Abstract
Understanding the processes underlying development and persistence of polarised opinions has been one of the key challenges in social networks for more than two decades. While plausible mechanisms have been suggested, they assume quite specialised interactions between individuals or groups that may only be relevant in particular contexts. We propose that a more broadly relevant explanation might be associated with the influence of external events. An agent-based bounded-confidence model has been used to demonstrate persistent polarisation of opinions within populations exposed to stochastic events (of positive and negative influence) even when all interactions between individuals are noisy and assimilative. Events can have a large impact on the distribution of opinions because their influence acts synchronistically across a large proportion of the population, whereas an individual can only interact with small numbers of other individuals at any particular time.
Subject terms: Complex networks, Computer modelling
Introduction
Social interactions through personal or virtual contact can influence the perceptions, opinions and beliefs of individuals1,2. Theories on social influence, supported to varying degrees by empirical laboratory data, have been incorporated into a range of social influence models drawing on established statistical physics methods3–6. While there have been renewed efforts to review and reconcile alternate models7–13, a unified framework linking robust predictions to alternative assumptions is yet to emerge.
Social influences are usually assimilative (Table 1A), with the opinions of individuals brought closer by factors such as convincing arguments14, the dominance of individuals with more knowledge or status15, or pressure to conform to group norms1. However, it has also been long recognised that differences in opinion can resist assimilative forces and persist over extended periods3. This can be partially explained by the concept of homophily, which describes the preference for communicating with like-minded individuals and a resulting tendency to be more strongly influenced by those individuals2.
Table 1.
Social influence model types, underlying assumptions and emergent behaviours.
| Model type | Underlying assumption | Emergent behaviour | Graphic summary |
|---|---|---|---|
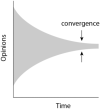
| (A) Assimilative influence | Individuals influence each other towards reducing opinion differences | Opinions converge towards a consensus |
|
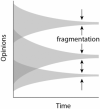
| (B) Bounded assimilative influence | Only individuals with similar opinions influence each other (homophily) | Opinions fragment into two or more converging clusters, all within the initial range of opinions |
|
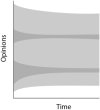
| (C) Noisy bounded assimilative influence | As in B except that opinions also experience random fluctuations due to external influences | Opinion clusters start to form (as in B) before converging towards a broad distribution of opinions (distribution becomes more uniform as noise amplitude increases) |
|
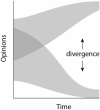
| (D) Differentiative influence | Individuals with very dissimilar opinions can influence each other towards even more dissimilar opinions (xenophobia) | Opinions diverge towards extremes that may fall outside the initial range of opinions |
|
Bounded confidence models explicitly represent the bounds placed on assimilative influence by homophily and successfully predict fragmentation of opinions into clusters (Table 1B). However, this fragmentation cannot be sustained in the presence of random fluctuations (noise) in opinions due to stochastic external factors. Such fluctuations will always be present in any realistic social network and allow opinions to occasionally move inside the homophily influence limit, resulting in a gradual convergence of opinion clusters16 (Table 1C). While large amplitude fluctuations block this convergence, they also tend to promote extreme individualism that prevents clustering. Time-varying clustering can be perpetuated by including a feedback, whereby the amplitude of fluctuations increases with the size of clusters17. However, this desire for individualism may only be applicable to specific issues or circumstances.
One of the most important types of fragmentation is the polarisation of opinion towards more extremist viewpoints. Polarisation has become increasingly problematic over the past decade, driving community conflict around many social and environmental issues18–20, as well as political extremism motivating activism and sometimes even violence21,22. Because extremist views sometimes lie outside the initial range of opinions, they cannot be explained by homophily and bounded confidence alone. This led to the suggestion that influences can be differentative (repulsive), whereby individuals influence each other towards more dissimilar opinions23,24 (Table 1D). However, the empirical evidence for differentative influence is far from conclusive25. An alternative mechanism has been proposed whereby intensifying discussion between like-minded individuals moves their common view towards a more extreme position14, sometimes referred to as bandwagoning or group-shifting26,27. Both mechanisms may well influence highly engaged individuals and lead to polarisation around emotive issues28, particularly when engagement is through social media. However, amongst the broader community, there is limited opportunity for either of these mechanisms to operate effectively23.
Here we propose a potentially more general hypothesis to explain both the perpetuation of opinion clustering and development of extreme opinions. We show that these behaviours tend to emerge when individuals are influenced, not only by other individuals, but also by influential events29,30. This differs fundamentally from suggested random changes in the opinions of individuals31 in that events are capable of influencing many individuals synchronistically over a limited period of time. Synchronicity across a broad community helps promote collective behaviour, potentially resulting in group-shifts towards more extreme viewpoints26.
