Abstract
Background
Staphylococcus pseudintermedius (SP) and Staphylococcus aureus (SA) are common colonizers of companion animals, but they are also considered opportunistic pathogens, causing diseases of diverse severity. This study focused on the identification and characterization of 33 coagulase-positive staphylococci isolated from diseased pets (28 dogs and five cats) during 2009–2011 in a veterinary hospital in Spain in order to stablish the circulating lineages and their antimicrobial resistance profile.
Results
Twenty-eight isolates were identified as SP and five as SA. Nine methicillin-resistant (MR) isolates (27%) carrying the mecA gene were detected (eight MRSP and one MRSA). The 55% of SP and SA isolates were multidrug-resistant (MDR). MRSP strains were typed as ST71-agrIII-SCCmecII/III-(PFGE) A (n=5), ST68-agrIV-SCCmecV-B1/B2 (n=2), and ST258-agrII-SCCmecIV-C (n=1). SP isolates showed resistance to the following antimicrobials [percentage of resistant isolates/resistance genes]: penicillin [82/blaZ], oxacillin [29/mecA] erythromycin/clindamycin [43/erm(B)], aminoglycosides [18–46/aacA-aphD, aphA3, aadE], tetracycline [71/tet(M), tet(K)], ciprofloxacin [29], chloramphenicol [29/catpC221], and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole [50/dfrG, dfrK]. The dfrK gene was revealed as part of the radC-integrated Tn559 in two SP isolates. Virulence genes detected among SP isolates were as follow [percentage of isolates]: siet [100], se-int [100], lukS/F-I [100], seccanine [7], and expB [7]. The single MRSA-mecA detected was typed as t011-ST398/CC398-agrI-SCCmecV and was MDR. The methicillin-susceptible SA isolates were typed as t045-ST5/CC5 (n=2), t10576-ST1660 (n=1), and t005-ST22/CC22 (n=1); the t005-ST22 feline isolate was PVL-positive and the two t045-ST45 isolates were ascribed to Immune Evasion Cluster (IEC) type F. Moreover, the t10576-ST1660 isolate, of potential equine origin, harbored the lukPQ and scneq genes. According to animal clinical history and data records, several strains seem to have been acquired from different sources of the hospital environment, while some SA strains appeared to have a human origin.
Conclusions
The frequent detection of MR and MDR isolates among clinical SP and SA strains with noticeable virulence traits is of veterinary concern, implying limited treatment options available. This is the first description of MRSA-ST398 and MRSP-ST68 in pets in Spain, as well the first report of the dfrK-carrying Tn559 in SP. This evidences that current transmissible lineages with mobilizable resistomes have been circulating as causative agents of infections among pets for years.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s12917-020-02726-4.
Keywords: MRSP, MRSA, MRSP-ST71, MRSA-CC398, Pets, Infection, Tn559
Background
Staphylococcus pseudintermedius (SP) and Staphylococcus aureus (SA) are harmless colonizers of the skin and mucosa of humans and animals [1], but they are also frequently implicated in opportunistic infections. In pets, especially in dogs, SP is most frequently detected than SA, both as colonizer and as causative agent of infection. It is recognized as the most common etiological agent implicated in skin and soft tissue infections, otitis, and urinary tract infections in dogs [2–4]. Moreover, SP can also cause diseases in humans, specially associated with dog exposure, which suggests zoonotic transmission [4]. SA is also found in healthy pets in rates between 8 and 12% [5–7].
Similar to methicillin-resistant SA (MRSA) in the clinical setting, methicillin-resistant SP (MRSP) has become a worldwide problem in animal health. It is frequently associated with a multidrug resistance phenotype, which limits the therapeutic options for veterinarians. Moreover, in recent years, several reports have evidenced an increase in the resistance rates for some important antimicrobials, such as fluoroquinolones, in SP isolates recovered from companion animals in European countries [8, 9]. In SP isolates recovered from diseased dogs, previous studies have reported methicillin resistance rates from 10 to 20% [8, 10, 11], although it varies notably depending on the geographic region. However, the methicillin resistance rate increases up to 60% in isolates recovered from canine pyoderma [12]. The spread of MRSP between countries is due to the dissemination of well-known specific genetic lineages such as the clone ST71 in Europe, ST68 in the USA, and ST45/ST112 in Asia [2–4, 10, 13], although all these clones have spread worldwide [4].
Regarding SA, molecular characterization has revealed that companion animals are colonized or infected by hospital-associated (HA) and community-associated (CA) MRSA clones from humans in close contact, which suggests an anthropozoonotic origin [14, 15]. Livestock-associated (LA) MRSA-CC398, which is mainly related with livestock and people with livestock contact, has also been reported causing infections in pets in few occasions [15, 16].
In this study, we identified and performed the molecular characterization of a collection of coagulase-positive staphylococci (CoPS) obtained from diseased pets during a 3-year-sampling period (2009–2011) in the veterinary laboratory at the University of Zaragoza, Spain.
Results
Isolates recovered and species identification
Of the 33 CoPS included in this study, 28 were identified as SP and five as SA. The infection site of the animals from which samples were recovered is indicated in Table 1 and Supplementary Table 1. Nine methicillin-resistant isolates carrying the mecA gene were detected (eight MRSP and one MRSA), representing 27% of the studied isolates; all of them, except one MRSP isolate, were recovered from dogs. The 55% of SP and SA isolates were multidrug-resistant (MDR) (resistant to at least three families of antimicrobial agents) (Table 1).
Table 1.
