Abstract
BACKGROUND
The efficacy of novel glucose-lowering drugs in treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is unknown.
AIM
To evaluate the efficacy of glucose-lowering drugs dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs), and sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors in treating NAFLD and to perform a comparison between these treatments.
METHODS
Electronic databases were systematically searched. The inclusion criteria were: Randomized controlled trials comparing DPP-4 inhibitors, GLP-1 RAs, or SGLT2 inhibitors against placebo or other active glucose-lowering drugs in NAFLD patients, with outcomes of changes in liver enzyme [alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and/or aspartate aminotransferase (AST)] from baseline.
RESULTS
Nineteen studies were finally included in this meta-analysis. Compared with placebo or other active glucose-lowering drug treatment, treatment with DPP-4 inhibitors, GLP-1 RAs, and SGLT2 inhibitors all led to a significant decrease in ALT change and AST change from baseline. The difference between the DPP-4 inhibitor and SGLT2 inhibitor groups in ALT change was significant in favor of DPP-4 inhibitor treatment (P < 0.05). The trends of reduction in magnetic resonance imaging proton density fat fraction and visceral fat area changes were also observed in all the novel glucose-lowering agent treatment groups.
CONCLUSION
Treatment with DPP-4 inhibitors, GLP-1 RAs, and SGLT2 inhibitors resulted in improvements in serum ALT and AST levels and body fat composition, indicating a beneficial effect in improving liver injury and reducing liver fat in NAFLD patients.
Keywords: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, Glucose-lowering drug, Meta-analysis, Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor, Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist
Core Tip: The efficacy of novel glucose-lowering drugs in treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is unknown. The results of this meta-analysis showed that treatment with dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, and sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors resulted in improvements in serum alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase levels, indicating a beneficial effect in the improvement of liver injury.
INTRODUCTION
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is one of the leading causes of liver disease worldwide. The prevalence of NAFLD has increased rapidly over the past two decades. Approximately 24% of the adult population are reported suffering from NAFLD worldwide[1]. NAFLD is characterized by the presence of > 5% hepatic fat accumulation without alcohol abuse, virus infection, autoimmunity, or other secondary causes of liver disease[2], leading to inflammation and subsequent dis-ruption of hepatic function[3]. There is growing evidence that NAFLD is not limited to liver-related morbidity and mortality, but also known to be a multisystem disease. NAFLD increases the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), chronic kidney disease, heart failure, cancer, and cardiovascular disease[4].
Nowadays, the effective treatment for NAFLD is limited. Lifestyle modification is the standard management, including calorie restriction, body weight control, and adequate physical activity[5]. Based on the common pathophysiological pathways shared by T2DM and NAFLD including insulin resistance, lipotoxicity, inflammation, and oxidative stress[6], pharmacotherapies treating T2DM might be effective for NAFLD.
Incretin-based therapies and sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors are novel classes of glucose-lowering drugs used in the management of T2DM. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors prevent the degradation of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulintropic polypeptide, while GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) directly mimic the action of GLP-1[7-9]. By improving insulin resistance and inflammation, and decreasing dietary fat, incretin-based therapies might offer potential benefits in treating NAFLD[10]. SGLT2 inhibitors are a class of novel glucose-lowering drugs by stimulating glucose excretion in the urine. SGLT2 inhibitors not only improve hyperglycemia, but also obesity, oxidative stress, and inflammation[11-13].
Although accumulated evidence suggests that these novel glucose-lowering drugs are promising in the treatment of NAFLD and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)[14-16], there is conflicting evidence and no convincing consensus on their long-term efficacy and outcome. In addition, there have been few head-to-head clinical trials comparing these novel glucose-lowering drugs directly. In this context, we carried out this meta-analysis to further evaluate the efficacy of novel glucose-lowering drugs in treating NAFLD and to perform a comparison between these treatments.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Data sources and searches
The inclusion criteria for this meta-analysis were: (1) Randomized controlled trials conducted in patients with NAFLD; (2) Studies comparing DPP-4 inhibitors, GLP-1 RAs, or SGLT2 inhibitors against placebo or other active glucose-lowering drugs; and (3) The primary outcome was the change of liver enzyme [alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and/or aspartate aminotransferase (AST)] from baseline. The secondary outcomes were the changes of magnetic resonance imaging proton density fat fraction (MRI-PDFF), visceral fat area (VFA), body weight, body mass index (BMI), and/or glycated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) from baseline. Case reports, animal studies, and case-control studies were excluded. The study selection followed the Preferred Reporting Items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses flow diagram[17].
Study selection
Two investigators (ZDF and XLC) independently conducted systematic searches of the databases MEDLINE, Cochrane central register of controlled trials, and Embase for studies up to May 30, 2020 according to the Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews for meta-analysis. The following terms were searched: Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor, DPP-4 inhibitor, DPP-IV inhibitor, sitagliptin, vildagliptin, saxagliptin, linagliptin, alogliptin, dutogliptin, teneligliptin, anagliptin, evogliptin, retagliptin, omarigliptin, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, GLP-1 receptor agonist, GLP-1 RA, GLP1RA, liraglutide, semaglutide, albiglutide, lixisenatide, taspoglutide, exenatide, dulaglutide, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor, SGLT2 inhibitor, SGLT-2 inhibitor, empagliflozin, dapagliflozin, canagliflozin, luseogliflozin, ipragliflozin, tofogliflozin, sotagliflozin, ertugliflozin, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, NAFLD, fatty liver, NASH, nonalcoholic steatohepatitides, NASH, NAFLD, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, and non-alcoholic steatohepatitides. To identify additional relevant data of eligible published trials, we also searched ClinicalTrial.gov.
Data extraction and quality assessment
Two independent reviewers (ZDF and XLC) extracted data from each publication, including sources of publication, title, year, first author, study design, baseline characteristics of study population (sample size, age, assessment of diagnosis, body weight, BMI, and HbA1c), treatment allocation, duration of treatment, and changes of ALT, AST, MRI-PDFF, VFA, body weight, BMI, and HbA1c from baseline. If the above relevant data was not reported in the published trial, the registry report of ClinicalTrials.gov was further extracted.
