Abstract
Cilia of higher animals sense various environmental stimuli. Proper ciliary signaling requires appropriate extent of BBSome‐mediated export of membrane receptors across ciliary barrier transition zone (TZ) through retrograde intraflagellar transport (IFT) machinery. How the barrier passage is controlled, however, remains unknown. Here, we show that small GTPase Rabl2 functions as a molecular switch for the outward TZ passage. Rabl2‐GTP enters cilia by binding to IFT‐B complex. Its GTP hydrolysis enables the outward TZ passage of the BBSome and its cargos with retrograde IFT machinery, whereas its persistent association leads to their shedding from IFT‐B during the passing process and consequently ciliary retention. Rabl2 deficiency or expression of a GTP‐locked mutant impairs the ciliary hedgehog signaling without interfering with ciliation and respectively results in different spectrums of mouse developmental disorders. We propose that the switch role of Rabl2 ensures proper turnover of the BBSome and ciliary membrane receptors to fine‐tune cilia‐dependent signaling for normal embryonic development and organismic homeostasis.
Keywords: BBSome, ciliary signaling, intraflagellar transport, small GTPase, transition zone
Subject Categories: Cell Adhesion, Polarity & Cytoskeleton; Development & Differentiation; Membrane & Intracellular Transport
Small GTPase Rabl2 regulates ciliary signaling, but not ciliogenesis, by gating the exit of membrane receptors through the ciliary transition zone.

Introduction
Cilia function as antennae to detect a wide variety of environmental stimuli including light, odorants, and biological ligands and transduce the signals into the cell bodies to trigger cellular and organismic responses. Accordingly, many transmembrane receptors, including approximately two dozens of G protein‐coupled receptors (GPCRs), have been reported to reside in cilia, and ciliary signaling is critical for embryonic development and organism sense such as vision, olfaction, and appetite (Berbari et al, 2009; Goetz & Anderson, 2010; Hilgendorf et al, 2016; Siljee et al, 2018). For instance, two ciliary GPCRs, Smoothened (Smo) and Gpr161, function in the hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway critical for vertebrate embryonic development and homeostasis (Briscoe & Therond, 2013; Bangs & Anderson, 2017; Kong et al, 2019). Mammalian Hh pathway operates mainly by controlling Gli1 expression through two paralogous transcriptional regulators, Gli2/3 (Hui et al, 1994; Hui & Angers, 2011; Niewiadomski et al, 2019). In the absence of Hh, ciliary Gpr161 mainly promotes the partial proteolytic processing of Gli3 into transcription repressor (Gli3‐R). In the presence of Hh, the ligand binds to its membrane receptor Patched, resulting in ciliary entry of Smo and the retrieval of ciliary Patched and Gpr161 to enhance Gli activator (Gli‐A, mainly Gli2‐A) production at the ciliary tip. Gli‐A then enters the nucleus to activate Gli1 expression. Gli1 expressed to high levels thereby activates its downstream genes to eventually trigger cellular responses (Briscoe & Therond, 2013; Mukhopadhyay et al, 2013; Pal et al, 2016; Bangs & Anderson, 2017; Kong et al, 2019). Defects in Hh signaling lead to developmental disorders including midgestation lethality, defective neural patterning and neural tube closure, and polydactyly (Hui & Joyner, 1993; Goetz & Anderson, 2010; Briscoe & Therond, 2013; Bangs & Anderson, 2017; Hwang et al, 2018).
Proper turnover of ciliary signaling components, including membrane receptors, is physiologically important. As the ciliary base contains diffusion barriers such as the transition zone (TZ), a train‐like intraflagellar transport (IFT) machinery powered by molecular motors associated with their accessory complexes IFT‐A and IFT‐B, is responsible for shuttling many ciliary components into and out of cilia (Nakayama & Katoh, 2018). Although membrane proteins can enter cilia by diffusion, their removal depends on retrograde IFT, in which BBSome, an octameric protein complex formed by Bardet–Biedl syndrome (BBS) proteins Bbs1, ‐2, ‐4, ‐5, ‐7, ‐8, ‐9, and ‐18, functions as an adaptor between the GPCRs and IFT‐B (Ye et al, 2013; Milenkovic et al, 2015; Mourao et al, 2016; Nachury, 2018; Ye et al, 2018). Disruption of the BBS proteins leads to ciliary accumulation of membrane receptors, abnormal signal transduction, and ciliopathy (Nishimura et al, 2004; Seo et al, 2011; Tadenev et al, 2011; Zhang et al, 2013). Interestingly, recent single‐molecule studies reveal that significant fractions of GPCRs are recycled back after reaching TZ through retrograde IFT (Nachury, 2018; Ye et al, 2018). How the fate of recycle or removal is regulated and its physiological importance, however, remain unclear.
The Rab family of small GTPases functions as a molecular switch in membrane trafficking by cycling between the GTP‐bound active and the GDP‐bound inactive states (Stenmark, 2009). Rabl2 is a Rab‐like small GTPase lacking membrane association property (Kanie et al, 2017; Blacque et al, 2018). Human cells possess two highly homologous and redundant paralogues, RABL2A and RABL2B. Depletion of both paralogues in RPE1 cells impairs ciliogenesis (Kanie et al, 2017). In the small portion of RABL2‐deficient RPE1 cells still forming cilia, 20–30% of the IFT‐B particles relative to those in wild‐type cilia are detected (Kanie et al, 2017). RABL2 is capable of self‐activation into GTP‐binding form, and RABL2‐GTP is proposed to stay at the ciliary base to capture IFT‐B and trigger the ciliary entry of IFT‐B, followed by its rapid inactivation through GTP hydrolysis (Kanie et al, 2017). Although exogenously expressed RABL2BQ80L, a GTP‐locked mutant, displays ciliary shaft localization, this has been attributed to artifact of the mutant (Kanie et al, 2017). Accordingly, its overexpression‐induced ciliary accumulations of BBS4, GPR161, and serotonin receptor 6 (HTR6) are attributed to their enhanced ciliary entry (Kanie et al, 2017; Nishijima et al, 2017; Dateyama et al, 2019). There is only one murine Rabl2, whose deficiency results in BBS‐like phenotypes polydactyly and retina degeneration (Kanie et al, 2017).
In this study, we show that Rabl2 is dispensable for IFT‐B entry and ciliation in mice but enters cilia to function as a molecular switch to control the BBSome‐mediated outward TZ passage for proper ciliary signaling.
Results
Rabl2‐deficient mice display ciliopathy‐like phenotypes but normal ciliation
We independently identified Rabl2 as a cilium‐related gene from our cDNA array analysis using mouse tracheal epithelial cells (mTECs) cultured at an air‐liquid interface (ALI) to induce multiciliogenesis (Xu et al, 2015) and confirmed the upregulation of Rabl2 during the multicilia formation (Fig 1A). Consistently, Rabl2 was highly expressed in cilia‐enriched tissues such as the trachea, lung, oviduct, and testis (Fig 1B).
Figure 1. Murine Rabl2 is dispensable for ciliogenesis.
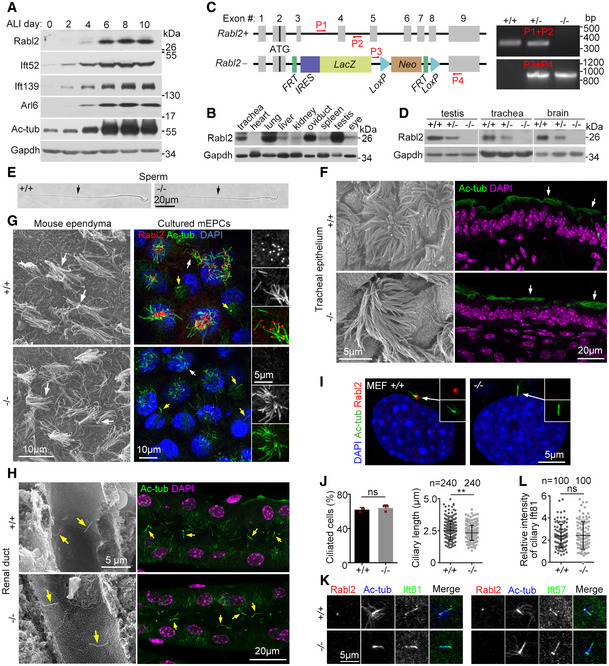
-
AUpregulation of Rabl2 during multiciliogenesis. Cultured mTECs were induced to undergo multicilia formation by growing at an air–liquid interface (ALI) for the indicated time and subjected to immunoblotting. Ift52, Ift139, Arl6, and acetylated tubulin (Ac‐tub) served as ciliary markers. Gapdh served as the loading control.
-
BRabl2 levels in different tissues from 8‐week‐old mice.
-
CRabl2 knockout strategy and representative genotyping PCR results using the indicated primers (P1–P4). FRT, flippase recognition target; LacZ, β‐galactosidase gene; Neo, neomycin‐resistant gene; IRES, internal ribosome entry site; LoxP, Cre recombinase recognition site.
-
DComplete depletion of Rabl2 in tissues (from 8‐week‐old mice) upon its gene knockout.
-
E–HNormal ciliary formation in representative bright‐field (E), scanning electron (F, G, H), or immunofluorescent (F, G, H) micrographs of the indicated tissues (from 8‐week‐old mice) or cells. Cultured mEPCs were fixed at day 7 post‐serum starvation. Ac‐tub served as ciliary marker. DAPI labeled nuclear DNA. Typical cilia or flagella are indicated by arrows, in which yellow arrows denote primary cilia.
-
I, JNormal ciliary formation of Rabl2 −/− MEFs. MEFs derived from E12.5 mouse embryos were serum‐starved for 48 h to induce primary cilia (I). Statistical results (J) were from three independent experiments. Ciliogenesis of at least 200 cells was scored in each experiment and condition. Ciliary lengths of 80 cells were measured in each experiment and condition, and the results of the same genotypes were pooled together.
-
K, LRabl2 deficiency did not repress ciliary localization of IFT‐B. Ciliated MEFs were immunostained for Ift81 and Ift57, two IFT‐B subunits (K; see Fig 4F for diagram of IFT‐B). Relative intensity of ciliary Ift81 (L), presented in arbitrary unit, was obtained by normalizing to that of corresponding Ac‐tub. Four MEF strains prepared, respectively, from two embryos per genotype were used for quantification. 50 cilia were quantified from each MEF strain, and results of the same genotypes were pooled together.
Data information: Statistical results are presented as mean ± s.d. Student's t‐test: ns, no significance; **P < 0.01.
Source data are available online for this figure.
We used the same knockout mouse line as Kanie and colleagues did (Kanie et al, 2017) and confirmed that Rabl2 was downregulated in Rabl2 +/− mice and undetectable in Rabl2 −/− mice (Fig 1C and D). Similarly, the Rabl2 −/− mice were born at the expected Mendelian ratio of genotypes, with 57% of them (n = 151) displaying polydactyly with the preaxial duplication of digit 1 in one or both sides of the hind limbs, and underwent retinal degeneration (Fig EV1A–D) (Kanie et al, 2017). Furthermore, we found that Rabl2 −/− male mice displayed infertility and defective sperm motility; they also outweighed their wild‐type littermates from after 2 months of age (Fig EV1E–G).
Figure EV1. Rabl2 null mice display ciliopathy‐like phenotypes (related to Fig 1).
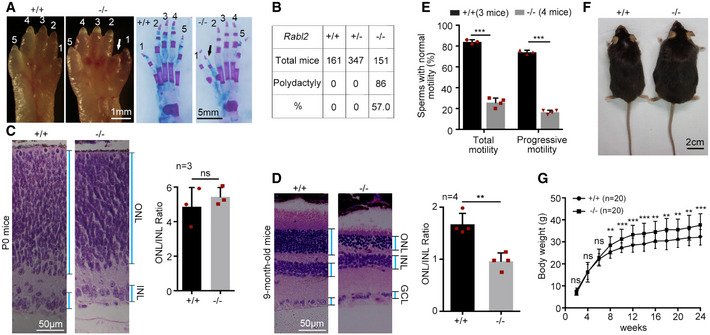
-
A, BRabl2 −/− neonatal mice manifested polydactyly. Unstained (left) and alcian blue‐stained (right) hind limbs (A) reveal preaxial duplication of digit 1 (arrow) in hind limbs of Rabl2 −/− P0 mice. Mice with polydactyly at one (n = 62) or both sides (n = 24) of hind limbs were scored (B).
-
C, DRabl2 −/− mice suffered from retina degeneration. Typical H&E stained retina sections from P0 (C) or 9‐month‐old (D) littermates are presented. ONL, outer nuclear layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer.
-
ERabl2 −/− male mice produced sperms with defective motility. Sperms from 2‐month‐old male mice were used for motility assays.
-
F, GMale Rabl2 −/− mice were obese as compared to their wildtype littermates. A typical pair of 6‐month‐old littermates are shown in (F). Growth curves are shown in (G).
Data information: Pooled data are presented as mean ± s.d. Student's t‐test: ns, no significance; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.
Source data are available online for this figure.