Characterization of the 28 S. pseudintermedius and five S. aureus isolates recovered from clinical samples of dogs and cats in this study
| Strain | Bacterial species | Year | Animal | Type of infectiona | spa-MLST/CC-agr-SCCmec | Antimicrobial resistance phenotypeb | Antimicrobial resistance genotype | Virulence genes detected |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C3871c | MRSP | 2009 | Dog | B-J | ST71-agrIII-SCCmecII-III | PEN-OXA-ERY-CLI-GEN-TOB-KAN-STR-TET-CIPf-CHL-SXT | blaZ, mecA, erm(B), aacA/aphD, aphA3, aadE, tet(K), catpC221, dfrG | lukS/F-I, siet, se-int |
| C3880 | MRSP | 2010 | Dog | S | ST71-agrIII-SCCmecII-III | PEN-OXA-ERY-CLI-GEN-TOB-STR-TET-CIPf-CHL-SXT | blaZ, erm(B), aacA/aphD, aphA3, aadE, tet(K), catpC221, dfrG | lukS/F-I, siet, se-int |
| C3885 | MRSP | 2010 | Dog | I | ST71-agrIII-SCCmecII-III | PEN-OXA-ERY-CLI-GEN-TOB-KAN-STR-TET-CIPf-CHL-SXT | blaZ, erm(B), aacA/aphD, aphA3, aadE, tet(K), catpC221, dfrG | lukS/F-I, siet, se-int |
| C5355 | MRSP | 2010 | Dog | B-J | ST71-agrIII-SCCmecII-III | PEN-OXA-ERY-CLI-GEN-TOB-KAN-STR-CIPf-SXT | blaZ, mecA, erm(B), aacA/aphD, aphA3, aadE, dfrG | lukS/F-I, siet, se-int |
| C5613 | MRSP | 2011 | Dog | U-R | ST71-agrIII-SCCmecII-III | PEN-OXA-ERY-CLI-GEN-TOB-KAN-STR-TET-CIPf-CHL-SXT | blaZ, mecA, erm(B), aacA/aphD, aphA3, aadE, tet(K), catpC221, dfrG | lukS/F-I, siet, se-int |
| C3866 | MRSP | 2009 | Cat | U-R | ST68-agrIV-SCCmecV | PEN-OXA-ERY-CLI-KAN-STR-TET-CIPf-SXT | blaZ, mecA, tet(M), erm(B), aphA3, aadE, dfrG | lukS/F-I, siet, se-int |
| C3870d | MRSP | 2009 | Dog | U-R | ST68-agrIV-SCCmecV | PEN-OXA-ERY-CLI-KAN-STR-TET-CIPf-SXT | blaZ, mecA, erm(B), aphA3, aadE, tet(M), dfrG | lukS/F-I, siet, se-int |
| C3869 | MRSP | 2009 | Dog | U-R | ST258-agrII-SCCmecIV | PEN-OXA-ERY-CLI-KAN-STR-TET-SXT | blaZ, mecA, erm(B), aphA3, aadE, tet(M), dfrG | lukS/F-I, siet, se-int |
| C5344 | MSSP | 2009 | Dog | U-R | PEN-ERY-CLI-KAN-STR-TET-CHL-SXT | blaZ, erm(B), aphA3, aadE, tet(M), catpC221, dfrG | lukS/F-I, siet, se-int | |
| C5345 | MSSP | 2009 | Cat | SI | PEN-ERY-CLI-KAN-STR-TET-CHL-SXT | blaZ, erm(B), aphA3, aadE, tet(M), catpC221, dfrG | lukS/F-I, siet, se-int | |
| C5360 | MSSP | 2011 | Dog | U-R | PEN-ERY-CLI-KAN-STR-TET-CHL-SXT | blaZ, erm(B), aphA3, aadE, tet(M), tet(K), dfrG, catpC221 | lukS/F-I, siet, se-int | |
| C5347 | MSSP | 2009 | Dog | U-R | PEN-ERY-CLI-TET-CHL-SXT | blaZ, erm(B), tet(M), catpC221, dfrG, dfrKh | lukS/F-I, siet, se-int | |
| C3877 | MSSP | 2010 | Dog | U-R | PEN-KAN-STR-TET | blaZ, aphA3, aadE, tet(M) | lukS/F-I, siet, se-int, expB | |
| C5351 | MSSP | 2010 | Cat | U-R | PEN-KAN-TET | blaZ, aphA3, tet(M) | lukS/F-I, siet, se-int | |
| C3881 | MSSP | 2010 | Dog | U-R | STR-TET-CIPf | str, tet(K), tet(M) | lukS/F-I, siet, se-int | |
| C5354 | MSSP | 2010 | Dog | U-R | PEN-TET-SXT | blaZ, tet(M), dfrG | lukS/F-I, siet, se-int | |
| C5358 | MSSP | 2011 | Dog | U-R | PEN-TET-SXT | blaZ, tet(M), dfrG, dfrKh | lukS/F-I, siet, se-int | |
| C3875 | MSSP | 2010 | Dog | I | PEN-TET | blaZ, tet(M) | lukS/F-I, siet, se-int | |
| C3876 | MSSP | 2010 | Dog | U-R | PEN-TET | blaZ, tet(M) | lukS/F-I, siet, se-int, expB | |
| C5356 | MSSP | 2011 | Dog | U-R | PEN-TET | blaZ, tet(M) | lukS/F-I, siet, se-int | |
| C5362 | MSSP | 2011 | Dog | I | PEN-TET | blaZ, tet(M) | lukS/F-I, siet, se-int | |
| C5353 | MSSP | 2010 | Dog | U-R | TET | tet(M) | lukS/F-I, siet, se-int, seccanine | |
| C3873 | MSSP | 2010 | Dog | U-R | PEN | blaZ | lukS/F-I, siet, se-int | |
| C3878 | MSSP | 2010 | Dog | U-R | PEN | blaZ | lukS/F-I, siet, se-int | |
| C3879 | MSSP | 2010 | Dog | I | PEN | blaZ | lukS/F-I, siet, se-int, seccanine | |
| C5357 | MSSP | 2011 | Dog | U-R | PEN | blaZ | lukS/F-I, siet, se-int | |
| C3874 | MSSP | 2010 | Dog | I | Susceptible | – | lukS/F-I, siet, se-int | |
| C5359 | MSSP | 2011 | Dog | U-R | Susceptible | – | lukS/F-I, siet, se-int | |
| C3883e | MRSA | 2010 | Dog | S | t011-ST398/CC398-agrI-SCCmecV | PEN-FOX-ERY-CLI-GEN-TOB-KAN-TET-CIPg-SXT | blaZ, mecA, erm(B), erm(C), aacA/aphD, tet(M), tet(K), dfrA, dfrG | hla, hlb, hld, hlg |
| C5612 | MSSA | 2009 | Dog | U-R | t10576-ST1660-agrII | PEN | blaZ | lukPQ, scneq, hla, hlb, hld, hlgv |
| C5650 | MSSA | 2009 | Cat | R | t005-ST22/CC22-agrI | PEN | blaZ | lukS/F-PV, hla, hlb, hld, hlg |
| C5610 | MSSA | 2011 | Dog | U-R | t045-ST5/CC5-agrII | PEN | blaZ | IEC type F, lukED, hla, hld, hlgv |
| C5609 | MSSA | 2011 | Cat | I | t045-ST5/CC5-agrII | Susceptible | – | IEC type F, lukED, hla, hld, hlgv |
aB-J, bones-joints infection; U-R, urinary-reproductive infection; R, respiratory infection; I, integumentary infection; S, surgical infection; SI, septic infection
bPEN, penicillin; OXA, oxacillin; FOX, cefoxitin; ERY, erythromycin; CLI, clindamycin; GEN, gentamicin; TOB, tobramycin; KAN, kanamycin; STR, streptomycin; TET, tetracycline; CIP, ciprofloxacin; CHL, chloramphenicol; SXT, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
cIsolated again one year later of the first recovery
dIsolated again two months later of the first recovery
eIsolated again three months later of the first recovery
fAmino acid change S84L and S80I in GyrA and GrlA proteins, respectively
gAmino acid change S84L and S80F in GyrA and GrlA proteins, respectively
hThe dfrK gene was located within the radC-integrated Tn559
Remarkably, persistent MRSP or MRSA carriage, based on the molecular characteristics of recovered isolates, was detected in three animals evaluated in subsequent samplings. Strains involved were MRSP ST68 clone C3870 (2 months later), MRSP ST71 clone C3871 (1 year later) and MRSA ST398 clone C3883 (after 3 months). Nonetheless, only the initial isolate per animal was included in this study.
