Abstract
Mycorrhizae are an important energy source for orchids that may replace or supplement photosynthesis. Most mature orchids rely on mycorrhizae throughout their life cycles. However, little is known about temporal variation in root endophytic fungal diversity and their trophic functions throughout whole growth periods of the orchids. In this study, the community composition of root endophytic fungi and trophic relationships between root endophytic fungi and orchids were investigated in Bletilla striata and B. ochracea at different phenological stages using stable isotope natural abundance analysis combined with molecular identification analysis. We identified 467 OTUs assigned to root-associated fungal endophytes, which belonged to 25 orders in 10 phyla. Most of these OTUs were assigned to saprotroph (143 OTUs), pathotroph-saprotroph (63 OTUs) and pathotroph-saprotroph-symbiotroph (18 OTUs) using FunGuild database. Among these OTUs, about 54 OTUs could be considered as putative species of orchid mycorrhizal fungi (OMF). For both Bletilla species, significant temporal variation was observed in the diversity of root endophytic fungi. The florescence and emergence periods had higher fungal community richness of total species and endemic species than did other periods. Both Bletilla species were dominated by Agaricomycetes and Basidiomycota fungi throughout the whole year; however, their abundances varied between two Bletilla species and among phenological stages. Meanwhile, the ranges of 13C and 15N natural abundance were also highly dynamic across all growth stages of Bletilla species. Compared with the surrounding autotrophic plants, significant 13C enrichments (ε13C) were found across all phenological stages, while significant 15N enrichment in the florescence period and strong 15N depletion during the fruiting period were found for both Bletilla species. We can deduce that both Bletilla species obtained carbon from root endophytic fungi during the whole year. Additionally, the temporal varying tendency of root endophytic fungal diversity was consistent with 13C enrichments, which was also accord with the nutritional requirement of plant.
Keywords: orchid mycorrhiza, stable isotope, phenological stages, community structure, root-associated endophytes
1. Introduction
Orchidaceae is one of the largest plant families, including almost 10% of all angiosperm species and about 28,000 species comprising 736 genera worldwide [1,2]. Members of this family are widely distributed among terrestrial ecosystems, with the notable exception of extremely cold and dry areas and accordingly have a great variety of life history strategies, ranging from epiphytic to terrestrial and from evergreen to achlorophyllous species [3,4]. Zettler et al. reported that unique characteristics of the orchid family, including its high diversity, might be attributable to its distinctive relationships with root endophytic fungi [5]. Although the family is species rich, many orchids are threatened or nearly threatened by extinction, and all wild orchids are listed in the convention on international trade in endangered species of wild fauna and flora [6]. Three main reasons exist for this: A lack of mycorrhizal fungi for seed germination and seedling recruitment [7], a lack of pollinators necessary for sexual reproduction [8], and the impact of human disturbances on many orchid species [9,10].
The tiny dust-like seeds of orchids have room for only marginal amounts of carbon reserves within embryos, and thus, orchids rely on root endophytic fungi (both mycorrhizal and non-mycorrhizal fungi) throughout their life cycle, especially during seed germination and seedling recruitment periods [11,12]. The initial developmental stage of all orchids is a nonphotosynthetic protocorm, totally dependent on C and nutrients supplied by fungal partners [13]. However, all mature orchids, with the exception of a few epiphytic tropical orchids, also maintain mycorrhizal associations throughout the rest of their life cycles [11,14]. Researchers have found that root endophytic fungi can not only transport carbohydrates and break down cellulose in the matrix but can also directly provide nutrients and hormones (e.g., amino acids, gibberellins and jasmonate) for growth [10,15]. In addition, root endophytic fungi were found to promote the absorption of macronutrient elements and micronutrient elements by orchids [16,17] and facilitate the production of metabolites, including antibiotics, phenolic compounds, peroxidase and hydrolase, thus enhancing disease resistance and stress tolerance in orchids [18,19]. Mycorrhizal partners can also influence orchid distributions and determine which habitats allow orchid growth and what environmental factors are critical for orchid recruitment [20].
Interactions with pollinators have shaped orchid floral morphology; similarly, interactions with root endophytic fungi have deeply influenced their trophism [21]. Root endophytic fungal communities in terrestrial ecosystems are diverse and play a vital role in connecting above- and below-ground nutrient cycles [22]. Stable isotope natural abundance analysis, together with molecular identification of mycorrhizal partners, is a powerful approach to assessing the nutritional relationship between mature orchids and their mycorrhizal partners [21,23]. By using stable isotopes, it is possible to evaluate nutrient fluxes under field conditions and trace the source of specific nutrients, through utilizing isotopic differences between plant- and fungus-derived C and N [24,25], enabled by fungal tissues being enriched with 13C and 15N compared with neighbouring autotrophic plants [26,27]. Meanwhile, different functional groups of fungi forming orchid mycorrhizae can obtain different sources of C and nutrients, thus shaping stable isotope abundance patterns in fungal tissues and their associated orchids [26,28]. Researchers have found that orchids associated with ectomycorrhizal fungi (i.e., achlorophyllous orchid species) [29,30] and saprotrophic wood-decomposers or litter-decaying fungi [31,32] were enriched for 13C and 15N isotopes in comparison to neighbouring autotrophic plants and that mature partially mycoheterotrophic orchids (i.e., green forest orchids associated with ectomycorrhizal fungi) were positioned between fully mycoheterotrophic orchids and autotrophic plants [23]. In contrast with mycoheterotrophic orchids, stable isotope natural abundance for photosynthetic orchids revealed variation among species [25]. Listera ovata and Orchis purpurea were found to exhibit 13C enrichment [23,33], while significant 13C depletion was found in the orchid tribes Orchideae and Cranichideae [34]. However, Gebauer and Meyer found that some rhizoctonia-associated orchids exhibited 13C abundance equivalent to that of autotrophic reference plants [23].
The trophic relationship between orchids and root endophytic fungi is greatly influenced by many factors, including abiotic factors, such as climate, irradiance, soil nutrients, pH and soil humidity, and biotic factors, such as orchid phylogenetic process, life form and growing period [20,35]. Phenological phase is a key factor regulating mycorrhizal community composition and its trophic relationship with orchids [16,25]. Thus far, trophic relationships between orchids and root endophytic fungi have been investigated in plants collected at single time points, which neglects possible seasonal variation in isotopic signatures that may reflect changes in plant nutritional requirements and variation in nutrient availability throughout the growing season. Meanwhile, mycorrhizal community compositions are often studied in steady-state situations [14,33,36]. It is unclear whether these fungal communities are temporally stable and whether seasonal changes in mycorrhizal associations could also lead to differences in the nutritional status of orchids.
In this study, we used stable isotope natural abundance analysis and DNA molecular identification methods to investigate temporal variation in C and N stable isotope abundance and root endophytic fungi assemblages associated with two mature greenish Bletilla spp., Bletilla striata (Thunb. ex A. Murray) Rchb. f. and Bletilla ochracea Schltr. Our main objectives are to answer the following questions: (1) What are the root endophytic fungi of the two Bletilla spp.? (2) Do the composition and abundance of root endophytic fungi and C and N stable isotope abundance of Bletilla vary among phenological stages or between the two species?
