Abstract
Important differences in comorbidities and clinical characteristics exist between women and men with heart failure (HF). In particular, differences in the kinetics of biological circulating biomarkers—a critical component of cardiovascular care—are highly relevant. Most circulating HF biomarkers are assessed daily by clinicians without taking sex into account, despite the multiple gender-related differences observed in plasma concentrations. Even in health, compared to men, women tend to exhibit higher levels of natriuretic peptides and galectin-3 and lower levels of cardiac troponins and the cardiac stress marker, soluble ST2. Many biological factors can provide a reliable explanation for these differences, like body composition, fat distribution, or menopausal status. Notwithstanding, these sex-specific differences in biomarker levels do not reflect different pathobiological mechanisms in HF between women and men, and they do not necessarily imply a need to use different diagnostic cut-off levels in clinical practice. To date, the sex-specific prognostic value of HF biomarkers for risk stratification is an unresolved issue that future research must elucidate. This review outlines current evidence regarding gender-related differences in circulating biomarkers widely used in HF, the pathophysiological mechanisms underlying these differences, and their clinical relevance.
Keywords: biomarker, heart failure, gender, troponin, natriuretic peptide, ST2, Galectine-3
Introduction
Heart failure (HF) is a major health care issue in both sexes; it is associated with significant morbidity, mortality, and health care costs (1). Several differences between women and men have been observed in HF, including the epidemiology, etiology, pathogenesis, risk factors, and prognosis (2). The incidence of HF also differs between men and women, depending on the study population analyzed (3, 4). For example, women had a lower risk of incident HF than men, in middle-aged to older individuals, but women had a higher HF risk than men in the oldest age groups (5). Men tended to be at higher risk of developing HF with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), and conversely, women were more likely to develop HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) (6). This distinction might be attributable to the predisposition of women to develop coronary microvascular dysfunction/endothelial inflammation and the predisposition in men to develop macrovascular coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction (7). These sex-related differences in HF phenotypes and underlying pathophysiology are also reflected in HF biomarker dissimilarities.
In 2007, the National Academy of Clinical Chemistry and the International Federation of Clinical Chemistry recommended the development of sex-specific reference ranges for cardiac biomarkers used routinely in clinical practice (8). Consequently, over the years, sex-driven differences in both reference and cut-off values have been described for several biomarkers in cardiovascular disease (9). However, most of these cardiovascular biomarkers are used day-to-day by clinicians without taking sex into account. It is hypothesized that the lack of sex-specific thresholds for cardiac biomarkers might contribute to under-diagnosing HF in women, which could potentially result in worse outcomes (10).
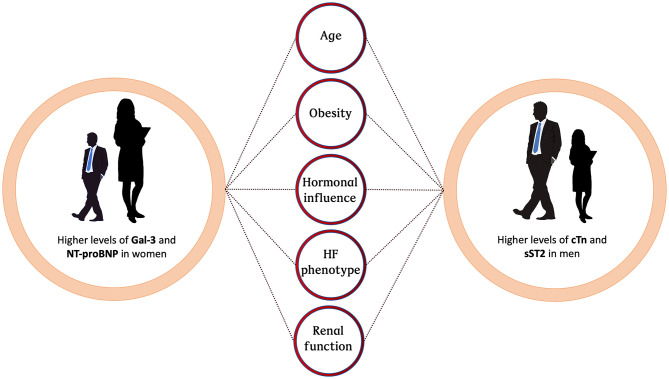
Improving HF care requires consideration of all gender-related differences. Moreover, improving our understanding of gender-specific differences in HF biomarkers might enrich our understanding of physiological differences between men and women with HF. Taking these points into consideration, this review covers the four most important and frequent HF biomarkers available in daily clinical practice, with a focus on differences between women and men (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Schematic of factors contributing to sex-related differences in HF biomarkers. HF, heart failure; Gal-3, Galectine 3; NT-proBNP, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide; cTn, cardiac troponin; sST2, soluble interleukin-like receptor-like-1.
Cardiac Troponin
Currently, assays are available for detecting cardiac troponin (cTn) with high clinical sensitivity and high specificity for myocardial tissue. Moreover, many assays are capable of early cTn detection, when necrosis is minimal or even in the absence of cell necrosis by different mechanisms (increased myocyte turnover or increased cell wall permeability among others). Due to these features, cTn has become the standard biomarker for myocardial damage and the preferred biomarker for diagnosing acute myocardial infarction. In addition, individuals in the HF population frequently have increased concentrations of high-sensitivity cTn (hs-cTn). In up to 93% of patients with acute HF and up to 74% of patients with stable chronic HF, hs-cTn concentrations are above the 99th percentile of the reference value (11). However, several studies and critical reviews have examined sex-related differences in cTn levels that might affect diagnostic and prognostic performance.
Variations in cTn Concentrations According to Gender
Marked variations in cTn concentrations have been detected between women and men, with higher values commonly found in men (12, 13). This difference has also been evident in patients with HF (14, 15). Consequently, when interpreting cTn results, sex-related peculiarities in the pathobiology of cardiac disease must be considered. Men tend to have a greater cardiac mass and a higher incidence of subclinical coronary artery disease than women (16, 17). Women tend to show less severity in atherosclerosis, left ventricular hypertrophy, and cardiomyocyte apoptosis than men (18, 19). In addition, HFrEF (from ischemic and non-ischemic etiologies) occurs more frequently in men than in women, and HFpEF is more prevalent among women than among men (6, 20). The possibility of an indirect hormonal influence should also be considered, in light of cardioprotective effects of estrogens, which suppress cardiomyocyte apoptosis, and the potentially harmful effects of testosterone, which induces hypertrophy and apoptosis in cardiomyocytes (21–23). Obesity was also independently associated with a positive, linear increase in the likelihood of high hs-cTn levels, as shown in a recent population-based study of subjects without cardiovascular disease at baseline. In that study, individuals with severe obesity and high hs-cTn levels had a >9-fold higher risk of incident HF compared to individuals with normal weight and undetectable hs-cTn levels (24). All these variations could contribute to sex-related differences in serum cTn concentrations and had allowed the thoroughly study of sex-tailored cut-off values of hs-cTn in the setting fundamentally of ACS, where sex-specific cut-off points might improve sensitivity for diagnosis of myocardial infarction in women (25). Diagnostic performance of hs-cTn for HF is however limited. In the general population, the application of dichotomous cut-off values of hs-cTn, lower in women than men: 4.7 vs. 7.0 pg/ml, respectively, for hs-cTnI as studied by Zeller et al., allowed substantial reclassification information for prediction of cardiovascular disease, including HF, being considered an independent predictor of cardiovascular events (26).
