pellet.
HPSEC-MALLS-Visc-RID
The Mw, polydispersity, radius of gyration, and intrinsic viscosity [η] of BSPs samples were determined on high-performance size exclusion chromatography coupled with multi-angle laser light scattering, viscometer, and refractive index detector (HPSEC-MALLS-Vis-RID) system equipped with an Agilent 1100 series LC/DAD system connected with P.L.aqua gel-OH Mixed-H column (300 mm × 7.8 mm, Agilent Technologies, USA) [14]. The procedure used to measure the [η] of BSPs followed the classic Huggins-Kramer equations. The enzymatically digested products (1 mL) were filtered through a 0.22 µm filter membrane, and then 50 µL of the filtrate was injected into the column, before being eluted with 0.1 mol/L NaNO3 at a flow rate of 0.5 mL/min. The column temperature was 35 °C. Data acquisition and analysis were carried out using the ASTRA 5.0 software.
Antioxidant activities
DPPH radical scavenging activity
A previously published protocol with slight modifications [15], was referred for evaluating DPPH radical scavenging efficacy of BSPs. BSPs samples (1 mL) at different concentrations were added into 1 mL DPPH solution dissolved in dehydrated alcohol (0.004%, w/v), then shaken and incubated for 30 min in a dark place. The absorbance values of BSPs were measured at 517 nm. DPPH radical scavenging efficacy (%) was calculated through the equation as previously described [16].
ABTS radical scavenging activity
The activity of BSPs samples in scavenging ABTS radicals was evaluated as described earlier, but with some minor modifications [17]. To generate ABTS radicals, a 5 mL ABTS solution (7 mmol/L) was mixed with 88 µL K2S2O8 (149 mmol/L), and the reaction mixture was incubated for 16 h (dark). Then, 1 mL of this solution was added to 10 µL of BSPs samples at various concentrations, and the absorbance was measured at 734 nm. ABTS radical scavenging activity (%) was calculated as previously described [17]. The 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) was defined as the concentration of BSPs samples that inhibited DPPH and ABTS radical formation by 50%. The IC50 values were calculated from the regression equations evaluated from the concentration of samples, and the percentage of inhibition for each system was calculated.
Results and discussion
Effect of PMP on the enzymatic products oligosaccharide derivation
Since carbohydrates have no UV absorbance, the reagents PMP is the most common labels that derivate with reducing sugars under mild conditions, which provides a high yield of single derivatives. A wealth of information is available on optimisation for single derivatives, but studies on the oligosaccharide derivatization were rarely reported. Accordingly, the PMP method, as reported so far, is not uniform for oligosaccharide measurements. Therefore, an optimised PMP-derivatization about oligosaccharide derivatization was developed. The condition of PMP derivates was optimised based on the ‘one-factor-at-a-time’ approach to optimise the condition of PMP concentration, reaction time, and temperature of PMP derivates.
To explore the optimised conditions of oligosaccharides-PMP derivatives, the standards of isomalto-oligosaccharides were initially investigated as models for the optimisation of PMP derivatization. The results were the sum of the peak area of oligosaccharides-PMP derivative detected by HPLC-DAD.
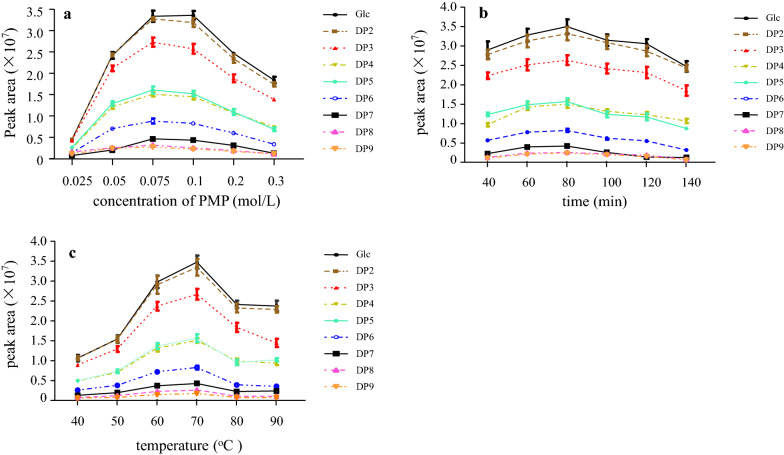
The product of oligosaccharide-PMP derivative could be influenced by the concentration of PMP, reaction time, and temperature of the derivatization. Therefore, the effect of various conditions on the derivatization potency was optimised by changing one argument at a time while keeping other arguments steady. To further research and display the optimised conditions of the above-mentioned oligosaccharide-PMP derivative, a line chart has been plotted, which distinctly reveals the effects of reciprocity of the independent variables. The results of the concentration of PMP, reaction time, and temperature of derivatization effect were shown in Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.