2. Results
2.1. Fungal Community Found in Bletilla Roots
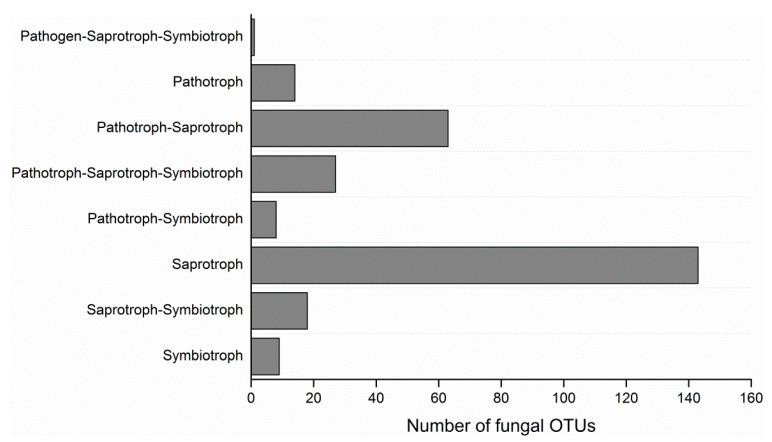
Illumina MiSeq sequencing yielded a total of 1381,534 sequences with a mean length of 265 bp that passed the quality filtering and could be assigned to the 30 samples. The number of sequences per individual orchid varied from 31,651 to 70,261. A total of 691 operational taxonomic units (OTUs) were identified using a 3% dissimilarity cutoff and removed chimeric sequences as well as global singletons. After discarding non-fungal sequences and data flattened, 467 OTUs could be assigned to root-associated fungal endophytes, which belonged to 25 classes in 10 phyla. The orders with the highest number of OTUs were Hypocreales (41 OTUs), Pleosporales (39 OTUs), Chaetosphaeriales (35 OTUs), Eurotiales (25 OTUs) and Helotiales (24 OTUs). Using FunGuild database, the putative life strategy was assigned only to OTUs with taxonomic assignment at ‘species’ level (283 OTUs). Analyzed OTUs were assigned to saprotroph (143 OTUs), pathotroph-saprotrop (63 OTUs), saprotroph-symbiotroph (18 OTUs), pathotroph-saprotroph-symbiotroph (27 OTUs), pathogen-saprotroph-symbiotroph (1 OTUs), symbiotroph (9 OTUs), pathotrophs (14 OTUs) or pathotroph-symbiotroph guilds (8 OTUs) (Figure 1). Among these OTUs, about 54 OTUs could be considered as putative species of OMF: They were related to Aspergillaceae (Aspergillus and Penicillium), Saccharomycetales_fam_Incertae_sedis (Candida), Nectriaceae (Fusarium), Tulasnellaceae (Tulasnella, Epulorhiza, and one unidentified Tulasnellaceae), Ceratobasidiaceae (Rhizoctonia), Glomerellaceae (Colletotrichum), Serendipitaceae (Serendipita), Pleosporaceae (Alternaria), Cucurbitariaceae (Pyrenochaeta), Pyronemataceae (Tricharina), Omphalotaceae (Gymnopus), Hypocreaceae (Trichoderma), Myxotrichaceae (Oidiodendron), Tricholomataceae (Mycena), and Nectriaceae (Cylindrocarpon).
Figure 1.
Frequency distribution displaying the number of operational taxonomic units (OTUs) belonging to the different trophic guilds identified in the roots of Bletilla.
2.2. Temporal Variation in Diversity of Root Endophytic Fungi
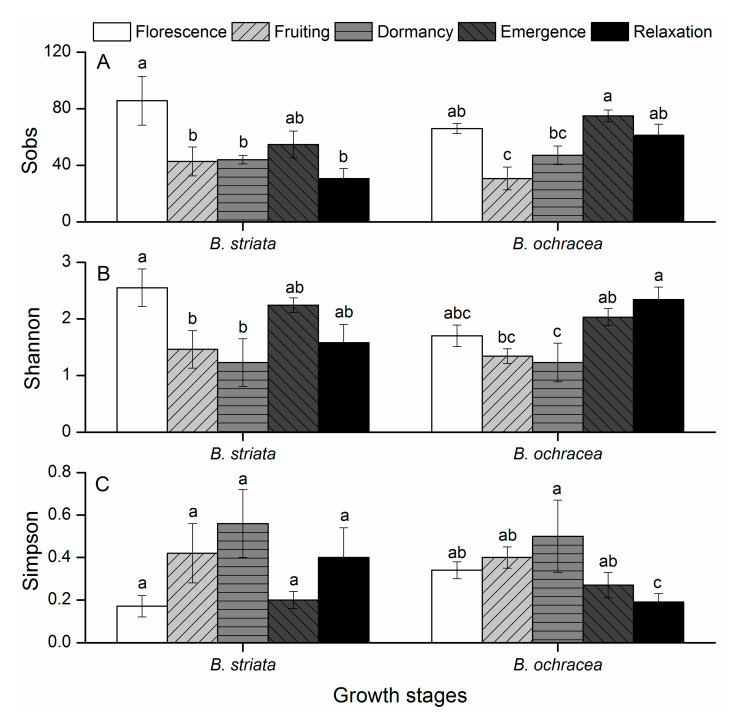
Fungal community richness (Sobs) and alpha diversity (Shannon and Simpson’s) index values were compared among five phenological stages for the two Bletilla species at the operational taxonomic unit (OTU) level (Figure 2). For B. striata, the florescence period had significantly higher Sobs and Shannon index values compared with the fruiting and dormancy periods. For B. ochracea, the emergency period had significantly higher Sobs value while the relaxation period had significantly higher Shannon index value compared with the fruiting and dormancy periods. In contrast, for both B. striata and B. ochracea, the dormancy and fruiting periods had higher Simpson’s index values than did the other phenological stages, though the differences were not very significant (Figure 2C). Good’s coverage scores of all phenological stages for the two Bletilla species were very high, ranging from 99.95% to 99.99%, indicating that the sequencing depth was adequate to reliably describe the root endophytic fungi associated with Bletilla species at different phenological stages, and no significant differences were observed among the five phenological stages for each species (Table S1).
Figure 2.
Alpha diversity estimates of mycorrhizal fungi associated with Bletilla striata and B. ochracea at different growth stages. Significant differences (p < 0.05) among different growth stages of each species for each index are indicated with lowercase letters. (A) Sobs, (B) Shannon, (C) Simpson.
2.3. Community Composition of Root Endophytic Fungi among Different Phenological Stages
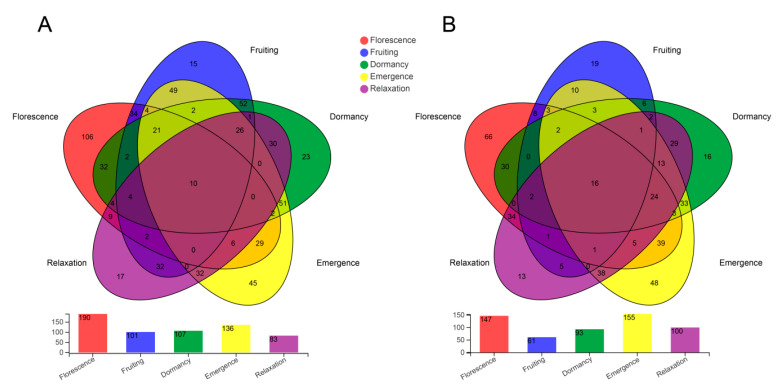
There were 10 and 16 fungal OTUs shared among all five phenological stages in association with B. striata and B. ochracea, respectively (Figure 3). The shared 10 OTUs for B. striata belong to unclassified_c_Agaricomycetes (42.44%), Exophiala (19.35%), unclassified_o_Sebacinales (13.05%), Rhizoctonia (8.55%), Neocosmospora (5.92%), Dactylonectria (3.00%), Cylindrocarpon (2.75%) and Aspergillus (1.97%). The shared 16 OTUs for B. ochracea belong to unclassified_c_Agaricomycetes (70.29%), Exophiala (11.66%), unclassified_p_Basidiomycota (7.97%), Paraphoma (4.12%), Fusarium (3.21%), Neocosmospora (2.42%), and others (0.34%) (Figure S1). Additionally, there were 106, 15, 23, 45 and 17 fungi OTUs specific to a single stage of florescence, fruiting, dormancy, emergence and relaxation for B. striata, respectively, while there were 66, 19, 16, 48 and 13 OTUs, respectively, for B. ochracea. There also exist some fungi OTUs shared by 2, 3, and 4 stages for both B. striata and B. ochracea.
Figure 3.
The operational taxonomic unit (OTU) level of species composition during different phenological stages for Bletilla striata (A) and B. ochracea (B).
