Abstract
We examined if plasma phosphorylated tau is associated with neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. We investigated 372 cognitively unimpaired participants, 554 mild cognitive impairment patients, and 141 Alzheimer’s disease dementia patients. Tau phosphorylated at threonine 181, regional cortical thickness (using magnetic resonance imaging) and hypometabolism (using fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography) were measured longitudinally. High plasma tau was associated with hypometabolism and cortical atrophy at baseline and over time, and longitudinally increased tau was associated with accelerated atrophy, but these associations were only observed in Aβ‐positive participants. Plasma phosphorylated tau may identify and track processes linked to neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease.
Introduction
Plasma P‐tau181 is increased in Alzheimer’s disease (AD), and correlates with brain deposition of aggregated β‐amyloid (Aβ) and tau, the core AD hallmarks. 1 , 2 , 3 Plasma P‐tau181 may potentially be used as a noninvasive proxy for tau pathology linked to neurodegeneration, 2 , 4 but longitudinal plasma P‐tau181 data have not been examined. To better understand the performance of plasma P‐tau181 to monitor tau pathology and subsequent neurodegeneration in AD, we need truly longitudinal analyses that incorporate change of both neuroimaging measures and P‐tau181. We tested associations between longitudinal plasma P‐tau181 and imaging measures for hypometabolism, using fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG‐PET) and for cortical atrophy, using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), in a large cohort of cognitively unimpaired (CU) individuals, patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and AD dementia patients. We tested the hypothesis that increased plasma P‐tau181 was associated with signs of neurodegeneration, both at baseline and over time. Since plasma P‐tau181 is strongly linked to AD, 1 , 2 , 3 we further hypothesized that these associations would only be seen in individuals who were on the AD trajectory (as indicated by a positive Aβ PET scan).
Methods
Study participants
Data were obtained from the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) database (adni.loni.usc.edu). The ADNI was launched in 2003 as a public‐private partnership, led by Principal Investigator Michael W. Weiner, MD. For up‐to‐date information, see www.adni‐info.org. We used data accessed at the ADNI database on 2020/06/25. We included all CU controls, MCI and AD dementia patients with plasma P‐tau181 and at least one available MRI or FDG‐PET scan. Inclusion and exclusion criteria have been described before. 5 In sum, CU participants had Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE) score ≥ 24, and Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR) score 0. MCI participants had MMSE score ≥ 24, objective memory loss tested by delayed recall of the Wechsler Memory Scale Logical Memory II, CDR 0.5, preserved activities of daily living, and absence of dementia. AD dementia patients fulfilled the National Institute of Neurological and Communicative Disorders and Stroke and the Alzheimer's Disease and Related Disorders Association (NINCDS‐ADRDA) criteria for probable AD, 6 had MMSE 20–26 and CDR 0.5‐1.0. The study data and samples were collected from 2005/10/24 to 2019/07/17. Ethical approval was given by the local ethical committees of all involved sites. All participants gave written informed consent.
Biomarker and imaging measurements
Plasma samples were taken annually. P‐tau181 was analyzed on a Single molecule array (Simoa) HD‐X Analyzer (Quanterix, Billerica, MA), using an in‐house assay developed in the Clinical Neurochemistry Laboratory, University of Gothenburg, Sweden. 2 In the P‐tau181 data file (UGOTPTAU181_06_18_20.csv at the ADNI database), we noted 33 outlying data points (P‐tau181‐concentrations more than three standard deviations above the mean, 63.3 ng/L) out of N = 3758 observations. We excluded those outliers from all analyses.
