Abstract
Executive functions demonstrate variable developmental and aging profiles, with protracted development into early adulthood and declines in older age. However, relatively few studies have specifically included middle-aged adults in investigations of age-related differences in executive functions. This study explored the age-related differences in executive function from late childhood through to old age, allowing a more informed understanding of executive functions across the lifespan. Three hundred and fifty participants aged 10 to 86 years-old completed a battery of tasks assessing the specific roles of inhibitory control, working memory, cognitive flexibility, and planning. Results highlighted continued improvement in working memory capacity across adolescence and into young adulthood, followed by declines in both working memory and inhibitory control, beginning from as early as 30–40 years old and continuing into older age. Analyses of planning abilities showed continued improvement across adolescence and into young adulthood, followed by a decline in abilities across adulthood, with a small (positive) change in older age. Interestingly, a dissociation was found for cognitive flexibility; switch costs decreased, yet mixing costs increased across the lifespan. The results provide a description of the developmental differences in inhibitory control, working memory, cognitive flexibility and planning, above any effects of IQ or SES, and highlight the importance of including middle-aged adults in studies seeking to establish a more comprehensive picture of age-related differences in executive function.
Subject terms: Cognitive ageing, Learning and memory
Introduction
Executive functions (EF) are high-level cognitive processes that include planning, initiation, shifting, monitoring, and inhibition of behaviours1. EFs play an important role in our everyday life, allowing us to focus attention on specific tasks, to engage in successful problem solving, and to plan for the future. EFs demonstrate variable developmental and aging profiles (e.g.,2,3), with protracted development into early adulthood and a decline into older age that is associated with structural and functional changes in the prefrontal cortex4–10. The majority of these studies have compared dichotomous young/old adult age groups, and few studies include middle-aged adults or adolescents in investigations of age-related changes in EF (c.f.11–13 who included middle-aged adults). Therefore, many open questions remain about how development changes across the lifespan, and whether these effects are consistent across multiple components of EF. We address this by exploring how different components of EF develop and change across the lifespan, from late childhood through to old age. Specifically, we tested whether four key components of EF (inhibition, working memory, cognitive flexibility and planning) show parallel or distinct developmental trajectories, and aimed to describe any age-related changes in multiple EFs.
EFs begin to emerge early in infancy, with basic skills needed for EFs emerging before three years of age, and more specific skills developing into early childhood14. It has been suggested that each component of EF develops at its own rate across childhood and adolescence, reaching maturity at different ages (see1). For instance, cognitive flexibility has been shown to emerge between the ages of 3 and 4 years old, becoming more complex between the ages of 7 and 9 years old, and reaching adult-like levels by age ~ 1215–17; in contrast, Zelazo et al.18 found that cognitive flexibility abilities continue to improve between the ages of 20 and 29 years old, suggesting prolonged development of these abilities into young adulthood, and highlighting the importance of using different approaches and tasks to assess EF abilities, providing further insight into when these abilities reach maturity. Working memory, inhibition, and planning have been shown to continue to develop throughout childhood and adolescence, and in some circumstances (e.g., task dependent), have also been shown to continue to develop into young adulthood (e.g.,19–23). The protracted development of EFs across childhood and adolescence is associated with neurological changes, particularly the development of the prefrontal cortex (e.g.,4,24,25). Given this, adolescence is a critical period to study, allowing further examination of the continued development of EFs beyond childhood and into early adulthood to establish when these components of EF reach maturity.
Cognitive performance peaks in young adulthood (e.g.,26), with declines emerging as early as 20 or 30 years old, including declines across adulthood in speed of processing27–30, reasoning29,30, face processing31, fluid intelligence26,27, crystallized intelligence26,27, working memory26,28,32,33, verbal and visuospatial memory34, and long-term memory27,28. There is a vast amount of heterogeneity in regards to when cognitive abilities peak and decline. For example, aspects of short-term memory decline from 18 years of age, working memory declines in the 30 s, and vocabulary peaks in the 40 s or even later26. In contrast, other aspects of cognition, such as autobiographical memory and semantic knowledge, remain relatively stable across adulthood35,36.
These findings raise the question of whether different components of EFs, specifically inhibition, working memory, cognitive flexibility, and planning, are stable across adulthood and decline in older age, or whether age-related declines in EFs begin soon after maturity in early adulthood. Studies have largely established that working memory reaches a peak at 30 years old and declines thereafter26,32,33,37. In addition, inhibitory control is poorest in younger children, improves in adulthood, and declines in older age38; however middle-aged adults were omitted from this study, so it is not clear when these declines started to emerge. Overall, there is a paucity of research specifically focussing on multiple components of EF across the lifespan, with studies into aging often limited in their focus due to comparing dichotomous ‘young’ versus ‘old’ adult groups (i.e. few studies include adolescents or middle-age adults in their lifespan sample). This approach means that important evidence is scarce to draw conclusions on the extended developmental trajectory of EF or earlier signs of decline. A notable exception to this is the Cognitive Battery of assessments developed as part of the National Institutes Health Toolbox in the U.S.A (NIHTB-CB;18,39,40). The NIHTB-CB sought to establish a series of tasks that could be used to assess cognitive function abilities across different populations of individuals, suitable for use in individuals aged from three to 85 years old, and includes measures of inhibitory control, cognitive flexibility, and working memory. Results from the NIHTB-CB support suggestions of an inverted-U-shaped curve in development of a number of EF abilities, including inhibition, cognitive flexibility, and working memory, with abilities first rising across childhood, and falling in later adulthood18,41,42. Ferriera et al.43 also investigated EF abilities in a specific cohort of healthy middle-aged adults, with results highlighting very early declines in EF before the age of 50; other studies that have included middle-aged adults in a broader adult sample have reported a linear decline across adulthood which is steeper among participants aged 65 + (e.g.,13).
Further to these behavioural studies, neuroimaging has revealed changes in both the structure and function of brain regions that underlie EFs in middle-age and older adulthood44,45, which is highly likely to impact EF performance in these age ranges. The studies cited above have provided important insights into the developmental trajectories of EF capacities across the lifespan, including highlighting the limited studies that have included middle-aged adults in investigations of EFs and, importantly, included analysing age as a continuous measure to track development throughout adulthood (c.f.11–13,46). More often, even when studies have included middle-age adults, they have analysed effects of age between groups rather than as a continuous predictor (e.g.,47,48), or rely on correlation or regression analyses to model only linear trends (e.g.,46). As illustrated, studies with middle-aged adults are essential to gain a comprehensive picture of the development of EFs throughout adulthood, to allow pinpointing of when declines in EFs first emerge, and whether the patterns of decline in early adulthood, as shown in other cognitive abilities, are also evident across the different components of EF across different paradigms, or whether they are limited to specific components. Conducting studies with a continuous age sample also provides vital insights to inform theories of healthy and abnormal aging, as, for example, the first pathophysiological changes can commence up to 20 years before a diagnosis of dementia49.
Older age is associated with significant declines in EF, including working memory (e.g.,50), inhibition (e.g.,51), planning (e.g.,52), and cognitive flexibility (e.g.,53). Additionally, different aspects of cognitive flexibility show distinct age-related effects. Mixing costs are greater in older adults (e.g.,54–58); however, there are mixed results in regard to switch costs, with some studies reporting an age-related increase (e.g.,59), a U-shaped trajectory53, or no age-related differences (e.g.,58, 59), most likely due to differences in paradigms. Age-related effects in EFs are thought to be relatively robust, and have been associated with changes in the frontal lobes, specifically age-related volume reduction in the prefrontal cortex60. There are some conflicting findings in the literature regarding age-related declines in EF, perhaps because many studies do not account for general slowing in response latencies (see61, for a discussion). When accounting for this general slowing, Verhaeghen61 failed to find evidence for specific age-related declines in inhibition and local task-shifting costs (termed switch costs herein), but found evidence for age-related declines in global task-shifting costs (termed mixing costs herein). Verhaeghen suggested that mixing costs reflect a dual-task cost, with dual-tasks affecting older adults more62. Thus, it is important for studies examining effects of cognitive decline in older age to account for age-related changes in response speed, to be sure that effects reflect true changes in executive capacities rather than more general slowing in response latencies.
In addition to age, several factors have been linked to cognitive decline, including genetics, health status, physical activity, socio-economic status (SES), IQ, and physical fitness (e.g.,63–68). Childhood SES has been consistently associated with EF56,69–71, with lower SES predicting poorer performance on tasks of EF in childhood72. Less is known about the link between adult SES and EF73. IQ is another factor that has been associated with EF, particularly with working memory74. IQ and EFs are dissociable yet related in childhood75, with evidence that inhibitory control and cognitive flexibility are related to IQ during childhood76. In adolescence, working memory is highly correlated with IQ, but inhibition and cognitive flexibility are not54. In older adults, IQ has been shown to be related to working memory, verbal fluency, inhibition, and cognitive flexibility77. Given that IQ and SES are related to EF abilities, the current study controlled for these factors in analysis, allowing us to assess the role of age in predicting differences in EFs, beyond effects of IQ and SES.
EFs play a critical role in everyday life, allowing individuals to plan ahead, focus their attention, and switch between different tasks. They play a key role in allowing individuals to maintain effective levels of independent functioning, and better EF abilities have been associated with improved self-reported quality of life in older age1,78. Further, deficits in EF abilities have been associated with issues with obesity79, social problems80,81, and lower levels of productivity82. It is therefore important to further our understanding of how these EF abilities continue to change and differ across the lifespan—contributing to our understanding of age-related cognitive changes—which ultimately may be able to provide insight into the optimum age at which cognitive training interventions could be utilized to help maintain real-world functioning across individuals.
The current study investigated how multiple components of EF differ across the lifespan, in a large, community-based sample of 350 10- to 86-year-olds, allowing differences across adolescence, early adulthood, middle adulthood, and older adulthood to be examined within one study. The study focussed on four components of EF: planning, inhibition (also termed inhibitory control and response inhibition), working memory, and cognitive flexibility (also called set shifting or mental flexibility). It is largely accepted that inhibitory control, working memory, and cognitive flexibility form the core components of EF abilities, reflecting largely (but not entirely) separable processes83. In the current study we also included a more complex aspect of EF, planning abilities. The ability to plan is a complex executive skill94,102 that plays an important role in daily living, such as the ability to identify a goal and subsequently planning and executing the steps needed to attain that goal72,83. It is noted that planning abilities themselves, whilst considered an aspect of EF, may require activation of other EFs, including inhibitory control and working memory in order to produce successful outcomes72,83. Given this, the inclusion of a measure of planning abilities in the current study allowed further insight into how planning capacities may change across the lifespan, and whether we are able to establish a relationship between ‘core’ EF abilities and planning capacities within this lifespan sample.
The aim of this study was to explore the developmental trajectories of these four components of EF, to identify when age-related differences emerge. A cross-sectional design was utilized, to provide insight into differences that can be established across different age cohorts in task performance; importantly, to address our research question, we selected tasks that were appropriate for all participants from 10 to 86 years of age, allowing direct comparisons in task performance to be made across different ages. We used curvilinear regression modelling to establish the shape and trajectory of change across ages for each EF. Due to research suggesting that some components of EF may be related to IQ and SES, we also controlled for the effects of IQ and socio-economic status.