Characterization of SP isolates
Five of the eight MRSP, recovered from diverse infection types, were typed as ST71, agr-III, harbored the Staphylococcal Cassette Chromosome mec (SCCmec) II-III, and belonged to the same clone (A). Two MRSP recovered from urinary-reproductive infections were typed as ST68, agr-IV, SCCmec V, and represented two different subclones (B1 and B2). The remaining MRSP isolate, also from a urinary infection, was typed as ST258, agr-II, SCCmec IV, and displayed pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) pattern C.
The antimicrobial resistance rates of the methicillin-susceptible SP (MSSP) and MRSP isolates, are shown in Fig. 1. Resistance to erythromycin, clindamycin, kanamycin, streptomycin, ciprofloxacin, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole were significantly higher among MRSP isolates. Moreover, resistance to gentamicin and tobramycin were solely detected in MRSP isolates (Fig. 1). Eight out of 28 SP isolates were MRSP (29%). Nine MSSP and all MRSP isolates were MDR, while two MSSP were susceptible to all antimicrobial agents evaluated. The blaZ and/or mecA resistance genes were responsible of β-lactam resistance in SP isolates. Macrolide and lincosamide resistance was mediated by the erm(B) gene in all cases, and aminoglycoside resistance by different combinations of aacA/aphD, aphA3, and aadE resistance genes. The tet(M) and/or tet(K) genes mediated tetracycline resistance. The eight isolates exhibiting chloramphenicol resistance harbored the catpC221 gene, while the dfrG gene was detected in the 14 isolates that displayed resistance to trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole, in combination with dfrK in two strains (C5358, C5347) (Table 1). The amino acid changes S84L and S80I in the genes encoding the GyrA and GrlA proteins, respectively, were detected in the eight ciprofloxacin-resistant SP isolates. None of the SP isolates showed resistance to vancomycin, linezolid, or fusidic acid.
Fig. 1.
Antimicrobial resistance rate of MSSP and MRSP investigated in this study. PEN, penicillin; ERY, erythromycin; CLI, clindamycin; GEN, gentamicin; TOB, tobramycin; KAN, kanamycin; STR, streptomycin; TET, tetracycline; CIP, ciprofloxacin; CHL, chloramphenicol; SXT, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. The p-value (Fisher’s Exact test) is shown below the figure. Asterisks indicate the antimicrobial agents for which statistical differences were found between the antimicrobial resistance rates of MSSP and MRSP (P < 0.05)
The virulence genes detected among SP isolates were as follows: siet (100%), se-int (100%), lukS/F-I (100%), seccanine (7%), and expB (7%).
Characterization of SA isolates
The single MRSA isolate detected was typed as t011-ST398/CC398-agrI-SCCmecV and was recovered from a surgical infection of a dog. This ST398 strain was resistant to β-lactams, macrolides and lincosamides, aminoglycosides, tetracycline, ciprofloxacin, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and carried the blaZ, mecA, erm(B), erm(C), aacA/aphD, tet(K), tet(M), dfrA, and dfrG resistance genes. Moreover, the amino acid changes S84L and S80F in the deduced sequences of GyrA and GrlA proteins, respectively, were detected. The MRSA isolate harbored the haemolysins hla, hlb, hld, and hlg (Table 1).
The methicillin-susceptible SA (MSSA) isolates were assigned to t045-ST5/CC5 (n=2), t10576-ST1660 (n=1), and t005-ST22/CC22 (n=1). One MSSA isolate was susceptible to all antimicrobial agents evaluated, and the remaining three only showed penicillin resistance and carried the blaZ gene. The MSSA t005-ST22 feline isolate harbored the genes enconding the Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL) and the two MSSA t045-ST45 carried the scn, chp, sak, and sep genes and, therefore, were ascribed to Immune Evasion Cluster (IEC) type F. Interestingly, the t10576-ST1660 isolate carried the equid-adapted leukocidin lukPQ and the equine variant of Staphylococcal Complement Inhibitor (SCIN). Different combinations of haemolysins, encoded by hla, hlb, hld, hlg, and hlgv, were detected among MSSA isolates (Table 1).