Structural brain images were acquired using 3 Tesla MRI scanners with T1‐weighted MRI scans using a sagittal volumetric magnetization prepared rapid gradient echo (MP‐RAGE) sequence. MRI scans were done at baseline, 3 months and 6 months, and thereafter annually. FreeSurfer (v5.1) was used for quantification of regional thickness and volumes according to the 2010 Desikan‐Killany atlas. 7 We used cortical thickness for a meta‐region of interest (“temporal composite”) involving entorhinal, inferior temporal, middle temporal, and fusiform cortex. 8 FDG‐PET scans were acquired annually. An FDG composite score was calculated as the average uptake in left and right angular, temporal, and posterior cingulate regions. 9 18F‐Florbetapir PET brain scans for Aβ deposition were acquired at baseline according to a previously described protocol, 9 using a cortical summary‐ROI consisting of frontal, anterior/posterior cingulate, lateral parietal, lateral temporal brain regions and with whole cerebellum as reference. Aβ positivity was defined as 18F‐florbetapir PET > 1.11 SUVR. 9
Statistical analyses
We determined associations between continuous plasma P‐tau181 and neuroimaging measures, using all available paired longitudinal data, in linear mixed‐effects (LME) models with P‐tau181 as predictor and neuroimaging measures as response. We next tested if baseline plasma P‐tau181 predicted change in neuroimaging measures. To use all available data for the imaging measures, we extracted slopes of change for temporal cortical thickness and FDG‐PET in separate linear regression models (without requiring paired P‐tau181 data). We then used neuroimaging slopes as response variables in linear regression models with continuous P‐tau181 as the predictor. We also tested if longitudinal change in P‐tau181 correlated with longitudinal change in neuroimaging measures. For this, we extracted slopes for P‐tau181 in separate linear regression models (without requiring paired imaging data). We used those slopes as predictors in linear regression models with a change in neuroimaging measures as outcomes. All these models were adjusted for age, sex, diagnostic group, APOE ε4 status (positive = at least one ε4 allele, or negative = no ε4 alleles), Aβ status, and the interaction between Aβ status and P‐tau181, and (for slope data) lag between first imaging scan and first P‐tau181 sampling. For the final analyses, we used binary P‐tau181 status. We defined a P‐tau181 cut‐point using two‐component mixture modeling of the P‐tau181 data in Aβ‐negative CU, at the mean concentration plus two standard deviations of the lower component. We divided the data in four groups by combinations of positivity and negativity on P‐tau181 and Aβ PET. We used this factor as the predictor of baseline and longitudinal neuroimaging measures in linear regression models, adjusted for age, sex, diagnostic group, and (for tests of slopes) lag between the first imaging scan and first P‐tau181 measure. We also performed sensitivity analyses within diagnostic subgroups and in a restricted dataset with paired MRI and FDG‐PET imaging data. All statistical analyses were done in R (v 4.0.0). Significance was determined at P < 0.05.
Results
Demographics are shown in Table 1.
Table 1.
Demographics.
| CU | MCI | AD dementia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 372 | 554 | 141 |
| Sex (M/F) | 196/176 | 241/313 | 59/82 |
| Age (y) | 73.6 (5.8) | 71.9 (7.4) | 74.4 (8.2) |
| Education (y) | 16.6 (2.6) | 16.1 (2.7) | 15.7 (2.7) |
| APOE ε4 (−−/− +/++) | 267/98/7 | 290/209/55 | 46/66/29 |
| Baeline Aβ‐status (−/+) | 245/127 | 243/311 | 16/125 |
| Baseline P‐tau181 (ng/L) | 15.2 (8.6) | 18.4 (10.5) | 22.8 (8.5) |
| Baseline temporal cortical thickness (mm) | 2.82 (0.15) | 2.76 (0.19) | 2.53 (0.22) |
| Baseline FDG‐PET (SUVR) | 1.31 (0.11) | 1.25 (0.14) | 1.07 (0.15) |
| Nr of P‐tau181 measures (median [IQR]) | 3 (2–4) | 4 (3–5) | 2 (1–2) |
| Duration from first to last P‐tau181 measure (y) (median [IQR]) | 2.05 (1.98–3.97) | 3.01 (2.00–3.99) | 0.99 (0.00–1.05) |
| Nr of MRI scans (median [IQR]) | 5 (4–6) | 5 (4–6) | 4 (4–4) |
| Duration from first to last MRI scan (y) (median [IQR]) | 2.07 (1.98–4.00) | 2.12 (1.98–4.00) | 1.02 (0.98–1.95) |
| Nr of FDG‐PET scans (median [IQR]) | 2 (1–2) | 2 (1–2) | 1 (1–1) |
| Duration from first to last FDG‐PET (y) (median [IQR]) | 1.95 (0.00–2.03) | 1.99 (0.00–3.97) | 0.00 (0.00–0.00) |
Continuous data are mean (standard deviation).