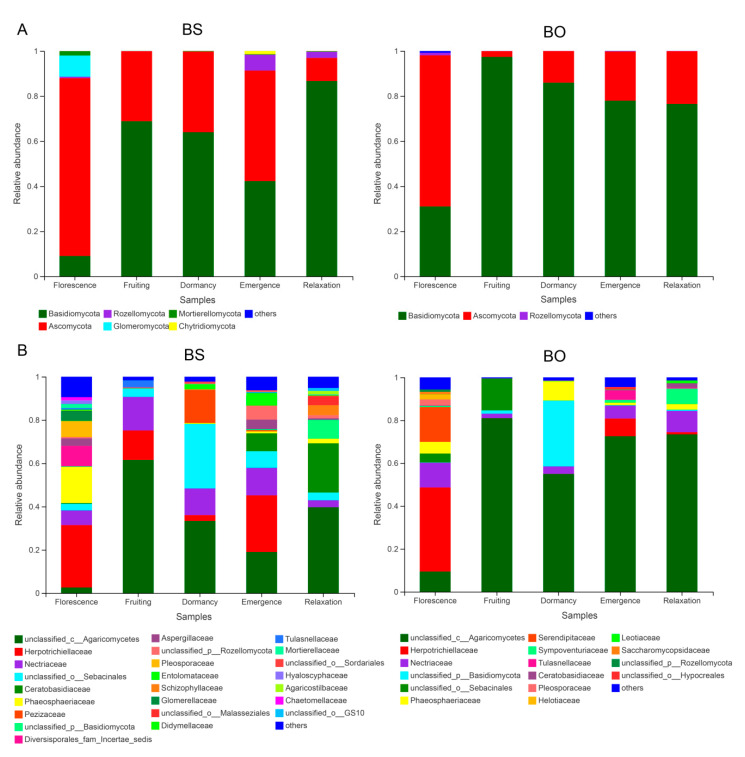
The predominant species in root endophytic fungal communities associated with the two Bletilla species were largely consistent among the five phenological stages at the phylum level. The fungal phyla with the highest relative abundances were Basidiomycota and Ascomycota. However, differences in relative abundances between the two species for a specific phenological stage or among different phenological stages for each Bletilla species were observed. Other minor phyla, such as Rozellomycota, Glomeromycota, Mortierellomycota and Chytridiomycota, were also found for B. striata, while only Rozellomycota was found for B. ochracea at some phenological stages (Figure 4). At the florescence stage, B. striata and B. ochracea fungal communities were dominated by Ascomycota, with percentages of 78.93% and 67.07%, respectively, while during the fruiting, dormancy and relaxation stages, B. striata and B. ochracea fungal communities were dominated by Basidiomycota, with percentages ranging from 63.94% to 86.71% and 76.53% to 97.39%, respectively. However, during emergence, associations with B. striata were dominated by Ascomycota (49.04%) and Basidiomycota (42.30%) while associations with B. ochracea were domianted by Basidiomycota (77.95%).
Figure 4.
Relative abundances of mycorrhizal fungi in different phenological stages at different phylogenetic levels. (A) Relative abundances of mycorrhizal fungi at the phylum level. (B) Relative abundances of mycorrhizal fungi at the family level. BS and BO represent Bletilla striata and B. ochracea, respectively.
At the family level, the florescence stage for both Bletilla species had the most diverse associated fungal species, with B. striata dominated by Herpotrichiellaceae, Phaeosphaeriaceae. Diversisporales_fam_Incertae_sedis, Pleosporaceae, Nectriaceae and Glomerellaceae, and B. ochracea dominanted by Herpotrichiellaceae, Serendipitaceae, Nectriaceae, Phaeosphaeriaceae and unclassfied_o_Sebacinales. Meanwhile, unclassifed_c_Agaricomycetes, Herpotrichiellaceae, Nectriaceae and Phaeosphaeriaceae were present among all five phenological stages for both Bletilla species. During the whole physiological period, B. ochracea had higher unclassifed_c_Agaricomycetes abundance and lower Herpotrichiellaceae abundance compared with B. striata. The florescence stage had higher unclassfied_o_Sebacinales abundance compared with other physiological stages for both Bletilla species (Figure 4).
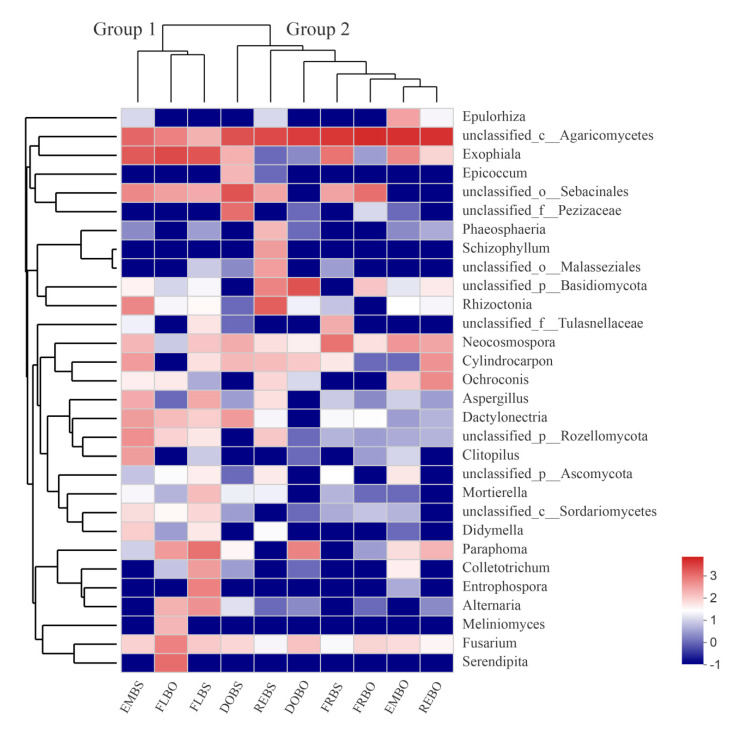
At the genus level, as shown by the heatmap in Figure 5, the samples were divided into two groups, and root endophytic fungi communities were divided into four groups. The fungal genera associated with the emergence and florescence stages of B. striata and the florescence stage of B. ochracea were clustered into one group (group 1), while the other samples were clustered into another group (group 2). Group 1 had higher abundances of Exophiala, Dactylonectria, unclassified_p_Rozellomycota and Fusarium than group 2, while group 2 had higher abundances of unclassified_c_Agaricomycetes than group 1.
Figure 5.
Heatmap of relative abundances of the top 30 fungal genera associated with Bletilla striata and B. ochracea species at different phenological stages. DOBS, B. striata dormancy; FRBS, B. striata fruiting; EMBS, B. striata emergence; REBS, B. striata relaxation; FLBS, B. striata florescence; DOBO, B. striata dormancy; FRBO, B. ochracea fruiting; EMBO, B. ochracea emergence; REBO, B. ochracea relaxation; FLBO, B. ochracea florescence. Rows are fungal genera, and columns are samples. Colors indicate taxa with a higher (red) or lower (blue) relative abundance in each sample.
2.4. Dynamics of Isotopic Abundances over the Bletilla Growth Season
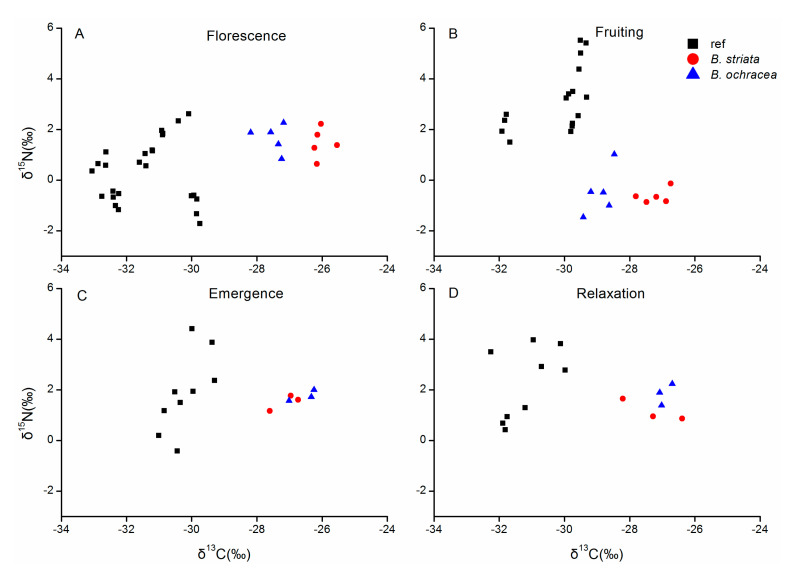
We compared the δ13C and δ15N values among the two Bletilla species and corresponding autotrophic reference plants at different phenological stages (Figure 6). The mean δ13C values varied significantly among the three groups across the four phenological stages. At the florescence and fruiting periods, the mean δ13C values of B. striata were highest, followed by B. ochracea and lastly the reference plants, with significant difference among each of the three groups. At the emergence and relaxation periods, the mean δ13C values of B. ochracea and B. striata were significantly higher than that of reference plants, but the two species did not significantly differ (Table 1). For the mean values of δ15N, significant differences among the three groups only existed in the florescence and fruiting periods. At florescence, B. striata and B. ochracea had significantly higher δ15N values than that of reference plants, while at fruiting, the two Bletilla species had significantly lower mean δ15N values than that of reference plants (Table 1).
Figure 6.
Overview of δ13C and δ15N values of two Bletilla species and autotrophic reference plants (ref) at four different phenological stages. (A) Florescence, (B) Fruiting, (C) Emergence, (D) Relaxation.
Table 1.
