Abstract
Background/Aims
The hepatic steatosis index (HSI) is a noninvasive method to assess the severity of hepatic steatosis. Antiviral therapy (AVT) can impact aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase levels, which are the main components of the HSI. Thus, we investigated the accuracy of the HSI in detecting hepatic steatosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB) receiving AVT, compared with those not receiving AVT and in those with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Methods
Patients with CHB or NAFLD who underwent a magnetic resonance imaging proton density fat fraction (MRI-PDFF) evaluation between March 2010 and March 2019 were recruited. Hepatic steatosis was diagnosed when the PDFF exceeded 5%. Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) analysis was used to assess the diagnostic accuracy of the HSI in the detection of hepatic steatosis.
Results
The mean age of the study population (189 men and 116 women; 244 with CHB [184 with and 60 without AVT] and 61 with NAFLD) was 55.6 years. The AUROC values for detecting hepatic steatosis were similar between patients with CHB (0.727; p<0.001) and those with NAFLD (0.739; p=0.002). However, when patients with CHB were subdivided into those receiving and not receiving AVT, the AUROC value decreased slightly in patients with CHB receiving AVT compared to those without not receiving AVT (0.707; p=0.001 vs 0.779; p=0.001).
Conclusions
Despite a slight attenuation, the diagnostic accuracy of the HSI in patients with CHB receiving AVT in detecting hepatic steatosis was still acceptable. Further large-scale studies are required for validation.
Keywords: Hepatic steatosis index, Fatty liver, Hepatitis B, Antiviral therapy, Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
INTRODUCTION
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is one of the most common causes of chronic liver disease worldwide.1,2 With improvements in living standards and lifestyle changes, NAFLD has become increasingly prevalent, occurring in 20% to 30% of the general population.3 Recent reports indicate that the prevalence of NAFLD in Asian counties is similar to the worldwide occurrence rate, and chronic hepatitis B (CHB) is a substantial public health concern in these countries.4
Accurate assessment of hepatic steatosis is important regardless of the presence or absence of underlying liver disease. The co-existence of hepatic steatosis and CHB may accelerate disease progression, influence the efficacy of antiviral treatment, and increase the risk of developing cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.5,6 Liver biopsy is the gold standard for assessing the severity of hepatic steatosis, but the efficacy and applicability of this procedure is significantly hampered by its invasive nature and the tendency for sampling errors to occur.7,8 Although conventional ultrasonography has been widely used as a first-line diagnostic tool for hepatic steatosis, there are several factors that diminish the effectiveness of this technique.9-11 These include a low sensitivity in detecting hepatic steatosis at an early stage and substantial interoperator discrepancies in the measurements acquired during the imaging.
Recently, controlled attenuation in transient elastography and magnetic resonance imaging-proton density fat fraction (MRI-PDFF) measurements have emerged as accurate, highly reproducible, and noninvasive surrogates in the evaluation of hepatic steatosis in various chronic liver diseases, including NAFLD.12-15 However, the high cost of the devices required for these evaluations has limited their widespread clinical use. Accordingly, several noninvasive diagnostic indices based on biochemical laboratory test results or demographic characteristics have been proposed to assess the severity of hepatic steatosis.16 Of these indices, the hepatic steatosis index (HSI) is an economical and noninvasive means for assessing the severity of hepatic steatosis with reasonable accuracy.17 The constituent variables of the HSI include sex, alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), body mass index (BMI), and diabetic status. A recent Chinese study reported a greater accuracy of the HSI for detecting biopsy-proven hepatic steatosis when compared to ultrasound (area under the receiver operating characteristic curve [AUROC]=0.755 for moderate-to-severe hepatic steatosis and 0.786 for severe hepatic steatosis).18 Another study found a significant positive correlation between the HSI and the histopathological grade of hepatic steatosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C infection.19
However, it is not clear whether the acceptable accuracy of the HSI persists in the presence of a therapeutic intervention, which can significantly affect the biochemical markers measured by noninvasive surrogates. Therefore, we investigated the accuracy of the HSI for evaluating hepatic steatosis in patients with CHB receiving antiviral therapy (AVT) when compared to those not receiving AVT, and to those with NAFLD.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
1. Patients
Between March 2010 and March 2019, patients with CHB or NAFLD who underwent MRI-PDFF evaluations at Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea were considered for eligibility in this retrospective, cross-sectional study.
The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) the presence of other etiologies of chronic liver disease other than CHB or NAFLD, (2) age ≤19 years, (3) insufficient clinical or laboratory information, (4) insufficient information for calculating HSI, (5) hepatocellular carcinoma or hepatic decompensation at enrollment or a history of either condition, (6) a history of organ transplantation, or (7) significant alcohol consumption (defined as >21 drinks per week in men and >14 drinks per week in women).20
The study protocol was consistent with the ethical guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Severance Hospital (IRB number: 4-2019-0639). Informed consent was waived in this study due to its retrospective design.