Optimization of oligosaccharides-PMP derivation. a The concentration of PMP. b Reaction temperature. c Reaction time
To investigate the PMP concentration effect on derivatization, a series of tested reactions with oligosaccharide as a model saccharide were performed. The result of the effect of reaction PMP concentration (0.025, 0.05, 0.075, 0.1, 0.2, and 0.3 mol/L) on total peak area (proportional to the yield of the derivative) were presented in Fig. 1a. The yield of the total peak area increased with the increase of the PMP concentration within a range from 0.025 to 0.075 mol/L. Performing the reaction at PMP concentration from 0.075 to 0.1 mol/L showed little effect. For a concentration ranging from 0.1 to 0.3 mol/L, the total peak area was negatively correlated with PMP concentration. Therefore, performing the labelling routine at 0.075 mol/L was recommended. The peak area of oligosaccharide at 0.075 mol/L and 0.1 mol/L PMP concentrations was similar; however, we recommend a working limit of 0.075 mol/L, which is in agreement with previous publications. When detecting carbohydrate-PMP derivatives, Rühmann et al. [18] considered that 0.075 mol/L PMP concentrations revealed to be optimal condition to minimise system peaks and enhance effectiveness.
To define the optimal amount of reaction time on the PMP derivatization reaction, a series of derivatization experiments with reaction time were carried out. As shown in Fig. 1b, the highest total peak area of oligosaccharide was obtained at 80 min. A low or high reaction time decreased the total peak area of oligosaccharide, as low reaction time reduces the efficiency of oligosaccharide-PMP derivatization, and high reaction time lead to oligosaccharide degradation. The effect of reaction time on oligosaccharide-PMP derivatization was in accordance with Han et al. [19] HPLC analysis of chitosan-PMP derivatives revealed the reaction time at 60 min was the optimum derivatization condition of oligosaccharide and which was close to our results.
Besides the concentration of PMP and reaction time, other parameters affecting the enzymatic products of oligosaccharide derivation using PMP were examined, and the results showed that temperature profoundly affected the PMP derivative which was determined by total peak area of oligosaccharides (Fig. 1c). The total peak area almost linearly upgrades below 70 °C; however, a decline was noted above this point due to partial decomposition of the reaction product at this condition. Based on the maximum peak area of derivative, the optimal reaction temperature was found to be 70 °C. These results are in accordance with Wang et al.., who concluded that the optimal condition based on response surface methodology for the glucose-PMP derivatization was between 70 and 73 °C for 120–140 min [20]. Therefore, it is recommended to perform the labelling at 70 °C.
Characterisation of BSPs on the basic of saccharide mapping
Brown seaweed polysaccharides (BSPs) were extracted by using hot water based on our previous work [21]. As shown in Table 1, the yield of BSPs ranged from 5.85 to 12.30%. The highest yield of polysaccharide (12.30%) was BA9, which obtained from Sargassum hemiphyllum.
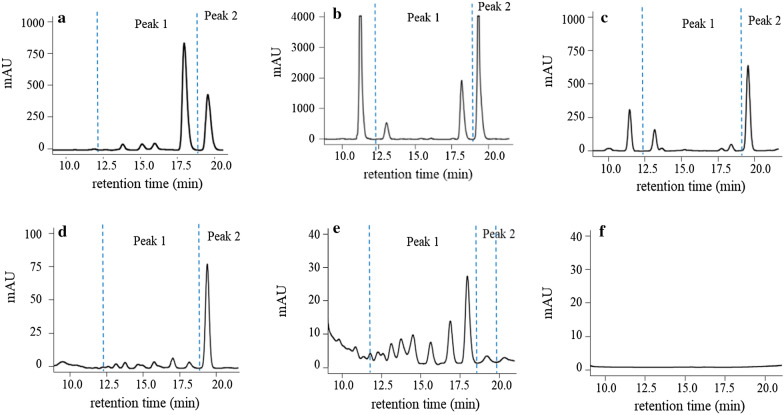
After enzymolysis, HPLC chromatogram of BSPs showed two main peaks. As shown in Fig. 2, peak 1 represented oligomers, and peak 2 indicated monosaccharide. Lichenase are glycosyl hydrolases that comprise of structurally diverse groups of enzymes that act on the β-glycosidic bonds between polysaccharides. Cellulase catalyzes the hydrolysis of β-1,4-glucosyl linkages, while lichenase catalyzes the hydrolysis of β-1,4-glucosyl linkages adjacent to a β-1,3-glucosyl linkage on the non-reducing end of β-1,3−1,4 type of polysaccharides [22]. The typical HPLC chromatogram of saccharide mapping of BSPs by cellulase and lichenase were showed in Fig. 2c and d, respectively. All the BSPs samples (BA1-BA9) showed positive responses to cellulase and lichenase (Table 2), which indicated all polysaccharides samples were composed of β-D-glucans and β-1,3−1,4 type of polysaccharides. The β-1,3−1,4-glucan, mostly found in the plant and fungi, has a peculiar distribution pattern among eukaryotes. More recent studies point out that some BSPs can build up β-1,3−1,4-glucan chains in their cell wall, for example, Monodus subterraneus, Laminaria hyperborean, and Saccharina latissima [23].
Fig. 2.
Typical HPLC chromatogram of saccharide mapping of brown seaweed polysaccharides, sample BA1. a Amylase; b pectinase; c cellulase; d lichenase; e fucosidase; f blank. Peak 1 area: oligomers, Peak 2: monosaccharide
Table 2.