We predicted, firstly, that these components of EF would continue to develop throughout adolescence, indicated by an improvement in performance across tasks up to ~ 30 years of age. Second, we predicted that there would be age-related declines in EF from ~ 50 years of age onwards43. Third, we explored whether this decline in EFs would start earlier in adulthood (i.e. between 30 and 50 years of age). We did not stipulate specific predictions in this middle age range due to the dearth of research in adulthood. Instead, we modelled and tested the fit of linear, quadratic and cubic age relationships for each component of EF. Note that each statistical model can represent multiple patterns/directions of effects, however we define our predictions for the linear, quadratic and cubic fit models used here based on existing research on cognitive development and decline with age. We posited that a predicted linear age relationship would indicate either an improvement or decline in EF from adolescence to older age. We predicted that a quadratic age relationship would indicate a developmental improvement in EF in adolescence through to young adulthood, and a decline in EF throughout adulthood. A predicted cubic age relationship would indicate a developmental improvement in EF in adolescence through to young adulthood, a decline in EF across adulthood, and a further steeper decline in EF in older age. Finally, in line with previous research (e.g.,84) we predicted that the different aspects of cognitive flexibility would should show distinct effects: we predicted that switching costs (i.e., changing task sets) would not show any age-related changes, but mixing costs (i.e., maintaining multiple task sets) would show an increase across adulthood (e.g.,84, 85).
Materials and method
Participants
The sample consisted of 354 participants who were recruited from the community, via newspaper/radio adverts, social media, and an institutional research participation database, as part of the CogSoCoAGE project. Two participants were excluded due to low IQ (< 70), one participant was excluded due to being a non-native English speaker, and one participant’s data was lost due to computer failure. The final sample consisted of 350 participants (10–86 years-old; 232 females, 118 males). Table 1 provides a summary of the sample and Table 2 details the demographic characteristics of the CogSoCoAGE sample, each divided into five age groups for illustrative purposes. All participants were native English-speakers, had normal or corrected-to-normal vision, had no known neurological disorders, and had no mental health or autism spectrum disorder diagnoses. The Ethical Committee of the School of Psychology, University of Kent, approved the study, and all methods were carried out in accordance with EU guidelines and regulations. Informed consent was obtained from all participants; for participants under 18 years of age, consent was additionally sought from a parent or legal guardian.
Table 1.
Summary of the CogSoCoAGE sample.
| All (10–86 years old) | Adolescents (10–17 years old) | Young adults (18–29 years old) | Adults (30–49 years old) | Middle-aged adults (50–64 years old) | Older adults (65–86 years old) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 350 | 62 | 60 | 76 | 74 | 78 |
| Age (years) | ||||||
| Mean (SD) | 43.22 (22.14) | 13.34 (2.39) | 22.63 (3.59) | 40.00 (5.62) | 57.19 (4.28) | 72.71 (5.64) |
| Gender | ||||||
| F:M ratio | 232:118 | 29:33 | 39:21 | 62:14 | 53:21 | 49:29 |
| IQ | ||||||
| Verbal IQ | 109.65 (12.38) | 105.74 (10.07) | 108.13 (11.06) | 103.05 (9.82) | 109.86 (11.50) | 120.14 (11.52) |
| Performance IQ | 108.48 (12.92) | 107.27 (13.47) | 104.70 (12.18) | 105.45 (11.57) | 110.18 (13.12) | 120.66 (11.30) |
| Full scale IQ | 110.35 (12.19) | 107.35 (11.07) | 107.45 (10.75) | 104.70 (9.81) | 110.18 (11.83) | 120.65 (10.43) |
| SES index | ||||||
| Mean (SD) | 13.74 (3.70) | 14.79 (3.41) | 11.18 (3.82) | 14.56 (3.78) | 13.91 (3.35) | 13.91 (3.22) |
Table 2.
Demographic characteristics of the CogSoCoAGE sample.
| Characteristic (N (%)) | All | Adolescents | Young adults | Adults | Middle-aged adults | Older adults |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethnicity | ||||||
| White | 316 (90.3) | 52 (83.9) | 46 (76.6) | 71 (93.4) | 70 (94.6) | 77 (98.7) |
| Mixed/multiple ethnic groups | 13 (3.7) | 7 (11.3) | 3 (5.0) | 1 (1.3) | 2 (2.7) | 0 |
| Asian/British Asian | 8 (2.3) | 0 | 5 (8.3) | 3 (4.0) | 0 | 0 |
| Black/African/Caribbean/Black British | 3 (0.9) | 0 | 2 (3.3) | 1 (1.3) | 0 | 0 |
| Other ethnic group | 3 (0.9) | 0 | 1 (1.7) | 0 | 1 (1.4) | 1 (1.3) |
| Not stated | 7 (2.0) | 3 (4.8) | 3 (5.0) | 0 | 1 (1.4) | 0 |
| Education | ||||||
| GCSEs | 35 (10.0) | 7 (11.3) | 1 (1.7) | 9 (11.8) | 10 (13.5) | 8 (10.3) |
| A-Levels | 60 (17.1) | 10 (16.1) | 32 (53.3) | 6 (7.9) | 8 (10.8) | 4 (5.1) |
| Undergraduate degree | 91 (26.0) | 14 (22.6) | 19 (31.7) | 18 (23.7) | 18 (24.3) | 22 (28.2) |
| Postgraduate degree | 90 (25.7) | 16 (25.8) | 5 (8.3) | 25 (32.9) | 21 (28.4) | 23 (29.5) |
| Other | 64 (18.3) | 12 (19.4) | 1 (1.7) | 17 (22.4) | 15 (20.3) | 19 (24.4) |
| No qualifications | 2 (0.6) | 0 | 0 | 1 (1.3) | 0 | 1 (1.3) |
| Not stated | 8 (2.3) | 3 (4.8) | 2 (3.3) | 0 | 0 | 1 (1.3) |
| Household income | ||||||
| < £9999 | 28 (8.0) | 3 (4.84) | 10 (16.67) | 3 (3.95) | 5 (6.76) | 7 (8.97) |
| £10,000–£19,999 | 44 (12.3) | 2 (3.23) | 7 (11.67) | 9 (11.84) | 8 (10.81) | 17 (21.79) |
| £20,000–£29,000 | 49 (14.0) | 6 (9.68) | 7 (11.67) | 6 (7.89) | 15 (20.27) | 15 (19.23) |
| £30,000–£39,000 | 52 (14.8) | 2 (3.23) | 7 (11.67) | 12 (15.79) | 15 (20.27) | 16 (20.51) |
| £40,000–£49,000 | 56 (16.0) | 15 (24.19) | 7 (11.67) | 11 (14.47) | 10 (13.51) | 13 (16.67) |
| £50,000–£69,999 | 56 (16.0) | 16 (25.81) | 7 (11.67) | 18 (23.68) | 11 (14.86) | 4 (5.13) |
| £70,000+ | 49 (14.0) | 13 (20.97) | 9 (15.00) | 16 (21.05) | 7 (9.46) | 4 (5.13) |
| Not stated | 17 (4.9) | 5 (8.06) | 6 (10.00) | 1 (1.32) | 3 (4.05) | 2 (2.56) |
| Occupational class | ||||||
| Higher managerial, administrative and professional | 55 (15.7) | 9 (14.52) | 1 (1.67) | 11 (14.47) | 13 (17.57) | 21 (26.92) |
| Lower managerial, administrative and professional | 124 (35.4) | 21 (33.87) | 8 (13.33) | 31 (40.79) | 30 (40.54) | 34 (43.59) |
| Intermediate occupations | 76 (21.7) | 21 (33.87) | 5 (8.33) | 19 (25.00) | 16 (21.62) | 15 (19.23) |
| Small employers and own account workers | 9 (2.6) | 0 | 2 (3.33) | 2 (2.63) | 2 (2.70) | 3 (3.85) |
| Lower supervisory and technical occupations | 4 (1.2) | 1 (1.61) | 1 (1.67) | 1 (1.32) | 1 (1.35) | 0 |
| Semi-routine occupations | 38 (10.9) | 7 (11.29) | 7 (11.67) | 10 (13.16) | 9 (12.16) | 5 (6.41) |
| Routine occupations | 12 (3.4) | 0 | 11 (18.33) | 1 (1.32) | 0 | 0 |
| Never worked and long-term unemployed | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Full-time student | 21 (6.0) | 0 | 19 (31.67) | 1 (1.32) | 1 (1.35) | 0 |
| Not stated | 11 (3.1) | 3 (4.84) | 6 (10.00) | 0 | 2 (2.70) | 0 |
Measures
Socio-economic status
Participants (if aged over 18) and parents of participants (if aged under 18) reported on their level of education, the household income, and their occupation (job title and industry). Occupational class was coded using the derivation tables provided by the Office for National Statistics116 using the simplified National Statistics Socio-Economic Classification (NS-SEC) based on Standard Occupational Classification 2010 (SOC2010). To calculate an SES index, education level was coded on a scale 1–6, and household income and occupational class were coded on a scale 1–7. These three scores were summed to derive an SES index between 3 and 2086, with lower scores indicating lower SES. In our sample, scores ranged from 5 to 20.
IQ
Intellectual ability was assessed using the Wechsler Abbreviated Scale of Intelligence-Second Edition (WASI;87). The WASI-II comprises of four subtests as a measure of intelligence for individuals aged 6–90 years old. The Vocabulary and Similarities subtests estimated a verbal IQ score. The Block Design and Matrix Reasoning subtests estimated a performance IQ score. Full-scale IQ comprised of both verbal and performance IQ.
Stroop colour-word task
A modified version of a standard Stroop Colour-Word task88 was used as a measure of inhibition. The words were printed in red, green, blue, or yellow for all trials and were printed on a grey background. The words used in both congruent and incongruent trials were “RED”, “GREEN”, “BLUE”, and “YELLOW”. For congruent trials, the colour word matched the printed colour (i.e., “RED” printed in red). For incongruent trials, the colour word did not match the printed colour (i.e., “RED” printed in green). For filler trials, the non-colour words were matched for length and frequency to the colour words. The filler words used were “TAX”, “CHIEF”, “MEET”, and “PLENTY”. The word stimuli were presented in the middle of the screen in font type Courier New and font size 28. See Fig. 1 for example stimuli.
Figure 1.