Comparison of δ13C and δ15N values (mean ± SE) among different species at each phenological stage and different phenological stages for each species.
| δ13C (‰) | δ15N (‰) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Florescence | Fruiting | Emergence | Relaxation | Florescence | Fruiting | Emergence | Relaxation | |
| B. striata | −26.02 ± 0.12 aA | −27.22 ± 0.2 aA | −27.1 ± 0.26 aA | −27.29 ± 0.52 aA | 1.46 ± 0.26 aA | −0.63 ± 0.13 bB | 1.51 ± 0.18 aA | 1.15 ± 0.25 aA |
| B. ochracea | −27.5 ± 0.18 bAB | −28.9 ± 0.18 bB | −26.53 ± 0.24 aA | −26.93 ± 0.12 aA | 1.66 ± 0.25 aA | −0.48 ± 0.42 bB | 1.76 ± 0.13 aA | 1.83 ± 0.25 aA |
| ref | −31.4 ± 0.22 cC | −30.17 ± 0.24 cA | −30.19 ± 0.20 bAB | −31.18 ± 0.27 bBC | 0.33 ± 0.25 bC | 3.18 ± 0.32 aA | 1.88 ± 0.52 aB | 2.25 ± 0.47 aAB |
Values followed by the same lowercase letters within a column did not have significantly different δ13C or δ15N values. Values followed by the same capital letters within a row did not have significantly different δ13C or δ15N values.
The δ13C and δ15N values among different phenological stages were also compared for each plant group (Table 1). For the values of δ13C, significant differences among the four phenological stages only existed in B. ochracea and autotrophic reference plants. For B. ochracea, the emergence and relaxation periods had significantly higher mean δ13C values than that of fruiting period. For the values of δ15N, significant differences among the four phenological stages existed for all the three plant groups. The fruiting period had significantly lower δ15N values than other three periods for both Bletilla species.
2.5. Enrichment Factors and N Concentrations of Two Bletilla Species at Different Phenological Stages
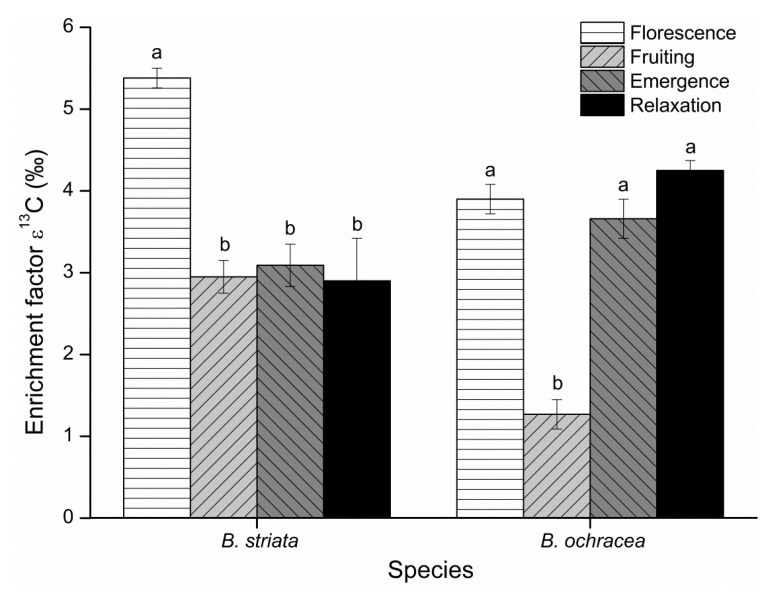
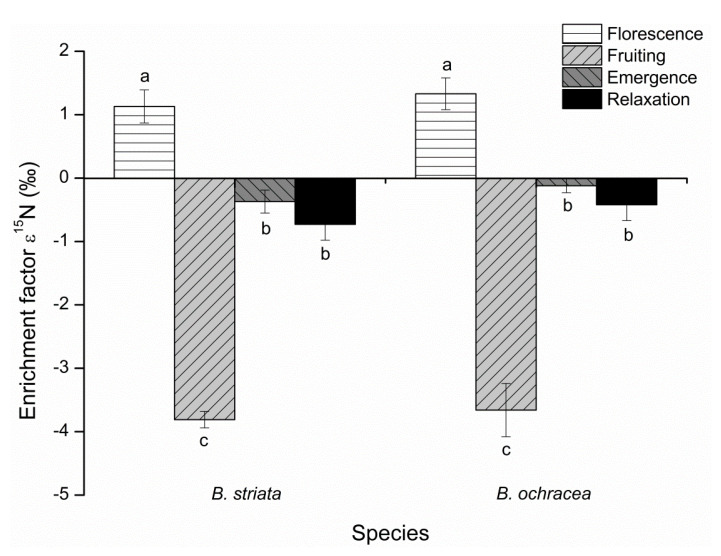
Relative enrichment factors (ε) for 13C and 15N were calculated for the two Bletilla species at four phenological stages. For B. striata, the ε13C value at florescence was significantly higher than those at emergence, fruiting and relaxation, and there were no significant differences among the latter three. For B. ochracea, the situation is rather different, with the ε13C values during relaxation, florescence and emergence periods being significantly higher than that during fruiting (Figure 7). However, the ε15N values at the different phenological stages for the two Bletilla species had the same temporal trend, with the values at florescence significantly higher than those at emergence and relaxation, and the values at emergence and relaxation being significantly higher than that at fruiting (Figure 8). The ε13C values confirmed a significant 13C enrichment for the two Bletilla species at the four phenological stages. The ε15N values confirmed significant 15N enrichment during florescence, with significant 15N depletion during fruiting for the two Bletilla species.
Figure 7.
Enrichment factor (ε) for 13C of Bletilla striata and B. ochracea collected at different phenological stages. Mean ε values of the autotrophic reference species are equal to zero. Different lowercase letters for each species indicate statistically significant differences among phenological stages (p < 0.05).
Figure 8.
Enrichment factor (ε) for 15N of Bletilla striata and B. ochracea collected at different phenological stages. Mean ε values of the autotrophic reference species are equal to zero. Different lowercase letters for each species indicate statistically significant differences among phenological stages (p < 0.05).
We also compared the ε13C and ε15N differences of the two Bletilla species at each phenological stage. At florescence and fruiting, B. striata had higher ε13C values than B. ochracea, while B. striata had lower ε13C values than B. ochracea at the emergence and relaxation stages. Meanwhile, based on ε15N values, B. ochracea had higher enrichment during florescence and less depletion at fruiting, emergence and relaxation stages compared with B. striata, though the differences were rather small.
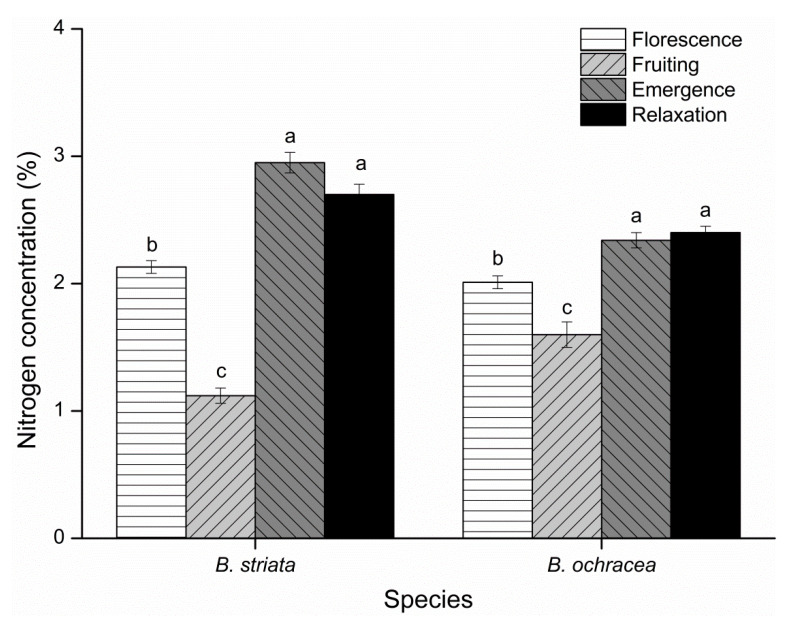
Nitrogen concentrations were compared among different phenological stages for B. striata and B. ochracea. For the two species, the nitrogen concentrations at the emergence and relaxation periods were significantly higher than those during florescence, while the values during florescence were significantly higher than those during fruiting. Meanwhile, there were no significant differences between the values during the emergence and relaxation periods (Figure 9).
Figure 9.
Temporal variation in leaf nitrogen concentration for Bletilla striata and B. ochracea. Different lowercase letters for each species indicate statistically significant differences among phenological stages (p < 0.05).