2. Estimation of hepatic steatosis severity
Ultrasonographically diagnosed NAFLD was defined according to ultrasonographic findings such as echogenic or bright liver on imaging consistent with fatty infiltration.21 The severity of hepatic steatosis was evaluated using the HSI, which was calculated as follows: HSI=8×(ALT/AST ratio)+BMI (+2, if female; +2, if diabetes mellitus).17 In addition, hepatic steatosis was also assessed using MRI-PDFF and a diagnosis of hepatic steatosis was made when the PDFF exceeded 5%.22
3. Diagnosis of liver cirrhosis and dyslipidemia
Liver cirrhosis was diagnosed based on ultrasonographic findings. These included findings such as altered parenchymal echogenicity with coarsened echotexture and surface nodularity, caudate hypertrophy, splenomegaly, and slow portal vein mean flow velocity.23,24 A diagnosis of dyslipidemia was made when low-density lipoprotein cholesterol was ≥160 mg/dL, total cholesterol was ≥240 mg/dL, or total triglyceride was ≥200 mg/dL.25
4. Statistical analysis
The patients’ demographic and laboratory data were summarized as means±standard deviation for continuous variables, and as medians with percentages for categorical variables. Correlation analysis between fat fraction and other variables were conducted using the Pearson method. Mean and frequency data were compared using an independent samples t-test or chi-square test. Logistic binary regression analysis was conducted to identify independent predictors of fatty liver. AUROC analysis was implemented to assess the diagnostic accuracy of the HSI for hepatic steatosis. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS version 23.0 software (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). A p-value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
1. Patient characteristics
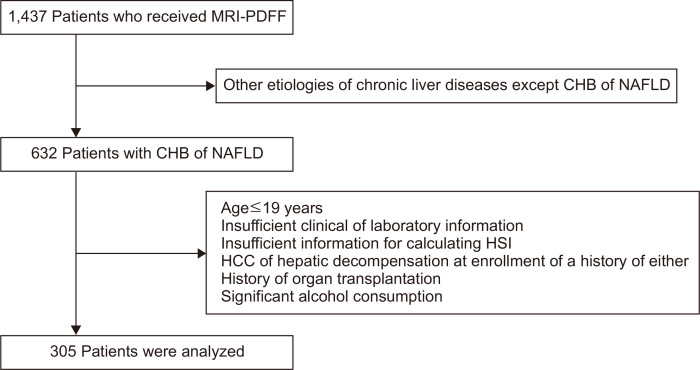
Among the 1,437 patients who received MRI-PDFF, 805 patients with other etiologies of chronic liver diseases, other than CHB or NAFLD, were excluded. Further, 327 patients were removed from our study population according to our established exclusion criteria. As a result, a final total of 305 patients were selected for the statistical analysis (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
A graphical representation of the patient selection process. Of 1,437 patients who received MRI-PDFF, 305 were selected for the statistical analysis according to our exclusion criteria.
MRI-PDFF, magnetic resonance imaging-proton density fat fraction; CHB, chronic hepatitis B; NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; HSI, hepatic steatosis index; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma.
The baseline characteristics of the study population (189 males and 116 females; 244 with CHB [184 with AVT and 60 without AVT] and 61 NAFLD) are shown in Table 1. The median age, BMI, HSI, and fat fraction as determined by MRI-PDFF of the study participants were 55.6 years, 25.5 kg/m2, 34.7, and 3.3%, respectively. A total of 83 patients (27.2%) had fatty liver based on the MRI-PDFF. A total of 36 (14.8%) patients with CHB had ultrasonographic fatty liver. The respective baseline characteristics of patients with NAFLD and CHB are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1.
Baseline Characteristics
| Variable | All (n=305) | NAFLD (n=61, 20.0%) |
HBV (n=244, 80.0%) | p-value* | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All HBV | Without AVT (n=60, 24.6%) |
With AVT (n=184, 75.4%) |
p-value | ||||
| Demographic variable | |||||||
| Age, yr | 55.6±13.3 | 50.3±21.5 | 56.9±9.9 | 59.2±9.2 | 56.2±9.7 | 0.042 | 0.022 |
| Male sex | 189 (62.0) | 29 (47.5) | 160 (65.6) | 43 (71.7) | 117 (63.6) | 0.253 | 0.009 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 25.5±3.7 | 27.5±4.5 | 25.0±3.3 | 25.9±3.5 | 24.7±3.2 | 0.016 | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 100 (32.8) | 24 (39.3) | 76 (31.1) | 22 (36.7) | 54 (29.3) | 0.288 | 0.223 |
| Diabetes | 87 (28.5) | 30 (49.2) | 57 (23.4) | 15 (25.0) | 42 (22.8) | 0.730 | 0.000 |
| Liver cirrhosis | 242 (79.3) | 32 (52.5) | 210 (86.1) | 45 (75.0) | 165 (89.7) | 0.004 | 0.000 |
| Dyslipidemia | 41 (13.4) | 11 (18.0) | 30 (12.3) | 6 (10.0) | 24 (13.0) | 0.533 | 0.240 |
| Laboratory variable | |||||||
| Total bilirubin, mg/dL | 1.0±0.5 | 0.8±0.4 | 1.0±0.5 | 1.0±0.5 | 1.0±0.5 | 0.782 | 0.006 |
| Serum albumin, g/dL | 4.3±0.4 | 4.3±0.4 | 4.3±0.4 | 4.2±0.4 | 4.3±0.3 | 0.384 | 0.570 |
| Aspartate aminotransferase, U/L | 31.4±23.7 | 40.7±32.7 | 29.1±20.3 | 29.3±19.6 | 29.0±20.6 | 0.918 | 0.010 |