Prognostic Utility of cTn in HF
In the HF spectrum, the diagnostic utility of cTn is limited; however, its prognostic value is highly relevant. Studies by Parikh et al. (27) and by de Boer et al. (28) demonstrated that cTn levels could predict incident HF in different community-based cohorts. Recently, a meta-analysis that pooled data from 16 prospective studies and included nearly 67,000 subjects demonstrated a strong association between cTn and the development of incident HF, and this association was found in both men and women (29). Robust evidence from a meta-analysis based on individual patient data from 10 studies and 11 cohorts (30) also suggested that cTn could become an affordable biomarker for risk stratification in patients with HF, due to the similarity of its prognostic value between men and women. However, data are inconsistent as to whether the prognostic value of cTn differs with sex. Current evidence has indicated that the 99th percentile cutoff values were higher in males than in females (26, 31). However, despite the widespread use of cTn in clinical practice, all available assays lack sex-specific reference values.
Natriuretic Peptides
Natriuretic peptides are a group of neurohormones that play a central role in the regulation of electrolytes and water balance through their diuretic and natriuretic effects (32). In humans, mainly three forms of natriuretic peptides are found: A-type natriuretic peptide (ANP), B-type type natriuretic peptide (BNP), and C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP). CNP is primarily produced in vascular endothelial cells; ANP and BNP are mostly found in the myocardium. Natriuretic peptides are released by the myocardium in response to stretch and hypoxic stimuli (33). The majority of clinical evidence on natriuretic peptides in the setting of HF is related to BNP and the amino terminal of the proBNP molecule (NT-proBNP). Therefore, this review focuses on NT-proBNP, because it is the best choice for a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in HF, according to the 2016 European Society of Cardiology HF clinical guidelines (34).
The most extensive evidence on the value of BNP-related in vitro diagnostic tests was published in the early 2000s. Comparative studies that measured concentrations of the active BNP hormone vs. NT-proBNP generally demonstrated diagnostic equivalency for differentiating HF from other causes of shortness of breath. The proBNP molecule contains 108 amino acids. The first 76 amino acids are biologically inactive, and amino acids 77–108 constitute the biologically active component of the molecule, BNP.
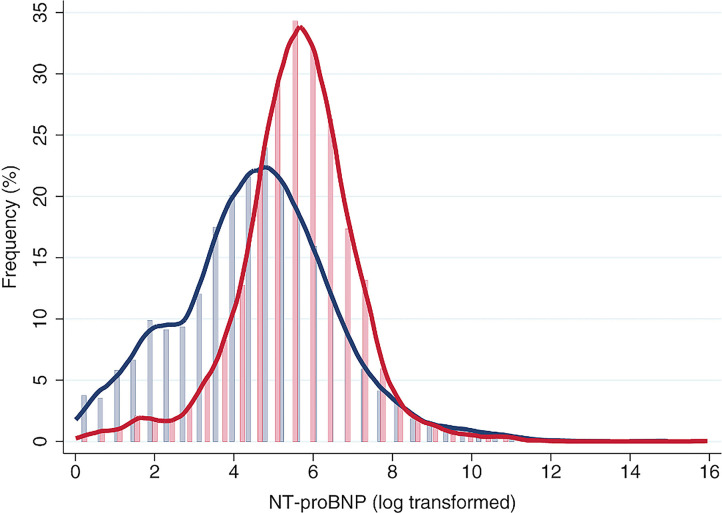
Currently, NT-proBNP is a well-established, powerful biomarker for the diagnosis and prognosis of HF (35–37). It is also a useful biomarker for risk stratification in other several cardiovascular disorders (38, 39). Strong clinical evidence has revealed that several factors influence NT-proBNP levels. Elevated concentrations were observed in patients with various cardiovascular disorders and in patients with renal dysfunction (40, 41). A previous study, which included 7,770 individuals from the Framingham Heart Study and the Malmö Diet and Cancer study, reported that obesity was associated with 6–20% lower NT-proBNP levels, compared to normal-weight status, and insulin resistance was associated with 10–30% lower levels of NT-proBNP, compared to insulin sensitive status (42). Age and sex are also important in modifying circulating levels of natriuretic peptides. Most studies found that at baseline NT-proBNP levels were lower in males than in females (Figure 2) and, in both genders, increases were correlated with age (44).
Figure 2.
Distribution of N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) in both sexes. Reproduced with permission from Suthahar et al. (43).
Sex Differences in NT-proBNP Levels
Although sex-specific differences in NT-proBNP levels have been documented, the precise mechanism that gives rise to higher NT-proBNP levels in women than in men is not well-established in healthy subjects. Several possible explanations have been explored. One reasonable pathobiological explanation involves the effects of sex hormones. Strong clinical evidence has shown that testosterone could lower cardiac natriuretic peptide levels, probably by upregulating neprilysin activity; this effect might explain why NT-proBNP levels are lower in men than in women (45, 46). Other studies showed that estrogen increased cardiac natriuretic peptide gene expression and its release, which might explain the elevated cardiac natriuretic peptides levels in women compared to men. However, other reports suggested that estrogen also increased neprilysin activity (43, 47). In postmenopausal women, hormone replacement therapy administered for 3 months resulted in elevations in ANP and BNP concentrations (48). Some research however hypothesized that free testosterone could increase lean mass and may directly decrease natriuretic peptide synthesis. This last statement goes beyond the notion that estrogens are primarily responsible for gender differences in natriuretic peptides considering that exogenous estrogen increased the sex hormone-binding globulin with a subsequent lower free testosterone (49). Of note, the profoundly different anthropometric characteristics and fat distributions found in males and females might also play a role in natriuretic hormone levels. Recent evidence from a general population study found that the relationship between NT-proBNP and obesity had a significant sex-associated component. The inverse association between NT-proBNP and obesity was more pronounced among females than among males. Furthermore, among females, but not males, individuals with abdominal (visceral) obesity had lower NT-proBNP levels than individuals with peripheral (subcutaneous) obesity (50). Some studies propose at a molecular level a higher clearance of BNP in obesity due to increased expression of natriuretic peptide receptor on adipose tissue, which binds BNP and leads to its internalization and degradation (51) A reduced release of natriuretic peptides from myocardial tissue in obese individuals have also been pustuled as an alternative hypothesis (52) Therefore, a combination of increased degradation and decreased release may contribute to relative deficiency of natriuretic peptides in obesity.