Methods
The proposed Social Influence and Event Model (SIEM) builds on the Hegselmann-Krause (HK) bounded confidence model4. The HK model4 was selected over the other seminal Deffuant–Weisbuch (DW) model32 (which treats pair-wise interactions sequentially) because of the need to synchonise influences of individuals and events. It represents a network of individuals (or groups) with potential to influence each other’s opinions in relation to a specific issue. Opinions of individuals are continuous (rather than being limited to discrete choices33) and individuals influence each other simultaneously at each timestep. Influence was assumed to be assimilative and could only occur between (randomly) linked individuals whose opinions were not too far from each other (i.e. homophily).
The opinion of individual at timestep is given by:
| 1 |
where is the set of individuals with which interacts (including itself) and is a weighting for the influence of individual on individual (all model variables are also defined in Table 2). For simplicity, an individual’s own opinion has been weighted equally to others. However, egocentric discounting of other opinions34 is implicit in the representation of bounded confidence. The bounded confidence assumption is:
| 2 |
where is usually referred to as the confidence threshold4,10 and is a characteristic of the social network (rather than varying between individuals). The model also included random fluctuations (noise) in the opinions of individuals that allowed opinions to drift and occasionally move inside the confidence threshold of other individuals. In the absence of other influences, these random fluctuations ultimately drive convergence of opinion clusters that may initially form due to homophily16.
Table 2.
Definitions of model variables describing both individual and system characteristics.
| Variable | Definition | Range |
|---|---|---|
| Individual characteristics | ||
| Opinion of individual at timestep | ||
| Weighting for the influence of individual on individual at timestep | ||
| Certainty of individual in their opinion at timestep | ||
| System characteristics | ||
| k | Average number of links per individual (not all influential) | |
| Confidence threshold (defining level of homophily) | ||
| Strength of an event occurring at timestep | ||
| Mean frequency of events (probability of an event within timestep) | ||
| Mean duration of events | ||
| Conflict level at timestep (standard deviation of ) | ||
Traditionally, bounded confidence models have assumed that all individuals are identical in their potential to influence other individuals, such that . Here we relax this assumption by considering the relative ranking of individuals in terms of their ability to influence others, which we specify in terms of the certainty in their opinion35. Certainty recognises differences not only in individual’s experiences, knowledge and access to relevant information35, but also personal characteristics such as persuasiveness, social status, open-mindedness and self-belief1. While model formulations vary, similar quantities are sometimes referred to as the influence strength or confidence of individuals36,37 (not to be confused with the confidence interval which is a property of the entire network system, Table 2). Ranking of certainty is consistent with experimental findings indicating that influential individuals also tend to be less susceptible to the influence of others38. An individual will only change their opinion if their certainty, , is less than the average certainty of other individuals with which they interact at time t. This can be expressed as:
| 3 |
which defaults to when all individuals have equal certainty. While Eq. (3) provides a straight forward extension of the traditional HK model4, an equivalent formulation could be achieved by using the default weighting and expanding Eq. (2) to include certainty-based restrictions on ; or by allowing confidence thresholds to vary across the population5 (i.e. ).
The key innovation in SIEM is representation of external events that can influence opinions. These could be major events, such as political upheavals or natural disasters, or events of more localised significance, such as release of new information or a change in legislation. An event may attract or repulse individuals towards a particular opinion, but either way the event can be considered to be aligned to an opinion (effectively the opinion of the event). Similarly, depending on the size and nature of the event, it will have a characteristic influencing strength (effectively the certainty of the event). This formulation allows model events to influence individuals in a similar way to how individuals influenced each other. Specifically, Eq. (1) was expanded to include the influence of events:
| 4 |
where is the strength of an event occurring at timestep . The weighting for the influence of an event on individual is given by:
| 5 |
where is selected randomly for each individual at every timestep. A random value for the weighting function allows for stochastic variability in the influence of any event across the population. Equation (5) could be made more general by defining independent measures for the effective opinion and effective certainty of events. However, given that they are likely to be highly correlated, both aspects have been represented here by .
Events were applied stochastically in the model with a mean frequency (equal to the probability of an event starting within any timestep) and a mean duration , with individual events allocated randomly within the range . The strength of events also varied stochastically around a mean value with .
