Abstract
Hermetia illucens, one kind of necrophagous insects, belongs to the family Stratiomyidae (Diptera). In this study, the complete mitochondrial genome of H. illucens was investigated. The total number of nucleic acids were 15,698 bp. The genome contains 13 protein-coding genes, 22 tRNA genes, 2 rRNA genes, and a non-coding control region. The phylogenetic relationship of H. illucens and its 12 related species was reconstructed to confirm the taxonomic status of our sample.
Keywords: Hermetia illucens, mitochondrial genome, Stratiomyidae
Hermetia illucens belongs to the family Stratiomyidae. It is one sort of necrophagous insects originating from America (Yang et al. 2016). Their larvae have many medicinal values such as anti-inflammatory, analgesia, and haematolysis (Li 2016). Complete mitochondrial genome has been considered as a useful tool for population genetic and phylogenetic studies (Cameron 2014). The complete mitochondrial genome of H. illucens was first reported in this paper.
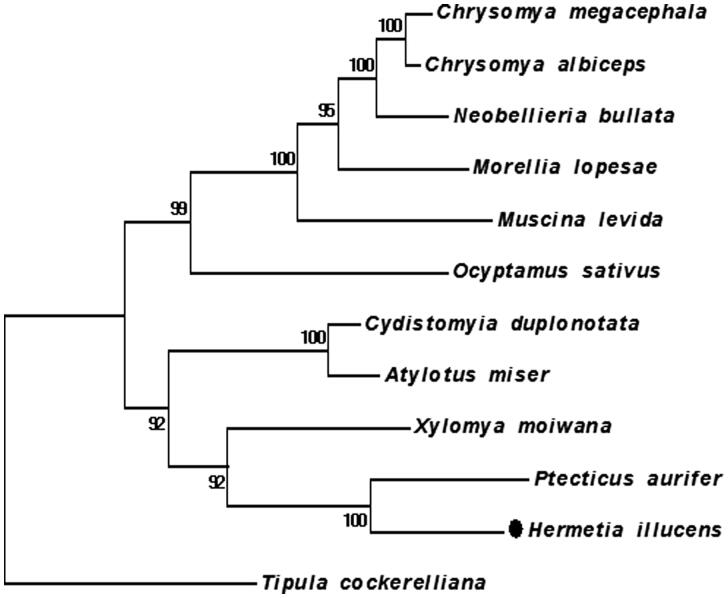
In this study, the individuals of H. illucens were provided by the Tianjin Institute of Plant Protection located in Tianjin city, China (voucher number: hsm-1). We used the high-throughput sequencing method to acquire the H. illucens complete mitochondrial genome sequences (GenBank accession number: KY679159). The complete genome is 15,698bp in length. The composition of the whole genome is 35.1% A, 39.3% T, 19.6% C, and 6.0% G. It contains 13 protein-coding genes (PCGs), 22 tRNA genes, and 2 rRNA genes. The longest gene within this molecule is ND5 containing 1719bp and the shortest is ATP8 gene which is 168 bp. Seven PCGs start from ATG, and five PCGs start from ATT while COX1 starts from TCG. ND5 and CytB use TAG as stop codon, and at the same time, ND1 uses incomplete stop codon, i.e. T––. Besides that, the other PCGs use TAA as stop codon. tRNAs were predicted by MITOS Web Server based on their cloverleaf secondary structure. As shown in Figure 1, the phylogenetic analysis among H. illucens and its related species was conducted.
Figure 1.
Twelve mitochondrial DNA were obtained from GenBank to build the maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree using MEGA (version 5.10) based on sequences of translated mitochondrial proteins. MUSCLE was used to align the sequences. 1000 replicates of bootstrap were set. Sequence data used in the study are the following: Ptecticus aurifer, KT225297.1; Xylomya moiwana, KT225302.1; Muscina levida, KT272866.1; Morellia lopesae, KT272863.1; Chrysomya megacephala, KT272865.1; C. albiceps, KT272864.1; Ocyptamus sativus, KT272862.1; Neobellieria bullata, KT272859.1; Atylotus miser, NC_030000.1; Cydistomyia duplonotata, NC_008756.1; Tipula cockerelliana, NC_030520.1.
Disclosure statement
The authors report that they have no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the manuscript.
References
- Cameron SL. 2014. Insect mitochondrial genomics: implications for evolution and phylogeny. Annu Rev Entomol. 59:95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang SY, Li WJ, Liu CX, Hu WF.. 2016. Effects of fermented swine manure on the conversion ratio of Hermetia illucens and nutritional components detection of Hermetia illucens larva and sandworm. AAPS J. 44:69–70. [Google Scholar]
- Li LG. 2016. [High quality live bait organisms-Hermetia illucens]. Sci Fish Farm. 7:33–33. Chinese. [Google Scholar]