3. Discussion
3.1. Temporal Variation in Root-Associated Fungal Diversity for Bletilla Species
In this study, significant temporal variation was observed in the diversity of root endophytic fungi associated with the two Bletilla species. Compared with the fruiting and dormancy periods, the florescence period of B. striata and the relaxation period of B. ochracea had significantly higher Shannon index values. This finding may be associated with dynamic changes in plant physiological process and interactions between root endophytic fungi and orchids because metabolic rate of plant and nutritional requirement vary among different physiological stages. Additionally, pelotons formed by orchid endophytic fungi are short-lived structures that undergo rapid turnover within orchid cells, allowing new colonization events [37]. Thus, the diversity of symbiotic fungi can also change quite rapidly [25]. Accordingly, temporal variation in fungal diversity across seasons has been found in many cases [38,39]. For example, Koide et al. [38] found variation in fungal diversity of ectomycorrhizae roots, and Jumpponen [39] found temporal changes in arbuscular mycorrhizal roots. In our study, Bletilla plants become dormant with extremely low metabolic rate during dormancy period, which may lead to the lowest root endophytic fungal diversity in this period. The fruiting period had lower root endophytic fungal diversity, which may be due to the weaker physiological activity, higher temperature or lower soil water content during summer. The senescence of plant accompanying weaker physiological activity during fruiting periods, which do not need too much nutrition supply, may reduce the dependence of plants on fungi [40]. Meanwhile, high temperature and drought would reduce microbial population size and thus restrain community diversity and complexity [41]. Tedersoo et al. [42] found that although host plant families had strong effects on the phylogenetic community composition of fungi, temperature and precipitation mostly affected ectomycorrhizal fungal richness. Han et al. [43] found that Paphiopedilum spicerianum was associated with obviously more mycorrhizal fungi OTUs with higher Shannon values during wet seasons (274 and 1.88, respectively) relative to dry seasons (143 and 1.54, respectively).
Significant temporal variation in root-associated fungal endophyte community structure across seasons was also found in this study. During florescence, B. striata and B. ochracea were dominated by Ascomycota, while during fruiting, dormancy and relaxation Basidiomycota were dominant. However, during emergence, B. striata fungal associations were dominated by Ascomycota, and B. ochracea fungal associations were dominated by Basidiomycota. Meanwhile, the abundance of dominant species at various phenological stages varied among Bletilla species. The reason root endophytic fungi community composition and its abundance varied among phenological stages requires further analysis. There are three possible reasons. First, some root endophytic fungi require metabolites produced by orchid plants at some particular period for its growth [19]. Second, mycorrhizal tissue structure varies among physiological periods, underlying different mycorrhizal fungi infection rates and fungi types. Third, the ecological factors extrinsic to host plant roots, such as precipitation, light irradiation, soil temperature and humidity, can vary among physiological periods, greatly influencing the root endophytic community composition. The reasons for different responses of fungi community composition and abundances to phenological changes by two species are difficult to identify. One most likely explanation may be genetic differences in the plant species. Tedersoo et al. [42] found that host plant family had the strongest effect on the phylogenetic community composition of fungi.
At the family level, the florescence stage for both Bletilla species had the highest fungal diversity, likely owing to orchid plants requiring considerable nutrients to bloom, exceeding the nutrients supplied by photosynthesis; accordingly, they may need root endophytic fungi to supply nutrients to enable blooming [44]. Data of ε13C and ε15N in this study substantiate this finding. Bellino et al. [45] found that phototrophic and mycotrophic nutrition alternate change with the seasons and nutritional requirements of plants. Another possible explanation is that the outer velamen tissue of orchids is destroyed to some extent during the fast-growing stages through friction with soil, which results in massive fungal invasion during later physiological stages (e.g., florescence). Thus, root cells are heavily colonized and have high activity of invading hyphae, which leads to the highest fungal infection rate occurring at the florescence stage. Rasmussen et al. [46] found that mycorrhizal infection reached its maximum intensity 2–6 months after mycotrophic root development.
In this study, the composition and abundance of total species, dominant species and endemic species varied between the two Bletilla species at each phenological stage and also varied among phenological stages for both species. This may reflect distinct mycorrhizal preferences for specific host species, or alternatively, this pattern could result from hosts undergoing natural selection for different fungal endophytes enabling better adaption to their environments [47,48].
3.2. Isotopic Abundance Trends over the Growth Season
Our results demonstrate that variation in 13C and 15N enrichment can be highly dynamic throughout the whole growth season for Bletilla spp. For B. striata, the florescence period had significantly higher ε13C values, while the ε13C value during fruiting in B. ochracea was significantly lower than that during the other three periods. For the two Bletilla species, the ε15N values during florescence were significantly higher than those during emergence and relaxation periods, and the values at the emergence and relaxation periods were significantly higher than that of the fruiting period. This indicates that Bletilla plants substantially change their isotopic content across phenological stages, which is inconsistent with the results of Ercole et al. [25], who reported only slight changes in 13C and 15N natural abundances in the evergreen species Anacamptis morio throughout all its growth stages.
In this study, the two Bletilla species were relatively enriched in 13C across all phenological stages (except dormancy), indicating that they obtained carbon from their root endophytic fungi throughout the whole year. Because fungal tissues have higher 13C stable isotope abundance compared with neighbouring autotrophic plants [26,27], according to the isotopic differences between plant- and fungus-derived C, we can trace the source of carbon by 13C enrichment across different phenological stages. Additionally, B. striata had higher ε13C values at florescence and fruiting and lower ε13C values at emergence and relaxation compared with B. ochracea, which indicates that the carbon obtained from root endophytic fungi varied among Bletilla species and phenological stages. This variation in 13C enrichment may be owing to variation in climate, genetic effects, soil nutrients and/or mycorrhizal associations [17,49,50]. However, in this study, soil total carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus content and pH did not differ substantially among B. striata and B. ochracea sites (Table S2). The observed interspecific variation in 13C enrichment at same time might owing to genetic variation within Bletilla spp. Meanwhile, the variation in 13C enrichment among phenological periods might be owing to variations in mycorrhizal tissue structure and ecological factors such as soil temperature, soil humidity and light radiation, which greatly influenced the ease with which fungi infect roots as well as root endophytic fungi types, thus affecting root endophytic fungal community composition. Additionally, 13C enrichment was positively correlated with the abundances of Ascomycota at the phylum level across all growth stages. Selosse et al. [51] found that Ascomycota species were often found in orchid roots and could form typical orchid mycorrhizae.
Obvious enrichment of 15N during the florescence period and significantly strong 15N depletion at the fruiting period were found for the two Bletilla species, indicating that Bletilla species obtained N from their mycorrhizal fungi during florescence and that a significant transfer of nitrogen from orchids to their mycorrhizal associates occurred during the fruiting period. Researchers found that a transfer of nutrients from the orchids to their mycorrhizal associates was consistent with such 13C and 15N depletions [52,53]. Meanwhile, compared with B. striata, B. ochracea had relatively higher enrichment during florescence and lower depletion of 15N at other phenological stages, indicating that B. ochracea obtained more nitrogen from their associated mycorrhizal fungi during the florescence period and transferred less N to mycorrhizal fungi during other phenological stages compared with B. striate.
For both B. striata and B. ochracea, leaf total nitrogen concentrations were significantly lower during the florescence and fruiting periods compared with the emergence and relaxation periods, which is most probably explained by nitrogen investments in flower and seed tissues. Liebel et al. [17] reported that compared with non-flowering/non-fruiting individuals, flowering/fruiting Goodyera repens individuals had lower leaf total nitrogen and chlorophyll concentrations, which is most probably explained by the plants using leaf nitrogen to form flowers and seeds. Andersson [54] showed that floral investment by Nigella sativa could cause reduced allocation to other plant functions. Based on the obvious enrichment of 15N during florescence and significantly strong 15N depletion during fruiting, we can infer that Bletilla species might compensate for low leaf total nitrogen concentrations by using 15N enriched fungal sources during flowering but that there was no such compensation during fruiting. One explanation is a relative paucity of root endophytic fungal species and lower activity owing to drought stress during the fruiting period. Another likely reason is that photosynthesis can mostly support fruiting costs and thus maintain the same seed production by increasing leaf, stem and fruit photosynthesis without increases in carbon fluxes from fungus to orchid [16,17].
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Species
Bletilla Rchb. f. is a genus of terrestrial orchids distributed across northern Burma, China and Japan, and it belongs to the tribe Epidendreae in the subfamily Orchidoideae within Orchidaceae [55]. B. striata and B. ochracea are two relatively widespread Bletilla species in China that are widely used for garden landscaping as well as traditional Chinese medicine [56]. Mature Bletilla plants enter dormancy in the winter and begin to bolt in the early spring under natural conditions. Adult plants form mycorrhizal associations, mainly with Ascomycota and Basidiomycota and are characterized by the phenological stages described in Table 2.