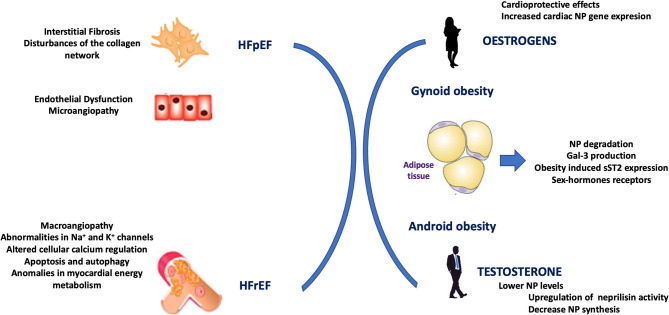
However, these sex-related dissimilarities observed in the general population appeared to be less pronounced in HF and other disease populations associated with upregulated NT-proBNP levels. Some studies have reported the opposite findings, noting that natriuretic peptide levels were similar or lower in women compared to men (53, 54). However, this change in tendency should be interpreted cautiously, because over the past decade, one of the most robust findings across numerous HF studies was that the gender distribution varied according to the HF phenotype. Among individuals with HF, women significantly outnumber men, and the gender ratio is ~2:1 in HFpEF (6, 20). Numerous reports have shown that natriuretic peptide levels are much lower in patients with HFpEF than in patients with HFrEF (35, 55, 56). Consequently, when studies analyze the convoluted relationship between sex, ejection fraction, and BNP levels in the setting of HF, the results show that women tend to have higher BNP levels than men (57, 58). However, despite the gender-related differences in the levels of natriuretic peptides, the performance of these peptides for diagnosing HF and their prognostic utility are similar in both sexes, and sex specific cut-off points are not usually recommended. At this point, it should also be noted that there is a lack of coincidences between molecular mechanisms that affect HF progression and gender particularities in the context of biomarker levels' variability (Figure 3).
Figure 3.
Representation of a lack of coincidences between mechanisms that affect heart failure progression and gender particularities in the context of biomarker levels' variability. HFpEF, heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; HFrEF, heart failure with reduced ejection fraction; NP, natriuretic peptide; Gal-3, Galectine 3; sST2, soluble interleukin-like receptor-like-1.
Prediction of HF Incidence
NT-proBNP levels have shown clinical relevance in predicting the incidence of HF in the general population. High levels were associated with a high risk of HF (59–61), which suggested that elevated baseline levels might reflect subclinical cardiac dysfunction that could subsequently manifest as overt HF. Recent studies have explored sex-specific differences in using NT-proBNP to evaluate cardiac functional competence. Evidence from two community-based studies (44, 61) showed that the optimal cut-off point for detecting moderate to severe left ventricular disfunction was higher in women than in men. The discriminatory ability of the biomarker was similar in both sexes, but the strength of the association might be different between men and women. Indeed, a recent meta-analysis of prospective studies (62) found that NT-proBNP was more strongly associated with incident HF in men than in women. In the near future, the use of natriuretic peptides to assess risk in asymptomatic adults is expected to become translated from clinical studies to routine clinical practice.
Soluble Interleukin-1 Receptor-Like 1 (ST2)
ST2 is a member of the interleukin-1 receptor family. ST2 exists in both membrane-bound (ST2L) and soluble (sST2) forms. Interleukin-33 (IL-33) is the functional ligand for ST2L, and in the heart, the IL-33/ST2L interaction mitigates cellular responses to mechanical stress. This function is thought to be mediated by the inhibition of apoptosis and cell death (63). Loss of IL-33/ST2L signaling results in unchecked remodeling in the ventricular myocardium, which leads to myocyte hypertrophy, fibrosis, and a decline in left ventricular function (64). In contrast, sST2 acts as a “decoy” receptor for IL-33; thus, sST2 inhibits the cardioprotective effects mediated by the IL-33/ST2L interaction, which indirectly promotes myocardial damage (65). With the development of a highly sensitive ELISA method for measuring sST2 (66), in the last decade, clinical evidence has highlighted the biological and clinical importance of plasma sST2 concentrations. Currently, sST2 is considered a strong, independent prognostic biomarker in patients with myocardial infarction and HF (67, 68).
Clinical data has suggested that sex has a potentially important effect on sST2 concentrations. Women exhibited lower sST2 levels than age-matched men (69). In a large population-based study of ambulatory individuals, women had lower sST2 levels than men, but among older women, an age-associated rise in sST2 concentrations was observed. However, even among older adults, men had higher sST2 levels than women (69). These differences, which seem to be evident beginning in late adolescence (70), were present both in patients with cardiovascular disease and in healthy subjects. Currently, the mechanism underlying these differences has not been elucidated. The hypothesis that sex hormones might be responsible for differences in sST2 levels has not been adequately proven, and current evidence remains controversial. Some studies have supported this hypothesis by showing that elevated testosterone levels were linked to elevated ST2 concentrations, and conversely, exogenous estrogen therapy was linked to lower sST2 levels. In contrast, another study did not find any significant correlation between sex hormones and sST2 levels (69, 71). Obesity is also an important factor to consider in this setting, because sex hormones are produced by adipose tissue, and gender-related differences have been shown in the association between obesity and metabolic diseases. A recent study by Zhao et al. revealed, in an animal model, that obesity induced sST2 expression and secretion in adipocytes (72). A deep physiological understanding of the reasons and clinical relevance of gender-specific differences in sST2 concentrations requires future research.
Due to the prognostic value of ST2 (73–75) and its ability to predict incident HF (76), it has become part of the risk stratification strategy in HF clinical practice guidelines (77). A cut-off point of 35 ng/ml ST2 has been universally adopted as a good indicator of prognosis in both sexes; thus, to date, sex-specific cut-off points have not been needed for risk predictions.