Genetic environment of the dfrK gene
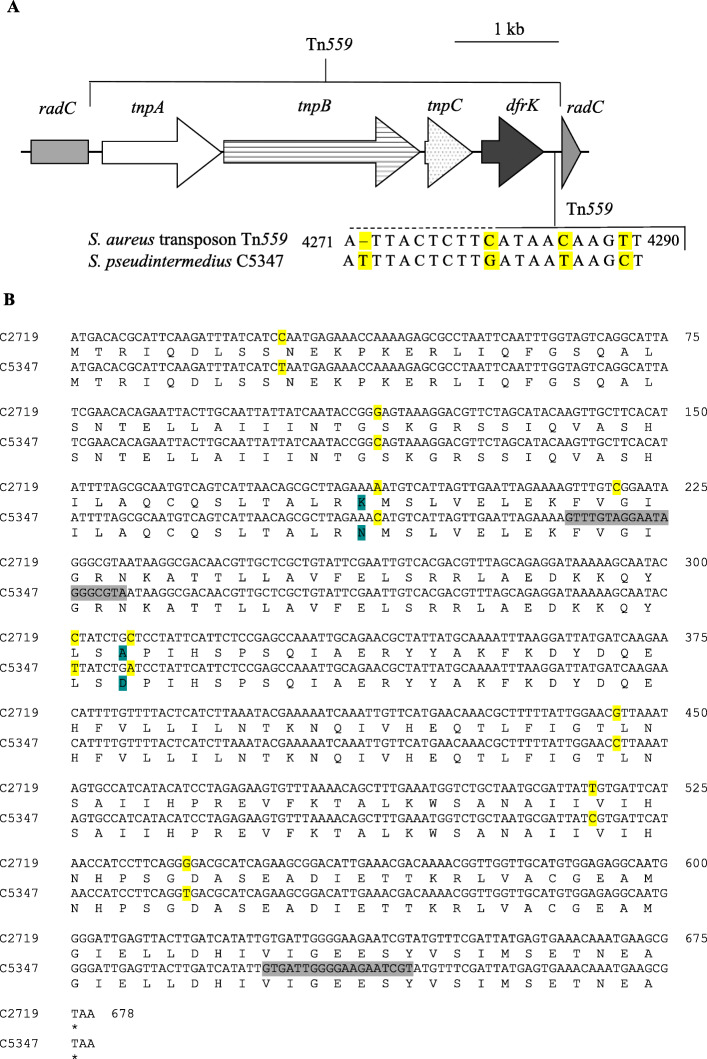
The Tn559-specific PCRs revealed that the MSSP C5358 harbored a complete Tn559, which was integrated in the chromosomal radC gene. Detection of the radC gene and the Tn559-radC linkage was not possible for strain MSSP C5347. The whole genome sequencing (WGS) analysis of this strain enabled the identification of the complete Tn559 and its integration position (Fig. 2) (GenBank accession number MT252966). Nucleotide and amino acid sequence alignment of Tn559 C5347 with reference Staphylococcus aureus transposon Tn559 (GenBank accession number FN677369) revealed the insertion of one nucleotide and three nucleotide substitutions in the non-coding region downstream the dfrK gene (Fig. 2). Remarkably, a single point mutation in the hybridization sequence of the radC forward primer was detected (radC-fw: 5′-GTC/AGGAATAGGGCGTA-3′), which resulted responsible for the absence of PCR amplification. Moreover, nucleotide and amino acid alignment with the radC gene of S. pseudintermedius strain C2719, harboring transposon Tn558 (GenBank accession number HF679552), revealed the presence of seven synonymous point mutations (C27T, G114C, C219A, C301T, G444C, T516C, G540T) plus two additional non-synonymous substitutions in the deduced RadC sequence (K63N, A103D) (Fig. 2). Tn559 circular intermediates were detected.
Fig. 2.
a Graphical representation of the Tn559 structure containing the dfrK gene integrated in the chromosomal radC gene of the isolate Staphylococcus pseudintermedius C5347 (GenBank accession number MT252966) and nucleotide substitutions detected in the non-coding region downstream the dfrK gene compared to Staphylococcus aureus transposon Tn559 (GenBank accession number FN677369). The nucleotide positions are set based on the whole Tn559. Nucleotide insertions and substitutions are colored in yellow. b Amino acid sequence alignment of radC gene and resultant RadC of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius strain C2719 (GenBank accession number HF679552), where transposon Tn558 was integrated, that of S. pseudintermedius C5347 (GenBank accession number MT252966). The position of the primer pair employed is indicated in grey. Nucleotide substitutions are colored in yellow and amino acid substitutions in blue
Discussion
This is the first description of MRSA-ST398 and MRSP-ST68 in pets in Spain, as well the first report of the dfrK-carrying Tn559 in SP. This evidences that current transmissible lineages with mobilizable resistomes have circulated unnoticeably in Spain as causative agents of infections in pets for years.
In this study, 28 of the 33 CoPS from diseased pets were identified as SP, which was expected since this is the most common staphylococcal species detected both as colonizer and cause of infection in companion animals, specially dogs [4, 5]. In this work, SP and SA were detected causing infection in three and two cats, respectively. These species have been formerly recovered from diseased cats [1, 17], however, a recent study has reported predominance of other staphylococcal species, such as S. felis and S. haemolyticus, among feline infections [1].
Five of the eight MRSP isolates detected in this study were ascribed to the genetic lineage ST71 and showed the same PFGE pattern. They were isolated from five different dogs in different years and there was no apparent relation among these animals; however, all of them underwent surgery in the veterinary hospital. Regardless they were assisted by different veterinarians, and the operating room and/or surgery material are recurrently disinfected, none of them can be excluded as potential infection sources. MRSP-ST71 is the major clone in Europe [2, 3], and there are already few descriptions of this genetic lineage in healthy dogs in Spain [18]. However, recent studies have reported a downward trend in the prevalence of the MRSP-ST71 lineage among companion animals in northern Europe [11, 19] and France [3]. The MRSP-ST258 lineage, which was detected in this study in 2009, seems to be replacing MRSP-ST71 in these countries [11, 19]. The remaining two MRSP detected in this study belonged to the ST68, a genetic lineage known to be predominant in USA, although it has been detected outside this country [4]. However, to the best of our knowledge, this is the first description of MRSP-ST68 isolated from companion animals in Spain.
Former studies reported MRSA belonging to the HA-MRSA and CA-MRSA lineages among isolates recovered from companion animals [9, 15]; however, in this work, the only MRSA isolate detected belonged to the LA-MRSA CC398 genetic lineage. Moreover, this isolate lacked the genes of the IEC system, which suggests an animal origin. LA-MRSA CC398 recovered from diseased dogs has been reported in few occasions [9, 15, 16], however, to our knowledge, this is the first description in Spain. Regarding MSSA, isolates belonging to CC22 and CC5 are clonal groups widespread among companion animals [9, 15, 20]. The remaining MSSA isolate was typed as t10576-ST1660, and, interestingly, the single description of this genetic lineage is in a contemporary isolate (obtained in the same week) recovered from one hospitalized equine in the same veterinary hospital, which displayed the same antimicrobial resistance pheno/genotype and virulence gene content [21]. Moreover, the SA t10576-ST1660 isolate recovered in this study harbored the leukocidin lukPQ and the scneq, which are equid-adapted virulence factors [22, 23]. This supports the hypothesis of a plausible equine origin and suggests the transmission of the MSSA strain between animal species in the veterinary hospital.