Saccharide mapping response of brown seaweed polysaccharides derived from brown algae
| Samples | Enzyme | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amylase | Pectinase | Cellulase | Lichenase | Fucosidase | |
| BA1a | A +b | A+ | A+ | A+ | A+ |
| BA2 | A+ | A+ | A+ | A+ | A+ |
| BA3 | A+ | A+ | A+ | A+ | A+ |
| BA4 | A+ | A+ | A+ | A+ | A+ |
| BA5 | A+ | A+ | A+ | A+ | A+ |
| BA6 | A+ | A+ | A+ | A+ | A+ |
| BA7 | A+ | A+ | A+ | A+ | A+ |
| BA8 | A+ | A+ | A+ | A+ | A+ |
| BA9 | A+ | A+ | A+ | A+ | A+ |
aThe sample codes were the same as Table 1
bPositive response
α-Amylase is a hydrolase enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of internal α-1,4-glycosidic linkages, while pectinase randomly attacks the α-1,4-glycosidic linkages of the polysaccharides chains [24]. All investigated seaweed samples (BA1–BA9) showed a positive response to α-amylase and pectinase (Table 2), and the typical chromatograms are shown in (Fig. 2a, b), which indicated that these samples contained the α-D-glycosidic linkages. The results are similar to Li et al. [25], who reported that bioactive polysaccharides extracted from Sargassum pallidum had a 1-4-glycosidic linkage.
The α-fucosidase can catalyze the hydrolysis of fucose from fucoidan, via cleavage of α-1,3-L-fucopyranose, α-1,4-L-fucopyranose, and possibly also of α-1,2-L-fucopyranose in fucoidan [26]. All investigated samples showed a positive response to α-fucosidase (Table 2). Typical chromatograms were shown in (Fig. 2e), which indicated that those samples contain fucoidan type of polysaccharides. According to Wu et al. [27], fucoidan is structurally made of the repetitive units of α-1,3-L-fucopyranose and α-1,4-linked L-fucopyranose.
Monosaccharide composition of different BSPs
The mole percentages of monosaccharides were summarized in Table 3. The results showed that polysaccharides in BSPs mainly consist of mannose, glucuronic acid, glucose, galactose, and fucose, with small amounts of rhamnose and arabinose. In BA1-4, included 8.3–12.2% of mannose, 11.7–14.5% of glucuronic acid, 12.1–23.4% of galactose, and 48.7–62.4% of fucose. This is consistent with previous study by Zhang et al. [21], results showed that polysaccharides extracted from Saccharina japonica were mainly composed of mannose, glucuronic acid, galactose, and fucose in a molar ratio of 1.0: 1.2: 3.6: 4.1. Other polysaccharides in BA5-7 contained glucose up to 55.6–74.0%, indicating that polysaccharides from Undaria pinnatifida were mainly composed of glucose. In BA8 and BA9, the monosaccharides consist of mannose, glucuronic acid, glucose, galactose, and fucose, with fucose up to 35.1–43.7%. The results suggested that brown seaweed polysaccharides from different species exhibited different monosaccharide compositions.
Table 3.
Monosaccharide composition of polysaccharides from brown seaweed polysaccharides samples
| Samples | Man (%) | Rha | GlcA (%) | GalA | Glc (%) | Gal (%) | Ara | Fuc (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BA1 | 10.3 | 0.7% | 13.8 | – | 1.4 | 23.4 | 1.7% | 48.7 |
| BA2 | 11.2 | 1.4% | 13.4 | – | 1.9 | 19.4 | 1.9% | 50.7 |
| BA3 | 12.2 | 0.8% | 14.5 | – | 0.6 | 21.2 | 1.8% | 48.9 |
| BA4 | 8.3 | 3.8% | 11.7 | – | 1.6 | 12.1 | 0.1% | 62.4 |
| BA5 | 7.0 | – | 13.7 | – | 55.6 | 11.8 | – | 11.9 |
| BA6 | 4.4 | – | 8.6 | – | 74.0 | 6.3 | – | 6.8 |
| BA7 | 5.2 | – | 10.1 | – | 68.1 | 8.3 | – | 8.3 |
| BA8 | 10.8 | – | 11.4 | – | 17.4 | 25.3 | – | 35.1 |
| BA9 | 10.3 | – | 12.2 | – | 6.8 | 27.0 | – | 43.7 |
Man Mannose, Rha Rhamnose, GlcA Glucuronic acid, GalA Galacturonic acid, Glc Glucose, Gal Galactose, Ara Arabinose, Fuc Fucose, – not detected
FT-IR of different BSPs
FT-IR spectroscopy is one of the important analytical techniques extensively used to study the molecular structures and the conformations of macromolecules to identify the vibrations between the different atoms in molecules. The spectrum obtained between 400 and 4000 cm− 1 can be used to analyse the structural features of polysaccharides, including glucosidic bonds and functional groups. Functional characteristics and structural features of BSPs were analysed using FT-IR. As shown in Fig. 3, the sharp band at 887.76 cm− 1 (C–S–O) suggested a pattern of sulfate substitution [28]. The band at 1034 cm− 1 was ascribed to uronic acid by the C-O stretching vibration [29]. The absorption peak presented at 1415 cm− 1 was assigned to the C=O stretching mode of the fucoidan [30]. The strong absorption band at 1240–1255 cm− 1 (S=O) stretching confirmed the existence of a significant amount of sulfate in the polysaccharides [31]. The band at 1250 cm− 1 and 1028 cm− 1 was attributed to the presence of asymmetric O=S=O stretching vibration of a sulfate group [32]. Previous report showed that signals at 1610–1635 cm− 1 were assigned to the asymmetric strength vibration of COO- of uronic acids [33]. The major absorption band at 3420 cm− 1 represents to O-H group [34].
Fig. 3.