Table 2.
Phenological stages and sample times of Bletilla and autotrophic reference plants.
| Season | Phenological Stage | Species | Sampling Dates | Leaf Samples (Bletilla Individuals) | Reference Plant Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Late spring | Flourishing with eighty percent flowers bloom. | B. striata | 04-May-2018 | 5 | Erigeron annuus (L.) Pers., Bischofia javanica Bl., Morus alba L., Broussonetia papyrifera (Linn.) LHer. ex Vent., Conyza canadensis (L.) Cronq. |
| B. ochracea | 14-May-2018 | 5 | |||
| Summer | Fruiting with capsules mature but closed. | B. striata | 27-Aug-2018 | 5 | Cirsium setosum (Willd.) MB., Celtis sinensis Pers., Metaplexis japonica (Thunb.) Makino, Morus alba L. |
| B. ochracea | 27-Aug-2018 | 5 | |||
| Winter | Plant dormancy. Leaves and floral stem have been dried out. | B. striata | 18-Dec-2018 | 0 | NA |
| B. ochracea | 18-Dec-2018 | 0 | |||
| Early spring | Buds emergence with leaves stacked together, and the tuber produces some roots. | B. striata | 13-Mar-2019 | 3 | Cirsium setosum, Sonchus oleraceus L., Conyza canadensis |
| B. ochracea | 25-Mar-2019 | 3 | |||
| Middle spring | Shoots developed with leaves expanded, and floral stems are produced. | B. striata | 02-Apr-2019 | 3 | Sonchus oleraceus, Conyza canadensis, Solanum nigrum L. |
| B. ochracea | 17-Apr-2019 | 3 |
4.2. Study Site
Samples were collected from the Bletilla germplasm resource nursery located at Shanghai Chenshan Botanical Garden (31°04′ N and 121°11′ E). The area has a subtropical monsoon climate with a cumulative mean annual precipitation of 1213 mm and a mean annual temperature of 15.6 °C. The soil matrix (within the top 0–5 cm) was composed of mountain clay, river sand and vermiculite, with a ratio of 1.5:1:1 and a pH of 6.5–7.5. The Bletilla plants examined had been cultivated for three years and were already fully established at the site.
4.3. Sampling
Sampling was conducted from May 2018 to April 2019 in the germplasm resource nursery of Shanghai Chenshan Botanical garden. Root samples were collected at five time points, while leaf samples were collected at four time points (outside of the dormancy period) spanning the different phenological stages (Table 2). Three 1 × 1 m plots were randomly established in the B. striata and B. ochracea sites. In each plot, two roots per plant from five orchid plants were collected. Collected roots from each plot were pooled and kept cold during transport to the laboratory for further analysis. For each species, we sampled fresh top leaves from several Bletilla individuals at four time points (five individuals at florescence and fruiting periods and three individuals at emergence and relaxation periods). Meanwhile, leaves of three to five autotrophic reference plants under the same microclimate were also sampled at each phenological stage. The autotrophic reference species were chosen based on the criteria described by Gebauer and Meyer [23]. For detailed information on reference species, please see Table 1. In total, 30 root samples and 32 leaf samples from two Bletilla species and 59 leaf samples from autotrophic reference species were collected in this study.
4.4. Identification of Root Endophytic Fungi
Roots were rinsed with tap water, sonicated to remove any adhering soil and dirt and sterilized as follows: Roots were rinsed with sterile water for 30 s and then 70% ethyl alcohol for 2 min, soaked in 2.5% sodium hypochlorite for 5 min, transferred to 70% ethyl alcohol for 30 s and finally washed with sterile water three times. Roots were then cut into small pieces with sterile scissors, and ten to twelve sections per sample were selected for genomic DNA extraction and purification using the FastDNA Spin Kit for Soil (MP Biomedicals, Irvine, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The nuclear ribosomal internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region was amplified with the fungal-specific primers ITS1F and ITS4 [17]. The PCR amplification was performed as follows: initial denaturation at 95 ℃ for 3 min, followed by 35 cycles of denaturing at 95 ℃ for 30 s, annealing at 55 ℃ for 30 s and extension at 72 ℃for 45 s, single extension at 72 ℃ for 10 min, and end at 10 ℃. The PCR reactions were performed in triplicate 20 μL mixture containing 2 μL of 10 × Pyrobest Buffer, 2 μL of 2.5 mM deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates (dNTPs), 0.8 μL of each primer (5 μM), 0.2 μL of Pyrobest DNA Polymerase (TaKaRa), 10 ng of template DNA, and finally ddH2O up to 20 μL. The PCR product was extracted from 2% agarose gel and purified using the AxyPrep DNA Gel Extraction Kit (Axygen Biosciences, Union City, CA, USA) according to manufacturer’s instructions and quantified using Quantus™ Fluorometer (Promega, Madison, WI, USA).
All positive PCR products were purified with the AxyPrep DNA Gel Extraction Kit (Axygen Biosciences, Union City, CA, USA) and sequenced bidirectionally using an Illumina MiSeq PE300 platform (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) according to the standard protocols from Majorbio Bio-Pharm Technology Co. Ltd. (Shanghai, China). The generated paired-end reads were merged once, but because the reads were longer than 300 bp, the paired-end reads could not be merged without overlap. Thus, we used single-end long reads for further analysis. The raw reads were deposited into the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA) database (Accession Number: SRP225764). Raw fastq files were demultiplexed and quality-filtered with Trimmomatic according to the following criteria: 300 bp reads that were truncated at any site receiving an average quality score of <20 over a 50 bp sliding window, and the truncated reads shorter than 50 bp were discarded; reads containing ambiguous characters were also discarded. Operational taxonomic units (OTUs) were clustered with a 97% similarity cut-off using UPARSE (version 7.1, http://drive5.com/uparse/), and chimeric sequences were removed using UCHIME. The taxonomy of each ITS rRNA gene sequence was analysed with the RDP Classifier algorithm (http://rdp.cme.msu.edu/) against the Unite 8.0 ITS rRNA database using a confidence threshold of 70%. Fungal OTUs were classified into different putative trophic strategies following the classification of the FunGuild v1.0 (http://www.stbates.org/guilds/app.php).
4.5. Analysis of Stable Isotope Abundance and N Concentration
Leaf samples were washed with deionized water, oven-dried at 105 °C, ground into a fine power and stored in a desiccator fitted with silica gel until subsequent analysis. Relative C and N isotope abundances and N content were measured using an elemental analyser (vario PYRO cube; Elementar Analysensysteme GmbH, Langenselbold, Germany) coupled with a continuous flow isotope ratio mass spectrometer (IsoPrime100, Elementar UK Ltd., Stockport, UK), as described by Bidartondo et al. [57]. Relative isotope abundances are denoted as δ values, which were calculated according to the equation:
| (1) |
where Rsa and Rst are the ratios of heavy isotopes to light isotopes in the samples and the respective standards. Standard gases were calibrated with USGS40 and USGS41a for carbon and nitrogen isotopes, provided by the United States Geological Survey (USGS). Reproducibility and accuracy of the isotope abundance measurements were routinely controlled by measures of laboratory standard acetanilide. The calculation of N concentrations in the samples followed the protocol by Gebauer and Schulze [58]. For relative C and N isotope natural abundance analyses, acetanilide was routinely analysed with variable sample weights once every 12 samples.
Enrichment factors (εs) for all samples were calculated according to the equation:
| (2) |
where δS is the relative isotope abundance of a Bletilla sample, and δref is the mean isotope abundance of all autotrophic reference plants.
4.6. Statistical Analyses
Isotopic data analyses were performed using SPSS 16.0 for Windows (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Before analysis, all variables were checked for normality by Shapiro–Wilks test and for homogeneity of variance by Levene’s test. Two-way ANOVA with Tukey HSD post hoc comparisons or Tamhane’s T2 test were used when data were normally distributed. We checked the differences in mean δ13C and δ15N values among the autotrophic reference plants, B. striata and B. ochracea as well as differences among different physiological stages for each species. Additionally, values of ε13C, ε15N and N concentration among the different physiological stages were also compared for each Bletilla species. Significant differences in three alpha diversity indexes (Sobs, Shannon and Simpson) and coverage among different physiological stages were also compared in this study. Significance was defined at the 95% confidence level throughout this article. Additionally, microbial species composition analysis was performed using the free online Majorbio I-Sanger Cloud Platform (www.i-sanger.com).