Continuous plasma P‐tau181 and temporal cortical thickness
Higher plasma P‐tau181 was associated with thinner cortices in Aβ+, but not in Aβ‐ individuals (Fig. 1A; in subgroup analyses, this was found in MCI and AD, but not in CU, Figs. [Link], [Link], [Link]). Higher baseline plasma P‐tau181 was also associated with more rapid decline of cortical thickness in Aβ+, but not in Aβ‐ individuals (Fig. 1B; in subgroup analyses, this was found in MCI, but not in CU or AD, Figs. [Link], [Link], [Link]). Greater slopes of plasma P‐tau181 were associated with more rapid decline of cortical thickness in Aβ+ individuals, but not in Aβ‐ individuals (Fig. 1C; in subgroup analyses, this was found in CU and AD, but not in MCI, Figs. S1, –S3).
Figure 1.
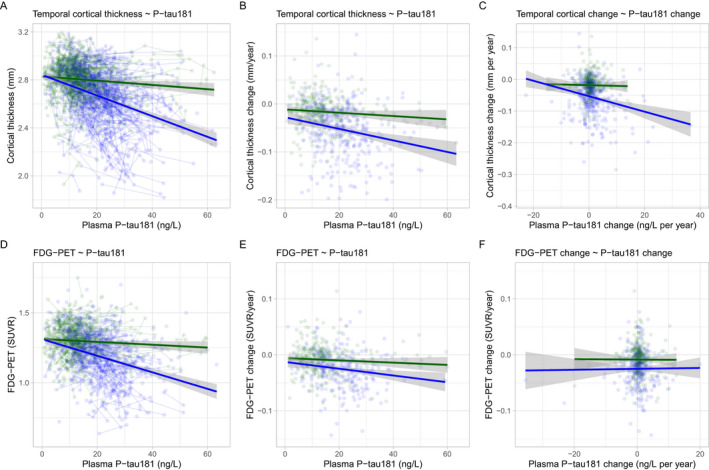
Plasma P‐tau181 and imaging measures of neurodegeneration. Associations between temporal cortical thickness (panels A–C) and fluorodeoxyglucose PET (panels D–F) with plasma P‐tau181 levels, testing associations with all available paired data (panels A and D), associations between slopes of imaging measures and baseline P‐tau181 (panels B and E), and associations between slopes of imaging measures and slopes of P‐tau181 (panels C and F). All models are adjusted for age, sex, diagnostic group, APOE ε4 status, and Aβ status. Slope models are also adjusted for lag between the first imaging scan and first P‐tau181 measure. The effects in Aβ‐negative subjects are shown in green and effects in Aβ‐positive subjects are shown in blue (for individual subjects and average effect). Panels A and D show results from linear mixed‐effects models, with several data points per individual (individual subjects as a random factor). P‐values are extracted from the models for associations in Aβ‐negative and Aβ‐positive subjects separately. P‐values are also indicated for the difference in slopes between Aβ‐positive and Aβ‐negative subjects.
Continuous plasma P‐tau181 and hypometabolism
Higher plasma P‐tau181 was associated with lower FDG‐PET SUVR in Aβ+, but not in Aβ‐ individuals (Fig. 1D; in subgroup analyses, this was found in MCI, but not in CU or AD, Figs. [Link], [Link], [Link]). Higher baseline plasma P‐tau181 was also associated with more rapid decline of FDG‐PET SUVR in Aβ+, but not in Aβ‐ individuals (Fig. 1E; in subgroup analyses, this was found in CU, but not in MCI or AD, Figs. S1, –S3). Slopes of plasma P‐tau181 were not associated with slopes of FDG‐PET SUVR in either Aβ‐ or Aβ+ (Fig. 1F).