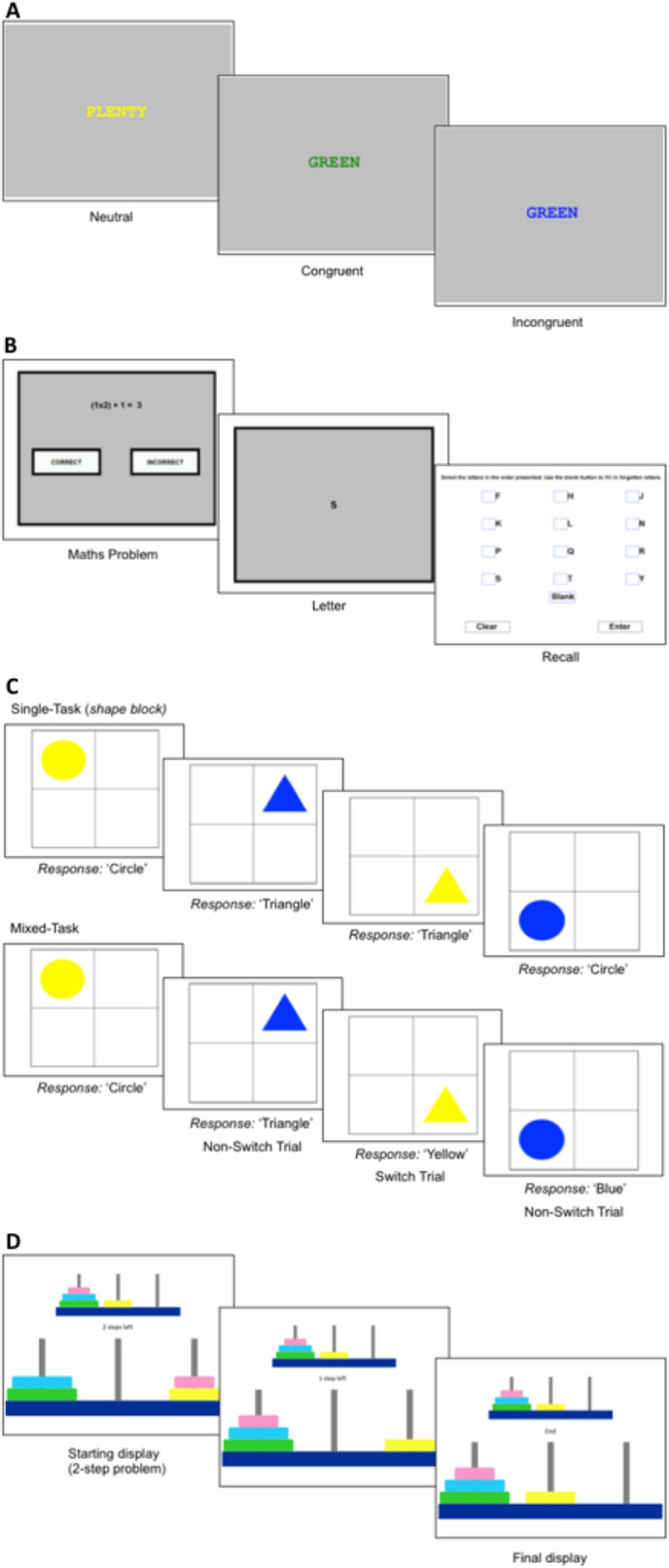
Illustrations of the stimuli and procedure employed in each of the four EF tasks: (A) Stroop colour-word task; (B) operation span; (C) task switching; (D) Tower of Hanoi.
Participants first completed 20 practice trials, which consisted of ten filler and ten congruent trials in a pseudo-randomised order. Participants were told that they would see a word and they were instructed to identify the colour of the word as fast as possible using a button-box (i.e., RED printed in green; participants press ‘green’ button). The experimental trials consisted of 50 congruent trials, 50 incongruent trials, and 50 filler trials presented in a pseudo-randomised order, in which the same colour word, the same printed colour, or the same colour word/printed colour could not appear on two consecutive trials to avoid priming effects. A blank screen appeared for 1000 ms at the start of the experimental trials. After the participant made a response, the next trial was started immediately.
Response times for filler, congruent and incongruent trials were calculated for accurate responses that were made 200 ms after stimuli onset and were within 2.5 SDs of each participant’s overall trial mean. The dependent variable was the Stroop congruency effect (incongruent trial mean RT minus congruent trial mean RT). In addition, we accounted for age-related slowing and declines in information processing speed, which led to positive skew and high kurtosis in reaction times, by log-transforming reaction times for each trial before calculating the Stroop congruency effect. The log-transformation of the Stroop congruency effect reduced skew and kurtosis (untransformed skew = 1.84, kurtosis = 8.84; log-transformed skew = 0.69, kurtosis = 3.44). The log-transformed Stroop congruency effects were reverse scored so that a higher score indicated better performance to aid interpretation of results alongside other measures. Internal consistency was excellent (Cronbach’s alpha = 0.99) and the average inter-item correlation was ideal (r = 0.53).
Operation span
This task was adapted from Unsworth et al.’s89 automated operation span task (OSpan) as a measure of working memory, which was based on the original OSpan task by Turner and Engle90. Participants were required to solve maths equations while remembering a sequence of letters. The letters used were F, H, J, K, L, N, P, Q, R, S, T, and Y. See Fig. 1 for example stimuli.
There were three practice blocks. The first practice block was a simple letter span. A single letter appeared in the middle of the screen for 800 ms. A two-letter span was used for two trials, and a three-letter span was used for a further two trials. At recall, participants were required to recall the letter sequence in the correct order by clicking a box next to the appropriate letter presented in a 4 × 3 matrix. After clicking a box, a number appeared that represented the position of the letter in the sequence. A ‘blank’ box was also presented and participants were told to click this box if they could not remember the letter in the sequence. Participants could also click a ‘clear’ box to clear responses. The letters clicked also appeared at the bottom of the screen. To finish the letter recall stage, participants clicked a box labelled ‘enter’. This recall phase was untimed. After the recall phase, participants were given feedback about how many letters they recalled correctly.
The second practice block introduced the maths equations. A maths equation was presented on screen (e.g., (2 × 1) + 1 = 3) along with a ‘correct’ box and an ‘incorrect’ box. Participants were required to identify whether the maths equation was correct or incorrect by clicking the appropriate box. Accuracy feedback was given. There were three trials in this second practice block.
In the last practice block, participants completed both the maths section and letter recall section together. The maths equation was presented first, and once participants had responded to the problem, a letter to be recalled appeared in the middle of the screen for 800 ms. This equation-letter sequence was repeated twice to create a two-letter span in this final practice block. The letter recall screen with the 4 × 3 letter matrix was then presented. Participants completed three full practice trials, and were given feedback on how many letters they recalled correctly and how many errors they made on the maths problems.
The experimental trials consisted of three trials for each of 2 to 7 letter spans (randomised). This made a total of 18 trials with 81 maths problems and 81 letters. Participants were encouraged to keep their maths accuracy at or above 85% at all times. During recall, a percentage in red was presented in the upper right-hand corner of the screen, indicating the percentage accuracy for the maths problems.
An absolute OSpan score was calculated as the sum of all perfectly recalled sets. A partial OSpan score was also calculated as the total number of letters recalled in the correct position. The absolute and partial OSpan scores were highly correlated (r = 0.92, p < 0.001) and due to the recommendations of Unsworth et al.89, the partial OSpan score was used as the dependent variable. Internal consistency was good (Cronbach’s alpha = 0.85) and the average inter-item correlation was ideal (r = 0.25).
Task switching
The task was adapted91,92 as a measure of cognitive flexibility. Participants were presented with a 2 × 2 matrix on a computer screen. Stimuli were presented one-by-one in the four quadrants of the screen, beginning in the upper-left quadrant and rotating in a clockwise manner. The stimuli were coloured-shapes (circle/triangle, in blue/yellow) that appeared in the quadrant. See Fig. 1 for example stimuli. The same shape/colour combination did not appear on consecutive trials (i.e., a blue triangle could not appear in consecutive trials). Participants’ task was to decide whether the shape was a circle or a triangle, and whether the colour was blue or yellow, dependent on trial-type (see descriptions below). Participants used a button box to respond, pressing the left-hand button for circle/blue and the right-hand button for triangle/yellow. Participants were instructed to respond as fast and as accurately as possible. The next stimulus was presented 150 ms after a key press or after a timeout of 5000 ms. Participants received feedback about their accuracy after practice trials and repeated the practice block if their accuracy was less than 80%.
In the single-task, there were 16 practice trials and 32 experimental trials per block. Participants had to identify whether the shape was a circle or a triangle in one block, and whether the colour was blue or yellow in a second block (single-task trials).
In the mixed-task, there were 16 practice trials, and four blocks of 32 experimental trials. Participants had to indicate whether the shape was a circle or a triangle when the coloured-shape appeared in the top two quadrants, and whether the colour was blue or yellow if the coloured-shape appeared in the bottom two quadrants. Categorising the coloured-shape in the upper left to upper right quadrant, or in the lower right to lower left quadrant did not require switching to a new category (i.e., non-switch trials). However, categorising the coloured-shape in the upper right to lower right quadrant, or in the lower left to upper left quadrant required switching to a new category (from shape to colours, and vice versa, i.e., switch trials). Switch and non-switch trials alternated predictably within these blocks.
Response times were calculated for accurate responses that were made 200 ms after stimuli onset, and were within 2.5 SDs of each participant’s overall trial mean. A switch cost of task-set switching was calculated by subtracting the mean response time for non-switch trials from the mean response time for switch trials in the mixed-task. A mixing cost (indicating maintenance of two task-sets) was calculated by subtracting the mean single-task trial response time from the mean non-switch response time in the mixed-task. To account for age-related slowing and declines in information processing speed, trial level response times were log-transformed before calculating a switch cost and mixing cost. The log-transformation reduced skew and kurtosis for switch cost (untransformed skew = 0.47, kurtosis = 3.25; log-transformed skew = 0.17, kurtosis = 2.54) and mixing cost (untransformed skew = 0.91, kurtosis = 3.39; log-transformed skew = 0.41, kurtosis = 2.83). The log-transformed switch and mixing costs were reverse scored so that a higher score indicated better performance. Internal consistency was excellent for both the single and mixed-task (both Cronbach’s alpha = 0.98). The average inter-item correlation for the single-task (r = 0.49) and for the mixed-task (r = 0.34) was ideal.
Tower of Hanoi
The Tower of Hanoi was used as a measure of planning (based on script obtained from: https://step.talkbank.org/scripts-plus/TOHx.zip). The Tower of Hanoi required the mouse-controlled movement of different-sized disks across three pegs from an initial state to a target state in a pre-defined number of steps. Participants were presented with three pegs (left, centre, right) and four disks; pink, yellow, blue and green, in increasing size. The target state was shown on the top-centre of the screen and was smaller than the initial state configuration. The initial state was presented on the bottom-centre of the screen. The number of steps remaining was shown in the centre of the screen. Participants were told that they needed to move the disks from their current positions on the bottom of the screen to match the target state in the given number of steps without placing larger disks on top of smaller disks. See Fig. 1 for example stimuli.
Participants first completed three practice trials: one one-step and two two-step problems. Participants continued to 16 experimental trials, which took three- to ten-steps to complete, with two trials at each step. Before the start of each trial, participants were told how many steps were required to complete each trial. During the trials, participants clicked on the disk that they wanted to move and this disk then turned red. The participant then clicked on the rod that they wanted to move the disk to. If the incorrect rod was selected, then an error message was shown and the participant restarted that trial. If the participant made five incorrect movements in a row then the task automatically ended. If the correct disk and rod were selected, then the selected disk moved to the selected rod and the participant moved on to the next step.