In sharp contrast to RABL2 (Kanie et al, 2017; Nishijima et al, 2017; Dateyama et al, 2019), however, Rabl2 deficiency did not impact formations and morphologies of both monocilium and multicilia in tissues or cultured mouse ependymal cells (mEPCs) and mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs; Fig 1E–J). Cilia length appeared to be slightly reduced when measured with MEFs (2.3 ± 0.6 μm vs. 2.5 ± 0.7 μm in wild‐type MEFs; Fig 1J). Consistent with previous reports (Kanie et al, 2017; Nishijima et al, 2017; Dateyama et al, 2019), Rabl2 was enriched at the distal appendage (or transition fiber) of the basal body in primary cilia. The same localization was observed in multicilia as well (Figs 1G and I, and EV2).
Figure EV2. Rabl2 is enriched at distal appendages in both primary and motile cilia (related to Fig 1).
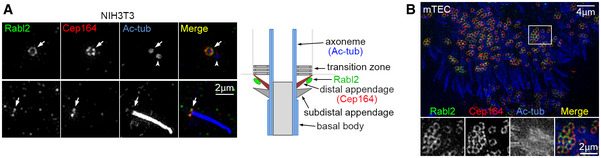
- Super‐resolution images of primary cilia. NIH3T3 cells serum‐starved for 48 h to induce primary cilia were immunostained and imaged through Three Dimensional Structured Illumination Microscopy (3D‐SIM). Cep164 served as marker for distal appendages (or transition fibers) (Yang et al, 2015). Acetylated tubulin (Ac‐tub) labeled the axoneme (bottom panel) or centrioles (top panel). The arrows and arrowheads indicate positions of mother centrioles and the daughter centriole, respectively. The diagram illustrates ciliary structure and localization of Rabl2.
- 3D‐SIM images of motile multicilia. mTECs were cultured at an air‐liquid interface (ALI) to induce multicilia formation. The framed region was magnified to show details.
Ciliogenesis is highly dependent on IFT‐B‐mediated anterograde IFT (Ishikawa & Marshall, 2011; Nakayama & Katoh, 2018). Although human RABL2 has been proposed to be critical for IFT‐B entry into cilia (Kanie et al, 2017; Nishijima et al, 2017), the normal ciliation of Rabl2 −/− cells (Fig 1E–J) suggested that murine Rabl2 was dispensable for the anterograde IFT. Indeed, IFT‐B components Ift81 and Ift57 displayed normal distributions in the Rabl2‐deficient MEFs (Fig 1K and L).
Rabl2 is a regulator of Hh signaling
As the polydactyly phenotype of the Rabl2 −/− mice (Fig 1A and B) (Kanie et al, 2017) strongly suggests defects in Hh signaling (Hui & Joyner, 1993; Briscoe & Therond, 2013; Bangs & Anderson, 2017; Tickle & Towers, 2017), we performed detailed analyses. When ciliated MEFs were treated with the Smo agonist SAG (Chen et al, 2002), Smo became similarly accumulated in the ciliary shaft in both Rabl2 +/+ and Rabl2 −/− MEFs (Fig 2A). The SAG‐induced accumulation of Gli2 at the ciliary tip (Santos & Reiter, 2014), however, decreased by 2.3‐fold in the Rabl2 −/− MEFs (Fig 2B), suggesting reduced formation of the Gli2 activator (Kong et al, 2019). Consistently, the upregulation of Gli1 was markedly reduced in the Rabl2 −/− MEFs as compared to the Rabl2 +/+ or Rabl2 +/− MEFs (Fig 2C). These results indicate attenuated Hh signaling (Kong et al, 2019) in the Rabl2 −/− cells.
Figure 2. Rabl2 deficiency attenuates Hh signaling.
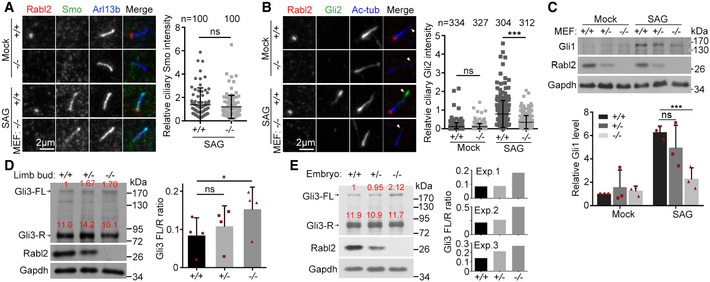
-
ANormal SAG‐induced ciliary accumulation of Smo. MEFs serum‐starved for 24 h were treated with DMSO (mock) or 100 nM SAG for an additional 24 h. Arl13b served as ciliary marker. We also examined Gpr161 but failed to observe specific immunofluorescent signals, though the antibody, prepared by using human GPR161, and recognized ciliary GPR161 well in human RPE1 cells (see Fig 3E). Quantification results were pooled from four MEF strains derived from two Rabl2 +/+ and two Rabl2 −/− embryos.
-
BReduced Gli2 accumulation at the ciliary tip. MEFs were treated as in (A). Ac‐tub served as ciliary marker. Arrowheads indicate ciliary tips. Quantification results were pooled from three independent experiments, each using MEFs from different embryos. At least 100 cells were scored in each experiment and condition.
-
CReduced Gli1 expression. MEFs treated as in (A) were lysed for immunoblotting. Gapdh served as the loading control. For quantification, three independent experiments were performed, each using MEFs from different embryos.
-
D, EIncreased Gli3 FL/R ratios in E11.5 hind limb buds and E10.5 mouse embryos. Relative band intensities of the full‐length (FL) and the repressor (R) forms of Gli3 were quantified (red). FL/R ratios were from four different sets of limb bud preparations (D) and three different sets of embryo preparations (E).
Data information: Quantification results are presented as mean ± s.d. Student's t‐test: ns, no significance; ***P < 0.001.
Source data are available online for this figure.
As the production of the Gli3 repressor (Gli3‐R) is critical for the limb formation (Wang et al, 2000; Tickle & Towers, 2017), we examined whether its levels were altered in the limb bud of Rabl2 −/− mouse embryos. We isolated hind limb bud tissues from E11.5 mouse embryos and examined the Gli3R levels relative to those of full‐length Gli3 (Gli3‐FL) by immunoblotting. The Gli3 FL/R ratio increased in the Rabl2 −/− limb bud as compared to the Rabl2 +/+ or Rabl2 +/− limb buds (Fig 2D), suggesting reduced production of Gli3‐R. Similar results were obtained using whole E10.5 embryos (Fig 2E).
GTP‐locked mutant Rabl2Q80L enters ciliary shaft to repress the retrieval of GPR161 and SMO
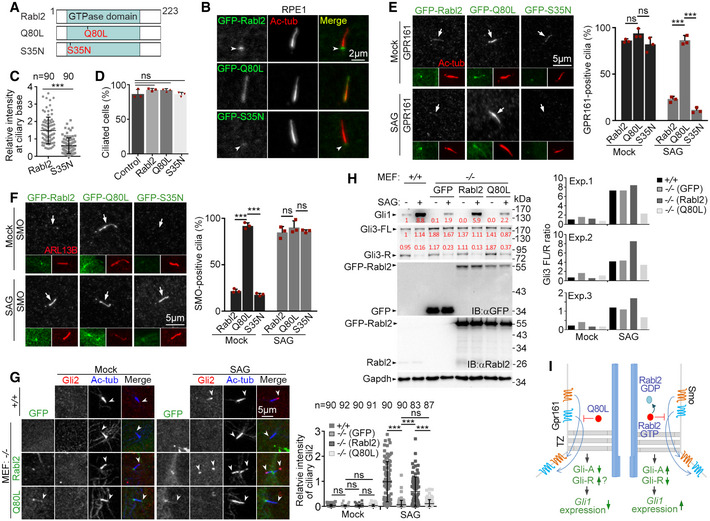
To verify whether Rabl2 regulated Hh signaling by influencing the turnover of its ciliary GPCRs, we created a GTP‐locked mutant Rabl2Q80L and a GDP‐locked mutant Rabl2S35N and overexpressed them in human RPE1 cells for a better comparison with previous publications (Fig 3A) (Kanie et al, 2017; Nishijima et al, 2017; Dateyama et al, 2019). Compared with RABL2BS35N (Nishijima et al, 2017; Dateyama et al, 2019), Rabl2S35N displayed similar weak ciliary base localization but did not significantly repress ciliogenesis (Fig 3B–D). Similar to RABL2BQ80L (Kanie et al, 2017; Dateyama et al, 2019), Rabl2Q80L also displayed ciliary shaft localization and enhanced the ciliary localization of GPR161 (Fig 3B and E). When the ciliary export of GPR161 upon the activation of Hh signaling was examined by treating the cells with SAG (Mukhopadhyay et al, 2013; Pal et al, 2016), the ciliary GPR161 was completely removed in the cells expressing GFP‐Rabl2 or GFP‐Rabl2S35N but persisted in those expressing GFP‐Rabl2Q80L (Fig 3E).
Figure 3. Ciliary Rabl2Q80L inhibits the export of SMO and GPR161 to repress Hh signaling.
-
ADiagrams of mouse Rabl2 and its GTP (Q80L)‐ or GDP (S35N)‐locked mutants.
-
BSubcellular localization of Rabl2 and mutants. RPE1 cells infected with adenovirus to express the GFP‐tagged proteins were serum‐starved for 48 h to induce ciliogenesis. Ac‐tub served as ciliary marker. Arrowheads indicate ciliary base. The cells were used for quantifications in (C) and (D).
-
CReduced ciliary base localization of GFP‐Rabl2S35N as compared to GFP‐Rabl2. Results from three independent experiments (n = 30 for each experiment and condition) were pooled together.
-
DGFP‐tagged Rabl2 and its mutants did not significantly affect ciliogenesis upon overexpression as compared to uninfected control cells. At least 104 cells were scored in each experiment and condition.
-
ERabl2Q80L retained ciliary GPR161 after SAG stimulation. RPE1 cells infected as in (B) were serum‐starved for 24 h, followed by DMSO (mock) or SAG treatment for 24 h. Arrows indicate cilia that are displayed in insets. At least 100 cilia were scored in each experiment and condition.
-
FRabl2Q80L led to SAG‐independent accumulation of ciliary Smoothened (SMO). RPE1 cells were treated as in (E). ARL13B served as ciliary marker. The white arrows point to positions of cilia. At least 100 cilia were scored in each experiment and condition.
-
G, HRabl2Q80L inhibited Hh signaling. MEFs from Rabl2 −/− E12.5 embryos infected with lentivirus to express GFP, GFP‐Rabl2, or GFP‐Rabl2Q80L were serum‐starved for 24 h and treated with DMSO (mock) or 100 nM SAG for an additional 24 h. Uninfected MEFs from the wild‐type littermate embryos served as the positive control. The samples were immunostained to examine ciliary Gli2 (G) or immunoblotted to examine levels of Gli1 and Gli3 (H). The white arrowheads (G) point to ciliary tips. Quantification results were from three independent experiments, each using MEFs from different Rabl2‐deficient embryos. Gli2 intensities, presented in arbitrary unit, were measured from at least 22 cilia in each experiment and condition and pooled together. In the samples for immunoblotting (H), GFP‐positive cells occupied 82.3% (GFP), 87.3% (GFP‐Rabl2), and 81.2% (GFP‐Rabl2Q80L), respectively, when 260 cells in each sample were scored. Relative band intensities are shown in red.
-
IA model summarizing the results in Fig 3 (left half) and speculating a switch role of endogenous Rabl2 for ciliary GPCR export and signaling, taking the Hh signaling as an example (right half). The GTP‐locked Q80L mutant represses the export of ciliary Gpr161 and Smo, leading to reduced Gli‐A and possibly increased Gli‐R formations and accordingly attenuated Gli1 expression. Endogenous ciliary Rabl2‐GTP would similarly repress the export of Gpr161 and Smo until it was converted to GDP‐binding form through GTP hydrolysis. Proper regulation of the GTP hydrolysis would therefore facilitate proper Hh signaling.
Data information: Quantification results are presented as mean ± s.d. Student's t‐test: ns, no significance; ***P < 0.001.
Source data are available online for this figure.
To clarify whether the ciliary retention of GPR161 after the SAG treatment (Fig 3E) was due to excessive ciliary entry through the elevated anterograde IFT (Kanie et al, 2017; Dateyama et al, 2019) or reduced ciliary exit, we examined SMO, which enters cilia at low levels through diffusion, i.e., independently of the anterograde IFT, in the absence of HH signaling (Ye et al, 2013; Milenkovic et al, 2015). We observed that SMO strongly localized in the ciliary shaft of GFP‐Rabl2Q80L‐expressing RPE1 cells even without SAG treatment (Fig 3F). By sharp contrast, in RPE1 cells expressing GFP‐tagged Rabl2 or Rabl2S35N, ciliary SMO emerged only after the SAG treatment (Fig 3F). These results strongly suggest that the presence of Rabl2Q80L in the ciliary shaft represses the retrieval of ciliary GPCRs.