The quality of all included studies was assessed using the Cochrane risk of bias tool. The following aspects were included: Selection bias, performance bias, detection bias, attrition bias, reporting bias, and others.
Statistical analysis
The continuous outcomes in this meta-analysis were evaluated by computing the weighted mean differences (WMDs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). The Ι2 statistic was analyzed to assess the heterogeneity. If Ι2> 50% and the P value of the χ2 < 0.10, representing statistical heterogeneity across studies, the random-effects model was used. The fixed-effects model was used with low levels of heterogeneity. Publication bias was assessed via visual inspection of funnel plot. All analyses were conducted with Review Manager, version 5.3 (Nordic Cochrane Centre, Copenhagen, Denmark). Meta-regression analyses were conducted with STATA statistical software package (Version 13.1, Stata Corp, College Station, TX, United States). A P value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Characteristics of enrolled studies
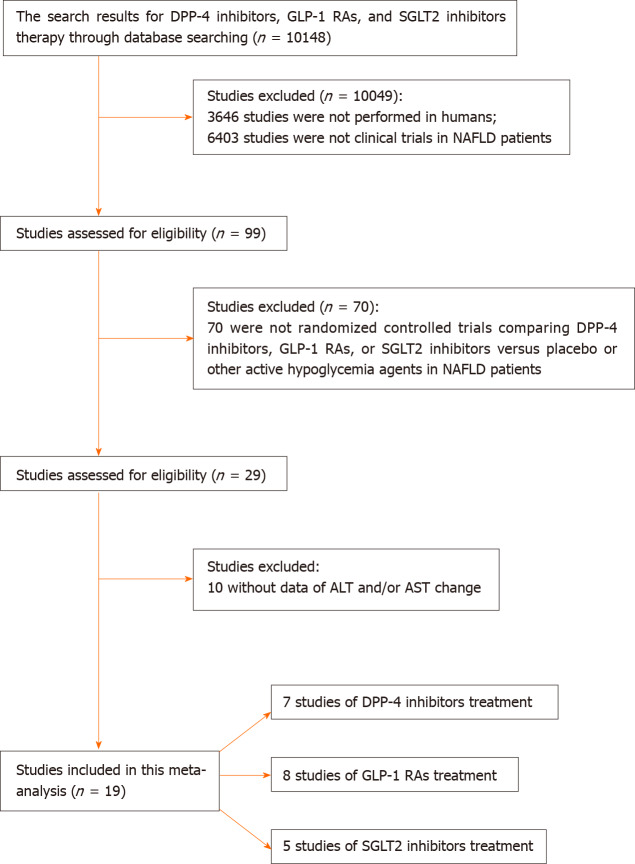
After literature search, 19 studies were included in the meta-analysis (Table 1). Among these 19 studies, 7 compared DPP-4 inhibitors with placebo or other active glucose-lowering drugs[18-24], 8 compared GLP-1 RAs with placebo or other active glucose-lowering drugs[24-31], and 5 compared SGLT2 inhibitors with placebo or other active glucose-lowering drugs[32-36]. The process of study selection is presented in Figure 1. The risks of bias of the included studies are presented in Supplementary Figure 1.
Table 1.
Summary of included studies
|
Ref.
|
Study duration
|
Population
|
Assessment of NAFLD
|
Intervention
|
No. of participants
|
| Alam et al[18], 2018 | 52 wk | NAFLD | Biopsy | Sitagliptin 100 mg QD + lifestyle modification | 20 |
| Lifestyle modification | 20 | ||||
| Cui et al[19], 2017 | 24 wk | NAFLD with prediabetes or early diabetes | MRI | Sitagliptin 100 mg QD | 25 |
| PBO | 25 | ||||
| Hussain et al[20], 2016 | 12 wk | NAFLD + dyslipidemia | Ultrasound | Vildagliptin 50 mg Bid | 29 |
| PBO | 29 | ||||
| Macauley et al[21], 2015 | 6 mo | T2DM with hepatic steatosis | Imaging (CT or ultrasound) | Vildagliptin 50 mg Bid | 22 |
| PBO | 22 | ||||
| Joy et al[22], 2017 | 24 wk | NASH | Biopsy | Sitagliptin 100 mg QD | 6 |
| PBO | 6 | ||||
| Li et al[23], 2019 | 24 wk | T2DM with NAFLD | Imaging or biopsy | Saxagliptin 5 mg QD | 31 |
| Glimepiride 2 mg QD | 33 | ||||
| Glimepiride 2 mg QD + polyenephosphatidylcholine 456 mg TID | 31 | ||||
| Yan et al[24], 2019 | 26 wk | T2DM with NAFLD | MRI | Liraglutide 1.8 mg + metformin | 24 |
| Sitagliptin + metformin | 27 | ||||
| Glargine 0.2 IU/Kg/d + metformin | 24 | ||||
| Armstrong et al[25], 2016 | 48 wk | T2DM with NASH | Biopsy | Liraglutide 1.8 mg QD | 26 |
| PBO | 26 | ||||
| Cusi et al[26], 2018 | 6 mo | T2DM with NAFLD/NASH | Laboratory liver tests | Duraglutide 1.5 mg QW | 971 |
| PBO | 528 | ||||
| Fan et al[27], 2013 | 12 wk | T2DM with NAFLD | Ultrasound | Exenatide | 49 |
| Metformin | 68 | ||||
| Feng et al[28], 2017 | 24 wk | T2DM with NAFLD | Ultrasound | Metformin 1000 mg Bid | 29 |
| Gliclazide 120 mg/d | 29 | ||||
| Liraglutide 1.8 mg QD | 29 | ||||
| Khoo et al[29], 2017 | 26 wk | NAFLD | MRI | Liraglutide 3.0 mg QD | 12 |
| Diet and exercise | 12 | ||||
| Shao et al[30], 2014 | 12 wk | T2DM with NAFLD | Ultrasound | Exenatide 10 μg bid + glargine | 30 |
| Intensive insulin therapy | 30 | ||||
| Tian et al[31], 2018 | 12 wk | T2DM with NAFLD | Ultrasound | Liraglutide 0.6-1.2 mg QD | 52 |
| Metformin 1000-1500 mg/d | 75 | ||||
| Eriksson et al[32], 2018 | 12 wk | T2DM with NAFLD | MRI | Dapagliflozin 10 mg QD | 21 |
| PBO | 21 | ||||
| Dapagliflozin 10 mg QD + OM-3CA | 22 | ||||
| OM-3CA 4 g | 20 | ||||
| Ito et al[33], 2017 | 24 wk | T2DM with NAFLD | Clinical laboratorytests or imaging | Ipragliflozin 50 mg QD | 32 |
| Pioglitazone 15–30 mg QD | 34 | ||||
| Kuchay et al[34], 2018 | 20 wk | T2DM with NAFLD | MRI | Empagliflozin 10 mg QD | 22 |
| Control | 20 | ||||
| Shibuya et al[35], 2018 | 6 mo | T2DM with NAFLD | Imaging (CT or ultrasound) | Luseogliflozin 2.5 mg QD | 16 |
| Metformin 1500 mg QD | 16 | ||||
| Shimizu et al[36], 2018 | 24 wk | T2DM with NAFLD | Transient elastography | Dapagliflozin 5 mg QD | 33 |
| Control | 24 |
NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus; NASH: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; CT: Computed tomography.