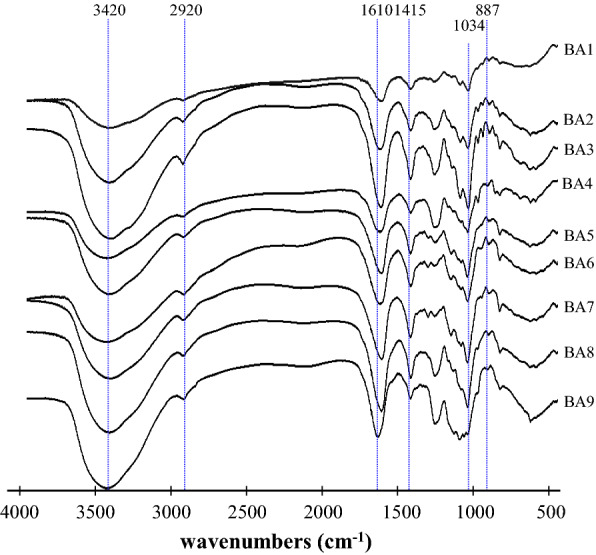
FT-IR spectra of brown seaweed polysaccharides samples. The codes of polysaccharide samples were the same as in Table 1
Conformation features of different BSPs
HPSEC-MALLS-Visc-RID has demonstrated to be a powerful technique for determining the Mw, [η], chain conformation features of polysaccharides without using a series of dextran standards [35]. In otherwords, the HPSEC chromatograms are helpful to determine physical properties of polysaccharides, which are in turn beneficial to discriminate and improve the quality of polysaccharides derived from natural resources. In this study, the Mw, [η], the radius of gyration (Rg), and chain conformation of BSPs samples were investigated by HPSEC-MALLS-Visc-RID.
The Mw distributions of BSPs analysed on the RID were shown in Fig. 4, while the values of [η] were obtained from viscometer. The values of Mw and Rg of BSPs were investigated by MALLS according to the Zimm method based on Rayleigh-Gans-Debye theory for light scattering using the following equation:
where the optical constant is represented as K = [4π2n2(dn/dc)2]/(NAλ4); C is the polysaccharides concentration; Rθ is the Rayleigh ratio; λ is the wavelength; n is the refractive index of the solvent (0.9% NaCl aqueous solution); N.A.is Avogadro’s number, and A2 is the second virial coefficient. The MALLS instrument was calibrated using filtered (0.2 µm, Millipore) HPLC-grade toluene, and normalised using a dextran standard (25 kDa, low polydispersity). All the obtained results are summarised in Table 4.
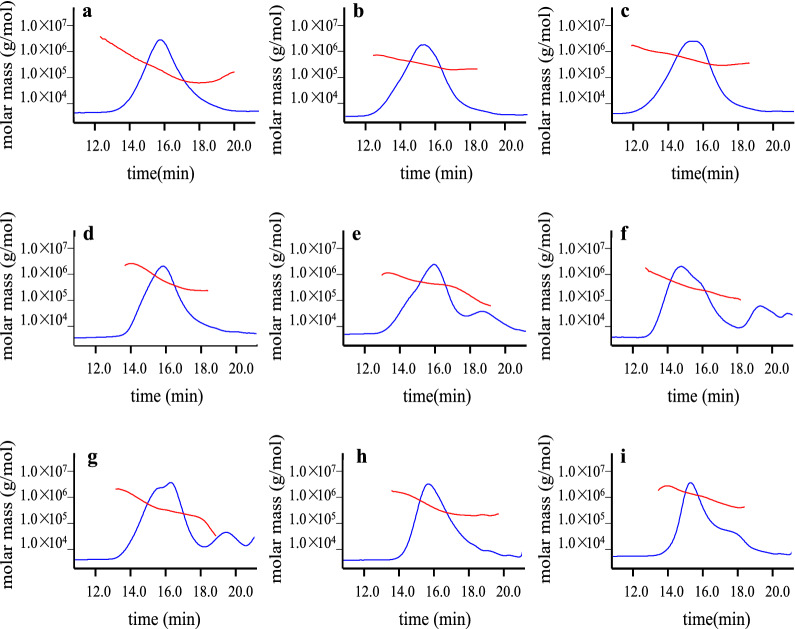
Fig. 4.
HPSEC chromatograms (solid lines) with molecular weight distribution (dots) of the brown seaweed polysaccharides samples a BA1, b BA2, c BA3, d BA4, e BA5, f BA6, g BA7, h BA8, i BA9 determined by multi-angle laser light scattering, viscometer, and refractive index detector. The codes of samples were the same as in Table 1
Table 4.