Dichotomous plasma P‐tau181 and neurodegeneration
A cut‐point for abnormal baseline plasma P‐tau181 was defined in the Aβ‐negative CU group (P‐tau181 > 19.8 ng/L). The data were divided into four parts based on P‐tau181 and Aβ status (Fig. 2A). P‐tau181+/Aβ+ (N = 302) had thinner baseline cortices (in subgroup analyses, this was found in MCI and AD, but not in CU, Figs. [Link], [Link], [Link]), lower baseline FDG‐PET SUVR (in subgroup analyses this was found in CU and MCI, but not in AD, Figs. [Link], [Link], [Link]), and more rapid decline in cortical thickness (but not in subgroup analyses, Figs. [Link], [Link], [Link]) and FDG‐PET SUVR (in subgroup analyses, this was found in MCI, but not in CU or AD, Figs. S4, –S6) than P‐tau181−/Aβ+ (N = 261). There were no differences between Ptau181‐/Aβ‐ (N = 425) and P‐tau181+/Aβ‐ (N = 79) for any comparison.
Figure 2.
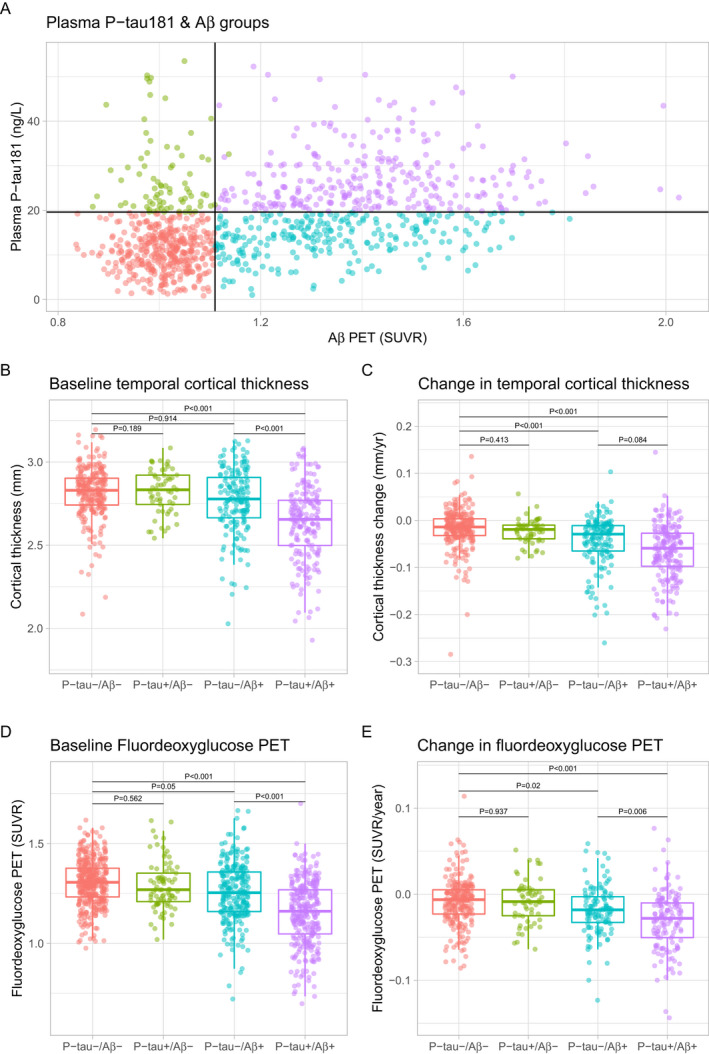
Fluorodeoxyglucose PET and temporal cortical thickness by groups av P‐tau181 and Aβ‐PET positivity. Panel A shows the overall P‐tau181 and Aβ PET data, cut‐points for P‐tau181 (>19.8 ng/L) and Aβ PET (>1.11 SUVR) positivity, and the four groups created by combinations of P‐tau181 and Aβ PET. Panels B–E show differences between groups for temporal cortical thickness and FDG‐PET, at baseline and over time. The groups were compared in linear regression models, adjusted for age, sex, APOE ε4 status, diagnostic group, and lag between the first imaging scan and first P‐tau181 measure. P‐values are extracted for comparisons between P‐tau181−/Aβ‐ (reference) and all other groups, and between P‐tau181‐negative and ‐positive groups within the Aβ groups.