Events differed from individuals in two key aspects: (i) events could potentially influence the entire population (within the constraints imposed by Eq. 5), whereas individuals could only interact with a relatively small number of other individuals within any model time-step; and (ii) events occurred stochastically and had limited duration that also varied stochastically, whereas all individuals persisted and interacted throughout the simulation. Point (ii) also distinguishes events from external information acting as a static influencing agent39,40.
The model consisted of a network of 490 individuals, although tests using 14–980 individuals indicated that results are insensitive to population size. The only characteristic used to differentiate individuals was their certainty. 70 individuals were randomly allocated to each of 7 overlapping certainty ranges of equal width (0.0–0.4, 0.1–0.5, 0.2–0.6, 0.3–0.7, 0.4–0.8, 0.5–0.9, 0.6–1.0). This allocation yielded a normal distribution of certainty across the population, with a mean value of 0.50 and a standard deviation of 0.25. The certainty of individuals was varied randomly at each timestep, while also being continuously attracted towards its initial value . This constraint on the range of an individual’s certainty through time reflects its dependence on relatively stable personal characteristics (knowledge, persuasiveness, social status, open-mindedness and self-belief).
At each model timestep, opinions of individuals were influenced according to the opinions and certainties of their linked neighbours (Fig. 1a) by following a decision tree (Fig. 1b):
A new random network was generated with each individual forming a node with the average degree (number of links per node) being k.
Where an individual’s certainty was greater than the average of their linked neighbours, their opinion changed by a random drift that was always small compared to the confidence threshold.
Where an individual’s certainty was less than the average of their linked neighbours, their opinion was replaced by the average of their own opinion and those of all linked neighbours within their confidence threshold ().
The certainty of all individuals was moved closer to their initial value by a random amount and then a small random drift was also applied [0 0.1].
Figure 1.
(a) Conditions under which individuals are influenced; and (b) workflow within each model timestep. Note that homophily is a system characteristic and hence confidence threshold is the same for all individuals, whereas certainty varies between individuals.
When an event occurred (or continued from the previous timestep):
Where an individual’s certainty was greater than the strength of an event or the event fell outside their confidence threshold, the event had no influence on their opinion.
Where an individual’s certainty was less than the strength of an event and the event fell inside their confidence threshold, their opinion moved closer to the event by a random amount .