Galectin-3
Galectin-3 (Gal-3), a unique member of the chimera-type galectins, is involved in a large number of disease processes. It is widely expressed in human tissues, including epithelial, endothelial, and immune cells (78). Gal-3 plays a role in both acute and chronic inflammation, and its effects on cell function include the activation of fibroblasts and macrophages, which lead to fibrosis in various organs, including the heart (79). As a biomarker, Gal-3 has been associated with cardiac function (80); several studies have demonstrated significantly higher Gal-3 levels in patients with HF, particularly those with HFpEF, compared to controls (80). Nevertheless, this biomarker is not predominantly produced in the heart; non-cardiac sources appear to be responsible for high Gal-3 levels in patients with HF (81).
Recent data from population-based studies (82–84) have indicated that plasma Gal-3 levels were slightly higher in women than in men. The physiological explanation for this gender-specific difference is not fully understood, but differences in fat mass might play a role, considering that, for the same body mass index, women typically have 10% more body fat than men (85). Indeed, prior studies have observed an association between total body fat and Gal-3 levels (86). Although the sex-specific prognostic value of Gal-3 in HF remains unknown, baseline Gal-3 concentrations were associated with adverse outcomes during follow-up in patients with acute and chronic HF (87–89). However, the prognostic value of Gal-3 in the setting of chronic HF remains controversial; other biomarkers, such as NT-proBNP or sST2, have frequently exhibited superior predictive value (90). Moreover, other studies have shown that the predictive value of Gal-3 in HF was less pronounced when the analysis was adjusted for renal function (87).
In the Framingham Heart Study, an analysis of more than 3,000 participants showed that elevated Gal-3 concentrations were associated with increases in the risk of new-onset HF (HR 1.28 per 1 standard deviation increase in the log-Gal-3 concentration). This association was clearly attenuated after adjusting for kidney function (82). This “renal implication” highlights the paramount relevance of cardio-renal interactions in the setting of HF, and it suggests that HF might involve a common profibrotic process in the heart and kidneys.
Less Common Biomarkers in Clinical Practice
In the last decade there has been an intensified interest in additional biomarkers as an objective alternative for diagnosis, prognosis or personalized treatment in HF. Among them is the growth differentiation factor-15 (GDF-15), a member of the transforming growth factor-?? cytokine superfamily with anti-apoptotic, anti-hypertrophic, and anti-inflammatory properties. GDF-15 is weakly expressed in tissues under normal conditions. Although its pathobiology is not fully understood, it is strongly induced by macrophages in response to inflammation and tissue injury. It appears to be only moderately expressed in the heart (81). Despite GDF-15 have been identified as an inflammatory biomarker with prognostic value in several conditions, particularly in cardiovascular diseases (91, 92), with strong association with incident HF (93), sex differences in plasma levels of this biomarker have not been clearly established (94, 95). It has been showed that testosterone together with estradiol significantly decreased GDF-15 levels through an androgren receptor/estrogen receptor-mediated pathway (96). Osteopontin, a glycoprotein expressed in various cell types, including cardiomyocytes and fibroblasts has also gained interest as a prognostic marker in HF. It had been found to be significantly elevated in patients with systolic HF (97). Its cardiac expression promotes myocardial fibrosis and increases left ventricular stiffness (98). It appears that plasma osteopontin levels are higher in men than in women as evidence in the study by Arnlöv et al. (99), however there are lacking evidence in the literature of sex differences in osteopontin expression, and this requires further investigation.
Conclusions and Perspectives
Most circulating HF biomarkers are used daily by clinicians without taking sex into account. Nevertheless, multiple gender-related differences have been observed in the plasma concentrations of several biomarkers. In the healthy population, women tend to exhibit higher levels of natriuretic peptides and Gal-3 and lower levels of cTn and sST2, compared to men. Plausible biological explanations for these sex-related differences have been postulated, like differences in body composition, fat distribution, or sex hormones. Nonetheless, several clinical studies have shown that these differences were attenuated in patients with HF, despite the fact that distinct gender distributions have been extensively described for different HF phenotypes. Moreover, these sex-related differences do not necessarily translate into a need to use different cut-off points for men and women, either for HF diagnosis or HF prognosis, in clinical practice. Future research should explore the clinical value of considering possible sex-related differences in specific HF biomarkers, in both diagnostic and prognostic settings, with the aim of improving HF management and patient care.
Author Contributions
GC drafted the manuscript with support from AB-G. All the authors contributed to manuscript revision and read and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of Interest
AB-G has received speaker fees from Roche Diagnostics. AB-G and JL report a relationship with Critical Diagnostics. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- 1.Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, Benjamin EJ, Berry JD, Blaha MJ, et al. American heart association statistics committee and stroke statistics subcommittee. heart disease and stroke statistics−2014 update: a report from the American heart association. Circulation. (2014) 129:e28–92. 10.1161/01.cir.0000441139.02102.80 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bozkurt B, Khalaf S. Heart failure in women. Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc J. (2017) 13:216–23. 10.14797/mdcj-13-4-216 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lehto HR, Lehto S, Havulinna AS, Salomaa V. Does the clinical spectrum of incident cardiovascular disease differ between men and women? Eur J Prev Cardiol. (2014) 21:964–71. 10.1177/2047487313482284 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lloyd-Jones DM, Larson MG, Leip EP, Beiser A, D'Agostino RB, Kannel WB, et al. Framingham heart study. Lifetime risk for developing congestive heart failure: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. (2002) 106:3068–72. 10.1161/01.cir.0000039105.49749.6f [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Magnussen C, Niiranen TJ, Ojeda FM, Gianfagna F, Blankenberg S, Vartiainen E, et al. Sex-Specific epidemiology of heart failure risk and mortality in europe: results from the BiomarCaRE consortium. JACC Heart Fail. (2019) 7:204–13. 10.1016/j.jchf.2018.08.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Scantlebury DC, Borlaug BA. Why are women more likely than men to develop heart failure with preserved ejection fraction? Curr Opin Cardiol. (2011) 26:562–8. 