Sensitivity analyses with paired imaging data
In the main analyses, we included all available MRI and FDG‐PET data, as measures of neurodegeneration. Although we did not aim to compare effects on MRI with effects on FDG‐PET, we also did a sensitivity analysis restricted to paired imaging data (from ADNI visits when both MRI and FDG‐PET data were available). This resulted in a smaller dataset, with 206 CU, 376 MCI, and 88 AD dementia patients. Most findings remained significant or borderline significant in this restricted data set (Figs. S7 and S8). In sum, higher plasma P‐tau181 remained associated with thinner cortices, more rapid decline of cortical thickness and lower FDG‐PET SUVR in Aβ+ (but not in Aβ‐) individuals. Greater slopes of plasma P‐tau181 remained associated with more rapid decline of cortical thickness in Aβ+ individuals. P‐tau181+/Aβ+ had thinner baseline cortices and lower baseline FDG‐PET SUVR than P‐tau181−/Aβ+, but the associations with decline in cortical thickness and FDG‐PET SUVR were no longer significant in this subset.
Discussion
Higher plasma P‐tau181 was associated with reduced brain glucose metabolism, reduced temporal lobe cortical thickness, and more rapid acceleration of hypometabolism and cortical atrophy, indicating worsening of neurodegeneration, but only in those with evidence of AD‐type pathophysiology in the form of a positive Aβ PET scan. Longitudinal increases of plasma P‐tau181 correlated with longitudinal cortical atrophy in Aβ PET‐positive individuals. Taken together, this suggests that plasma P‐tau181 reflects downstream longitudinal neurodegeneration due to AD, linked to either accumulation of paired‐helical filament (PHF) positive neurites surrounding amyloid plaques or to intracellular tangles.
Several studies have found correlations between CSF P‐tau181 and neurodegeneration, although comparisons involving longitudinal CSF data are rare. 10 , 11 , 12 Previous studies have also suggested correlations between plasma P‐tau181 and atrophy, using MRI. 2 , 4 Mielke et al. showed that higher plasma P‐tau181 was associated cross sectionally with less cortical thickness in a group of 269 CU individuals, MCI and AD dementia patients, but there were no associations in the individual diagnostic groups. 4 Karikari et al. showed that plasma P‐tau181 was associated with cross‐sectional and 1‐year longitudinal gray matter atrophy in 88 individuals, including CU, MCI, and AD dementia patients, but again there were no associations within individual diagnostic groups. 2 Our study is, to our knowledge, the first truly longitudinal study on the topic (using longitudinal data for both imaging measures and plasma P‐tau181). We also found associations when adjusting for clinical diagnosis, which may otherwise confound the relationship between atrophy and biochemical measures.
The longitudinal link between plasma P‐tau181 and signs of atrophy in people with (but not without) biomarker signs of Aβ pathology, suggests that plasma P‐tau181 may be useful as a noninvasive marker to track neurodegeneration in AD. Plasma P‐tau181 also performs well as a diagnostic marker for AD. 1 , 2 , 4 Together, this suggests that measurement of plasma P‐tau181 concentration may be useful in clinical trials (and perhaps in clinical practice) as a noninvasive, affordable way to monitor disease progression. As in previous studies, 1 , 2 , 3 we note high P‐tau181 levels despite a normal Aβ PET scan in a minority of subjects. Since these subjects do not show signs of increased neurodegeneration, this may not indicate a malign condition.