Ciliary Rabl2Q80L‐caused inhibition of GPCR export impairs Hh signaling
As proper turnover of ciliary Gpr161 and Smo is critical for Hh signaling (Bangs & Anderson, 2017; Kong et al, 2019), we speculated that their abnormal accumulations in cells expressing Rabl2Q80L (Fig 3E and F) would impair the Gli‐FL production and Gli1 expression. To verify this, we infected Rabl2 −/− MEFs with lentivirus to express GFP, GFP‐Rabl2, or GFP‐Rabl2Q80L and treated the cells with SAG after inducing ciliogenesis. In contrast to GFP, GFP‐Rabl2 restored the SAG‐induced ciliary tip‐accumulation of Gli2 as compared to the wild‐type MEFs (Fig 3G). The effect of GFP‐Rabl2Q80L, however, was indistinguishable to that of GFP (Fig 3G).
Immunoblotting revealed that the levels of exogenous Rabl2 and Rabl2Q80L highly exceeded that of endogenous Rabl2 in wild‐type MEFs (Fig 3H). Despite this, the SAG treatment still strongly induced Gli1 expression in the Rabl2 −/− MEFs expressing GFP‐Rabl2; GFP‐Rabl2Q80L, however, displayed similar efficacy as GFP (Fig 3H). We also examined Gli3‐R levels and observed that SAG induced Gli3‐R reduction in all groups (Fig 3H). Quantification suggested that, in the absence of SAG, Gli3 FL/R ratios increased in the GFP groups as compared to the wild‐type MEFs or the GFP‐Rabl2 groups (Fig 3H). After SAG treatment, Gli3 FL/R ratios in the GFP‐Rabl2Q80L groups displayed the least increase as compared to the other groups (Fig 3H). Taken together, we conclude that ciliary Rabl2Q80L inhibits Hh signaling (Fig 3I).
Wild‐type Rabl2‐GTP enters cilia by binding to IFT‐B and undergoes IFT
If wild‐type Rabl2 never entered cilia as proposed previously for RABL2 (Kanie et al, 2017), the ciliary retention of GPCRs by Rabl2Q80L (Fig 3E and F) would be artificial effects. Alternatively, as both Rabl2‐deficiency and Rabl2Q80L expression inhibited Hh signaling without affecting ciliogenesis (Figs 1, EV1, 2, 3 and EV1A), endogenous Rabl2‐GTP might actually enter cilia to regulate the proper turnover of ciliary GPCRs through its GTP hydrolysis (Fig 3I). It has been shown that RABL2‐GTP is specifically recruited to distal appendages by CEP19, where it binds to IFT‐B (Kanie et al, 2017; Nishijima et al, 2017). The consistent localization of Rabl2 and Rabl2Q80L at distal appendages (Figs EV2 and EV3) suggested that Rabl2‐GTP is recruited to distal appendages by the same mechanism to interact with IFT‐B. Kanie and colleagues propose that IFT‐B subsequently separates from RABL2 and enters cilia alone. Nevertheless, could Rabl2‐GTP actually enter cilia together with IFT‐B? To clarify this, we investigated whether we could detect wild‐type Rabl2 in cilia.
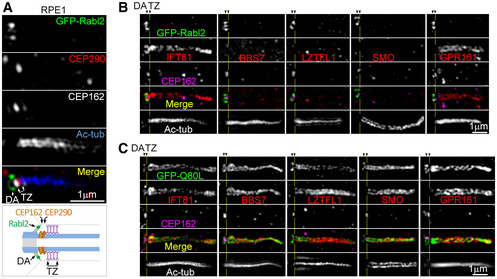
Figure EV3. Rabl2Q80L induces ciliary accumulation of BBS proteins and GPCRs above TZ (related to Fig 5).
-
A3D‐SIM images showing the spatial relationship among different makers in a presentative primary cilium of RPE1 cells. Transition zone (TZ) markers CEP290 and CEP162 were closely spaced at the base of Ac‐tub‐labeled axoneme. GFP‐Rabl2 localized to distal appendages (DA), similar to endogenous Rabl2 (see Fig EV2A). The diagram illustrates their locations relative to TZ (Yang et al, 2015; Garcia‐Gonzalo & Reiter, 2017).
-
B, CDistribution of the indicated proteins (red) in cilia. RPE1 cells expressing GFP‐Rabl2 (B) or GFP‐Rabl2Q80L (C) were imaged through 3D‐SIM. Yellow lines mark the middle of TZ.
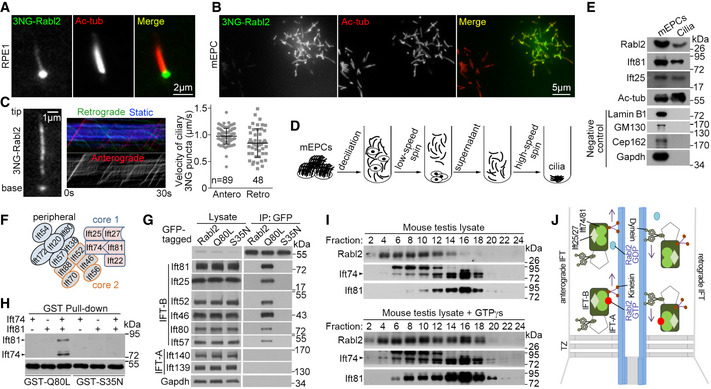
As we usually needed to perform immunofluorescent staining to clearly visualize the ciliary GFP‐Rabl2Q80L (Fig 3), we speculated that the ciliary Rabl2, if any, must be in very low levels. To boost detection sensitivity, we fused three tandem repeats of the super‐bright NeonGreen (Shaner et al, 2013) to the wild‐type Rabl2 (3NG‐Rabl2) and readily observed punctate 3NG‐Rabl2 autofluorescence in the shaft of both primary cilia of RPE1 cells and multicilia of cultured mEPCs (Fig 4A and B). More importantly, live imaging by total internal reflection fluorescence (TIRF) microscopy revealed clear anterograde and, less frequently and clearly, retrograde movements of 3NG‐Rabl2 puncta in the primary cilia (Fig 4C and Movie EV1), with velocities of 0.97 ± 0.14 and 0.85 ± 0.27 μm/s, respectively, similar to those of reported IFT particles (He et al, 2014; Ishikawa & Marshall, 2015).
Figure 4. Rabl2‐GTP enters cilia through IFT.
-
A, BWild‐type Rabl2 was observed in the shaft of both primary cilium (A) and multicilia (B). Ciliated RPE1 cells (A) or mEPCs (B) expressing Rabl2 tagged with 3×mNeonGreen (3NG) were fixed at 48 h or day 7 post‐serum starvation, respectively.
-
CCiliary 3NG‐Rabl2 in living RPE1 cells underwent bidirectional IFT. The 1st frame and kymographs of a representative cilium (also see Movie EV1) are shown. Quantification results, presented as mean ± s.d, were measured from 34 cilia.
-
D, EDetection of endogenous Rabl2 in purified multicilia. Multicilia purified from cultured mEPCs (D) were analyzed by immunoblotting (E). Ac‐tub, Ift25, and Ift81 served as positive controls for cilia, whereas Lamin B1, GM130, Cep162, and Gapdh served as quality controls for the ciliary preparation to exclude major contaminations from the nucleus, Golgi, basal body, and cytosolic proteins, respectively. 1/400 of the mEPC lysate and 1/20 of the cilia lysate were loaded per lane.
-
FDiagram of IFT‐B. The core 1, core 2, and peripheral subcomplexes (Nakayama & Katoh, 2018) are depicted in different colors.
-
GRabl2Q80L strongly associated with IFT‐B. GFP‐Rabl2 or mutants stably expressed in NIH3T3 cells were immunoprecipitated with anti‐GFP beads.
-
HRabl2Q80L interacted with the IFT74/81 heterodimer. FLAG‐tagged Ift74 and Ift81 and GST‐tagged Rabl2Q80L and Rabl2S35N expressed in Escherichia coli were mixed as indicated and pulled down with glutathione‐conjugated beads. Antibodies to GST and FLAG were used for immunoblotting.
-
IAssociation of endogenous Rabl2‐GTP with IFT‐B. Mouse testis lysates with or without 1 mM GTPγS were subjected to sucrose gradient ultracentrifugation. Fractions were collected from top (low MW) to bottom (high MW). Note the obvious enrichment of Rabl2 in fraction #16 in the presence of GTPγS.
-
JA model delineating relationships between Rabl2 and IFT machinery. Rabl2‐GTP enters cilia by binding to the Ift74‐Ift81 heterodimer of IFT‐B. After reaching the ciliary tip through anterograde IFT, it undergoes retrograde IFT toward the ciliary base. When its GTP is hydrolyzed into GDP during its IFT, the resultant Rabl2‐GDP dissociates from IFT‐B. The trafficking of IFT machinery continues in the absence of Rabl2.
Source data are available online for this figure.
We next examined whether endogenous Rabl2 was present in purified cilia. As we were unable to purify enough primary cilia for this purpose, we purified multicilia from cultured mEPCs (Fig 4D) (Zheng et al, 2019). Our cilia preparation did not contain detectable Gapdh, Lamin B1, GM130, and Cep162 (Fig 4E), suggesting free of major cytosolic, nuclear, and membranous organelle contaminations and the basal body (Shelton et al, 1981; Nakamura et al, 1995; Wang et al, 2013). By contrast, known ciliary proteins, Ift81, Ift25, and acetylated tubulin, together with Rabl2, were clearly detected in the purified cilia (Fig 4E). Therefore, Rabl2 enters cilia through anterograde IFT and also undergoes retrograde IFT.
Similar to RABL2BQ80L (Kanie et al, 2017; Nishijima et al, 2017), Rabl2Q80L strongly associated with IFT‐B by binding to the IFT74‐IFT81 heterodimer (Fig 4F–H). On the other hand, Rabl2S35N and even Rabl2 failed to display detectable interaction with IFT‐B (Fig 4G and H). In sucrose gradient centrifugation of mouse testis lysates, IFT‐B, marked by Ift74 and Ift81, was mainly enriched in fraction #16, whereas Rabl2 was abundant in low‐MW fractions #4‐#10 (Fig 4I). In parallel samples containing GTPγs, a non‐degradable GTP analogue, however, a substantial portion of Rabl2, became co‐fractionated with IFT‐B (Fig 4I).
Therefore, we revise the model of Kanie and colleagues (Kanie et al, 2017) and propose that Rabl2‐GTP enters cilia by tightly binding to IFT‐B and undergoes both anterograde and retrograde IFT (Fig 4J). Dissociation is expected to occur when Rabl2‐GTP is converted into Rabl2‐GDP through GTP hydrolysis (Fig 4J) (Kanie et al, 2017; Nishijima et al, 2017).
Rabl2Q80L induces robust ciliary accumulations of BBSome but not IFT components
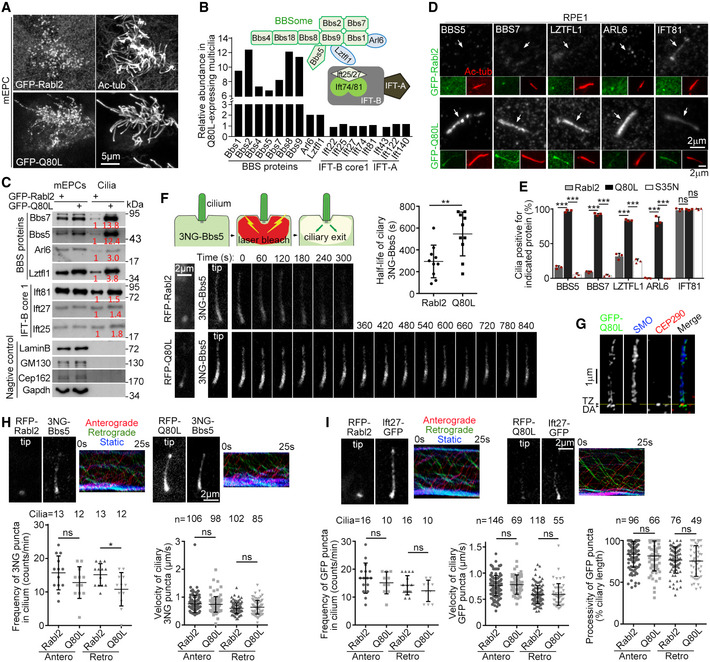
To understand the mechanism underlying the ciliary GPCR export defects in the Rabl2Q80L‐expressing cells (Fig 3), we performed quantitative proteomic analyses on multicilia purified from mEPCs expressing GFP‐tagged Rabl2Q80L or Rabl2 (Fig 5A and B) (Zhu et al, 2010; Zhang et al, 2019). Strikingly, while the abundances of IFT‐B and IFT‐A subunits were similar between the two samples, seven (Bbs1, ‐2, ‐4, ‐5, ‐7, ‐8, and ‐9) out of the eight known BBSome subunits (Mourao et al, 2016; Nakayama & Katoh, 2018) increased by more than sixfold in the Rabl2Q80L cilia sample (Fig 5B). Only Bbs18 was not detected by the mass spectrometry, possibly due to its small size (< 10 kDa). Arl6/Bbs3 and Lztfl1/Bbs17, BBS proteins involved in the coupling of the BBSome to ciliary membrane (Mourao et al, 2014; Nakayama & Katoh, 2018) and IFT‐B (Seo et al, 2011; Eguether et al, 2014; Jiang et al, 2016; Chou et al, 2019), respectively, displayed moderate increases (twofold). Immunoblotting validated the sample quality and the proteomic results (Fig 5C).
