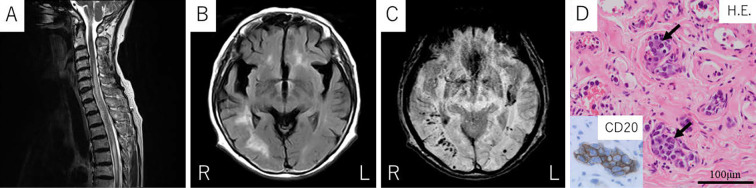
An 82-year-old woman presented with subacute progression of paraplegia. Spinal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed longitudinally extensive spinal cord lesions (LESCLs) on T2-weighted imaging (Picture A). Brain MRI showed multiple hyperintensity lesions on fluid-attenuated inversion recovery imaging (Picture B) with hemorrhagic lesions on susceptibility-weighted imaging (Picture C). The patient was negative for the anti-aquaporin-4 antibody. A cerebrospinal fluid analysis showed no neoplastic cells, but her IL-10 level was elevated (20 pg/mL). A random skin biopsy revealed atypical lymphocytes (arrow) positive for CD20 and CD79a in the subcutaneous vessels (Picture D). The patient was diagnosed with intravascular lymphoma (IVL) and given best supportive care. Myelopathy accounts for 5.78% of neurological complications of IVL (1). IVL can manifest as LESCLs, which can be a differential diagnosis of neuromyelitis optica (2). Intracranial hemorrhagic lesions are also reported in patients with IVL (3). One possible mechanism of hemorrhages is injury of the vessel walls caused by the infiltration of malignant cells into the small arterioles or venules (3). To our knowledge, our patient is the first case simultaneously exhibiting myelopathy and intracranial hemorrhages. A random skin biopsy should be considered when multiple intracranial hemorrhages exist in a patient with myelopathy.
Picture.
The authors state that they have no Conflict of Interest (COI).
References
- 1.Fonkem E, Dayawansa S, Stroberg E, et al. . Neurological presentations of intravascular lymphoma (IVL): meta-analysis of 654 patients. BMC Neurol 16: 9, 2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kumar N, Keegan BM, Rodriguez FJ, Hammack JE, Kantarci OH. Intravascular lymphoma presenting as a longitudinally-extensive myelitis: diagnostic challenges and etiologic clues. J Neurol Sci 303: 146-149, 2011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Passarin MG, Wen PY, Vattemi E, et al. . Intravascular lymphomatosis and intracerebral haemorrhage. Neurol Sci 31: 793-797, 2010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]