Molecular weight, intrinsic viscosity, and chain conformation of the investigated brown seaweed polysaccharides samples
| Samples | M w(Da) | R g(nm) | [η] (mL/g) | α |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BA1 | 1.718 × 105 (± 0.407%) | 32.5 (± 0.1%) | 386.75 (± 0.75%) | 0.689 |
| BA2 | 3.663 × 105 (± 0.655%) | 44.5 (± 0.1%) | 704.26 (± 0.47%) | 0.971 |
| BA3 | 4.276 × 105 (± 0.943%) | 51.5 (± 0.1%) | 729.62 (± 0.46%) | 0.635 |
| BA4 | 6.630 × 105 (± 0.690%) | 49.6 (± 0.1%) | 389.39 (± 0.69%) | 0.700 |
| BA5 | 2.803 × 105 (± 0.506%) | 43.8 (± 0.1%) | 865.52 (± 0.44%) | 0.827 |
| BA6 | 2.949 × 105 (± 0.408%) | 48.8 (± 0.0%) | 708.46 (± 1.10%) | 0.884 |
| BA7 | 2.438 × 105 (± 0.469%) | 39.3 (± 0.1%) | 816.83 (± 0.41%) | 0.888 |
| BA8 | 1.909 × 105 (± 0.239%) | 30.2 (± 0.1%) | 406.01 (± 1.25%) | 0.663 |
| BA9 | 5.136 × 105 (± 0.426%) | 32.2 (± 0.1%) | 360.99 (± 1.85%) | 0.652 |
M w: Molecular weight; Rg: radius of gyration; [η]: intrinsic viscosity; α: exponent of Mark-Houwink-Sakurada equation. The sample codes were the same as Table 1.
The Mw of BSPs samples were determined ranging from 1.718 × 105 Da to 6.630 × 105 Da. It was observed that there was a molecular weight difference in the investigated seaweed samples, which may be due to the disparity of brown algae in species and their growth condition [36]. Similarly, Ali et al. [37] also reported that the molecular weight of brown algae Stypocaulon scoparium polysaccharide was determined as 2.236 × 105 Da. The BA1, BA4, BA8, and BA9 samples have relatively low [η] values ranging from 360.99 to 406.01 mL/g, while the BA2, BA3, BA5, BA6, and BA7 samples have high [η] values, which were determined to be in the range of 704.26–865.52 mL/g. The relative low [η] values were in agreement with water-soluble polysaccharides isolated from the Tunisian brown seaweed Cystoseira compressa with the [η] of 400 mL/g [38]. Similarly, the relative high [η] values were also in accordance with polysaccharide extracted from Cystoseira trinode, Sargassum latifolium, and Cystoseira myrica in the range of 860–870 mL/g [39].
Moreover, the values of Rg and Mw were then utilised to establish the double logarithmic relationships of Mw–Rg based on the following equations:
According to the theory of macromolecules solution, the exponent α values of 0.33, 0.50 to 0.60, and 1.0 reflected chain shape corresponding to spheres, random coils, and rigid rods, respectively [40]. It also gives access to information on the conformation of the polysaccharides. The exponent α values of the polysaccharides from brown algae was calculated to be in the range of 0.635 to 0.971. These results indicated that the BSPs adopted a rigid rod. Khajouei et al. [41] reported that the exponent α values of polysaccharides derived from Nizimuddinia zanardini as 0.64 that corresponds to the rod conformation.
BSPs possess anti-oxidant activities in vitro
The DPPH has a stable free radical, which has been widely accepted as a tool for estimating the free radical-scavenging activities of antioxidants. This assay is used to test the anti-oxidative ability of polysaccharide functioning as hydrogen donors. The amounts of DPPH scavenging activity of various BSPs were recorded in Table 5. Among the nine different seaweeds, BA6 (Undaria pinnatifida) showed a relatively higher IC50 with 1.28 mg/mL. Followed by BA7 (Undaria pinnatifida), which was 1.21 mg/mL. While the lowest IC50 were recorded in BA9 (Sargassum hemiphyllum, 0.85 mg/mL) and BA4 (Saccharina japonica, 0.87 mg/mL). Thus, the seaweed BA9 (Sargassum hemiphyllum) collected from Jining City was determined to be the richest source of antioxidant as compared to the other seaweeds tested in this study. The antioxidant capacity of fucoidan is due to the ability to donate the H atoms to form stable DPPH-H molecule [42]. The obtained results were similar to the earlier study that witnessed a reduction in the activity towards the increasing concentration of fucoidan extracted from Spatoglossum asperum, with an IC50 value of 93.69 µg/mL [43]. Similarly, Sargassum pallidum sulfated polysaccharide [44] and Cystoseria barbata polysaccharide [45] also exhibited favourable DPPH radical-scavenging activity.
Table 5.
Effect of brown seaweed polysaccharides samples in scavenging DPPH and ABTS radicals.Values are given as IC50, which are means of triplicate determinations
| Samples | IC50 values (mg/mL) | |
|---|---|---|
| DPPH radicals | ABTS radicals | |
| Control (Vc) | 0.31 (± 0.91%) | 0.34 (± 0.51%) |
| BA1a | 0.91 (± 0.42%) | 0.57 (± 1.12%) |
| BA2 | 1.12 (± 0.87%) | 0.69 (± 0.13%) |
| BA3 | 0.90 (± 0.73%) | 0.59 (± 0.84%) |
| BA4 | 0.87 (± 0.53%) | 0.55 (± 0.46%) |
| BA5 | 1.16 (± 0.35%) | 0.66 (± 0.65%) |
| BA6 | 1.28 (± 0.93%) | 0.78 (± 0.52%) |
| BA7 | 1.21 (± 1.13%) | 0.83 (± 0.76%) |
| BA8 | 1.05 (± 1.07%) | 0.63 (± 0.43%) |
| BA9 | 0.85 (± 0.59%) | 0.58 (± 1.04%) |
aThe sample codes were the same as Table 1
ABTS assay is to determine the capability of hydrogen-donating antioxidants to scavenge ABTS radical in the solution and prevent lipid oxidation via chain-breaking antioxidants. The IC50 of ABTS scavenging activity of various BSPs was tabulated in Table 5. The lowest IC50 value (0.55 mg/mL) was observed in BA4 (Saccharina japonica) collected from Ningde City, followed by BA1 (Saccharina japonica) from Lianyungang City (IC50 = 0.57 mg/mL). The highest IC50 (0.83 mg/mL) was observed in BA7 (Undaria pinnatifida) obtained from Dalian City and followed by BA6 (Undaria pinnatifida) collected from Lianyungang City. Thus, the best hydrogen-donating ability to scavenge ABTS was observed in BA4 (Saccharina japonica) collected from Ningde City. Previous studies in other species of algae suggested that sulfated polysaccharide had antioxidant activities. For example, sulfated polysaccharides from Gracialria corticata had a maximum scavenging activity of 74.5% with a concentration of 125 µg/mL [46]. The ABTS• cation radical activity plays a vital role by H abstraction reaction, due to the chemical structure of sulfated polysaccharide [47]. The observations of the study revealed that BSPs had excellent scavenging ability on ABTS radical. The potent antioxidant activities of BSPs may represent an exciting advancement in search of novel functional applications relevant to following industrial field, including pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, cosmeceuticals, and functional foods.
