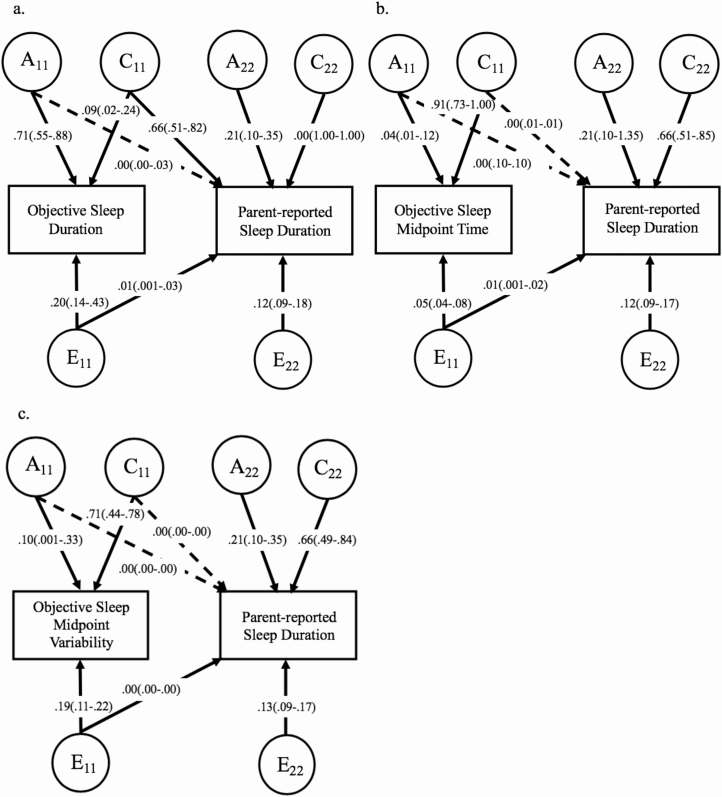
Figure 2.
Full bivariate Cholesky decompositions for associations between objective and subjective sleep indicators. Full bivariate Cholesky decomposition models are shown. Objective assessments were obtained using actigraphy. Sex and age were regressed out of variables prior to model fitting. Estimates are provided with variance-based confidence intervals provided in parentheses and are based on standardized path estimates. Standardized path estimates for the second phenotype in each model are adjusted after accounting for the covariance between phenotypes Solid lines indicate significant (retained) paths in both the full and best-fitting models, whereas dashed lines signify paths that were dropped from the final, best-fitting models without significant loss of fit to the data (see Table 4 for best-fitting model standardized path estimates and corresponding confidence intervals, and Supplementary Tables S5–S7 for fit statistics and genetic and environmental correlations). A11, additive genetic components for first phenotype; C11, shared environment component for first phenotype; E11, nonshared environment component for first phenotype. A22, C22, E22, residual additive genetic, shared environmental, and nonshared environmental components for second phenotype not shared with first phenotype, respectively. (A) rG = 0.02, rC = 0.89, rE = 0.09. (B) rG = 0.00, rC = 0.00, rE = 0.07. (C) rG = 0.00, rC = 0.00, rE = 0.14.