Figure 5. GTP‐locked Rabl2 represses outward passage of the BBSome and SMO through TZ.
-
ARabl2Q80L localized in multicilia. Cultured mEPCs were infected with adenovirus to express GFP‐Rabl2 or GFP‐Rabl2Q80L at 24 h prior to and fixed at day 7 post‐serum starvation.
-
B, CRabl2Q80L selectively induced ciliary accumulation of BBS proteins. Multicilia were purified from adenovirus‐infected mEPCs harvested at day 10 and subjected to label‐free quantitative (LFQ) mass spectrometric analyses (B) or immunoblotting (C). The abundance (B) is relative to LFQ intensities in the GFP‐Rabl2 sample. Relationships among the BBS proteins, IFT‐B, and IFT‐A are depicted according to literature (Eguether et al, 2014; Nakayama & Katoh, 2018). Lztfl1 has been proposed to link BBSome to IFT‐B through interaction with Ift27 (Eguether et al, 2014). Lamin B1, GM130, Cep162, and Gapdh served as quality controls for the ciliary preparations (C). The values in red are relative band intensities. 1/400 of the mEPC lysates and 1/20 of the cilia lysates were loaded per lane.
-
D, ECiliary accumulation of BBS proteins in Rabl2Q80L‐expressing RPE1 cells. The white arrows (D) point to positions of cilia. Quantification results (E) were from three independent experiments. At least 100 GFP‐positive cells were scored in each experiment and condition.
-
FFLIP assays revealed that ciliary Rabl2Q80L impaired BBSome export. RPE1 cells co‐expressing 3NG‐Bbs5 with RFP‐Rabl2Q80L or RFP‐Rabl2 were serum‐starved to induce ciliogenesis. Photobleaching of 3NG in cells around the ciliary base was performed at t = 0 s as illustrated. Ciliary 3NG autofluorescence in the living cells was imaged at 30‐s intervals after a snapshot for RFP. Images of representative cilia and half‐life (t 1/2) of 10 cilia from one typical set of experiments are shown.
-
GCiliary SMO was accumulated above the transition zone (TZ; yellow line) in RPE1 cells expressing GFP‐Rabl2Q80L. Images were acquired through 3D‐SIM. CEP290 served as TZ marker. DA, distal appendage. Also see Fig EV3.
-
H, IBBSomes and IFT‐B were able to reach the ciliary base through retrograde IFT in the presence of Rabl2Q80L. Ciliary 3NG‐Bbs5 (H) or Ift27‐GFP (I) in IMCD3 cells co‐expressing RFP‐Rabl2 or RFP‐Rabl2Q80L was live imaged at 4 fps. Snapshots for the ciliary RFP proteins, the first frames from Movies [Link], [Link], [Link], [Link], corresponding kymographs, and quantification results from the indicated numbers of cilia are presented. For processivity analysis (I), only traceable puncta were scored.
Data information: Data are presented as mean ± s.d. Student's t‐test: ns, no significance; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.
Source data are available online for this figure.
We next confirmed the effects in primary cilia of RPE1 cells by immunostaining. It is known that endogenous BBS proteins are hardly visible in cilia by immunostaining (Eguether et al, 2014; Liew et al, 2014). Indeed, BBS5, BBS7, and ARL6 were rarely detected in the ciliary shaft of RPE1 cells expressing GFP‐Rabl2 or GFP‐Rabl2S35N, whereas ciliary LZTFL1 was only observed weakly in < 32% of the cells on average (Fig 5D and E). Nevertheless, they were strongly located in the ciliary shaft of more than 81% of GFP‐Rabl2Q80L‐positive RPE1 cells (Fig 5D and E). By contrast, IFT81 was generally positive in the cilia regardless of the GFP‐tagged proteins (Fig 5D and E).
Therefore, Rabl2Q80L selectively causes ciliary accumulations of the BBSome and its adaptor proteins Arl6 and Lztfl1, but not IFT‐A and IFT‐B complexes.
Ciliary Rabl2‐GTP represses outward TZ passage of the BBSome and its cargos
To clarify whether the ciliary BBSome accumulation by the constitutively activated Rabl2 mutant was due to increased entry or decreased exit, we examined the ciliary exit rates of 3NG‐Bbs5 in living RPE1 cells through fluorescence loss in photobleaching (FLIP; Fig 5F) (Liew et al, 2014). In the cells expressing RFP‐Rabl2, ciliary 3NG‐Bbs5 declined rapidly after the photobleaching, with an average half‐life (t 1/2) of 294 ± 150 s (Fig 5F). In sharp contrast, ciliary 3NG‐Bbs5 persisted for a longer time in cells expressing RFP‐Rabl2Q80L, with an average half‐life of 546 ± 201 s (Fig 5F), indicating that ciliary Rabl2Q80L inhibits the BBSome export.
It is recently shown that two barriers, TZ and the periciliary barrier, gate the outward passage of membrane receptors at the ciliary base. The BBSome‐mediated transport enables the passage through TZ but not the periciliary barrier (Nachury, 2018; Ye et al, 2018). We thus examined detailed ciliary protein localizations in RPE1 cells expressing GFP‐Rabl2Q80L through super‐resolution imaging. By using CEP290 or CEP162 as TZ markers, which localize to the bottom of TZ (Fig EV3A) (Wang et al, 2013; Yang et al, 2015; Garcia‐Gonzalo & Reiter, 2017), we confirmed that Rabl2Q80L and IFT‐B (visualized through IFT81) distributed both on distal appendages and in the ciliary shaft (Fig EV3) (Kanie et al, 2017). BBSomes (visualized through BBS7), LZTFL1, SMO, and GPR161, however, distributed exclusively above TZ (Fig 5G and EV3C).
To further clarify whether the accumulation of the BBSome and its cargo proteins above TZ was due to their failure to cross TZ (Nachury, 2018; Ye et al, 2018) or be incorporated into the retrograde machinery at the ciliary tip (Eguether et al, 2014; Liew et al, 2014; Nakayama & Katoh, 2018), we monitored BBSome motility. Tracking the BBSome movement was somehow difficult in RPE1 cells, due to the lack of obvious consecutive movement of the 3NG‐Bbs5 puncta, but feasible in mouse IMCD3 cells, which might be why the cells are commonly used to visualize mammalian BBSome motility (Liew et al, 2014; Ye et al, 2018). In IMCD3 cells expressing either RFP‐Rabl2 or RFP‐Rabl2Q80L, ciliary puncta of 3NG‐Bbs5 or Ift27‐GFP (representing IFT‐B) underwent both anterograde and retrograde IFTs (Fig 5H and I and Movies [Link], [Link], [Link], [Link]). IFT frequency of the puncta appeared to be slightly decreased in cilia of the Rabl2Q80L‐expressing cells, but only the reduction in the retrograde frequency of 3NG‐Bbs5 puncta was statistically significant (Fig 5H and I). Comparing to RFP‐Rabl2, RFP‐Rabl2Q80L did not significantly alter IFT velocities of BBSomes or IFT‐B (Fig 5H and I, and Movies [Link], [Link], [Link], [Link]). Retrograde 3NG‐Bbs5 puncta were observed to reach the base of Rabl2Q80L‐positive cilia (Fig 3H and Movie EV3), though the highly accumulated ciliary 3NG‐Bbs5 precluded quantification on processivity of motile 3NG‐Bbs5 puncta. When processivity of ciliary Ift27‐GFP puncta was analyzed, we did not observe significant changes between the Q80L and the Rabl2 groups (Fig 5I). Therefore, GTP‐locked Rabl2 does not significantly alter ciliary IFT frequency, velocity, and processivity. Furthermore, the BBSome‐containing retrograde IFT machinery can be assembled in the presence of Rabl2Q80L and actively reach the ciliary base. Taken together, these results suggest that Rabl2Q80L, or Rabl2‐GTP in physiological situations, specifically impair the outward TZ passage of the BBSome and its cargos.
Outward TZ passage of BBSomes requires the release of ciliary Rabl2 from IFT‐B
To understand how Rabl2‐GTP blocks the BBSome passage through TZ, we screened for a Rabl2Q80L‐based mutant that entered cilia without causing BBSome accumulation and identified the Rabl2D73GQ80L double mutant. Similar to Rabl2Q80L, GFP‐Rabl2D73GQ80L localized in primary cilia of RPE1 cells without affecting the efficiency of ciliogenesis (Fig 6A). It underwent anterograde (0.94 ± 0.12 μm/s) and retrograde (0.72 ± 0.15 μm/s) IFT in the living cells (Fig 6B and Movie EV6). Rabl2D73GQ80L, however, did not induce ciliary accumulation of BBS proteins (Fig 6C and D). Nor did it induce ciliary SMO accumulation in the absence of SAG or retain ciliary GPR161 upon SAG stimulation (Fig 6E and F). In comparison, GFP‐tagged Rabl2D73G, a mutant that causes infertility and obesity in mice (Lo et al, 2012; Lo et al, 2016), localized at the basal body in RPE1 cells (Fig EV4A). It also did not affect ciliogenesis, induce ciliary accumulation of BBSome and SMO, or alter the ciliary translocation of SMO in response to SAG treatment (Fig EV4).
Figure 6. TZ passage of ciliary BBSome‐GPCR requires dissociation of Rabl2 from IFT‐B.
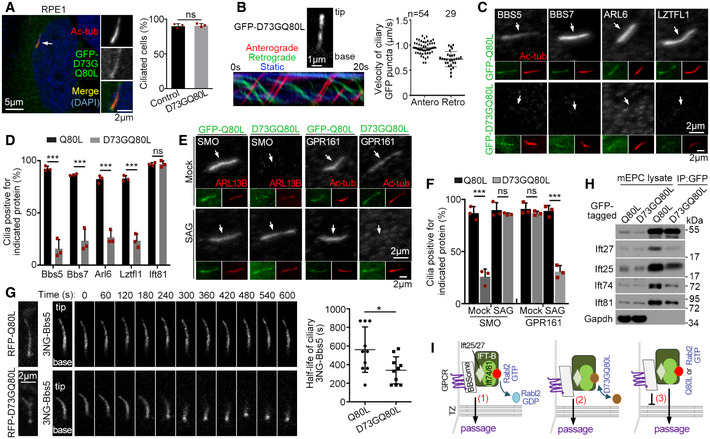
-
ARabl2D73GQ80L localized in the ciliary shaft and did not affect ciliogenesis efficiency. RPE1 cells infected with adenovirus to express GFP‐Rabl2D73GQ80L were serum‐starved for 48 h. The white arrow denotes the cilium shown in insets. Quantification results were from three independent experiments. Uninfected RPE1 cells served as control. At least 107 cells were scored in each experiment and condition.
-
BRabl2D73GQ80L underwent bidirectional IFT. Ciliary GFP‐Rabl2D73GQ80L in RPE1 cells was live imaged at 5 fps. The 1st frame and kymograph of a representative cilium (also see Movie EV6) are shown. Velocities were quantified from 10 cilia.
-
C, DRabl2D73GQ80L did not induce ciliary accumulation of BBS proteins. Ciliated RPE1 cells expressing GFP‐tagged Rabl2Q80L or Rabl2D73GQ80L were immunostained (C). The white arrows (C) point to positions of cilia. In quantification results (D), at least 100 cells were scored in each experiment and condition.
-
E, FRabl2D73GQ80L did not repress ciliary translocation of SMO and GPR161. RPE1 cells expressing GFP‐tagged Rabl2Q80L or Rabl2D73GQ80L were serum‐starved for 24 h and treated with DMSO (mock) or SAG for an additional 24 h prior to immunostaining (E). The white arrows (E) point to positions of cilia. In quantification results (F), at least 100 cells were scored in each experiment and condition.
-
GCiliary Rabl2D73GQ80L did not repress the BBSome export. FLIP assays were performed in RPE1 cells co‐expressing 3NG‐Bbs5 with RFP‐tagged Rabl2Q80L or Rabl2D73GQ80L as depicted in Fig 5F. Photobleaching was executed at t = 0. Quantification results on half‐life (t 1/2) were from 10 cilia for each condition.
-
HRabl2D73GQ80L displayed an attenuated association with IFT‐B as compared to Rabl2Q80L. mEPCs infected with adenovirus to express GFP‐Rabl2Q80L or Rabl2D73GQ80L were lysed and immunoprecipitated using anti‐GFP beads. Gapdh served as the negative control.
-
IA model delineating the effects of Rabl2 and mutants on the TZ passage of ciliary BBSome and its cargo GPCR: (1) In physiological conditions, the GTP hydrolysis of Rabl2‐GTP results in Rabl2‐free IFT‐B capable of mediating the TZ passage of the BBSome and its cargos together with the retrograde IFT machinery; (2) Rabl2D73GQ80L dissociates from IFT‐B to allow similar TZ passage; (3) The BBSome sheds from IFT‐B in the presence of Rabl2Q80L or Rabl2‐GTP during the passing process and is therefore blocked in the ciliary shaft with its cargos.
Data information: Quantification results are presented as mean ± s.d. Student's t‐test: ns, no significance; *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001.
Source data are available online for this figure.
Figure EV4. Rabl2D73G does not repress ciliogenesis and ciliary exit of BBSome and SMO (related to Fig 6).