5. Conclusions
Identifying the trophic relationship of endangered Bletilla with its root endophytic partners is critical for understanding plant growth and ultimately restoring wild populations. We investigated temporal variation in root endophytic fungal diversity, as well as the natural abundance of carbon and nitrogen stable isotopes in two Bletilla species (B. striata and B. ochracea) at different phenological stages. Our results suggest that variations in 13C and 15N natural abundance and root endophytic fungi for Bletilla spp. can be highly dynamic across all phenological stages. Both Bletilla species obtained carbon from their mycorrhizal fungi during the whole year. B. striata obtained more carbon during the florescence and fruiting periods but obtained less carbon during the emergence and relaxation periods compared with B. ochracea. For both Bletilla species, the florescence stage had relatively more 13C and 15N enrichment compared with the other phenological stages. Due to the two-way selection of plant species and root endophytic fungi, the community structure and abundance of total species, dominant species and endemic species varied between the two Bletilla species and among phenological stages. Additionally, the varying tendency of root endophytic fungal diversity across the whole growth stage was consistent with 13C enrichments, which was also accord with the nutritional requirement of plant. Our results have important implications for the current understanding of fungus–host relationships and also provide practical information for Bletilla conservation efforts.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Environmental Stable Isotope Laboratory, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, for supporting the stable isotope analyses. We thank Majorbio Bio-Pharm Technology Co. Ltd. for supporting the RNA-seq experiments and bioinformatic analysis. We also thank the editor and the reviewers for their insightful and constructive comments.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2223-7747/10/1/18/s1, Figure S1: Microbial community pieplots of fungi species shared among all five phenological stages in association with Bletilla striata (A) and B. ochracea (B) on genus level. Table S1: Temporal variation in mycorrhizal diversity associated with Bletilla striata and B. ochracea. Table S2: Soil nutrients and pH for Bletilla striata and B. ochracea sites (mean ± SE values).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and methodology, W.H.; software, X.Z.; validation, X.Z.; formal analysis, X.Z. and H.D.; investigation, X.Z.; resources, Z.N.; data curation, L.S. and K.J.; writing—original draft preparation, X.Z.; writing—review and editing, X.Z., C.H. and Q.H.; supervision, W.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31902108), the Shanghai Municipal Administration of Forestation and City Appearances (No. G192420) and Shanghai Agriculture Research System, China (No. 201908).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Chase M.W., Cameron K.M., Freudenstein J.V., Pridgeon A.M., Salazar G., van den Berg C., Schuiteman A. An updated classification of Orchidaceae. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2015;177:151–174. doi: 10.1111/boj.12234. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Christenhusz M.J.M., Byng J.W. The number of known plants species in the world and its annual increase. Phytotaxa. 2016;261:201–217. doi: 10.11646/phytotaxa.261.3.1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 3.McCormick M.K., Whigham D.F., O’Neill J. Mycorrhizal diversity in photosynthetic terrestrial orchids. New Phytol. 2004;163:425–438. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2004.01114.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Roberts D., Dixon K. Orchids. Curr. Biol. 2008;18:325–329. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2008.02.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zettler L.W., Sharma J., Rasmussen F. Mycorrhizal diversity. In: Dixon K., Cribb P., Kell S., Barrett R., editors. Orchid Conservation. Natural History Publications; Kota Kinabalu, Sabah, Malaysia: 2004. pp. 185–203. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Jin W.T., Xiang X.G., Jin X.H. Generic delimitation of Orchidaceae from China: Current situation and perspective. Biodivers. Sci. 2015;23:237–242. doi: 10.17520/biods.2014268. (In Chinese) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bailarote B.C., Lievens B., Jacquemyn H. Does mycorrhizal specificity affect orchid decline and rarity? Am. J. Bot. 2012;99:1655–1665. doi: 10.3732/ajb.1200117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Waterman R.J., Bidartondo M.I. Deception above, deception below: Linking pollination and mycorrhizal biology of orchids. J. Exp. Bot. 2008;59:1085–1096. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erm366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Swarts N.D., Dixon K.W. Terrestrial orchid conservation in the age of extinction. Ann. Bot. 2009;104:543–556. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcp025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Herrera H., Valadares R., Oliveira G., Fuentes A., Almonacis L., Bashan Y., Arriagada C. Adaptation and tolerance mechanisms developed by mycorrhizal Bipinnula fimbriata plantlets (Orchidaceae) in a heavy metal-polluted ecosystem. Mycorrhiza. 2018;28:651–663. doi: 10.1007/s00572-018-0858-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Smith S.E., Read D.J. Mycorrhizal Symbiosis. 3rd ed. Academic Press; New York, NY, USA: 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Schiebold J.M.I., Bidartondo M.I., Karasch P., Gravendeel B., Gebauer G. You are what you get from your fungi: Nitrogen stable isotope patterns in Epipactis species. Ann. Bot. 2017;119:1085–1095. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcw265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Stockel M., Tesitelova T., Jersakova J., Bidartondo M.I., Gebauer G. Carbon and nitrogen gain during the growth of orchid seedlings in nature. New Phytol. 2014;202:606–615. doi: 10.1111/nph.12688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Schiebold J.M.I., Bidartondo M.I., Lenhard F., Makiola A., Gebauer G. Exploiting mycorrhizas in broad daylight: Partial mycoheterotrophy is a common nutritional strategy in meadow orchids. J. Ecol. 2018;106:168–178. doi: 10.1111/1365-2745.12831. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Liu S.S., Chen J., Li S.C., Zeng X., Meng Z.X., Guo S.X. Comparative transcriptome analysis of genes involved in GA-GID1-DELLA regulatory module in symbiotic and asymbiotic seed germination of Anoectochilus roxburghii (Wall.) Lindl. (Orchidaceae) Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015;16:30190–30203. doi: 10.3390/ijms161226224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gonneau C., Jersakova J., de Tredern E., Till-Bottraud I., Saarinen K., Sauve M., Roy M., Hajek T., Selosse M.A. Photosynthesis in perennial mixotrophic Epipactis spp. (Orchidaceae) contributes more to shoot and fruit biomass than to hypogeous survival. J. Ecol. 2014;102:1183–1194. doi: 10.1111/1365-2745.12274. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Liebel H.T., Bidartondo M.I., Gebauer G. Are carbon and nitrogen exchange between fungi and the orchid Goodyera repens affected by irradiance? Ann. Bot. 2015;115:251–261. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcu240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Burke R.M., Cairney J.W.G. Carbohydrate oxidases in ericoid and ectomycorrhizal fungi: A possible source of Fenton radicals during the degradation of lignocelluloses. New Photol. 1998;139:637–645. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-8137.1998.00235.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Slezack S., Dumas-Gaudot E., Rosendahl S., Kjoller R. Endoproteolytic activities in pea roots inoculated with the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus mosseae and/or Aphanomyces euteiches in relation to bioprotection. New Photol. 1999;142:517–529. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-8137.1999.00421.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.McCormick M.K., Taylor D.L., Juhaszova K., Burnett J.R., Whigham D.F., Oneill J.P. Limitations on orchid recruitment: Not a simple picture. Mol. Ecol. 2012;21:1511–1523. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2012.05468.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hynson N.A., Madsen T.P., Selosse M.A., Adam I.K.U., Ogura-Tsujita Y., Roy M., Gebauer G. The physiological ecology of mycoheterotrophy. In: Merckx V.S.F.T., editor. Mycoheterotrophy. The Biology of Plants Living on Fungi. Springer; New York, NY, USA: 2013. pp. 297–342. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Van der Heijden M.G.A., Bardgett R.D., van Straalen N.M. The unseen majority: Soil microbes as drivers of plant diversity and productivity in terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2008;11:296–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2007.01139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Gebauer G., Meyer M. 15N and 13C natural abundance of autotrophic and mycoheterotrophic orchids provides insight into nitrogen and carbon gain from fungal association. New Phytol. 2003;160:209–223. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-8137.2003.00872.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Dawson T.E., Mambelli S., Plamboeck A.H., Templer P.H., Tu K.P. Stable isotopes in plant ecology. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2002;33:507–559. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.33.020602.095451. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ercole E., Adamo M., Rodda M., Gebauer G., Girlanda M., Perotto S. Temporal variation in mycorrhizal diversity and carbon and nitrogen stable isotope abundance in the wintergreen meadow orchid Anacamptis morio. New Phytol. 