Figure 1.
Flow chart of included studies.
Changes in ALT and AST
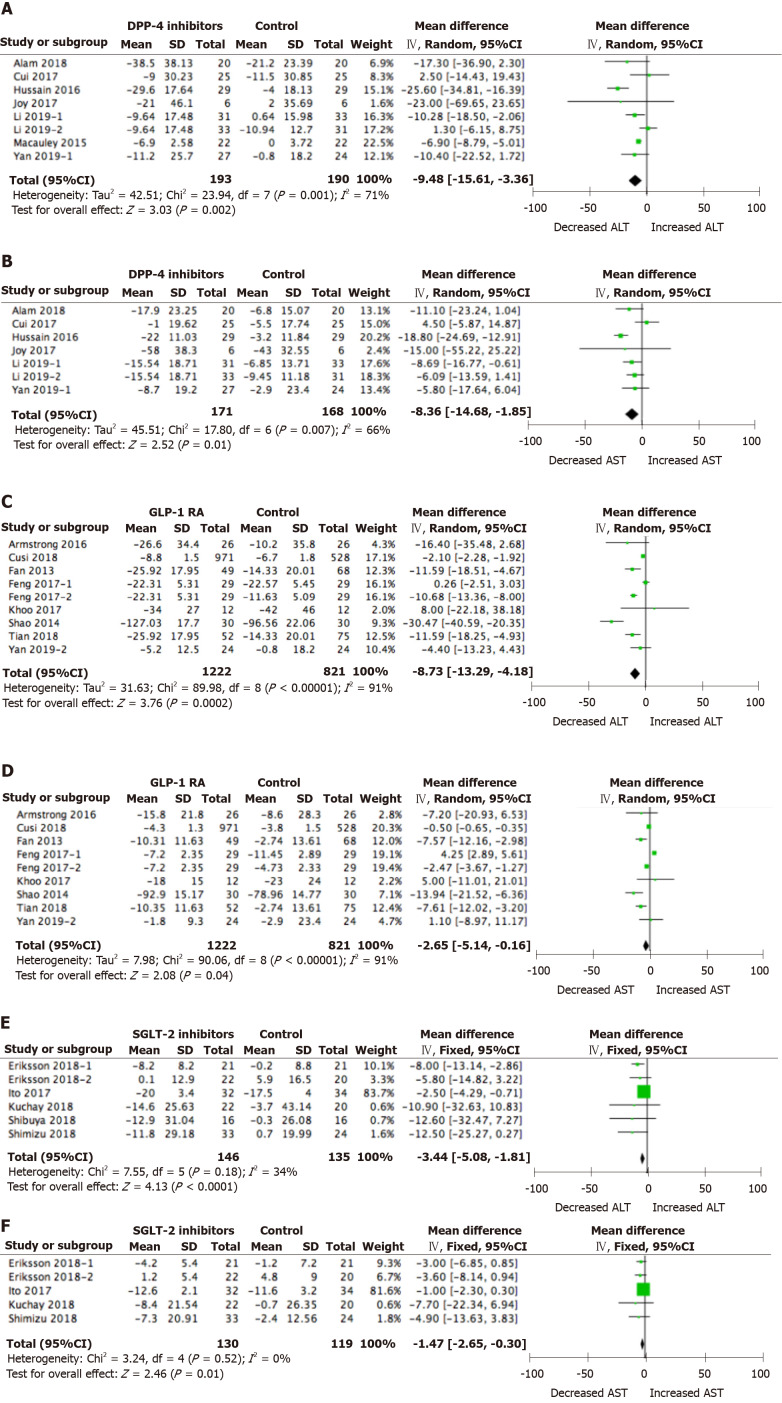
Overall, compared with placebo or other active glucose-lowering drug treatment, DPP-4 inhibitor treatment led to a significant decrease in ALT (WMD = -9.48 IU/L, 95%CI: -15.61 to -3.36 IU/L, P < 0.01) and AST from baseline (WMD = -8.36 IU/L, 95%CI: -14.86 to -1.85 IU/L, P = 0.01) in NAFLD patients (Figure 2A and B). Compared with placebo or other active glucose-lowering drug treatment, GLP-1 RA treatment led to a significant decrease in ALT (WMD = -8.73 IU/L, 95%CI: -13.29 to -4.18 IU/L, P < 0.01) and AST from baseline (WMD = -2.65 IU/L, 95%CI: -5.14 to -0.16 IU/L, P = 0.04) (Figure 2C and D). Compared with placebo or other active glucose-lowering drug treatment, SGLT2 inhibitor treatment also led to a significant decrease in ALT (WMD = -3.44 IU/L, 95%CI: -5.08 to -1.81 IU/L, P < 0.01) and AST from baseline (WMD = -1.47 IU/L, 95%CI: -2.65 to -0.30 IU/L, P = 0.01) (Figure 2E and F).