Results have been described in terms of the development of the distribution of opinions across the population through time. The width of this distribution provides a simple measure of the conflict in the population, which we define here as the standard deviation in population opinions: . Conflict levels reached a statistically steady state within 500 timesteps, after which the long-term mean was stable and repeatable. For example, when runs were repeated 10 times or runtime was extended 10 times, ensemble means always fell within one standard deviation of the mean based on any single run. Means and variances were also insensitive to population sizes for tests ranging from 14 to 980 individuals (i.e. 2.9–200% of the default population).
Results
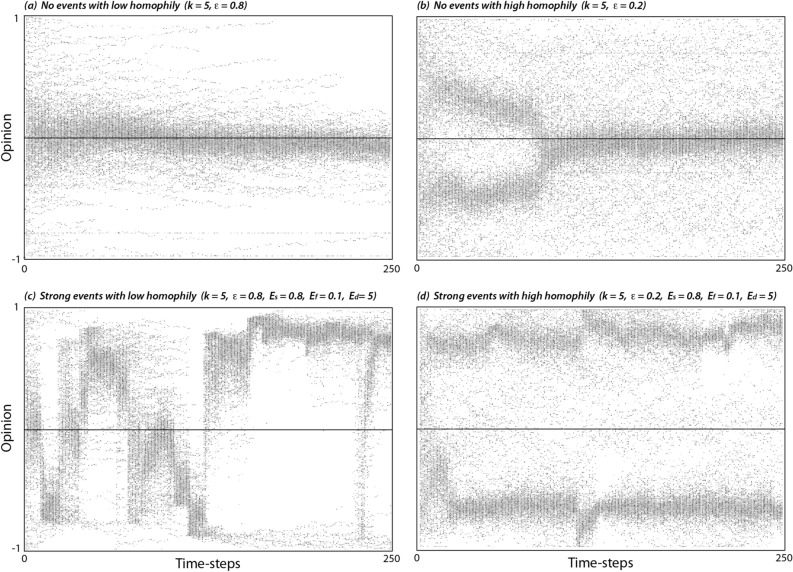
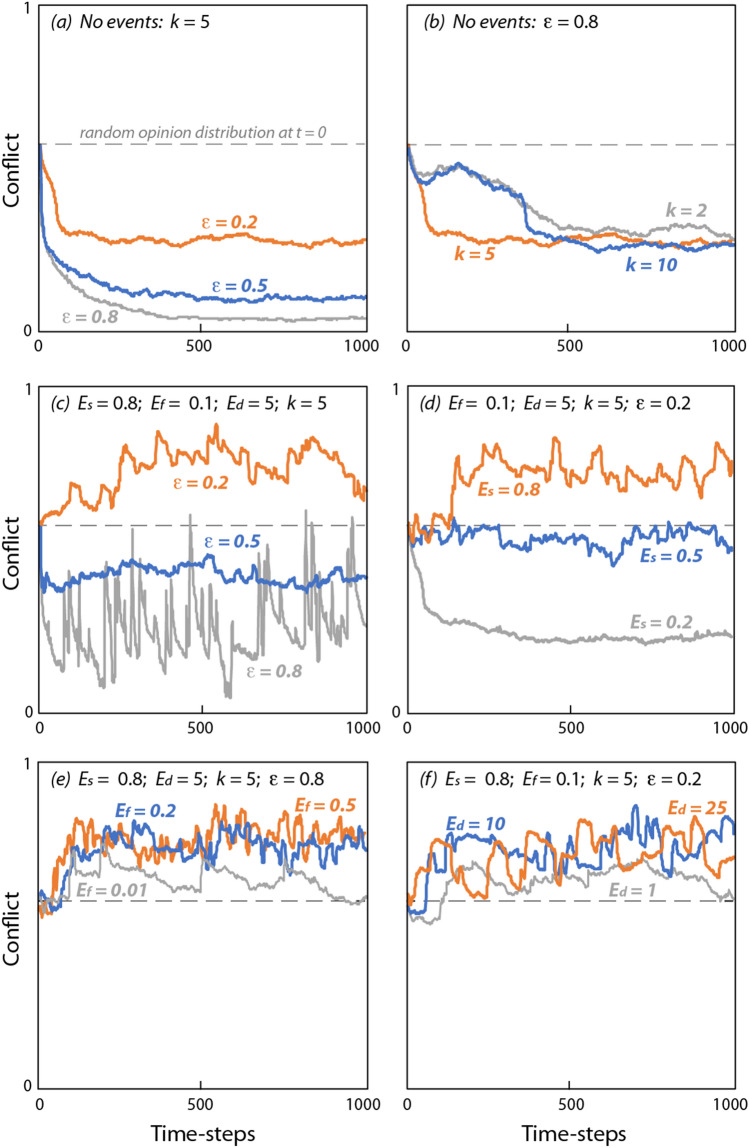
SIEM exhibited the range of behaviours generated by other influence models under differing levels of homophily, including both assimilative influence leading to consensus (Fig. 2a), and bounded assimilative influence leading to initial fragmentation that diminishes over time due to random fluctuations in opinions and certainty (Fig. 2b). These trends were also reflected in conflict levels, which declined rapidly under low homophily, or were temporarily sustained under high homophily before population opinions suddenly converged (Fig. 3a). Because convergence was triggered by random noise in the opinion of individuals, its timing was highly variable (Fig. 3b). Over the long-term, conflict levels increased with homophily (Fig. 3a), whereas the average number of connections per individual had a much smaller effect (Fig. 3b).
Figure 2.
Opinions of individuals starting from a random distribution [− 1 1] under a range of conditions (first 250 timesteps shown).
Figure 3.
Conflict () tracked over 1000 timesteps, starting from a uniform random distribution of opinions (). Shown are dependencies on: (a) confidence threshold when there were no events; (b) average number of connections per individual per timestep when there were no events; (c) confidence interval when there were events; (d) event strength; (e) event frequency; and (f) event duration.
Large stochastic events () generated two types of behaviour dependent on the homophily level. When homophily was low, the opinions of most of the population responded to every event, causing opinions to swing between extremes (Fig. 2c). Associated conflict levels were also highly variable, although the long-term average remained relatively low (Fig. 3c). When homophily was high, opinions diverged and became more extreme (Fig. 2d). Importantly, this polarisation was sustained as long as there were stochastic events. Average conflict levels again scaled with homophily and were sustained at high levels (Fig. 3d). Conflict was only weakly dependent on the frequency (Fig. 3e) and duration (Fig. 3f) of events, with no detectable effect once events became quasi-continuous ().