| Alanine aminotransferase, U/L | 31.3±31.3 | 44.6±51.2 | 28.0±22.9 | 25.8±18.0 | 28.7±24.3 | 0.407 | 0.016 |
| Total cholesterol, mg/dL | 168.6±37.3 | 176.0±44.7 | 167.1±35.0 | 170.9±35.5 | 165.8±34.9 | 0.338 | 0.151 |
| Platelet count, ×109/L | 160±71 | 212±85 | 146±60 | 159±59 | 142±60 | 0.064 | <0.001 |
| Prothrombin time, INR | 1.07±0.21 | 1.04±0.13 | 1.07±0.23 | 1.08±0.19 | 1.07±0.24 | 0.863 | 0.388 |
| HBV-related variable | |||||||
| HBeAg positivity | - | - | 50 (21.6) | 3 (5.6) | 47 (26.4) | 0.001 | - |
| HBV DNA, log10 IU/mL | - | - | 1.28±0.92 | 1.67±1.13 | 1.15±0.80 | 0.574 | - |
| Medication | |||||||
| Entecavir/tenofovir/others | - | - | - | - | 76 (41.3)/90 (48.9)/18 (9.8) | - | - |
| Hepatotonics | - | 44 (72) | - | - | - | - | - |
| Hepatic steatosis index | 34.7±5.3 | 38.1±6.4 | 33.8±4.6 | 34.3±4.8 | 33.7±4.5 | 0.409 | <0.001 |
| Fat fraction by MRI-PDFF, % | 3.3±7.6 | 9.9±11.0 | 1.6±5.2 | 2.7±7.1 | 1.3±4.4 | 0.138 | <0.001 |
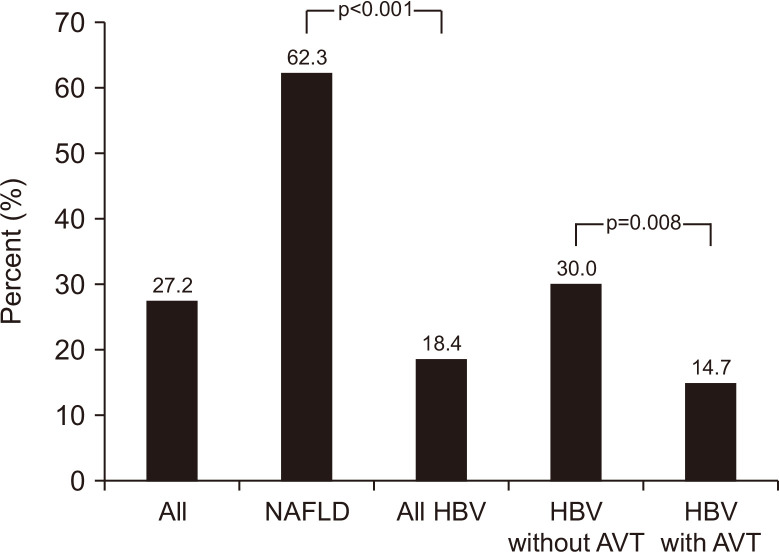
| Fatty liver by MRI-PDFF | 83 (27.2) | 38 (62.3) | 45 (18.4) | 18 (30.0) | 27 (14.7) | 0.008 | <0.001 |
Data are presented as mean±SD or number (%).
NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; HBV, hepatitis B virus; AVT, antiviral therapy; BMI, body mass index; HBeAg, hepatitis B e antigen; MRI-PDFF, magnetic resonance imaging-proton density fat fraction.
*p-value indicates the comparison between patients with NAFLD and those with HBV.
2. Comparison between patients with NAFLD and CHB
The baseline characteristics of patients with NAFLD and those with CHB were analyzed and compared (Table 1). Patients with NAFLD were significantly younger (mean: 50.3 years vs 56.9 years) and had a significantly lower proportion of male gender (47.5% vs 65.6%), a higher BMI (mean: 27.5 kg/m2 vs 25.0 kg/m2), a higher proportion of diabetes (49.2% vs 23.4%), and a lower proportion of liver cirrhosis (52.5% vs 86.1%) than those with CHB (all comparisons p<0.05). In addition, patients with NAFLD had a lower total bilirubin level (mean: 0.8 mg/dL vs 1.0 mg/dL), a higher AST level (mean: 40.7 U/L vs 29.1 U/L), a higher ALT level (mean: 44.6 U/L vs 28.0 U/L), a higher platelet count (mean: 212 ×109/L vs 146 ×109/L), a higher HSI (mean: 38.1 vs 33.8), a higher fat fraction by MRI-PDFF (9.9% vs 1.6%), and a higher proportion of fatty liver by MRI-PDFF (62.3% vs 18.4%) than those of patients with CHB (all comparisons p<0.05) (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2.
The prevalence of fatty liver as assessed using MRI-PDFF (magnetic resonance imaging-proton density fat fraction).
NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; HBV, hepatitis B virus; AVT, antiviral therapy.
3. Comparison between patients with CHB receiving AVT and those not receiving AVT
The baseline characteristics of patients with CHB receiving AVT and those not receiving AVT were compared (Table 1). Patients with CHB receiving AVT were significantly younger (mean: 56.2 years vs 59.2 years) and had a significantly lower BMI (mean: 24.7 kg/m2 vs 25.9 kg/m2), a higher proportion of liver cirrhosis (89.7% vs 75.0%) and HBeAg positivity (26.4% vs 5.6%), and a lower proportion of fatty liver by MRI-PDFF (14.7% vs 30.0%) than that those not receiving AVT (all comparisons p<0.05) (Fig. 2).
4. Correlations between fat fraction and other variables
In the entire study population, the fat fraction as determined by MRI-PDFF showed a significant positive correlation with platelet count, HSI, ALT, BMI, serum albumin, total cholesterol, diabetes, AST, and total protein (all correlations p<0.05). There was a significant negative correlation between fat fraction as determined by MRI-PDFF and the presence of liver cirrhosis, age, and total bilirubin (all correlations p<0.05) (Supplementary Table 1).
In patients with NAFLD, fat fraction as determined by MRI-PDFF showed a significant positive correlation with serum albumin, ALT, total cholesterol, and HSI. In contrast, fat fraction as determined by MRI-PDFF presented with a significant negative correlation with age, hypertension, and presence of liver cirrhosis (all correlations, both positive and negative, p<0.05) (Table 2). In patients with CHB, fat fraction presented with a significant positive correlation with BMI, presence of dyslipidemia, total cholesterol and HSI, and a significant negative correlation with the presence of liver cirrhosis (all p<0.05) (Table 2). The correlation between fat fraction and other variables in patients with CHB receiving AVT and those not receiving AVT are listed in Table 2.
Table 2.