The dependent variable was an overall Tower of Hanoi score that used the traditional absolute scoring method, and was the sum of all perfectly completed trials (i.e., score of 5 for a trial with 5 steps completed perfectly with no errors). Internal consistency was acceptable (Cronbach’s alpha = 0.80) and the average inter-item correlation was ideal (r = 0.20).
Procedure
Participants attended one or two visits to the university to complete the 5 h testing session, which included questionnaires on behaviour and demographic information, computer-based testing to assess cognitive and social skills, and an IQ assessment. The order of tasks was counterbalanced over 12 different lists to ensure that order effects were minimised. All tasks reported here were programmed using E-Prime software.
Results
Analyses were conducted in R version 3.6.0. The datasets and code are available on the Open Science Framework (https://osf.io/qzrwu). Descriptive data on the EF measures are summarised in Table 3, alongside the total number of participants retained per task. For the Stroop task, two participants did not complete the task due to equipment failure and one participant was colour-blind. For the Operation Span, one participant did not complete the task due to equipment failure, 3 participants did not return for their second testing session to complete the task, and 12 participants declined to complete the task or withdrew. For Task Switching, two participants did not complete the task due to equipment failure, 3 participants did not return for their second testing session to complete the task, 10 participants declined to complete the task or withdrew, and two participants’ data was lost due to computer error. For the Tower of Hanoi, two participants did not return for their second testing session to complete the task.
Table 3.
Descriptive statistics for the executive function measures, showing means and standard deviations in parentheses, divided into five age groups for illustrative purposes.
| Executive function measure | N | All | Adolescents | Young adults | Adults | Middle-aged adults | Older adults |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stroop task (inhibitory control)a | |||||||
| Filler words RT (log ms) | 347 | 6.89 (.21) | 6.88 (.18) | 6.72 (.13) | 6.81 (.17) | 6.93 (.15) | 7.07 (.21) |
| Congruent words RT (log ms) | 347 | 6.86 (.22) | 6.84 (.18) | 6.67 (.15) | 6.79 (.18) | 6.92 (.16) | 7.05 (.21) |
| Incongruent words RT (log ms) | 347 | 7.01 (.25) | 6.98 (.21) | 6.81 (.17) | 6.91 (.21) | 7.06 (.17) | 7.24 (.23) |
| Congruency effect (log ms) | 347 | − .14 (.09) | − .14 (.09) | − .14 (.08) | − .13 (.07) | − .14 (.08) | − .19 (.11) |
| Operation span (working memory) | |||||||
| Absolute score | 334 | 44.60 (18.82) | 47.39 (18.11) | 52.67 (17.67) | 46.85 (16.84) | 42.77 (18.43) | 35.68 (18.97) |
| Partial score | 334 | 61.77 (13.82) | 64.52 (11.02) | 67.51 (9.89) | 64.38 (11.37) | 59.84 (14.04) | 54.47 (16.48) |
| Task switching (cognitive flexibility)a | |||||||
| Single-task trials (log ms) | 333 | 6.42 (.21) | 6.38 (.20) | 6.27 (.18) | 6.36 (.18) | 6.49 (.17) | 6.59 (.18) |
| Non-switch trials (log ms) | 333 | 6.88 (.30) | 6.77 (.25) | 6.64 (.22) | 6.84 (.30) | 6.99 (.27) | 7.10 (.23) |
| Switch trials (log ms) | 333 | 7.21 (.25) | 7.16 (.22) | 7.02 (.20) | 7.18 (.25) | 7.26 (.24) | 7.40 (.18) |
| Switch cost (log ms) | 333 | − .35 (.16) | − .38 (.16) | − .38 (.18) | − .34 (.15) | − .27 (.16) | − .30 (.17) |
| Mixing cost (log ms) | 333 | − .41 (.22) | − .39 (.20) | − .37 (.21) | − .48 (.24) | − .50 (.26) | − .51 (.22) |
| Tower of Hanoi (planning) | |||||||
| Absolute score | 348 | 49.97 (25.82) | 40.16 (20.06) | 56.74 (26.53) | 55.16 (25.76) | 47.90 (25.56) | 49.29 (27.37) |
aLog transformed response times.
Age-related effects on executive function
A series of regression models were conducted to investigate the relationship between the measures of EF and age, over and above any potential effects of IQ and SES. The models specified the outcome variable as the dependent measure for the specific EF measure, the first predictor variable was age using linear, quadratic or cubic orthogonal polynomial coefficients, and IQ and SES index were included as the second and third predictor variables. Note that quadratic models included both linear and quadratic age coefficients, and cubic models included linear, quadratic and cubic age coefficients.
The best fitting model for each EF measure was deduced by comparing several goodness-of-fit indices shown in Table 4. Established goodness-of-fit measures were used to evaluate model fit. The ANOVA test and likelihood test contrasted the simpler model against the more complex model (e.g., the model with linear vs. quadratic age coefficients). If the p value was greater than 0.05, then the simpler model was selected as the best fitting model. If the p value was less than 0.05, then the more complex model was selected as the best fitting model. Model comparison also used Akaike’s Information Criterion (AIC) and Bayesian Information Criteria (BIC), with increasingly negative values corresponding to increasingly better fitting models. Model selection evaluated these goodness-of-fit indices and the model (linear, quadratic, or cubic model) with the greatest number of goodness-of-fit indices was selected as the overall best fitting model (see Table 4). The model predictions for the overall best fitting models for each EF are plotted in Fig. 2 with the observed data. Analyses for the untransformed variables are reported in Supplementary Materials (S1, S2).
Table 4.
Goodness-of-fit indices for the executive function models with age as the predictor variable (with linear, quadratic, or cubic age coefficients) for each outcome variable.
| Model | Model fit indices | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANOVA | Likelihood test | AIC | BIC | |||||
| RSS | FΔ | p | − 2LL | χ2 | p | |||
| Stroop task (congruency effect) | ||||||||
| Linear | 318.98 | – | – | − 471.59 | – | – | 953.18 | 972.32 |
| Quadratica | 294.93 | 27.31 | < 0.001 | − 458.26 | 26.65 | < 0.001 | 928.53 | 951.50 |
| Cubic | 294.93 | 0.00 | 0.990 | − 458.26 | 0.00 | 0.990 | 930.53 | 957.33 |
| Operation span (partial score) | ||||||||
| Linear | 251.50 | – | – | − 421.07 | – | – | 852.14 | 871.09 |
| Quadratica | 225.71 | 36.79 | < 0.001 | − 403.38 | 35.38 | < 0.001 | 818.76 | 841.50 |
| Cubic | 224.20 | 2.15 | 0.143 | − 402.29 | 2.19 | 0.139 | 818.57 | 845.10 |
| Task switching (switch cost) | ||||||||
| Lineara | 304.29 | – | – | − 452.22 | – | – | 914.45 | 933.40 |
| Quadratic | 302.82 | 1.56 | 0.213 | − 451.43 | 1.58 | 0.209 | 914.87 | 937.61 |
| Cubic | 299.85 | 3.19 | 0.075 | − 449.82 | 3.23 | 0.0722 | 913.64 | 940.17 |
| Task switching (mixing cost) | ||||||||
| Lineara | 295.83 | – | – | − 447.62 | – | – | 905.23 | 924.18 |
| Quadratic | 294.43 | 1.53 | 0.216 | − 446.84 | 1.55 | 0.213 | 905.68 | 928.42 |
| Cubic | 293.45 | 1.07 | 0.301 | − 446.30 | 1.09 | 0.296 | 906.59 | 933.12 |
| Tower of Hanoi (score) | ||||||||
| Linear | 308.21 | – | − 467.49 | – | – | 944.97 | 964.15 | |
| Quadratic | 289.21 | 22.14 | < 0.001 | − 456.61 | 21.76 | < 0.001 | 925.21 | 948.22 |
| Cubica | 273.74 | 18.99 | < 0.001 | − 447.20 | 18.80 | < 0.001 | 908.41 | 935.25 |
Bold values indicate best fitting model according to goodness-of-fit index; RSS = residual sum of squares; FΔ denotes the comparison of models (i.e., linear vs. quadratic); − 2LL = log-likelihood.
aOverall best-fitting model taking all goodness-of-fit indices into consideration.
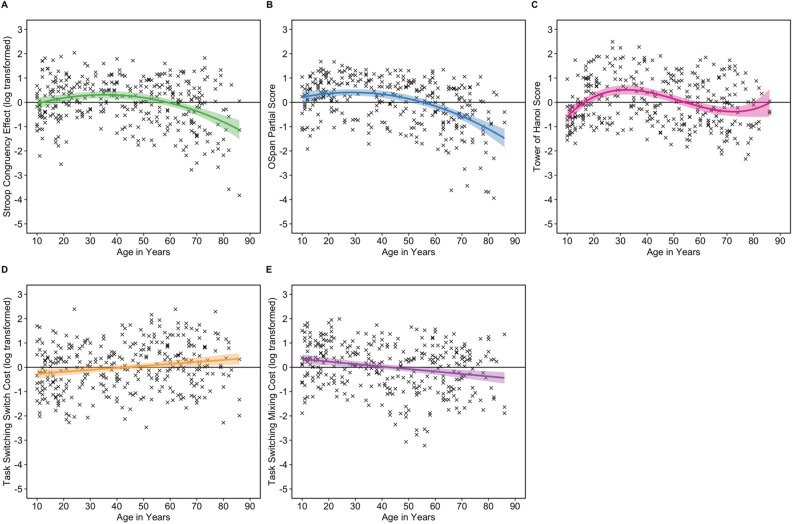
Figure 2.
Relationship between age and executive function measures, adjusted for IQ and SES index. (A) log-transformed Stroop congruency effect, (B) OSpan partial score, (C) Tower of Hanoi score, (D) log-transformed Task Switching switch cost; and (E) log-transformed Task Switching mixing cost. The bold line indicates the best-fitting regression line and the dashed line indicates the 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Stroop congruency effect and Task Switching switch and mixing costs are reversed scored so that a higher value indicates better performance and all variables are z-scored for ease of comparison. Note: All measures were adjusted for IQ and SES to be comparable to the described regression models. To adjust for IQ and SES, the residuals were obtained from the regression line fit when fitting each executive function measure as a dependent variable in a linear model and IQ and SES index as predictor variables.
The best fitting model for the log-transformed congruency effect in the Stroop task included linear and quadratic age coefficients. The results of the model indicated that there was a significant association between the Stroop congruency effect and age, IQ, and SES (R2 = 0.14, F(4, 335) = 13.46, p < 0.001). Age was significantly associated with the Stroop congruency effect (linear β = − 0.27, p < 0.001; quadratic β = − 0.28, p < 0.001). To interpret the curvilinear relationship between the Stroop congruency effect and age, we consider the model predictions displayed in Fig. 2A. Figure 2A indicates that there is some increase in the Stroop congruency effect between 10 and 35 years of age (i.e., an improvement in inhibitory control) and a decrease in the Stroop congruency effect from 36 to 86 years of age (i.e., a decline in inhibitory control). IQ was also significantly associated with the Stroop congruency effect (β = 0.20, p < 0.001), but SES was not (β = 0.09, p = 0.106). The model remained significant when IQ and SES covariates were removed (quadratic R2 = 0.09, F(2, 344) = 17.27, p < 0.001), showing that age was significantly associated with the Stroop congruency effect in our sample (linear β = − 0.19, p < 0.001; quadratic β = − 0.27, p < 0.001).