Figure 2.
Alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase changes from baseline in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients treated with novel glucose-lowering drugs. A: Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) changes with dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor treatment; B: Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) changes with dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor treatment; C: ALT changes with glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist treatment; D: AST changes with glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist treatment; E: ALT changes with sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor treatment; F: AST changes with sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor treatment.
When DPP-4 inhibitor treatment was compared with SGLT2 inhibitor treatment, the difference between groups in AST change was significant in favor of DPP-4 inhibitors treatment (P = 0.04). When GLP-1 RA treatment was compared with SGLT2 inhibitor treatment, the difference between groups in ALT change and AST change was not significant (P > 0.05). While comparisons between DPP-4 inhibitor treatment and GLP-1 RA treatment also indicated no significant difference between groups in ALT or AST change relative to baseline (P > 0.05).
Changes in body weight and BMI
The absolute body weight change relative to baseline after DPP-4 inhibitor treatment was -1.20 kg (95%CI: -1.44 to -0.95 kg, P < 0.01) when compared with placebo or other active glucose-lowering drug treatment, while the absolute BMI change relative to baseline showed no significant difference. When GLP-1 RA treatment was compared with placebo or other active glucose-lowering drug treatment, the difference between groups in body weight and BMI were both significant (WMD = -3.61 kg, 95%CI: -5.74 to -1.48 kg, P < 0.01; WMD = -1.46 kg/m2, 95%CI: -2.23 to -0.69 kg/m2, P < 0.01, respectively). When SGLT2 inhibitor treatment was compared with placebo or other active glucose-lowering drug treatment, the difference between groups in body weight and BMI were both significant (WMD = -2.53 kg, 95%CI: -3.35 to -1.71 kg, P < 0.01; WMD = -1.72 kg/m2, 95%CI: -2.68 to -0.75 kg/m2, P < 0.01, respectively) (Table 2).
Table 2.
Comparison of body weight and body mass index changes from baseline in different treatment groups
|
|
Studies
|
Participants
|
WMD
|
95%CI
|
P
value
|
|
| Body weight change | ||||||
| DPP-4 inhibitors | 4 | 140/138 | -1.20 | -1.44 | -0.95 | < 0.0001 |
| GLP-1 RAs | 8 | 1222/821 | -3.61 | -5.74 | -1.48 | 0.0009 |
| SGLT2 inhibitors | 5 | 146/135 | -2.53 | -3.35 | -1.71 | < 0.0001 |
| BMI change | ||||||
| DPP-4 inhibitors | 5 | 144/146 | -0.59 | -1.80 | 0.61 | 0.33 |
| GLP-1 RAs | 7 | 251/293 | -1.46 | -2.23 | -0.69 | 0.0002 |
| SGLT2 inhibitors | 4 | 114/101 | -1.72 | -2.68 | -0.75 | 0.0005 |
WMD: Weighted mean difference; CI: Confidence interval; DPP-4: Dipeptidyl peptidase-4; GLP-1 RA: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist; SGLT2: Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2; BMI: Body mass index.
The body weight change from baseline and BMI change from baseline were significantly greater with GLP-1 RA treatment and SGLT2 inhibitor treatment when compared with DPP-4 inhibitor treatment (P < 0.05). No significant difference was observed in the change of body weight or BMI from baseline between the GLP-1 RA treatment and SGLT2 inhibitor treatment groups (P > 0.05).
Change in HbA1c
The majority of the included studies evaluated the change in HbA1c from baseline. The results showed that DPP-4 inhibitor treatment, compared with placebo or other active glucose-lowering drug treatment, had a significant reduction in HbA1c level from baseline (WMD = -0.425%, 95%CI: -0.58% to -0.25%, P < 0.01). While GLP-1 RA and SGLT2 inhibitor treatment showed no statistical difference in HbA1c reductions (WMD = -0.29, 95%CI: -0.85% to 0.26%, P < 0.30; WMD = -0.36, 95%CI: -0.80% to 0.08%, P = 0.11, respectively) (Table 3). Subgroup analyses only comprising studies that evaluated the studied drugs against placebo showed that HbA1c levels decreased significantly in the DPP-4 inhibitor, GLP-1 RA, and SGLT2 inhibitor treatment groups (Table 3). The difference of HbA1c change from baseline between all these three treatment groups was not significant (P > 0.05).
Table 3.
Comparison of hemoglobin A1c change from baseline in different treatment groups
|
|
Studies
|
Participants
|
WMD
|
95%CI
|
P
value
|
|
| HbA1c change | ||||||
| DPP-4 inhibitors | 6 | 166/166 | -0.42 | -0.58 | -0.25 | < 0.0001 |
| GLP-1 RAs | 7 | 1210/809 | -0.29 | -0.85 | 0.26 | 0.30 |
| SGLT2 inhibitors | 5 | 146/135 | -0.36 | -0.80 | 0.08 | 0.11 |
| HbA1c change (placebo-controlled studies only) | ||||||
| DPP-4 inhibitors | 5 | 102/102 | -0.38 | -0.71 | -0.05 | 0.02 |
| GLP-1 RAs | 3 | 1009/566 | -0.88 | -1.56 | -0.19 | 0.01 |
| SGLT2 inhibitors | 1 | 21/21 | -0.50 | -0.84 | -0.16 | 0.004 |
HbA1c: Hemoglobin A1c; WMD: Weighted mean difference; CI: Confidence interval; DPP-4: Dipeptidyl peptidase-4; GLP-1 RA: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists; SGLT2: Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2.
Changes in MRI-PDFF and VFA
Two studies provided information on MRI-PDFF change in the comparison between the DPP-4 inhibitor and control groups. The results showed no significant reduction in MRI-PDFF, with a WMD of -2.31% (95%CI: -4.92% to 0.29%, P = 0.08). The only one study used the indicator of MRI-PDFF in the comparison between the GLP-1 RA and control groups showed a significant -3.20% reduction (95%CI: -5.98% to -0.42%, P = 0.02). MRI-PDFF was observed in two studies with SGLT2 inhibitor treatment, and the results suggested that SGLT2 inhibitor treatment decreased MRI-PDFF with marginal significance in the comparison with the control group (WMD = -1.18%, 95%CI: -2.38% to 0.03%, P = 0.06) (Table 4). The difference of MRI-PDFF change from baseline between all these three treatment groups was not significant (P > 0.05).