Correlation between the Fat Fraction and Other Variables (Pearson's Correlation Analysis)
| Variable | NAFLD | All HBV | HBV without AVT | HBV with AVT | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correlation coefficient |
p-value | Correlation coefficient |
p-value | Correlation coefficient |
p-value | Correlation coefficient |
p-value | ||||
| Age, yr | –0.608 | <0.001 | –0.111 | 0.082 | –0.080 | 0.544 | –0.160 | 0.030 | |||
| Male sex | 0.151 | 0.245 | 0.004 | 0.949 | 0.023 | 0.861 | –0.019 | 0.802 | |||
| BMI, kg/m2 | 0.063 | 0.629 | 0.229 | <0.001 | 0.409 | 0.001 | 0.112 | 0.129 | |||
| Hypertension | –0.345 | 0.007 | –0.045 | 0.482 | –0.064 | 0.627 | –0.050 | 0.500 | |||
| Diabetes | 0.031 | 0.810 | 0.063 | 0.325 | 0.086 | 0.515 | 0.050 | 0.502 | |||
| Liver cirrhosis | –0.471 | <0.001 | –0.266 | <0.001 | –0.252 | 0.052 | –0.249 | 0.001 | |||
| Dyslipidemia | –0.188 | 0.148 | 0.164 | 0.010 | 0.545 | <0.001 | 0.005 | 0.942 | |||
| Total bilirubin, mg/dL | –0.208 | 0.108 | –0.077 | 0.229 | –0.042 | 0.750 | –0.103 | 0.162 | |||
| Serum albumin, g/dL | 0.347 | 0.006 | 0.122 | 0.057 | 0.206 | 0.114 | 0.087 | 0.240 | |||
| Aspartate aminotransferase, U/L | 0.037 | 0.779 | 0.080 | 0.213 | 0.228 | 0.080 | 0.010 | 0.890 | |||
| Alanine aminotransferase, U/L | 0.262 | 0.042 | 0.118 | 0.066 | 0.414 | 0.001 | 0.025 | 0.731 | |||
| Total cholesterol, mg/dL | 0.367 | 0.004 | 0.141 | 0.029 | 0.127 | 0.338 | 0.136 | 0.067 | |||
| Platelet count, ×109/L | 0.557 | <0.001 | 0.268 | <0.001 | 0.375 | 0.003 | 0.203 | 0.007 | |||
| Prothrombin time, INR | –0.221 | 0.259 | –0.055 | 0.506 | –0.101 | 0.551 | –0.051 | 0.597 | |||
| Hepatic steatosis index | 0.382 | 0.002 | 0.256 | <0.001 | 0.469 | <0.001 | 0.138 | 0.062 | |||
NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; HBV, hepatitis B virus; AVT, antiviral therapy; BMI, body mass index; INR, international normalized ratio.
5. Predictors of the presence of fatty liver
In entire study population, a higher platelet count (odds ratio [OR], 1.012; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.006 to 1.019) and higher HSI (OR, 1.155; 95% CI, 1.076 to 1.240) predicted the presence of fatty liver (all comparisons p<0.05) (Supplementary Table 2).
In patients with NAFLD, age, hypertension, and liver cirrhosis were negatively associated with the presence of fatty liver, whereas serum albumin level, platelet count, and HSI were positively associated with the presence of fatty liver in univariate analysis (all p<0.05). No predictor of fatty liver was identified in multivariate analysis (Table 3).
Table 3.
Predictors of the Presence of Fatty Liver in Patients with NAFLD
| Variable | Univariate | Multivariate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p-value | OR (95% CI) | p-value | ||
| Age, yr | 0.920 (0.882–0.960) | <0.001 | 0.972 (0.907–1.041) | 0.415 | |
| Hypertension | 0.230 (0.076–0.694) | 0.009 | 0.562 (0.064–4.943) | 0.603 | |
| Liver cirrhosis | 0.109 (0.031–0.390) | 0.001 | 0.877 (0.093–8.270) | 0.909 | |
| Dyslipidemia | 0.429 (0.114–1.612) | 0.210 | - | - | |
| Total bilirubin, mg/dL | 0.537 (0.164–1.753) | 0.303 | - | - | |
| Serum albumin, g/dL | 33.588 (4.027–280.164) | 0.001 | 9.477 (0.293–306.421) | 0.205 | |
| Platelet count, ×109/L | 1.027 (1.013–1.040) | <0.001 | 1.012 (0.997–1.028) | 0.116 | |
| Hepatic steatosis index | 1.211 (1.067–1.375) | 0.003 | 1.161 (0.958–1.407) | 0.128 | |
NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval.
In all patients with CHB, a higher platelet count (OR, 1.009; 95% CI, 1.002 to 1.017) and a higher HSI (OR, 1.163; 95% CI, 1.069 to 1.266) independently predicted the presence of fatty liver (all p<0.05) (Table 4). When patients with CHB were stratified into two groups with and without AVT, a higher HSI was the only predictor of fatty liver in CHB patients without AVT (OR, 1.241; 95% CI, 1.044 to 1.014; p=0.014), whereas a higher platelet count (OR, 1.011; 95% CI, 1.003 to 1.019) and a higher HSI (OR, 1.142; 95% CI, 1.027 to 1.269) independently predicted the presence of fatty liver in CHB patients receiving AVT (all p<0.05) (Table 4).
Table 4.
Predictors of the Presence of Fatty Liver in Patients with HBV
| Variable | All HBV | HBV without AVT | HBV with AVT | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univariate p-value |
Multivariate | Univariate p-value |
Multivariate | Univariate p-value |
Multivariate | ||||||||
| OR (95% CI) | p-value | OR (95% CI) | p-value | OR (95% CI) | p-value | ||||||||
| Age, yr | 0.320 | - | - | 0.220 | - | - | 0.432 | - | - | ||||
| Hypertension | 0.480 | - | - | 0.815 | - | - | 0.623 | - | - | ||||
| Liver cirrhosis | 0.008 | 0.627 (0.238–1.654) | 0.346 | 0.110 | - | - | 0.139 | - | - | ||||
| Dyslipidemia | 0.463 | - | - | 0.058 | - | - | 0.747 | - | - | ||||
| Total bilirubin, mg/dL | 0.016 | 0.604 (0.220–1.657) | 0.328 | 0.331 | - | - | 0.017 | 0.346 (0.084–1.425) | 0.142 | ||||
| Serum albumin, g/dL | 0.075 | - | - | 0.154 | - | - | 0.192 | - | - | ||||
| Platelet count, ×109/L | <0.001 | 1.009 (1.002–1.017) | 0.010 | 0.020 | 1.007 (0.994–1.019) | 0.309 | <0.001 | 1.011 (1.003–1.019) | 0.010 | ||||
| Hepatic steatosis index | <0.001 | 1.163 (1.069–1.266) | <0.001 | 0.003 | 1.241 (1.044–1.475) | 0.014 | <0.001 | 1.142 (1.027–1.269) | 0.014 | ||||
HBV, hepatitis B virus; AVT, antiviral therapy; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval.