One limitation was that only one cohort was used. ADNI is tailored to represent a clinical trial population, and further studies are needed on more general and diverse populations, where neurodegeneration is more likely to also be impacted by other (non‐AD) processes. The study cohort did, however, include Aβ‐negative MCI and (clinically diagnosed) AD dementia subjects, which are likely to have cognitive impairment due to non‐AD conditions, including depression and cerebrovascular disease. 13 , 14 We only included subjects with Aβ data, so that we could stratify the analyses by Aβ‐status, but we did not perform complete ATN classification, 15 since measures of neurodegeneration were key outcome data, and since we did not have an independent measure of T‐status (tau PET data were lacking in most subjects, and CSF P‐tau181 data were not suitable for this analysis, since it is very closely correlated with plasma P‐tau181, the main predictor in this study 1 , 3 ).
Author Contributions
NMC and OH conceived the study. NMC and NC performed the statistical analysis. HZ and KB were responsible for biochemical analyses. NMC and OH drafted the initial manuscript. All authors contributed to the revision and editing of the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
NC, and NMC have nothing to disclose. OH has acquired research support (for the institution) from Roche, Pfizer, GE Healthcare, Biogen, Eli Lilly and AVID Radiopharmaceuticals. In the past 2 years, he has received consultancy/speaker fees (paid to the institution) from Biogen and Roche. HZ has served at scientific advisory boards for Denali, Roche Diagnostics, Wave, Samumed, Siemens Healthineers, Pinteon Therapeutics and CogRx, has given lectures in symposia sponsored by Fujirebio, Alzecure and Biogen, and is a co‐founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program. KB has served as a consultant, at advisory boards, or at data monitoring committees for Abcam, Axon, Biogen, JOMDD/Shimadzu. Julius Clinical, Lilly, MagQu, Novartis, Roche Diagnostics, and Siemens Healthineers, and is a co‐founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program.
Supporting information
Figure S1. Plasma P‐tau181 and imaging measures of neurodegeneration in CU subjects.
Figure S2. Plasma P‐tau181 and imaging measures of neurodegeneration in MCI subjects.
Figure S3. Plasma P‐tau181 and imaging measures of neurodegeneration in AD dementia subjects.
Figure S4. Fluorodeoxyglucose PET and temporal cortical thickness by groups av P‐tau181 and Aβ‐PET positivity in CU subjects.
Figure S5. Fluorodeoxyglucose PET and temporal cortical thickness by groups av P‐tau181 and Aβ‐PET positivity in MCI subjects.
Figure S6. Fluorodeoxyglucose PET and temporal cortical thickness by groups av P‐tau181 and Aβ‐PET positivity in AD dementia subjects.
Figure S7. Sensitivity analyses for plasma P‐tau181 and imaging measures of neurodegeneration.
Figure S8. Sensitivity analyses for fluorodeoxyglucose PET and temporal cortical thickness by groups av P‐tau181 and Aβ‐PET positivity.
Data S1. Member list for the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative.
Funding Information
Work at the authors’ laboratory at Lund University was supported by the Swedish Research Council, the Wallenberg Center for Molecular Medicine, the Knut and Alice Wallenberg foundation, The Medical Faculty at Lund University, Region Skåne, the Marianne and Marcus Wallenberg foundation, the Strategic Research Area MultiPark (Multidisciplinary Research in Parkinson’s disease) at Lund University, the Swedish Alzheimer Foundation, the Swedish Brain Foundation, the Swedish Medical Association, the Konung Gustaf V:s och Drottning Victorias Frimurarestiftelse, the Bundy Academy, the Skåne University Hospital Foundation, and the Swedish federal government under the ALF agreement. HZ is a Wallenberg Scholar supported by grants from the Swedish Research Council (#2018‐02532), the European Research Council (#681712), Swedish State Support for Clinical Research (#ALFGBG‐720931), the Alzheimer Drug Discovery Foundation (ADDF), USA (#201809‐2016862), and the UK Dementia Research Institute at UCL. KB is supported by the Swedish Research Council (#2017‐00915), the Alzheimer Drug Discovery Foundation (ADDF), USA (#RDAPB‐201809‐2016615), the Swedish Alzheimer Foundation (#AF‐742881), Hjärnfonden, Sweden (#FO2017‐0243), the Swedish state under the agreement between the Swedish government and the County Councils, the ALF‐agreement (#ALFGBG‐715986), and European Union Joint Program for Neurodegenerative Disorders (JPND2019‐466‐236). Data collection and sharing for this project was funded by the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) (National Institutes of Health Grant U01 AG024904) and DOD ADNI (Department of Defense award number W81XWH‐12‐2‐0012). ADNI is funded by the National Institute on Aging, the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering, and through generous contributions from the following: AbbVie, Alzheimer’s Association; Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation; Araclon Biotech; BioClinica, Inc.; Biogen; Bristol‐Myers Squibb Company; CereSpir, Inc.; Cogstate; Eisai Inc.; Elan Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; Eli Lilly and Company; EuroImmun; F. Hoffmann‐La Roche Ltd and its affiliated company Genentech, Inc.; Fujirebio; GE Healthcare; IXICO Ltd.; Janssen Alzheimer Immunotherapy Research & Development, LLC.; Johnson & Johnson Pharmaceutical Research & Development LLC.; Lumosity; Lundbeck; Merck & Co., Inc.; Meso Scale Diagnostics, LLC.; NeuroRx Research; Neurotrack Technologies; Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation; Pfizer Inc.; Piramal Imaging; Servier; Takeda Pharmaceutical Company; and Transition Therapeutics. The Canadian Institutes of Health Research is providing funds to support ADNI clinical sites in Canada. Private sector contributions are facilitated by the Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (www.fnih.org). The grantee organization is the Northern California Institute for Research and Education, and the study is coordinated by the Alzheimer’s Therapeutic Research Institute at the University of Southern California. ADNI data are disseminated by the Laboratory for Neuro Imaging at the University of Southern California.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by Swedish Research Council grants #2018‐02532 and #2017‐00915; Wallenberg Center for Molecular Medicine grant ; Knut and Alice Wallenberg foundation grant ; The Medical Faculty at Lund University grant ; Region Skåne grant ; Marianne and Marcus Wallenberg foundation grant ; Strategic Research Area MultiPark grant ; the Swedish Alzheimer Foundation grant #FO2017‐0243; the Swedish Brain Foundation grant ; the Swedish Medical Association grant ; the Konung Gustaf V:s och Drottning Victorias Frimurarestiftelse grant ; the Bundy Academy grant ; the Skåne University Hospital Foundation grant ; the Swedish federal government grant ; the European Research Council grant #681712; Swedish State Support for Clinical Research grant #ALFGBG‐720931; the Alzheimer Drug Discovery Foundation grants #201809‐2016862 and #RDAPB‐201809‐2016615; UK Dementia Research Institute grant ; the ALF‐agreement grant #ALFGBG‐715986; European Union Joint Program for Neurodegenerative Disorders grant JPND2019‐466‐236; National Institutes of Health grant U01 AG024904; DOD ADNI grant W81XWH‐12‐2‐0012; National Institute on Aging grant ; National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering grant ; AbbVie grant ; Alzheimer’s Association grant ; Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation grant ; Araclon Biotech grant ; BioClinica, Inc. grant ; Biogen grant ; Bristol‐Myers Squibb Company grant ; CereSpir, Inc. grant ; Cogstate grant ; Eisai Inc. grant ; Elan Pharmaceuticals, Inc. grant ; Eli Lilly and Company grant ; EuroImmun grant ; F. Hoffmann‐La Roche Ltd grant ; Genentech, Inc. grant ; Fujirebio grant ; GE Healthcare grant ; IXICO Ltd. grant ; Janssen Alzheimer Immunotherapy Research & Development, LLC. grant ; Johnson & Johnson Pharmaceutical Research & Development LLC. grant ; Lumosity grant ; Lundbeck; Merck & Co., Inc. grant ; Meso Scale Diagnostics, LLC. grant ; NeuroRx Research grant ; Neurotrack Technologies grant ; Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation grant ; Pfizer Inc. grant ; Piramal Imaging grant ; Servier grant ; Takeda Pharmaceutical Company grant ; Transition Therapeutics grant ; The Canadian Institutes of Health grant ; ADNI grant ; Northern California Institute for Research and Education grant ; Alzheimer’s Therapeutic Research Institute grant ; University of Southern California grant .