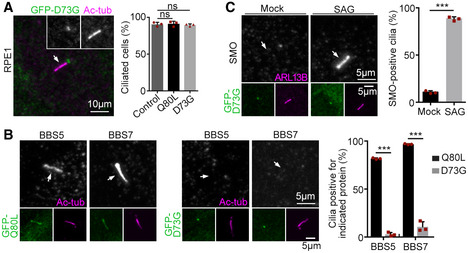
- Rabl2D73G did not affect ciliogenesis efficiency. RPE1 cells that were either uninfected (control) or infected with adenovirus to express GFP‐tagged Rabl2Q80L or Rabl2D73G were serum‐starved for 48 h. The white arrow denotes cilium. At least 100 cells were scored in each experiment and condition.
- Rabl2D73G did not cause ciliary BBSome accumulation. Rabl2Q80L served as positive control. The white arrows indicate positions of cilia. At least 105 cells were scored in each experiment and condition.
- Rabl2D73G did not alter ciliary translocation of SMO. RPE1 cells expressing GFP‐Rabl2D73G were serum‐starved for 24 h and treated with DMSO (mock) or SAG for an additional 24 h prior to immunostaining. The white arrows indicate positions of cilia. At least 100 cells were scored in each experiment and condition.
Data information: Quantification results are presented as mean ± s.d. Student's t‐test: ns, no significance; ***P < 0.001.
Fluorescence loss in photobleaching assays confirmed that RFP‐Rabl2D73GQ80L did not repress the ciliary exit of 3NG‐Bbs5 as compared to RFP‐Rabl2Q80L (Fig 6G). The average half‐life of ciliary 3NG‐Bbs5 in the RFP‐Rabl2D73GQ80L‐expressing cells, 333 ± 151 s, was comparable to that in the RFP‐Rabl2‐expressing cells (Fig 6G vs. Fig 5F). Compared with Rabl2Q80L, Rabl2D73GQ80L displayed a markedly reduced association with IFT‐B (Fig 6H), suggesting that it is prone to dissociation from IFT‐B in the ciliary shaft to achieve a similar effect as the GTP hydrolysis of Rabl2‐GTP on the TZ passage of the BBSome and its cargos together with the IFT machinery (Fig 6I). Accordingly, persistent binding of Rabl2Q80L or Rabl2‐GTP to IFT‐B results in shedding of the BBSome and its cargos during the TZ passing process and thus their accumulation in the ciliary shaft (Fig 6I).
Rabl2Q80L expression in mice closely resembles Ift27 deficiency
As in vitro assays including gradient centrifugation are unable to detect the complex formation between BBSome and IFT‐B (Seo et al, 2011), probably due to autoinhibition of BBSome in solution (Chou et al, 2019), so far proteins involved in their coupling, Lztfl1 on the BBSome side and Ift27 on the IFT‐B side, are identified through genetic approaches (Eguether et al, 2014). To verify that the BBSome and its cargos were indeed prone to shedding from the Rabl2‐GTP‐bound IFT‐B, we likewise utilized genetic approach by generating Rabl2Q80L knock‐in (KI) mice using template‐mediated repair of Cas9‐induced DNA mutation (mt) in zygotes (Fig 7A) (Wu et al, 2013). Of 125 neonatal F1 mice subjected to genotyping, nine mice displayed uniform “TT” mutations in the PCR products indicative of homozygous Rabl2KI / KI mutations (Fig 7B and C). Three mice were still wildtype, whereas the remaining 113 mice showed mixed peaks in sequencing that could be interpreted as heterozygous mice of varying genotypes or chimeric mice (Figs 7C and EV5). As our genotyping method could not distinguish heterozygous mice from chimeric mice, we only examined viability for this population (Fig 7C).
Figure 7. Rabl2Q80L knock‐in mice display neonatal death and duplex kidney that phenocopy Ift27‐deficient mice.
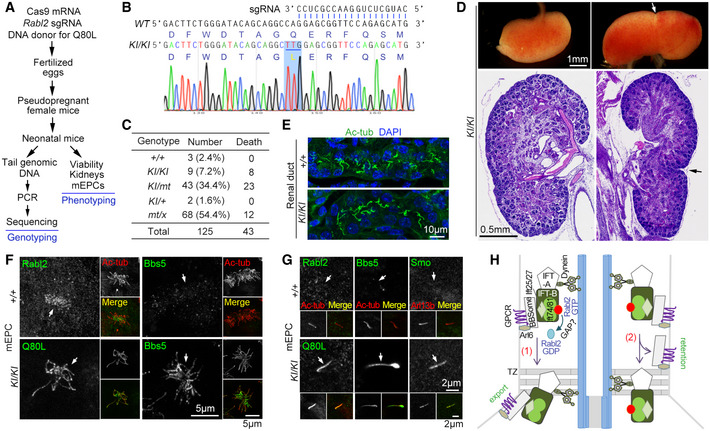
-
AExperimental scheme for the knock‐in (KI) mice production and characterization. The single‐stranded DNA donor‐mediated repair of the Cas9‐induced Rabl2 DNA breaks is expected to introduce the Q80L mutation in fertilized eggs or early embryos. Neonatal F1 mice were obtained through the cesarean section at E18.5. Genotyping was performed by directly sequencing the PCR products that covered the expected Cas9‐cleavage region of Rabl2.
-
BRepresentative sequencing results for Rabl2KI / KI mice, shown with corresponding sequences for wildtype Rabl2 and the 3′ end of the sgRNA. The TTG codon for the Q80L mutation is underlined.
-
CViability of neonatal mice in the day of birth after the cesarean section at E18.5. +, wildtype allele of Rabl2; KI, knock‐in allele with Q80L mutation; mt, allele with Cas9‐induced mutation; x, ambiguous allele. Refer to Fig EV5 for additional genotyping results. As these "heterozygous" mice might contain chimeric ones, the putative genotypes are used only for simplicity.
-
DMorphologically normal and duplex kidneys of Rabl2KI / KI mice. The whole kidneys were from a single mouse. The histological sections, stained with hematoxylin and eosin, were from different mice. Arrows point to the constriction of the duplex kidneys.
-
ERenal ducts of Rabl2KI / KI kidney displayed normal ciliary formation as compared to wildtype kidney. Nuclear DNA was stained with DAPI.
-
F, GEndogenous Rabl2Q80L entered ciliary shaft to repress the export of the BBSome (Bbs5) and its cargo GPCR (Smo). mEPCs cultured from Rabl2KI / KI and wild‐type neonatal mice were fixed at day 7 post‐serum starvation. Anti‐Rabl2 antibody was used to visualize Rabl2 and Rabl2Q80L. Ac‐tub or Arl13b served as ciliary marker. Representative micrographs of multicilia (F) and primary cilia (G) are shown. The white arrows point to positions of cilia.
-
HA model delineating the switch role of ciliary Rabl2 in the BBSome‐mediated GPCR turnover: (1) GTP hydrolysis induced presumably by a GTPase‐activating protein (GAP) dissociates Rabl2 from IFT‐B to enable a tight BBSome‐IFT‐B interaction in the retrograde IFT machinery for concomitant TZ passage; (2) Without the GTP hydrolysis, Rabl2‐GTP (or Rabl2Q80L) binds persistently to IFT‐B, resulting in shedding of the BBSome and its cargos from the IFT machinery in the TZ passing process and accordingly their ciliary retention. See Discussion for details. For simplicity, kinesin motor is not illustrated.
Figure EV5. Additional representative genotyping results for Rabl2 gene‐edited mice (related to Fig 7).
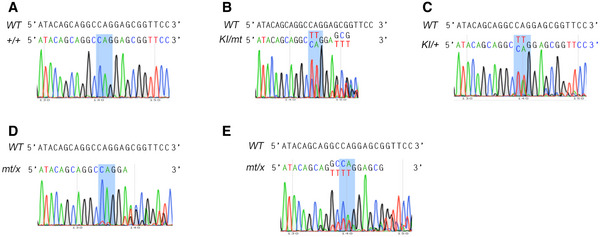
-
A–ERepresentative sequencing results for the Rabl2 +/+ (A) and putatively Rabl2KI / mt (B), Rabl2KI /+ (C), and Rabl2mt / x (D, E) groups of mice. The Rabl2 fragments covering the expected Cas9‐cleavage region were amplified by PCR from tail genomic DNAs prepared, respectively, from Rabl2 gene‐edited neonatal mice (Fig 7A) and subjected to sequencing analyses. The blue boxes mark the position of the codon (CAG) for glutamine‐80 (Q80) in wildtype (WT) Rabl2. 61 mice showed sequencing results of mixed peaks after the CAG codon (D), whose genotypes are putatively Rabl2mt /+ or Rabl2mt / mt. 7 mice showed mixed peaks before the CAG codon (E) and are putatively Rabl2mt /+, Rabl2mt / mt, or Rabl2mt / KI. We thus used x to represent the ambiguous allele. As some of these "heterozygous" mice might actually be chimeric ones, the putative genotypes are used only for simplicity.
Source data are available online for this figure.
Compared with an overall death rate of 34.4% for the 125 mice within the day of birth, the death rate for the Rabl2KI / KI mice was 88.9% (Fig 7C), indicating that mice expressing only Rabl2Q80L are prone to neonatal death. The death rate (53.4%) for the Rabl2KI / mt mice was threefold over the rate (17.6%) for the Rabl2mt / x mice, suggesting a dose‐dependent lethality of Rabl2Q80L. Furthermore, all the Rabl2KI / KI mice examined (7/7) contained duplex kidney on either one side (6/7) (Fig 7D) or both sides (1/7), though their ciliary formation in renal ducts was normal (Fig 7E). We did not observe obvious polydactyly in them. We also started to maintain the F1 Rabl2KI /+ mice and found that, among the first batch of their seven F2 neonatal progeny, three wild‐type and two Rabl2KI /+ puppies were viable with normal kidneys. By contrast, the two Rabl2KI / KI littermates died after a natural birth and respectively possessed single and double duplex kidneys, confirming the phenotypes of Rabl2KI / KI mice (Fig 7C and D) and also indicating that the gene editing‐produced F1 Rabl2KI /+ mice are indeed heterozygotes and capable of germline transmission.
We examined cultured mEPCs from Rabl2KI / KI brain tissues and found that the endogenous Rabl2Q80L entered the shaft of both multicilia and primary cilia (Fig 7F and G). Consistent with the effect of exogenous Rabl2Q80L (Fig 5), the endogenous Rabl2Q80L also induced ciliary BBSome accumulation suggested by the strong Bbs5 staining (Fig 7F and G). Smo was also accumulated in the Rabl2KI / KI primary cilia in the absence of SAG treatment (Fig 7G). These results further strengthen the idea that the GTP hydrolysis of IFT‐B‐bound Rabl2‐GTP is key to the outward TZ passage of the BBSome and its cargos (Fig 7H).
Notably, the neonatal lethality, duplex kidney, normal ciliation, and ciliary accumulation of BBSome and GPCRs are also characteristic phenotypes of the Ift27 null mice (Eguether et al, 2014; Desai et al, 2018). Ift27 is a Rab‐like small GTPase (also termed Rabl4) stabilized by Ift25 through heterodimerization and also the essential subunit for the coupling of IFT‐B to the BBSome and its cargos (Fig 7H) (Bhogaraju et al, 2011; Keady et al, 2012; Eguether et al, 2014; Blacque et al, 2018; Nakayama & Katoh, 2018). Ift25‐deficient mice also show similar phenotypes except for the less extent of neonatal death (Keady et al, 2012; Desai et al, 2018). Therefore, the Rabl2Q80L expression is largely equivalent to the depletion of Ift27. More importantly, the high similarity in mouse genetic models validates our proposed function of Rabl2 (Fig 7H).
Discussion
In sharp contrast to human RABL2 (Kanie et al, 2017; Nishijima et al, 2017), murine Rabl2 is largely dispensable for ciliogenesis and ciliary entry of IFT‐B. Rabl2 deficiency did not obviously interrupt the formation of either primary or motile cilia in tissues and cultured cells (Fig 1). The fact that Rabl2‐deficient mice are viable (Fig EV1) (Kanie et al, 2017) is also consistent with this because severe ciliary defect is known to cause early embryonic lethality (Bangs & Anderson, 2017; Nakayama & Katoh, 2018). Furthermore, overexpression of wild‐type Rabl2 or its GTP‐locked (Q80L) or GDP‐locked (S35N) mutants in RPE1 cells also did not alter ciliogenic efficiency (Figs 3D and EV4A). As ciliary IFT‐B is essential for anterograde IFT and, consequently, ciliary elongation, these observations already suggest that Rabl2 is unlikely critical for the ciliary entry of IFT‐B. In agreement with this, ciliary Ift81 levels were similar between the wild‐type and Rabl2 −/− MEFs (Fig 1K and L), and overexpression of Rabl2Q80L did not significantly alter IFT frequencies of IFT‐B (Fig 5I) or ciliary levels of IFT‐B and IFT‐A subunits (Figs 5B and EV3). Our current results, however, do not exclude the possibility that the interaction between Rabl2‐GTP and IFT‐B at distal appendages or transition fibers (Figs 3F–I and EV3) also subtly facilitates the ciliary entry of IFT‐B. RABL2 might become more important in this in evolution through the generation of two paralogous genes. Alternatively, as the Chlamydomonas orthologue is critical for flagella formation (Nishijima et al, 2017), evolution might somehow largely relieve murine Rabl2 of this role. In addition, it is also worth noting that studies on RABL2 are solely based on RPE1 cells. Results in other human cells, especially primary cells, still await future investigations. For simplicity, we take Rabl2 as the common name in the following discussion unless the human orthologue is specifically mentioned.