2015;205:1308–1319. doi: 10.1111/nph.13109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Gebauer G., Dietrich P. Nitrogen isotope ratios in different compartments of a mixed stand of spruce, larch and beech trees and of understory vegetation including fungi. Isot. Isot. Environ. Health Stud. 1993;29:35–44. doi: 10.1080/10256019308046133. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Gleixner G., Danier H.J., Werner R.A., Schmidt H.L. Correlations between the 13C content of primary and secondary plant products in different cell compartments and that in decomposing basidiomycetes. Plant Physiol. 1993;102:1287–1290. doi: 10.1104/pp.102.4.1287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Taylor D.L., Bruns T.D., Szaro T.M., Hodges S.A. Divergence in mycorrhizal specialization within Hexalectris spicata (Orchidaceae), a nonphotosynthetic desert orchid. Am. J. Bot. 2003;90:1168–1179. doi: 10.3732/ajb.90.8.1168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Roy M., Watthana S., Richard F., Vessabutr S., Selosse M.A. Mycoheterotrophic orchids from Thailand tropical dipterocarpacean forests associate with a broad diversity of ectomycorrhizal fungi. BMC Biol. 2009;7:51. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-7-51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Yagame T., Orihara T., Selosse M., Yamato M., Iwase K. Mixotrophy of Platanthera minor, an orchid associated with ectomycorrhiza-forming Ceratobasidiaceae fungi. New Phytol. 2012;193:178–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2011.03896.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Martos F., Dulormne M., Pailler T., Bonfante P., Faccio A., Fournel J., Dubois M.P., Selosse M.A. Independent recruitment of saprotrophic fungi as mycorrhizal partners by tropical achlorophyllous orchids. New Phytol. 2009;184:668–681. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.02987.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ogura-Tsujita Y., Gebauer G., Hashimoto T., Umata H., Yukawa T. Evidence for novel and specialised mycorrhizal parasitism: The orchid Gastrodia confusa gains carbon from saprotrophic Mycena. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2009;276:761–767. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2008.1225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Girlanda M., Segreto R., Cafasso D., Liebel H.T., Rodda M., Ercole E., Salvatore C., Gebauer G., Perotto S. Photosynthetic Mediterranean meadow orchids feature partial mycoheterotrophy and specific mycorrhizal associations. Am. J. Bot. 2011;98:1148–1163. doi: 10.3732/ajb.1000486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Liebel H.T., Bidartondo M.I., Preiss K., Segreto R., Stockel M., Rodda M., Gebauer G. C and N stable isotope signatures reveal constraints to nutritional modes in orchids from the Mediterranean and macaronesia. Am. J. Bot. 2010;97:903–912. doi: 10.3732/ajb.0900354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Phillips R.D., Barrett M.D., Dixon K.W., Hopper S.D. Do mycorrhizal symbioses cause rarity in orchids? J. Ecol. 2011;99:858–869. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2745.2011.01797.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Ogura-Tsujita Y., Gebauer G., Xu H., Fukasawa Y., Umata H., Tetsuka K., Kubota M., Schweiger J.M.I., Yamashita S., Maekawa N. The giant mycoheterotrophic orchid Erythrorchis altissima is associated mainly with a divergent set of wood-decaying fungi. Mol. Ecol. 2018;27:1324–1337. doi: 10.1111/mec.14524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Peterson R.L., Uetake Y., Bonfante P., Faccio A. The interface between fungal hyphae and orchid protocorm cells. Can. J. Bot. 1996;74:1861–1870. doi: 10.1139/b96-223. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Koide R.T., Durland L., Shumway D.L., Xu B., Sharda J.N. On temporal partitioning of a community of ectomycorrhizal fungi. New Phytol. 2007;174:420–429. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2007.02000.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Jumpponen A. Analysis of ribosomal RNA indicates seasonal fungal community dynamics in Andropogon gerardii roots. Mycorrhiza. 2011;21:453–464. doi: 10.1007/s00572-010-0358-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Hou T.W., Jin H., Liu H.X., An D.J., Luo Y.B. The variations of mycorrhizal fungi diversity among different growing periods of the dominant orchids from two habitats in the Huanglong valley, Sichuan. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2010;30:3424–3432. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- 41.Zhang X.M., Johnston E.R., Li L.H., Konstantinidis K.T., Han X.G. Experimental warming reveals positive feedbacks to climate change in the Eurasian Steppe. ISME J. 2017;11:885–895. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2016.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Tedersoo L., Bahram M., Toots M., Diedhiou A.G., Henkel T.W., Kjoller R., Morris M.H., Nara K., Nouhra E., Peay K.G., et al. Towards global patterns in the diversity and community structure of ectomycorrhizal fungi. Mol. Ecol. 2012;21:4160–4170. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2012.05602.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Han J.Y., Xiao H.F., Gao J.Y. Seasonal dynamics of mycorrhizal fungi in Paphiopedilum spicerianum (Rchb. f) Pfitzer-A critically endangered orchid from China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2016;6:327–338. doi: 10.1016/j.gecco.2016.03.011. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Lendenmann M., Thonar C., Barnard R.L., Salmon Y., Werner R.A., Frossard E., Jansa J. Symbiont identity matters: Carbon and phosphorus fluxes between Medicago truncatula and different arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Mycorrhiza. 2011;21:689–702. doi: 10.1007/s00572-011-0371-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Bellino A., Alfani A., Selosse M.A., Guerrieri R., Borghetti M., Baldantoni D. Nutritional regulation in mixotrophic plants: New insights from Limodorum abortivum. Oecologia. 2014;175:875–885. doi: 10.1007/s00442-014-2940-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Rasmussen H.M., Whigham D.F. Phenology of roots and mycorrhiza in orchid species differing in phototrophic strategy. New Phytol. 2002;154:797–807. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-8137.2002.00422.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Bruns T.D., Bidartondo M.I., Taylor D.L. Host specificity in ectomycorrhizal communities: What do the exceptions tell us? Integr. Comp. Biol. 2002;42:352–359. doi: 10.1093/icb/42.2.352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Hynson N.A., Preiss K., Gebauer G. Is it better to give than receive? A stable isotope perspective to orchid–fungal carbon transport in the green orchid species Goodyera repens and G. oblongifolia. New Phytol. 2009;182:8–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.02778.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Mujica M.I., Saez N., Cisternas M., Manzano M., Armesto J.J., Perez F. Relationship between soil nutrients and mycorrhizal associations of two Bipinnula species (Orchidaceae) from central Chile. Ann. Bot. 2016;118:149–158. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcw082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Sakamoto Y., Ogura-Tsujita Y., Ito K., Suetsugu K., Yokoyama J., Yamazaki J., Yukawa T., Maki M. The tiny-leaved orchid Cephalanthera subaphylla obtains most of its carbon via mycoheterotrophy. J. Plant Res. 2016;129:1013–1020. doi: 10.1007/s10265-016-0856-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Selosse M.A., Faccio A., Scappaticci G., Bonfante P. Chlorophyllous and achlorophyllous specimens of Epipactis microphylla (Neottieae, Orchidaceae) are associated with ectomycorrhizal septomycetes, including truffles. Microb. Ecol. 2004;47:416–426. doi: 10.1007/s00248-003-2034-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Cameron D.D., Johnson I., Read D.J., Leake J.R. Giving and receiving: Measuring the carbon cost of mycorrhizas in the green orchid, Goodyera repens. New Phytol. 2008;180:176–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02533.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Hynson N.A., Bruns T.D. Evidence of a myco-heterotroph in the plant family Ericaceae that lacks mycorrhizal specificity. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B. 2009;276:4053–4059. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2009.1190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Andersson S. Floral costs in Nigella sativa (Ranunculaceae): Compensatory responses to perianth removal. Am. J. Bot. 2005;92:279–283. doi: 10.3732/ajb.92.2.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Flora of China Editorial Committee . Flora of China. Science press; Beijing, China: 1999. p. 46. [Google Scholar]
- 56.Qian C.D., Jiang F.S., Yu H.S., Fu Y.H., Cheng D.Q., Gan L.S., Ding Z.S. Antibacterial biphenanthrenes from the fibrous roots of Bletilla striata. J. Nat. Prod. 2015;78:939–943. doi: 10.1021/np501012n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Bidartondo M.I., Burghardt B., Gebauer G., Bruns T.D., Read D.J. Changing partners in the dark: Isotopic and molecular evidence of ectomycorrhizal liaisons between forest orchids and trees. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2004;271:1799–1806. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2004.2807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Gebauer G., Schulze E.D. Carbon and nitrogen isotope ratios in different compartments of a healthy and a declining Picea abies forest in the Fichtelgebirge, NE Bavaria. Oecologia. 1991;87:198–207. doi: 10.1007/BF00325257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.