The frequency of methicillin resistance and MDR isolates among CoPS recovered from pets in this study represents a great concern for veterinary medicine. This is also a public health problem due to the exposure and interspecies transmission of SA/SP among pets and owners [6, 24], as well as potential transference of resistance genes to human-adapted staphylococcal strains. The rate of methicillin resistance observed in this study (27%) is higher than the one determined among clinical isolates from companion animals in several countries, such as Australia (12%) [10, 17], Finland (14%) [19], the Netherlands [11], and France [8]. As in this report, MRSP-ST71 are often MDR [2, 11], and they are more likely to display fluoroquinolone resistance than other STs [10, 11]. Fortunately, in line with former reports, all isolates recovered here, both SA and SP, were susceptible to important or last resort antimicrobials in human medicine, such as vancomycin and linezolid [2, 9].
All SP isolates, both MSSP and MRSP, carried the virulence determinants lukS/F-I, siet, and se-int, which have been previously detected in both commensal and clinical SP isolates, suggesting they may be ubiquitous in this staphylococcal species [5, 18, 20]. One MSSA t005-ST22/CC2 recovered from a respiratory infection of a cat was PVL-positive. The PVL is one of the most important virulence determinants produced by SA, which has a critical role in the pathogenesis of skin and soft tissue infections. CC22 is an important genetic lineage of PVL-positive MSSA also implicated in hospital outbreaks [25, 26]. Moreover, the two MSSA t045-ST5/CC5 isolates carried the human-adapted scn, chp, sak, and sep genes of the IEC system, which suggests a human-to-animal transmission. To this regard, former studies have determined the interspecies transmission ability of SA from humans to pets [6, 24], which represents a source for further transmission and a risk for infection.
The dfrK gene has been rarely detected in SP isolates [9, 27]. Indeed, the dfrK-carrying transposon Tn559 was firstly reported in a porcine MSSA ST398 isolate [28] and thereafter in SA belonging to the same genetic lineage [21], but also in Enterococcus faecium [29]. However, to the best of our knowledge, we report here the first description of the Tn559 in SP. This could suggest an exchange of resistance genes between staphylococci and other Gram-positive bacteria, including enterococci, of animal but also from human origin.
Conclusions
Presently relevant MRSP and MRSA genetic lineages with noticeable virulence traits were detected in isolates recovered during 2009–2011, including the first description of MRSA ST398 and MRSP ST68 in pets in Spain. In addition, the apparent dissemination of CoPS strains in the veterinary hospital highlights the importance of further investigating SA and SP sources and survival ability as contaminants, their population structure and epidemiology, as well as their antimicrobial resistance pattern and transmission ability.
Methods
Study population
A total of 33 CoPS isolates obtained from 28 and five diseased dogs and cats (one isolate/animal), respectively, were obtained in the Veterinary Laboratory of the University of Zaragoza (Zaragoza, Spain) during the years 2009 (9 isolates), 2010 (15), and 2011 (9), and were included in this study. The samples were taken from the infection site (Supplementary Table S1). The isolates were stored frozen at − 80 °C until they were studied.
Isolation and identification of SP and SA isolates
Identification of isolates was performed by biochemical assays, including colony morphology, Gram staining, catalase and DNase activities, and API20-STAPH. The identification of SA and SP was determined by a multiplex PCR that amplifies the specific nuc gene of SA or S. intermedius/SP [30]. Discrimination between S. intermedius and SP was carried out by digestion of the pta gene amplicon with MboI enzyme [31].
Molecular typing and clonal relatedness
All SA were subjected to spa-typing by PCR and amplicon sequencing, and the obtained sequences were analyzed using Ridom Staph-Type software version 1.5.21 (Ridom GmbH, Münster, Germany) [32]. Multi Locus Sequence Typing (MLST) was performed in all SA isolates [32], and according to the sequence-type (ST), the isolates were ascribed to the different clonal complexes (CC). MLST of SP isolates was likewise performed as previously described [33]. All isolates were characterized by agr-typing following standard methodology [32, 33]. SCCmec-typing was undergone in MRSP and MRSA as previously described [13, 34].
PFGE of total DNA restricted with SmaI enzyme was performed on MRSP as previously described [35]. Isolates were considered different clones when they exhibited more than three bands of difference in PFGE band patterns and subclones when PFGE band patterns differed between 1 and 3 bands [36].
Antimicrobial resistance phenotype and genotype
The susceptibility to 17 antimicrobials was determined by agar disk-diffusion method. The antimicrobial agents tested were as follows (μg/disk): penicillin (10 units), oxacillin (1), cefoxitin (30) erythromycin (15), clindamycin (2), gentamicin (10), tobramycin (10), kanamycin (30), streptomycin (10), tetracycline (30), ciprofloxacin (5), mupirocin (200), vancomycin (30), chloramphenicol (30), linezolid (30), fusidic acid (10), and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (1.25+ 23.75). The CLSI guidelines [37] was used for all antimicrobials, except for streptomycin, mupirocin, and fusidic acid, for which the methods and breakpoints recommended by the Société Française de Microbiologie [38] were employed.
The presence of 34 antimicrobial resistance genes was investigated by PCR: mecA, blaZ, erm(A), erm(B), erm(C), erm(T), mph(C), msr(A), msr(B), lnu(A), vga(A), vga(C), aacA-aphD, aphA3, aadE, aadD, aadA, str, tet(K), tet(M), tet(L), sat4 (even though streptothricin susceptibility was not tested), fexA, fexB, cfr, optrA, poxtA, catps194, catpC221, catpC223, dfrA, dfrD, dfrG, and dfrK [18, 39, 40]. Positive controls from the collection of the University of La Rioja were included in all PCR assays.