Data from Fig. 3 is consistent with a linear dependency of long-term average conflict (timesteps 500–1000) on both homophily (Fig. 3c) and event strength (Fig. 3d). Whereas dependencies on event frequency (Fig. 3e) and duration (Fig. 3f) are much weaker and can be described by a simple power law for the dimensionless quantity . These dependencies can be combined into a single empirical relationship:
| 6 |
which is supported by a high level of correlation (r = 0.99, N = 17, p < 0.001, Fig. 4). Because of the challenges associated with quantifying variables such as confidence threshold and event certainty, the values of the coefficients in Eq. (3) are less important than the structure of the relationship. Key aspects of the relationship are: (i) in the absence of events, conflict increases linearly with confidence threshold (while still being limited to relatively low levels); (ii) the effect of events on conflict increases with the product of confidence threshold and event certainty; and (iii) conflict is only weakly dependent on the frequency and duration of events. While completely removing the dependence on (by assuming ) results in only a minor deterioration in the correlation (r = 0.98, N = 17, p < 0.001), its retention ensures a smooth transition from infrequent events of short duration () to no events ().
Figure 4.
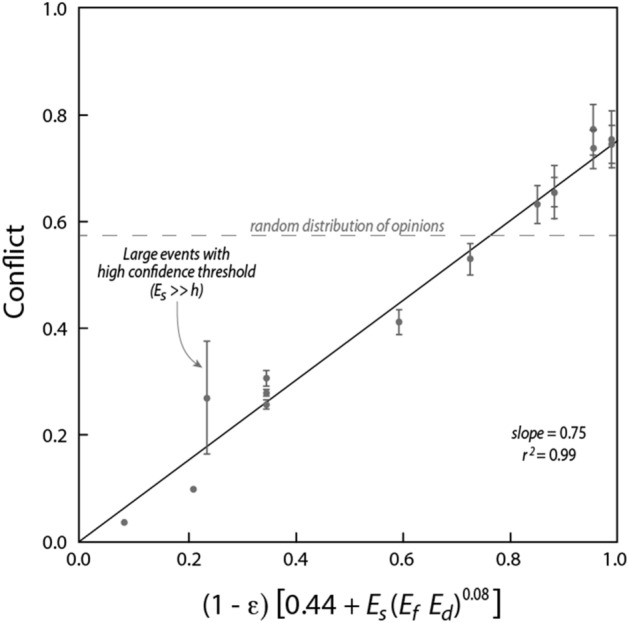
Average population conflict calculated from model results (over the period t = 500–1000 timesteps) plotted against the functional relationship defined by Eq. (6). The correlation was significant (r = 0.99, N = 17, p < 0.001) with a slope of 0.75.
Discussion
Polarisation, including the emergence of views more extreme than initially present, has previously been explained by either differentative (repulsive) interactions, whereby opposing individuals influence each other towards more dissimilar opinions23,24; or by intensifying discussion between like-minded individuals encouraging adoption of more extreme views14. Both mechanisms rely on quite specific forms of interaction that have limited supporting empirical evidence outside of social media25,26,41. In contrast, most contested issues are influenced by events that are external to the individuals themselves30. These can be major events capable of influencing opinions on national or international issues, such as natural disasters, catastrophic accidents, or socio-political upheaval42–44. Alternatively, opinions on local issues may be influenced by smaller events, such as news releases, political decisions, or legal rulings45,46. In the current context, the key characteristic of any event is that it is time-bounded and can influence many individuals synchronistically.
Strong events were found to generate and indefinitely sustain polarised opinions (high conflict) among populations with relatively small confidence thresholds due to homophily (Figs. 2d and 3c). Larger confidence thresholds () resulted in reduced conflict levels, although still well above those where no events were present. Relatively high conflict levels (above a random distribution of population opinions) were maintained even when events were rare () (Fig. 3e,f). Overall, stochastic events were very effective in polarising population opinions and maintaining conflict. The net long-term effect of homophily and stochastic events on conflict in the model were well described by Eq. (6).
Equation (6) is not dependent on the distribution of certainty across individuals and, indeed, mean conflict levels do not change significantly when all individuals are given equal certainty. However, with uniform certainty, distributions of opinions at any time are essentially binary with individuals on each side of the polarisation having near identical opinions. This is clearly less realistic than the more continuous distribution of opinions evident in Fig. 2. Consideration of individual certainty will become even more important as influence models begin to resolve differences in the demographic characteristics and the vested interests of individuals and groups38,47.
The polarising effect of events is partly of concern because some events are not random, but rather are constructed or distorted for financial, political, or ideological reasons. These ‘hoax’ events are often labelled as crises or emergencies by their proponents48 and may be designed to damage individuals or organisations49,50, gain popular support51, divert scrutiny52,53, or justify otherwise unpopular actions54. Our results suggest that conflicts might be perpetuated indefinitely if one or both sides of an issue can orchestrate influential events or otherwise maintain a perception of crisis.