Conclusion
In this study, BSPs from different species that were collected from several regions of China were characterized using a chromatographic method based on saccharide mapping. Results showed that different species of brown seaweed had similar chemical characteristics, which showed a positive response to cellulase, α-amylase, lichenase, pectinase, and α-fucosidase. All investigated BSPs samples were found to have a rigid rod confirmation features through theory of macromolecules solution. In addtion, the Mw and [η] of BSPs are vital factor in the expression of bioactivities and thus were confirmed in this study. The Mw of BSPs samples were in the range of 1.718 × 105– 6.630 × 105 Da, while [η] was ranging from 360.99 to 865.52 mL/g. The BSPs from different species of brown seaweed exhibited profitable antioxidant activities in terms of DPPH and ABTS radicals scavenging abilities, which revealed that BSPs could be employed as antioxidants in the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetics industry. Therefore, this study is beneficial to improve the quality of brown seaweed as well as their performance in pharmaceutical and biomedical applications.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- BSPs
Brown seaweed polysaccharides
- HPLC
High-performance liquid chromatography
- HPSEC-MALLS-Vis-RID
Multi-angle laser light scattering, viscometer, and refractive index detector
- FT-IR
Fourier transform infrared
- BA1-9
Brown algae
- Mw
Molecular weight
- PMP
1-phenyl-3-methyl-5-pyrazolone
- DAD
Diode array detector
- η
Intrinsic viscosity
- DPPH
1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl
- ABTS
2, 2’-azino-bis-3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid
- IC50
50% inhibitory concentration
- Man
Mannose
- Rha
Rhamnose
- GlcA
Glucuronic acid
- GalA
Galacturonic acid
- Glc
Glucose
- Gal
Galactose
- Ara
Arabinose
- Fuc
Fucose
- Rg
Radius of gyration
- C
Polysaccharides concentration
- Rθ
Rayleigh ratio
- n
Refractive index of the solvent
- N.A
Avogadro’s number
Authors’ contributions
MS, WZ, ST, YL and KC design and supervise of the work; SC, XZ investigate and data analysis; SC writes original draft; WZ, ST, YL and KC review and edite the draft. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was financially supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31901692); Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China (2018A030310151); and 2020 Li Ka Shing Foundation Cross-Disciplinary Research Grant (2020LKSFG02E).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Ethics approval and consent to participate:
Not applicable.
Consent for publication:
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Shengqin Chen, Malairaj Sathuvan and Xiao Zhang contributed equally to this work
Contributor Information
Shijie Tang, Email: sjtang3@stu.edu.cn.
Yang Liu, Email: liuyanglft@stu.edu.cn.
Kit-Leong Cheong, Email: klcheong@stu.edu.cn.