Mutations in the genes encoding the GyrA and GrlA proteins were investigated in ciprofloxacin-resistant SA and SP isolates by PCR and sequencing [18, 41]. The corresponding sequences of S. aureus NCTC 8325 (GenBank accession number CP000253) and S. pseudintermedius KM1381 (GenBank accession number AM262969 and AM262972) were used as references.
Detection of virulence genes
The presence of the leukocidin genes lukSF-PV, lukM, lukED, and lukPQ was investigated in all SA isolates [21, 23]. They were also screened for the presence of haemolysin genes (hla, hlb, hld, hlg, and hlgv), exfoliative genes (eta, etb, and etd), and the toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 (tst) [21]. PCR-based determination of the five genes (scn, chp, sak, sea, and sep) that comprises the IEC system as well the equine variant of SCIN encoded by scneq were likewise investigated [32, 42]. In addition, SP isolates were screened for the presence of the leukocidin gene lukS/F-I, the exfoliative genes siet, expA, and expB, and the enterotoxin genes si-ent and seccanine by PCR [20].
Statistical analysis
Potential statistical differences between the antimicrobial resistance rates in MRSP and MSSP isolates were compared using the Fisher’s Exact test with the R Commander program. P < 0.05 was considered a statistically significant result.
Genetic environment of the dfrK gene in S. pseudintermedius isolates
The possibility that the dfrK gene was located within the Tn559 and integrated within the chromosomal radC gene was investigated by specific PCRs targeting the different constituents of Tn559 and their physical linkage to radC, as previously described [21, 43]. Strains negative for at least one primer combination were submitted to WGS.
Whole genome sequencing of Tn559 carrying strain negative for radC integration
WGS was performed on SP strain C5347 using PacBio Sequel and Illumina Miseq 2 × 300 bp platforms prior phenol-chloroform DNA extraction, as previously described [44]. Raw PacBio reads were assembled using Canu [45] with default parameters and setting an estimated genome size of 3 Mb. The resulting assembled contigs were then polished as follows: First, Illumina raw reads were quality-trimmed using Trimmomatic [46] and aligned against the assembled PacBio contigs using Bowtie2 [47]. Then, the resulting bam files were used to fix individual base errors, indels and local missassemblies using Pilon [48].
Resulting genes on the assembled contigs were predicted using Prodigal [49]. tRNA and rRNA genes were predicted using tRNAscan-SE [50], ssu-align [51] and meta-rna [52]. Predicted protein sequences were compared against the NCBI nr database using DIAMOND [53], and against COG [54] and TIGFRAM [55] using HMMscan [56] for taxonomic and functional annotation.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Table S1. Type of infection, sample and sampling method used to obtain the thirty-three coagulase-positive staphylococci of this study.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. Jose Manuel Haro-Moreno (Miguel Hernandez University, Spain), for his direct support in WGS assembly and annotation of S. pseudintermedius C5347.
Abbreviations
- SP
Staphylococcus pseudintermedius
- SA
Staphylococcus aureus
- MR
methicillin-resistant
- MDR
multidrug-resistant
- SCCmec
Staphylococcal cassette chromosome
- ST
sequence type
- CC
clonal complex
- PVL
Panton-Valentine leukocidin
- IEC
immune evasion cluster
- MRSA
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- MRSP
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius
- HA
hospital-associated
- CA
community-associated
- LA
livestock-associated
- CoPS
coagulase-positive staphylococci
- PFGE
pulsed-field gel electrophoresis
- MSSP
methicillin-susceptible S. pseudintermedius
- MSSA
methicillin-susceptible S. aureus
- SCIN
staphylococcal complement inhibitor
- MLST
multilocus sequence typing
- CLSI
clinical laboratory standards institute
- PCR
polymerase chain reaction
- WGS
whole genome sequencing
Authors’ contributions
LRR, SC and EGS carried out the experiments and analyzed the data. CS and CO isolated the strains used in this work. MZ, CT and EGS designed the project and supervised the research. All authors drafted the manuscript and approved it.
Funding
The development of this study was supported by projects SAF2012–35474 and SAF2016–76571-R from the Agencia Estatal de Investigación (AEI) of Spain and the Fondo Europeo de Desarrollo Regional (FEDER) of EU and by the Instituto Aragonés de Ciencias de la Salud ICS of Spain. E. Gómez-Sanz was initially funded by a fellowship from the Gobierno de La Rioja, Spain (sample collection and experimental work) and later on (data analysis and manuscript revision) by the European Union’s Framework Program for Research and Innovation Horizon 2020 (2014–2020) under the Marie Sklodowska-Curie Grant Agreement No. 659314 and by internal funds of ETHZ. Laura Ruiz-Ripa has a pre-doctoral fellowship from the Universidad de La Rioja (Spain). The funding organisms neither affect the design of the research nor the interpretation of the data.
Availability of data and materials
The entire transposon Tn559 plus the truncated radC gene of S. pseudintermedius C5347, comprising 5′069 bps, have been deposited in the Genbank database with accession number MT252966.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Laura Ruiz-Ripa and Elena Gómez-Sanz contributed equally to this work.