The best fitting model for the OSpan partial score included linear and quadratic age coefficients. The results of the model indicated that there was a significant association between the OSpan partial score and age, IQ, and SES (R2 = 0.28, F(4, 322) = 32.59, p < 0.001). Age was significantly associated with the OSpan partial score (linear β = − 0.48, p < 0.001; quadratic β = − 0.30, p < 0.001). To interpret the curvilinear relationship between the OSpan partial score and age, we consider the model predictions displayed in Fig. 2B. Figure 2B indicates that there is some increase in the OSpan scores from 10 to 30 years of age (i.e., an improvement in working memory capacity), and a decrease from 30 onwards (i.e., a decline in working memory capacity). IQ was also significantly associated with the OSpan partial score (β = 0.44, p < 0.001), but SES was not (β = 0.004, p = 0.930). The model remained significant when IQ and SES covariates were removed (quadratic R2 = 0.11, F(2, 331) = 20.78, p < 0.001), showing that age was significantly associated with the OSpan partial score in our sample (linear β = − 0.27, p < 0.001; quadratic β = − 0.22, p < 0.001).
The best fitting model for the Task Switching switch cost included the linear age coefficient. The results of the model indicated that there was a significant association between the Task Switching switch cost and age, IQ, and SES (R2 = 0.05, F(3, 323) = 5.19, p = 0.002). Age was significantly associated with the log-transformed switch cost (linear β = 0.20, p < 0.001), indicating a decrease in switch cost from 10 to 86 years old (i.e., an improvement in cognitive flexibility in terms of ‘switch cost’; Fig. 2D). IQ and SES were not significantly associated with switch cost (both ps > 0.134). The model remained significant when IQ and SES covariates were removed (linear R2 = 0.04, F(1, 331) = 14.81, p < 0.001), showing that age was significantly associated with the Task Switching switch cost in our sample (linear β = 0.21, p < 0.001).
The best fitting model for the Task Switching mixing cost included the linear age coefficient. The results of the model indicated that there was a significant association between the Task Switching mixing cost and age, IQ, and SES (R2 = 0.07, F(3, 323) = 8.24, p < 0.001). Age was significantly associated with the log-transformed switch cost (linear β = − 0.26, p < 0.001), indicating an increase in mixing cost from 10 to 86 years old (i.e., a decline in cognitive flexibility in terms of ‘mixing cost’; Fig. 2E). IQ and SES were not significantly associated with switch cost (both ps > 0.103). The model remained significant when IQ and SES covariates were removed (linear R2 = 0.07, F(1, 331) = 23.86, p < 0.001), showing that age was significantly associated with the Task Switching mixing cost in our sample (linear (β = − 0.26, p < 0.001).
The best fitting model for the Tower of Hanoi absolute score included linear, quadratic, and cubic age coefficients. The results of the model indicated that there was a significant association between the Tower of Hanoi absolute score and age, IQ, and SES (R2 = 0.20, F(5, 336) = 17.00, p < 0.001). Age was significantly associated with Tower of Hanoi absolute score (linear β = − 0.15, p = 0.004; quadratic β = − 0.25, p < 0.001; cubic β = 0.21, p < 0.001). To interpret the curvilinear relationship between the Tower of Hanoi absolute score and age, we consider the model predictions displayed in Fig. 2C. Figure 2C indicates that there is an initial increase in Tower of Hanoi absolute scores from 10 to 30 years of age (i.e., an increase in planning ability), a decrease from 30 to 70 years of age (i.e., a decrease in planning ability), and a small, but variable, increase from 70 years of age onwards. IQ was also significantly associated with the Tower of Hanoi absolute score (β = 0.43, p < 0.001), but SES was not (β = 0.005, p = 0.921). The model remained significant when IQ and SES covariates were removed (cubic R2 = 0.05, F(3, 344) = 6.65, p < 0.001), showing that age was significantly associated with the Tower of Hanoi absolute score in our sample (linear β = − 0.41, p = 0.002; quadratic β = − 0.25, p < 0.001; cubic β = 0.26, p < 0.001).
Relationships between measures of executive functions
A series of Pearson’s correlations were conducted between the four EF tasks to investigate the relationship between the measures of EF (Table 5). Partial correlations were also conducted to control for the effects of age. These effects of age for each EF measure were determined from the previously described regression models, i.e., the EF measures were adjusted for the linear, quadratic or cubic age effects. To adjust for age, the residuals were obtained from the regression line fit when fitting each EF measure as a dependent variable in a linear model and age coefficients (linear, quadratic, or cubic age coefficients) as predictor variables.
Table 5.
Correlation matrix of the executive function measures of interest (partial correlation coefficients controlling for the effects of age are presented in parentheses).
| Measure | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Stroop congruency effecta (inhibitory control) | – | ||||
| 2. Operation span partial score (working memory) | 0.18** (0.09) | – | |||
| 3. Task switching switch costa (cognitive flexibility) | 0.06 (0.08) | − 0.06 (− 0.02) | – | ||
| 4. Task switching mixing costa (cognitive flexibility) | 0.02 (− 0.01) | 0.12 (0.07) | − 0.46*** (− 0.43***) | – | |
| 5. Tower of Hanoi Score (planning) | 0.09 (0.07) | 0.30*** (0.29***) | 0.02 (0.03) | 0.00 (0.01) | – |
*p < .05, **p < .01, ***p < .001.
aResponse time measures log-transformed and reverse scored.
The OSpan partial score showed a positive correlation with both the Stroop congruency effect and the Tower of Hanoi score, with only a relationship with the Tower of Hanoi score remaining once accounting for the effects of age. These findings suggest that individuals with a higher working memory capacity also possess better planning ability, and these relationships are present irrespective of any age effects. Finally, Task Switching switch and mixing costs showed a negative correlation, reflecting that individuals with a greater switch cost also had a smaller mixing cost, and vice versa, and this pattern remained when accounting for the effect of age.
Comparing developmental trajectories of executive function
To examine whether each component of EF followed comparable or distinct developmental trajectories, we conducted across model comparisons for the age-related effects in the different EFs. This statistical method allows us to compare EF regression models with the same number of predictor variables, allowing direct comparisons between trajectories across these tasks. In our data, Task Switching switch and mixing cost models have three predictors (i.e., linear age coefficient, plus IQ and SES), Stroop congruency effect and OSpan partial score models have four predictors (i.e., linear and quadratic age coefficients, plus IQ and SES), and the Tower of Hanoi absolute score model has five predictors (i.e., linear, quadratic, and cubic age coefficients, plus IQ and SES). Therefore, Task Switching switch cost and mixing cost and Tower of Hanoi absolute score revealed different age-related effects (i.e., linear-only age effects vs. cubic age effect) and so were not directly compared with any other component of EF; analysis focused on the Stroop congruency effect versus OSpan partial scores.
Stroop congruency effect and OSpan partial score revealed similar curvature in the previous regression models (i.e., a quadratic effect of age), and so were directly compared. Two regression models were conducted and compared to statistically assess whether the age-related effects in the Stroop task and OSpan were significantly different. In the first step, a model was conducted that specified the outcome variable as the z-scores for the Stroop congruency effect and the OSpan partial score, with the predictor variable as the linear and quadratic age coefficients. In the second step, the same model was specified with the addition of an interaction term that included a grouping variable (i.e., a dummy variable) for the Stroop congruency effect (coded as 1) and the OSpan partial score (coded as 2). In the final step, these two models were compared using an ANOVA. If the p value was less than 0.05, then the regression slopes for the relationship between Stroop congruency effect and age versus OSpan partial score and age could be considered significantly different. If the p value was more than 0.05, then the regression slopes could be considered not statistically different.
The results indicated that the regression slopes for the Stroop congruency effect and OSpan partial score were not significantly different (RSSΔ = 2.96, FΔ = 1.11, p = 0.344), suggesting that inhibitory control and working memory show similar developmental trajectories. As illustrated in Fig. 2, the regression slopes for the other components of EF follow different patterns over age, indicating that only inhibitory control and working memory have similar developmental trajectories and all other components of EF show distinct developmental trajectories.
Discussion
The current study explored age-related differences in EF from late childhood through to old age in a large, community-based sample. Three-hundred and fifty individuals aged 10 to 86-years-old completed tasks to measure inhibitory control, working memory, cognitive flexibility, and planning, to identify when age-related changes in these EFs first become apparent. After controlling for any potential effects of IQ and SES, analyses revealed that inhibitory control and working memory capacity was higher in young adulthood compared to adolescence, with inhibitory control showing a decline in participants from ~ 35-years-old, and working memory capacity showing a decline in participants from ~ 30-years-old. Planning ability was also higher in young adulthood compared to adolescence, but then declined across adulthood, with a small positive change in older age. In line with our hypothesis, a dissociation was found for the measures of cognitive flexibility: interestingly, however, this reflected that switch costs decreased across the lifespan, yet mixing costs increased across the lifespan.
These findings provide insight into the developmental trajectories of inhibitory control, working memory, cognitive flexibility, and planning ability across the lifespan, providing a more comprehensive picture of the age-related changes in EF than has previously been established. Many of the existing studies that have examined aging and EFs have compared a dichotomous sample of younger versus older adults (e.g.,51,93–95), have combined individuals into smaller age groups during analysis (e.g.,53,55), or have focused on single aspects of EF, such as inhibitory control (e.g.,19,23). Instead, in the current study, we used a continuous age sample to model curvilinear age relationships to show the development of EFs from adolescence through to older adulthood, and to highlight changes in EFs that emerge throughout adulthood and not specifically at the onset of old age (typically considered 65 years old plus). Studies have largely overlooked adulthood as a period of change, with many studies omitting middle-aged adults in their samples examining lifespan changes. Moreover, cognitive performance among adolescents has rarely been compared to middle- or older-aged adults. The current study therefore makes a unique contribution to the literature by demonstrating developmental changes in different EFs, using the same set of tasks for all participants, with evidence that declines emerge in inhibitory control, working memory, and planning as early as the third decade of life. In addition, inhibitory control and working memory follow comparable developmental trajectories, with distinct developmental trajectories apparent for the other measures of EF.