Table 4.
Comparison of magnetic resonance imaging proton density fat fraction and visceral fat area change from baseline in different treatment groups
|
|
Studies
|
Participants
|
WMD
|
95%CI
|
P
value
|
|
| MRI-PDFF change | ||||||
| DPP-4 inhibitors | 2 | 52/49 | -2.31 | -4.92 | 0.29 | 0.08 |
| GLP-1 RAs | 1 | 24/24 | -3.20 | -5.98 | -0.42 | 0.02 |
| SGLT2 inhibitors | 2 | 65/61 | -1.18 | -2.38 | 0.03 | 0.06 |
| VFA change | ||||||
| DPP-4 inhibitors | 1 | 27/24 | -23.10 | -38.84 | -7.36 | 0.004 |
| GLP-1 RAs | 1 | 24/24 | -30.40 | -46.86 | -13.94 | 0.0003 |
| SGLT2 inhibitors | 2 | 48/50 | -23.48 | -25.85 | -21.12 | < 0.0001 |
MRI-PDFF: Magnetic resonance imaging proton density fat fraction; VAF: Visceral fat area; WMD: Weighted mean difference; CI: Confidence interval; DPP-4: Dipeptidyl peptidase-4; GLP-1 RA: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist; SGLT2: Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2.
One study comprising sitagliptin and liraglutide arms reported the effect of VFA change in the comparison with glargine insulin treatment. The results of this study indicated that both sitagliptin and liraglutide could obviously decrease VFA (WMD -23.10 cm2, 95%CI: -38.84 to -7.36 cm2, P = 0.004; WMD -30.40 cm2, 95%CI: -46.86 to -13.94 cm2, P < 0.001; respectively). Although only two studies used the indicator of VFA in the included studies comparing the SGLT2 inhibitor and control groups, both of which showed that SGLT2 inhibitors could reduce it (WMD -23.48 cm2, 95%CI: -25.85 to -21.12 cm2, P < 0.001) (Table 4). The difference of VFA change from baseline between all these three treatment groups was not significant (P > 0.05).
Association between changes in transaminase, body fat composition, and weight loss
Meta-regression analyses indicated that the weight change difference was not associated with the difference of ALT, AST, MRI-PDFF, and VFA between antidiabetes drugs and controls (Table 5).
Table 5.
Meta-regression analyses of association between weight change difference and difference of alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, magnetic resonance imaging proton density fat fraction, and visceral fat area between antidiabetes drugs and controls (ß coefficient value, P value, and 95%CI are shown)
|
|
ß
|
P
value
|
95%CI
|
| ALT | 0.064 | 0.267 | -0.053-0.181 |
| AST | 0.020 | 0.735 | -0.104-0.144 |
| MRI-PDFF | 0.308 | 0.701 | -2.678-3.294 |
| VFA | 1.776 | 0.343 | -11.723-15.275 |
ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; MRI-PDFF: Magnetic resonance imaging proton density fat fraction; VFA: Visceral fat area.
DISCUSSION
In the present meta-analysis, we found that compared with placebo or other active glucose-lowering agents, pooling of results from the included studies revealed significant improvements in serum ALT and AST levels following treatment with the novel agents (DPP-4 inhibitors, GLP-1 RAs, and SGLT2 inhibitors) in NAFLD patients. VFA and MRI-PDFF are quantitative biomarkers that can accurately estimate liver fat content. Although there were just four studies, all of them showed that novel glucose-lowering agents could decrease VFA. Furthermore, the trends of reduction in MRI-PDFF changes were also observed in all the novel glucose-lowering agent treatment groups. Therefore, all these novel glucose-lowering agents showed a beneficial effect in improving liver injury and reducing liver fat in NAFLD patients.
Apart from the proven effect on glucose control, GLP-1 RAs have several metabolic functions, including decreasing insulin resistance and lipotoxicity, enhancing liver glucose uptake, and improving peripheral insulin sensitivity[37]. DPP-4 inhibitors act on the enzyme DPP-4, which are expected to prolong the action of GLP-1. SGLT2 inhibitors also appear to have a beneficial hepatic effect in patients with NAFLD and T2DM[38]. The incretin-based therapies and SGLT2 inhibitors act in numerous potential ways in the pathogenesis of NAFLD: (1) Weight loss is a recognized predictor of reductions in liver fat[39]. The amount of weight loss is considered to be a determinant of histologic improvements in liver injury[40]. Clearly, the evidence that GLP-1 RAs and SGLT2 inhibitors lead to significant weight loss has been proven in many clinical trials conducted in various populations, although through different mechanisms. In the current meta-analysis, significant reductions in BMI and body weight were also observed in NAFLD patients treated with GLP-1 RAs and SGLT2 inhibitors; (2) Improvement of inflammation and oxidation: DPP-4 inhibitors were shown to affect inflammatory pathways in animal models of NASH, including reduced expression of proinflammatory mediators and attenuation of endoplasmic reticulum stress and hepatocyte apoptosis[41,42]. In an animal model of non-obese NASH, GLP-1 RAs were shown to inhibit hepatic inflammation through inhibition of hepatic free fatty acid influx and oxidative stress[43]. In addition, GLP-1 RAs can act directly on Kupffer cell function to reduce the influx of macrophages to the liver[44]. SGLT2 inhibitor treatments were also shown to attenuate the development of NASH through anti-inflammatory and oxidation effects in rodent models[11,45]; (3) Hyperglycaemia plays an important role in the process of liver lipogenesis by activating the key modulator-carbohydrate-responsive element-binding protein transcriptional factor[46]. Therefore, improvement in glycaemic control observed in the current meta-analysis might also contribute to the amelioration of NAFLD; and (4) The above effects help to ameliorate the condition of insulin resistance, which is a common and key feature of NAFLD that contributes to its pathogenesis[47]. All these effects provide the possibility for the treatment of NAFLD with incretin-based therapies and SGLT2 inhibitors.