References
- 1.Bierowiec K, Korzeniowska-Kowal A, Wzorek A, Rypuła K, Gamian A. Prevalence of Staphylococcus species colonization in healthy and sick cats. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:4360525. doi: 10.1155/2019/4360525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Somayaji R, Rubin JE, Priyantha MA, Church D. Exploring Staphylococcus pseudintermedius: an emerging zoonotic pathogen? Future Microbiol. 2016;11:1371–1374. doi: 10.2217/fmb-2016-0137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bergot M, Martins-Simoes P, Kilian H, Châtre P, Worthing KA, Norris JM, et al. Evolution of the population structure of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius in France. Front Microbiol. 2018;9:3055. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.03055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Pires Dos Santos T, Damborg P, Moodley A, Guardabassi L. Systematic review on global epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius: inference of population structure from Multilocus Sequence Typing Data. Front Microbiol. 2016;7:1599. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.van Duijkeren E, Catry B, Greko C, Moreno MA, Pomba MC, Pyörälä S, et al. Review on methicillin resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011;66(12):2705–2714. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkr367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Gómez-Sanz E, Torres C, Lozano C, Zarazaga M. High diversity of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus pseudintermedius lineages and toxigenic traits in healthy pet-owning household members. Underestimating normal household contact? Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2013;36(1):83–94. doi: 10.1016/j.cimid.2012.10.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kaspar U, von Lützau A, Schlattmann A, Roesler U, Köck R, Becker K. Zoonotic multidrug-resistant microorganisms among small companion animals in Germany. Plos One. 2018;13(12):e0208364. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0208364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Haenni M, de Moraes NA, Châtre P, Médaille C, Moodley A, Madec JY. Characterisation of clinical canine meticillin-resistant and meticillin-susceptible Staphylococcus pseudintermedius in France. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2014;2(2):119–123. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2014.02.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Couto N, Monchique C, Belas A, Marques C, Gama LT, Pomba C. Trends and molecular mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance in clinical staphylococci isolated from companion animals over a 16 year period. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2016;71(6):1479–1487. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkw029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Worthing KA, Abraham S, Coombs GW, Pang S, Saputra S, Jordan D, et al. Clonal diversity and geographic distribution of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius from Australian animals: discovery of novel sequence types. Vet Microbiol. 2018;213:58–65. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2017.11.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Duim B, Verstappen KM, Broens EM, Laarhoven LM, van Duijkeren E, Hordijk J, et al. Changes in the population of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius and dissemination of antimicrobial-resistant phenotypes in the Netherlands. J Clin Microbiol. 2016;54(2):283–288. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01288-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kawakami T, Shibata S, Murayama N, Nagata M, Nishifuji K, Iwasaki T, et al. Antimicrobial susceptibility and methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus pseudintermedius and Staphylococcus schleiferi subsp. coagulans isolated from dogs with pyoderma in Japan. J Vet Med Sci. 2010;72(12):1615–1619. doi: 10.1292/jvms.10-0172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Perreten V, Kadlec K, Schwarz S, Andersson UG, Finn M, Greko C, et al. Clonal spread of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius in Europe and North America: an international multicentre study. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2010;65(6):1145–1154. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkq078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Loeffler A, Pfeiffer DU, Lindsay JA, Soares Magalhães RJ, Lloyd DH. Prevalence of and risk factors for MRSA carriage in companion animals: a survey of dogs, cats and horses. Epidemiol Infect. 2011;139(7):1019–1028. doi: 10.1017/S095026881000227X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Wipf JR, Perreten V. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from dogs and cats in Switzerland. Schweiz Arch Tierheilkd. 2016;158(6):443–450. doi: 10.17236/sat00070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Witte W, Strommenger B, Stanek C, Cuny C. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus ST398 in humans and animals, Central Europe. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13(2):255–258. doi: 10.3201/eid1302.060924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Saputra S, Jordan D, Worthing KA, Norris JM, Wong HS, Abraham R, et al. Antimicrobial resistance in coagulase-positive staphylococci isolated from companion animals in Australia: a one year study. Plos One. 2017;12(4):e0176379. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gómez-Sanz E, Torres C, Lozano C, Sáenz Y, Zarazaga M. Detection and characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius in healthy dogs in La Rioja, Spain. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2011;34(5):447–453. doi: 10.1016/j.cimid.2011.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Grönthal T, Eklund M, Thomson K, Piiparinen H, Sironen T, Rantala M. Antimicrobial resistance in Staphylococcus pseudintermedius and the molecular epidemiology of methicillin-resistant S. pseudintermedius in small animals in Finland. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2017;72(4):1021–1030. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkw559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gómez-Sanz E, Torres C, Benito D, Lozano C, Zarazaga M. Animal and human Staphylococcus aureus associated clonal lineages and high rate of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius novel lineages in Spanish kennel dogs: predominance of S. aureus ST398. Vet Microbiol. 2013;166(3–4):580–589. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2013.07.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gómez-Sanz E, Simón C, Ortega C, Gómez P, Lozano C, Zarazaga M, et al. First detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus ST398 and Staphylococcus pseudintermedius ST68 from hospitalized equines in Spain. Zoonoses Public Health. 2014;61(3):192–201. doi: 10.1111/zph.12059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.de Jong NWM, Vrieling M, Garcia BL, Koop G, Brettmann M, Aerts PC, et al. Identification of a staphylococcal complement inhibitor with broad host specificity in equid Staphylococcus aureus strains. J Biol Chem. 2018;293(12):4468–4477. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.000599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Koop G, Vrieling M, Storisteanu DM, Lok LS, Monie T, van Wigcheren G, et al. Identification of LukPQ, a novel, equid-adapted leukocidin of Staphylococcus aureus. Sci Rep. 2017;7:40660. doi: 10.1038/srep40660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Gómez-Sanz E, Torres C, Ceballos S, Lozano C, Zarazaga M. Clonal dynamics of nasal Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus pseudintermedius in dog-owning household members. Detection of MSSA ST(398) Plos One. 2013;8(7):e69337. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Gopal Rao G, Batura R, Nicholl R, Coogan F, Patel B, Bassett P, et al. Outbreak report of investigation and control of an outbreak of Panton-Valentine Leukocidin-positive methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (PVL-MSSA) infection in neonates and mothers. BMC Infect Dis. 2019;19(1):178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 26.Shore AC, Tecklenborg SC, Brennan GI, Ehricht R, Monecke S, Coleman DC. Panton-Valentine leukocidin-positive Staphylococcus aureus in Ireland from 2002 to 2011: 21 clones, frequent importation of clones, temporal shifts of predominant methicillin-resistant S. aureus clones, and increasing multiresistance. J Clin Microbiol. 