6. Diagnostic accuracy of HSI and other variables in the diagnosis of fatty liver
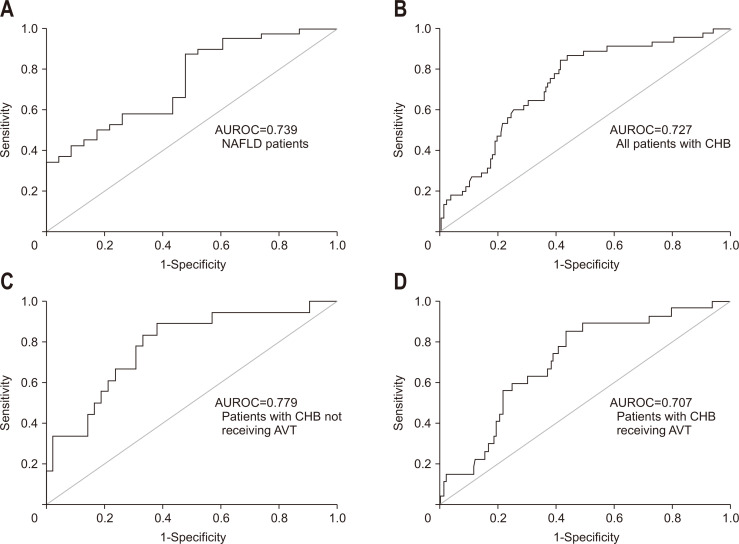
The diagnostic accuracy of the HSI was assessed in each subgroup (Table 5, Fig. 3). In NAFLD group, platelet count had the highest AUROC value in the diagnosis of fatty liver (AUROC, 0.886; 95% CI, 0.793 to 0.978), followed by the HSI (AUROC, 0.739; 95% CI, 0.613 to 0.865) (both p<0.05). In CHB group, AUROC value of platelet count was also highest (AUROC, 0.733; 95% CI, 0.658 to 0.808), and that of HSI was second (AUROC, 0.727; 95% CI, 0.649 to 0.805), but the difference of both values was less than that in NAFLD group.
Table 5.
Accuracy of the HSI and Other Variables to Diagnose Fatty Liver
| Predictor | AUROC | 95% CI | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAFLD | |||
| HSI | 0.739 | 0.613–0.865 | 0.002 |
| Age, yr | 0.154 | 0.055–0.254 | <0.001 |
| Platelet count, ×109/L | 0.886 | 0.793–0.978 | <0.001 |
| All HBV | |||
| HSI | 0.727 | 0.649–0.805 | <0.001 |
| Age, yr | 0.464 | 0.371–0.557 | 0.451 |
| Platelet count, ×109/L | 0.733 | 0.658–0.808 | <0.001 |
| HBV without AVT | |||
| HSI | 0.779 | 0.651–0.907 | 0.001 |
| Age, yr | 0.394 | 0.250–0.537 | 0.194 |
| Platelet count, ×109/L | 0.679 | 0.538–0.821 | 0.029 |
| HBV with AVT | |||
| HSI | 0.707 | 0.608–0.805 | 0.001 |
| Age, yr | 0.465 | 0.341–0.589 | 0.563 |
| Platelet count, ×109/L | 0.744 | 0.652–0.835 | <0.001 |
HSI, hepatic steatosis index; AUROC, area under the receiver operating characteristic curve; CI, confidence interval; NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; HBV, hepatitis B virus; AVT, antiviral therapy.
Fig. 3.
ROC curves of the HSI for the diagnosis of fatty liver in patients with NAFLD and CHB receiving or not receiving AVT. (A) AUROC=0.739 in NAFLD patients, (B) AUROC=0.727 in all patients with CHB, (C) AUROC=0.779 in patients with CHB not receiving AVT, and (D) AUROC=0.707 in patients with CHB receiving AVT.
ROC, receiver operating characteristic; HSI, hepatic steatosis index; NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; CHB, chronic hepatitis B; AVT, antiviral therapy; AUROC, area under the receiver operating characteristic curve.
When patients with CHB were divided into two groups with or without AVT, the AUROC of the HSI in diagnosing fatty liver was increased in patients not receiving AVT (AUROC, 0.779; 95% CI, 0.651 to 0.907), whereas it was decreased in patients receiving AVT (AUROC, 0.707; 95% CI, 0.608 to 0.805), when compared to the overall AUROC of all patients with CHB (all comparisons p<0.05).
7. Cutoff value for the HSI in the diagnosis of fatty liver
The calculated cutoff values of the HSI which maximized the sum of sensitivity and specificity and the proportion of patients with fatty liver are summarized in Table 6. The cutoff values ranged from 33.1 to 33.9 in the subgroups and the HSI accurately predicted fatty liver in 60.3% to 73.8% of patients. We then implemented the generally accepted cutoff value of 36 to diagnose fatty liver,17 and the changes in diagnostic indices are summarized in Table 6.
Table 6.