We demonstrated that Rabl2‐GTP enters cilia to undergo anterograde and retrograde IFT (Figs 3B, 4 and 6B; Movies EV1 and EV6). As the interaction of RABL2‐GTP with CEP19 and the IFT74‐IFT81 heterodimer is mutually exclusive (Nishijima et al, 2017), we revise the previous model (Kanie et al, 2017) to propose that the ciliary entry of Rabl2‐GTP from distal appendages is triggered by IFT‐B through direct interaction. Ciliary Rabl2 is undetectable through fluorescent microscopy even upon overexpression (Figs 1, EV2, 3, 5A, and EV3) (Kanie et al, 2017; Nishijima et al, 2017; Dateyama et al, 2019), unless tagged with super‐bright fluorescent proteins such as 3NG (Fig 4A–C). By contrast, ciliary IFT‐B components can be readily detected (Figs 1K and EV3) (Hirano et al, 2017; Kanie et al, 2017), indicating that only a small portion of IFT‐B entering cilia is Rabl2‐bound. Such a dependency on IFT‐B also explains why the ciliary fluorescent intensity of exogenous Rabl2Q80L is always moderate (Figs 3, 5A, and EV3) (Kanie et al, 2017; Dateyama et al, 2019), even with its levels in cells markedly exceeding those of endogenous Rabl2 (Fig 3H, lanes 7–8 vs. lanes 1–2).
Our results suggest that Rabl2 functions as a switch for the BBSome‐mediated export of ciliary signaling proteins such as GPCRs (Figs 5, 6 and 7F–H). As Rabl2Q80L did not strongly alter the IFT behaviors of IFT‐B and BBSome (Fig 5H and I), the Rabl2Q80L‐induced accumulation of the BBSome and multiple GPCRs (Figs 5B–D, and 7F and G) (Kanie et al, 2017; Dateyama et al, 2019) above TZ (Figs 5G and EV3) is attributed to their shedding from the retrograde IFT machinery during the TZ passage (Fig 7H) (Nachury, 2018; Ye et al, 2018). As the accumulation effect of Rabl2Q80L was comprised by an additional mutation (D73G) that attenuated its interaction with IFT‐B (Fig 6), dissociation of Rabl2‐GTP from IFT‐B through its GTP hydrolysis would similarly allow efficient TZ passage of the BBSome and its cargos (Fig 7H).
The switch role of Rabl2 appears to control the extent of the BBSome‐mediated export of ciliary membrane receptors to fine‐tune cilia‐dependent signaling for normal embryonic development and organismic homeostasis. While ciliary Rabl2‐GTP represses the GPCR export as suggested by the accumulation effect of Rabl2Q80L (Figs 3, 7G and H, and EV3) (Kanie et al, 2017; Dateyama et al, 2019), Rabl2 deficiency results in reduced levels of ciliary GPCRs (Dateyama et al, 2019). As both the Rabl2 deficiency and Rabl2Q80L expression impaired Hh signaling (Figs 2 and 3 and 7), a proper balance between the TZ export and the ciliary retention of Smo and Gpr161 is critical for optimal Hh signaling (Fig 7H). Accordingly, the polydactyly of Rabl2‐deficient mice (Fig EV1A and B) (Kanie et al, 2017) and the neonatal lethality and duplex kidney of the Rabl2KI / KI mice (Fig 7C and D) may result from aberrant Hh signaling (Eguether et al, 2014; Tickle & Towers, 2017; Desai et al, 2018; D'Cruz et al, 2020). The retina degeneration, obesity, and male infertility of the Rabl2‐deficient mice (Fig EV1C–G) (Kanie et al, 2017) and Rabl2Mot / Mot mice (Lo et al, 2012; Lo et al, 2016), whose etiology could be attributed to premature dissociation of ciliary Rabl2D73G‐GTP from IFT‐B according to our results (Fig 6) to partly resemble Rabl2 deficiency, also implicate abnormal ciliary signaling of other GPCRs (Forsythe & Beales, 2013; Hilgendorf et al, 2016).
The largely shared phenotypes between our Rabl2KI / KI mice (Fig 7A–G) and the Ift27‐deficient mice (Eguether et al, 2014; Desai et al, 2018) appear to indicate that the ciliary Rabl2‐GTP functions to counteract or repress Ift27 on IFT‐B. Unlike many other IFT‐B core subunits, mammalian Ift27 and Ift25 are dispensable for anterograde IFT, ciliogenesis, and early embryo viability. Rather, the Ift25‐Ift27 heterodimer functions in the coupling of the BBSome and its cargos to IFT‐B for retrograde IFT to regulate ciliary signaling (Keady et al, 2012; Eguether et al, 2014; Bangs & Anderson, 2017; Nakayama & Katoh, 2018). The overall analogous phenotypes between the Rabl2KI / KI and the Ift27 −/− mice, such as the neonatal death and duplex kidney, suggest that the accumulated ciliary BBSome and membrane receptors resulting from either the Rabl2Q80L‐induced shedding and the Ift27 deficiency‐resultant decoupling have similar influences on ciliary signaling, whereas the differential phenotypes, such as preaxial polydactyly observed in Ift27‐deficient but not our Rabl2KI / KI mice, may be attributed to the difference in detailed mechanisms (Fig 7) (Eguether et al, 2014; Desai et al, 2018). As the duplex kidney is unlikely sufficient to cause the neonatal lethality, detailed examinations in the future are expected to reveal more defects in the Rabl2KI / KI mice, e.g., abnormal neural tube patterning observed in Ift27‐deficient mice (Eguether et al, 2014). As both Rabl2‐GTP (Fig 4H) (Kanie et al, 2017; Nishijima et al, 2017) and Ift27 (Lucker et al, 2010; Taschner et al, 2014; Nakayama & Katoh, 2018) bind to the Ift74‐Ift81 heterodimer (Fig 7H), Rabl2‐GTP may weaken the association of IFT‐B with the BBSome by inducing conformational changes of Ift27. On the other hand, as small GTPases usually require GTPase‐activating proteins (GAP) for rapid GTP hydrolysis (Blacque et al, 2018), a GAP might exist in cilia to specifically inactivate Rabl2‐GTP. Therefore, further investigations are required to fully understand the regulatory mechanisms underlying the BBSome‐IFT‐B interaction.
Materials and Methods
Plasmids
The mouse full‐length cDNAs of Rabl2 (NM_026817), Ift27 (NM_025931), Ift74 (NM_026319), Ift81 (NM_009879), and Bbs5 (NM_028084) were PCR amplified from mouse testis cDNAs. The full‐length of Rabl2 were, respectively, cloned into pLV‐GFP‐C1, pLV‐RFP‐C1, pGEX‐4T‐1, and pET‐28a to express GFP‐, RFP‐, GST‐, and His‐tagged proteins. The point mutations of Rabl2, including Rabl2S35N, Rabl2Q80L, Rabl2D73GQ80L, and Rabl2D73G were generated using site‐directed mutagenesis. To generate the adenoviral plasmids of Rabl2 and its mutants, the PCR‐amplified DNA fragments were subcloned into pYR‐1.1 and a subsequent LR recombination reaction with pAd/Block‐it‐DEST was performed using LR Clonase II enzyme mix (11791020, Thermo Fisher). To construct the plasmids of 3×mNeonGreen‐Bbs5 (3NG‐Bbs5) and 3NG‐Rabl2, the full‐length DNA fragments of Bbs5 and Rabl2 were subcloned into pLV‐mNeonGreen (modified from pLV vector carrying an insertion of three tandem repeats of mNeonGreen). To express Ift27‐GFP, the DNA fragment of Ift27 was subcloned into pLV‐GFP‐C1. The DNA fragments of Ift74 and Ift81 were constructed into pFLAG‐1 to express FLAG‐tagged proteins in Escherichia coli. All constructs were verified by sequencing. The detailed information of plasmid constructs and used primers is listed in Appendix Table S1.
Mice
All mice experiments were performed in accordance with protocols approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Shanghai Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology. Mice were selected solely based on genotypes.
Rabl2tm1(KOMP)Wtsi mice were purchased from the KOMP Repository (University of California Davis). Heterozygous offspring were intercrossed to generate Rabl2 −/− mice. Genotyping was performed by PCR with genomic DNA extracted from mouse tails. The sequences of the PCR primers were 5′ TCCCTATCTG TATTGTTGTT CC 3′ (P1), 5′ ACCATTGATT CCTTGTCTCC 3′ (P2), 5′ ACACCTCCCC CTGAACCTGA AA 3′ (P3), and 5′ CTCAAGGGTT TGCATCATTC TCTCGG 3′ (P4).
Rabl2Q80L knock‐in (Rabl2KI / KI) mice that endogenously expressed Rabl2Q80L were generated using a CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing protocol as described previously (Wu et al, 2013). Briefly, Cas9 mRNA (100 ng/μl), sgRNA (50 ng/μl) containing Rabl2 targeting sequence (5′ GCAUGCUCUG GAACCGCUCC 3′), and 120‐nucleotide single‐stranded DNA donor (100 ng/μl; 5′ CCCTCAACCC CCAGAGTTGT GTTCTTGTTG CAGACTTCTG GGATACAGCA GGCTTGGAGC GGTTCCAGAG CATGCATGCT TCCTACTACC ACAAGGCTCA CGCCTGCATC ATGGTATGAA 3′) were co‐injected into the cytoplasm of fertilized C57BL/6 eggs. The injected eggs were cultured in KSOM medium to the two‐cell stage and then transplanted into the uterus of pseudopregnant ICR female mice. The neonatal mice were obtained through the cesarean section at E18.5. For genotyping, a 340‐bp Rabl2 fragment covering the mutation site was PCR amplified using mouse‐tail genomic DNA as template and then subjected to sequencing. The sequences of the PCR primers were 5′ GGTTCTCTCC CTCCACTTAC 3′ and 5′ GGTAGCGGGC TGAGGACCAT 3′.
Cell culture, viral production, and transfection
HEK293T cells and HEK293A were maintained in DMEM medium (Hyclone) supplemented with 10% FBS (Biochrom), 100 U/ml penicillin (Thermo Fisher), 100 mg/ml streptomycin (Thermo Fisher), and 0.3 mg/ml l‐glutamine (Sigma). hTERT‐RPE1 and IMCD3 cells were maintained in DMEM/F12 medium (GE Healthcare) supplemented with 10% FBS, 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 mg/ml streptomycin, and 0.3 mg/ml l‐glutamine. Additionally, hygromycin B (10 μg/ml; Thermo Fisher) was added into the RPE1 culture medium. Cultured cells were routinely tested for mycoplasma contamination. Primary MEFs were prepared from E12.5 mouse embryos and cultured in DMEM medium supplemented with 10% FBS, 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 mg/ml streptomycin, and 0.3 mg/ml l‐glutamine. MEFs cultured for less than six passages were used in experiments. To induce primary cilia formation, culture medium was replaced with serum starvation medium (DMEM with 0.25% FBS for MEFs or DMEM/F12 for RPE1 and IMCD3 cells) for 48 h. To activate Shh signaling, cells were serum‐starved for 24 h and then treated with 100 nM of SAG (566661, Millipore) for another 24 h. mTECs and mEPCs were isolated and cultured as described previously (Cao et al, 2012; Delgehyr et al, 2015; Zheng et al, 2019).
To express exogenous proteins, HEK293T cells were transfected using polyethylenimine (PEI 23966‐2, Polysciences). IMCD3 and PRE1 cells were transfected using lipofectamine 2000 (Life Technologies). Lentiviral production was performed as described (Zhao et al, 2013). MEFs were infected by culturing in the 1:1 mixture of lentivirus‐containing medium and fresh culture medium for 24 h and then in culture medium for another 24 h. To produce adenovirus, the plasmids were first digested with Pac I overnight. The linearized plasmids were purified by gel extraction and then transfected into HEK293A cells with Lipofectamine 2000. After approximately 80% cells showed a cytopathic effect (CPE), the cells were harvested and viral particles were released by three freeze‐and‐thaw (−80ºC to 37ºC) cycles. The harvested adenoviral particles were used for infection at a 1:1,000 dilution.
Cilia purification and label‐free quantitative mass spectrometry
Purification of ependymal cilia and label‐free quantitative (LFQ) mass spectrometric analyses were carried out as described (Zhang et al, 2019; Zheng et al, 2019). For each preparation, two 75‐cm2 flasks of ependymal cells derived from 10 P0 mice were harvested at day 10 post‐serum starvation. Purification of ependymal cilia was performed (Fig 4D) as described (Zheng et al, 2019). The purified cilia were lysed in 100 μl of lysis buffer (20 mM Tris–HCl [pH 7.5], 100 mM KCl, 0.1% NP‐40, 1 mM EDTA, 10 mM Na4O7P2, and protease inhibitors) and boiled for 10 min. 5 μl of the lysate was loaded for immunoblotting. For LFQ mass spectrometry (Zhu et al, 2010), 50 μl of each preparation was used. Ciliary proteomes identified by the LFQ mass spectrometry (related to Fig 5B) are provided in the Source Data for Fig 5.