10.1097/HCO.0b013e32834b7faf [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Lam CSP, Arnott C, Beale AL, Chandramouli C, Hilfiker-Kleiner D, Kaye DM, et al. Sex differences in heart failure. Eur Heart J. (2019) 40:3859–68c. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz835 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Apple FS, Jesse RL, Newby LK, Wu AH, Christenson RH, Cannon CP, et al. IFCC committee on standardization of markers of cardiac damege, Jaffe AS, Mair J, Ordonez-Llanos J, Pagani F, Panteghini M, Tate J; National academy of clinical biochemistry. National academy of clinical biochemistry and IFCC committee for standardization of markers of cardiac damage laboratory medicine practice guidelines: analytical issues for biochemical markers of acute coronary syndromes. Clin Chem. (2007) 53:547–51. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.185266 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Daniels LB, Maisel AS. Cardiovascular biomarkers and sex: the case for women. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2015) 12:588–96. 10.1038/nrcardio.2015.105 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sobhani K, Nieves Castro DK, Fu Q, Gottlieb RA, Van Eyk JE, Noel Bairey Merz C. Sex differences in ischemic heart disease and heart failure biomarkers. Biol Sex Differ. (2018) 9:43. 10.1186/s13293-018-0201-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Eggers KM, Lindahl B. Application of cardiac troponin in cardiovascular diseases other than acute coronary syndrome. Clin Chem. (2017) 63:223–35. 10.1373/clinchem.2016.261495 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sandoval Y, Apple FS. The global need to define normality: the 99th percentile value of cardiac troponin. Clin Chem. (2014) 60:455–62. 10.1373/clinchem.2013.211706 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Apple FS, Sandoval Y, Jaffe AS, Ordonez-Llanos J. IFCC task force on clinical applications of cardiac biomarkers. cardiac troponin assays: guide to understanding analytical characteristics and their impact on clinical care. Clin Chem. (2017). 63:73–81. 10.1373/clinchem.2016.255109 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Grodin JL, Neale S, Wu Y, Hazen SL, Tang WHW. Prognostic comparison of different sensitivity cardiac troponin assays in stable heart failure. Am J Med. (2015) 128:276−82. 10.1016/j.amjmed.2014.09.029 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gravning J, Askevold ET, Nymo SH, Ueland T, Wikstrand J, McMurray JJV, et al. Prognostic effect of high-sensitive troponin T assessment in elderly patients with chronic heart failure: results from the CORONA trial. Circ Heart Fail. (2014) 7:96–103. 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.113.000450 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Salton CJ, Chuang ML, O'Donnell CJ, Kupka MJ, Larson MG, Kissinger KV, et al. Gender differences and normal left ventricular anatomy in an adult population free of hypertension. a cardiovascular magnetic resonance study of the Framingham heart study offspring cohort. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2002) 39:1055–60. 10.1016/S0735-1097(02)01712-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Laufer EM, Mingels AM, Winkens MH, Joosen IA, Schellings MW, Leiner T, et al. The extent of coronary atherosclerosis is associated with increasing circulating levels of high sensitive cardiac troponin T. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2010) 30:1269–75. 10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.200394 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Piro M, Della Bona R, Abbate A, Biasucci LM, Crea F. Sex-related differences in myocardial remodeling. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2010) 55:1057–65. 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.09.065 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Westerman S, Wenger NK. Women and heart disease, the underrecognized burden: sex differences, biases, and unmet clinical and research challenges. Clin Sci. (2016) 130:551–63. 10.1042/CS20150586 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Borlaug BA, Redfield MM. Diastolic and systolic heart failure are distinct phenotypes within the heart failure spectrum. Circulation. (2011) 123:2006–13. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.954388 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Papamitsou T, Barlagiannis D, Papaliagkas V, Kotanidou E, Dermentzopoulou-Theodoridou M. Testosterone-induced hypertrophy, fibrosis and apoptosis of cardiac cells – an ultrastructural and immunohistochemical study. Med Sci Monit. (2011) 17:BR266–273. 10.12659/MSM.881930 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Liu H, Pedram A, Kim JK. Oestrogen prevents cardiomyocyte apoptosis by suppressing p38α-mediated activation of p53 and by down-regulating p53 inhibition on p38??. Cardiovasc Res. (2011) 89:119–28. 10.1093/cvr/cvq265 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Iorga A, Cunningham CM, Moazeni S, Ruffenach G, Umar S, Eghbali M. The protective role of estrogen and estrogen receptors in cardiovascular disease and the controversial use of estrogen therapy. Biol Sex Differ. (2017) 8:33. 10.1186/s13293-017-0152-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ndumele CE, Coresh J, Lazo M, Hoogeveen RC, Blumenthal RS, Folsom AR, et al. Obesity, subclinical myocardial injury, and incident heart failure. JACC Heart Fail. (2014) 2:600–7. 10.1016/j.jchf.2014.05.017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Shah AS, Griffiths M, Lee KK, McAllister DA, Hunter AL, Ferry AV, et al. High sensitivity cardiac troponin and the under-diagnosis of myocardial infarction in women: prospective cohort study. BMJ. (2015) 350:g7873. 10.1136/bmj.g7873 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Zeller T, Tunstall-Pedoe H, Saarela O, Ojeda F, Schnabel RB, Tuovinen T, et al. High population prevalence of cardiac troponin I measured by a high-sensitivity assay and cardiovascular risk estimation: the MORGAM biomarker project Scottish cohort. Eur Heart J. (2014) 35:271–81. 10.1093/eurheartj/eht406 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Parikh RH, Seliger SL, de Lemos J, Nambi V, Christenson R, Ayers C, et al. Prognostic significance of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T concentrations between the limit of blank and limit of detection in community-dwelling adults: a metaanalysis. Clin Chem. (2015) 61:1524–31. 10.1373/clinchem.2015.244160 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.de Boer RA, Nayor M, DeFilippi CR, Enserro D, Bhambhani V, Kizer JR, et al. Association of cardiovascular biomarkers with incident heart failure with preserved and reduced ejection fraction. JAMA Cardiol. (2018) 3:215–24. 10.1001/jamacardio.2018.1623 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Evans JDW, Dobbin SJH, Pettit SJ, di Angelantonio E, Willeit P. High-sensitivity cardiac troponin and new-onset heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 67,063 patients with 4,165 incident heart failure events. JACC Heart Fail. (2018) 6:187–97. 10.1016/j.jchf.2017.11.