In this meta-analysis, we also tried to figure out the difference of these novel drugs' effects on NAFLD. To the best of our knowledge, there is no head-to-head study comparing their effect. The serum ALT is a specific indicator of hepatic inflammation, which is recommended as a means of monitoring disease improvement[48]. The indirect comparison result from our meta-analysis suggested that GLP-1 RAs can better improve serum ALT level when compared with SGLT2 inhibitors. Regarding VFA and MRI-PDFF, no significance difference was observed between these treatment groups. As mentioned above, the incretin-based therapies and SGLT2 inhibitors shared several targets in the pathogenesis of NAFLD. However, GLP-1 RAs and SGLT2 inhibitors also possess additive benefits, respectively. Ketogenesis plays an important role in the pathogenesis of NAFLD. It has been found that SGLT2 inhibitors could enhance ketone body metabolism by upregulating transporters and ketogenic enzymes in the liver[49]. Besides, the benefits of GLP-1 RAs in amelioration of lipotoxicity were observed in several clinical trials[25,50]. In addition, it is worth noting that heterogeneity existed between different treatment groups. Therefore, we should explain the results with caution, and it is still hard to judge which treatment is more effective. Individualized treatment options for patients with different characteristics might be more appropriate. More head-to-head studies are needed to further illuminate the underlying difference between these treatments.
As a meta-analysis, this study has several potential limitations. First, as mentioned above, this meta-analysis included studies with different treatment durations, baseline characteristics, and predefined outcomes, which might result in bias. Second, the numbers of participants with available reports of VFA and MRI-PDFF were limited, which might weaken the statistical power. Third, the diagnostic criteria for NAFLD were different, leading to heterogeneity across studies. Additionally, the included trials were relatively short in duration compared to the timescale of progression of NAFLD. As we know, the histological progression or resolution is recognized as the "gold standard" of disease evaluation. However, a search of the previous literature showed that controlled trials with histological outcomes were limited. In this context, we used the indirect quantified measures (changes in ALT and AST levels) as the primary outcome measures.
CONCLUSION
According to this study, treatment with DPP-4 inhibitors, GLP-1 RAs, and SGLT2 inhibitors resulted in improvements in serum ALT and AST levels and body fat composition, indicating that all these novel glucose-lowering agents have a beneficial effect in improving liver injury and reducing liver fat in NAFLD patients.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
The efficacy of novel glucose-lowering drugs in treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is unknown.
Research motivation
Although accumulated evidence suggests that these novel glucose-lowering drugs are promising in the treatment of NAFLD and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, there is conflicting evidence and no convincing consensus on their long-term efficacy and outcome. In addition, there have been few head-to-head clinical trials comparing these novel glucose-lowering drugs directly.
Research objectives
We carried out this meta-analysis to evaluate the efficacy of novel glucose-lowering drugs in treating NAFLD.
Research methods
Electronic databases were systematically searched. The inclusion criteria were: Randomized controlled trials comparing dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs), or sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors against placebo or other active glucose-lowering drugs in NAFLD patients, with outcomes of changes in liver enzyme [alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and/or aspartate aminotransferase (AST)] from baseline.
Research results
Treatment with DPP-4 inhibitors, GLP-1 RAs, and SGLT2 inhibitors resulted in improvements in serum ALT and AST levels. The trends of reduction in magnetic resonance imaging proton density fat fraction and visceral fat area changes were also observed in the DPP-4 inhibitor, GLP-1 RA, and SGLT2 inhibitor treatment groups.
Research conclusions
Treatment with DPP-4 inhibitors, GLP-1 RAs, and SGLT2 inhibitors resulted in improvements in serum ALT and AST levels and body fat composition, indicating a beneficial effect in improving liver injury and reducing liver fat in NAFLD patients.
Research perspectives
In this meta-analysis, we made a comprehensive evaluation of the efficacy of novel glucose-lowering drugs in treating NAFLD.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank Professor Li-Nong Ji at the Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Peking University People's Hospital for his assistance during this study.
Footnotes
Conflict-of-interest statement: We declare no competing interests.
PRISMA 2009 Checklist statement: The authors have read the PRISMA 2009 Checklist, and the manuscript was prepared and revised according to the PRISMA 2009 Checklist.
Manuscript source: Unsolicited manuscript
Peer-review started: September 21, 2020
First decision: November 16, 2020
Article in press: December 2, 2020
Specialty type: Endocrinology and metabolism
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Rayner CK S-Editor: Zhang L L-Editor: Wang TQ P-Editor: Ma YJ
Contributor Information
Zuo-Di Fu, Department of Endocrinology, Beijing Friendship Hospital Pinggu Campus, Beijing 101200, China.
Xiao-Ling Cai, Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China.
Wen-Jia Yang, Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China.
Ming-Ming Zhao, The Institute of Cardiovascular Sciences, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Health Science Center, Peking University, Beijing 100079, China.
Ran Li, Sport Science School, Beijing Sport University, Beijing 100078, China.
Yu-Feng Li, Department of Endocrinology, Beijing Friendship Hospital Pinggu Campus, Capital Medical University, Beijing 101200, China. yflee@bjmu.edu.cn.