While it is the conceptual and structural aspects of the model that are critical to the current study, the longer-term objective for influence modelling should be its application to real social systems55. This transition will pose significant challenges related to the parameterisation and calibration of the model. Because all aspects of the model are expressed in relative units, relationships such as Eq. (6) are of limited practical use unless key factors, such as the influence threshold of the network and the strength of events, can be calibrated relative to the opinion and certainty scales. If the temporal evolution of opinions is of interest, then the timestep will also need to relate to real time, with frequencies and average durations of events set accordingly (Supplementary Information).
These aspects can be illustrated using the example of effects of extreme weather events in the United States influencing opinions relating to climate change. In 2012, Weather Forecasting Offices across the United States recorded event frequencies () ranging from 0 to 22 per month56. Comparisons of the timing of extreme weather events with climate opinions from national surveys indicate the duration () of a statistically significant influence from these events was only around 0.1 months56,57, implying that 1.2. Being a particularly contentious issue in the United States18, we can safely assume that homophily is relatively high with respect to opinions on climate change (say 0.2). While the size of extreme weather events () in terms of their potential influence on opinions is difficult to estimate from the available data, Eq. (6) suggests that values as low as 0.2 could contribute to conflict levels ( 0.4 compared to 0.26 in the absence of events). This can be compared with the statistical analysis of the national survey responses (130,000 individuals) indicating that the influence on people experiencing the highest rate of extreme events was larger than any demographic effects, although still much smaller than the effects of partisan identification (Republican or Democrat)56. If the size of extreme events continues to increase, the model suggests that their contribution to conflict levels may become more significant. For example, values around 0.5 yield conflict levels around 0.6 (Eq. 6), which is above randomly distributed opinions and indicative of strong polarisation.
While the example above helps demonstrate the potential relevance of social influence models to contested issues such as climate change, more targeted data collection coupled with rigorous calibration procedures may in future provide powerful tools able to test a wide range of strategies aimed at reducing conflict within and across communities.
Supplementary Information
Acknowledgements
C.M.C. is supported by an Australian Government Research Training Program Scholarship and would like to thank Dr Karen Alexander, Dr Katie Cresswell, Professor Fred Gale and Dr Joanna Vince for their advice and guidance. Thanks also Dr Ingrid van Puttin for providing valuable suggestions on the manuscript.
Author contributions
Both authors contributed to the conceptualisation of the model, analysis of outputs and writing of the manuscript. S.A.C. also coded and ran the model.
Data availability
The model output dataset generated during the current study is provided as Supplementary material.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1038/s41598-020-80353-7.
References
- 1.Wood W. Attitude change: Persuasion and social influence. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2000;51:539–570. doi: 10.1146/annurev.psych.51.1.539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.McPherson M, Smith-Lovin L, Cook JM. Birds of a feather: Homophily in social networks. Annu. Rev. Sociol. 2001;27:415–444. doi: 10.1146/annurev.soc.27.1.415. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Axelrod R. The dissemination of culture—A model with local convergence and global polarization. J. Conflict Resolut. 1997;41:203–226. doi: 10.1177/0022002797041002001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hegselmann, R. & Krause, U. Opinion dynamics and bounded confidence: Models, analysis and simulation. Jasss J. Artif. Soc. S5(3), 2. http://jasss.soc.surrey.ac.uk/5/3/2.html (2002).