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Aimo A, Januzzi JL, Vergaro G, Ripoli A, Latini R, Masson S, et al. Prognostic value of high-sensitivity troponin T in chronic heart failure: an individual patient data meta-analysis. Circulation. (2018) 137:286–97. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.031560 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Apple FS, Ler R, Murakami MM. Determination of 19 cardiac troponin I and T assay 99th percentile values from a common presumably healthy population. Clin Chem. (2012) 58:1574–81. 10.1373/clinchem.2012.192716 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Omland T, Hagve T-A. Natriuretic peptides: physiologic and analytic considerations. Heart Fail Clin. (2009) 5:471–87. 10.1016/j.hfc.2009.04.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Maeder MT, Mariani JA, Kaye DM. Hemodynamic determinants of myocardial B-type natriuretic peptide release: relative contributions of systolic and diastolic wall stress. Hypertension. (2010) 56:682–9. 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.110.156547 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Ponikowski P, Voors AA, Anker SD, Bueno H, Cleland JGF, Coats AJS, et al. (2016). ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis treatment of acute chronic heart failure: the task force for the diagnosis treatment of acute chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC)Developed with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J. (2016) 37:2129–200. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw128 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Salah K, Stienen S, Pinto YM, Eurlings LW, Metra M, Bayes-Genis A, et al. Prognosis and NT-proBNP in heart failure patients with preserved versus reduced ejection fraction. Heart. (2019) 105:1182–9. 10.1136/heartjnl-2018-314173 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Ferreira S, Almeida R, Guerrero H, Lourenço-Ferreira S, Fonseca L, Rocha R, et al. Prognosis of decompensated heart failure: role of NT-proBNP. Rev Port Cardiol. (2007) 26:535–45 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Taylor CJ, Roalfe AK, Iles R, Hobbs FD. The potential role of NT-proBNP in screening for and predicting prognosis in heart failure: a survival analysis. BMJ Open. (2014) 4:e004675. 10.1136/bmjopen-2013-004675 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Zhang B, Xu H, Zhang H, Liu Q, Ye Y, Hao J, et al. CHINA-DVD Collaborators. prognostic value of N-terminal Pro-B-type natriuretic peptide in elderly patients with valvular heart disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2020) 75:1659–72. 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.02.031 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Bergler-Klein J, Gyöngyösi M, Maurer G. The role of biomarkers in valvular heart disease: focus on natriuretic peptides. Can J Cardiol. (2014) 30:1027–34. 10.1016/j.cjca.2014.07.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Anwaruddin S, Lloyd-Jones DM, Baggish A, Chen A, Krauser D, Tung R, et al. Renal function, congestive heart failure, and amino-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide measurement: results from the ProBNP investigation of dyspnea in the emergency department (PRIDE) Study. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2006) 47:91–7. 10.1016/j.jacc.2005.08.051 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.du Fay de Lavallaz J, Badertscher P, Nestelberger T, Zimmermann T, Miró Ò, Salgado E, et al. B-Type natriuretic peptides and cardiac troponins for diagnosis and risk-stratification of syncope. Circulation. (2019) 139:2403–18. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.042847 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Khan AM, Cheng S, Magnusson M, Larson MG, Newton-Cheh C, McCabe EL, et al. Cardiac natriuretic peptides, obesity, and insulin resistance: evidence from two community-based studies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2011) 96:3242–9. 10.1210/jc.2011-1182 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Huang J, Guan H, Booze RM, Eckman CB, Hersh LB. Estrogen regulates neprilysin activity in rat brain. Neurosci Lett. (2004) 367:85–7. 10.1016/j.neulet.2004.05.085 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Redfield MM, Rodeheffer RJ, Jacobsen SJ, Mahoney DW, Bailey KR, Burnett JC, Jr. Plasma brain natriuretic peptide concentration: impact of age and gender. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2002) 40:976–82. 10.1016/S0735-1097(02)02059-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Bachmann KN, Huang S, Lee H, Dichtel LE, Gupta DK, Burnett JC, et al. Effect of testosterone on natriuretic peptide levels. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2019) 73:1288–96. 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.12.062 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Yao M, Nguyen TV, Rosario ER, Ramsden M, Pike CJ. Androgens regulate neprilysin expression: role in reducing beta-amyloid levels. J Neurochem. (2008) 105:2477–88. 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05341.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kuroski de Bold ML. Estrogen, natriuretic peptides and the renin–angiotensin system. Cardiovasc Res. (1999) 41:524–31.44. 10.1016/S0008-6363(98)00324-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Maffei S, Del Ry S, Prontera C, Clerico A. Increase in circulating levels of cardiac natriuretic peptides after hormone replacement therapy in postmenopausal women. Clin Sci. (2001) 101:447–53. 10.1042/cs1010447 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Chang AY, Abdullah SM, Jain T, Stanek HG, Das SR, McGuire DK, et al. Associations among androgens, estrogens, and natriuretic peptides in young women: observations from the dallas heart study. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2007) 49:109–16. 10.1016/j.jacc.2006.10.040 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Suthahar N, Meijers WC, Ho JE, Gansevoort RT, Voors AA, van der Meer P, et al. Sex-specific associations of obesity and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide levels in the general population. Eur J Heart Fail. (2018) 20:1205–14. 10.1002/ejhf.1209 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Potter LR. Natriuretic peptide metabolism, clearance and degradation. FEBS J. (2011) 278:1808–17. 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08082.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Licata G, Volpe M, Scaglione R, Rubattu S. Salt-regulating hormones in young normotensive obese subjects. Effects of saline load. Hypertension. (1994) 23(1 Suppl):I20–4. 10.1161/01.HYP.23.1_Suppl.I20 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Maisel AS, Clopton P, Krishnaswamy P, Nowak RM, McCord J, Hollander JE, et al. BNP multinational study investigators. impact of age, race, and sex on the ability of B-type natriuretic peptide to aid in the emergency diagnosis of heart failure: results from the Breathing Not Properly (BNP) multinational study. Am Heart J. (2004) 147:1078–84. 10.1016/j.ahj.2004.01.