Data Availability Statement
Anonymized study data for the primary analyses presented herein are available upon request from any qualified investigator for purposes of replicating reported results.
References
- 1. Janelidze S, Mattsson N, Palmqvist S, et al. Plasma P‐tau181 in Alzheimer’s disease: relationship to other biomarkers, differential diagnosis, neuropathology and longitudinal progression to Alzheimer’s dementia. Nat Med 2020;26:379–386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Karikari TK, Pascoal TA, Ashton NJ, et al. Blood phosphorylated tau 181 as a biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease: a diagnostic performance and prediction modelling study using data from four prospective cohorts. Lancet Neurol 2020;19:422–433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Thijssen EH, La Joie R, Wolf A, et al. Diagnostic value of plasma phosphorylated tau181 in Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Nat Med 2020;26:387–397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Mielke MM, Hagen CE, Xu J, et al. Plasma phospho‐tau181 increases with Alzheimer’s disease clinical severity and is associated with tau‐ and amyloid‐positron emission tomography. Alzheimers Dement 2018;14:989–997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Petersen RC, Aisen PS, Beckett LA, et al. Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI): clinical characterization. Neurology 2010;74:201–209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, et al. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS‐ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology 1984;34:939–944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Jack CR Jr, Bernstein MA, Fox NC, et al. The Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI): MRI methods. J Magn Reson Imaging 2008;27:685–691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Jack CR, Wiste HJ, Weigand SD, et al. Different definitions of neurodegeneration produce similar amyloid/neurodegeneration biomarker group findings. Brain 2015;138:3747–3759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Landau SM, Mintun MA, Joshi AD, et al. Amyloid deposition, hypometabolism, and longitudinal cognitive decline. Ann Neurol 2012;72:578–586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Falcon C, Tucholka A, Monté‐Rubio GC, et al. Longitudinal structural cerebral changes related to core CSF biomarkers in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease: a study of two independent datasets. Neuroimage Clin 2018;19:190–201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Tarawneh R, Head D, Allison S, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid markers of neurodegeneration and rates of brain atrophy in early Alzheimer disease. JAMA Neurol 2015;72:656–665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Wang L, Fagan AM, Shah AR, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid proteins predict longitudinal hippocampal degeneration in early‐stage dementia of the Alzheimer type. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 2012;26:314–321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Nettiksimmons J, DeCarli C, Landau S, Beckett L. Biological heterogeneity in ADNI amnestic MCI. Alzheimers Dement 2014;10:511–521.e1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Landau SM, Horng A, Fero A, Jagust WJ. Amyloid negativity in patients with clinically diagnosed Alzheimer disease and MCI. Neurology 2016;86:1377–1385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Jack CR, Bennett DA, Blennow K, et al. NIA‐AA Research Framework: toward a biological definition of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 2018;14:535–562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Figure S1. Plasma P‐tau181 and imaging measures of neurodegeneration in CU subjects.
Figure S2. Plasma P‐tau181 and imaging measures of neurodegeneration in MCI subjects.
Figure S3. Plasma P‐tau181 and imaging measures of neurodegeneration in AD dementia subjects.
Figure S4. Fluorodeoxyglucose PET and temporal cortical thickness by groups av P‐tau181 and Aβ‐PET positivity in CU subjects.
Figure S5. Fluorodeoxyglucose PET and temporal cortical thickness by groups av P‐tau181 and Aβ‐PET positivity in MCI subjects.
Figure S6. Fluorodeoxyglucose PET and temporal cortical thickness by groups av P‐tau181 and Aβ‐PET positivity in AD dementia subjects.
Figure S7. Sensitivity analyses for plasma P‐tau181 and imaging measures of neurodegeneration.
Figure S8. Sensitivity analyses for fluorodeoxyglucose PET and temporal cortical thickness by groups av P‐tau181 and Aβ‐PET positivity.
Data S1. Member list for the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative.
Data Availability Statement
Anonymized study data for the primary analyses presented herein are available upon request from any qualified investigator for purposes of replicating reported results.