Microscopy
Fluorescence microscopy was carried out as described previously (Cao et al, 2012; Zhao et al, 2019). MEF and RPE1 cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS. To better visualize primary cilia, cells were kept on ice for 30 min before fixation to destabilize cytoplasmic microtubules. GFP‐tagged Rabl2 and mutants were immunostained with anti‐GFP antibody and Alexa 488‐conjugated secondary antibody to visualize ciliary localization. For immunofluorescence of mouse trachea and kidney, wild‐type and Rabl2 −/− mice of 2‐month‐old were firstly perfusion‐fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS and then fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS overnight at 4°C. The kidneys of E18.5 wild‐type and Rabl2KI / KI mice were dissected and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS for 2 h at 4°C. The samples were subsequently equilibrated with 30% sucrose in PBS overnight at 4°C, embedded in OCT Tissue Freezing Medium (NE‐50TM, Thermo Fisher) and sectioned into 10‐μm slices. The cryo‐sections were blocked in PBS with 10% goat serum and 0.5% Triton X‐100 at room temperature for 1 h, followed by overnight incubation with primary antibodies at 4°C. Confocal images were captured using a Leica TCS SP8 system with a 63×/1.40 oil immersion objective and processed with maximum intensity projections. 3D‐SIM super‐resolution images were taken with a DeltaVision OMX SR system (GE Healthcare) with a 100×/1.40 oil immersion objective (Olympus). Immersion oil with a refractive index of 1.516 was used to obtain optimal images and serial z‐stack optical sectioning was set at 125‐nm intervals. Images were reconstructed by softWoRx 5.0 software (GE Healthcare). Antibodies used are listed in Appendix Table S1.
Live‐cell imaging
For live‐cell imaging, cells were seeded in 35‐mm glass‐bottom dishes (D35‐20‐1.5‐N, Cellvis). For imaging ciliary motility of 3NG‐Rabl2 or GFP‐Rabl2D73GQ80L, RPE1 cells were transfected with lentiviral plasmids for 24 h, followed by a 48‐h serum starvation. Ciliary images were captured at 200‐ms intervals for 30 s with a Leica DMi8 TIRF microscope equipped with a 100×/1.47 oil immersion objective. For imaging ciliary motility of 3NG‐Bbs5 or Ift27‐GFP, IMCD3 cells were co‐transfected with lentiviral plasmids to co‐express RFP‐Rabl2 or RFP‐Rabl2Q80L. The cells were transfected for 24 h, followed by a 48‐h serum starvation. Ciliary images were captured at 250‐ms intervals for 25 s with a Zeiss LSM 880 Airyscan microscope equipped with a 63×/1.4 oil immersion objective.
Kymographs were generated from the time‐lapse image sequence with KymographClear 2.0 of Image J (Fiji). Particle velocities were measured as described (Ishikawa & Marshall, 2015). Traffic frequencies were measured from kymographs as the number of particles crossing ciliary middle line per min. Particle processivity was quantified from kymographs for events lasting for > 3 s (Ye et al, 2018).
Fluorescence loss in photobleaching assay
Fluorescence loss in photobleaching assays were performed as described (Snapp et al, 2003; Esposito et al, 2009; Wustner et al, 2012; Liew et al, 2014) with modifications. RPE1 cells were transfected with lentiviral plasmids to co‐express 3NG‐Bbs5 with RFP‐tagged Rabl2 or mutants for 24 h, followed by serum starvation for 48 h to induce ciliogenesis. The cytoplasmic fluorescence of 3NG‐Bbs5 around the ciliary base was photobleached in multiple areas with a 488‐nm laser prior to imaging. Ciliary images were captured at 30‐s intervals for up to 30 frames with a laser confocal microscope (Leica SP8) equipped with a 63×/1.4 oil immersion objective. Fluorescent intensities of ciliary 3NG‐Bbs5 following time were measured with Adobe Photoshop.
Skeletal staining and H&E staining
Skeletal staining was performed as described previously (Zou et al, 2013) with some modifications. All steps were performed at room temperature. Eviscerated and skinned neonates were fixed in 95% ethanol overnight, transferred into acetone for degreasing, and stained with Alizarin red/Alcian blue for 4 days. After three times of wash with 95% ethanol, soft tissues were cleared in 1% potassium hydroxide. Specimens were imaged with an Olympus SZX16 stereo microscope.
Eyes from P0 and 9‐month‐old wild‐type or Rabl2 −/− mice and kidneys from E18.5 wild‐type or Rabl2KI / KI mice were dissected and fixed in Bouin's solution overnight at 4°C. The fixed tissues were paraffin‐embedded and sectioned into 8‐μm‐thick slices with a microtome (Leica RM2235). The sections were deparaffinized with xylene, rehydrated, and stained with hematoxylin for 5 min and eosin for 1 min. The images of eye sections were captured with an Olympus BX51 microscope. The images of kidney sections were captured with a Zeiss Axio Scan.Z1 Slide Scanner equipped with a 10× objective.
Sperm motility assay
Epididymal sperms from 8‐week‐old Rabl2 +/+ or Rabl2 −/− mice were incubated in 500 μl of sperm analysis buffer (120 mM NaCl, 20 mM KCl, 1 mM CaCl2, 25 mM NaHCO3, 1.2 mM MgSO4, 0.36 mM NaH2PO4, 5.5 mM Glucose, 0.45 mM Na‐Pyruvate, 20 mM Sucrose, 10 mM TAPSO, 57 mg/l Penicillin, 29 mg/l Streptomycin, pH 7.4) at 37ºC for 30 min, and a 5‐μl aliquot was used for the motility analysis with a computer‐assisted semen analysis machine (TOX IVOS Sperm Analyzer, Hamilton Thorne).
Scanning electron microscopy
Ependymal, tracheal, and kidney tissues from 2‐month‐old mice were fixed with 2.5% glutaraldehyde in PBS overnight at 4°C, post‐fixed with 1% OsO4 in PBS on ice for 1 h, and dehydrated with a graded ethanol series (30, 50, 70, 80, 95, 100%). Critical point drying was carried out before metal shadowing. Specimens were imaged with a scanning electron microscope (FEI Quanta 250).
Sucrose gradient centrifugation
Testes from two 8‐week‐old mice were homogenized in 600 μl of lysis buffer (20 mM Tris–HCl [pH 7.5], 100 mM KCl, 0.1% NP‐40, 1 mM EDTA, 10 mM Na4P2O7, 10% glycerol, and a cocktail of proteinase inhibitors [539134, Millipore]). The lysates were cleared by centrifugation at 16,000 g for 20 min at 4°C. 200 μl supernatants were incubated with 1 mM GTPγS or DMSO for 1 h at 30°C. After incubation, the lysates were loaded on top of a 5‐ml 10–40% continuous sucrose gradient and centrifugated at 100,000 g for 20 h at 4°C. 200‐μl fractions were collected from top to bottom for immunoblotting.
Immunoprecipitation and GST pull down
Co‐immunoprecipitation was performed as described previously (Zhao et al, 2013). NIH3T3 cells infected with lentivirus to stably express GFP‐tagged Rabl2, Rabl2Q80L, or Rabl2S35N were serum‐starved for 48 h before harvest, whereas cultured mEPCs were infected with adenovirus at 1 day before serum starvation and harvested at day 7 post‐serum starvation. The cells were lysed in ice‐cold lysis buffer (20 mM Tris–HCl [pH 7.5], 0.1% NP‐40, 100 mM KCl, 50 mM NaF, 10 mM Na‐Pyrophosphate, 1 mM Na3VO4, 1 mM EDTA, 10% Glycerol, 1 mM DTT, 1 mM PMSF, and protease inhibitors cocktail). The lysates were cleared by centrifugation at 16,000 g for 20 min at 4°C. The supernatants were incubated with anti‐GFP beads (gta‐400, Chromotek) for 2 h at 4°C. After washing, the beads were boiled in SDS‐loading buffer for immunoblotting.
For GST pull‐down assays, bacterial lysates expressing GST‐tagged Rabl2Q80L and Rabl2S35N were incubated with Glutathione‐agarose (G4510, Sigma) for 2 h at 4°C. After washing, the beads were incubated with bacterial lysates expressing FLAG‐tagged Ift74, Ift81, or their mixture for another 2 h. After washing, the beads were boiled in SDS‐loading buffer for immunoblotting.
Statistics
Band intensities in immunoblots and ciliary fluorescent intensities in micrographs were measured with Adobe Photoshop as described (Hoffman et al, 2001). Band intensities in immunoblots were normalized to the loading control. Statistical analysis was performed with paired or unpaired Student's t‐test with GraphPad Prism 6. No blinding strategy was used in this study.
Author contributions
XZ and XY conceived and directed the project; SD, HL performed major experiments; YZ initiated this project; SY and JL generated KI mice; YC purified mEPC cilia; BQ maintained KI mouse line; CH assisted in live imaging; JW produced the Rabl2 antibody; XZ, XY, SD, YZ and HL designed experiments, interpreted data, and wrote the paper.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supporting information
Appendix
Expanded View Figures PDF
Movie EV1
Movie EV2
Movie EV3
Movie EV4
Movie EV5
Movie EV6
Source Data for Expanded View
Review Process File
Source Data for Figure 1
Source Data for Figure 2
Source Data for Figure 3
Source Data for Figure 4
Source Data for Figure 5
Source Data for Figure 6
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Center for Biological Imaging (Institute of Biophysics, CAS) for supports on 3D‐SIM imaging, mass spectrometry and integrated laser microscopy systems (National Facility for Protein Science Shanghai), and institutional core facilities for cell biology and molecular biology for instrumental and technical supports. This work was supported by National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFA0503500 to X.Z. and X.Y.), National Natural Science Foundation of China (31991192 to X.Z.), Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDB19000000 to X.Z.), and NSFC grants (31471323 to X.Y. and 31730062 to J.L.).
The EMBO Journal (2021) 40: e105499.
Contributor Information
Xueliang Zhu, Email: xlzhu@sibcb.ac.cn.
Xiumin Yan, Email: yanx@sibcb.ac.cn.
Data availability
This study includes no data deposited in external repositories. The proteomic results of isolated cilia (Fig 5B) are provided as source data for Fig 5.