- 5.Lorenz J. Continuous opinion dynamics under bounded confidence: A survey. Int. J. Mod. Phys. C. 2007;18:1819–1838. doi: 10.1142/S0129183107011789. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Castellano C, Fortunato S, Loreto V. Statistical physics of social dynamics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2009;81:591–646. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.81.591. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Yin XC, Wang HW, Yin P, Zhu HM. Agent-based opinion formation modeling in social network: A perspective of social psychology. Phys. A. 2019 doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2019.121786. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Urena R, Kou G, Dong YC, Chiclana F, Herrera-Viedma E. A review on trust propagation and opinion dynamics in social networks and group decision making frameworks. Inf. Sci. 2019;478:461–475. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2018.11.037. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Anderson BDO, Ye MB. Recent advances in the modelling and analysis of opinion dynamics on influence networks. Int. J. Autom. Comput. 2019;16:129–149. doi: 10.1007/s11633-019-1169-8. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Flache A, et al. Models of social influence: Towards the next frontiers. Jasss J. Artif. Soc. S. 2017 doi: 10.18564/jasss.3521. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Dong YC, Zhan M, Kou G, Ding ZG, Liang HM. A survey on the fusion process in opinion dynamics. Inf. Fusion. 2018;43:57–65. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2017.11.009. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Flache A. Between monoculture and cultural polarization: Agent-based models of the interplay of social influence and cultural diversity. J. Archaeol. Method Theory. 2018;25:996–1023. doi: 10.1007/s10816-018-9391-1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Perc M. The social physics collective. Sci. Rep. U.K. 2019 doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53300-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Mas M, Flache A. Differentiation without distancing. Explaining bi-polarization of opinions without negative influence. PLoS ONE. 2013 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bikhchandani S, Hirshleifer D, Welch I. A theory of fads, fashion, custom, and cultural-change as informational cascades. J. Polit. Econ. 1992;100:992–1026. doi: 10.1086/261849. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Pineda M, Toral R, Hernandez-Garcia E. Noisy continuous-opinion dynamics. J. Stat. Mech. Theory E. 2009 doi: 10.1088/1742-5468/2009/08/P08001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mas M, Flache A, Helbing D. Individualization as driving force of clustering phenomena in humans. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2010 doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Dunlap RE, McCright AM, Yarosh JH. The political divide on climate change: Partisan polarization widens in the US. Environment. 2016;58:4–23. doi: 10.1080/00139157.2016.1208995. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Colvin RM, Witt GB, Lacey J. The social identity approach to understanding socio-political conflict in environmental and natural resources management. Glob. Environ. Change. 2015;34:237–246. doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2015.07.011. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Colvin RM, et al. Learning from the climate change debate to avoid polarisation on negative emissions. Environ. Commun. 2020;14:23–35. doi: 10.1080/17524032.2019.1630463. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kleiner TM. Public opinion polarisation and protest behaviour. Eur. J. Polit. Res. 2018;57:941–962. doi: 10.1111/1475-6765.12260. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ravndal JA. Explaining right-wing terrorism and violence in Western Europe: Grievances, opportunities and polarisation. Eur. J. Polit. Res. 2018;57:845–866. doi: 10.1111/1475-6765.12254. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Baldassarri D, Bearman P. Dynamics of political polarization. Am. Sociol. Rev. 2007;72:784–811. doi: 10.1177/000312240707200507. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Mark NP. Culture and competition: Homophily and distancing explanations for cultural niches. Am. Sociol. Rev. 2003;68:319–345. doi: 10.2307/1519727. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Krizan Z, Baron RS. Group polarization and choice-dilemmas: How important is self-categorization? Eur. J. Soc. Psychol. 2007;37:191–201. doi: 10.1002/ejsp.345. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Johnson NR, Glover M. Individual and Group shifts to extreme—Laboratory experiment on crowd polarization. Sociol. Focus. 1978;11:247–254. doi: 10.1080/00380237.1978.10570322. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hahn U, Hansen JU, Olsson EJ. Truth tracking performance of social networks: How connectivity and clustering can make groups less competent. Synthese. 2020;197:1511–1541. doi: 10.1007/s11229-018-01936-6. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Abramowitz AI, Saunders KL. Is polarization a myth? J. Polit. 2008;70:542–555. doi: 10.1017/S0022381608080493. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Berelson B. Events as an influence upon public opinion. J. Quart. 1949;26:145–148. doi: 10.1177/107769904902600202. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Atkeson, L. R. & Maestas, C. D. Extraordinary events and public opinion. Catastrophic Politics: How Extraordinary Events Redefine Perceptions of Government, 1-+. 10.1017/Cbo9781139108560 (2012).