In line with our predictions, and supporting previous studies61, the current study highlighted that different aspects of cognitive flexibility showed distinct age effects. As expected, there was an increase in mixing costs across adulthood, but switch costs decreased across adulthood. Mixing costs have generally been found to be greater in older adults (e.g.,54–58) there are mixed results in regard to switch costs, with some studies reporting an age-related increase (e.g.,59), a U-shaped trajectory53 or no age-related differences (e.g.,58,59), most likely due to differences in the task switching paradigms. We note that the current study used an alternating-runs paradigm without a preparatory cue-stimulus interval, which is analogous to Huff et al.’s84 task-switching paradigm with comparable aging results. In addition, switch and mixing costs showed a negative correlation, reflecting that individuals with a greater switch cost also had a reduced mixing cost, and vice versa, and this pattern also remained when accounting for the effect of age. This finding replicates that seen in Huff et al.84 in which a dissociation was found between switch and mixing costs across age groups. Huff et al.84 suggested that this dissociation is due to differences in the attentional systems in younger versus older adults. They suggest that younger and middle-aged adults experience a larger switch cost as their attentional systems become tuned to the task set in the single-task, and this inertia to executing the same rule in the single-task slows the reconfiguration to respond to the switch trials in the mixed-task. Older adults experience a reduced switch cost as their attentional systems are less well tuned to the task set in the single-task, and so do not experience the same slow down to respond to switch trials in the mixed-task. Moreover, older adults experience a larger mixing cost due to the additional attentional demands of maintaining two task sets in the mixed-task as compared to a single task set in the single-task. In summary, results of the task switching paradigm demonstrate dissociations between switch and mixing costs across the lifespan, indicating that adolescents and younger adults have more difficulty switching between task sets, and middle-aged and older adults have more difficulty maintaining task sets.
In the current study, we utilized four widely used tasks to measure inhibitory control, working memory, cognitive flexibility, and planning as components of EF. We investigated the relationship between these measures and found that individuals with a higher working memory capacity also had better planning ability, and these relationships remained when accounting for the effects of age. This finding suggests a link between working memory capacity and planning ability, or alternatively it could suggest that some EF tasks purported to measure singular aspects of EF may also require other EF processes to complete. This is supported by prior literature which has suggested that ‘planning’ may be indicative of a more complex executive skill, requiring activation of other aspects of EF to be successful (e.g.,26,96,97). For instance, working memory may be required when utilizing planning abilities to allow thinking ahead and execution of steps to achieve a set goal26,97; Hill and Bird98 also suggest that the traditional tower tasks (as used here to assess planning abilities) may require working memory, the inhibition of prepotent responses, and the generation of problem-solving ideas.
Interestingly, there were no other relationships between the measures of EF. Other research has documented very weak relationships between EF tests and EF factors, leading to the conclusion that these are dissociable components of EF and providing support for the fractionated EF theory (e.g.,83,97,99). Studies that do report relationships between components of EF tend to use several different EF tasks to assess each component and use an SEM approach to fit and compare models. For instance, Miyake et al.83 report in their study that, following completion of nine tasks used to assess shifting, updating, and inhibition, a three-factor model fitted the data best, highlighting distinguishable factors of: cognitive flexibility (shifting), updating, and inhibition. In the current study, we did not aim to assess whether EF is a unitary or diverging construct, and as such data is not optimised to investigate this specifically. However, the lack of correlations between tasks in the current data suggest that the tasks are tapping into distinguishable capacities rather than ‘umbrella’ EFs. Furthermore, EFs differentiate from middle to late childhood100. Our study is unique in exploring four separate measures of EFs (as opposed to an aggregated measure of cognitive performance), allowing across model comparisons which revealed that inhibitory control and working memory follow similar developmental trajectories, and all other measures of EF show distinct developmental trajectories.
In general, there is no single task or task battery that can exhaustively measure all aspects of EF, and tests of individual EF are rarely “process pure”97,101. Furthermore, there is some debate about whether tasks measure the underlying concept that they are purported to measure. For example, it has been suggested that participants may solve the Tower of Hanoi problems in a step-by-step manner instead of in a multi-step, planful manner102. It is also likely that the specific processes involved in each task differ across individuals and cohorts. For example, the method of administration used in the OSpan task here (i.e. requiring participants to select their answer from letters in a 4 × 3 grid) is likely to have differentially affected performance among the older participants since they are less familiar with computers and are known to experience age-related difficulties in visual search tasks and motor control (e.g.,103,104). In addition, it is noted that we used a single task to measure each component of EF. There may be specific aspects of each EF that may follow different developmental trajectories—for example, inhibitory control could be divided into automatic and effortful inhibition105. However, the aim of the current study was to examine how four separable EFs (inhibitory control, working memory, cognitive flexibility, and planning) may continue to change and differ across the lifespan, to further our understanding of age-related cognitive changes that may be present; to do this, we selected four well-established tasks that were suitable for use across the participant sample age-range, 10–86 years. This allowed direct comparison of task performance across different participant ages. It is noted, as previously recommended106, that in future studies it would be beneficial to include multiple measures of each component of EF to elucidate whether these age-related changes reflect the underlying EF or whether the age-related effects are task- or paradigm-specific. Furthermore, dual-tasks of EF may reveal greater age-related declines as multiple EFs are loaded in a single task; for example, loading working memory in younger adults has been found to reduce both inhibitory control and switching ability107. Tasks need to be sensitive enough to detect age-related declines108 and should account for general cognitive processing61. The four EF tasks in the current study were found to be age-sensitive after adjusting for general cognitive declines in response latencies and for IQ and SES, and therefore suitably provide an overall lifespan description of EF. We note that our analyses did not factor in the influence of gender on EFs, though gender was unequally distributed across the age groups in our sample (e.g., 47% females among adolescents but 82% females among adults). Previous research has provided mixed evidence for gender or sex differences in executive functioning (e.g.,109), and these analyses were beyond the scope of the current paper, however it would be beneficial for future studies to systematically explore this influence further. Gender details in our sample are available alongside task data on the OSF repository.
Here, we describe the overall developmental trajectories of EFs. To increase confidence in findings relating to this main aim, we controlled for any effects of IQ and SES when exploring age effects on EFs, due to evidence suggesting that some components of EF may be related to IQ and SES54,56,67. For IQ measures, our results highlighted a relationship with inhibitory control, working memory, and planning ability, above the effects of age. This may also explain why, in our measure of planning ability, a small, variable, improvement in abilities is seen from 70 years old onwards. Notably, the older age participants who took part in this study had higher IQ scores (full scale, verbal, and performance) than any other age group included in analysis; participants in this study were community-based, and this higher IQ may reflect that those experiencing the optimum ‘healthy’ aging experience are more likely to agree to take part in research studies such as these. This provides insight into healthy aging processes and may indicate that IQ holds a protective role against age-related declines in EF, although further research aimed at directly examining this suggestion, particularly its role in predicting planning abilities, is required. It is interesting to note that in this study, SES was not related to any component of EF, above the effects of IQ and age. So far, no other study has examined current SES on adult EF; literature has instead used a longitudinal approach to examine how SES during a distinct period (typically childhood) predicts later EF (e.g.,110). The current findings therefore suggest that an individual’s SES can change over the lifespan, which may have an additional effect on cognition111, and that SES may be less critical for EF after childhood.
It is interesting to note that not every individual demonstrated the same developmental profile of EF; for example, some older adults show equivalent performance in tasks to younger adults. The current study used a cross-sectional design to identify when age-related differences emerge when examining performance on four key measures of EF abilities. Given the scope of this design, results can only assess group-level age-related changes. Cross-sectional studies are potentially confounded by cohort effects and might therefore overestimate age-related changes, potentially failing to accurately explore age-related changes in task performance at an individual-level (i.e., how an individual’s EF capacities change over time; see112). For instance, prior studies using longitudinal analysis have highlighted that during middle age (i.e., 20–60 years), cognitive abilities such as speed of processing decline, but at a smaller rate than may be indicated in cross-sectional analyses (e.g.,113). The current study provides insight into the presence of age-related differences in EF abilities across the lifespan using a cross-sectional approach; it would be of interest in future to further this research by utilizing longitudinal designs to furthering our understanding of how EFs change with age, and individual differences that may influence these changes. It is also noted that the current sample consisted of a community sample of healthy adult volunteers functioning at high levels and may therefore, as discussed above, represent ‘successful’ aging within this particular population. There may be other factors that influence an individual’s performance on the EF tasks over and above age-related effects, which would be of interest to examine in future research; for example, there may be protective factors that offset declines in EFs, such as increased cardiovascular fitness in older age relating to better inhibitory control114.
As previously stated, EFs play an important role in daily life. Poor EFs can lead to social problems80,81, obesity and overeating79,115, lower productivity and difficulty keeping a job82, and people with better EF abilities have been shown to enjoy an improved quality of life78. Diamond1 highlights the importance of EFs for maintenance of mental and physical health. Given this, it is important to further our understanding of how EF abilities continue to change and evolve across the lifespan, examining not only childhood/adolescence and older adulthood, but observing differences across all of adulthood. Furthering prior research that has sought to establish changes in EFs across the lifespan (e.g.,40,42,48; see also41), the current study used four tasks to assess key EF abilities, including inhibitory control, working memory, cognitive flexibility, and planning abilities, providing further insight into cross-sectional changes seen in EF abilities across the lifespan. EF is a ‘functional construct’, involved in helping individuals conduct deliberate, goal-directed thoughts and actions48; by examining which aspects of EF do or do not change across the lifespan, and which tasks are able to sensitively assess differences in EF abilities across different ages, we are able to gain information about the overall EF construct. The tasks used in the current study were shown to be suitable for use with individuals from ten to 86 years of age, sensitively detecting differences in EF abilities. Additionally, by identifying the ages at which changes in EFs are seen, we may be able to develop targeted interventions to help maintain efficient EF capacities, in turn assisting in increased success in real-world scenarios. By analysing the data in the current study as a continuous sample, allowing curvilinear relationships to be examined, results highlight changes in EF abilities can be observed from young adulthood, and emphasise the importance of looking at all ages when examining cognitive changes, rather than focussing on ‘younger’ versus ‘older’ age groups.
Conclusion
We explored developmental changes in inhibitory control, working memory, cognitive flexibility, and planning ability from 10 years old to 86 years old in a large, community-based sample of healthy individuals. We show that working memory capacity and planning ability continue to develop over adolescence and into early adulthood. Crucially, we show that declines emerge as early as the third decade of life in inhibitory control, working memory, and planning, which is much earlier than has previously been considered. In addition, we demonstrate a dissociation for measures of cognitive flexibility, with switch costs decreasing and mixing costs increasing up to older age, indicating that adolescents and young adults have difficulties switching tasks sets, whereas middle-aged and older adults have difficulties maintaining task sets. In general, studies have largely overlooked adulthood as a period of change in EFs, with studies focussing on their development in childhood, or comparing dichotomous groups of young versus older adults in studies of cognitive aging. The findings of the current study highlight the value of including adolescents and middle-aged adults to provide a comprehensive lifespan description of the distinct developmental trajectories of EFs.
Supplementary information
Acknowledgements
This work was carried out with the support of a European Research Council grant to HF (Ref: CogSoCoAGE; 636458). The datasets and code supporting this article are available on the Open Science Framework (https://osf.io/qzrwu).
Author contributions
H.F. conceived of the study, designed the study, won the funding, data analysis and interpretation, and revised the manuscript; V.B. contributed to study design, data collection, data analysis and interpretation, and drafting the manuscript; E.B. contributed to study design, data collection, and revising the manuscript. All authors gave final approval for publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1038/s41598-020-80866-1.