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Krauser DG, Chen AA, Tung R, Anwaruddin S, Baggish AL, Januzzi JL, Jr. Neither race nor gender influences the usefulness of amino-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide testing in dyspneic subjects: a ProBNP Investigation of Dyspnea in the Emergency Department (PRIDE) substudy. J Card Fail. (2006) 12:452–7. 10.1016/j.cardfail.2006.04.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Maeder MT, Rickenbacher P, Rickli H, Abbühl H, Gutmann M, Erne P, et al. TIME-CHF investigators. N-terminal pro brain natriuretic peptide-guided management in patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction: findings from the trial of Intensified versus standard medical therapy in elderly patients with congestive heart failure (TIME-CHF). Eur J Heart Fail. (2013) 15:1148–56. 10.1093/eurjhf/hft076 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Valle R, Aspromonte N, Feola M, Milli M, Canali C, Giovinazzo P, et al. B-type natriuretic peptide can predict the medium-term risk in patients with acute heart failure and preserved systolic function. J Card Fail. (2005) 11:498–503. 10.1016/j.cardfail.2005.05.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Hsich EM, Grau-Sepulveda MV, Hernandez AF, Eapen ZJ, Xian Y, Schwamm LH, et al. Relationship between sex, ejection fraction, and B-type natriuretic peptide levels in patients hospitalized with heart failure and associations with inhospital outcomes: findings from the Get With The Guideline-Heart Failure Registry. Am Heart J. (2013) 166:1063–71.e3. 10.1016/j.ahj.2013.08.029 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Hsich EM, Grau-Sepulveda MV, Hernandez AF, Peterson ED, Schwamm LH, Bhatt DL, et al. Sex differences in in-hospital mortality in acute decompensated heart failure with reduced and preserved ejection fraction. Am Heart J. (2012) 163:430–7:437.e1–3. 10.1016/j.ahj.2011.12.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Choi EY, Bahrami H, Wu CO, Greenland P, Cushman M, Daniels LB, et al. N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide, left ventricular mass, and incident heart failure: multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. Circ Heart Fail. (2012) 5:727–34. 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.112.968701 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Agarwal SK, Chambless LE, Ballantyne CM, Astor B, Bertoni AG, Chang PP, et al. Prediction of incident heart failure in general practice: the atherosclerosis risk in communities (ARIC) study. Circ Heart Fail. (2012) 5:422–9. 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.111.964841 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Wang TJ, Larson MG, Levy D, Benjamin EJ, Leip EP, Omland T, et al. Plasma natriuretic peptide levels and the risk of cardiovascular events and death. N Engl J Med. (2004) 350:655–63. 10.1056/NEJMoa031994 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Willeit P, Kaptoge S, Welsh P, Butterworth A, Chowdhury R, Spackman S, et al. Natriuretic peptides studies collaboration. Natriuretic peptides and integrated risk assessment for cardiovascular disease: an individual-participant-data meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. (2016) 4:840–9. 10.1016/S2213-8587(16)30196-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Seki K, Sanada S, Kudinova AY, Steinhauser ML, Handa V, Gannon J, et al. Interleukin-33 prevents apoptosis and improves survival after experimental myocardial infarction through ST2 signaling. Circ Heart Fail. (2009) 2:684–91. 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.109.873240 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Sanada S, Hakuno D, Higgins LJ, Schreiter ER, McKenzie AN, Lee RT. IL-33 and ST2 comprise a critical biomechanically induced and cardioprotective signaling system. J Clin Invest. (2007) 117:1538–49. 10.1172/JCI30634 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Bayés-Genis A, González A, Lupón J. ST2 in heart failure. Circ Heart Fail. (2018) 11:e005582. 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.118.005582 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Dieplinger B, Januzzi JL, Jr, Steinmair M, Gabriel C, Poelz W, Haltmayer M, et al. Analytical and clinical evaluation of a novel high-sensitivity assay for measurement of soluble ST2 in human plasma: the Presage ST2 assay. Clin Chim Acta. (2009) 409:33–40. 10.1016/j.cca.2009.08.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Weinberg EO, Shimpo M, Hurwitz S, Tominaga S, Rouleau JL, Lee RT. Identification of serum soluble ST2 receptor as a novel heart failure biomarker. Circulation. (2003) 107:721–6. 10.1161/01.CIR.0000047274.66749.FE [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Daniels LB, Bayes-Genis A. Using ST2 in cardiovascular patients: a review. Future Cardiol. (2014) 10:525–39. 10.2217/fca.14.36 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Coglianese EE, Larson MG, Vasan RS, Ho JE, Ghorbani A, McCabe EL, et al. Distribution and clinical correlates of the interleukin receptor family member soluble ST2 in the Framingham heart study. Clin Chem. (2012) 58:1673–81. 10.1373/clinchem.2012.192153 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Meeusen JW, Johnson JN, Gray A, Wendt P, Jefferies JL, Jaffe AS, et al. Soluble ST2 and galectin-3 in pediatric patients without heart failure. Clin Biochem. (2015) 48:1337–40. 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2015.08.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Dieplinger B, Egger M, Poelz W, Gabriel C, Haltmayer M, Mueller T. Soluble ST2 is not independently associated with androgen and estrogen status in healthy males and females. Clin Chem Lab Med. (2011) 49:1515–8. 10.1515/CCLM.2011.239 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Zhao XY, Zhou L, Chen Z, Ji Y, Peng X, Qi L, et al. The obesity-induced adipokine sST2 exacerbates adipose T(reg) and ILC2 depletion and promotes insulin resistance. Sci Adv. (2020) 6:eaay6191. 10.1126/sciadv.aay6191 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Lupón J, de Antonio M, Vila J, Peñafiel J, Galán A, Zamora E, et al. Development of a novel heart failure risk tool: the barcelona bio-heart failure risk calculator (BCN bio-HF calculator). PLoS ONE. (2014) 9:e85466. 10.1371/journal.pone.0085466 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Lupón J, Cediel G, Moliner P, de Antonio M, Domingo M, Zamora E, et al. A bio-clinical approach for prediction of sudden cardiac death in outpatients with heart failure: the ST2-SCD score. Int J Cardiol. (2019) 293:148–52. 10.1016/j.ijcard.2019.05.046 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Emdin M, Aimo A, Vergaro G, Bayes-Genis A, Lupón J, Latini R, et al. sST2 predicts outcome in chronic heart failure beyond NT-proBNP and high-sensitivity troponin T. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2018) 72:2309–20. 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.08.2165 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Parikh RH, Seliger SL, Christenson R, Gottdiener JS, Psaty BM, DeFilippi CR. Soluble ST2 for prediction of heart failure and cardiovascular death in an elderly, community-dwelling population. J Am Heart Assoc. (2016) 5:e003188. 10.1161/JAHA.115.003188 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, Butler J, Casey DE, Jr, Colvin MM, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA focused Update of the 2013. ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American heart association task force on clinical practice guidelines and the heart failure society of America. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2017) 70:776–803. H 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000509 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.de Oliveira FL, Gatto M, Bassi N, Luisetto R, Ghirardello A, Punzi L, et al. Galectin-3 in autoimmunity and autoimmune diseases. Exp Biol Med. (2015) 240:1019–28. 10.1177/1535370215593826 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.McCullough PA, Olobatoke A, Vanhecke TE. Galectin-3. a novel blood test for the evaluation and management of patients with heart failure. Rev Cardiovasc Med. (2011) 12:200–10. 10.3909/ricm0624 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Wu CK, Su MY, Lee JK, Chiang FT, Hwang JJ, Lin JL, et al. Galectin-3 level and the severity of cardiac diastolic dysfunction using cellular and animal models and clinical indices. Sci Rep. (2015) 5:17007. 10.1038/srep17007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Du W, Piek A, Schouten EM, van de Kolk CWA, Mueller C, Mebazaa A, et al. Plasma levels of heart failure biomarkers are primarily a reflection of extracardiac production. Theranostics. (2018) 8:4155–69. 10.7150/thno.26055 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Ho JE, Liu C, Lyass A, Courchesne P, Pencina MJ, Vasan RS, et al. Galectin-3, a marker of cardiac fibrosis, predicts incident heart failure in the community. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2012) 60:1249–56. 10.1016/j.jacc.2012.04.053 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Daniels LB, Clopton P, Laughlin GA, Maisel AS, Barrett-Connor E. Galectin-3 is independently associated with cardiovascular mortality in community-dwelling older adults without known cardiovascular disease: the rancho bernardo study. Am Heart J. (2014) 167:674–82.e1. 10.1016/j.ahj.2013.12.031 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Jagodzinski A, Havulinna AS, Appelbaum S, Zeller T, Jousilahti P, Skytte-Johanssen S, et al. Predictive value of galectin-3 for incident cardiovascular disease and heart failure in the population-based FINRISK 1997 cohort. Int J Cardiol. (2015) 192:33–9. 10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.05.040 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Jackson AS, Stanforth PR, Gagnon J, Rankinen T, Leon AS, Rao DC, et al. The effect of sex, age and race on estimating percentage body fat from body mass index: the heritage family study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. (2002) 26:789–96. 10.1038/sj.ijo.0802006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Pang J, Nguyen VT, Rhodes DH, Sullivan ME, Braunschweig C, Fantuzzi G. Relationship of galectin-3 with obesity, IL-6, and CRP in women. J Endocrinol Invest. (2016) 39:1435–43. 10.1007/s40618-016-0515-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Lopez-Andrès N, Rossignol P, Iraqi W, Fay R, Nuée J, Ghio S, et al. Association of galectin-3 and fibrosis markers with long-term cardiovascular outcomes in patients with heart failure, left ventricular dysfunction, and dyssynchrony: insights from the CARE-HF (cardiac resynchronization in heart failure) trial. Eur J Heart Fail. (2012) 14:74–81. 10.1093/eurjhf/hfr151 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.van Kimmenade RR, Januzzi JL, Jr, Ellinor PT, Sharma UC, Bakker JA, Low AF, et al. Utility of amino-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide, galectin-3, and apelin for the evaluation of patients with acute heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2006) 48:1217–24. 10.1016/j.jacc.2006.03.061 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Hara A, Niwa M, Kanayama T, Noguchi K, Niwa A, Matsuo M, et al. Galectin-3. a potential prognostic and diagnostic marker for heart disease and detection of early stage pathology. Biomolecules. (2020) 10:E1277. 10.3390/biom10091277 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Bayes-Genis A, de Antonio M, Vila J, Peñafiel J, Galán A, Barallat J, et al. Head-to-head comparison of 2 myocardial fibrosis biomarkers for long-term heart failure risk stratification: ST2 versus galectin-3. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2014) 63:158–66. 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.07.087 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Khan SQ, Ng K, Dhillon O, Kelly D, Quinn P, Squire IB, et al. Growth differentiation factor-15 as a prognostic marker in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. (2009) 30:1057–65. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehn600 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Rueda F, Cediel G, García-García C, Aranyó J, González-Lopera M, Aranda Nevado MC, et al. Growth differentiation factor 15 and early prognosis after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Ann Intensive Care. (2019) 9:119. 10.1186/s13613-019-0593-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Fluschnik N, Ojeda F, Zeller T, Jørgensen T, Kuulasmaa K, Becher PM, et al. Predictive value of long-term changes of growth differentiation factor-15 over a 27-year-period for heart failure and death due to coronary heart disease. PLoS ONE. (2018) 13:e0197497. 10.1371/journal.pone.0197497 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Ho JE, Mahajan A, Chen MH, Larson MG, McCabe EL, Ghorbani A, et al. Clinical and genetic correlates of growth differentiation factor 15 in the community. Clin Chem. (2012) 58:1582–91. 10.1373/clinchem.2012.190322 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Gohar A, Gonçalves I, Vrijenhoek J, Haitjema S, van Koeverden I, Nilsson J, et al. Circulating GDF-15 levels predict future secondary manifestations of cardiovascular disease explicitly in women but not men with atherosclerosis. Int J Cardiol. (2017) 241:430–6. 10.1016/j.ijcard.2017.03.101 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Liu H, Dai W, Cui Y, Lyu Y, Li Y. Potential associations of circulating growth differentiation factor-15 with sex hormones in male patients with coronary artery disease. Biomed Pharmacother. (2019) 114:108792. 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108792 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Rosenberg M, Zugck C, Nelles M, Juenger C, Frank D, Remppis A, et al. Osteopontin, a new prognostic biomarker in patients with chronic heart failure. Circ Heart Fail. (2008) 1:43–9. 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.107.746172 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.López B, González A, Lindner D, Westermann D, Ravassa S, Beaumont J, et al. Osteopontin-mediated myocardial fibrosis in heart failure: a role for lysyl oxidase? Cardiovasc Res. (2013) 99:111–20. 10.1093/cvr/cvt100 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Arnlöv J, Evans JC, Benjamin EJ, Larson MG, Levy D, Sutherland P, et al. Clinical and echocardiographic correlates of plasma osteopontin in the community: the Framingham heart study. Heart. (2006) 92:1514–5. 10.1136/hrt.2005.081406 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]