Cutoff Value of the HSI Used to Diagnose Fatty Liver
| Diagnostic index | NAFLD | All HBV | HBV without AVT |
HBV with AVT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients with fatty liver, No. (%) | 38 (62.3) | 45 (18.4) | 18 (30.0) | 27 (14.7) |
| Calculated cutoff value | 33.9 | 33.4 | 33.1 | 33.4 |
| Sensitivity, % | 86.8 | 84.4 | 83.3 | 85.2 |
| Specificity, % | 52.2 | 57.8 | 61.9 | 56.1 |
| Positive predictive value, % | 75.0 | 31.2 | 48.4 | 25.0 |
| Negative predictive value, % | 70.6 | 94.3 | 89.7 | 95.7 |
| Positive likelihood ratio | 1.82 | 2.00 | 2.19 | 1.94 |
| Negative likelihood ratio | 0.25 | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.26 |
| Correctly predicted, % | 73.8 | 62.7 | 68.3 | 60.3 |
| Predefined cutoff value of HSI >36 | ||||
| Patients with HSI >36, No. (%) | 28 (45.9) | 78 (32.0) | 10 (16.7) | 58 (31.5) |
| Sensitivity, % | 65.8 | 60.0 | 61.1 | 59.3 |
| Specificity, % | 54.3 | 74.4 | 78.6 | 73.3 |
| Positive predictive value, % | 71.4 | 34.6 | 55.0 | 27.6 |
| Negative predictive value, % | 50.0 | 89.2 | 82.5 | 91.3 |
| Positive likelihood ratio | 1.51 | 2.34 | 2.85 | 2.22 |
| Negative likelihood ratio | 0.61 | 0.54 | 0.49 | 0.56 |
| Correctly predicted, % | 62.3 | 71.7 | 73.3 | 71.2 |
HSI, hepatic steatosis index; NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; HBV, hepatitis B virus; AVT, antiviral therapy.
DISCUSSION
Liver biopsy has been regarded as the ‘gold standard’ for assessing the severity of liver disease.26 However, due to its invasive nature and the resultant complications, it has not exhibited a widespread application in clinical practice.27 Radiological assessment using ultrasonography, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging have been shown to accurately assess the degree of liver fibrosis or steatosis.28-31 However, this noninvasive procedure also has limitations, including the required specialized equipment and high cost of assessment. As such, varying simple and noninvasive tests have been proposed and validated in the identification of patients who are at a high risk of incurring NAFLD.17 Of these tests, we focused our investigation on the accuracy of the HSI with simple constituent variables, based on the fat quantity assessed using MRI-PDFF, to diagnose the presence of NAFLD in patients with NAFLD and CHB with or without AVT.17
It is currently accepted that the presence of hepatic steatosis in patients with CHB is significantly associated with a non-physiological response to AVT and accelerated liver fibrosis progression.5,32,33 Further, there remains a substantial need for noninvasive predictors of fatty liver in patients with CHB, and recently several noninvasive surrogates, such as the HSI, have been implemented.34 However, these surrogate tests rely on biochemical laboratory results, results such as AST or ALT, which are significantly influenced by AVT in patients with CHB. Thus, the diagnostic accuracy of the HSI should be confirmed in patients with CHB undergoing AVT. To this end, the aim of our study was to investigate the diagnostic accuracy of the HSI utilizing NAFLD patients as a control group, and comparing the accuracy of the test between NAFLD patients and those with CHB. In addition, we investigated whether the accuracy of the HSI is altered by AVT in patients with CHB.
In our study, we found that the AUROC values for detecting hepatic steatosis were similar between patients with CHB and those with NAFLD (0.727 vs 0.739). This indicates that there is good applicability for the HSI in patients with CHB. However, the accuracy of the HSI in NAFLD patients in this study seems relatively low when compared to the original study which proposed the HSI for the diagnosis of fatty liver (AUROC, 0.812).17 However, when patients with CHB were subdivided into those with or without AVT, the AUROC value decreased slightly in patients with CHB receiving AVT compared to those without AVT (0.707 vs 0.779). However, the AUROC values remained within an acceptable range for both groups.
Our study has several clinical implications. First, the prevalence of fatty liver assessed using MRI-PDFF was only 62.3% in the ultrasonography defined NAFLD group. The accuracy of MRI-PDFF is noted to be highly significant in recent studies,22,35,36 and as such this discrepancy in the diagnosis of fatty liver is likely due to false positivity of ultrasonography in cases with increased hepatic parenchymal echogenicity. The coarse parenchymal echogenicity in chronic liver disease is often misdiagnosed as the diffuse increased parenchymal echogenicity in fatty liver. However, as there remains a significant overlap in diagnosing fatty liver between two modalities, no predictor was identified to detect MRI-PDFF-based fatty liver in the ultrasonographically defined NAFLD group.
Second, we found a significant relationship between the presence of hepatic steatosis and platelet count in our study. The platelet count was significantly higher in patients with NAFLD and those with CHB (mean: 212×109/L vs 146×109/L). Further, there was a significant correlation between platelet count and fat fraction as determined by MRI-PDFF. After adjustment, the diagnostic value of platelet count remained significant across the entire study population (OR, 1.012) and in those with CHB (OR, 1.009). Indeed, platelet count and HSI are the two factors with the highest AUROC values in our study. Our results are supported by findings from previous studies which have demonstrated that platelet count has a positive correlation with hepatic steatosis.37,38 In addition, this phenomenon might be associated with the burn-out theory indicating that hepatic steatosis is reduced in advanced fibrosis or cirrhosis stage in the natural history of NAFLD.39 Platelets are active participants in the process of liver inflammation, promoting leukocyte recruitment through hepatic sinusoids, and activating effector cells.40
Third, we quantified fat content using MRI-PDFF which is the gold standard technique for this measurement. Although other histological features, such as necroinflammation or fibrosis, cannot be detected by MRI-PDFF, MRI-PDFF has been shown to be a precise, accurate, and reproducible noninvasive imaging surrogate for the quantification of liver fat content.41-43 Performing a liver biopsy to establish liver fat content is not clinically feasible, and as such our strategy in using the MRI-PDFF for the diagnosis of fatty liver, in the determination of the diagnostic accuracy of the HSI, is particularly relevant.
