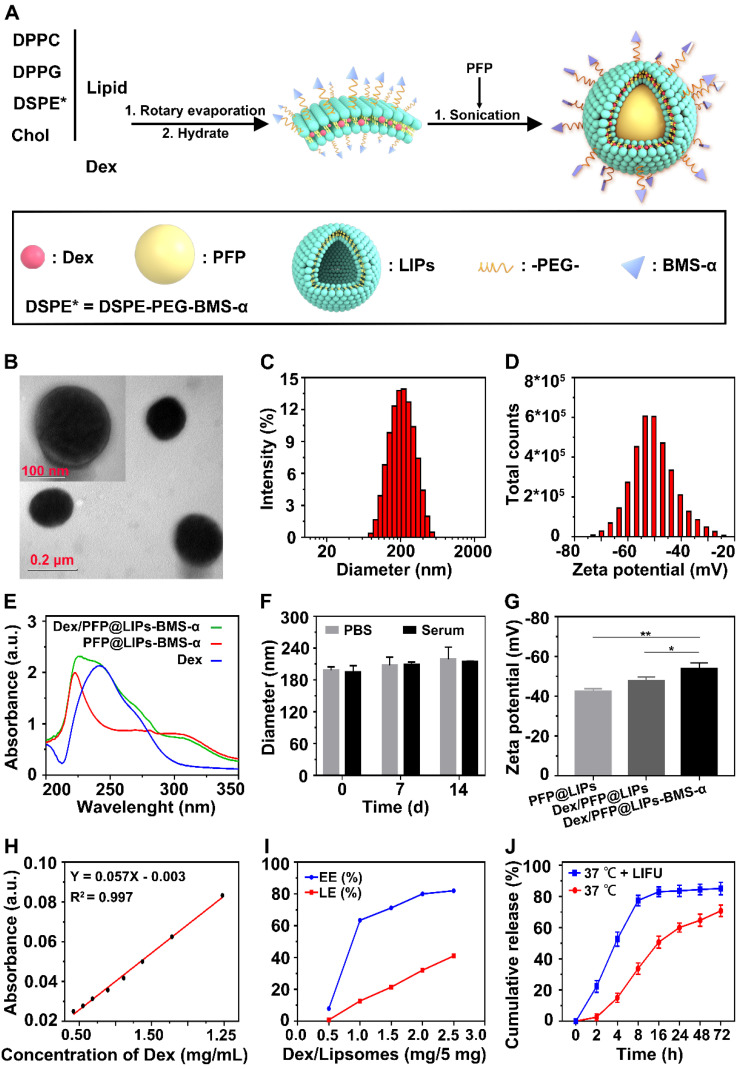
Figure 1.
Synthetic process and characterization of the Dex/PFP@LIPs-BMS-α. (A) Development agreement of Dex/PFP@LIPs-BMS-α. DPPC: 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphatidylcholine, DPPG: 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-(1-rac-glycerol), Chol: cholesterol, PFP: perfluoropentane, Dex: dexamethasone. (B) TEM image of Dex/PFP@LIPs-BMS-α, scale bar = 0.1 μm. (C) The size distribution of Dex/PFP@LIPs-BMS-α. (D) The Zeta potential of Dex/PFP@LIPs-BMS-α. (E) The optical absorption properties of Dex, PFP@LIPs-BMS-α and Dex/PFP@LIPs-BMS-α. (F) The size distribution of Dex/PFP@LIPs-BMS-α at 0th, 7th and 14th in PBS and serum (P < 0.05). (G) The Zeta potential of PFP@LIPs, Dex/PFP@LIPs and Dex/PFP@LIPs-BMS-α. (H) Standard concentration curve of Dex by UV-vis. (I) The EE% and LE% of Dex. (J) The release rate of Dex under different conditions (LIFU, 1 MHz, 2.4 W/cm2, 3 min, duty cycle of 50%). Data are presented as mean ± SD, n = 3, one-way ANOVA, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.