References
- Bangs F, Anderson KV (2017) Primary cilia and mammalian hedgehog signaling. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 9: a028175 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berbari NF, O'Connor AK, Haycraft CJ, Yoder BK (2009) The primary cilium as a complex signaling center. Curr Biol 19: R526–R535 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhogaraju S, Taschner M, Morawetz M, Basquin C, Lorentzen E (2011) Crystal structure of the intraflagellar transport complex 25/27. EMBO J 30: 1907–1918 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blacque OE, Scheidel N, Kuhns S (2018) Rab GTPases in cilium formation and function. Small GTPases 9: 76–94 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briscoe J, Therond PP (2013) The mechanisms of Hedgehog signalling and its roles in development and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 14: 416–429 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao J, Shen Y, Zhu L, Xu Y, Zhou Y, Wu Z, Li Y, Yan X, Zhu X (2012) miR‐129‐3p controls cilia assembly by regulating CP110 and actin dynamics. Nat Cell Biol 14: 697–706 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen JK, Taipale J, Young KE, Maiti T, Beachy PA (2002) Small molecule modulation of Smoothened activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99: 14071–14076 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou HT, Apelt L, Farrell DP, White SR, Woodsmith J, Svetlov V, Goldstein JS, Nager AR, Li Z, Muller J et al (2019) The molecular architecture of native BBSome obtained by an integrated structural approach. Structure 27: 1384–1394.e1384 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Cruz R, Stronks K, Rowan CJ, Rosenblum ND (2020) Lineage‐specific roles of hedgehog‐GLI signaling during mammalian kidney development. Pediatric Nephrology 35: 725–731 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dateyama I, Sugihara Y, Chiba S, Ota R, Nakagawa R, Kobayashi T, Itoh H (2019) RABL2 positively controls localization of GPCRs in mammalian primary cilia. J Cell Sci 132: jcs224428 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delgehyr N, Meunier A, Faucourt M, Bosch Grau M, Strehl L, Janke C, Spassky N (2015) Ependymal cell differentiation, from monociliated to multiciliated cells. Methods Cell Biol 127: 19–35 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai PB, San Agustin JT, Stuck MW, Jonassen JA, Bates CM, Pazour GJ (2018) Ift25 is not a cystic kidney disease gene but is required for early steps of kidney development. Mech Dev 151: 10–17 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eguether T, San Agustin JT, Keady BT, Jonassen JA, Liang Y, Francis R, Tobita K, Johnson CA, Abdelhamed ZA, Lo CW et al (2014) IFT27 links the BBSome to IFT for maintenance of the ciliary signaling compartment. Dev Cell 31: 279–290 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito A, Schlachter S, Schierle GS, Elder AD, Diaspro A, Wouters FS, Kaminski CF, Iliev AI (2009) Quantitative fluorescence microscopy techniques. Methods Mol Biol 586: 117–142 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsythe E, Beales PL (2013) Bardet‐Biedl syndrome. Eur J Hum genet 21: 8–13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia‐Gonzalo FR, Reiter JF (2017) Open sesame: how transition fibers and the transition zone control ciliary composition. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 9: a028134 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetz SC, Anderson KV (2010) The primary cilium: a signalling centre during vertebrate development. Nat Rev Genet 11: 331–344 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He M, Subramanian R, Bangs F, Omelchenko T, Liem KF Jr, Kapoor TM, Anderson KV (2014) The kinesin‐4 protein Kif7 regulates mammalian Hedgehog signalling by organizing the cilium tip compartment. Nat Cell Biol 16: 663–672 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilgendorf KI, Johnson CT, Jackson PK (2016) The primary cilium as a cellular receiver: organizing ciliary GPCR signaling. Curr Opin Cell Biol 39: 84–92 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T, Katoh Y, Nakayama K (2017) Intraflagellar transport‐A complex mediates ciliary entry and retrograde trafficking of ciliary G protein‐coupled receptors. Mol Biol Cell 28: 429–439 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman DB, Pearson CG, Yen TJ, Howell BJ, Salmon ED (2001) Microtubule‐dependent changes in assembly of microtubule motor proteins and mitotic spindle checkpoint proteins at PtK1 kinetochores. Mol Biol Cell 12: 1995–2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui CC, Joyner AL (1993) A mouse model of greig cephalopolysyndactyly syndrome: the extra‐toesJ mutation contains an intragenic deletion of the Gli3 gene. Nat Genet 3: 241–246 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui CC, Slusarski D, Platt KA, Holmgren R, Joyner AL (1994) Expression of three mouse homologs of the Drosophila segment polarity gene cubitus interruptus, Gli, Gli‐2, and Gli‐3, in ectoderm‐ and mesoderm‐derived tissues suggests multiple roles during postimplantation development. Dev Biol 162: 402–413 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui CC, Angers S (2011) Gli proteins in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 27: 513–537 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang SH, White KA, Somatilaka BN, Shelton JM, Richardson JA, Mukhopadhyay S (2018) The G protein‐coupled receptor Gpr161 regulates forelimb formation, limb patterning and skeletal morphogenesis in a primary cilium‐dependent manner. Development 145: dev154054 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa H, Marshall WF (2011) Ciliogenesis: building the cell's antenna. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 12: 222–234 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa H, Marshall WF (2015) Efficient live fluorescence imaging of intraflagellar transport in mammalian primary cilia. Methods Cell Biol 127: 189–201 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang J, Promchan K, Jiang H, Awasthi P, Marshall H, Harned A, Natarajan V (2016) Depletion of BBS protein LZTFL1 affects growth and causes retinal degeneration in mice. J Genet Genomics 43: 381–391 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanie T, Abbott KL, Mooney NA, Plowey ED, Demeter J, Jackson PK (2017) The CEP19‐RABL2 GTPase complex binds IFT‐B to initiate intraflagellar transport at the ciliary base. Dev Cell 42: 22–36.e12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keady BT, Samtani R, Tobita K, Tsuchya M, San Agustin JT, Follit JA, Jonassen JA, Subramanian R, Lo CW, Pazour GJ (2012) IFT25 links the signal‐dependent movement of Hedgehog components to intraflagellar transport. Dev Cell 22: 940–951 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong JH, Siebold C, Rohatgi R (2019) Biochemical mechanisms of vertebrate hedgehog signaling. Development 146: dev166892 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew GM, Ye F, Nager AR, Murphy JP, Lee JS, Aguiar M, Breslow DK, Gygi SP, Nachury MV (2014) The intraflagellar transport protein IFT27 promotes BBSome exit from cilia through the GTPase ARL6/BBS3. Dev Cell 31: 265–278 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo JC, Jamsai D, O'Connor AE, Borg C, Clark BJ, Whisstock JC, Field MC, Adams V, Ishikawa T, Aitken RJ et al (2012) RAB‐like 2 has an essential role in male fertility, sperm intra‐flagellar transport, and tail assembly. PLoS Genet 8: e1002969 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo JCY, O'Connor AE, Andrews ZB, Lo C, Tiganis T, Watt MJ, O'Bryan MK (2016) RABL2 is required for hepatic fatty acid homeostasis and its dysfunction leads to steatosis and a diabetes‐like state. Endocrinology 157: 4732–4743 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucker BF, Miller MS, Dziedzic SA, Blackmarr PT, Cole DG (2010) Direct interactions of intraflagellar transport complex B proteins IFT88, IFT52, and IFT46. J Biol Chem 285: 21508–21518 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milenkovic L, Weiss LE, Yoon J, Roth TL, Su YS, Sahl SJ, Scott MP, Moerner WE (2015) Single‐molecule imaging of Hedgehog pathway protein Smoothened in primary cilia reveals binding events regulated by Patched1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112: 8320–8325 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mourao A, Nager AR, Nachury MV, Lorentzen E (2014) Structural basis for membrane targeting of the BBSome by ARL6. Nat Struct Mol Biol 21: 1035–1041 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mourao A, Christensen ST, Lorentzen E (2016) The intraflagellar transport machinery in ciliary signaling. Curr Opin Struct Biol 41: 98–108 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukhopadhyay S, Wen X, Ratti N, Loktev A, Rangell L, Scales SJ, Jackson PK (2013) The ciliary G‐protein‐coupled receptor Gpr161 negatively regulates the Sonic hedgehog pathway via cAMP signaling. Cell 152: 210–223 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachury MV (2018) The molecular machines that traffic signaling receptors into and out of cilia. Curr Opin Cell Biol 51: 124–131 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura N, Rabouille C, Watson R, Nilsson T, Hui N, Slusarewicz P, Kreis TE, Warren G (1995) Characterization of a cis‐Golgi matrix protein, GM130. J Cell Biol 131: 1715–1726 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama K, Katoh Y (2018) Ciliary protein trafficking mediated by IFT and BBSome complexes with the aid of kinesin‐2 and dynein‐2 motors. J Biochem 163: 155–164 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niewiadomski P, Niedziolka SM, Markiewicz L, Uspienski T, Baran B, Chojnowska K (2019) Gli proteins: regulation in development and cancer. Cells 8: 147 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura DY, Fath M, Mullins RF, Searby C, Andrews M, Davis R, Andorf JL, Mykytyn K, Swiderski RE, Yang B et al (2004) Bbs2‐null mice have neurosensory deficits, a defect in social dominance, and retinopathy associated with mislocalization of rhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 16588–16593 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishijima Y, Hagiya Y, Kubo T, Takei R, Katoh Y, Nakayama K (2017) RABL2 interacts with the intraflagellar transport‐B complex and CEP19 and participates in ciliary assembly. Mol Biol Cell 28: 1652–1666 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pal K, Hwang SH, Somatilaka B, Badgandi H, Jackson PK, DeFea K, Mukhopadhyay S (2016) Smoothened determines beta‐arrestin‐mediated removal of the G protein‐coupled receptor Gpr161 from the primary cilium. J Cell Biol 212: 861–875 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos N, Reiter JF (2014) A central region of Gli2 regulates its localization to the primary cilium and transcriptional activity. J Cell Sci 127: 1500–1510 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seo S, Zhang Q, Bugge K, Breslow DK, Searby CC, Nachury MV, Sheffield VC (2011) A novel protein LZTFL1 regulates ciliary trafficking of the BBSome and Smoothened. PLoS Genet 7: e1002358 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaner NC, Lambert GG, Chammas A, Ni Y, Cranfill PJ, Baird MA, Sell BR, Allen JR, Day RN, Israelsson M et al (2013) A bright monomeric green fluorescent protein derived from Branchiostoma lanceolatum. Nat Methods 10: 407–409 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelton KR, Egle PM, Cochran DL (1981) Nuclear envelope proteins: identification of lamin B subtypes. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 103: 975–981 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siljee JE, Wang Y, Bernard AA, Ersoy BA, Zhang SM, Marley A, Von Zastrow M, Reiter JF, Vaisse C (2018) Subcellular localization of MC4R with ADCY3 at neuronal primary cilia underlies a common pathway for genetic predisposition to obesity. Nat Genet 50: 180–185 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snapp EL, Altan N, Lippincott‐Schwartz J (2003) Measuring protein mobility by photobleaching GFP chimeras in living cells. Curr Protoc Cell Biol Chapter 21: Unit 21 21 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenmark H (2009) Rab GTPases as coordinators of vesicle traffic. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10: 513–525 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tadenev AL, Kulaga HM, May‐Simera HL, Kelley MW, Katsanis N, Reed RR (2011) Loss of Bardet‐Biedl syndrome protein‐8 (BBS8) perturbs olfactory function, protein localization, and axon targeting. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108: 10320–10325 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taschner M, Kotsis F, Braeuer P, Kuehn EW, Lorentzen E (2014) Crystal structures of IFT70/52 and IFT52/46 provide insight into intraflagellar transport B core complex assembly. J Cell Biol 207: 269–282 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tickle C, Towers M (2017) Sonic Hedgehog signaling in limb development. Front Cell Dev Biol 5: 14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang B, Fallon JF, Beachy PA (2000) Hedgehog‐regulated processing of Gli3 produces an anterior/posterior repressor gradient in the developing vertebrate limb. Cell 100: 423–434 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang WJ, Tay HG, Soni R, Perumal GS, Goll MG, Macaluso FP, Asara JM, Amack JD, Tsou MF (2013) CEP162 is an axoneme‐recognition protein promoting ciliary transition zone assembly at the cilia base. Nat Cell Biol 15: 591–601 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Y, Liang D, Wang Y, Bai M, Tang W, Bao S, Yan Z, Li D, Li J (2013) Correction of a genetic disease in mouse via use of CRISPR‐Cas9. Cell Stem Cell 13: 659–662 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wustner D, Solanko LM, Lund FW, Sage D, Schroll HJ, Lomholt MA (2012) Quantitative fluorescence loss in photobleaching for analysis of protein transport and aggregation. BMC Bioinformatics 13: 296 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Y, Cao J, Huang S, Feng D, Zhang W, Zhu X, Yan X, (2015) Characterization of tetratricopeptide repeat-containing proteins critical for cilia formation and function. PLoS One 10: e0124378 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang TT, Su J, Wang WJ, Craige B, Witman GB, Tsou MF, Liao JC (2015) Superresolution pattern recognition reveals the architectural map of the ciliary transition zone. Sci Rep 5: 14096 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ye F, Breslow DK, Koslover EF, Spakowitz AJ, Nelson WJ, Nachury MV (2013) Single molecule imaging reveals a major role for diffusion in the exploration of ciliary space by signaling receptors. eLife 2: e00654 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ye F, Nager AR, Nachury MV (2018) BBSome trains remove activated GPCRs from cilia by enabling passage through the transition zone. J Cell Biol 217: 1847–1868 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Q, Nishimura D, Vogel T, Shao J, Swiderski R, Yin T, Searby C, Carter CS, Kim G, Bugge K et al (2013) BBS7 is required for BBSome formation and its absence in mice results in Bardet‐Biedl syndrome phenotypes and selective abnormalities in membrane protein trafficking. J Cell Sci 126: 2372–2380 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y, Chen Y, Zheng J, Wang J, Duan S, Zhang W, Yan X, Zhu X (2019) Vertebrate Dynein‐f depends on Wdr78 for axonemal localization and is essential for ciliary beat. J Mol Cell Biol 11: 383–394 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao H, Zhu L, Zhu Y, Cao J, Li S, Huang Q, Xu T, Huang X, Yan X, Zhu X (2013) The Cep63 paralogue Deup1 enables massive de novo centriole biogenesis for vertebrate multiciliogenesis. Nat Cell Biol 15: 1434–1444 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao H, Chen Q, Fang C, Huang Q, Zhou J, Yan X, Zhu X (2019) Parental centrioles are dispensable for deuterosome formation and function during basal body amplification. EMBO Rep 20: e46735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng J, Liu H, Zhu L, Chen Y, Zhao H, Zhang W, Li F, Xie L, Yan X, Zhu X (2019) Microtubule‐bundling protein Spef1 enables mammalian ciliary central apparatus formation. J Mol Cell Biol 11: 67–77 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu W, Smith JW, Huang CM (2010) Mass spectrometry‐based label‐free quantitative proteomics. J Biomed Biotechnol 2010: 840518 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zou W, Greenblatt MB, Brady N, Lotinun S, Zhai B, de Rivera H, Singh A, Sun J, Gygi SP, Baron R et al (2013) The microtubule‐associated protein DCAMKL1 regulates osteoblast function via repression of Runx2. J Exp Med 210: 1793–1806 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Appendix
Expanded View Figures PDF
Movie EV1
Movie EV2
Movie EV3
Movie EV4
Movie EV5
Movie EV6
Source Data for Expanded View
Review Process File
Source Data for Figure 1
Source Data for Figure 2
Source Data for Figure 3
Source Data for Figure 4
Source Data for Figure 5
Source Data for Figure 6
Data Availability Statement
This study includes no data deposited in external repositories. The proteomic results of isolated cilia (Fig 5B) are provided as source data for Fig 5.