References
- 1.Younossi ZM, Koenig AB, Abdelatif D, Fazel Y, Henry L, Wymer M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology. 2016;64:73–84. doi: 10.1002/hep.28431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Brown GT, Kleiner DE. Histopathology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Metabolism. 2016;65:1080–1086. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2015.11.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Benedict M, Zhang X. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: An expanded review. World J Hepatol. 2017;9:715–732. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v9.i16.715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Vanni E, Marengo A, Mezzabotta L, Bugianesi E. Systemic Complications of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: When the Liver Is Not an Innocent Bystander. Semin Liver Dis. 2015;35:236–249. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1562944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Grattagliano I, Portincasa P, Palmieri VO, Palasciano G. Managing nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: recommendations for family physicians. Can Fam Physician. 2007;53:857–863. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hu M, Phan F, Bourron O, Ferré P, Foufelle F. Steatosis and NASH in type 2 diabetes. Biochimie. 2017;143:37–41. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2017.10.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Campbell JE, Drucker DJ. Pharmacology, physiology, and mechanisms of incretin hormone action. Cell Metab. 2013;17:819–837. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2013.04.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Janardhan S, Sastry GN. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors: a new paradigm in type 2 diabetes treatment. Curr Drug Targets. 2014;15:600–621. doi: 10.2174/1389450115666140311102638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gerich J. Pathogenesis and management of postprandial hyperglycemia: role of incretin-based therapies. Int J Gen Med. 2013;6:877–895. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S51665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Blaslov K, Bulum T, Zibar K, Duvnjak L. Incretin based therapies: a novel treatment approach for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:7356–7365. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i23.7356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Qiang S, Nakatsu Y, Seno Y, Fujishiro M, Sakoda H, Kushiyama A, Mori K, Matsunaga Y, Yamamotoya T, Kamata H, Asano T. Treatment with the SGLT2 inhibitor luseogliflozin improves nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in a rodent model with diabetes mellitus. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2015;7:104. doi: 10.1186/s13098-015-0102-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Tahara A, Kurosaki E, Yokono M, Yamajuku D, Kihara R, Hayashizaki Y, Takasu T, Imamura M, Li Q, Tomiyama H, Kobayashi Y, Noda A, Sasamata M, Shibasaki M. Effects of SGLT2 selective inhibitor ipragliflozin on hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, hepatic steatosis, oxidative stress, inflammation, and obesity in type 2 diabetic mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013;715:246–255. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.05.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Yokono M, Takasu T, Hayashizaki Y, Mitsuoka K, Kihara R, Muramatsu Y, Miyoshi S, Tahara A, Kurosaki E, Li Q, Tomiyama H, Sasamata M, Shibasaki M, Uchiyama Y. SGLT2 selective inhibitor ipragliflozin reduces body fat mass by increasing fatty acid oxidation in high-fat diet-induced obese rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014;727:66–74. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.01.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Carbone LJ, Angus PW, Yeomans ND. Incretin-based therapies for the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;31:23–31. doi: 10.1111/jgh.13026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Xing B, Zhao Y, Dong B, Zhou Y, Lv W, Zhao W. Effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Diabetes Investig. 2020 doi: 10.1111/jdi.13237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Raj H, Durgia H, Palui R, Kamalanathan S, Selvarajan S, Kar SS, Sahoo J. SGLT-2 inhibitors in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review. World J Diabetes. 2019;10:114–132. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v10.i2.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ. 2009;339:b2535. doi: 10.1136/bmj.b2535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Alam S, Ghosh J, Mustafa G, Kamal M, Ahmad N. Effect of sitagliptin on hepatic histological activity and fibrosis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis patients: a 1-year randomized control trial. Hepat Med. 2018;10:23–31. doi: 10.2147/HMER.S158053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Cui J, Philo L, Nguyen P, Hofflich H, Hernandez C, Bettencourt R, Richards L, Salotti J, Bhatt A, Hooker J, Haufe W, Hooker C, Brenner DA, Sirlin CB, Loomba R. Sitagliptin vs. placebo for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized controlled trial. J Hepatol. 2016;65:369–376. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.04.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hussain M, Majeed Babar MZ, Hussain MS, Akhtar L. Vildagliptin ameliorates biochemical, metabolic and fatty changes associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Pak J Med Sci. 2016;32:1396–1401. doi: 10.12669/pjms.326.11133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Macauley M, Hollingsworth KG, Smith FE, Thelwall PE, Al-Mrabeh A, Schweizer A, Foley JE, Taylor R. Effect of vildagliptin on hepatic steatosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100:1578–1585. doi: 10.1210/jc.2014-3794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Joy TR, McKenzie CA, Tirona RG, Summers K, Seney S, Chakrabarti S, Malhotra N, Beaton MD. Sitagliptin in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial. World J Gastroenterol. 2017;23:141–150. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Li JJ, Zhang P, Fan B, Guo XL, Zheng ZS. The efficacy of saxagliptin in T2DM patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: preliminary data. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992) 2019;65:33–37. doi: 10.1590/1806-9282.65.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Yan J, Yao B, Kuang H, Yang X, Huang Q, Hong T, Li Y, Dou J, Yang W, Qin G, Yuan H, Xiao X, Luo S, Shan Z, Deng H, Tan Y, Xu F, Xu W, Zeng L, Kang Z, Weng J. Liraglutide, Sitagliptin, and Insulin Glargine Added to Metformin: The Effect on Body Weight and Intrahepatic Lipid in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatology. 2019;69:2414–2426. doi: 10.1002/hep.30320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Armstrong MJ, Gaunt P, Aithal GP, Barton D, Hull D, Parker R, Hazlehurst JM, Guo K LEAN trial team; Abouda G; Aldersley MA; Stocken D; Gough SC; Tomlinson JW; Brown RM; Hübscher SG; Newsome PN. Liraglutide safety and efficacy in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (LEAN): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 study. Lancet. 2016;387:679–690. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00803-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Cusi K, Sattar N, García-Pérez LE, Pavo I, Yu M, Robertson KE, Karanikas CA, Haupt A. Dulaglutide decreases plasma aminotransferases in people with Type 2 diabetes in a pattern consistent with liver fat reduction: a post hoc analysis of the AWARD programme. Diabet Med. 2018;35:1434–1439. doi: 10.1111/dme.13697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Fan H, Pan Q, Xu Y, Yang X. Exenatide improves type 2 diabetes concomitant with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol. 2013;57:702–708. doi: 10.1590/s0004-27302013000900005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Feng W, Gao C, Bi Y, Wu M, Li P, Shen S, Chen W, Yin T, Zhu D. Randomized trial comparing the effects of gliclazide, liraglutide, and metformin on diabetes with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Diabetes. 