References
- 1.Gupta S, Abu Ghannam N. Bioactive potential and possible health effects of edible brown seaweeds. Trends Food Sci Tech. 2011;22:315–326. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2011.03.011. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cheong KL, Wu DT, Deng Y, Leong F, Zhao J, Zhang WJ, Li SP. Qualitation and quantification of specific polysaccharides from Panax species using GC–MS, saccharide mapping and HPSEC-RID-MALLS. Carbohyd Polym. 2016;153:47–54. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.07.077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lin SL, Wang ZY, Lam KL, Zeng SX, Tan BK, Hu JM. Role of intestinal microecology in the regulation of energy metabolism by dietary polyphenols and their metabolites. Food Nutr Res. 2019;63:12. doi: 10.29219/fnr.v63.1518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kumar S, Sahoo D, Levine I. Assessment of nutritional value in a brown seaweed Sargassum wightii and their seasonal variations. Algal Res. 2015;9:117–125. doi: 10.1016/j.algal.2015.02.024. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sanjeewa KKA, Lee JS, Kim WS, Jeon YJ. The potential of brown-algae polysaccharides for the development of anticancer agents: An update on anticancer effects reported for fucoidan and laminaran. Carbohyd Polym. 2017;177:451–459. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.09.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Senthilkumar K, Manivasagan P, Venkatesan J, Kim SK. Brown seaweed fucoidan: Biological activity and apoptosis, growth signaling mechanism in cancer. Int J Biol Macromol. 2013;60:366–374. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2013.06.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zheng LX, Chen XQ, Cheong KL. Current trends in marine algae polysaccharides: The digestive tract, microbial catabolism, and prebiotic potential. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;151:344–354. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Xu SY, Huang X, Cheong KL. Recent advances in marine algae polysaccharides: Isolation, structure, and activities. Mar Drugs. 2017;15:388. doi: 10.3390/md15120388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Yan JK, Wang C, Yu YB, Wu LX, Chen TT, Wang ZW. Physicochemical characteristics and in vitro biological activities of polysaccharides derived from raw garlic (Allium sativum L.) bulbs via three-phase partitioning combined with gradient ethanol precipitation method. Food Chem. 2021;339:128081. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Zhang R, Zhang XX, Tang YX, Mao JL. Composition, isolation, purification and biological activities of Sargassum fusiforme polysaccharides: A review. Carbohyd Polym. 2020;228:115381. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zhao J, Deng Y, Li SP. Advanced analysis of polysaccharides, novel functional components in food and medicine dual purposes Chinese herbs. Trac Trends Anal Chem. 2017;96:138–150. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2017.06.006. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Wu DT, Cheong KL, Wang LY, Lv GP, Ju YJ, Feng K, Zhao J, Li SP. Characterization and discrimination of polysaccharides from different species of Cordyceps using saccharide mapping based on PACE and HPTLC. Carbohyd Polym. 2014;103:100–109. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.12.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Xu SY, Liu JP, Huang XS, Du LP, Shi FL, Dong R, Huang XT, Zheng K, Liu Y, Cheong KL. Ultrasonic-microwave assisted extraction, characterization and biological activity of pectin from jackfruit peel. LWT. 2018;90:577–582. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2018.01.007. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zhang X, Aweya JJ, Huang ZX, Kang ZY, Bai ZH, Li KH, He XT, Liu Y, Chen XQ, Cheong KL. In vitro fermentation of Gracilaria lemaneiformis sulfated polysaccharides and its agaro-oligosaccharides by human fecal inocula and its impact on microbiota. Carbohyd Polym. 2020;234:115894. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.115894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Yan JK, Yu YB, Wang C, Cai WD, Wu LX, Yang Y, Zhang HN. Production, physicochemical characteristics, and in vitro biological activities of polysaccharides obtained from fresh bitter gourd (Momordica charantia L.) via room temperature extraction techniques. Food Chem. 2021;337:127798. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Khan BM, Qiu H-M, Xu SY, Liu Y, Cheong KL. Physicochemical characterization and antioxidant activity of sulphated polysaccharides derived from Porphyra haitanensis. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;145:1155–1161. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.10.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Khan BM, Qiu HM, Wang XF, Liu ZY, Zhang JY, Guo YJ, Chen WZ, Liu Y, Cheong KL. Physicochemical characterization of Gracilaria chouae sulfated polysaccharides and their antioxidant potential. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;134:255–261. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.05.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Rühmann B, Schmid J, Sieber V. Fast carbohydrate analysis via liquid chromatography coupled with ultra violet and electrospray ionization ion trap detection in 96-well format. J Chromatogr A. 2014;1350:44–50. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2014.05.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Han Z, Zeng Y, Lu H, Zhang L. Determination of the degree of acetylation and the distribution of acetyl groups in chitosan by HPLC analysis of nitrous acid degraded and PMP labeled products. Carbohyd Res. 2015;413:75–84. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2015.03.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wang W, Chen F, Wang Y, Wang L, Fu H, Zheng F, Beecher L. Optimization of reactions between reducing sugars and 1-phenyl-3-methyl-5-pyrazolone (PMP) by response surface methodology. Food Chem. 2018;254:158–164. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Zhang X, Liu Y, Chen XQ, Aweya JJ, Cheong KL. Catabolism of Saccharina japonica polysaccharides and oligosaccharides by human fecal microbiota. LWT. 2020;130:109635. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109635. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Irina VGP, Alexander АT, Orkhan NM. The features that distinguish lichenases from other polysaccharide-hydrolyzing enzymes and the relevance of lichenases for biotechnological applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018;102:3951–3965. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-8904-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Salmeán AA, Duffieux D, Harholt J, Qin F, Michel G, Czjzek M, Willats WGT, Hervé C. Insoluble (1 → 3), (1 → 4)-β-D glucan is a component of cell walls in brown algae (Phaeophyceae) and is masked by alginates in tissues. Sci Rep. 2017;7:2880. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-03081-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Khan M, Nakkeeran E, Umesh Kumar S. Potential application of pectinase in developing functional foods. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol. 2012;4:21–34. doi: 10.1146/annurev-food-030212-182525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Li C, Li XS, You LJ, Fu X, Liu RH. Fractionation, preliminary structural characterization and bioactivities of polysaccharides from Sargassum pallidum. Carbohydr Polym. 2017;155:261–270. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.08.075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ale MT, Meyer AS. Fucoidans from brown seaweeds: An update on structures, extraction techniques and use of enzymes as tools for structural elucidation. Rsc Advances. 2013;3:8131–8141. doi: 10.1039/C3RA23373A. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wu XD, Jiang W, Lu JJ, Yu Y, Wu B. Analysis of the monosaccharide composition of water-soluble polysaccharides from Sargassum fusiforme by high performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2014;145:976–983. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.09.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Yang LQ, Zhang LM. Chemical structural and chain conformational characterization of some bioactive polysaccharides isolated from natural sources. Carbohydr Polym. 2009;76:349–361. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2008.12.015. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Fenoradosoa TA, Ali G, Delattre C, Laroche C, Petit E, Wadouachi A, Michaud P. Extraction and characterization of an alginate from the brown seaweed Sargassum turbinarioides Grunow. J Appl Phycol. 2010;22:131–137. doi: 10.1007/s10811-009-9432-y. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ho TTM, Bremmell KE, Krasowska M, Macwilliams SV, Richard CJE, Stringer DN, Beattie DA. In situ ATR FTIR spectroscopic study of the formation and hydration of a Fucoidan/Chitosan polyelectrolyte multilayer. Langmuir. 2015;31:11249–11259. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b01812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Pielesz A, Biniaś W. Cellulose acetate membrane electrophoresis and FTIR spectroscopy as methods of identifying a fucoidan in Fucus vesiculosus Linnaeus. Carbohyd Res. 2010;345:2676–2682. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2010.09.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Marudhupandi T, Ajith Kumar TT, Lakshmanasenthil S, Suja G, Vinothkumar T. In vitro anticancer activity of fucoidan from Turbinaria conoides against A549 cell lines. Int J Biol Macromol. 2015;72:919–923. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.10.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Hu T, Liu D, Chen Y, Wu J, Wang S. Antioxidant activity of sulfated polysaccharide fractions extracted from Undaria pinnitafida in vitro. Int J Biol Macromol. 2010;46:193–198. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2009.12.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Wijesinghe WAJP, Athukorala Y, Jeon YJ. Effect of anticoagulative sulfated polysaccharide purified from enzyme-assistant extract of a brown seaweed Ecklonia cava on Wistar rats. Carbohydr Polym. 2011;86:917–921. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.05.047. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Xu XQ, Xue CH, Chang YG, Liu GC. Chain conformation, rheological and charge properties of fucoidan extracted from sea cucumber Thelenota ananas: A semi-flexible coil negative polyelectrolyte. Food Chem. 2017;237:511–515. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.05.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Wijesinghe WAJP, Jeon YJ. Biological activities and potential industrial applications of fucose rich sulfated polysaccharides and fucoidans isolated from brown seaweeds: A review. Carbohydr Polym. 2012;88:13–20. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.12.029. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ali B, Emmanuel P, Redouan E, Roland M, Salima A, Rachida ZY. Production of guluronate oligosaccharide of alginate from brown algae Stypocaulon scoparium using an alginate lyase. J Appl Phycol. 2017;29:509–519. doi: 10.1007/s10811-016-0928-y. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Hentati F, Delattre C, Ursu AV, Desbrières J, Le Cerf D, Gardarin C, Abdelkafi S, Michaud P, Pierre G. Structural characterization and antioxidant activity of water-soluble polysaccharides from the Tunisian brown seaweed Cystoseira compressa. Carbohyd Polym. 2018;198:589–600. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.06.098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Larsen B, Salem DMSA, Sallam MAE, Mishrikey MM, Beltagy AI. Characterization of the alginates from algae harvested at the Egyptian Red Sea coast. Carbohyd Res. 2003;338:2325–2336. doi: 10.1016/S0008-6215(03)00378-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Picton L, Bataille I, Muller G. Analysis of a complex polysaccharide (gum arabic) by multi-angle laser light scattering coupled on-line to size exclusion chromatography and flow field flow fractionation. Carbohydr Polym. 2000;42:23–31. doi: 10.1016/S0144-8617(99)00139-3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Khajouei RA, Keramat J, Hamdami N, Ursu AV, Delattre C, Laroche C, Gardarin C, Lecerf D, Desbrières J, Djelveh G, Michaud P. Extraction and characterization of an alginate from the Iranian brown seaweed Nizimuddinia zanardini. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;118:1073–1081. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.06.154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Wang J, Zhang Q, Zhang Z, Song H, Li P. Potential antioxidant and anticoagulant capacity of low molecular weight fucoidan fractions extracted from Laminaria japonica. Int J Biol Macromol. 2010;46:6–12. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2009.10.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Palanisamy S, Vinosha M, Marudhupandi T, Rajasekar P, Prabhu NM. In vitro antioxidant and antibacterial activity of sulfated polysaccharides isolated from Spatoglossum asperum. Carbohydr Polym. 2017;170:296–304. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.04.085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Ye H, Wang KQ, Zhou CH, Liu J, Zeng XX. Purification, antitumor and antioxidant activities in vitro of polysaccharides from the brown seaweed Sargassum pallidum. Food Chem. 2008;111:428–432. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.04.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Sellimi S, Kadri N, Barragan-Montero V, Laouer H, Hajji M, Nasri M. Fucans from a Tunisian brown seaweed Cystoseira barbata: Structural characteristics and antioxidant activity. Int J Biol Macromol. 2014;66:281–288. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.02.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Sanjeewa KKA, Kang N, Ahn G, Jee Y, Kim YT, Jeon YJ. Bioactive potentials of sulfated polysaccharides isolated from brown seaweed Sargassum spp in related to human health applications: A review. Food Hydrocolloid. 2018;81:200–208. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.02.040. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Saravana PS, Cho YJ, Park YB, Woo HC, Chun BS. Structural, antioxidant, and emulsifying activities of fucoidan from Saccharina japonica using pressurized liquid extraction. Carbohydr Polym. 2016;153:518–525. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.08.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.