- 31.Kurahashi-Nakamura T, Mas M, Lorenz J. Robust clustering in generalized bounded confidence models. Jasss J. Artif. Soc. S. 2016 doi: 10.18564/jasss.3220. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Deffuant G, Neau D, Amblard F, Weisbuch G. Mixing beliefs among interacting agents. Appl. Simul. Soc. Sci. 2000 doi: 10.1142/S0219525900000078. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sznajd-Weron K, Sznajd J. Opinion evolution in closed community. Int. J. Mod. Phys. C. 2000;11:1157–1165. doi: 10.1142/S0129183100000936. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Yaniv I, Kleinberger E. Advice taking in decision making: Egocentric discounting and reputation formation. Organ. Behav. Hum. Dec. 2000;83:260–281. doi: 10.1006/obhd.2000.2909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Tormala ZL. The role of certainty (and uncertainty) in attitudes and persuasion. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 2016;10:6–11. doi: 10.1016/j.copsyc.2015.10.017. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sobkowicz P. Effect of Leader's strategy on opinion formation in networked societies with local interactions. Int. J. Mod. Phys. C. 2010;21:839–852. doi: 10.1142/S0129183110015518. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Moussaid M, Kammer JE, Analytis PP, Neth H. Social influence and the collective dynamics of opinion formation. PLoS ONE. 2013 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Aral S, Walker D. Identifying influential and susceptible members of social networks. Science. 2012;337:337–341. doi: 10.1126/science.1215842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Sirbu A, Loreto V, Servedio VDP, Tria F. Opinion dynamics with disagreement and modulated information. J. Stat. Phys. 2013;151:218–237. doi: 10.1007/s10955-013-0724-x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Peres LR, Fontanari JF. The mass media destabilizes the cultural homogenous regime in Axelrod's model. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 2010 doi: 10.1088/1751-8113/43/5/055003. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Baumann F, Lorenz-Spreen P, Sokolov IM, Starnini M. Modeling echo chambers and polarization dynamics in social networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.124.048301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Xu JP, Wang ZQ, Shen F, Ouyang C, Tu Y. Natural disasters and social conflict: A systematic literature review. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2016;17:38–48. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdrr.2016.04.001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Bytzek E. Questioning the obvious: Political events and public opinion on the government's standing in Germany 1977–2003. Int. J. Public Opin. R. 2011;23:406–436. doi: 10.1093/ijpor/edr016. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Bishop BH. Focusing events and public opinion: Evidence from the deepwater horizon disaster. Polit. Behav. 2014;36:1–22. doi: 10.1007/s11109-013-9223-7. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Cullen-Knox C, Fleming A, Lester L, Ogier E. Publicised scrutiny and mediatised environmental conflict: The case of Tasmanian salmon aquaculture. Mar. Policy. 2019;100:307–315. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2018.11.040. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Paolino P. Surprising events and surprising opinions: The importance of attitude strength and source credibility. J. Conflict Resolut. 2017;61:1795–1815. doi: 10.1177/0022002715616167. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Hegselmann R, Krause U. Opinion dynamics under the influence of radical groups, charismatic leaders, and other constant signals: A simple unifying model. Netw. Heterog. Med. 2015;10:477–509. doi: 10.3934/nhm.2015.10.477. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Spector B. Constructing crisis: Leaders, crises, and claims of urgency. Constr. Crisis Lead. Crises Claims Urgency. 2019 doi: 10.1017/9781108551663. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Veil SR, Sellnow TL, Petrun EL. Hoaxes and the paradoxical challenges of restoring legitimacy: Dominos' response to its YouTube crisis. Manag. Commun. Q. 2012;26:322–345. doi: 10.1177/0893318911426685. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Park K, Rim H. Social media hoaxes, political ideology, and the role of issue confidence. Telemat. Inform. 2019;36:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.tele.2018.11.001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Bykov IA, Kuzmin A. Sociology of political support in Russia: The Ukraine crisis, putin and the dynamics of public opinion. Pertanika J. Soc. Sci. 2017;25:1689–1701. [Google Scholar]
- 52.Ismail NBM, Pagulayan IMA, Francia CMA, Pang A. Communicating in the post-truth era: Analyses of crisis response strategies of Presidents Donald Trump and Rodrigo Duterte. J. Public Aff. 2019 doi: 10.1002/pa.1883. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Knill C, Steinebach Y, Fernndez-i-Marn X. Hypocrisy as a crisis response? Assessing changes in talk, decisions, and actions of the European Commission in EU environmental policy. Public Admin. 2020;98:363–377. doi: 10.1111/padm.12542. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Peevers C. The Politics of Justifying Force: The Suez Crisis, the Iraq War, and International Law. 1. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2013. [Google Scholar]
- 55.Sobkowicz, P. Modelling opinion formation with physics tools: Call for closer link with reality. Jasss J. Artif. Soc. S12(1), 11. http://jasss.soc.surrey.ac.uk/12/1/11.html (2009).
- 56.Konisky DM, Hughes L, Kaylor CH. Extreme weather events and climate change concern. Clim. Change. 2016;134:533–547. doi: 10.1007/s10584-015-1555-3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Egan PJ, Mullin M. Turning personal experience into political attitudes: The effect of local weather on Americans' perceptions about global warming. J. Polit. 2012;74:796–809. doi: 10.1017/S0022381612000448. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The model output dataset generated during the current study is provided as Supplementary material.