Finally, in patients with NAFLD, the accuracy of the calculated prediction rate using our own HSI cutoff (33.9) in the diagnosis of fatty liver was higher than that presented previously calculated using a predefined HSI cutoff (36) (73.8% vs 62.3%).17 In contrast, in patients with CHB, the correctly predicted rate calculated using our own HSI cutoff (33.4) to diagnose fatty liver was relatively lower than that calculated using the predefined HSI cutoff (36) (62.7% vs 71.7%). Similar findings were observed in the subgroup analysis of those with CHB undergoing or not undergoing AVT. Although the precise reason for this discrepancy according to the etiology of specific chronic liver disease might be unclear, one of the reasons may be the different proportion of patients with various severity of liver diseases. However, our data suggests that the predefined HSI cutoff value of 36 can be used in the diagnosis of fatty liver in patients with CHB, while this value may require some modification to enhance its accuracy in patients with NAFLD. Therefore, we suggest that further validation studies are warranted to establish and confirm the optimal HSI cutoff values for the various etiologies of chronic liver disease.
We are also aware of some limitations of our study which remain unresolved. First, our study has a retrospective design. Thus, the decision to prescribe MRI-PDFF may be different according to the etiology of chronic liver diseases. Indeed, MRI-PDFF could have been performed in patients with NAFLD, whereas it was only done in patients with CHB as a surveillance imaging technique in the detection of hepatocellular carcinoma.44 Accordingly, the overall diagnostic accuracy of HSI in our study might have been significantly influenced due to the high proportion of patients with MRI PDFF-based fatty liver (about 62%). In addition, the high prevalence of cirrhotic patients might have been caused by selection bias. Indeed, in our study, MRI-PDFF was mostly performed for patients with advanced fibrosis or cirrhosis, as well as those with poor ultrasonographic echo window, or suspicious co-existing hepatic nodules. All of these issues should be resolved in future prospective studies that includes the general population and all patients with full spectrum of the diseases (simple steatosis and NASH in NAFLD patients and inactive and active phases in CHB patients).
Second, our study contains a relatively small sample size. This is particularly true when the study population was divided according to the etiology of chronic liver diseases and AVT status. Large prospective studies will be required to resolve this issue and validate our results.
Third, due to the heterogeneity in the type and duration of hepatotonics, we could not investigate their potential influence on the accuracy of the HSI. In addition, the lack of histological information could be a significant limitation of this study.
In conclusion, the diagnostic accuracy of the HSI in patients with NAFLD was acceptable. Further, despite a slight decrease in accuracy, the diagnostic accuracy of the HSI in patients with CHB receiving AVT was still acceptable in detecting hepatic steatosis. Future larger scale studies will be required for the validation of our results.
Supplemental Materials
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This study was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (grant number: 2019R1A2C4070136).
Footnotes
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conception: J.W.C., S.U.K. Study design: J.W.C., S.U.K. Participation in patient management and data collection: H.W.L., B.K.K., J.Y.P., D.Y.K., S.H.A., K.H.H., S.U.K. Contributions to the data acquisition, responsible for writing the manuscript, and performing statistical analysis: J.W.C., S.U.K. All authors reviewed the paper and approved the final version. Guarantor: S.U.K.
REFERENCES
- 1.Younossi ZM, Koenig AB, Abdelatif D, Fazel Y, Henry L, Wymer M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology. 2016;64:73–84. doi: 10.1002/hep.28431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Loomba R, Sanyal AJ. The global NAFLD epidemic. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;10:686–690. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2013.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Petta S, Muratore C, Craxì A. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease pathogenesis: the present and the future. Dig Liver Dis. 2009;41:615–625. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2009.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Fan JG, Kim SU, Wong VW. New trends on obesity and NAFLD in Asia. J Hepatol. 2017;67:862–873. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.06.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ateş F, Yalnız M, Alan S. Impact of liver steatosis on response to pegylated interferon therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis B. World J Gastroenterol. 2011;17:4517–4522. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i40.4517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Negro F, Clément S. Impact of obesity, steatosis and insulin resistance on progression and response to therapy of hepatitis C. J Viral Hepat. 2009;16:681–688. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2009.01186.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Shackel NA, McCaughan GW. Liver biopsy: is it still relevant? Intern Med J. 2006;36:689–691. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.2006.01210.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Emanuele E. Is biopsy always necessary? Toward a clinico-laboratory approach for diagnosing nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in obesity. Hepatology. 2008;48:2086–2087. doi: 10.1002/hep.22622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Saadeh S, Younossi ZM, Remer EM, et al. The utility of radiological imaging in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2002;123:745–750. doi: 10.1053/gast.2002.35354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hernaez R, Lazo M, Bonekamp S, et al. Diagnostic accuracy and reliability of ultrasonography for the detection of fatty liver: a meta-analysis. Hepatology. 2011;54:1082–1090. doi: 10.1002/hep.24452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Schwenzer NF, Springer F, Schraml C, Stefan N, Machann J, Schick F. Non-invasive assessment and quantification of liver steatosis by ultrasound, computed tomography and magnetic resonance. J Hepatol. 2009;51:433–445. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2009.05.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Reeder SB, Hu HH, Sirlin CB. Proton density fat-fraction: a standardized MR-based biomarker of tissue fat concentration. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012;36:1011–1014. doi: 10.1002/jmri.23741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Reeder SB, Robson PM, Yu H, et al. Quantification of hepatic steatosis with MRI: the effects of accurate fat spectral modeling. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2009;29:1332–1339. doi: 10.1002/jmri.21751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Springer F, Machann J, Claussen CD, Schick F, Schwenzer NF. Liver fat content determined by magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16:1560–1566. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i13.1560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Reeder SB, Cruite I, Hamilton G, Sirlin CB. Quantitative assessment of liver fat with magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2011;34:729–749. doi: 10.1002/jmri.22580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Zhang Z, Wang G, Kang K, Wu G, Wang P. Diagnostic accuracy and clinical utility of a new noninvasive index for hepatic steatosis in patients with hepatitis B virus infection. Sci Rep. 2016;6:32875. doi: 10.1038/srep32875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lee JH, Kim D, Kim HJ, et al. Hepatic steatosis index: a simple screening tool reflecting nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig Liver Dis. 2010;42:503–508. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2009.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Xu L, Lu W, Li P, Shen F, Mi YQ, Fan JG. A comparison of hepatic steatosis index, controlled attenuation parameter and ultrasound as noninvasive diagnostic tools for steatosis in chronic hepatitis B. Dig Liver Dis. 2017;49:910–917. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2017.03.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Elwan N, Elfert A, Abd-Elsalam S, et al. Study of hepatic steatosis index in patients with chronic HCV infection. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci. 2016;5:266–274. doi: 10.20546/ijcmas.2016.505.029. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, et al. The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, American College of Gastroenterology, and the American Gastroenterological Association. Hepatology. 2012;55:2005–2023. doi: 10.1002/hep.25762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Puri P, Sanyal AJ. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: definitions, risk factors, and workup. Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken) 2012;1:99–103. doi: 10.1002/cld.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Caussy C, Alquiraish MH, Nguyen P, et al. Optimal threshold of controlled attenuation parameter with MRI-PDFF as the gold standard for the detection of hepatic steatosis. Hepatology. 2018;67:1348–1359. doi: 10.1002/hep.29639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Gaiani S, Gramantieri L, Venturoli N, et al. What is the criterion for differentiating chronic hepatitis from compensated cirrhosis? A prospective study comparing ultrasonography and percutaneous liver biopsy. J Hepatol. 1997;27:979–985. doi: 10.1016/S0168-8278(97)80140-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Di Lelio A, Cestari C, Lomazzi A, Beretta L. Cirrhosis: diagnosis with sonographic study of the liver surface. Radiology. 1989;172:389–392. doi: 10.1148/radiology.172.2.2526349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Committee for the Korean Guidelines for the Management of Dyslipidemia, author. 2015 Korean Guidelines for the Management of Dyslipidemia: executive summary (English translation) Korean Circ J. 2016;46:275–306. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2016.46.3.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bravo AA, Sheth SG, Chopra S. Liver biopsy. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:495–500. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200102153440706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Castéra L, Nègre I, Samii K, Buffet C. Pain experienced during percutaneous liver biopsy. Hepatology. 1999;30:1529–1530. doi: 10.1002/hep.510300624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Hamaguchi M, Kojima T, Itoh Y, et al. The severity of ultrasonographic findings in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease reflects the metabolic syndrome and visceral fat accumulation. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007;102:2708–2715. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2007.01526.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Duman DG, Celikel C, Tüney D, Imeryüz N, Avsar E, Tözün N. Computed tomography in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a useful tool for hepatosteatosis assessment? Dig Dis Sci. 2006;51:346–351. doi: 10.1007/s10620-006-3136-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lee SW, Park SH, Kim KW, et al. Unenhanced CT for assessment of macrovesicular hepatic steatosis in living liver donors: comparison of visual grading with liver attenuation index. Radiology. 2007;244:479–485. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2442061177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Fishbein MH, Gardner KG, Potter CJ, Schmalbrock P, Smith MA. Introduction of fast MR imaging in the assessment of hepatic steatosis. Magn Reson Imaging. 1997;15:287–293. doi: 10.1016/S0730-725X(96)00224-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Jin X, Chen YP, Yang YD, Li YM, Zheng L, Xu CQ. Association between hepatic steatosis and entecavir treatment failure in Chinese patients with chronic hepatitis B. PLoS One. 2012;7:e34198. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kim DS, Jeon MY, Lee HW, et al. Influence of hepatic steatosis on the outcomes of patients with chronic hepatitis B treated with entecavir and tenofovir. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2019;25:283–293. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2018.0054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Han E, Lee YH, Kim BK, et al. Sarcopenia is associated with the risk of significant liver fibrosis in metabolically unhealthy subjects with chronic hepatitis B. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2018;48:300–312. doi: 10.1111/apt.14843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Tada T, Kumada T, Toyoda H, et al. Utility of attenuation coefficient measurement using an ultrasound-guided attenuation parameter for evaluation of hepatic steatosis: comparison with MRI-determined proton density fat fraction. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2019;212:332–341. doi: 10.2214/AJR.18.20123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Haufe WM, Wolfson T, Hooker CA, et al. Accuracy of PDFF estimation by magnitude-based and complex-based MRI in children with MR spectroscopy as a reference. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2017;46:1641–1647. doi: 10.1002/jmri.25699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Fang KC, Cheng YL, Su CW, et al. Higher platelet counts are associated with metabolic syndrome independent of fatty liver diagnosis. J Chin Med Assoc. 2017;80:125–132. doi: 10.1016/j.jcma.2016.07.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Cao W, Zhao C, Shen C, Wang Y. Cytokeratin 18, alanine aminotransferase, platelets and triglycerides predict the presence of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. PLoS One. 2013;8:e82092. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.van der Poorten D, Samer CF, Ramezani-Moghadam M, et al. Hepatic fat loss in advanced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: are alterations in serum adiponectin the cause? Hepatology. 2013;57:2180–2188. doi: 10.1002/hep.26072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Chauhan A, Adams DH, Watson SP, Lalor PF. Platelets: no longer bystanders in liver disease. Hepatology. 2016;64:1774–1784. doi: 10.1002/hep.28526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Noureddin M, Lam J, Peterson MR, et al. Utility of magnetic resonance imaging versus histology for quantifying changes in liver fat in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease trials. Hepatology. 2013;58:1930–1940. doi: 10.1002/hep.26455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Reeder SB. Emerging quantitative magnetic resonance imaging biomarkers of hepatic steatosis. Hepatology. 2013;58:1877–1880. doi: 10.1002/hep.26543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Yoo JJ, Kim W, Kim MY, et al. Recent research trends and updates on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2019;25:1–11. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2018.0037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.An C, Kim DY, Choi JY, Han KH, Roh YH, Kim MJ. Noncontrast magnetic resonance imaging versus ultrasonography for hepatocellular carcinoma surveillance (MIRACLE-HCC): study protocol for a prospective randomized trial. BMC Cancer. 2018;18:915. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4827-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.