References
- 1.Diamond A. Executive functions. Annu. Rev Psychol. 2013;64:135–168. doi: 10.1146/annurev-psych-113011-143750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Best J, Miller PH. A developmental perspective on executive function. Child Dev. 2010;81:1641–1660. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8624.2010.01499.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.De Luca CR, et al. Normative data from the CANTAB. I: Development of executive function over the lifespan. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2003;25:242–254. doi: 10.1076/jcen.25.2.242.13639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gogtay N, et al. Dynamic mapping of human cortical development during childhood through early adulthood. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2004;101:8174–8179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0402680101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Huttenlocher PR. Synaptic density in human frontal cortex—Developmental-changes and effects of aging. Brain Res. 1979;163:195–205. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90349-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Huttenlocher PR. Dendritic and synaptic development in human cerebral cortex: Time course and critical periods. Dev. Neuropsychol. 1999;16:347–349. doi: 10.1207/S15326942DN1603_12. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Raz N, et al. Selective aging of the human cerebral cortex observed in vivo: Differential vulnerability of the prefrontal gray matter. Cereb. Cortex. 1997;7:268–282. doi: 10.1093/cercor/7.3.268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Raz N, et al. Regional brain changes in aging healthy adults: General trends, individual differences and modifiers. Cereb. Cortex. 2005;15:1676–1689. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhi044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sowell ER, Thompson PM, Tessner KD, Toga AW. Mapping continued brain growth and gray matter density reduction in dorsal frontal cortex: Inverse relationships during postadolescent brain maturation. J. Neurosci. 2001;21:8819–8829. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-22-08819.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.West RL. An application of prefrontal cortex function theory to cognitive aging. Psychol. Bull. 1996;120:272–292. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.120.2.272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Salthouse TA. Effects of aging on reasoning. In: Holyoak KJ, Morrison RG, editors. The Cambridge Handbook of Thinking and Reasoning. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2005. pp. 589–605. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Salthouse TA, Atkinson TM, Berish DE. Executive functioning as a potential mediator of age-related cognitive decline in normal adults. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 2003;132:566–594. doi: 10.1037/0096-3445.132.4.566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Salthouse TA, Meinz EJ. Aging, inhibition, working memory, and speed. J. Gerontol. 1995;508:297–306. doi: 10.1093/geronb/50B.6.P297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Garon N, Bryson SE, Smith IM. Executive function in preschoolers: A review using an integrative framework. Psycholol. Bull. 2008;134:31–60. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.134.1.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Anderson P. Assessment and development of executive function (EF) during childhood. Child Neuropsychol. 2002;8(2):71–82. doi: 10.1076/chin.8.2.71.8724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Cragg L, Nation K. Go or nogo? Developmental improvements in the efficiency of response inhibition in mid-childhood. Dev. Sci. 2008;11:819–827. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-7687.2008.00730.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Crone EA, Bunge SA, Van der Molen MW, Ridderinkhof KR. Switching between tasks and responses: A developmental study. Dev. Sci. 2006;9:278–287. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-7687.2006.00490.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zelazo PD, et al. NIH Toolbox Cognition Battery (CB): Validation of executive function measures in adults. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2014;20(6):620. doi: 10.1017/S1355617714000472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Bedard AC, et al. The development of selective inhibitory control across the life span. Dev. Neuropsychol. 2002;21(1):93–111. doi: 10.1207/S15326942DN2101_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bishop DVM, Aamodt-Leeper G, Creswell C, McGurk R, Skuse DH. Individual differences in cognitive planning on the Tower of Hanoi task: Neuropsychological maturity of measurement error? J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry. 2001;42:551–556. doi: 10.1111/1469-7610.00749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gathercole SE, Pickering SJ, Ambridge B, Wearing H. The structure of working memory from 4 to 15 years of age. Dev. Psychol. 2004;40:177–190. doi: 10.1037/0012-1649.40.2.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Van den Wildenberg WPM, van der Molen M. Developmental trends in simple and selective inhibition of compatible and incompatible responses. J. Exp. Child Psychol. 2004;87:201–220. doi: 10.1016/j.jecp.2003.11.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Williams BR, Ponesse JS, Schachar RJ, Logan GD, Tannock R. Development of inhibitory control across the life span. Dev. Psychol. 1999;35:205–213. doi: 10.1037/0012-1649.35.1.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Luna B, Padmanabhan A, O’Hearn K. What has fMRI told us about the development of cognitive control through adolescence? Brain Cogn. 2010;72:101–113. doi: 10.1016/j.bandc.2009.08.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Paus T. Mapping brain maturation and cognitive development during adolescence. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2005;9:60–68. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2004.12.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hartshorne JK, Germine LT. When does cognitive functioning peak? The asynchronous rise and fall of different cognitive abilities across the lifespan. Psychol. Sci. 2015;26:433–443. doi: 10.1177/0956797614567339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ghisletta P, Rabbitt P, Lunn M, Lindenberger U. Two thirds of the age-based changes in fluid and crystallized intelligence, perceptual speed, and memory in adulthood are shared. Intelligence. 2012;40:260–268. doi: 10.1016/j.intell.2012.02.008. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Park DC, et al. Models of visuospatial and verbal memory across the adult life span. Psychol. Aging. 2002;17:299–320. doi: 10.1037/0882-7974.17.2.299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Salthouse TA. Independence of age-related influences on cognitive abilities across the life span. Dev. Psychol. 1998;34:851–864. doi: 10.1037/0012-1649.34.5.851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Salthouse TA. When does age-related decline begin? Neurobiol. Aging. 2009;30:507–514. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2008.09.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Germine LT, Duchaine B, Nakayama K. Where cognitive development and aging meet: Face learning ability peaks after age 30. Cognition. 2011;118:201–210. doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2010.11.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Johnson W, Logie RH, Brockmole JR. Working memory tasks differ in factor structure across age cohorts: Implications for dedifferentiation. Intelligence. 2010;38:513–528. doi: 10.1016/j.intell.2010.06.005. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Logie RH, Maylor EA. An Internet study of prospective memory across adulthood. Psychol. Aging. 2009;24:767–774. doi: 10.1037/a0015479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Murre JMJ, Janssen SMJ, Rouw R, Meeter M. The rise and fall of immediate and delayed memory for verbal and visuospatial information from late childhood to late adulthood. Acta Psychol. 2013;142:96–107. doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2012.10.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Fitzgerald JM, Lawrence R. Autobiographical memory across the life-span. J. Gerontol. 1984;39:692–698. doi: 10.1093/geronj/39.6.692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Nilsson L-G. Memory function in normal aging. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2003;107:7–13. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0404.107.s179.5.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Schroeder DH, Salthouse TA. Age-related effects on cognition between 20 and 50 years of age. Pers. Individ. Differ. 2004;36:393–404. doi: 10.1016/S0191-8869(03)00104-1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Comalli PE, Wapner S, Werner H. Interference effects of Stroop color-word test in childhood, adulthood, and aging. J. Genet. Psychol. 1962;100:47–53. doi: 10.1080/00221325.1962.10533572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Carlozzi NE, Beaumont JL, Tulsky DS, Gershon RC. The NIH toolbox pattern comparison processing speed test: Normative data. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2015;30(5):359–368. doi: 10.1093/arclin/acv031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Weintraub S, et al. The cognition battery of the NIH toolbox for assessment of neurological and behavioral function: Validation in an adult sample. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2014;20(6):567. doi: 10.1017/S1355617714000320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Jacques S, Marcovitch S. Development of executive function across the lifespan. In: Overton WF, editor. Cognition, Biology, and Methods Across the Lifespan. The Handbook of Life-Span Development. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley; 2010. pp. 431–466. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Tulsky DS, et al. NIH toolbox cognition battery (CB): Measuring working memory. Monogr. Soc. Res. Child. Dev. 2013;78(4):70–87. doi: 10.1111/mono.12035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ferriera D, Correia R, Nieto A, Machado A, Molina Y, Barroso J. Cognitive decline before the age of 50 can be detected with sensitive cognitive measures. Psicothema. 2015;27:216–222. doi: 10.7334/psicothema2014.192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Ferriera D, Molina Y, Machado A, Westman E, Wahlund L, Nieto A, Correia R, Junqué C, Diaz L, Barroso J. Cognitive decline is mediated by gray matter changes during middle age. Neurobiol. Aging. 2014;35:1086–1094. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.10.095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Petrican R, Taylor MJ, Grady CL. Trajectories of brain system maturation from childhood to older adulthood: Implications for lifespan cognitive functioning. NeuroImage. 2017;163:125–149. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.09.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Delis DC, Kaplan E, Kramer JH. Delis–Kaplan Executive Function System (D-KEFS) San Antonio, TX: The Psychological Corporation; 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 47.McNab F, et al. Age-related changes in working memory and the ability to ignore distraction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2015;112:6515–6518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1504162112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Zelazo PD, Craik FI, Booth L. Executive function across the life span. Acta psychol. 2004;115(2–3):167–183. doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2003.12.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Jack C, et al. Brain beta-amyloid measures and magnetic resonance imaging atrophy both predict time-to-progression from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer's disease. Brain. 2010;133:3336–3348. doi: 10.1093/brain/awq277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Braver TS, West RL. Working memory, executive processes, and aging. In: Craik FI, Salthouse TL, editors. Handbook of Aging and Cognition. 3. New York, NY: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; 2008. pp. 311–372. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Spieler DH, Balota DA, Faust ME. Stroop performance in healthy younger and older adults and in individuals with dementia of the Alzheimer’s type. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 1996;22:461–479. doi: 10.1037/0096-1523.22.2.461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Davis HP, Klebe KJ. A longitudinal study of the performance of the elderly and young on the Tower of Hanoi puzzle and Rey recall. Brain Cogn. 2001;46:95–99. doi: 10.1016/S0278-2626(01)80043-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Cepeda NJ, Kramer AF, Gonzalez de Sather JCM. Changes in executive control across the life span: Examination of task-switching performance. Dev. Psychol. 2001;37:715–730. doi: 10.1037/0012-1649.37.5.715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Friedman NP, et al. Not all executive functions are related to intelligence. Psychol. Sci. 2006;17:172–179. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9280.2006.01681.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Kray J, Lindenberger U. Adult age differences in task switching. Psychol. Aging. 2000;15:126–147. doi: 10.1037/0882-7974.15.1.126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Lawson GM, Hook CJ, Farah MJ. A meta-analysis of the relationship between socioeconomic status and executive function performance among children. Dev. Sci. 2018;21:E12529. doi: 10.1111/desc.12529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Reimers S, Maylor EA. Task switching across the life span: Effects of age on general and specific switch costs. Dev. Psychol. 2005;41:661–671. doi: 10.1037/0012-1649.41.4.661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Wasylyshyn C, Verhaeghen P, Sliwinski MJ. Aging and task switching: A meta-analysis. Psychol. Aging. 2011;26:15–20. doi: 10.1037/a0020912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Meiran N, Gotler A, Perlman A. Old age is associated with a pattern of relatively intact and relatively impaired task-set switching abilities. J. Gerontol. Ser. B. 2001;56:88–102. doi: 10.1093/geronb/56.2.P88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Gunning-Dixon FM, Raz N. Neuroanatomical correlates of selected executive functions in middle-aged and older adults: A prospective MRI study. Neuropsychologia. 