2014;52(3):859–70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 27.Ruzauskas M, Couto N, Pavilonis A, Klimiene I, Siugzdiniene R, Virgailis M, et al. Characterization of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius isolated from diseased dogs in Lithuania. Pol J Vet Sci. 2016;19(1):7–14. doi: 10.1515/pjvs-2016-0002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kadlec K, Schwarz S. Identification of the novel dfrK-carrying transposon Tn559 in a porcine methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus ST398 strain. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010;54(8):3475–3477. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00464-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.López M, Kadlec K, Schwarz S, Torres C. First detection of the staphylococcal trimethoprim resistance gene dfrK and the dfrK-carrying transposon Tn559 in enterococci. Microb Drug Resist. 2012;18(1):13–18. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2011.0073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Baron F, Cochet MF, Pellerin JL, Ben Zakour N, Lebon A, Navarro A, et al. Development of a PCR test to differentiate between Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus intermedius. J Food Prot. 2004;67(10):2302–2305. doi: 10.4315/0362-028X-67.10.2302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Bannoehr J, Franco A, Iurescia M, Battisti A, Fitzgerald JR. Molecular diagnostic identification of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius. J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47(2):469–471. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01915-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ruiz-Ripa L, Alcalá L, Simón C, Gómez P, Mama OM, Rezusta A, et al. Diversity of Staphylococcus aureus clones in wild mammals in Aragon, Spain, with detection of MRSA ST130-mecC in wild rabbits. J Appl Microbiol. 2019;127(1):284–291. doi: 10.1111/jam.14301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Bannoehr J, Ben Zakour NL, Waller AS, Guardabassi L, Thoday KL, van den Broek AH, et al. Population genetic structure of the Staphylococcus intermedius group: insights into agr diversification and the emergence of methicillin-resistant strains. J Bacteriol. 2007;189(23):8685–8692. doi: 10.1128/JB.01150-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Zhang K, McClure JA, Elsayed S, Louie T, Conly JM. Novel multiplex PCR assay for characterization and concomitant subtyping of staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec types I to V in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 2005;43(10):5026–5033. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.10.5026-5033.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Murchan S, Kaufmann ME, Deplano A, de Ryck R, Struelens M, Zinn CE, et al. Harmonization of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis protocols for epidemiological typing of strains of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a single approach developed by consensus in 10 European laboratories and its application for tracing the spread of related strains. J Clin Microbiol. 2003;41(4):1574–1585. doi: 10.1128/JCM.41.4.1574-1585.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Tenover FC, Arbeit RF, Goering RV, Mickelsen PA, Murray BE, Persing DH, et al. Interpreting chromosomal DNA restriction patterns produced by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis: criteria for bacterial strain typing. J Clin Microbiol. 1995;33(9):2233–2239. doi: 10.1128/JCM.33.9.2233-2239.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.CLSI . Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing, vol. M100. 27. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne; 2017. [Google Scholar]
- 38.CA-SFM. Comité de l’Antibiogramme de la Société Française de Microbiologie Recommandations. Recommandations 2013. Comité de l’Antibiogramme de la Société Française de Microbiologie; 2013.
- 39.Gómez-Sanz E, Torres C, Lozano C, Fernández-Pérez R, Aspiroz C, Ruiz-Larrea F, et al. Detection, molecular characterization, and clonal diversity of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus CC398 and CC97 in Spanish slaughter pigs of different age groups. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2010;7(10):1269–1277. doi: 10.1089/fpd.2010.0610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Ruiz-Ripa L, Feßler AT, Hanke D, Sanz S, Olarte C, Eichhorn I, et al. Detection of poxtA- and optrA-carrying E faecium isolates in air samples of a Spanish swine farm. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2020;22:28-31. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 41.Schmitz FJ, Hofmann B, Hansen B, Scheuring S, Lückefahr M, Klootwijk M, et al. Relationship between ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, levofloxacin, sparfloxacin and moxifloxacin (BAY 12-8039) MICs and mutations in grlA, grlB, gyrA and gyrB in 116 unrelated clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1998;41(4):481–484. doi: 10.1093/jac/41.4.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Mama OM, Gómez P, Ruiz-Ripa L, Gómez-Sanz E, Zarazaga M, Torres C. Antimicrobial resistance, virulence, and genetic lineages of staphylococci from horses destined for human consumption: high detection of S. aureus isolates of lineage ST1640 and those carrying the lukPQ gene. Animals (Basel). 2019;9(11):900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 43.Gómez-Sanz E, Kadlec K, Feßler AT, Zarazaga M, Torres C, Schwarz S. A novel fexA variant from a canine Staphylococcus pseudintermedius isolate that does not confer florfenicol resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57(11):5763–5766. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00948-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Gómez-Sanz E, Schwendener S, Thomann A, Brawand SG, Perreten V. First staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec containing a mecB-carrying gene complex independent of transposon Tn6045 in a Macrococcus canis isolate from a canine infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59(8):4577–4583. doi: 10.1128/AAC.05064-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Koren S, Walenz BP, Berlin K, Miller JR, Phillippy AM. Canu: scalable and accurate long-read assembly via adaptive k-mer weighting and repeat separation. Genome Res. 2017;27(5):722–736. doi: 10.1101/gr.215087.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B. Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics. 2014;30(15):2114–2120. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Langmead B, Salzberg S. Fast gapped-read alignment with bowtie 2. Nat Methods. 2012;9(4):357–359. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Walker BJ, Abeel T, Shea T, Priest M, Abouelliel A, Sakthikumar S, et al. Pilon: an integrated tool for comprehensive microbial variant detection and genome assembly improvement. PLoS One. 2014;9(11):e112963. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Hyatt D, Chen GL, Locascio PF, Land ML, Larimer FW, Hauser LJ. Prodigal: prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site identification. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010;11:119. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Lowe TM, Eddy SR. TRNAscan-SE: a program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997;25(5):955–964. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.5.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Nawrocki EP. Structural RNA Homology Search and Alignment Using Covariance Models. 2009. PhD Thesis. USA: Washington University School of Medicine.
- 52.Huang Y, Gilna P, Li W. Identification of ribosomal RNA genes in metagenomic fragments. Bioinformatics. 2009;25(10):1338–1340. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Buchfink B, Xie C, Huson DH. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat Methods. 2015;12(1):59–60. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Tatusov RL, Natale DA, Garkavtsev IV, Tatusova TA, Shankavaram UT, Rao BS, et al. The COG database: new developments in phylogenetic classification of proteins from complete genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001;29(1):22–28. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.1.22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Haft DH, Loftus BJ, Richardson DL, Yang F, Eisen JA, Paulsen IT, et al. TIGRFAMs: a protein family resource for the functional identification of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001;29(1):41–43. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Eddy SR. Accelerated profile HMM searches. Plos Comput Biol. 2011;7(10):e1002195. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1: Table S1. Type of infection, sample and sampling method used to obtain the thirty-three coagulase-positive staphylococci of this study.
Data Availability Statement
The entire transposon Tn559 plus the truncated radC gene of S. pseudintermedius C5347, comprising 5′069 bps, have been deposited in the Genbank database with accession number MT252966.