2017;9:800–809. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.12555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Khoo J, Hsiang J, Taneja R, Law NM, Ang TL. Comparative effects of liraglutide 3 mg vs structured lifestyle modification on body weight, liver fat and liver function in obese patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A pilot randomized trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017;19:1814–1817. doi: 10.1111/dom.13007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Shao N, Kuang HY, Hao M, Gao XY, Lin WJ, Zou W. Benefits of exenatide on obesity and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with elevated liver enzymes in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2014;30:521–529. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.2561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Tian F, Zheng Z, Zhang D, He S, Shen J. Efficacy of liraglutide in treating type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Biosci Rep. 2018;38 doi: 10.1042/BSR20181304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Eriksson JW, Lundkvist P, Jansson PA, Johansson L, Kvarnström M, Moris L, Miliotis T, Forsberg GB, Risérus U, Lind L, Oscarsson J. Effects of dapagliflozin and n-3 carboxylic acids on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in people with type 2 diabetes: a double-blind randomised placebo-controlled study. Diabetologia. 2018;61:1923–1934. doi: 10.1007/s00125-018-4675-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ito D, Shimizu S, Inoue K, Saito D, Yanagisawa M, Inukai K, Akiyama Y, Morimoto Y, Noda M, Shimada A. Comparison of Ipragliflozin and Pioglitazone Effects on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized, 24-Week, Open-Label, Active-Controlled Trial. Diabetes Care. 2017;40:1364–1372. doi: 10.2337/dc17-0518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kuchay MS, Krishan S, Mishra SK, Farooqui KJ, Singh MK, Wasir JS, Bansal B, Kaur P, Jevalikar G, Gill HK, Choudhary NS, Mithal A. Effect of Empagliflozin on Liver Fat in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial (E-LIFT Trial) Diabetes Care. 2018;41:1801–1808. doi: 10.2337/dc18-0165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Shibuya T, Fushimi N, Kawai M, Yoshida Y, Hachiya H, Ito S, Kawai H, Ohashi N, Mori A. Luseogliflozin improves liver fat deposition compared to metformin in type 2 diabetes patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A prospective randomized controlled pilot study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018;20:438–442. doi: 10.1111/dom.13061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Shimizu M, Suzuki K, Kato K, Jojima T, Iijima T, Murohisa T, Iijima M, Takekawa H, Usui I, Hiraishi H, Aso Y. Evaluation of the effects of dapagliflozin, a sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor, on hepatic steatosis and fibrosis using transient elastography in patients with type 2 diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019;21:285–292. doi: 10.1111/dom.13520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Sumida Y, Yoneda M. Current and future pharmacological therapies for NAFLD/NASH. J Gastroenterol. 2018;53:362–376. doi: 10.1007/s00535-017-1415-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Polyzos SA, Kountouras J, Mantzoros CS. Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: From pathophysiology to therapeutics. Metabolism. 2019;92:82–97. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2018.11.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Thoma C, Day CP, Trenell MI. Lifestyle interventions for the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in adults: a systematic review. J Hepatol. 2012;56:255–266. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2011.06.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Vilar-Gomez E, Martinez-Perez Y, Calzadilla-Bertot L, Torres-Gonzalez A, Gra-Oramas B, Gonzalez-Fabian L, Friedman SL, Diago M, Romero-Gomez M. Weight Loss Through Lifestyle Modification Significantly Reduces Features of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2015; 149: 367-78. :quiz e14–5. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.04.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Shirakawa J, Fujii H, Ohnuma K, Sato K, Ito Y, Kaji M, Sakamoto E, Koganei M, Sasaki H, Nagashima Y, Amo K, Aoki K, Morimoto C, Takeda E, Terauchi Y. Diet-induced adipose tissue inflammation and liver steatosis are prevented by DPP-4 inhibition in diabetic mice. Diabetes. 2011;60:1246–1257. doi: 10.2337/db10-1338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Jung YA, Choi YK, Jung GS, Seo HY, Kim HS, Jang BK, Kim JG, Lee IK, Kim MK, Park KG. Sitagliptin attenuates methionine/choline-deficient diet-induced steatohepatitis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2014;105:47–57. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2014.04.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Liu Y, Wei R, Hong TP. Potential roles of glucagon-like peptide-1-based therapies in treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:9090–9097. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i27.9090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Trevaskis JL, Griffin PS, Wittmer C, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Brunt EM, Dolman CS, Erickson MR, Napora J, Parkes DG, Roth JD. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonism improves metabolic, biochemical, and histopathological indices of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012;302:G762–G772. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00476.2011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Jojima T, Tomotsune T, Iijima T, Akimoto K, Suzuki K, Aso Y. Empagliflozin (an SGLT2 inhibitor), alone or in combination with linagliptin (a DPP-4 inhibitor), prevents steatohepatitis in a novel mouse model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and diabetes. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2016;8:45. doi: 10.1186/s13098-016-0169-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Ishii S, Iizuka K, Miller BC, Uyeda K. Carbohydrate response element binding protein directly promotes lipogenic enzyme gene transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:15597–15602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0405238101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Loomba R, Abraham M, Unalp A, Wilson L, Lavine J, Doo E, Bass NM Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Clinical Research Network. Association between diabetes, family history of diabetes, and risk of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and fibrosis. Hepatology. 2012;56:943–951. doi: 10.1002/hep.25772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Farrell GC, Chitturi S, Lau GK, Sollano JD Asia-Pacific Working Party on NAFLD. Guidelines for the assessment and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in the Asia-Pacific region: executive summary. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;22:775–777. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2007.05002.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Kim JH, Lee M, Kim SH, Kim SR, Lee BW, Kang ES, Cha BS, Cho JW, Lee YH. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors regulate ketone body metabolism via inter-organ crosstalk. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019;21:801–811. doi: 10.1111/dom.13577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Frias JP, Nauck MA, Van J, Kutner ME, Cui X, Benson C, Urva S, Gimeno RE, Milicevic Z, Robins D, Haupt A. Efficacy and safety of LY3298176, a novel dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist, in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomised, placebo-controlled and active comparator-controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet. 2018;392:2180–2193. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32260-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]