2003;41:1929–1941. doi: 10.1016/S0028-3932(03)00129-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Verhaeghen P. Aging and executive control: Reports of a demise greatly exaggerated. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2011;20:174–180. doi: 10.1177/0963721411408772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Brustio PR, Magistro D, Zecca M, Rabaglietti E, Liubicich ME. Age-related decrements in dual-task performance: Comparison of different mobility and cognitive tasks. A cross sectional study. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0181698. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0181698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Barnes DE, Yaffe K, Satariano WA, Tager IB. A longitudinal study of cardiorespiratory fitness and cognitive function in healthy older adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2003;51:459–465. doi: 10.1046/j.1532-5415.2003.51153.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Brunner EJ. Social and biological determinants of cognitive aging. Neurobiol. Aging. 2005;26:17–20. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2005.09.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Ritchie SJ, et al. Predictors of ageing-related decline across multiple cognitive functions. Intelligence. 2016;59:115–126. doi: 10.1016/j.intell.2016.08.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Salthouse TA. Correlates of cognitive change. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 2014;143:1026–1048. doi: 10.1037/a0034847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Weng PH, et al. The effect of lifestyle on late-life cognitive change under different socioeconomic status. PLoS ONE. 2018;13:e0197676. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0197676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Zaninotto P, Batty GD, Allerhand M, Deary IJ. Cognitive function trajectories and their determinants in older people: 8 years of follow-up in the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing. J. Epidemiol. Community Health. 2018;72:685–694. doi: 10.1136/jech-2017-210116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Farah MJ, et al. Childhood poverty: Specific associations with neurocognitive development. Brain Res. 2006;1110:166–174. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.06.072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Noble KG, McCandliss BD, Farah MJ. Socioeconomic gradients predict individual differences in neurocognitive abilities. Dev. Sci. 2007;10:464–480. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-7687.2007.00600.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Noble KG, Norman MF, Farah MJ. Neurocognitive correlates of socioeconomic status in kindergarten children. Dev. Sci. 2005;8:74–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-7687.2005.00394.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Hackman DA, Gallop R, Evans GW, Farah MJ. Socioeconomic status and executive function: Developmental trajectories and mediation. Dev. Sci. 2015;18:1–17. doi: 10.1111/desc.12246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Lawson GM, Hook CJ, Hackman DA, Farah MJ. Socioeconomic status and neurocognitive development: Executive function. In: Griffin JA, Freund LS, McCardle P, editors. Executive Function in Preschool Children: Integrating Measurement, Neurodevelopment, and Translational Research. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association Press; 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 74.Colom R, Abad FJ, Quiroga MA, Shih PC, Flores-Mendoza C. Working memory and intelligence are highly related constructs, but why? Intelligence. 2008;36:584–606. doi: 10.1016/j.intell.2008.01.002. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Brydges CR, Reid CL, Fox AM, Anderson M. A unitary executive function predicts intelligence in children. Intelligence. 2012;40:458–469. doi: 10.1016/j.intell.2012.05.006. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Arffa S. The relationship of intelligence to executive function and non-executive function measures in a sample of average, above average, and gifted youth. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2007;22:969–978. doi: 10.1016/j.acn.2007.08.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Lee T, Mosing MA, Henry JD, et al. Genetic influences on four measures of executive functions and their covariation with general cognitive ability: The Older Australian Twins Study. Behav. Gen. 2012;42:528. doi: 10.1007/s10519-012-9526-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Davis JC, Marra CA, Najafzadeh M, Lui-Ambrose T. The independent contribution of executive functions to health related quality of life in older women. BMC Geriatr. 2010;10(1):16. doi: 10.1186/1471-2318-10-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Miller HV, Barnes JC, Beaver KM. Self-control and health outcomes in a nationally representative sample. Am. J. Health Behav. 2011;35(1):15–27. doi: 10.5993/AJHB.35.1.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Broidy LM, et al. Developmental trajectories of childhood disruptive behaviours and adolescent delinquency: A six-site cross-national study. Dev. Psychol. 2003;30:222–245. doi: 10.1037/0012-1649.39.2.222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Denson TF, Pederson WC, Friese M, Hahm A, Roberts L. Understanding impulsive aggression: Angry rumination and reduced self-control capacity are mechanisms underlying the provocation–aggression relationship. Pers. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 2011;37(6):850–862. doi: 10.1177/0146167211401420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Bailey CE. Cognitive accuracy and intelligent executive function in the brain and in business. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007;1118(1):122–141. doi: 10.1196/annals.1412.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Miyake A, Friedman NP, Emerson MJ, Witzki AH, Howerter A. The unity and diversity of executive functions and their contributions to complex “frontal lobe” tasks: A latent variable analysis. Cogn. Psychol. 2000;41:49–100. doi: 10.1006/cogp.1999.0734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Huff MJ, Balota DA, Minear M, Aschenbrenner AJ, Duchek JM. Dissociative global and local task-switching costs across younger adults, middle-aged adults, older adults, and very mild Alzheimer's disease individuals. Psychol. Aging. 2015;30:727–739. doi: 10.1037/pag0000057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Verhaeghen P, Cerella J, Bopp KL, Basak C. Aging and varieties of cognitive control: A review of meta-analyses on resistance to interference, coordination, and task switching, and an experimental exploration of age-sensitivity in the newly identified process of focus switching. In: Engle RW, Sedek G, von Hecker U, McIntosh DN, editors. Cognitive Limitations in Aging and Psychopathology. Cambridge: University Press; 2005. pp. 160–189. [Google Scholar]
- 86.Lampert T, Kroll L, Müters S, Stolzenberg H. Measurement of socioeconomic status in the German Health Interview and Examination Survey for Adults (DEGS1) Bundesgesundheitsblatt. 2013;56:631–636. doi: 10.1007/s00103-012-1663-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Wechsler D. Wechsler Abbreviated Scale of Intelligence. San Antonio, TX: The Psychological Corporation; 1999. [Google Scholar]
- 88.Stroop JR. Studies of interference in serial verbal reactions. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 1935;18:643–662. doi: 10.1037/h0054651. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Unsworth N, Heitz R, Schrock J, Engle R. An automated version of the operation span task. Behav. Res. Methods. 2005;37:498–505. doi: 10.3758/BF03192720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Turner M, Engle R. Is working memory capacity task dependent? J. Mem. Lang. 1989;28:127–154. doi: 10.1016/0749-596X(89)90040-5. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Barenberg J, Berse T, Dutke S. Ergometer cycling enhances executive control in task switching. J. Cogn. Psychol. 2015;27:692–703. doi: 10.1080/20445911.2015.1024256. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Rogers R, Monsell S. Costs of a predictable switch between simple cognitive tasks. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 1995;124:207–231. doi: 10.1037/0096-3445.124.2.207. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Kray J, Li KZH, Lindenberger U. Age-related changes in task-switching components: The role of task uncertainty. Brain Cogn. 2002;49:363–381. doi: 10.1006/brcg.2001.1505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Phillips L, Gilhooly K, Logie R, Della Sala S, Wynn V. Age, working memory, and the Tower of London task. Eur. J. Cogn. Psychol. 2003;15:291–312. doi: 10.1080/09541440244000148. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Smith EE, et al. The neural basis of task-switching in working memory: Effects of performance and aging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2001;98:2095–2100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.98.4.2095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Carlson SM, Moses LJ, Claxton LJ. Individual differences in executive functioning and theory of mind: An investigation of inhibitory control and planning ability. J. Exp. Child Psychol. 2004;87(4):299–319. doi: 10.1016/j.jecp.2004.01.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Miyake A, Friedman NP. The nature and organization of individual differences in executive functions: Four general conclusions. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2012;21(1):8–14. doi: 10.1177/0963721411429458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Hill EL, Bird CM. Executive processes in Asperger syndrome: Patterns of performance in a multiple case series. Neuropsychologia. 2006;44:2822–2835. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2006.06.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Testa R, Bennett P, Ponsford J. Factor analysis of nineteen executive function tests in a healthy adult population. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2012;27:213–224. doi: 10.1093/arclin/acr112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Brydges CR, Fox AM, Reid CL, Anderson M. The differentiation of executive functions in middle and late childhood: A longitudinal latent-variable analysis. Intelligence. 2014;47:34–43. doi: 10.1016/j.intell.2014.08.010. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Hill EL. Evaluating the theory of executive dysfunction in autism. Dev. Rev. 2004;24:189–233. doi: 10.1016/j.dr.2004.01.001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Patsenko EG, Altmann EM. How planful is routine behaviour? A selective-attention model of performance in the Tower of Hanoi. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 2010;139:95–116. doi: 10.1037/a0018268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Seidler RD, et al. Motor control and aging: Links to age-related brain structural, functional, and biochemical effects. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2010;34(5):721–733. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2009.10.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Störmer V, Li S-C, Heekeren HR, Lindenberger U. Normal aging delays and compromises early multifocal visual attention during object tracking. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2013;25:188–202. doi: 10.1162/jocn_a_00303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Howard SJ, Johnson J, Pascual-Leone J. Clarifying inhibitory control: Diversity and development of attentional inhibition. Cogn. Dev. 2014;31:1–21. doi: 10.1016/j.cogdev.2014.03.001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Friedman NP. Research on individual differences in executive function: Implications for the bilingual advantage hypothesis. Linguist. Approaches Biling. 2016;6:535–548. doi: 10.1075/lab.15041.fri. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Hester R, Garavan H. Working memory and executive function: The influence of content and load on the control of attention. Mem. Cognit. 2005;33:221–233. doi: 10.3758/BF03195311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Bryan J, Luszcz MA. Measurement of executive function: Considerations for detecting adult age differences. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2000;22:40–55. doi: 10.1076/1380-3395(200002)22:1;1-8;FT040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Grissom NM, Reyes MR. Let’s call the whole thing off: Evaluating gender and sex differences in executive function. Neuropsychopharmacol. Rev. 2019;44:86–96. doi: 10.1038/s41386-018-0179-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Hackman DA, Farah MJ. Socioeconomic status and the developing brain. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2009;13:65–73. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2008.11.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Turrell G, et al. Socioeconomic position across the lifecourse and cognitive function in late middle age. J. Gerontol. 2002;57:S43–S51. doi: 10.1093/geronb/57.1.S43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Goh J, An Y, Resnick SM. Differential trajectories of age-related changes in components of executive and memory processes. Psychol. Aging. 2012;27:707–719. doi: 10.1037/a0026715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Fozard JL, Vercruyssen M, Reynolds SL, Hancock PA, Quilter RE. Age differences and changes in reaction-time: The Baltimore Longitudinal-Study of aging. J. Geront. Ser. B. 1994;49:179–189. doi: 10.1093/geronj/49.4.P179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Colcombe SJ, et al. Cardiovascular fitness, cortical plasticity, and aging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2004;101:3316–3321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400266101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Crescioni AW, et al. High trait self-control predicts positive health behaviours and success in weight lost. J. Health Psychol. 2011;16:750–759. doi: 10.1177/1359105310390247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.ONS. The National Statistics Socio-Economic Classification (NS-SEC) accessed 17 January 2017; https://www.ons.gov.uk/methodology/classificationsandstandards/otherclassifications/thenationalstatisticssocioeconomicclassificationnssecrebasedonsoc2010#understanding-soc2010 (2017).
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.